1. Introduction
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a severe debilitating disease with a mortality rate of 27%–45% [
1,
2]. Patients in intensive care units (ICUs) with this syndrome often require mechanical ventilation (MV) for oxygenation. Ventilator-induced lung injury is characterized by an uneven lung inflammatory response after exposure to mechanical stretching; this is followed by a fibroproliferative reaction with extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, ultimately leading to ventilator-induced lung injury–associated lung fibrosis [
1,
2,
3,
4]. High mechanical stress, a local increase of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and the presence of the extra domain A splice variant of fibronectin have been demonstrated to induce the differentiation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts [
1,
2]. The injurious effects of MV on the ECM are triggered by increased transpulmonary pressure, heterogeneous distribution of ventilation, and increased tissue stretching and are exacerbated by limited pulmonary lymphatic drainage [
1,
4,
5]. In addition to causing ventilator-induced lung injury, MV can result in diaphragmatic weakness and the rapid decline of diaphragm muscle contractility and endurance, a phenomenon commonly referred to as ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction (VIDD) [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Diaphragm muscle dysfunction can aggravate underlying respiratory insufficiency, contributing to the disability burden of critically ill patients. Myofiber loss and replacement of fibrotic tissue due to aberrant repair are characterized by excessive accumulation of ECM components, such as collagen; the accompanying increase in muscle fragility and stiffness can prevent the diaphragm from achieving the optimal excursion lengths required for normal respiration [
10,
11]. The factors that determine the development of diaphragm injury, regeneration, and progressive fibrosis leading to diaphragm weakness are unclear.
Diaphragm fibrosis is the result of abnormal accumulation of ECM components, including collagens, either due to increased ECM generation, reduced ECM degradation activity, or a combination of both [
12,
13]. Excessive ECM deposition can be observed in the endomysium and perimysium of the skeletal muscles. Several growth factors, such as TGF-β1 [
12,
14], connective tissue growth factor, myostatin, Wnt signaling, platelet-derived growth factor family, vascular endothelial growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor, have been demonstrated to enhance the progression of skeletal muscle fibrosis. As a primary profibrogenic cytokine, TGF-β1 is a potent profibrogenic factor and crucial in the control of ECM production, remodeling, and degradation [
10,
12,
15].
MV-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrogenesis are capable of reducing diaphragm contractility and are primary contributors to the activation of proteolytic pathways, such as muscle-specific ubiquitin E3 ligases F-box protein atrogin-1 and muscle RING-finger proteins-1 (MuRF-1) [
4,
9]. Research has revealed that patients with long-term MV-dependency are highly susceptible to ventilator-associated pneumonia and lung fibrogenesis, which can lead to restrictive ventilatory impairment [
4,
6,
7,
16]. Therefore, research should clarify the potential molecular mechanisms responsible for acute lung injury (ALI) and diaphragm dysfunction, which hamper the weaning of patients from long-term MV.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), a family of cellular lipid kinases, phosphorylates the 3-hydroxyl of the phosphatidylinositol ring to produce lipid second messengers such as 3,4,5-triphosphate [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Several studies have researched class I PI3Ks, comprising class IA (p110α, β, and δ) and class IB (p110γ) isoforms [
18,
19]. Binding of the complexes of class IA kinases with regulatory p85-related subunits containing SH2 is substantially enhanced through receptor tyrosine kinases; by contrast, class IB p110γ associates with G-protein-coupled receptors through its regulatory subunit p101 or p84 and G-protein subunits upon receptor stimulation [
18,
19]. PI3K-γ is expressed in many cell types involved in airway inflammation and fibrogenesis, including endothelial cells and fibroblasts, and may regulate the influx of leukocytes into the diaphragm [
17,
18,
19,
20]. The absence of PI3K-γ can lead to reduced leukocyte activation and recruitment, decreased angiogenesis, and diminished transcription of fibrogenic markers in fibrotic lung tissue [
17,
18,
19,
20]. However, the underlying mechanisms, including that related to the PI3K-γ pathway, in MV-induced diaphragm fibrosis remain to be elucidated.
In the current study, we employed a bleomycin-induced VIDD mouse model [
1,
2] to 1) evaluate the role of PI3K-γ expression in diaphragm fibrogenesis during MV, 2) compare oxidative load and inflammatory cytokine production between MV and bleomycin-induced diaphragm damage, 3) examine the role of PI3K-γ in VIDD through PI3K-γ homozygous knockout and inhibition with AS605240 [
21], and 4) investigate the role of the PI3K-γ signaling pathway in bleomycin-induced myonuclear apoptosis. We hypothesized that MV with or without bleomycin pretreatment would enhance diaphragm injury, the production of free radicals, and diaphragm fibrogenesis through PI3K-γ pathway upregulation.
2. Results
2.1. AS605240 Mitigated the Effects of MV on Bleomycin-Induced VIDD
Mice were administered either 6 mL/kg MV (V
T6 group) or 10 mL/kg MV (V
T10 group) with room air for 8 h to induce VIDD. We analyzed the injurious effects of overdistension and treatment effects of intraperitoneally delivered AS605240. The physiological conditions at the beginning and end of MV are summarized in
Table S1. We monitored the mean arterial pressure of the mice and maintained normovolemic states. Transmission electron microscopy was used to explore MV- and bleomycin-induced changes in diaphragm ultrastructure. Studies have demonstrated that diaphragm myofiber atrophy due to disuse could be a crucial contributor to weaning difficulties [
6,
7]. Relative to the V
T6 group and the nonventilated controls, the V
T10 mice exhibited considerable disruptions in their diaphragmatic myofibrillar structures, with larger lipid droplets, unclear A-bands and I-bands, damaged Z-bands, and mitochondrial swelling (
Figure 1A–E) as well as a substantial reduction in muscle fiber diameter (
Figure 1G) being observed. The administration of AS605240 substantially reduced damage to the diaphragmatic fibers (
Figure 1F,G). Ultrasonography is a noninvasive tool for assessing the diaphragm in patients receiving MV [
6,
8]; therefore, to determine the effects of MV and bleomycin on diaphragm contractile function, we measured diaphragm dysfunction in the mice by using small animal ultrasound (VEVO 2100, Visual Sonics, Toronto, Canada). Relative to the V
T6 group and the nonventilated control mice, the V
T10 group exhibited decreased diaphragm excursion and thickening fraction (
Figure 1H,I). Thus, MV-mediated diaphragmatic weakness was substantially inhibited by AS605240 administration (
Figure 1H,I).
2.2. AS605240 Inhibited Bleomycin-Stimulated, MV-Induced Diaphragmatic Inflammatory Cytokine Production; Oxidative Stress; and Expression of Caspase-3, Calpain, Atrogin-1, MuRF-1, and PGC-1α
Research has highlighted the key role of inflammatory cytokine expression and oxygen radicals in MV-induced diaphragm damage [
7,
9,
13]. In the current study, we observed increased levels of TGF-β1 and malondialdehyde (a marker of lipid peroxidation) in the V
T10 group relative to those in the V
T6 group and the nonventilated controls (
Figure 2A,B). Furthermore, we performed Western blot analyses to identify the effects of MV on bleomycin-stimulated oxidative loads (casase-3 and calpain), the ubiquitin–proteasome system (atrogin-1 and MuRF-1), and PGC-1α (a regulator of muscle oxidative capacity) associated with VIDD (
Figure 2C–G). We observed increased levels of caspase-3, calpain, atrogin-1, and MuRF-1 but a decreased level of PGC-1α in the V
T10 group relative to those in the V
T6 group and the nonventilated controls (
Figure 2C–G). However, AS605240 administration normalized the levels of the markers.
