Submitted:
23 April 2024
Posted:
23 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
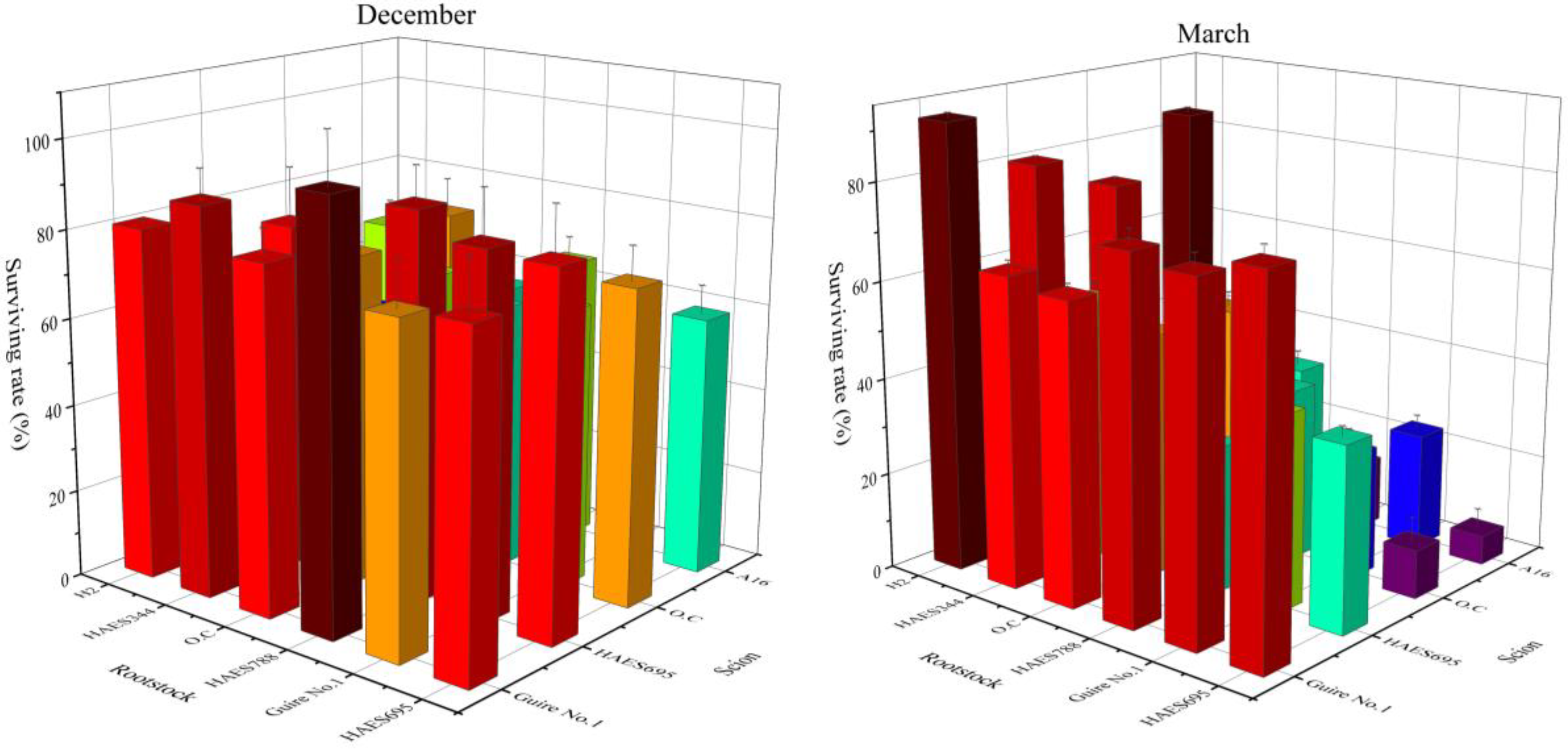
2.1. Effect of Macadamia Scion and Rootstock on Survival Rate
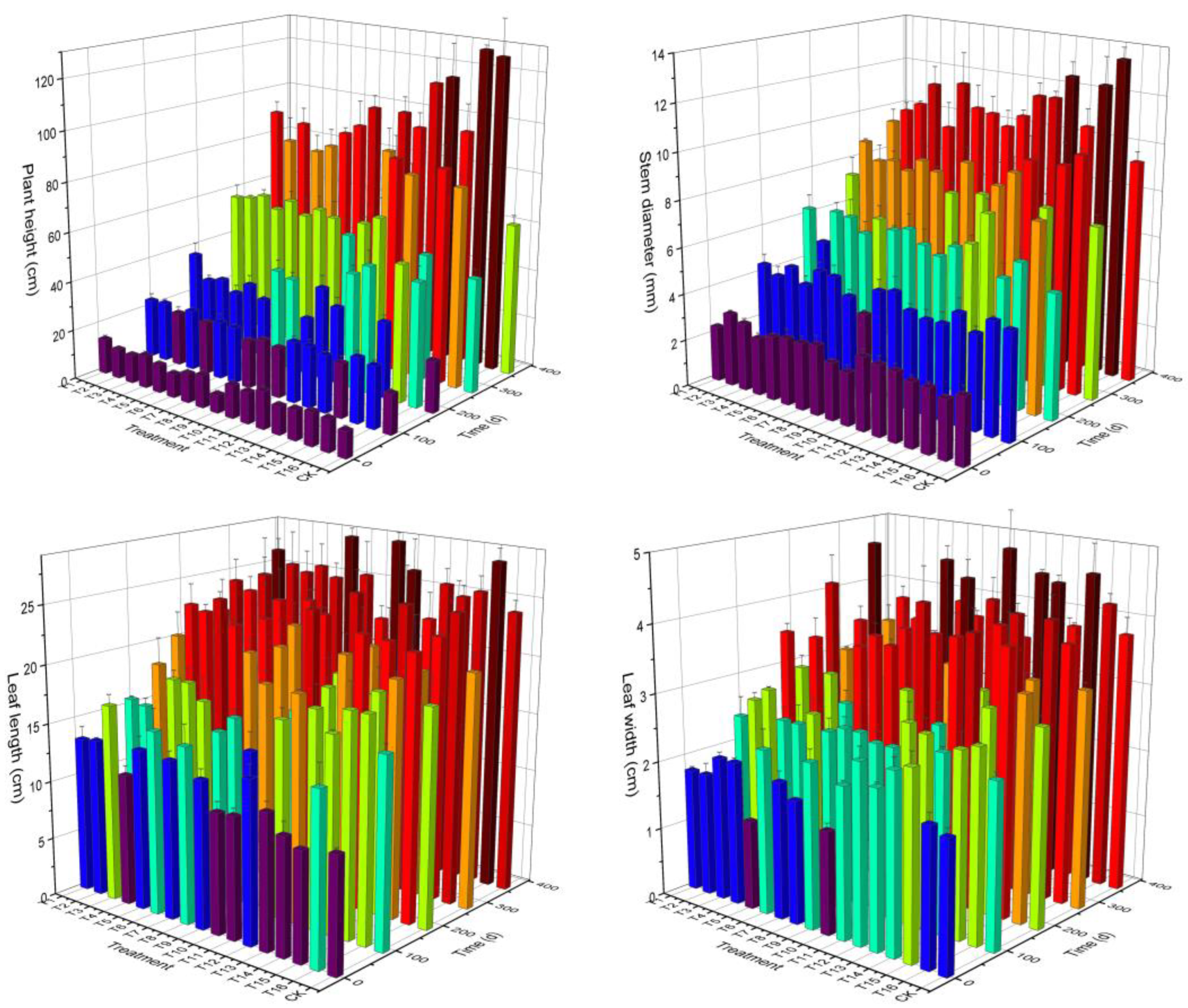
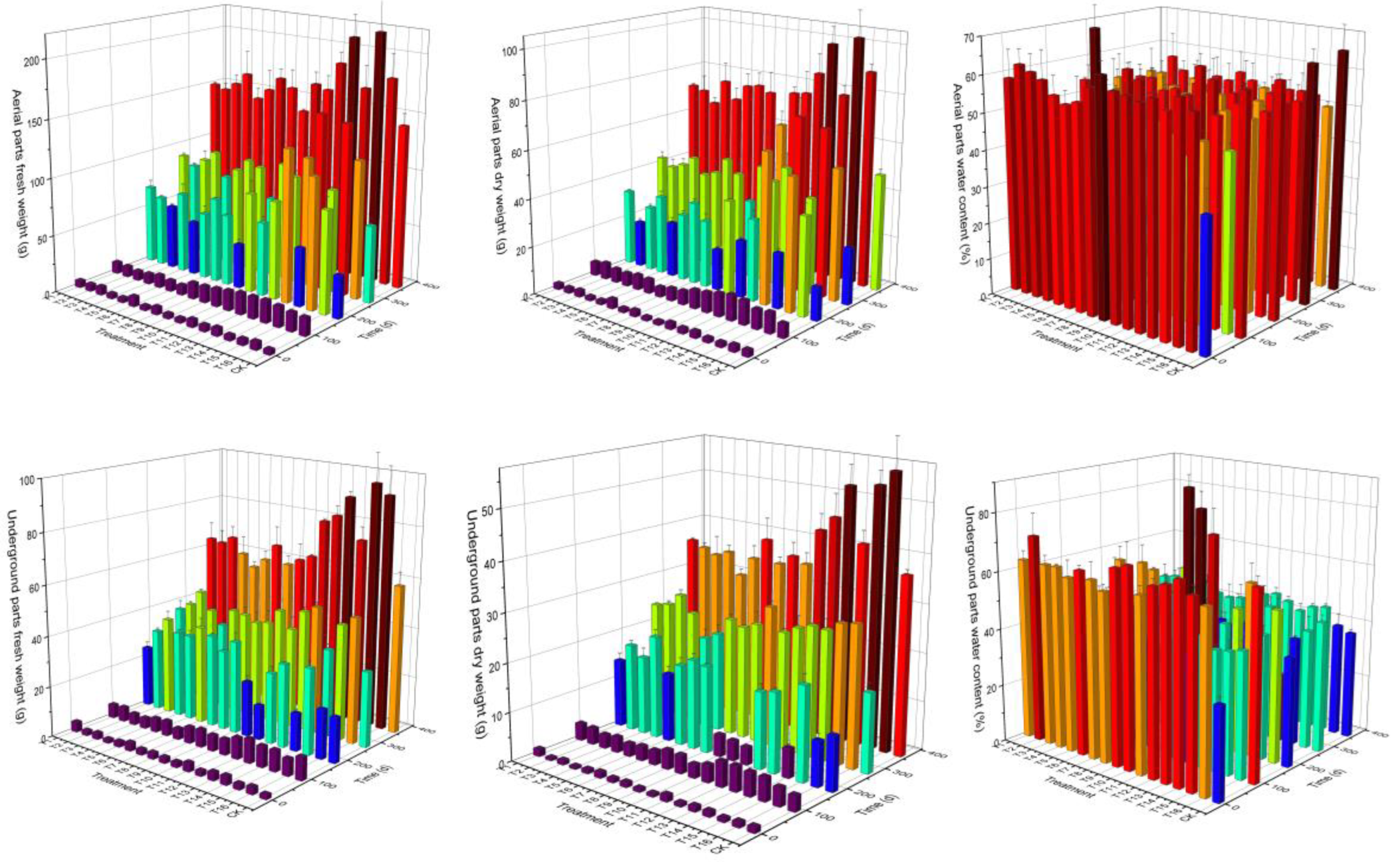
2.2. Effect of Different Substrate Composition on the Growth of Graft Seedlings
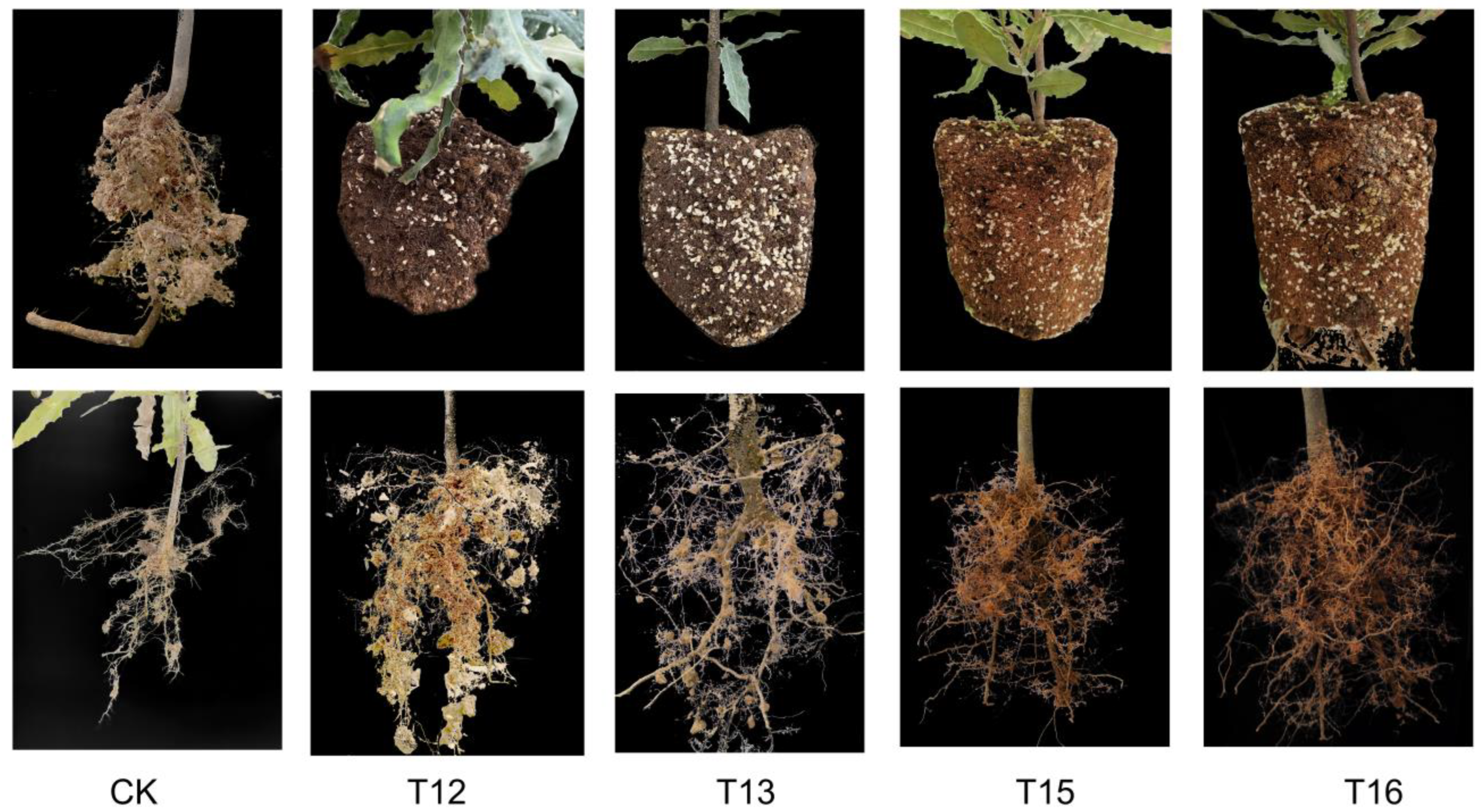
2.2.1. Root Phenotypes of Graft Seedlings Cultivated with Different Substrate Composition
2.2.2. Effect of Substrate Composition on the Growth of Graft Seedlings
2.2.3. Nutrient Composition Changes in Different Substrate Compositions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Seedling Cultivation
4.3. Grafting Test
4.4. Substrate Composition Analysis
4.5. Measurement of Nutrient Composition Substrate Composition
