Submitted:
21 April 2024
Posted:
22 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods:
|
| A) Initiate antibiotics in all or almost all premature infants[5] ≤ 32 weeks gestational age after birth due to the risk of infection? |
| B) Select premature infants ≤ 32 weeks gestation for antibiotic administration based on risk factors or laboratory tests. |
|
| A) Yes |
| B) No |
|
| A) Yes |
| B) No |
|
| A) Yes |
| B) No |
|
| A) Select premature infants based on risk factors. |
| B) Select premature infants based on laboratory results obtained within the first 24 hours. |
| C) Do not perform tests and rely on clinical follow-up. |
| D) Both A and B. |
|
| A) If the premature infant is stable and the blood cultures are negative, antibiotics are discontinued within 24 to 72 hours. |
| B) Despite negative results, antibiotics are often continued for 5 to 10 days due to a lack of confidence in the results. |
|
| A) Complete blood count |
| B) C-reactive protein |
| C) A and B, or A and D |
| D) Procalcitonin |
| E) No tests are used to make this decision |
| F) Other tests not listed |
| Antibiotics initiated after the second day of life: |
|
| A) Blood cultures are taken, and antibiotics are initiated regardless of the results of other tests, if performed. |
| B) Blood cultures and other tests are taken, and antibiotics are initiated based on the results of the other tests. |
| C) Antibiotics are initiated before taking blood cultures or other tests, if performed. |
|
| A) If the premature infant is stable, there have been no changes in the laboratory findings, and blood cultures are negative, antibiotics are discontinued within 24 to 72 hours. |
| B) Despite negative blood cultures, antibiotics are often continued for more than 72 hours due to a lack of confidence in the results. |
|
| A) Antibiotics are discontinued when symptoms resolve or 2-3 days later, regardless of the treatment duration. |
| B) Antibiotics are only discontinued if a new blood culture is negative and/or the previously positive laboratory tests completely normalize, regardless of symptoms. |
| C) The duration depends on the type of organism. |
| D) The established treatment duration in the unit is always completed (7, 10, 14, 21 days). |
| E) Options C and D include our management in the unit. |
|
| A) It is common to complete the antibiotic course, even if blood cultures are negative due to a lack of confidence in them. |
| B) It is uncommon to continue antibiotics with negative blood cultures, only in highly symptomatic patients or in conditions such as enterocolitis. |
| C) All premature infants at a predetermined gestational age (< 30, < 28, or < 26 weeks gestation) receive antibiotic regimens of 7, 10, 14, or 21 days regardless of symptoms or laboratory tests. |
| Use of antibiotics in your unit: |
|
| A) Antibiotics are used excessively. |
| B) Antibiotics are used sparingly. |
Results
Discussion
References
- Z. Willis and A. de St Maurice, "Strategies to improve antibiotic use in the neonatal ICU," (in eng), Curr Opin Pediatr, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 127-134, Feb 2019. [CrossRef]
- EpicLatino, "Epiclatino Repport 2021," https://www.epiclatino.co/reports-2021, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.epiclatino.co/reports. 2021.