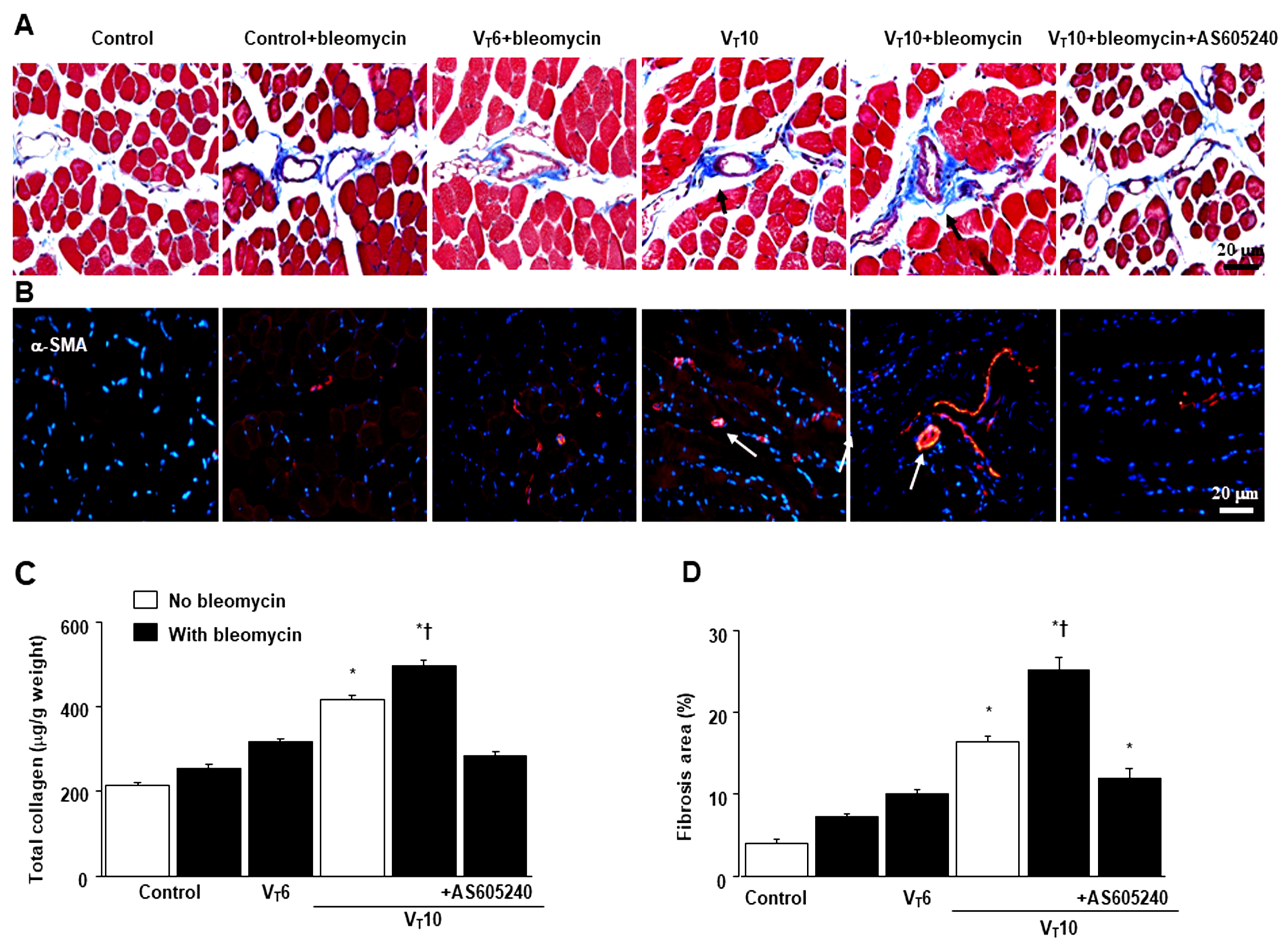
2.3. AS605240 Mitigated the Effects of MV on Bleomycin-Induced Collagen Fiber Production and Fibrogenic Markers
Masson’s trichrome staining was performed to determine the effects of MV on ECM collagen fiber accumulation. We observed more collagen fibers in the ECM in the V
T10 group than in the V
T6 group and the nonventilated control mice (
Figure 3A). To identify the cell types involved in the MV-induced diaphragm fibrogenesis, we measured the expression of α-SMA, a myofibroblast marker, by using immunofluorescent staining (
Figure 3B). In addition, to quantify the effects of MV on ECM deposition, we quantified the number of collagen fibers in the ECM by considering the total diaphragm collagen content and calculated a fibrosis score by using Masson’s trichrome staining (
Figure 3C,D). Our results indicate that treatment with the PI3K-γ inhibitor AS605240 substantially reduced the MV-induced increase in collagen fibers and upregulation of α-SMA (
Figure 3).
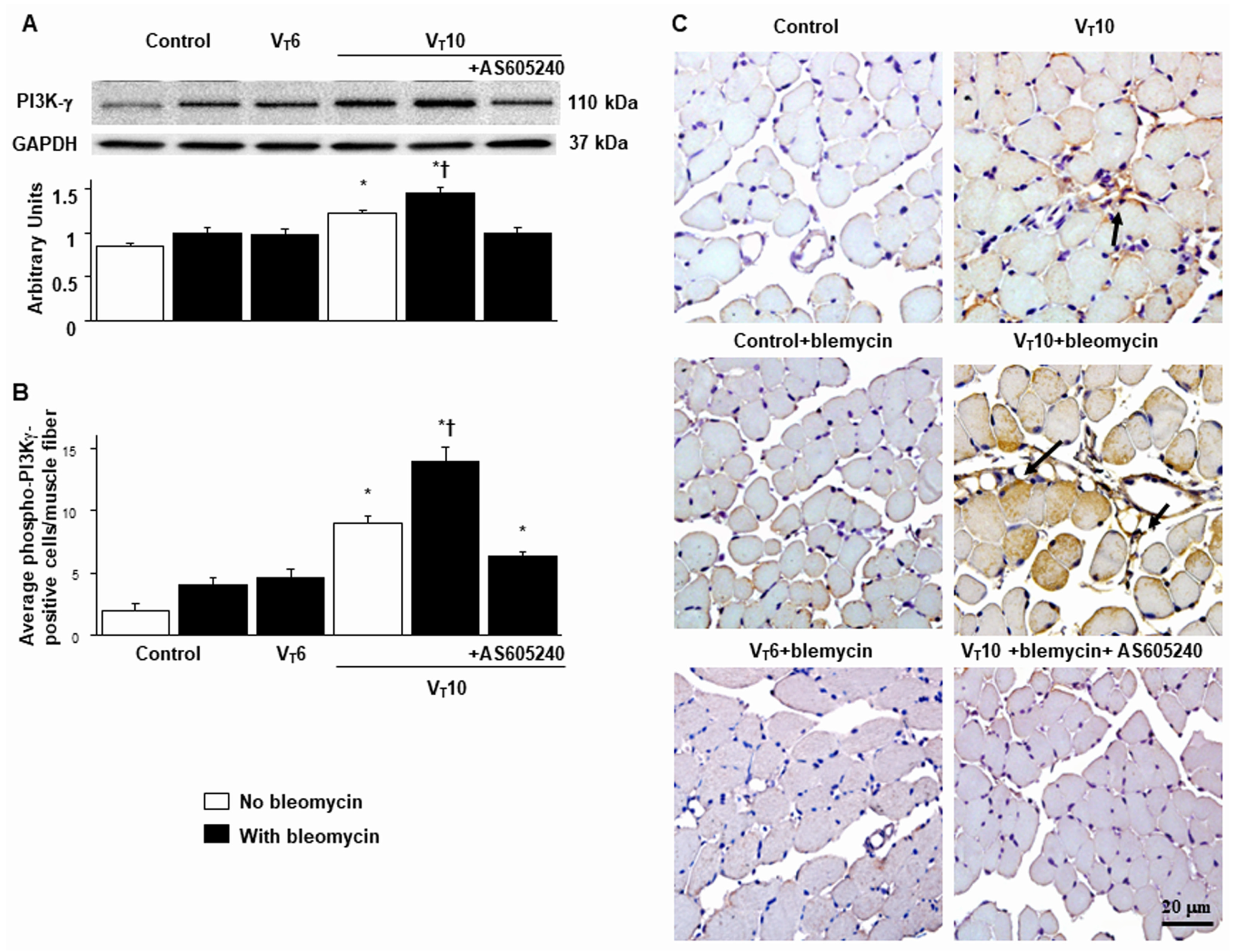
2.4. AS605240 Mitigated the Effects of MV on Bleomycin-Stimulated PI3K-γ Protein Expression
PI3K-γ activation has been reported to play a crucial role in regulating inflammatory cytokines and MV-augmented lung fibrosis; we thus assessed PI3K-γ protein expression to verify the role of the PI3K-γ signaling pathway in VIDD and diaphragm fibrosis (
Figure 4) [
17,
18,
21]. We performed Western blot analyses to measure the effects of V
T = 10 mL/kg on bleomycin-associated PI3K-γ protein expression in the diaphragm (
Figure 4A
). Relative to the V
T6 group and the nonventilated control mice, the V
T10 group had higher PI3K-γ protein expression (
Figure 4A). This increase in PI3K-γ protein expression was substantially attenuated following AS605240 administration (
Figure 4A). We subsequently performed immunohistochemistry to determine the cell types involved in the MV-induced fibrogenesis and verify the effects of AS605240 on PI3K-γ activation in VIDD (
Figure 4B,C). Consistent with our Western blot results, we observed a substantial increase in the number of diaphragm muscle fibers positively stained for PI3K-γ in the V
T10 group relative to those in the V
T6 group and the nonventilated control mice. Thus, AS605240 administration prevented the V
T10-induced expression of PI3K-γ (
Figure 4B,C).
