Submitted:
25 April 2024
Posted:
26 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Lymph Nodes Analysis
3.1.1. Micro-RNA in Lymph Nodes
3.1.2. REEP1, RNF145, CTONG2002744, MYO5A, and FBXO32
3.1.3. CK14, eIF4E, and DSG3
3.1.4. The Loss of Heterozygosity at D9S 171 (9p21)
3.1.4. Squamos Cell Carcinoma Antigen and Cytokeratins
3.1.5. Tumour Budding Score
3.1.6. Desmoglein 3
3.1.7. HPV-DNA in Lymph Nodes
3.1.8. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Immunohistochemistry
3.1.9. Histological Techniques for Sentinel Lymph Node Analysis
3.1.10. Single Fiber Reflectance Spectroscopy
3.1.11. PET/MRI
3.1.12. PET/CT
3.2. Tumour Tissue Analysis
3.2.1. Activin A and Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts
3.2.2. Cyclins
3.2.2.1. Cyclin D1
3.2.2.2. Cyclin L1
3.2.2.3. Cyclin B
3.2.3. β-catenin
3.2.4. Histopathological Characteristics
3.2.5. Genetic Amplifications
3.2.6. DNA Methylation
3.2.7. Ecotropic Viral Integration Site 1
3.2.8. CC-Chemokine Receptor 7
3.2.9. Connexins, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin
3.2.10. E-Cadherin
3.2.11. Melanoma Associated-A Antigens
3.2.12. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor - C
3.2.13. Panitumumab and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
3.2.14. Cornulin and Total Protein Analysis
3.2.15. Markers of Cancer Stem Cells CD133, NANOG and NOTCH1
3.2.16. Metastasis-Associated Protein 1
3.2.17. SFN, TCTP and 14-3-3-Zeta
3.2.18. E-Cadherin and Focal Adhesion Kinase
3.2.19. p-EMT and SPRR1B
3.2.20. NKX3-1 and DNA Copy Number Aberrations
3.2.21. MFAP5, TNNC1, MGP, FBFBP1 and FBXO32
3.2.22. Homo Sapiens Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5
3.2.23. B cell-Specific Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus Integration Site 1
3.2.24. Podoplanin
3.2.25. p53, Bcl-2, EGFR, Ki67, Cyclin D1 and Cox-2
3.2.26. Semaphorin-3F and Neuropilin-2
3.2.27. Histologic Features
3.2.28. Cellular Dissociation Grade
3.2.29. MRI Size for Oral Tongue SCC
3.2.30. Prospero Homeobox Protein 1
3.2.31. SPECT/CT
3.2.32. SUV PET/CT
3.2.33. Ultrasonography
3.2.34. E-Cadherin
3.2.35. Ki-67, PARP, BAD, Caspase-9, VEGF-A
3.2.36. HPV and p16
3.2.37. Methylation Status of Long INterspersed Element 1 (LINE-1) and Alu Elements (Alu)
3.2.38. MET
3.2.39. Gene Expression Analyses and Molecular Subtypes
3.3. Blood Markers
3.3.1. Indexes and Rations from Standard Blood Analysis
3.3.2. Circulating Tumour Cells
3.3.3. Circulating Tumour Cells
3.3.4. Circulating HPV DNA
3.3.5. CD31
3.3.6. Bone Marrow
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of Worldwide Burden of Cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.L.; Kligerman, J.; Matos De Sá, G.; Arcuri, R.A.; Freitas, E.Q.; Farias, T.; Matos, F.; Lima, R.A. Elective Neck Dissection versus Observation in Stage I Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Tongue and Floor of the Mouth. Otolaryngol. - Head Neck Surg. 2001, 125, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlito, A.; Silver, C.E.; Rinaldo, A. Neck Dissection: Present and Future? Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2008, 265, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.C.; Zhang, S.; Ishii, G.; Endoh, Y.; Kodama, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Hayashi, R.; Ebihara, S.; Cho, J.S.; Ochiai, A. Predictive Markers for Late Cervical Metastasis in Stage I and II Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Jeevan, M.; Trivedi, N.; Hiran, K.R.; Kekatpure, V.; Kuriakose, M.A. Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorlag, R.; Boeve, K.; Witjes, M.J.H.; Koole, R.; Peeters, T.L.M.; Schuuring, E.; Willems, S.M.; van Es, R.J.J. Amplification and Protein Overexpression of Cyclin D1: Predictor of Occult Nodal Metastasis in Early Oral Cancer. Head Neck 2017, 39, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothandaraman, S.; James, B.L.; Raghavan, N.; Suresh, A.; Kuriakose, M.A. Clinical Application of Bio-Markers for Detection of Nodal Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2017, 39, E96. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlito, A.; Rinaldo, A.; Robbins, K.T.; Silver, C.E. Neck Dissection: Past, Present and Future? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2006, 120, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.I.; Ferlito, A.; Rinaldo, A.; Gourin, C.G.; Lowry, J.; Ho, W.K.; Leemans, C.R.; Shaha, A.R.; Suárez, C.; Clayman, G.L.; et al. Management of the N0 Neck - Reference or Preference. Oral Oncol. 2006, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudioso, P.; Borsetto, D.; Polesel, J.; Tirelli, G.; Emanuelli, E.; Menegaldo, A.; Molteni, G.; Nicolai, P.; Tomasoni, M.; Montenegro, C.; et al. Blood Markers Predicting Clinically Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. ORL. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2024, 86, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermod, M.; Bongiovanni, M.; Petrova, T.V.T.V.; Dubikovskaya, E.A.E.A.; Simon, C.; Tolstonog, G.; Monnier, Y. Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity and the Oropharynx Using Peritumoral Prospero Homeobox Protein 1 Lymphatic Nuclear Quantification. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network, N.C.C. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology - Head and Neck Cancers Version 2.2022. NCCN 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a Big Role in Gene Regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagadia, R.; Pandit, P.; Coman, W.B.; Cooper-White, J.; Punyadeera, C. MiRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer Revisited. Cell. Oncol. 2013, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, G.; Fazzari, M.; Kung, G.; Kawachi, N.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; McLemore, M.; Chen, Q.; Burk, R.D.; Smith, R. V.; Prystowsky, M.B.; et al. Low-Level Expression of MicroRNAs Let-7d and MiR-205 Are Prognostic Markers of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.B.Y.; Lenarduzzi, M.; Krushel, T.; Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Shi, W.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Jurisica, I.; O’Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; et al. Comprehensive MicroRNA Profiling for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Calvopiña, D.; Punyadeera, C. MiRNAs in Human Papilloma Virus Associated Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Nagadia, R.; Pandit, P.; Cooper-White, J.; Banerjee, N.; Dimitrova, N.; Coman, W.B.; Punyadeera, C. A Novel Saliva-Based MicroRNA Biomarker Panel to Detect Head and Neck Cancers. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 37, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.M.; Heaford, A.C.; Trask, D.K. Detection of Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using the Relative Expression of Tissue-Specific Mir-205. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 1, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, A.C.A.C.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Maia, D.C.C.D.C.C.; Evangelista, A.F.A.F.; Morini, M.A.M.A.; Carvalho, A.L.A.L.; Vettore, A.L.A.L. Accuracy of MicroRNAs as Markers for the Detection of Neck Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. MYO5A Inhibition by MiR-145 Acts as a Predictive Marker of Occult Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Human Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2018, 11, 3619–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, E.; Lohavanichbutr, P.; Fan, W.; Houck, J.R.; Rue, T.C.; Doody, D.R.; Futran, N.D.; Upton, M.P.; Yueh, B.; Zhao, L.P.; et al. Can a Metastatic Gene Expression Profile Outperform Tumor Size as a Predictor of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Cancer Patients? Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, B.L.; Kontharaman, S.; Kumar, M.; Ravindra, D.R.; Mitha, S.; Dwivedi, N.; Nisheena, R.; Pillai, V.; Hedne, N.; Suresh, A.; et al. Molecular Marker Based Intra-Operative Diagnostic Assay for Detection of Lymph Node Metastasis in Hnscc. Head Neck 2017, 39, E108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Takashima, S.; Takayama, F.; Wang, J.C.; Kawakami, S.; Saito, A.; Matsushita, T.; Sone, S. Detection of Occult Metastatic Lymph Nodes in the Neck with Gray-Scale and Power Doppler US. Acta Radiol. 2001, 42, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, A.; Nakashiro, K.-I.; Mihara, M.; Sumida, T.; Kawamata, H.; Shintani, S.; Aida, T.; Tachikawa, T.; Hamakawa, H. Basic and Clinical Studies on Quantitative Analysis of Lymph Node Micrometastasis in Oral Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shores, C.G.; Yin, X.; Funkhouser, W.; Yarbrough, W. Clinical Evaluation of a New Molecular Method for Detection of Micrometastases in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Otolaryngol. - Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Lefèvre, M.; Ricci, S.; Saintigny, P.; Callard, P.; Périé, S.; Lacave, R.; Bernaudin, J.-F.; Lacau, St. Guily, J. Detection of Occult Carcinomatous Diffusion in Lymph Nodes from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Real-Time RT-PCR Detection of Cytokeratin 19 MRNA. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, I.; Sandhu, S. V; Bhandari, R.; Sood, N.; Bhullar, R.K.; Sethi, N. Detection of Cervical Lymph Node Micrometastasis and Isolated Tumor Cells in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Immunohistochemistry and Serial Sectioning. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2016, 20, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, J.E.; Miller, M.E.; Said, S.; Jafek, B.W.; Campana, J.P.; Shroyer, K.R. Detection of Occult Cervical Micrometastases in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Samir, M.; Hamid, O.A.; El-Maraghy, M. Evaluation of Cytokeratin Tissue Marker in Detection of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Cases of Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Mol. Biol. 1996, 3, 955–960. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, R.; Nakashiro, K.