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habibi, F.; Liu, T.; Folta, K.; Sarkhosh, A. Physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects of grafting in fruit trees. Hortic Res 2022, 9, uhac032. [CrossRef]
- Gisbert-Mullor, R.; Ceccanti, C.; Gara Padilla, Y.; López-Galarza, S.; Calatayud, Á.; Conte, G.; Guidi, L. Effect of Grafting on the Production, Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Nutritional Quality of Fruit from Pepper Landraces. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 501. [CrossRef]
- Musa, I.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ahmad, K.; Ramlee, S.I.; Md Hatta, M.A.; Oladosu, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Chukwu, S.C.; Mat Sulaiman, N.N.; Ayanda, A.F.; Halidu, J. Effects of Grafting on Morphophysiological and Yield Characteristic of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Grafted onto Wild Relative Rootstocks. Plants (Basel) 2020, 9, 1583. [CrossRef]
- Gibas, C.; Kumari, A.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhury, A.; Singh, S.P. Grafting Triggers Differential Responses between Scion and Rootstock. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124438. [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.; Shengjie, Z.; Xuqiang, L.; Nan, H.; Wenge, L. Rootstock mediates transcriptional regulation of citrulline metabolism in grafted watermelon. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 125-136. [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Shi, Y.N.; Mou, Z.