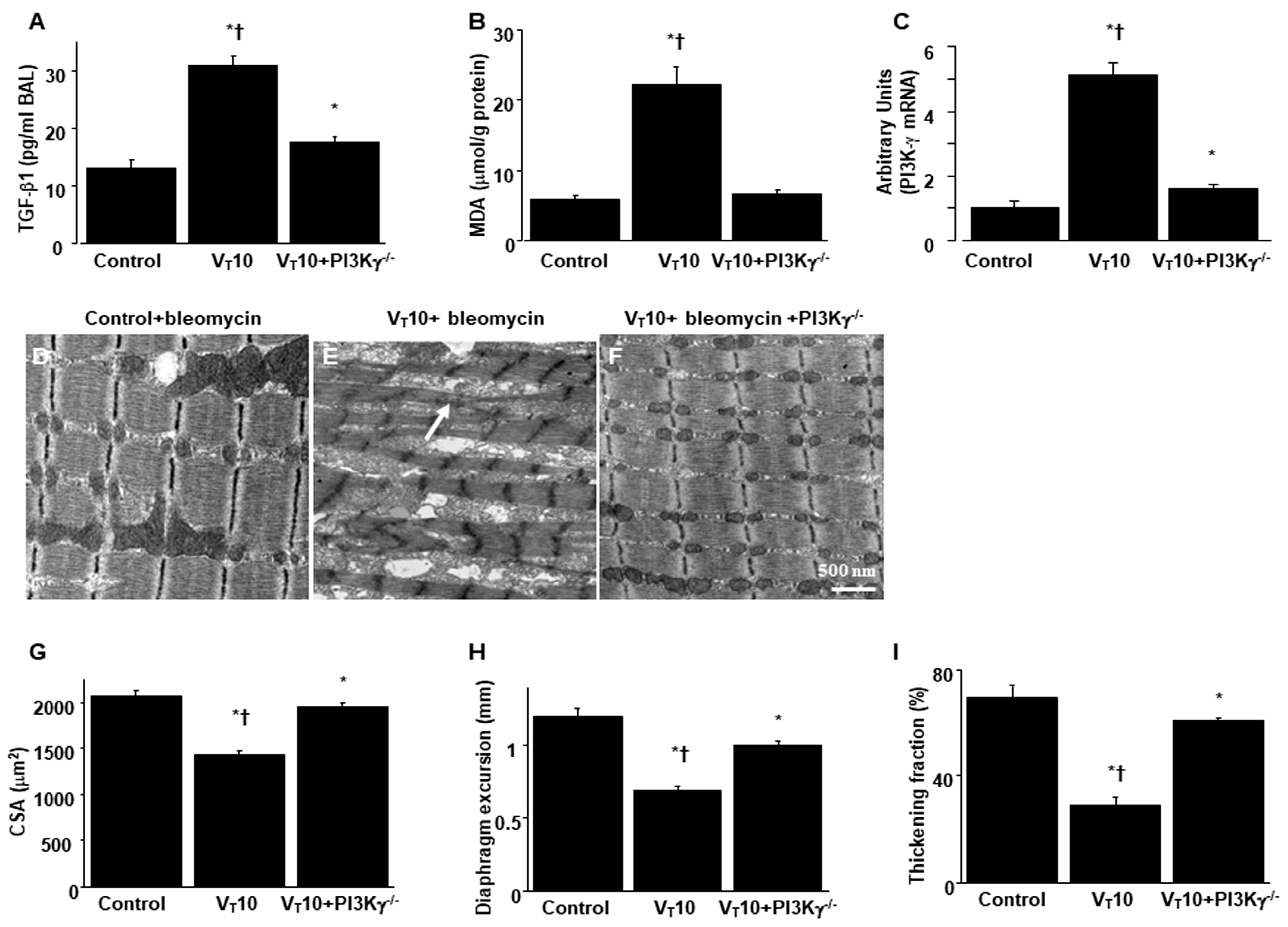
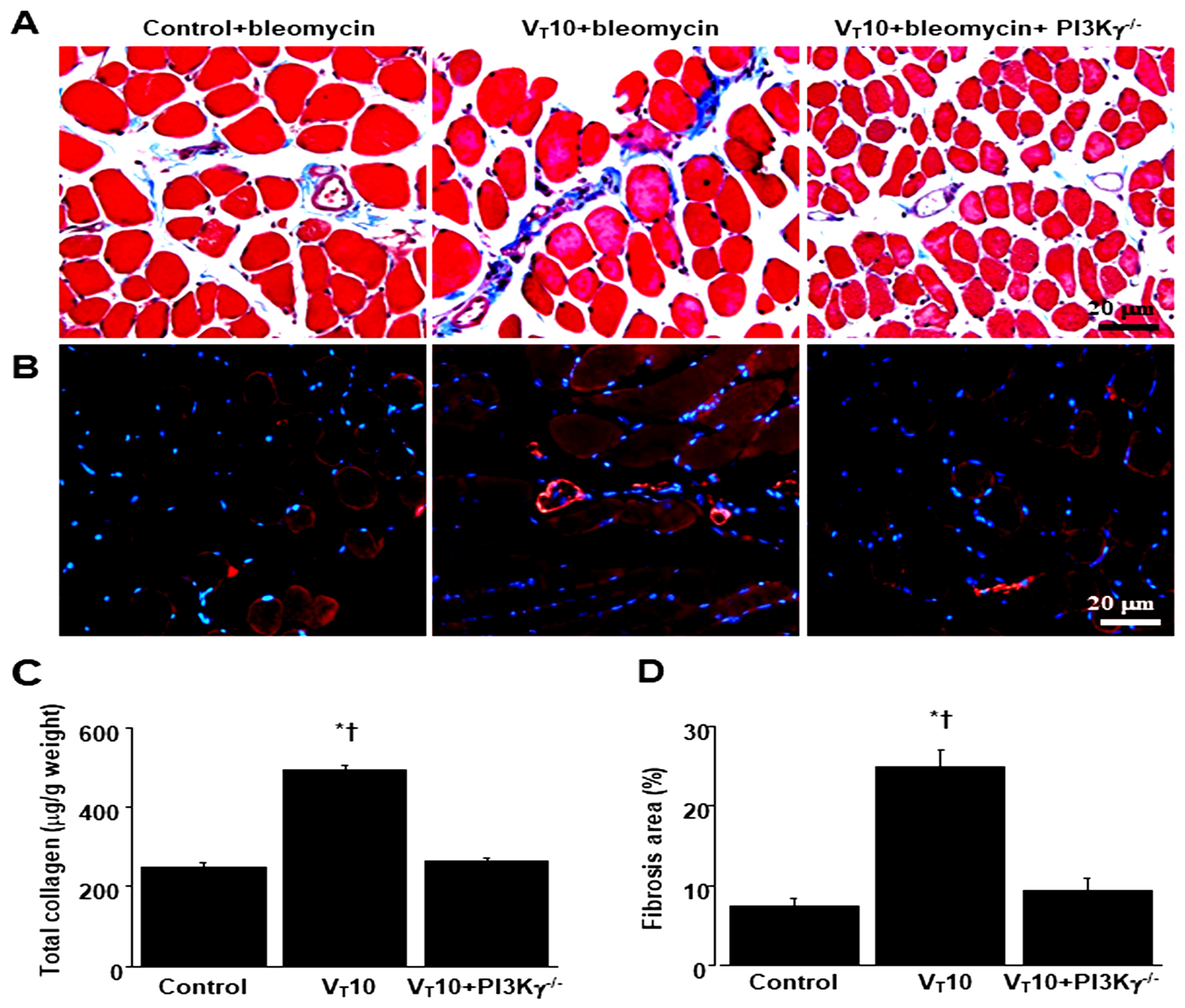
2.5. PI3K-γ-Deficient Mice Exhibited Reduced Bleomycin-Stimulated, MV-Induced VIDD and Diaphragm Fibrosis
We employed PI3K-γ-deficient mice to determine the role of PI3K-γ in MV-induced diaphragm injury; we investigated whether the improvements in diaphragm injuries and fibrogenesis following AS605240 administration were prompted by PI3K-γ expression (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). The effects of MV on changes in TGF-β1 production, oxidative stress, PI3K-γ mRNA expression, diaphragm contractile function, accumulation of collagen fibers, fibrogenic markers, and fibrosis area in mice treated with bleomycin and MV were significantly attenuated in the PI3K-γ-deficient mice (P < 0.05;
Figure 5 and
Figure 6).
2.6. Suppression of the Effects of MV on Bleomycin-Stimulated Expression of BNIP-3 and Muscle Fiber Apoptosis in PI3K-γ-Deficient Mice
BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein–interacting protein 3 (BNIP-3) overexpression may contribute to the progression of cell death through apoptosis [
22]. We thus measured BNIP-3 expression levels and performed terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining to explore the role of the BNIP-3 pathway in the apoptosis of diaphragm muscle fibers in bleomycin-aggravated VIDD. We observed a substantial increase in the BNIP-3 expression levels and more TUNEL-positive apoptotic nuclei in the diaphragm muscle fibers in the V
T10 group relative to those in the V
T6 group and the nonventilated control mice (
Figure 7). Notably, AS605240 administration resulted in a reduction in MV-augmented and bleomycin-enhanced BNIP-3 activities and apoptosis in the diaphragm muscle fibers. The levels of BNIP-3 activity and myonuclear apoptosis were also lower in the PI3K-γ-deficient mice. However, following AS605240 administration, the levels of apoptotic mediators in the injured mice and PI3K-γ-deficient mice remained higher than those in the control mice, indicating other mechanistic pathways are involved in apoptosis; this finding warrants further investigation. Our results indicate that PI3K-γ pathway inhibition leads to a suppression of MV-augmented and bleomycin-induced inflammatory and fibroproliferative processes in the diaphragm (
Figure 8).
3. Discussion
In this study, we investigated 1) whether pathologic fibrogenesis following ALI in individuals receiving MV involves not only the lungs but also the diaphragm and 2) the relevant pathogenic mechanisms; we used a murine model to investigate the influence of MV in bleomycin-induced ALI [
23]. Our results indicate that 1) bleomycin increases MV-induced diaphragmatic ultrastructural injury, reduces the cross-sectional area of diaphragm myofibers, and reduces both the diaphragm excursion and thickening fraction; 2) bleomycin
augments MV-induced oxidative loads (malondialdehyde
, calpain, and caspase-3) and upregulates the production of
profibrogenic factor TGF-
β1; 3) bleomycin stimulates MV-induced expression of the apoptotic markers caspase-3 and BNIP-3; 4) bleomycin aggravates diaphragm muscle proteolysis through increases in atrogin-1 and MuRF-1; 5) bleomycin downregulates the mitochondrial biogenesis activator PGC-1
α and upregulates the mitophagic marker BNIP-3; 6) bleomycin increases MV-induced diaphragmatic mesenchymal marker
α-SMA, total collagen production, and the diaphragm fibrosis area; and 7) bleomycin stimulates MV-induced expression of PI3K-γ in the diaphragm. Notably, these deleterious effects associated with diaphragmatic fibrogenesis were attenuated by the PI3K-γ inhibitor AS605240 or gene knockout of PI3K-γ. Therapeutic targeting of PI3K-γ may thus result in a morphological and functional improvement in diaphragm fibrosis.