-I.; Goda, H.; Tanaka, H.; Hamakawa, H. Identification of Novel Molecular Markers for Detecting Lymph Node Metastasis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigné, L.; Godey, F.; Le Gallo, M.; Le Gall, F.; Fautrel, A.; Morcet, J.; Jégoux, F. One-Step Nucleic Acid Amplification for Detecting Lymph Node Metastasis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, D.; Wenig, B.M.; Smith, R. V. The Significance of Immunohistochemically Demonstrated Nodal Micrometastases in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, J.; Yamana, K.; Yoshida, R.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Arita, H.; Nakashima, H.; Nagata, M.; Hirosue, A.; Kawaguchi, S.; et al. Tumor Budding as a Novel Predictor of Occult Metastasis in CT2N0 Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamana, K.; Sakata, J.; Yoshida, R.; Gohara, S.; Kawaguchi, S.; Nagao, Y.; Arita, H.; Nakashima, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kawahara, K.; et al. Tumor Budding Is a Predict Marker of Occult Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Patients with CT2N0 TSCC. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Nagvekar, S.; Spadigam, A.; Dhupar, A. Determining the Potential of Desmoglein 3 as a Sensitive and Specific Immunohistochemical Marker for the Detection of Micrometastasis in Patients with Primary Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Contemp. Oncol. (Poznan, Poland) 2016, 20, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Martin, D.; Malhotra, R.; Marsh, C.A.; Doçi, C.L.; Veenstra, T.D.; Nathan, C.-A.O.; Sinha, U.K.; Singh, B.; Molinolo, A.A.; et al. DSG3 as a Biomarker for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Cancer Using Nanostructured Immunoarrays. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirghani, H.; Moreau, F.; Lefèvre, M.; Tam, C.; Périé, S.; Soussan, P.; St Guily, J.L. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Oropharyngeal Cancers in Lymph Nodes as a Marker of Metastases. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghani, H.; Ferchiou, M.; Moreau, F.; Vourexakis, Z.; Amen, F.; Breuskin, I.; Lefèvre, M.; Casiraghi, O.; Drusch, F.; Soussan, P.; et al. Oropharyngeal Cancers: Significance of HPV16 Detection in Neck Lymph Nodes. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukens, J.N.; Pustylnikov, S.; Montone, K.; Lin, A.; Swisher-McClure, S.D.; Ghiam, A.F.; Weinstein, G.S.; Cohen, R.; Facciabene, A. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Occult Primary HPV+ Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OPSCC): Comparison of the Primary Tumor and Regional Lymph Node Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, E425–E426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.P.; Ravindran, H.K.; Sundram, S.; Iyer, S.; Kekatpure, V.; Durah, S.; Kuriakose, M.A. Pathologic Evaluation of Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugter, O.; Aaboubout, Y.; Algoe, M.; de Bruijn, H.S.; Keereweer, S.; Sewnaik, A.; Monserez, D.A.; Koljenović, S.; Hardillo, J.A.U.; Robinson, D.J.; et al. Detecting Head and Neck Lymph Node Metastases with White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy; a Pilot Study. Oral Oncol. 2021, 123, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebeci, S.; Aydos, U.; Yeniceri, A.; Pula, D.; Duzlu, M.; Atay, L.O.; Yilmaz, M. Diagnostic Performance of FDG PET/MRI for Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Clinically N0 Head and Neck Cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 4528–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosko, A.; Birkeland, A.; Shuman, A.; Prince, M.; Bradford, C.; Wolf, G.; Worden, F.; Eisbruch, A.; Srinivasan, A.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography-CT Prediction of Occult Nodal Metastasis in Recurrent Laryngeal Cancer. Head Neck 2017, 39, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coletta, R.D.; Bufalino, A.; Sobral, L.M.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Graner, E.; Kowalski, L.P.; Salo, T. Activin A Regulates Cell Interactions in the Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2015, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelner, N.; Rodrigues, P.C.P.C.; Bufalino, A.; Fonseca, F.P.F.P.; Santos-Silva, A.R. dos; Miguel, M.C.C.M.C.C.; Pinto, C.A.L.C.A.L.; Leme, A.F.P.A.F.P.; Graner, E.; Salo, T.; et al. Activin A Immunoexpression as Predictor of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis and Overall Survival in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2015, 37, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, R.; Rodrigues, P.; Kelner, N.; Bufalino, A.; Fonseca, F.; Santos- Silva, A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Salo, T.; Graner, E. Activin A Immunoexpression Is Useful to Predict Occult Lymph Node Metastasis and Overall Survival in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaccio, P.; Pruneri, G.; Carboni, N.; Pagliari, A.V.; Quatela, M.; Cesana, B.M.; Pignataro, L. Cyclin D1 Expression Is Predictive of Occult Metastases in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with Clinically Negative Cervical Lymph Nodes. Head Neck 2000, 22, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myo, K.; Uzawa, N.; Miyamoto, R.; Sonoda, I.; Yuki, Y.; Amagasa, T. Cyclin D1 Gene Numerical Aberration Is a Predictive Marker for Occult Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in TNM Stage I and II Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity. Cancer 2005, 104, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.A.; Shawky, A.E.