1. Introduction
Exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) causes molecular and cellular damage, depending on the radiation type, dose, dose rate, and the genetic makeup of the exposed individual. Exposure to a single large dose of IR results in acute radiation syndrome (ARS), which could subsequently result in cumulative delayed effects of acute radiation exposure (DEARE) as time passes. ARS could manifest as gastrointestinal tract (GIT) injuries and hemopoietic disorders, while the survivors of ARS might experience delayed effects which include a myriad of chronic illnesses affecting multiple organ systems including the skin, kidney, heart, and brain [
1].
The general population is at risk of exposure to IR, as radiological events are largely unpredictable. Thus, radiation mitigators are needed to counteract both acute and delayed radiation toxicity, especially for emergency first responders or soldiers. Countermeasures that have been approved thus far are primarily aimed at alleviating acute radiation toxicities by enhancing bone marrow function. Currently, there are no FDA approved therapeutics tailored against late radiation effects. Radiation mitigators have been found to improve endothelial cell (EC) function and reduce late organ injury, thus enhancing survival [
2,
3]. Endothelial and vascular dysfunction are thought to play a key role in radiation-induced multiple organ injury. Post radiation exposure, a loss of thrombin-thrombomodulin complex from EC leads to decreased activated protein C (APC) production and/or activation [
4]. APC is a component of plasma that possesses potent anti-inflammatory, anti-coagulant and cytoprotective properties [
5]. The attenuation of IR-induced changes in the rat urine metabolome by two bolus injections of APC at 24 and 48 h following 13.0 Gy of partial body X-irradiation has been previously observed [
6].
This study was designed to investigate the potential attenuation of delayed radiation effects in genetically altered mice expressing supraphysiologic levels of APC (APCHi), since the role of APC in the development of DEARE is still largely unexplored. The APCHi mouse model was generated on a C57BL/6N background that expresses the D168F/N173K mouse analogue of the hyper-activatable human D167F/D172K protein C variant [
7,
8], which allows for increased circulating APC levels throughout the lifetime of the mouse. We have previously shown gender dependent modulation in DEARE in the GIT, heart and skin in APCHi mic [
9].
Metabolomics is a tool of choice to delineate radiation-induced metabolic alterations and help identify potential differences based on gender or individual genotypes as metabolomics can provide phenotypic signatures that are downstream of other -omics technologies [
10]. Employing metabolomics to analyze and quantify changes in metabolic profiles can help to characterize the underlying physiological conditions of an individual well before symptoms of tissue injury or organ dysfunction become apparent [
11]. In this study, male and female cohorts of C57BL/6N wild-type (WT) and APCHi transgenic mice were exposed to 9.5 Gy of γ-radiation to determine changes in plasma metabolic profiles. The goal of this study was two-fold; first to identify the long-term metabolomic biomarkers of radiation injury at six months post-irradiation, and secondly, to understand how genotype and gender modulate delayed radiation response. We found that radiation exposure induced perturbations in mouse plasma profiles that were indicative of dyslipidemia, and disruption of the metabolic alterations related to initial gut injuries, amino acid metabolism and energy metabolism. Some of the perturbations were different between male and female mice, and between the two genotypes, where APCHi mice showed fewer late effects of IR exposure.
2. Results
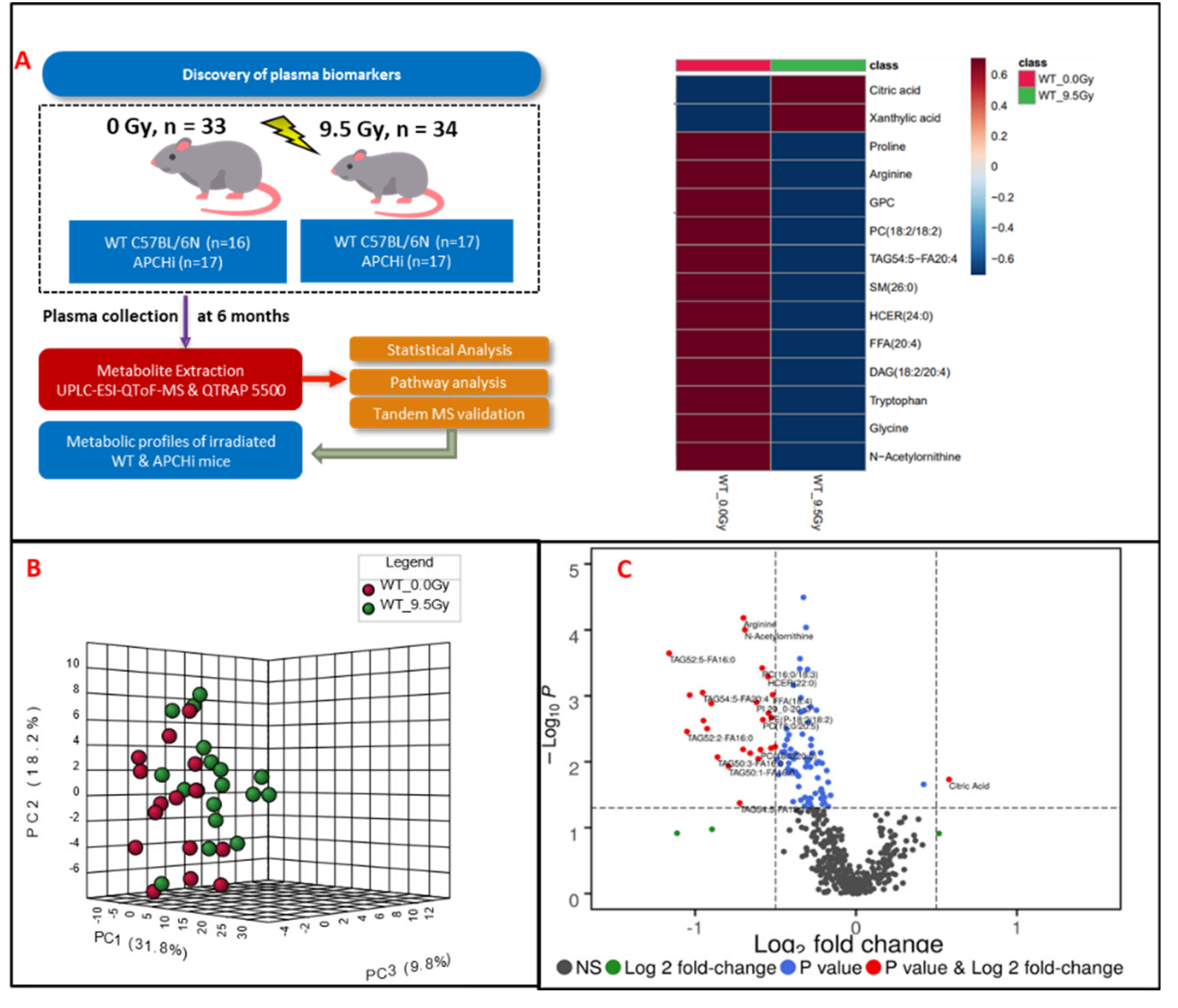
C57BL/6N WT (n= 20 male and n= 13 female) and transgenic APCHi mice (n= 17 male and n= 17 female) were subjected to γ radiation at a single dose of 9.5 Gy with both hindlegs shielded from IR to allow long-term survival. Plasma samples were obtained at 6 months after IR exposure and subjected to LC-MS based metabolomic profiling (
Figure 1, panel A). Preprocessing of untargeted profiling data using XCMS resulted in 3258 and 904 features detected in electrospray positive and negative ionization modes, respectively. Data normalization and log transformation was performed prior to univariate analysis. Binary group comparisons between sham and irradiated plasma samples resulted in the selection of 345 significantly dysregulated features based on fold-change cut-off of >2 and FDR adjusted p-value less than 0.05, and these dysregulated features were further selected for validation using fragment-based tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). Of the features selected for MS/MS validation, a subset of 48 metabolites were validated using fragmentation pattern matching by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) or METLIN (Scripps Institute, La Jolla, CA, USA) databases; this methodology has been used by several research groups [
12,
13] (Supplementary Table 1 and 2).