In critically ill patients, respiratory failure following ALI necessitates the use of MV [
6,
7,
11]. However, MV has been proven to induce diaphragm muscle damage leading to impaired contractility and weakness, ultimately increasing the rate of complications and mortality associated with ventilator-dependency [
6,
7,
11]. VIDD was long thought to be a consequence of atrophy from diaphragm muscle disuse. However, research employing ultrasound has revealed both increased and decreased diaphragm thickness in patients with prolonged MV [
24]. In animal studies, MV dysynchrony and MV application with positive end-expiratory pressure have been highlighted as factors contributing to elevated levels of connective tissue components and fibrotic change in the diaphragm [
11,
25]. Research has also reported an increased accumulation of ECM, particularly collagen, in the injured diaphragms of critically ill patients with MV and that diaphragm fibrosis rapidly occurs following admission to ICUs [
24,
26]. These results indicate that the increased stiffness and fragility of the diaphragm due to fibrosis as well as myofiber atrophy are key contributors to impaired diaphragm strength and function.
Similar to other skeletal muscles, the diaphragm can be damaged and regenerated. However, damage to the diaphragm can also progress to muscle remodeling and fibrosis due to muscular dystrophies or clinical events such as VIDD-induced myotrauma [
12,
27]. The ECM is an indispensable constituent of the skeletal muscles, comprising 5%–10% of the skeletal muscle weight and aiding in force transmission, protection, and repair of injured muscle fibers [
12,
15,
27]. Notably, laboratory and clinical studies have observed reductions in normal diaphragm muscle accompanied by an increased proportion of abnormal muscle and connective tissue in the injured diaphragms of critically ill patients receiving MV; an increase in the ECM that partially replaces the void caused by muscle fiber atrophy is referred to as replacement fibrosis [
11,
24,
25,
26]. Diaphragm fibrosis caused by ALI and MV undermines the structural integrity and functional performance of the diaphragm; previous research has underestimated these effects as well as their detrimental effects when combined with muscle disuse atrophy [
24,
26]. ECM accumulation is governed by several growth factors, including TGF-
β1, which plays a central role in the pathogenesis of diaphragm fibrogenesis [15].
TGF-
β1 can be released from infiltrating inflammatory cells (activated M2 macrophage) or injured muscle fibers as skeletal muscle injury progresses to fibrosis [12,27]. TGF-
β1 stimulates resident fibroblasts to transdifferentiate into myofibroblasts, which express α-SMA and synthesize excessive ECM proteins and lead to fibrosis [12]. Moreover, TGF-
β1 can activate the production of the tissue inhibitor metalloproteinases and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, which simultaneously suppress the ECM degradation induced by matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase
-9 [12]. In addition, oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular senescence play a role in the activation and proliferation of fibroblasts in the TGF-
β signaling pathway, which leads to the production of ECM during the progression of fibrogenesis [28]. In our study, we observed that MV stimulated the key fibrogenic drivers TGF-
β1 and malondialdehyde
, which may result in diaphragm injury progressing to fibrosis (Figure 2). We also observed the classic characteristics of skeletal muscle fibrosis, including myofibrillar disorganization, muscle fiber atrophy, decreased diaphragm muscle motility and performance, increased fibrosis staining and myofibroblast expression of α-SMA, and elevated collagen content and an expanded fibrosis area (Figure 3).
We also observed increased diaphragm oxidative stress and muscle proteolysis, as evidenced by upregulation of calpain, caspase-3, atrogin-1, and MuRF-1, and increased diaphragm apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by elevated levels of BNIP-3 and caspase-3, apoptosis-positive cells, and TUNEL staining. Calpain, a calcium-dependent cysteine protease, and caspase-3 can destruct myofilament structures by cleaving myosin and actin; they also participate in the ubiquitin–proteasome system for the proteolysis of disrupted proteins [
20]. BNIP-3 and caspase-3 are also involved in triggering apoptosis in muscles such as the diaphragm [
24,
29]. The resulting protein degradation and myocellular apoptosis ultimately lead to a disruption of the myofilament structure, reduction in muscle mass, and functional loss related to force generation. Notably, mitochondrial dysfunction is instrumental in the mechanisms underlying ICU-acquired muscle weakness, including in VIDD [
20]. In our VIDD murine model with bleomycin-induced ALI, we also observed that downregulation of PGC-1
α and upregulation of BNIP-3 contribute to impaired mitochondrial biogenesis and aggravate mitochondrial fragmentation and mitophagy during diaphragm fibrogenesis accompanied by muscle atrophy. We have previously demonstrated that MV induced TGF-
β1 production as well as type I and III procollagen, lumican, and α-SMA gene expression in the diaphragm [30]. Other studies have reported increased oxidative stress and impaired energetic metabolism in the diaphragm in bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation [31] and lower glycogen content in the diaphragm in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis [33]. However, our study is the first to investigate the mechanism underlying diaphragm fibrogenesis; we observed that bleomycin augments MV-induced diaphragmatic injury and contributes to diaphragm fibrosis in an animal model simulating critically ill patients receiving MV following ALI.
Previous animal studies have revealed that PI3K-γ activation induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and contributed to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis [
33,
34,
35]. However, a PI3K-γ inhibitor can attenuate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis [
36]. Our recent study demonstrated that the PI3K-γ pathway mediates MV-induced aggravation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis after bleomycin-induced ALI [
23]. Notably, elevated levels of PI3K-γ have been observed in the fibroblasts and lung tissues of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [
18,
37]. However, the relationship between PI3K-γ and diaphragm fibrogenesis has yet to be investigated. Studies have reported that a PI3K-γ inhibitor can suppress cardiac fibrosis, a devastating form of skeletal muscle fibrosis similar to diaphragm fibrosis [
38], and that tumor necrosis factor–induced myocardial remodeling and fibrosis are mediated through the activation of PI3K-γ [
39]. In the present study, we observed elevated PI3K-γ expression levels in the diaphragm tissues of mice receiving MV after bleomycin-induced ALI. Administration of the PI3K-γ inhibitor AS605240 or PI3K-γ homozygous gene knockout mitigated the elevated oxidative stress and TGF-
β1 activation; the heightened apoptosis, muscle proteolysis, and mitochondrial dysfunction; the increased myofibroblast differentiation, collagen formation, and fibrosis area; and the consequent structural damage and functional impairment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics of Experimental Animals
Wild-type or PI3K-γ-deficient C57BL/6 mice, weighing between 20 and 25 g, aged between 6 and 8 weeks, were obtained from Jackson Laboratories (catalog number 024587 (PI3K-γ), Bar Harbor, ME) and National Laboratory Animal Center (Taipei, Taiwan) [
40]. Briefly, homozygotes mutants (PI3K-γ-/-) exhibit an impaired neutrophil chemotaxis and respiratory burst in response to formyl peptide N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe and C5a induction, as well as reduced thymocyte survival and activation of mature T lymphocytes [
22]. The lower expressions of the PI3K-γ protein in PI3K-γ-/- mice were confirmed by using a Western blot analysis. The study was performed in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (Permit number: 2021111002). All surgery was performed under ketamine and xylazine anesthesia, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.
4.2. Bleomycin Administration
Bleomycin, which acts by preventing incorporation of thymidine into the DNA, promotes EMT by inducing DNA strand breaks [
1,
2]. The mice received a single dosage of 0.075 units of bleomycin in 100 μl of sterile normal saline (2 mg/kg, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) intratracheally for 5 days. Bleomycin exposure results in an acute inflammatory reaction followed by pulmonary fibrosis that slowly resolves [
1,
2].
4.3. Pharmacological Inhibitors
PI3K-γ inhibitor (AS605240, Sigma, St. Louis, MO) 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before MV based on our present and previous studies that showed 5 mg/kg inhibited PI3K-γ activity [
21].
4.4. Experimental Groups
Animals were randomly distributed into 7 groups in each experiment: group 1, nonventilated control wild-type mice with normal saline; group 2, nonventilated control wild-type mice with bleomycin; group 3, VT 6 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin; group 4, VT 10 mL/kg wild-type mice with normal saline; group 5, VT 10 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin; group 6, VT 10 mL/kg Pi3K-γ-/- mice with bleomycin; group 7, VT 10 mL/kg wild-type mice after AS605240 (5 mg/kg) administration with bleomycin. In each group, three mice underwent TEM and micro-CT, and five mice underwent measurement for immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescent assay, inflammatory cytokines, oxidative and antioxidative loads, Masson’s trichrome staining, and Western blots.
4.5. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines
Active TGF-β1 with a lower detection limit of 4.61 pg/ml were measured in BAL fluid using a commercially available immunoassay kit containing primary polyclonal anti-mouse antibodies that were cross-reactive with rat and mouse TGF-β1 (Biosource International, Camarillo, CA, USA). Each sample was run in duplicate according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.6. Immunoblot Analysis
The diaphragm was homogenized in 0.5 ml of lysis buffer as previously described [
1,
2]. Crude cell lysates were matched for protein concentration, resolved on a 10% bis-acrylamide gel, and electrotransferred to Immobilon-P membranes (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA, USA). For the assay of caspase-3, calpain, atrogin-1, MuRF-1, PGC-1α, PI3K-γ, and glyceraldehydes-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), Western blot analyses were performed with respective antibodies (New England BioLabs, Beverly, MA, USA, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, and Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO, USA). Blots were developed by enhanced chemiluminescence (NEN Life Science Products, Boston, MA, USA).