-A.; Hamed, R.H. Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 and E-Cadherin Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticht, C.; Hofele, C.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Bosch, F.X.X.; Freier, K.; Lichter, P.; Joos, S. Amplification of Cyclin L1 Is Associated with Lymph Node Metastases in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H.; Omura, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Mogi, S. Cyclin B1 Is Useful to Predict Occult Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Tongue Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 25, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosado, P.; Lequerica-Fernández, P.; Fernández, S.; Allonca, E.; Villallaín, L.; De Vicente, J.C. E-Cadherin and β-Catenin Expression in Well-Differentiated and Moderately-Differentiated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Relations with Clinical Variables. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazit, Y.; Bakir, K.; Ucak, R.; Mumbuc, S.; Ozer, E.; Kanlikama, M. Clinical and Histopathological Correlates of the Proliferative Activity in Squamous Cell Laryngeal Carcinoma. Rev. Laryngol. Otol. Rhinol. (Bord). 2002, 123, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Keum, K.C.K.C.; Chung, E.J.E.J.; Koom, W.S.W.S.; Cho, J.H.J.H.; Cho, S.H.S.H.; Choi, E.C.E.C.; Lee, C.G.C.G.; Suh, C.O.C.O.; Kim, G.E.G.E. Predictive Value of P53 and PCNA Expression for Occult Neck Metastases in Patients with Clinically Node-Negative Oral Tongue Cancer. Otolaryngol. neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kempen, P.M.W.; Noorlag, R.; Braunius, W.W.; Moelans, C.B.; Rifi, W.; Savola, S.; Koole, R.; Grolman, W.; van Es, R.J.J.; Willems, S.M. Clinical Relevance of Copy Number Profiling in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaraj, S.V.S.V.; Shyamsundar, V.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Ramshankar, V. Deregulation of Extracellular Matrix Modeling with Molecular Prognostic Markers Revealed by Transcriptome Sequencing and Validations in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.J.A.M.; Melchers, L.J.; De Bruin, L.B.; Mastik, M.F.; Slagter-Menkema, L.; Groen, H.J.M.; Van Der Vegt, B.; Van Der Laan, B.F.A.M.; De Meyer, T.; Van Criekinge, W.; et al. Discovery of DNA Methylation Markers That Predict Nodal Metastases in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idel, C.; Ribbat-Idel, J.; Kuppler, P.; Krupar, R.; Offermann, A.; Vogel, W.; Rades, D.; Kirfel, J.; Wollenberg, B.; Perner, S. EVI1 as a Marker for Lymph Node Metastasis in HNSCC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenc¸o, S.; Silami, M.; Camisasca, D.; Diblasi, E.; Fonseca, E.; Faria, P.; Dias, F. Expression of Chemokine Receptor CCR7 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with and without Cervical Metastasis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizdrak, I.; Mizdrak, M.; Racetin, A.; Bošković, B.; Benzon, B.; Durdov, M.G.; Vukojević, K.; Filipović, N. Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Genes (Basel). 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Domínguez, F.; Alvarez, C.; Manrique, C.; Herrero, A.; Suárez, C. Expression of E-Cadherin in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Supraglottic Larynx with Correlations to Clinicopathological Features. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollaoglu, N.; Vairaktaris, E.; Nkenke, E.; Neukam, F.W.; Ries, J. Expression of MAGE-A12 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2008, 24, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, S.E.S.; Oliveira, D.T.; Nonogaki, S.; Landman, G.; Carvalho, A.L.; Kowalski, L.P. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Does Not Predict Occult Lymph-Node Metastasis in Early Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, N. Feasibility of Panitumumab-IRDye800 for Metastatic Lymph Node Identification in Patients with Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, S515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, G.; van den Berg, N.S.; Nishio, N.; Juniper, G.; Pei, J.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, G.; Lee, Y.-J.; Ramos, K.; Iagaru, A.H.; et al. Metastatic and Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping Using Intravenously Delivered Panitumumab-IRDye800CW. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7188–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, P.M.; Merkley, M.; Jackson, L.; Dynan, W.S. Overexpression of Cornulin in Histologically Normal Adjacent Tissue Predicts Occult Nodal Metastases in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, E. Prognostic Implication of NOTCH1 in Early Stage Oral Squamous Cell Cancer with Occult Metastases. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-O.; Jung, C.-K.; Sun, D.-I.; Joo, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-S. Relationships between Metastasis-Associated Protein (MTA) 1 and Lymphatic Metastasis in Tonsil Cancer. Eur. Arch. oto-rhino-laryngology Off. J. Eur. Fed. Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Soc. Affil. with Ger. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngology - Head Neck Surg. 2011, 268, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Malgundkar, S.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Sadhana, K.; D’Cruz, A.; Zingde, S. Proteomic Markers in Early Buccal Mucosa Squamous Cell Cancers. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Dominguez, F.; Suárez, V.; Canel, M.; Secades, P.; Chiara, M.D. Focal Adhesion Kinase and E-Cadherin as Markers for Nodal Metastasis in Laryngeal Cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.S.A.S.; Puram, S.V.S. V; Faquin, W.C.W.C.; Richmon, J.D.J.D.; Emerick, K.S.K.S.; Deschler, D.G.D.G.; Varvares, M.A.M.A.; Tirosh, I.; Bernstein, B.E.B.E.; Lin, D.T.D.T. Immunohistochemical Quantification of Partial-EMT in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma Primary Tumors Is Associated with Nodal Metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2019, 99, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaguchi, K.; Uzawa, N.; Mogushi, K.; Takahashi, K.-I.; Michikawa, C.; Nakata, Y.; Sumino, J.; Okada, N.; Mizushima, H.; Fukuoka, Y.; et al. Loss of NKX3-1 as a Potential Marker for an Increased Risk of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, K.; Li, S.; Hu, L.; Han, J.; Zhu, D.; Tian, X.; Liu, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhong, L.; et al. MFAP5 and TNNC1: Potential Markers for Predicting Occult Cervical Lymphatic Metastasis and Prognosis in Early Stage Tongue Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, R.S.R.S.; Naresh, K.N.K.N.; D’Cruz, A.K.A.K.; Mulherkar, R.; Borges, A.M.A.M. Metastasis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue Is Associated with Down-Regulation of Epidermal Fatty Acid Binding Protein (E-FABP). Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, E.; Puzzo, L.; Zuccalà, V.; Trapasso, S.; Vasquez, E.; Garozzo, A.; Caltabiano, R. Nuclear BMI-1 Expression in Laryngeal Carcinoma Correlates with Lymph Node Pathological Status. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.F.G.F.; Fritzsche, F.R.F.R.; Züllig, L.; Storz, M.; Graf, N.; K. Haerle, S.; Jochum, W.; Stoeckli, S.J.S.J.; Moch, H.; Haerle, S.K.; et al. Podoplanin Expression Correlates with Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx. Int. J. cancer 2011, 129, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iype, E.M.; Balakrishnan, L.S.R. Selected Molecular Markers as Indicators of Clinical Profile, Tumor Characteristics and Treatment Outcome in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Larynx. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meler-Claramonte, C.; Avilés-Jurado, F.X.; Vilaseca, I.; Terra, X.; Bragado, P.; Fuster, G.; Vintró, X.L.; Camacho, M. Semaphorin-3F/Neuropilin-2 Transcriptional Expression as a Predictive Biomarker of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in HNSCC. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, A.; Weinstein, G.; Chalian, A.; Yodul, M.; Weber, R. Multivariate Predictors of Occult Neck Metastasis in Early Oral Tongue Cancer. Otolaryngol. - Head Neck Surg. 2004, 131, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, K.; Vance, C.; Budnick, S.; Muller, S. Muscle Invasion in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma as a Predictor of Nodal Status and Local Recurrence: Just as Effective as Depth of Invasion? Head Neck Pathol. 2011, 5, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Kubota, A.; Yokose, T.; Furukawa, M.; Matsushita, T.; Takita, M.; Mitsunaga, S.; Mizoguchi, N.; Nonaka, T.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Predictive Significance of Tumor Depth and Budding for Late Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Clinical N0 Early Oral Tongue Carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Saito, Y.; Tateishi, Y.; Yamazawa, S.; Fukuoka, O.; Kobayashi, K.; Omura, G.; Akashi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Ando, M.; et al. Tumor–Stroma Ratio Can Predict Lymph-Node Metastasis in CT1/2N0 Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Independent of Tumor Budding Grade. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksic, I.; Suton, P.; Manojlovic, S.; Virag, M.; Petrovecki, M.; Macan, D. Significance of Myofibroblast Appearance in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity on the Occurrence of Occult Regional Metastases, Distant Metastases, and Survival. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Medicine, D.L.-; 2021, undefined The Occult Nodal Metastasis Rate of Early Tongue Cancer (T1–T2): A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. journals.lww.com.