An in-house multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) system was developed based on quantitative metabolomics and lipidomic analytical methodologies and used for the identification and quantification of metabolites that exhibited IR-induced alteration in their abundance. Data processing followed by quality control measures provided us with 447 reliable metabolites, of which 63 were observed significantly dysregulated (fold-change cut-off of >1.5 and p-value < 0.05) for binary group comparisons between sham and irradiated animals within each genotype (Supplementary Table 3).
2.1. Exposure to γ Radiation Induces Robust Changes in Mice
To delineate the alterations in the plasma metabolic profiles at 6 month post-irradiation, we first compared the irradiated and sham treated WT mice, irrespective of gender. Principal component analysis dictated the distinctive plasma profile for irradiated mice compared to the sham group (
Figure 1, panel B). A volcano plot (
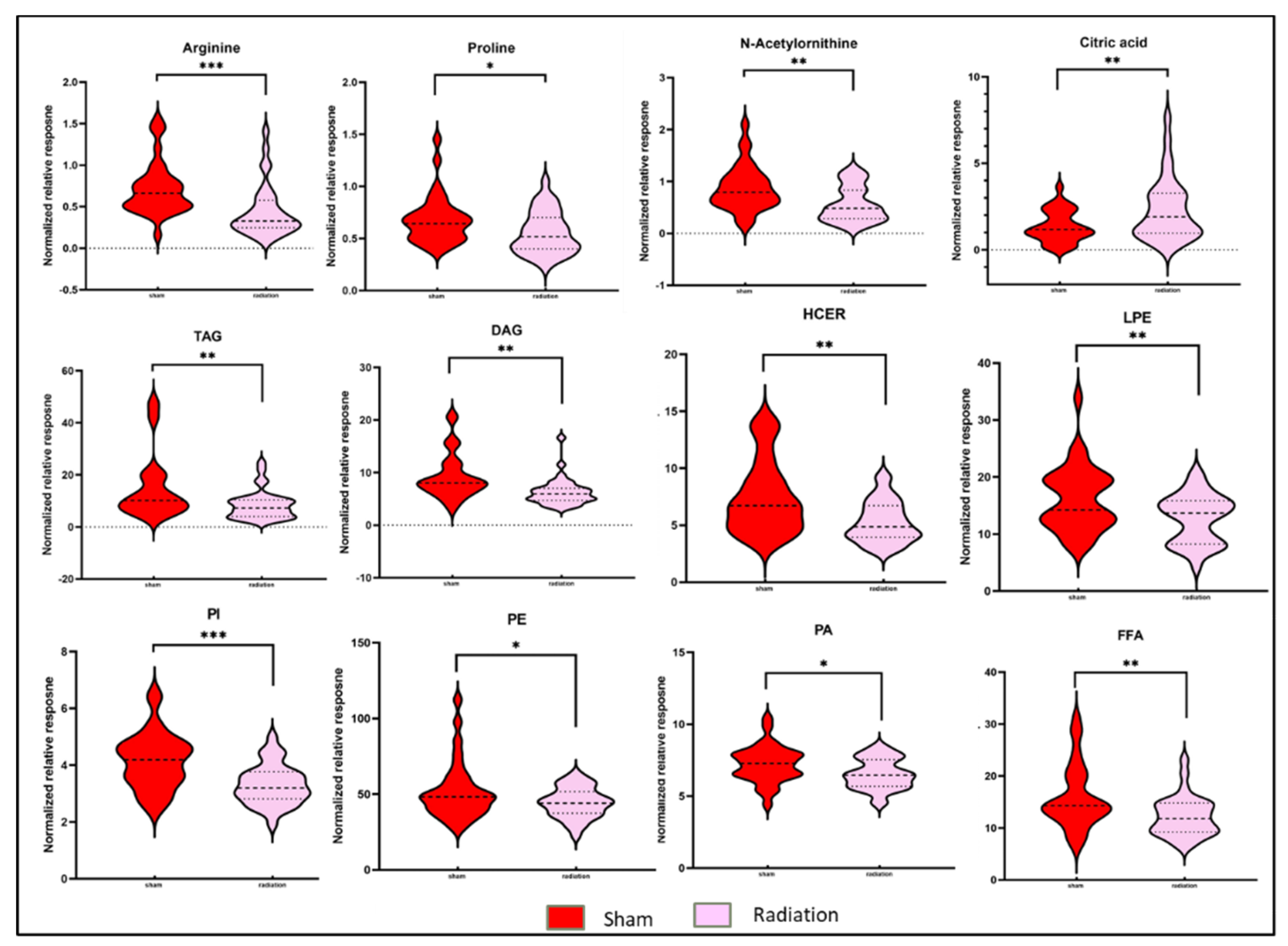
Figure 1, panel C) was used to visualize differential abundance of significant (p-value <0.05) metabolites. A total of 36 metabolites were observed as significantly dysregulated in radiation exposed mice (Supplementary Table 3). Notable downregulations across several classes of lipids such as fatty acyls, glycerophospholipids, glycerolipids and sphingolipids (
Figure 2) are reflective of radiation induced dyslipidemia. The subsided levels of amino acids, such as N-acetyl-ornithine, arginine and proline are suggestive of altered arginine (Arg) biosynthesis. Altered Arg levels could also be indicative of perturbations in the urea cycle. Arg is reported to mitigate the radiation-induced host immune dysfunction [
14]. Tryptophan (Trp) is a product of intestinal microbiota, and the dysregulated Trp levels could be a consequence of early damage to the gut tissue [
15]. Further, elevated citrate levels could be indicative of an altered TCA cycle. KEGG pathway analysis revealed perturbations in several pathways including glycerophospholipid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism after exposure of IR.