4.7. Masson’s Trichrome Stain and Fibrosis Area
The diaphragm from control, nonventilated mice, mice exposed to MV for 8 h while breathing room air were paraffin embedded, sliced at 4 μm, deparaffinized, stained sequentially with Weigert’s iron hematoxylin solution, Biebrish scarlet-acid fuchsin solution, and aniline blue solution according to the manufacturer’s instruction of a trichrome kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). A blue signal indicated positive staining of collagen. The diaphragmatic blue-stained fibrotic area in Masson’s trichrome stained slice was analyzed using NIH image 1.6 software. Average number of 5 nonoverlapping fields in Masson’s trichrome staining of paraffin lung sections, 6 mice per group, was analyzed for each section by a single investigator blinded to the mouse genotype [
41].
4.8. Statistical Evaluation
The Western blots were quantitated using a National Institutes of Health (NIH) image analyzer Image J 1.27z (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD) and presented as arbitrary units. Values were expressed as the mean ± SD from at least 5 separate experiments. The data of MDA, histopathologic assay, and oxygenation were analyzed using Statview 5.0 (Abascus Concepts Inc. Cary, NC; SAS Institute, Inc.). All results of Western blots were normalized to the nonventilated control wild-type mice with room air. ANOVA was used to assess the statistical significance of the differences, followed by multiple comparisons with a Scheffe′s test, and a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Collagen assay, Cross-sectional area of the muscle fibers, immunofluorescence labelling, immunohistochemistry, measurement of diaphragm excursion and thickness, measurement of MDA, TEM, TUNEL assay, and ventilator protocol were performed as previously described [
1,
2,
8].
5. Conclusions
Overall, we successfully induced diaphragm fibrogenesis with muscle loss in our animal model to simulate diaphragm injury in critically ill patients receiving MV following ALI. Our results indicate that the PI3K-γ pathway partially mediates the pathogenic mechanisms involved in diaphragm fibrogenesis and dysfunction. Antifibrotic therapy targeting the inhibition of PI3K-γ signaling may help to preserve the structural integrity and performance of the diaphragm as well as mitigate the consequences of diaphragm injury such as fibrosis and muscle atrophy; however, such therapy may also reduce VIDD-associated complications and disabilities in ICU patients with ALI receiving MV.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Physiologic conditions at the beginning and end of ventilation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.-F.L. and Y.-Y.L.; methodology, C.-C.Y. and Y.-Y.L.; software, L.-F.L.; validation, L.-F.L. and C.-C.Y.; formal analysis, H.-P.W. and C.-M.C.; investigation, L.-F.L.; resources, L.-F.L.; data curation, L.-F.L., C.-Y.H., P.-C.L. and Y.-Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, L.-F.L., H.-P.W. and Y.-Y.L.; supervision, L.-F.L., C.-M.C., C.-Y.H. and P.-C.L.; project administration, L.-F.L.; funding acquisition, L.-F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Chang Gung Medical Research Project (CMRPG2L0302 and CMRPG2P0101). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol of this murine study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Change Gung Memorial Hospital (Permit number: 2021111002)
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable for animal study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chang-Hung Tien, Laboratory Animal Center, and the Microscope Core Laboratory, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou and Wallace Academic Editing, for their help with the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and declared that no competing interests exist.
Abbreviations
| ALI = acute lung injury |
| ARDS = acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage |
| BNIP-3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein–interacting protein 3 |
| ECM = extracellular matrix |
| EMT = epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FiO2 = fraction of inspired oxygen |
| GAPDH = glyceraldehydes-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| MDA = malondialdehyde |
| MuRF-1 = muscle RING-finger proteins-1 |
| MV = mechanical ventilation |
| ROS = reactive oxygen species |
| PI3K-γ-/- = PI3K-γ-deficient mice |
| α-SMA = α-smooth muscle actin |
| TGF-β1 = tranforming growth factor-β1 |
| VILI = ventilator-induced lung injury |
| VIDD = ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction. |
References
- Li, L.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Kao, K.C.; Wu, C.T.; Chang, C.H.; Hung, C.H.;Hung, C.T. Mechanical ventilation augments bleomycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Src pathway. Lab. Invest. 2014, 94, 1017-1029. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Kao, K.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, N.H.; Lee, C.S.; Wang, C.W.; Yang, C.T. Nintedanib reduces ventilation-augmented bleomycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung fibrosis through suppression of the Src pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2937-2949. [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.; Girdhar, A.; Usman, F.; Cury, J.; Bajwa, A. Approach to acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann .Thorac. Med. 2013, 8, 71-77. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Benítez, N.E.; Parotto, M.; Post, M.; Han, B.; Spieth, P.M.; Cheng, W.E.; Valladares, F.; Villar, J.; Liu, M.; Sato, M.; et al. Mechanical stress induces lung fibrosis by epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Crit. Care .Med. 2012, 40, 510-517. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heise, R.L.; Stober, V.; Cheluvaraju, C.; Hollingsworth, J.W.; Garantziotis, S. Mechanical stretch induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelia via hyaluronan activation of innate immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17435-17444. [CrossRef]
- Dot, I.; Pérez-Teran, P.; Samper, M.A.; Masclans, J.R. Diaphragm Dysfunction in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2017, 53, 150-156. [CrossRef]
- Supinski, G.S.; Morris, P.E.; Dhar, S.; Callahan, L.A. Diaphragm Dysfunction in Critical Illness. Chest. 2018, 153, 1040-1051. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, N.H.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, S.W.; Kao, K.C.; Hu, H.C.; Chang, G.J.; Li, L.F. Ethyl pyruvate attenuates ventilation-induced diaphragm dysfunction through high-mobility group box-1 in a murine endotoxaemia model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5679-5691. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Wei, X.J.; Li, S.P.; Liu, R.N.; Yu, M.X.; Zhao, Y. Interactions between Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Activation and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production in the Development of Ventilator-Induced Diaphragm Dysfunction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2561929. [CrossRef]
- Sahani, R.; Wallace, C.H.; Jones, B.K.; Blemker, S.S. Diaphragm muscle fibrosis involves changes in collagen organization with mechanical implications in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Appl. Physiol (1985). 2022, 132, 653-672. [CrossRef]
- Qian ,X.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Shen, W.; Ding, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, P.; Pan, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H. PEEP application during mechanical ventilation contributes to fibrosis in the diaphragm. Respir. Res. 2023, 24: 46. [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, M.A.A. Skeletal muscle fibrosis: an overview. Cell. Tissue. Res. 2019, 375, 575-588. [CrossRef]
- Alameddine, H.S.; Morgan, J.E. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases in Inflammation and Fibrosis of Skeletal Muscles. J. Neuromuscul Dis. 2016, 3, 455-473. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, A.L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Fibrosis development in early-onset muscular dystrophies: Mechanisms and translational implications. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2017, 4, 181-190. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, K.; Kasprzycka, P.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Zimowska, M. The role of TGF-β1 during skeletal muscle regeneration. Cell .Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 706-715. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, S.; Petrof ,B.J.; Jung, B.; Chanques, G.; Berthet, J.P.; Rabuel, C.; Bouyabrine, H.; Courouble, P.; Koechlin-Ramonatxo, C.; Sebbane, M.; et al. Rapidly progressive diaphragmatic weakness and injury during mechanical ventilation in humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2011, 183, 364-371. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Azad, N.; Wang, L.; Iyer, A.K.; Castranova, V.; Jiang, B.H.; Rojanasakul ,Y. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/akt regulates bleomycin-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. Am. J. Respir .Cell. Mol. Biol. 2010 ,42, 432-441. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu ,K.; Cai ,X.; Yang ,B.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Weng, Q. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2022, 12, 18-32. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, G. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3547-3554. [CrossRef]
- Kanova, M.; Kohout, P. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness and Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8396. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Han, J.; Chen, Z.Z.; Qi, B.W.; Wang, G.C.; Ma, Y.H.; Zheng, H.; Luo, Y.F.; Wei, Y.Q.; Chen, L.J. A phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma inhibitor, AS605240 prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 311-317. [CrossRef]
- Smuder, A.J.; Sollanek, K.J.; Nelson, W.B.; Min, K.; Talbert ,E.E.; Kavazis, A.N.; Hudson, M.B.; Sandri, M.; Szeto, H.H. ; Powers, S.K. Crosstalk between autophagy and oxidative stress regulates proteolysis in the diaphragm during mechanical ventilation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 179-190. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Yu, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wu, H.P.; Chu, C.M.; Liu, P.C.; Liu, Y.Y. Attenuation of Ventilation-Enhanced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-γ in a Murine Bleomycin-Induced Acute Lung Injury Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5538. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; van den, M.; Bogaards, S.; Conijn, S.; Paul, M.; Beishuizen, A.; Heunks, L.; Ottenheijm, C.A.C. Replacement Fibrosis in the Diaphragm of Mechanically Ventilated Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2023, 207, 351-354. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Yoshida, T.; Firstiogusran, A.M.F.; Taenaka, H.; Nukiwa, R.; Koyama, Y.; Uchiyama, A.; Fujino, Y. Asynchrony Injures Lung and Diaphragm in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care. Med. 2023, 51, e234-e242. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; de Vries, H.J.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; van der Hoeven, J.; Boon, R.A.; Heunks, L.M.A.; Ottenheijm, C.A.C.; Dutch COVID-19 Diaphragm Investigators. Diaphragm Pathology in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 and Postmortem Findings From 3 Medical Centers. JAMA. Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 122-124. [CrossRef]
- Lieber, R.L.; Ward, S.R. Cellular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 4. Structural and functional consequences of skeletal muscle fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 305, C241-252. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Cao, Y.; Kong, G.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang ,Q.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. Gasotransmitters: Potential Therapeutic Molecules of Fibrotic Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 3206982. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Li, L.F. Ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction in critical illness. Exp. Biol. Med (Maywood). 2018, 243, 1329-1337. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.F.; Chen, B.X.; Tsai ,Y.H.; Kao, W.W.; Yang, C.T.; Chu, P.H. Lumican expression in diaphragm induced by mechanical ventilation. PLoS. One. 2011, 6, e24692. [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.A.; Silva, C.A.; Polacow, M.L. Effect of early treatment with transcutaneous electrical diaphragmatic stimulation (TEDS) on pulmonary inflammation induced by bleomycin. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2013, 17, 606-613. [CrossRef]
- Borges, E.L.; de Barros Pinheiro, M.; Prata, L.O.; Sales, W.A.; Silva, Y.A.; Caliari, M.V. Rodrigues-Machado, M.G. Effect of lung fibrosis on glycogen content in different extrapulmonary tissues. Lung. 2014, 192, 125-131. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Mechanotransduction Regulates the Interplays Between Alveolar Epithelial and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Lung. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 818394. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Xia ,Y. Targeting Growth Factor and Cytokine Pathways to Treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918771. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wei, Q.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, J.; Su, G.; Peng, L.; Fu, B.; et al. Tangeretin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1247800. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xi, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Duvelisib attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 422-434. [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.M.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.J.; Xu, C.X.; Deng, M.S.; Li, T.; Zhang, D.D.; Duan, Z.X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Li, G.H.; et al. Bleomycin induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via bFGF/PI3K/ESRP1 signaling in pulmonary fibrosis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20190756. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song,. LF.; Jiang, W.; Qing, Y.; Hu, X.H.; Li, Y.; Tong, Q.Y.; Wu , X.H. [The antagonistic effect of PI3K-gamma inhibitor AS605240 on cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis induced by isoproterenol in rats]. Sichuan. Da. Xue. Xue. Bao. Yi. Xue. Ban. 2011, 42, 471-474.