- Stögbauer, F.; Beck, S.; Ourailidis, I.; Hess, J.; Poremba, C.; Lauterbach, M.; Wollenberg, B.; Buchberger, A.M.S.; Jesinghaus, M.; Schirmacher, P.; et al. Tumour Budding-Based Grading as Independent Prognostic Biomarker in HPV-Positive and HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velosa, C.; Shi, Q.; Stevens, T.M.; Chiosea, S.I.; Purgina, B.; Carroll, W.; Rosenthal, E.; Morlandt, A.; Loree, T.; Brandwein-Weber, M.S. Worst Pattern Of Invasion and Occult Cervical Metastases for Oral Squamous Carcinoma. Head Neck 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesinghaus, M.; Steiger, K.; Stögbauer, F.; Haller, B.; Kolk, A.; Straßen, U.; Pickhard, A.; Wirth, M.; Silva, M.; Budczies, J.; et al. Pre-Operative Cellular Dissociation Grading in Biopsies Is Highly Predictive of Post-Operative Tumour Stage and Patient Outcome in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Moon, H.; Nam, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Roh, J.-L.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Clinical Significance of Three-Dimensional Measurement of Tumour Thickness on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Dhake, S.; Agrawal, A.; Shah, S.; Purandare, N.; Rangarajan, V.; Dutta, S.; Chaturvedi, P. Does SPECT/CT Offer Incremental Benefit over Planar Lympho-Scintigraphy in Sentinel Node Biopsies in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinomas? Indian J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 30, S19. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Li, H.; Seng, D.; Liu, F. Significance of SUV Max for Predicting Occult Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Early-Stage Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 6241637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźmińska, M.; Osuch-Wójcikiewicz, E.; Fronczewska-Wieniawska, K.; Królicki, L.; Niemczyk, K. Usefulness of 18F-FDG PET/CT examination in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer - Preliminary results. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2011, 65, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, R.; Buron, B.M.D.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Henriksen, B.M.; Von Buchwald, C.; Nielsen, M.B. Staging of Cervical Lymph Nodes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Adding Ultrasound in Clinically Lymph Node Negative Patients May Improve Diagnostic Work-Up. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvorović, L.; Milutinović, Z.; Strbac, M.; Markovski, S. What Is Important for Ultrasound Evaluation of Occult Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Laryngeal Cancer: Size, Shape, Vascularity or Cytological Findings? ORL. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2007, 69, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.F.G.F.; Züllig, L.; Soltermann, A.; Roessle, M.; Graf, N.; Haerle, S.K.S.K.; Studer, G.; Jochum, W.; Moch, H.; Stoeckli, S.J.S.J. Down Regulation of E-Cadherin (ECAD) - a Predictor for Occult Metastatic Disease in Sentinel Node Biopsy of Early Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghirad, H.; Monkman, J.; Mehdi, A.M.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Hughes, B.G.M.B.G.M.; Kulasinghe, A.; O’Byrne, K.; Hughes, B.G.M.B.G.M.; Kulasinghe, A. Dissecting Tissue Compartment-Specific Protein Signatures in Primary and Metastatic Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 895513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkitticharoen, V.; Kulapaditharom, B.; Leopairut, J.; Kraiphibul, P.; Larbcharoensub, N.; Cheewaruangroj, W.; Chintrakarn, C.; Pochanukul, L. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor a and Proliferation Marker in Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral and Pharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mofty, S.K.; Zhang, M.Q.; Davila, R.M. Histologic Identification of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Related Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Cervical Lymph Nodes: A Reliable Predictor of the Site of an Occult Head and Neck Primary Carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2008, 2, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitkumthorn, N.; Keelawat, S.; Rattanatanyong, P.; Mutirangura, A. LINE-1 and Alu Methylation Patterns in Lymph Node Metastases of Head and Neck Cancers. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4469–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesina, G.; Martone, T.; Galeazzi, E.; Olivero, M.; De Stefani, A.; Bussi, M.; Valente, G.; Comoglio, P.M.M.; Di Renzo, M.F.F. Staging of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using the MET Oncogene Product as Marker of Tumor Cells in Lymph Node Metastases. Int. J. cancer 2000, 89, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevallos, J.P.J.P.; Mazul, A.L.A.L.; Walter, V.; Hayes, D.N.D.N. Gene Expression Subtype Predicts Nodal Metastasis and Survival in Human Papillomavirus-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, G.; Perri, F.; Maglitto, F.; Togo, G.; De Fazio, G.R.; Apolito, M.; Calabria, F.; Laface, C.; Vaira, L.A.; Committeri, U.; et al. Pre-Treatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios as Predictors of Occult Cervical Metastasis in Clinically Negative Neck Supraglottic and Glottic Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, V.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G.; Salzano, G.; Bonavolontà, P.; Maglitto, F.; Romano, A.; Tarabbia, F.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Attanasi, F.; Di Lauro, A.E.; et al. Pre-Treatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor for Occult Cervical Metastasis in Early Stage (T1-T2 CN0) Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, E.; Barros, J.; Salgado, I.; Millán, A.; Vilares, M.; Zagalo, C.; Gomes, P. Pretreatment Blood Markers in the Prediction of Occult Neck Metastasis: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Cureus 2021, 13, e16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, G.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G.; Abbate, V.; Vaira, L.A.; Committeri, U.; Bonavolontà, P.; Piombino, P.; Maglitto, F.; Russo, C.; Russo, D.; et al. The Prognostic Role of the Pre-Treatment Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Tumor Depth of Invasion (DOI) in Early-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Tongue. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 26, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyumi, B.; Bharde, A.; Aland, G.; D’Souza, A.; Jayant, S.; Singh, N.; Tripathi, S.; Badave, R.; Kale, N.; Singh, B.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Predictor for Poor Prognostic Factors and Overall Survival in Treatment Naïve Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 134, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Y.; Wong, M.H.; Clayburgh, D. Circulating Hybrid Cells as a Marker of Nodal Metastases in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 1125–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, T.E.; Anderson, A.N.; Hollett, Y.R.; Sutton, T.L.; Walker, B.S.; Swain, J.R.; Sauer, D.A.; Clayburgh, D.R.; Wong, M.H. Circulating Hybrid Cells Predict Presence of Occult Nodal Metastases in Oral Cavity Carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, R.B.B.; Pai, S.I.I.; Koch, W.M.M.; Gillison, M.L.L.; Danish, H.N.N.; Westra, W.H.H.; Daniel, R.; Shah, K.V. V; Sidransky, D. Detection and Quantitation of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in the Sera of Patients with HPV-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4171–4175. [Google Scholar]
- Mermod, M.; Bongiovanni, M.; Petrova, T.; Goun, E.; Simon, C.; Tolstonog, G.; Monnier, Y. Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Head and Neck Cancer with CD31 Vessel Quantification. Otolaryngol. neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, B.; Walz, A.; Kolbow, K.; Pauli, C.; Chaubal, S.; Andratschke, M. Clinical Relevance of Circulating Tumour Cells in the Bone Marrow of Patients with SCCHN. Onkologie 2004, 27, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, M.N.; Rinaldo, A.; Hamakawa, H.; Mahfouz, M.E.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Brennan, J.; Devaney, K.O.; Grandis, J.R.; Ferlito, A. Importance of Molecular Analysis in Detecting Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2006, 28, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, D.; Wenig, B.M.; Smith, R. V The Significance of Immunohistochemically Demonstrated Nodal Micrometastases in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Shah, J.P.; Silver, C.E.; Medina, J.E.; Takes, R.P.; Robbins, K.T.; Rinaldo, A.; Werner, J.A.; Ferlito, A. Management of the Clinically Negative Neck in Early-Stage Head and Neck Cancers after Transoral Resection. Head Neck 2011, 33, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, J.B.; Christensen, R.K.; Sørensen, J.A.; Krogdahl, A. Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Cancer of the Oral Cavity: Is Central Step-Sectioning Enough? J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 36, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kligerman, J.; Lima, R.A.; Soares, J.R.; Prado, L.; Dias, F.L.; Freitas, E.Q.; Olivatto, L.O. Supraomohyoid Neck Dissection in the Treatment of T1/T2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity. Am. J. Surg. 1994, 168, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, A.C.; Maia, D.C.C.; Horst, M.A.; Carvalho, A.L.