2.2. Gender Based Metabolic Changes Following 9.5 Gy γ Radiation Exposure
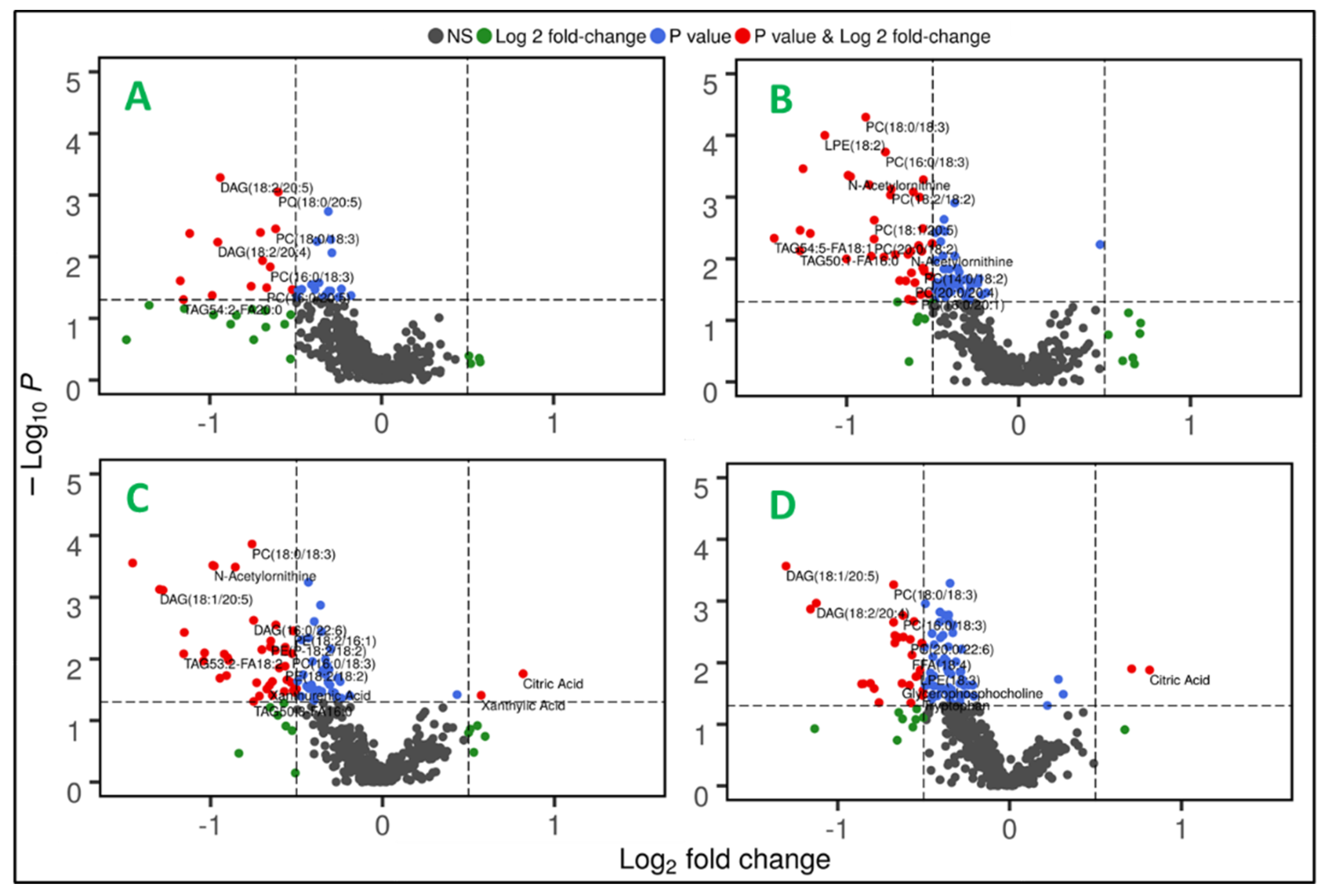
Next, gender and genotype dependent metabolic alterations were examined. Volcano plots portrayed in
Figure 3 A-D describe the distinctive metabolic phenotypes in WT and APCHi, as well as gender-based modulation in host response.
Gender-based data analysis revealed noteworthy differences in the plasma metabolic profiles upon radiation exposure. Comparative sub-cohort analyses of irradiated versus sham mice showed significant dysregulation (FC>1.5 and p-value <0.05) of 48 and 28 metabolites in female and male mice, respectively (Supplementary Table 2 and 3). Downregulation of glycerophospholipids and fatty acyls, and metabolites such as Arg, tyrosine, prostaglandin E1 ethanolamide and some indole metabolites were common to both male and female irradiated cohorts in comparison to their sham counterparts. Low tyrosine levels may indicate renal injury, which is a well-known metabolic alteration post radiation exposure. Along with Trp, the metabolic disturbances in indole-3-lactic acid (I3LA), indole-3-propionic acid (I3PA), and tryptophol levels indicate disturbances in the gut microbiota-promoted shikimate pathway. The upregulation of lathosterol, which is a precursor for cholesterols, also overlapped in both genders post-IR. Radiation-induced gut damage could result in bile-salt malabsorption and trigger enhanced hepatic production of cholesterol precursors. Bile-salts are sterol metabolites, and dysregulations in cholesterol levels are associated with increased risk of cancer and cardiovascular diseases [
16]. N-Oleoyl-L-serine, an endogenous orphan lipid that mediates energy homeostasis and bone metabolism was also upregulated in both genders.