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhao, D.K. Grafting: a potential method to reveal the differential accumulation mechanism of secondary metabolites. Hortic Res 2022, 9, uhac050. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, B. Influence of rootstock on endogenous hormones and color change in Cabernet Sauvignon grapes. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 6608. [CrossRef]
- Nazir, F.; Ahmad, T.; Malik, S.I.; Ahmed, M.; Bashir, M.A. Wild grapevines as rootstock regulate the oxidative defense system of in vitro grafted scion varieties under drought stress. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274387. [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.A.; Taha, N.A.; Rakha, M.T.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Shehata, W.F.; Ramadan, K.M.A.; El-Ramady, H.; Bayoumi, Y.A. Can Grafting Manage Fusarium Wilt Disease of Cucumber and Increase Productivity under Heat Stress? Plants (Basel) 2022, 11, 1147. [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Li, Z.; Gu, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, L.; Qi, X.; Fang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, C. Effects of Kiwifruit Rootstocks with Opposite Tolerance on Physiological Responses of Grafting Combinations under Waterlogging Stress. Plants (Basel) 2022, 11, 2098. [CrossRef]
- Munck, N.; Smith, J.; Bates, J.; Glass, K.; Hald, T.; Kirk, M.D. Source Attribution of Salmonella in Macadamia Nuts to Animal and Environmental Reservoirs in Queensland, Australia. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 357-364. [CrossRef]
- Ako, H.; Okuda, D.; Gray, D. Healthful new oil from macadamia nuts. Nutrition 1995, 11, 286-288.