- Awad, A.E.; Kandalam, V.; Chakrabarti, S.; Wang, X.; Penninger, J.M.; Davidge, S.T.; Oudit, G.Y.; Kassiri, Z. Tumor necrosis factor induces matrix metalloproteinases in cardiomyocytes and cardiofibroblasts differentially via superoxide production in a PI3Kgamma-dependent manner. Am. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 298, C679-692. [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.C.; Garcia, C.C.; Barcelos, L.S.; Rachid, M.A.; Guabiraba, R.; Roffê, E.; Souza, A.L.; Sousa, L.P.; Mirolo, M.; Doni,A.; et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ plays a critical role in bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 269-282. [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Mehmood, S. Protective effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on diaphragm muscle fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp. Biol. Med (Maywood). 2020, 245, 1280-1289. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Electron microscopy, excursion, and thickening of the diaphragm. A-F Representative micrographs of the longitudinal sections of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume (VT) of 6 mL/kg (VT 6) or 10 mL/kg (VT 10) for 8 h with room air (×40,000, n = 3 per group). A, B Non-ventilated control wild-type mice with or without bleomycin treatment: normal sarcomeres with distinct A bands, I bands, and Z bands; C 6 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin treatment: reduction of diaphragmatic disruption compared to that of 10 mL/kg groups; D 10 mL/kg wild-type mice without bleomycin treatment (normal saline): increase of diaphragmatic disarray; E 10 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin treatment: disruption of sarcomeric structure with loss of streaming of Z bands, mitochondrial swelling, and accumulation of lipid droplets (asterisks); F 10 mL/kg wild-type mice pretreated with AS605240: attenuation of diaphragmatic disruption. G Cross-sectional area of diaphragm muscle fiber was measured as described in Methods (n = 5 per group). H, I Excursion and thickness variation of diaphragm. AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before mechanical ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; †P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bar represents 500 nm. CSA = cross-sectional area.
Figure 1.
Electron microscopy, excursion, and thickening of the diaphragm. A-F Representative micrographs of the longitudinal sections of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume (VT) of 6 mL/kg (VT 6) or 10 mL/kg (VT 10) for 8 h with room air (×40,000, n = 3 per group). A, B Non-ventilated control wild-type mice with or without bleomycin treatment: normal sarcomeres with distinct A bands, I bands, and Z bands; C 6 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin treatment: reduction of diaphragmatic disruption compared to that of 10 mL/kg groups; D 10 mL/kg wild-type mice without bleomycin treatment (normal saline): increase of diaphragmatic disarray; E 10 mL/kg wild-type mice with bleomycin treatment: disruption of sarcomeric structure with loss of streaming of Z bands, mitochondrial swelling, and accumulation of lipid droplets (asterisks); F 10 mL/kg wild-type mice pretreated with AS605240: attenuation of diaphragmatic disruption. G Cross-sectional area of diaphragm muscle fiber was measured as described in Methods (n = 5 per group). H, I Excursion and thickness variation of diaphragm. AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before mechanical ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; †P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bar represents 500 nm. CSA = cross-sectional area.
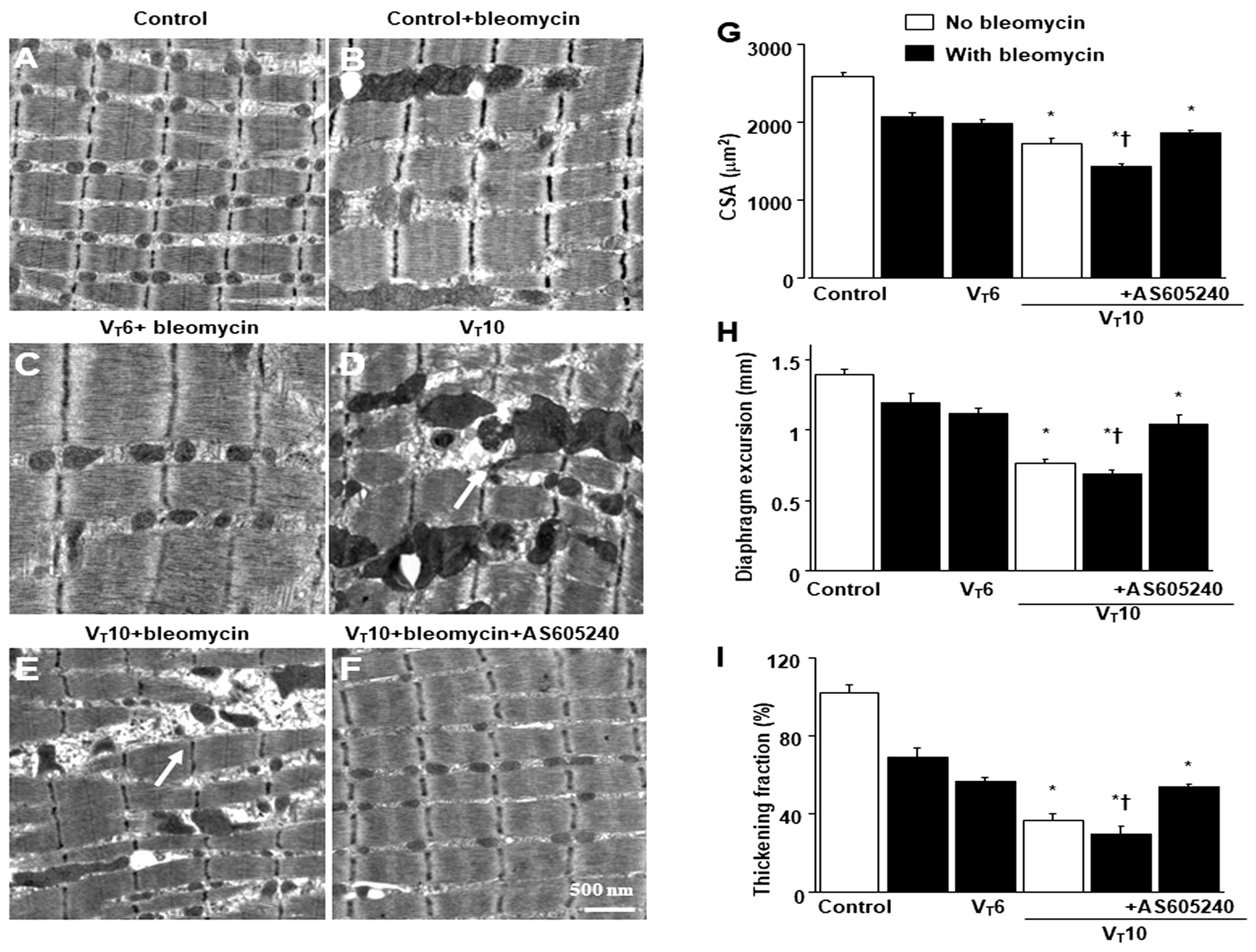
Figure 2.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-mediated TGF-β1 production, oxidative stress, caspase-3, calpain, atrogin-1, MuRF-1, and PGC-1α expression by AS605240. Five days after administering bleomycin, A BAL fluid TGF-β1 and B MDA (diaphragm) were from nonventilated control mice and those subjected to a tidal volume at 6 mL/kg or at 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize C caspase-3, D calpain, E atrogin-1, F MuRF-1, G PGC-1α, and GAPDH expression from the diaphragms of non-ventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with or without bleomycin administration (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative activation (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before mechanical ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; †P< 0.05 versus all other groups. BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MDA = malondialdehyde; MuRF-1 = muscle ring finger-1; PGC-1α = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β1.