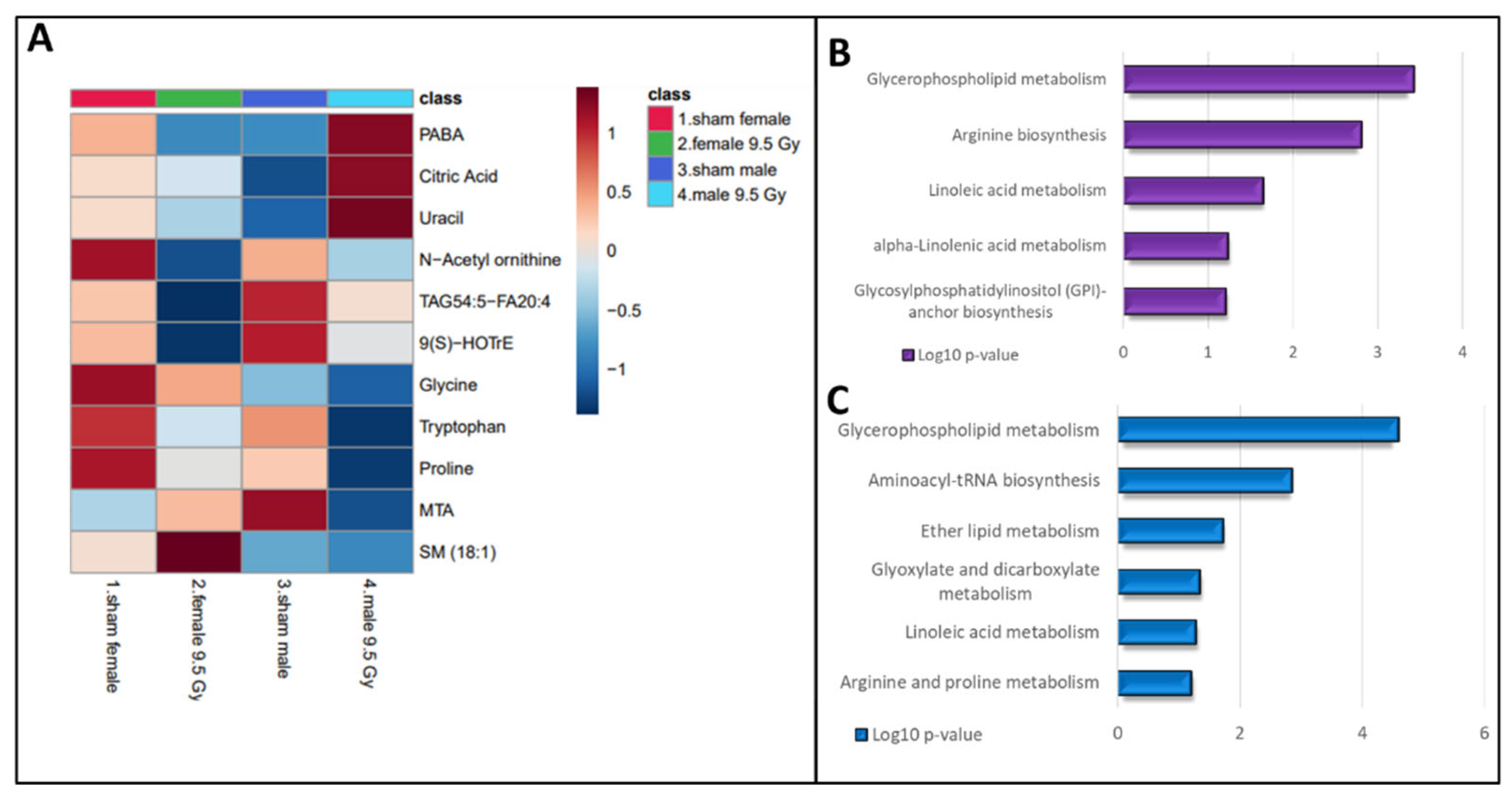
Conversely, some metabolites showed gender-specific modulation in radiation response. For example, the downregulated levels of amino acids (tryptophan, glycine and proline) and upregulations in metabolites such as citric acid, 4-aminobenzoic acid and uracil were observed to be specific to male mice. Altered abundance of purine metabolism intermediates and uracil are suggestive of perturbed nucleic acid biosynthesis. Likewise, a decrease in levels of TAGs, N-acetylornithine, 9(S)-HOTrE, and an increase in SM (18:1) were unique for irradiated female mice (
Figure 4, panel A). Dysregulated dopamine levels could be attributed to lower tyrosine levels that could potentially impact the functions of neuronal system. The post-irradiation increase in GSH levels could be in response to combat enhanced oxidative stress burden. Pathway analysis showed dysregulation in glycerophospholipid, and linoleic acid metabolism pathways were common to both genders after IR exposure. However, perturbations in Arg biosynthesis were found unique to female mice while alterations in arginine and proline metabolism were specific to male mice (
Figure 4, panel B-C).
2.3. Genotype Specific Metabolic Changes Following 9.5 Gy γ Radiation Exposure
Next, the modulation of radiation response by the genotypic makeup of the mice was studied. Gender-independent binary comparisons were performed between the metabolic profiles of the 9.5 Gy irradiated APCHi group with the respective sham irradiated animals. Radiation-induced alterations in APCHi mice were then analyzed alongside the phenotyping changes exhibited by irradiated WT mice to assess differences in radiation response.
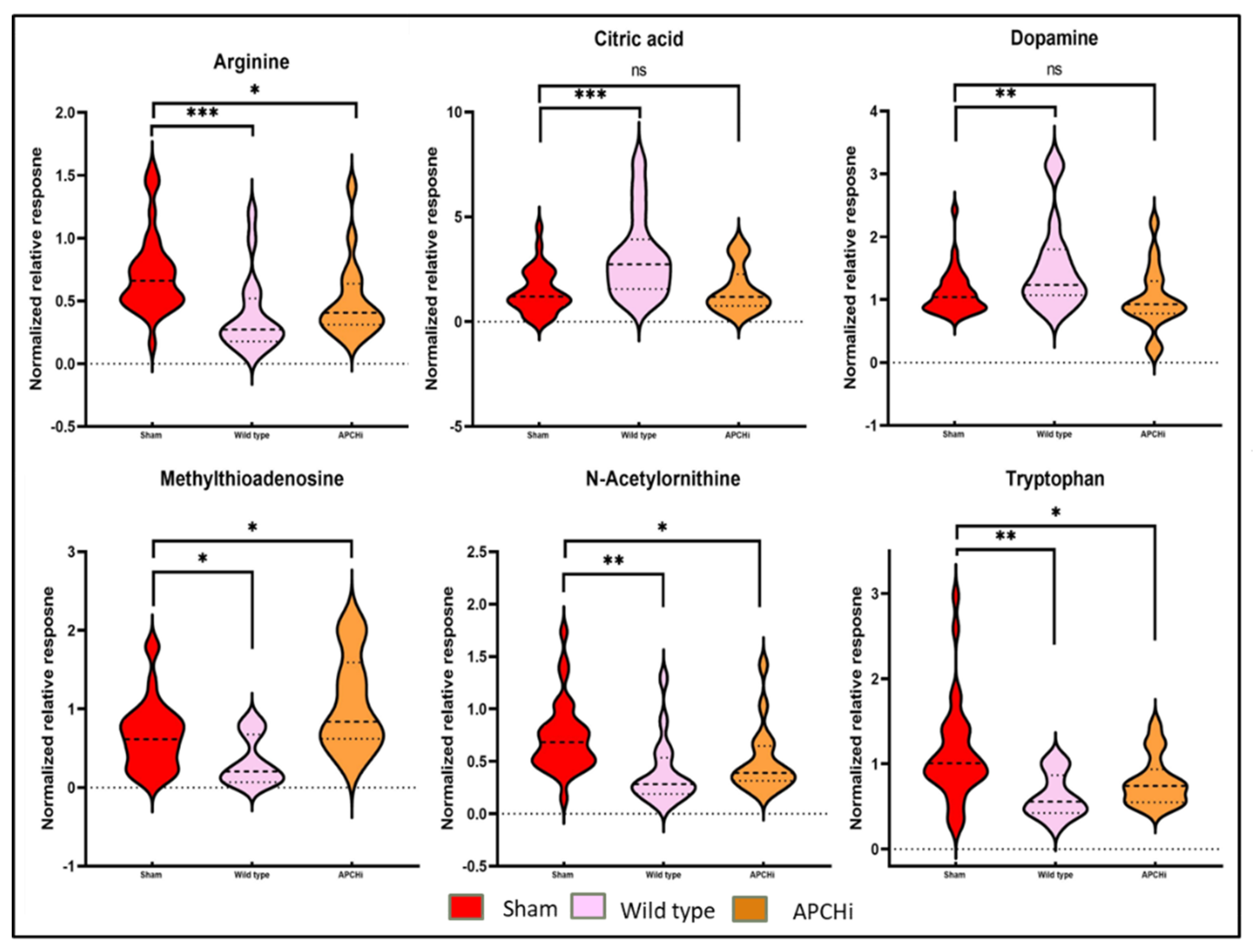
The lipid classes, such as phospholipids (PAs, PEs, LPAs) and FFAs, which were found downregulated in irradiated WT mice, showed near normal abundance in the irradiated APCHi mice. Similarly, APCHi mice showed fewer IR-induced perturbations for a variety of small molecules including amino acids (
Figure 5). Amino acids are considered as key regulators in maintaining vascular homeostasis by modulating EC proliferation, migration survival, and function [
17,
18]. Near normal levels of citrate in APCHi mice suggest a normalized TCA cycle. Upregulation of the TCA cycle plays a pivotal role in oncogenesis and inflammation [
19]. Xanthurenic acid (XA) has been reported as a novel vasoactive compound, and its formation is a key event in the pathophysiology of inflammation-induced hypotension [
20]. XA, which is a potential biomarker of radiation exposure and possibly renal failure [
21,
22,
23], showed dysregulated abundance post-IR, however, exhibited near sham levels in APCHi mice. Subsided hypoxathine levels in APCHi mice are suggestive of improved nucleic acid biosynthesis compared to irradiated WT mice. Also, higher levels of hypoxanthine are known to induce endothelial dysfunction through reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [
24].