- Maguire, L.S.; O'Sullivan, S.M.; Galvin, K.; O'Connor, T.P.; O'Brien, N.M. Fatty acid profile, tocopherol, squalene and phytosterol content of walnuts, almonds, peanuts, hazelnuts and the macadamia nut. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2004, 55, 171-178. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Liao, Z.; Lin, J.; et al. Signatures of selection in recently domesticated macadamia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 242. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sar, P. Role of cost-effective organic carbon substrates in bioremediation of acid mine drainage-impacted soil of Malanjkhand Copper Project, India: a biostimulant for autochthonous microbial populations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 27407-27421. [CrossRef]
- Nuid, M.; Aris, A.; Krishnen, R.; Chelliapan, S.; Muda, K. Pineapple wastewater as co-substrate in treating real alkaline, non-biodegradable textile wastewater using biogranulation technology. J Environ Manage 2023, 344, 118501. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lyu, Y.; Dong, Q.Q.; He, X.Y.; Yue, H.; Yang, L.P.; Tao, L.; Gong, L.D.; Zheng, H.X.; Wen, S.J.; et al. Biomass partitioning and ionomics of Macadamia with high manganese and low phosphorus concentrations. Funct. Plant Biol. 2023, 50, 559-570. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fei, Y.; Huang, J.; Ni, J.; Xu, Z.F. Macadamia germplasm and genomic database (MacadamiaGGD): A comprehensive platform for germplasm innovation and functional genomics in Macadamia. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 1007266. [CrossRef]
- Zuza, E.J.; Araya, Y.N.; Maseyk, K.; Bhagwat, S.; Brandenburg, R.L.; Emmott, A.; Rawes, W.; Phiri, P.; Mkengala, K.; Kenamu, E. Farmer preference for macadamia varieties and constraints to production in Malawi. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0293488. [CrossRef]
- Nock, C.J.; Baten, A.; Mauleon, R.; Langdon, K.S.; Topp, B.; Hardner, C.; Furtado, A.; Henry, R.J.; King, G.J. Chromosome-Scale Assembly and Annotation of the Macadamia Genome (Macadamia integrifolia HAES 741). G3 (Bethesda) 2020, 10, 3497-3504. [CrossRef]
- O'Connor, K.; Hayes, B.; Hardner, C.; Nock, C.; Baten, A.; Alam, M.; Henry, R.; Topp, B. Genome-wide association studies for yield component traits in a macadamia breeding population. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 199. [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.E.; Kamper, W.; Trueman, S.J.; Wallace, H.M.; Ogbourne, S.M.; Brooks, P.R.; Nichols, J.; Hosseini Bai, S. Relationships between Nut Size, Kernel Quality, Nutritional Composition and Levels of Outcrossing in Three Macadamia Cultivars. Plants (Basel) 2020, 9, 228. [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Particulate Soil Organic-Matter Changes across a Grassland Cultivation Sequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 777-783. [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Xin, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, F.; Yu, H.; Sun, Z.; Xu, C. Scion-to-Rootstock Mobile Transcription Factor CmHY5 Positively Modulates the Nitrate Uptake Capacity of Melon Scion Grafted on Squash Rootstock. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 162. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Villacis, D.X.; Erazo-Garcia, P.; Quijia-Pillajo, J.; Llerena-Llerena, S.; Barriga-Medina, N.; Jones, C.D.; Leon-Reyes, A. Influence of Grafting on Rootstock Rhizosphere Microbiome Assembly in Rosa sp. 'Natal Brier'. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12, 663. [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, B. Effect of rootstock on growth and water use efficiency of Hevea during water stress. Journal of Rubber Research 1999, 2, 99-119.
- Xia, C.X.; Jiang, S.R.; Tan, Q.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.J.; Bao, Y.T.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.J.; Deng, K.; et al. Chromosomal-level genome of macadamia (Macadamia integrifolia). Tropical Plants 2022, 1, 3. [CrossRef]
- Potdar, R.P.; Shirolkar, M.M.; Verma, A.J.; More, P.S.; Kulkarni, A. Determination of soil nutrients (NPK) using optical methods: a mini review. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 1826-1839. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, D. Determination of total phosphorus in natural waters with a simple neutral digestion method using sodium persulfate. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2017, 15, 372-380. [CrossRef]


| Proportion | Peat soil | perlite | Wood bran | loess | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate formulations |
|||||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| T1 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| T2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| T3 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| T4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
| T5 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| T6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |
| T7 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| T8 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| T9 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| T10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| T11 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| T12 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| T13 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| T14 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| T15 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| T16 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