- M. Ibáñez-Pinilla, S. Villalba-Niño, and N. N. Olaya-Galán, "Negative log-binomial model with optimal robust variance to estimate the prevalence ratio, in cross-sectional population studies," (in eng), BMC Med Res Methodol, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 219, Oct 04 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Grembi and E. T. Rogawski McQuade, "Introducing riskCommunicator: An R package to obtain interpretable effect estimates for public health," (in eng), PLoS One, vol. 17, no. 7, p. e0265368, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Sengupta, and K. M. Puopolo, "Challenges and opportunities for antibiotic stewardship among preterm infants," (in eng), Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed, vol. 104, no. 3, pp. F327-F332, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- Viel-Thériault, A. Agarwal, E. Bariciak, N. Le Saux, and N. Thampi, "Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: An Antimicrobial Stewardship Target That Deserves Attention!," (in eng), Am J Perinatol, vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 1288-1291, Sep 2022. [CrossRef]
- Katz S, Banerjee R, Schwenk H. Antibiotic Stewardship for the Neonatologist and Perinatologist. Clin Perinatol. 2021 Jun;48(2):379-391. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morowitz MJ, Katheria AC, Polin RA, Pace E, Huang DT, Chang CH, Yabes JG. The NICU Antibiotics and Outcomes (NANO) trial: a randomized multicenter clinical trial assessing empiric antibiotics and clinical outcomes in newborn preterm infants. Trials. 2022 May 23;23(1):428. PMCID: PMC9125935. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
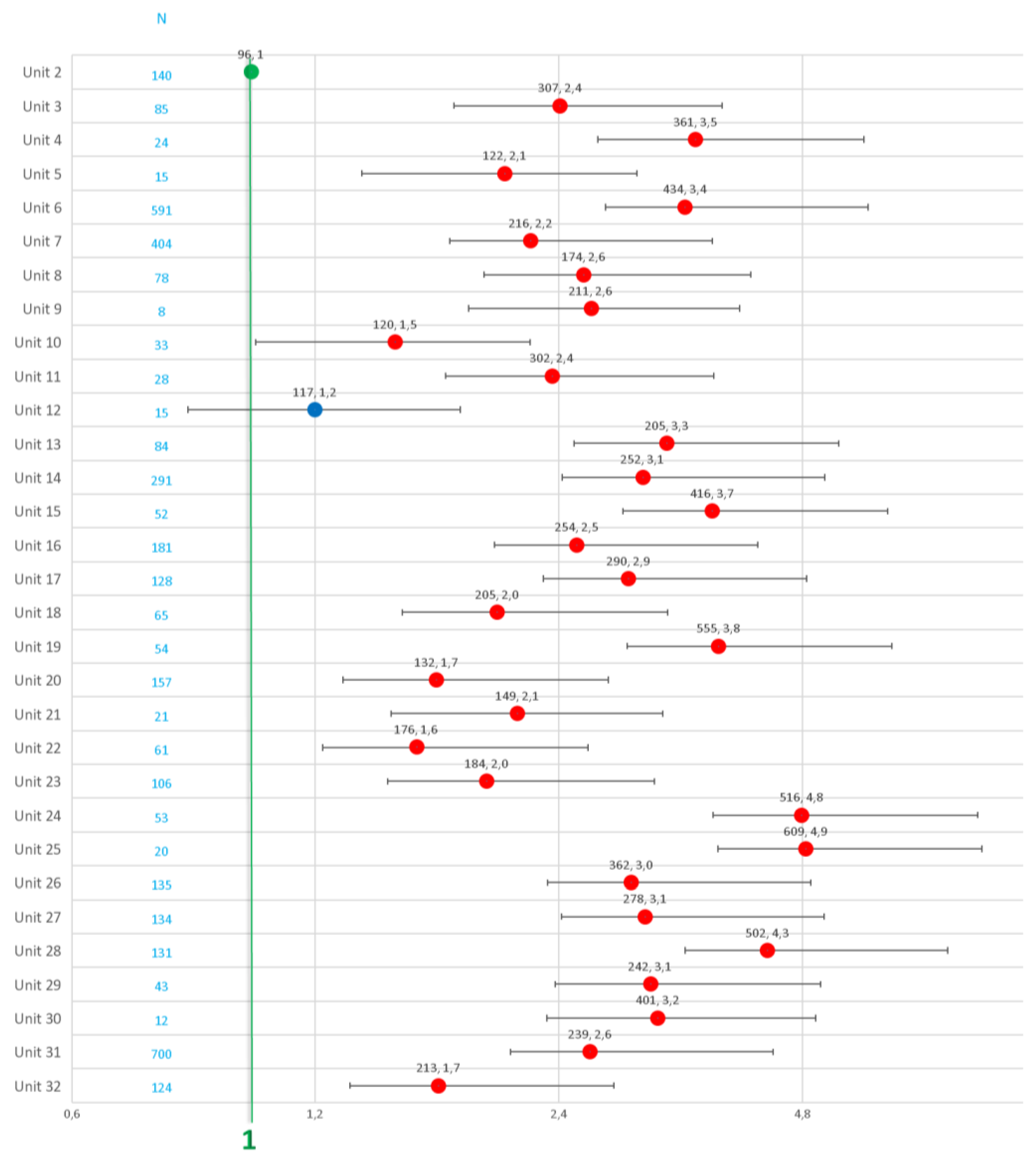
| UNITS | CITY/COUNTRY |
| Centenario H. de Esp. Miguel Hidalgo | Aguascalientes, Mexico |
| Clínica Dávila | Santiago, Chile |
| Clínica de Santa María de Santiago | Santiago, Chile |
| Clínica del Country | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Clínica la Colina | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Clínica Materno Infantil San Luis | Bucaramanga, Colombia |
| Clínica San Felipe | Lima, Perú |
| Clínica Santa Bárbara | Quito, Ecuador |
| Clínica Somer | Rio Negro, Colombia |
| Clínica Universitaria Colombia | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Clínica Vespucio | Santiago, Chile |
| Colsanitas – Clínica Pediátrica UCI Neonatal | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Curaçao Medical Center | Willemstad, Curaçao |
| H Regional DR Rafael Pascacio Gamboa | Tuxtla Gutiérrez, México |
| Hospital Central Dr. Ignacio Morones Prieto | San Luis Potosí, México |
| Hospital Civil de Ipiales E.S.E | Ipiales, Colombia |
| Hospital de los Valles | Quito, Ecuador |
| Hospital Departamental San Vicente de Paul | Garzón, Huila, Colombia |
| Hospital Dr. Florencio Escardó | Tigre, Argentina |
| Hospital Español de Mendoza | Mendoza, Argentina |
| Hospital General EISS de Manta | Manta, Ecuador |
| Hospital Italiano de La Plata | La Plata, Argentina |
| Hospital Luis Lagomaggiore | Mendoza, Argentina |
| Hospital Metropolitano | Quito, Ecuador |
| Hospital Militar Central | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Hospital Regional Universitario de Colima | Colima, México |
| Hospital San Francisco de Quito | Quito, Ecuador |
| Hospital San José | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Hospital Santísima Trinidad | Asunción, Paraguay |
| Los Cobos Medical Center | Bogotá, Colombia |
| Maternidad Nuestra Sra. de las Mercedes | Tucumán, Argentina |
| S.E.S. Hospital de Caldas | Manizales, Colombia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