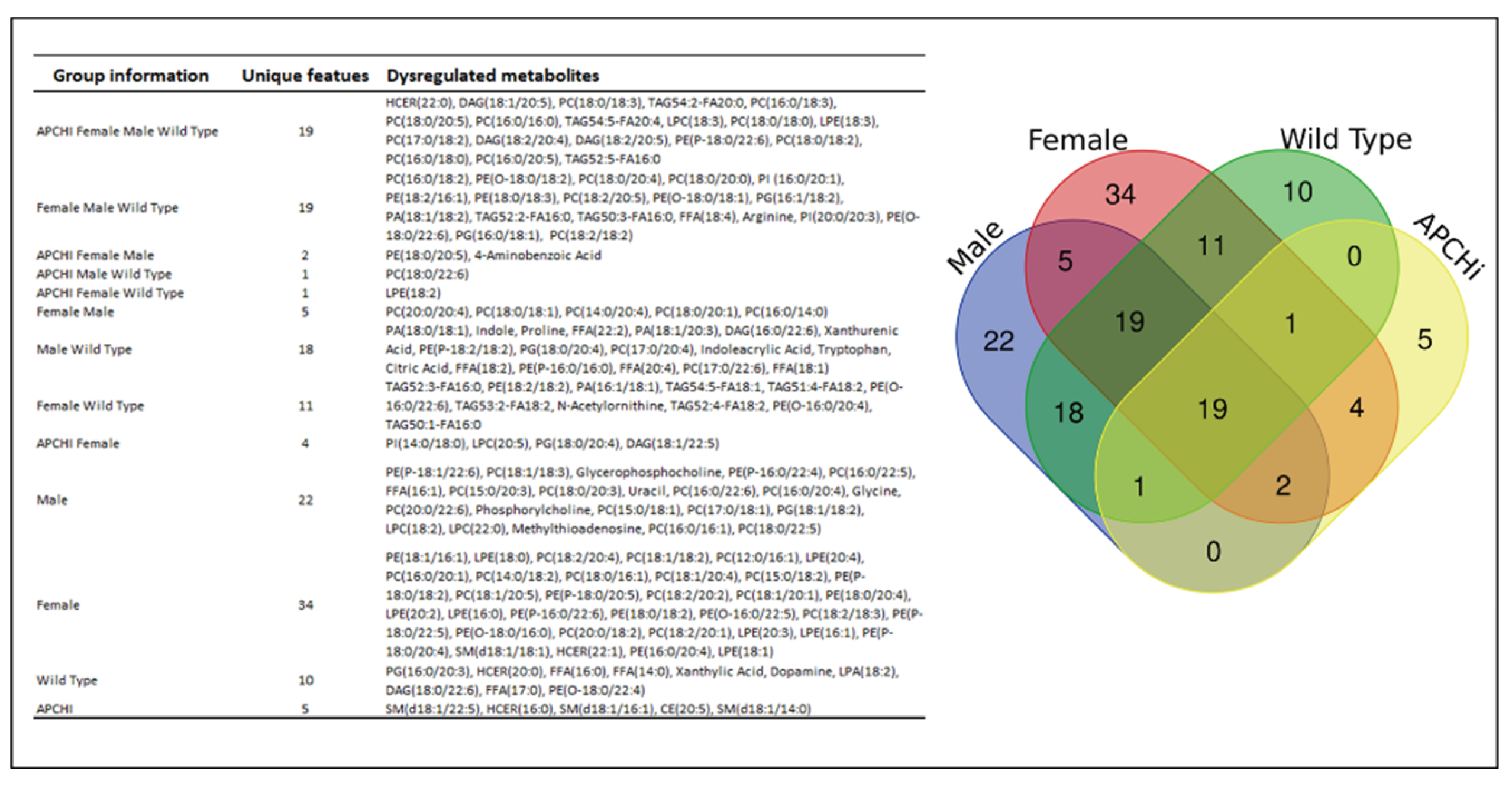
The Venn diagram in
Figure 6 details the significantly dysregulated metabolites, common and unique, from all binary group comparisons in the study.
3. Discussion
Accidental or intentional exposure to IR is a major public health concern that requires substantial efforts to manage and treat exposed individuals. Here, we utilized a metabolic phenotyping approach to characterize the molecular response to irradiation (9.5 Gy γ-radiation) and its modulation by genotype and gender using C57BL/6N and APCHi on the C57BL/6N background as mouse models. Plasma samples collected at six months after exposure from male and female cohorts of mice were characterized using LC-MS based metabolomics and lipidomics. Several lipidomic perturbations were identified, supporting existing evidence that significant dyslipidemia is a delayed effect of IR and may be used as an indicator of radiation exposure [
24]. Additional long-term studies also indicate that lipid measures are appropriate biomarkers for DEARE [
25]. Downregulation of glycerophospholipids may be an indication of chronic oxidative stress in irradiated mice [
25]. Biosynthesis and degradation of phosphatidylcholines (PCs) are considered necessary for cell cycle progression, and the dysregulation of PC metabolism has been identified during apoptosis [
26,
27,
28]. Glycerophospholipids are involved in several essential physiological activities, so their dysregulation may be an indicator of radiation induced injury to several organs such as the kidney, brain and heart [
29,
30]. Subsided levels of free fatty acids following IR exposure could be a cellular response as a protective mechanism [
31].