Figure 2.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-mediated TGF-β1 production, oxidative stress, caspase-3, calpain, atrogin-1, MuRF-1, and PGC-1α expression by AS605240. Five days after administering bleomycin, A BAL fluid TGF-β1 and B MDA (diaphragm) were from nonventilated control mice and those subjected to a tidal volume at 6 mL/kg or at 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize C caspase-3, D calpain, E atrogin-1, F MuRF-1, G PGC-1α, and GAPDH expression from the diaphragms of non-ventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with or without bleomycin administration (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative activation (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before mechanical ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; †P< 0.05 versus all other groups. BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MDA = malondialdehyde; MuRF-1 = muscle ring finger-1; PGC-1α = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β1.
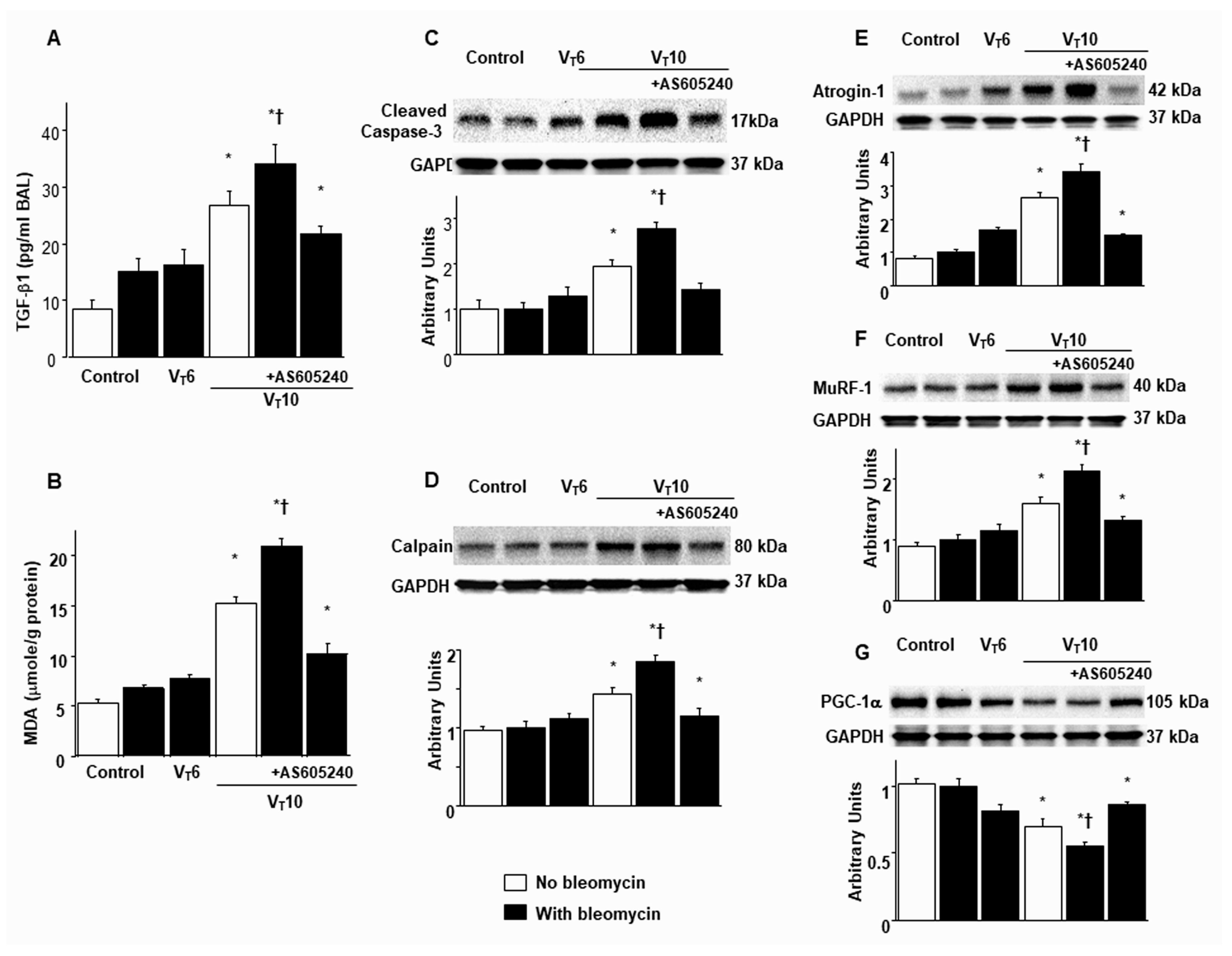
Figure 3.
Suppression of mechanical ventilation-induced collagen production and fibrogenic marker by AS605240. A Representative micrographs (x400) with Masson’s trichrome staining, B representative photomicrographs (x400) with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, red), and Hoechst (blue) immunofluorescent staining of paraffin sections of diaphragm, C collagen of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Positive red staining in the diaphragm muscle fibers is identified by arrows (n = 5 per group). D The fibrosis area was quantified as the average number of 10 nonoverlapping fields in Masson’s trichrome staining of paraffin diaphragm sections (n = 5 per group). * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 μm.
Figure 3.
Suppression of mechanical ventilation-induced collagen production and fibrogenic marker by AS605240. A Representative micrographs (x400) with Masson’s trichrome staining, B representative photomicrographs (x400) with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, red), and Hoechst (blue) immunofluorescent staining of paraffin sections of diaphragm, C collagen of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Positive red staining in the diaphragm muscle fibers is identified by arrows (n = 5 per group). D The fibrosis area was quantified as the average number of 10 nonoverlapping fields in Masson’s trichrome staining of paraffin diaphragm sections (n = 5 per group). * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 μm.
Figure 4.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-induced PI3K-γ protein expression by AS605240. A Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize PI3K-γ and GAPDH expression 5 days after administering bleomycin from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative PI3K-γ expression (n = 5 per group). B, C Representative micrographs (x400) with PI3K-γ staining of paraffin diaphragm sections and quantification 5 days after administering bleomycin were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 μm. PI3K-γ = phosphoinositide 3-kinase-γ.
Figure 4.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-induced PI3K-γ protein expression by AS605240. A Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize PI3K-γ and GAPDH expression 5 days after administering bleomycin from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative PI3K-γ expression (n = 5 per group). B, C Representative micrographs (x400) with PI3K-γ staining of paraffin diaphragm sections and quantification 5 days after administering bleomycin were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before ventilation. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 μm. PI3K-γ = phosphoinositide 3-kinase-γ.
Figure 5.
Reduction of mechanical ventilation-induced diaphragm dysfunction in PI3K-γ-deficient mice. A BAL fluid TGF-β1, B MDA (diaphragm), and C Real-time PCR performed for PI3K-γ mRNA expression five days after bleomycin administration were from the nonventilated control mice and those subjected to a tidal volume 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). D-F Representative micrographs of the longitudinal sections of diaphragm after five days of bleomycin administration were from non-ventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (×40,000, n = 3 per group). G Cross-sectional area of diaphragm muscle fiber was measured as described in Methods (n = 5 per group). (H, I) Excursion and thickness variation of diaphragm. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin; † P< 0.05 versus PI3K-γ-deficient mice. Scale bar represents 500 nm.
Figure 5.
Reduction of mechanical ventilation-induced diaphragm dysfunction in PI3K-γ-deficient mice. A BAL fluid TGF-β1, B MDA (diaphragm), and C Real-time PCR performed for PI3K-γ mRNA expression five days after bleomycin administration were from the nonventilated control mice and those subjected to a tidal volume 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). D-F Representative micrographs of the longitudinal sections of diaphragm after five days of bleomycin administration were from non-ventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (×40,000, n = 3 per group). G Cross-sectional area of diaphragm muscle fiber was measured as described in Methods (n = 5 per group). (H, I) Excursion and thickness variation of diaphragm. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin; † P< 0.05 versus PI3K-γ-deficient mice. Scale bar represents 500 nm.
Figure 6.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-induced collagen accumulation and fibrogenic markers in PI3K-γ-deficient mice. A Representative micrographs (x400) with Masson’s trichrome staining, B representative photomicrographs (x400) with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, red), and Hoechst (blue) immunofluorescent staining of paraffin sections of diaphragm, C collagen of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Positive red staining in the diaphragm muscle fibers is identified by arrows (n = 5 per group). D The fibrosis area was quantified as the average number of 10 nonoverlapping fields in Masson’s trichrome staining of paraffin diaphragm sections (n = 5 per group). * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus PI3K-γ-deficient mice. Scale bars represent 20 μm.
Figure 6.
Inhibition of mechanical ventilation-induced collagen accumulation and fibrogenic markers in PI3K-γ-deficient mice. A Representative micrographs (x400) with Masson’s trichrome staining, B representative photomicrographs (x400) with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, red), and Hoechst (blue) immunofluorescent staining of paraffin sections of diaphragm, C collagen of diaphragm five days after bleomycin administration were from nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Positive red staining in the diaphragm muscle fibers is identified by arrows (n = 5 per group). D The fibrosis area was quantified as the average number of 10 nonoverlapping fields in Masson’s trichrome staining of paraffin diaphragm sections (n = 5 per group). * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus PI3K-γ-deficient mice. Scale bars represent 20 μm.
Figure 7.
Suppression of mechanical ventilation-augmented expression of BNIP-3, and muscle fiber apoptosis by AS605240 and in PI3K-γ deficient mice. A, B Representative micrographs (×400) with TUNEL staining of paraffin diaphragm sections and quantification five days after bleomycin administration were from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). C Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize BNIP-3 and GAPDH expression 5 days after administering bleomycin from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative BNIP-3 expression (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before ventilation. Apoptotic cells are identified by arrows. A bright green signal indicates positive staining of apoptotic cells, and shades of dull green signify non-reactive cells. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 µm. BNIP3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; TUNEL = terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling.