Disruption of amino acid metabolism following IR is well documented [
32]. The decreased levels of Arg may affect physiological functions like cell proliferation, survival, and protein synthesis. Arg is a precursor of nitric oxide (NO) which is the most important endothelium-derived vasodilator molecule capable of promoting vascular health. However, ROS-promoted NO breakdown is the primary cause of endothelial dysfunction. Radiation-induced immune dysfunction is reported to be reversed by L-arginine [
14]. Since Arg is an intermediate in the urea cycle, altered Arg levels could be indicative of perturbed urea cycle and have impacts on downstream pathways such as creatine synthesis. The significance of arginine as a regulator of the mTORC1 (mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1) pathway lies in its role in mediating cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism. mTORC1 acts as a central hub in the cell, integrating signals from various sources including nutrients, growth factors, and energy levels [
33,
34]. Arginine, an amino acid, is known to influence mTORC1 activity, thereby affecting cellular processes crucial for growth and proliferation [
34]. Additionally, it suggests that mTOR inhibition (with rapamycin or its analogs), combined with radiation therapy, could potentially enhance the efficacy of cancer treatment by increasing radiation sensitivity [
35]. Activation of mTORC1 in pericryptal mesenchymal cells through the induction of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) following radiation injury has been reported by Bohin et al. This finding suggests a potential mechanism by which radiation injury triggers cellular responses mediated by IGF-1, ultimately leading to mTORC1 activation in the mesenchymal cells surrounding the crypts [
36]. Indeed, Wang et al. have reported that mTORC1 signaling is activated following irradiation and plays a crucial role in facilitating the timely regeneration of the transient amplifying cell (TAC) pool within hair follicles. This underscores the importance of mTORC1 signaling in tissue regeneration and repair following radiation-induced damage, particularly in the context of hair follicle regeneration [
37]. Near normal levels of arginine observed in APCHi mice indicate that APC might confer radiation resistance by activating mTORC1. Future studies will be required to understand the mechanism of mTORC1 activation by APC.
Alterations in Trp metabolism are associated with many pathological states such as gastrointestinal disorders including inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) [
15,
38]. Radiation-induced changes in the Trp/Kyn ratios typically manifest as inflammation, renal failure and cancer [
22,
39]. The TCA cycle is a hub for generating cellular energy, and the precursors for these biosynthetic pathways are known to modulate different aspects of cancer progression [
40]. Upregulation of serum lathosterol levels, as observed in this study, is reported to cause perturbations in whole body cholesterol synthesis [
41]. Overall, the WT mice in this study were observed to exhibit IR-induced disruptions in several of metabolic pathways relating to lipid metabolism, amino acid/protein metabolism, gut metabolome, energy metabolism, cholesterol and nucleic acids biosynthesis that could potentially manifest to disorders relating to kidney damage, urea cycle, DNA damage or GIT injury.
The role of APC-modulated protective effects in long-term radiation toxicity is still largely unknown and further exploration is requisite. In this study, higher endogenous levels of APC were found to partially normalize post-IR plasma metabolic profiles, possibly indicating the alleviation of radiation injury in the irradiated APCHi group. Vascular phosphatidylethanolamine levels are believed to be a marker for endothelial dysfunction associated with hypertension [
42,
43]. Since Arg is known to improve EC functions through the promotion of NO production, the near sham levels of Arg and the related amino acids are reflective of normal Arg biosynthesis [
14] and alleviated EC function. Also, observance of normal tryptophan abundance could be indicative of healthy intestine functions. In our study, APC was found to prevent TCA cycle irregularities as indicated by normal citrate levels in the irradiated APCHi cohort compared to the sham cohort. Citrate can act as a metabolic regulator and is involved in numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes such as inflammation, cancer, insulin secretion, and neurological disorders [
44,
45,
46]. Elevated hypoxanthine levels could enhance ROS production and induce endothelial dysfunction, thus leading to vascular complications [
24]. However, near sham hypoxanthine levels as observed in APCHi animals is suggestive of ameliorated endothelial functions. Collectively, these findings suggest that the APCHi genotype imparts attenuation of metabolic perturbations caused by radiation exposure which may be attributed to vascular endothelial repair.
Our prior study demonstrating metabolic alterations associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury, particularly showcasing differences in trends between APCHi and WT mice at 6 months after exposure to 9.5 Gy, indicates that there are distinct pathways affected by radiation exposure [
9]. These findings suggest that perturbations in pathways could potentially be leveraged to mitigate the effects of delayed effects of acute radiation exposure (DEARE) on late-responding organ systems. Overall, these findings underscore the importance of elucidating the molecular pathways involved in radiation-induced tissue damage and highlight the potential for targeted therapeutic strategies to alleviate the late effects of radiation exposure on organ systems.
In conclusion, plasma metabolic profiles were used to characterize DEARE signatures in mice at 6-months post-IR. Our data show that increased circulating levels of endogenous APC constituted in mice normalized some IR-induced metabolic perturbations. Additional studies will be required to test the administration of APC as a mitigator of late radiation injuries and identify biological mechanisms by which APC may have different effects on certain DEARE in males compared to females.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
All animal work was performed at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS). We used male and female mice on a C57BL/6N background. All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) under protocol #3763. Male and female mice carrying the D168F/N173K transgene (obtained from Hartmut Weiler, PhD, Blood Center of Wisconsin) were bred with WT C57BL/6N mice (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME) to obtain APCHi and WT mice. Male and female mice of both genotypes were shipped to UAMS and housed 4-5 per cage in conventional plastic cages and subjected to 12-hour light–dark cycles (lights on 7:00 AM–7:00 PM) and controlled ambient temperature and air humidity. Water and standard chow were given ad libitum. The Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine (DLAM) at UAMS and the Biomedical Resource Center at Medical College of Wisconsin are fully accredited by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC, Animal Welfare Assurance number A3063-01 and A-3225-01).
4.2. Experimental Design
Male and female WT and APCHi mice were randomly divided into sham and irradiated cohorts, as follows. Group 1 consisted of C57BL/6N wild type mice (n=33). Of these 33 mice, 20 were males and 13 were females. Of these mice, 8 males and 8 females were assigned to sham treatment, and 12 male and 5 female mice received radiation treatment (9.5 Gy). Group 2 consisted of transgenic APCHi mice (n=34). Of these 34 mice, 17 were males and 17 were females. There were 8 males and 9 females in the sham condition in group 2, while the radiation cohort (9.5 Gy) contained 9 males and 8 females.
4.3. Radiation Exposure
At the age of 12–14 weeks, APCHi and WT mice of both genders (34 mice in total) were exposed to 9.5 Gy of γ-rays delivered at 1 Gy/min, using a 137Cs source cabinet irradiator (Mark 1, Model 68A, JL Shepherd & Associates, San Fernando, CA) without the use of anesthesia. Unanesthetized mice were placed in Plexiglas mouse holders on a Plexiglas base plate, and blocks of 2 cm thick tungsten (4 half-value layers) were carefully placed over both hind-legs of the animals. A separate cohort of mice was exposed to sham-irradiation by bringing them to the radiation room and placing them in the holders for 9.5 minutes without exposing them to radiation.
Dosimetry was performed with Gafchromic film (DOSE-MAP, Ashland Specialty Ingredients, Wayne, NJ) and an ion chamber (Exradin A20, Standard Imaging, Middleton, WI) and electrometer (X4000, Standard Imaging) that are calibrated for γ-rays once a year.
Animals were monitored daily by trained animal care technicians and laboratory staff for signs of radiation sickness or distress as instructed by institutional veterinarians. Criteria to determine when animals should be euthanized were hunched position, lethargy, and significant weight loss. None of the animals reached these humane endpoints. All 67 animals survived until 6 months after irradiation.
4.5. Plasma Sample Collection
At 6 months after IR, animals were placed under anesthesia, and a blood sample was collected from the inferior vena cava into EDTA-coated tubes and immediately processed to prepare plasma. Plasma samples were stored at −80 °C until shipped on dry ice to Georgetown University Medical Center (Washington, DC) for -omics analysis.
4.6. Chemicals
All LC-MS grade solvents including acetonitrile and water were purchased from Fisher Optima grade, Fisher Scientific. High purity formic acid (99%) was purchased from Thermo-Scientific. Debrisoquine and 4-nitrobenzoic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (MO, USA). EquiSPLASH® LIPIDOMIX®, 15:0-18:1-d7-PA, C15 Ceramide-d7 (d18:1-d7/15:0) and 18:1 Chol (D7) ester were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (AL, USA). Internal standard for free fatty acid (FFA), dihydroceramides (DCER), hexosylceramides (HCER), lactosylceramides (LCER) were purchased from Sciex (MA, USA) as Lipidyzer platform kit.
4.7. Untargeted Metabolomics Using UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS
A total of 75 μL of chilled 35% water, 25% methanol and 40% isopropanol containing internal standards (debrisoquine and 4-nitrobenzoic acid) was added to 25 µL of plasma sample. Next, the samples were vortexed and incubated at 4 °C for 20 min, followed by the addition of 100 μL of chilled acetonitrile to each sample and incubated at -20 °C for 20 min. Finally, the samples were centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 20 min at 4 ℃. The supernatant of each sample was transferred to MS vials for data acquisition. The sample queue was randomized to avoid bias. Each sample (1 μL) was injected to a 1.7 μm, 2.1 mm × 50 mm Acquity BEH C18 column (Waters Corporation, MA, USA) using an Acquity UPLC system connected to an electrospray ion source coupled with a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer (ESI-Q-TOF, Xevo-G2S, Waters Corporation, MA, USA) operating in positive and negative ionization modes. The data were acquired in centroid TOF-MS mode over a mass range from 50 to 1,200 m/z.
4.8. Targeted Metabolomics Using 5500 QTRAP
The targeted metabolomics method was developed in-house to quantitate 270 endogenous molecules using QTRAP® 5500 LC-MS/MS System (Sciex, MA, USA). To the 10 µL of each plasma sample, was added 50 μL of chilled isopropanol containing internal standards. The samples were vortexed for 1 min and kept at 4 °C for 20 minutes. Samples were incubated at -20 °C for 2 hours for complete protein precipitation. The samples were centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4 °C. The supernatant was transferred to MS vial for LC-MS analysis. 5 µL of the sample was injected onto a Kinetex 2.6 μm 100 Å 100 × 2.1 mm (Phenomenex, CA, USA) using SIL-30 AC auto sampler (Shimazdu, Kytoto, Japan) connected with a high flow LC-30AD solvent delivery unit (Shimazdu, Kytoto, Japan) and CBM-20A communication bus module (Shimazdu, Kytoto, Japan) online with QTRAP 5500 (Sciex, MA, USA) operating in positive and negative ion mode.
4.9. Targeted Lipdomics Using 5500 QTRAP
Targeted lipidomics method was developed in-house to measure all major lipid classes including glycerolipids, phospholipids, sphingolipids, fatty acyls, sterols etc., using QTRAP® 5500 LC-MS/MS System (Sciex, MA, USA). The above prepared targeted metabolomics samples were resolved on Xbridge amide 3.5 µm, 4.6 X 100 mm (Waters, MA, USA) column online with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (5500 QTRAP, SCIEX, MA, USA) operating in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. 5 µL of each sample was injected using SIL-30 AC auto sampler (Shimazdu, Kyoto, Japan) connected with a high flow LC-30AD solvent delivery unit (Shimazdu, Kyoto, Japan) and CBM-20A communication bus module (Shimazdu, Kyoto, Japan) online with QTRAP 5500 (Sciex, MA, USA) operating in positive and negative ion modes.
4.10. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis:
The quality and reproducibility of LC-MS data was ensured using several measures. The column was conditioned using a pooled QC sample that was prepared as a pooled aliquot of all samples in the study set. The QC sample was injected periodically (after every 10 sample injections) to monitor shifts in signal intensities and retention time as measures of reproducibility and ensure high quality data acquisition. A solvent blank sample was also run periodically to monitor and minimize the sample-to-sample carry-over. For targeted data, the detected metabolites were filtered using a signal/noise ratio >20:1 and retention time (RT) tolerance of 5 seconds criteria, to identify the reliable features. The details on LC gradient and mass spectrometry instrument parameters have been provided in the Supplementary information. Data pre-processing include normalization of the raw LC-MS data initially using internal standards. The detected metabolites/features (m/z_rt pairs) with more than 20% missing value were filtered out and with less than 20% of missing value were imputed by half of the minimum positive value in the original data. The features with more than 15% of coefficient of variance (CV) were also filtered out. The remaining high-quality features were normalized by QC-RLSC followed by statistical analyses using R (version 4.0.1). For the 67 samples in the study set, the level of differential expression for each metabolite was calculated using an unpaired t-test, comparing sham versus irradiated plasma samples, constrained by
p-value<0.05. We also compared gender and genotype based metabolic differences post irradiation in mice plasma. The identities of significantly dysregulated metabolites were confirmed using tandem mass spectrometry. Raw files from untargeted data were converted into MSP format with an in-house developed R package “msmsr” (Li et al., unpublished) and the NIST 2017 MS/MS spectra database. Mummichog v2.0, a Python package specifically designed for untargeted metabolomics was used for pathway analysis [
47]. Mummichog v2.0 tests pathway enrichment patterns using permutations and computes the probability for involvement in each pathway.
Figures were created using R and BioRender (
www.BioRender.com).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Supplementary Table 1-3
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, Marjan Boerma and Amrita K Cheema; Methodology, Shivani Bansal, Yaoxiang Li, Baldev Singh, Meth Jayatilake, Sunil Bansal, Vijayalakshmi Sridharan; Software, Shivani Bansal and Yaoxiang Li; Validation, Shivani Bansal, Meth Jayatilake, Sunil Bansal; Formal Analysis, Shivani Bansal, Yaoxiang Li, Meth Jayatilake, Sunil Bansal; Investigation, Amrita K Cheema; Resources, Amrita K Cheema; Data Curation, Shivani Bansal, Meth Jayatilake, Sunil Bansal; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Shivani Bansal, Sunil Bansal; Writing—Review & Editing, Shivani Bansal, William Klotzbier, Sunil Bansal, Jose A. Fernández, John H. Griffin, Hartmut Weiler, Marjan Boerma, Amrita K Cheema; Visualization, Yaoxiang Li; Supervision, Amrita K Cheema; Project Administration, Marjan Boerma and Amrita K Cheema; Funding Acquisition: Marjan Boerma, Hartmut Weiler, John H. Griffin, Amrita K Cheema.