Figure 7.
Suppression of mechanical ventilation-augmented expression of BNIP-3, and muscle fiber apoptosis by AS605240 and in PI3K-γ deficient mice. A, B Representative micrographs (×400) with TUNEL staining of paraffin diaphragm sections and quantification five days after bleomycin administration were from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). C Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize BNIP-3 and GAPDH expression 5 days after administering bleomycin from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg or 10 mL/kg for 8 h with room air (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative BNIP-3 expression (n = 5 per group). AS605240 5 mg/kg was given intraperitoneally 1h before ventilation. Apoptotic cells are identified by arrows. A bright green signal indicates positive staining of apoptotic cells, and shades of dull green signify non-reactive cells. * P< 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with bleomycin pretreatment; † P< 0.05 versus all other groups. Scale bars represent 20 µm. BNIP3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; TUNEL = terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling.
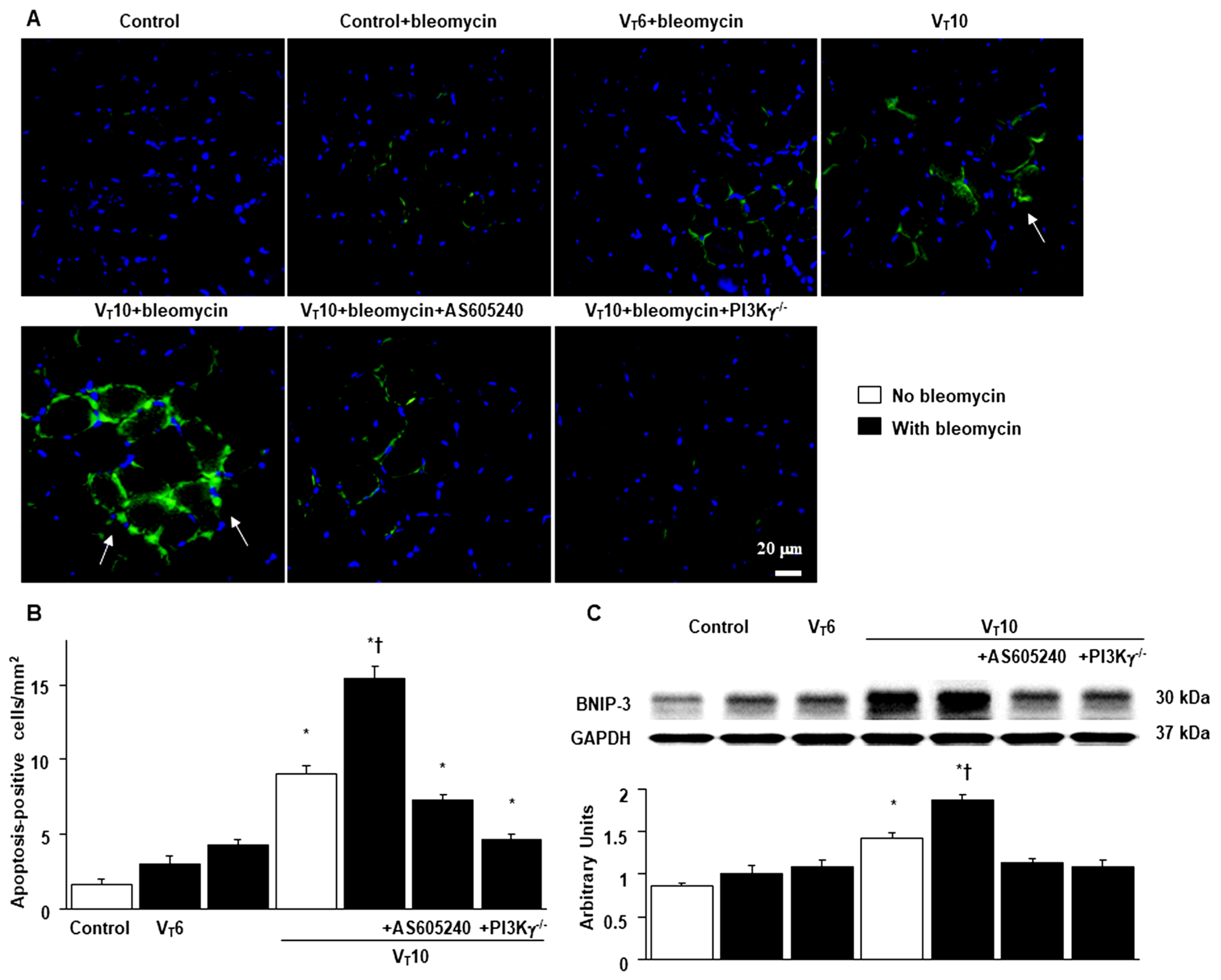
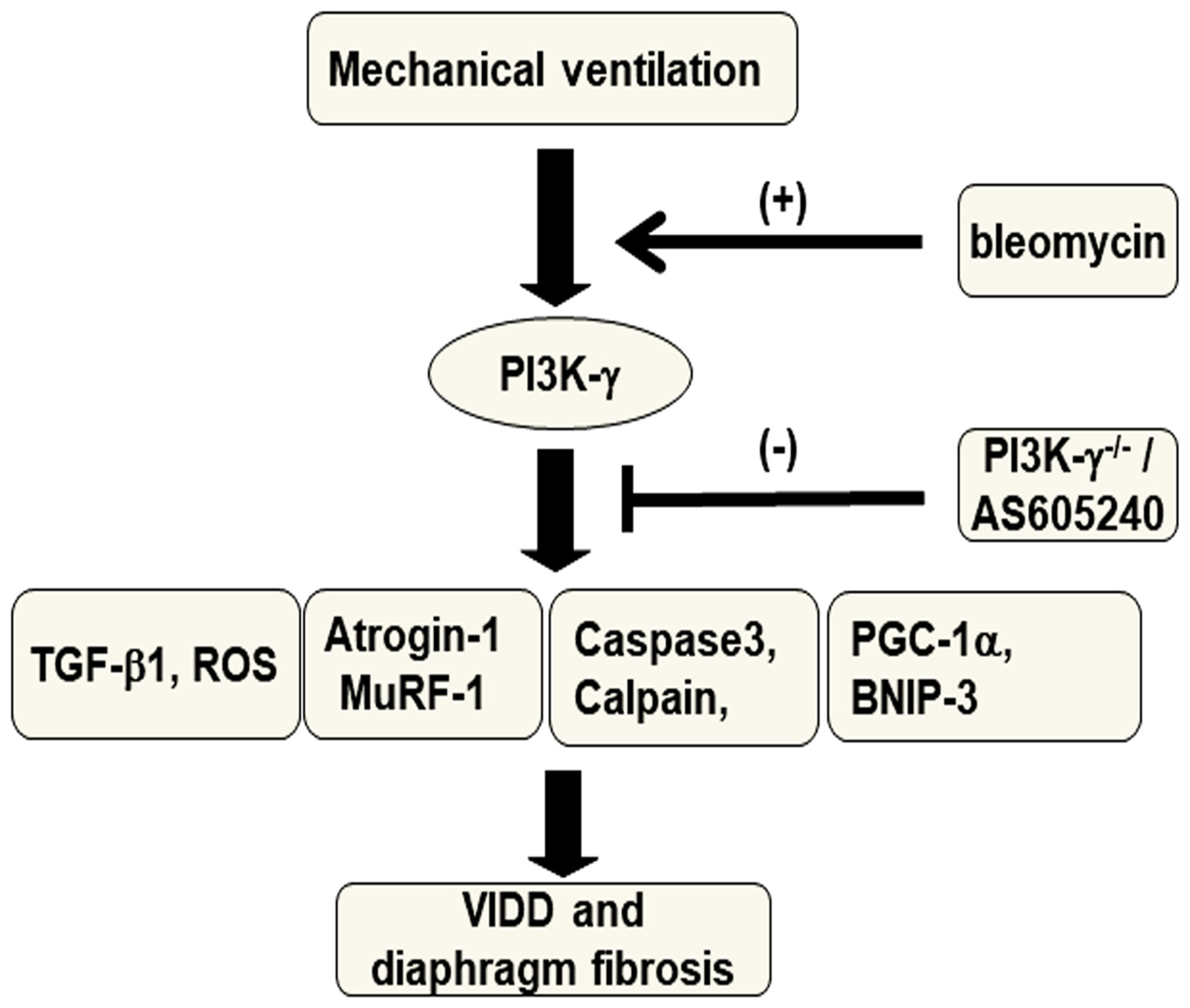
Figure 8.
Schematic figure illustrating the signaling pathway activation with mechanical ventilation and bleomycin. Bleomycin-induced augmentation of mechanical stretch-mediated cytokine production, diaphragm damage and fibrosis were attenuated in PI3K-γ-deficient mice and pharmacological inhibition with AS605240. BNIP3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; MDA = malondialdehyde; MuRF-1 = muscle ring finger-1; PGC-1α = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator; PI3K-γ-/- = PI3K-γ-deficient mice; ROS = reactive oxygen species; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β1; VIDD = ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction.
Figure 8.
Schematic figure illustrating the signaling pathway activation with mechanical ventilation and bleomycin. Bleomycin-induced augmentation of mechanical stretch-mediated cytokine production, diaphragm damage and fibrosis were attenuated in PI3K-γ-deficient mice and pharmacological inhibition with AS605240. BNIP3 = BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; MDA = malondialdehyde; MuRF-1 = muscle ring finger-1; PGC-1α = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator; PI3K-γ-/- = PI3K-γ-deficient mice; ROS = reactive oxygen species; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β1; VIDD = ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).