Funding
The study was supported by NIH/NIAID through grants U01 AI148308 to MB, HW and JHG, U01 AI133561 to MB and AKC, and NIH/NIHGMS through grant P20 GM109005 to MB.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Metabolomics Shared Resource in Georgetown University (Washington, DC, USA) partially supported by NIH/NCI/CCSG grant P30-CA051008. The authors would also like to acknowledge Dr. McKenzie Pearson, Application Specialist at Sciex for her support in the optimization of LC-MRM methodologies for deep lipidomics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Unthank, J.L. Delayed Effects of Acute Radiation Exposure in a Murine Model of the H-ARS: Multiple-Organ Injury Consequent to <10 Gy Total Body Irradiation. Health Phys 2015, 109, 511–521. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; et al. Significance of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of early and delayed radiation enteropathy. World J Gastroenterol 2007, 13, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guipaud, O.; et al. The importance of the vascular endothelial barrier in the immune-inflammatory response induced by radiotherapy. Br J Radiol 2018, 91, 20170762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C.T.; F. B. Taylor, Jr., and T.R. Snow, Inflammation and coagulation: Linked processes potentially regulated through a common pathway mediated by protein C. Thromb Haemost 1991, 66, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, L.O.; et al. Activated protein C variants with normal cytoprotective but reduced anticoagulant activity. Blood 2004, 104, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; et al. Analysis of the urinary metabolic profiles in irradiated rats treated with Activated Protein C (APC), a potential mitigator of radiation toxicity. International Journal of Radiation Biology 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isermann, B.; et al. Activated protein C protects against diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting endothelial and podocyte apoptosis. Nature Medicine 2007, 13, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mens, T.E.; et al. Variable phenotypic penetrance of thrombosis in adult mice after tissue-selective and temporally controlled Thbd gene inactivation. Blood Adv 2017, 1, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, V.; et al. Sex-dependent effects of genetic upregulation of activated protein C on delayed effects of acute radiation exposure in the mouse heart, small intestine, and skin. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; J. Ivanisevic, and G. Siuzdak, Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salek, R.M.; et al. A metabolomic comparison of urinary changes in type 2 diabetes in mouse, rat, and human. Physiol Genomics 2007, 29, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leoz, M.L.A.; et al. Cross-Ring Fragmentation Patterns in the Tandem Mass Spectra of Underivatized Sialylated Oligosaccharides and Their Special Suitability for Spectrum Library Searching. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2019, 30, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, B.T.; et al. Hybrid Search: A Method for Identifying Metabolites Absent from Tandem Mass Spectrometry Libraries. Anal Chem 2019, 91, 13924–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, J.; et al. L-Arginine reverses radiation-induced immune dysfunction: The need for optimum treatment window. Radiat Res 2009, 171, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; J. Planchais, and H. Sokol, Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, J.; et al. A role of the bile salt receptor FXR in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2010, 30, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Y. Wu, and L. Ye, The Role of Amino Acids in Endothelial Biology and Function. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, X.; L. Xie, and C. Patterson, Emerging Roles of Vascular Endothelium in Metabolic Homeostasis. Circ Res 2018, 123, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scagliola, A.; F. Mainini, and S. Cardaci, The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle at the Crossroad Between Cancer and Immunity. Antioxid Redox Signal 2020, 32, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; et al. Vasorelaxing Action of the Kynurenine Metabolite, Xanthurenic Acid: The Missing Link in Endotoxin-Induced Hypotension? Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, H.Z.; et al. Pathological apoptosis by xanthurenic acid, a tryptophan metabolite: Activation of cell caspases but not cytoskeleton breakdown. BMC Physiol 2001, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, D.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenine pathway in experimental chronic renal failure. Nephron 2002, 90, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; et al. The effect of low dose rate on metabolomic response to radiation in mice. Radiation and Environmental Biophysics 2014, 53, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; et al. Hypoxanthine causes endothelial dysfunction through oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017, 482, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, J.; et al. Contribution of reactive oxygen species to cartilage degradation in rheumatic diseases: Molecular pathways, diagnosis and potential therapeutic strategies. Curr Med Chem 2003, 10, 2123–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal-Esteban, L.C. and L. Fajas, Cell cycle regulators in cancer cell metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020, 1866, 165715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.F.; et al. Phosphatidylcholine-Derived Lipid Mediators: The Crosstalk Between Cancer Cells and Immune Cells. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 768606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, N.D. ; The role of phosphatidylcholine and choline metabolites to cell proliferation and survival. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 48, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirthensohn, G.; Beck, F.X.; Guder, W.G. Role and regulation of glycerophosphorylcholine in rat renal papilla. Pflugers Arch 1987, 409, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Horrocks, L.A.; Farooqui, T. Glycerophospholipids in brain: Their metabolism, incorporation into membranes, functions, and involvement in neurological disorders. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2000, 106, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, R.; et al. Lipid metabolism in cancer cells under metabolic stress. Br J Cancer 2019, 120, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiakis, E.C.; et al. Metabolic phenotyping reveals a lipid mediator response to ionizing radiation. J Proteome Res 2014, 13, 4143–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.; et al. Control of TSC2-Rheb signaling axis by arginine regulates mTORC1 activity. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. and K.L. Guan, mTOR as a central hub of nutrient signalling and cell growth. Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.; et al. Modulation of mTOR signaling by radiation and rapamycin treatment in canine mast cell cancer cells. Can J Vet Res 2022, 86, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohin, N.; et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and mTORC1 Signaling Promote the Intestinal Regenerative Response After Irradiation Injury. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020, 10, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; et al. Activation of mTORC1 Signaling is Required for Timely Hair Follicle Regeneration from Radiation Injury. Radiat Res 2017, 188, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burr, R.L.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolites in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Overnight Time-course Study. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019, 25, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; et al. Increased serum kynurenine/tryptophan ratio correlates with disease progression in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eniafe, J. and S. Jiang, The functional roles of TCA cycle metabolites in cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WC, D. ; Serum lathosterol levels in human subjects reflect changes in whole body cholesterol synthesis induced by lovastatin but not dietary cholesterol. journal of lipid research 1995, 36, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M. Imaging Vascular Phosphatidylethanolamine. National Institute of Health (NIH): Northwestern University at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States.
- Appendix, in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 2016. p. 577-600.
- Icard, P.; Poulain, L.; Lincet, H. Understanding the central role of citrate in the metabolism of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1825, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Infantino, V.; et al. The mitochondrial citrate carrier: A new player in inflammation. Biochem J 2011, 438, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, A.R.; et al. The mitochondrial citrate carrier (CIC) is present and regulates insulin secretion by human male gamete. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; et al. Predicting network activity from high throughput metabolomics. PLoS Comput Biol 2013, 9, e1003123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).