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Vettore, A.L. Concord Ance of Pathologic Examination and QRT-PCR for MicroRNA Expressi on in Lymph Nodes from Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, S104–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farlow, J.L.; Birkeland, A.C.; Rosko, A.J.; VanKoevering, K.; Haring, C.T.; Smith, J.D.; Brenner, J.C.; Shuman, A.G.; Chinn, S.B.; Stucken, C.L.; et al. Elective Paratracheal Lymph Node Dissection in Salvage Laryngectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2542–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.; Khanna, M.; Thomas, J.; Gazala, F.; El-Hakim, M. DEPTH OF INVASION CUTOFF FOR RECOMMENDING ELECTIVE NECK DISSECTION IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 52, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.M.; Farquhar, D.R.; Vanleer, J.P.; Patel, S.N.; Hackman, T.G. Depth of Invasion on Pathological Outcomes in Clinical Low-Stage Oral Tongue Cancer Patients. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaboubout, Y.; van der Toom, Q.M.Q.M.; de Ridder, M.A.J.M.A.J.; De Herdt, M.J.M.J.; van der Steen, B.; van Lanschot, C.G.F.C.G.F.; Barroso, E.M.E.M.; Nunes Soares, M.R.; ten Hove, I.; Mast, H.; et al. Is the Depth of Invasion a Marker for Elective Neck Dissection in Early Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.-Y.; Wang, C.P.; Lee, L.-Y.; Lee, S.-R.; Ng, S.-H.; Kang, C.-J.; Lin, J.-C.; Terng, S.-D.; Hua, C.-H.; Chen, T.-M.; et al. Indications for Elective Neck Dissection in CT1N0M0 Oral Cavity Cancer According to the AJCC Eight Edition: A Nationwide Study. Oral Oncol. 2023, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
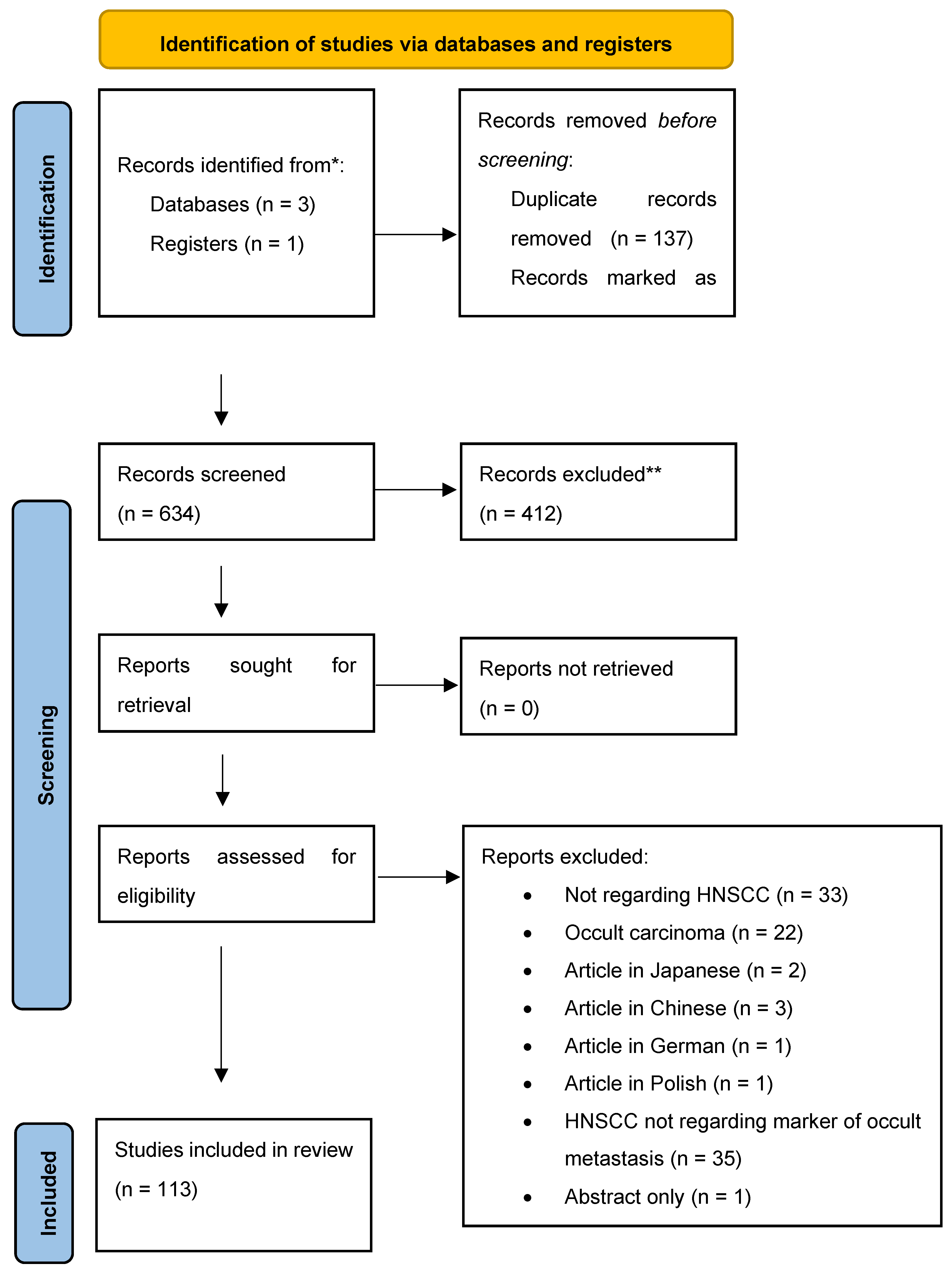
| Title | Year | Authors | Journal | Doi | Population | Subsites | Material | Results | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of cytokeratin tissue marker in detection of metastatic lymph nodes in cases of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma | 1996 | Hamed M, Samir M, Hamid O et al. | Cancer Molecular Biology | 51 cases of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma. | Laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma | Nodal specimens | Analysis of the percentage of occult metastases cases detected by cytokeratin immunostaining and missed by Haematoxilin and Eosin gave significant value | p > 0.001 | |
| Staging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using the MET oncogene product as marker of tumor cells in lymph node metastases. | 2000 | Cortesina G, Martone T, Galeazzi E et al. | International journal of cancer | 10.1002/1097-0215(20000520)89:3<286::AID-IJC12>3.0.CO;2-U | 20 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | Nodal specimens | MET- encoded sequences were found in 61 of 151 nodes (40%), of which 24 (16%) were found metastatic by in-depth histopathology. Western blot analysis demonstrated the presence of the full-size MET receptor in primary tumors and lymph node metastases: immunohistochemistry showed receptor localization in tumor cells. | |
| Detection and quantitation of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in the sera of patients with HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | 2000 | Capone R, Pai S, Koch W et al. | Clinical cancer research | 70 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | Serum DNA extracts | Four of these patients with HPV-positive tumors later developed distant metastases, suggesting that HPV DNA in serum may represent occult hematogenous spread of cancer cells in this subset of patients. | ||
| Cyclin D1 expression is predictive of occult metastases in head and neck cancer patients with clinically negative cervical lymph nodes | 2000 | Capaccio P, Pruneri G, Carboni N et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0347(200005)22:3<234::AID-HED5>3.0.CO;2-3 | 32 HNSCC patients with clinically and radiologically negative lymph nodes in whom metastatic involvement was subsequently demonstrated at histologic examination (pN+);Group of 64 head and neck cancer patients with histologically negative laterocervical lymph nodes (pN0) was used as control | HNSCC | Biopsy samples of lymph nodes | Cyclin D1 expression significantly correlated with the presence of occult lymph node metastases | p =0 .0007 |
| Detection of occult metastatic lymph nodes in the neck with gray-scale and power Doppler US. | 2001 | Wang Q, Takashima S, Takayama F et al. | Acta radiologica | 10.1080/028418501127346701 | 57 patients without wide echogenic hilum on GSUS that measured less than 10 mm in minimal axial diameter were prospectively studied | HNSCC | Findings of 69 pathologically verified cervical nodes (38 benign, 31 malignant) | Of the vascularity patterns, spotted or peripheral pattern had the highest accuracy (80%) with 61% sensitivity and 93% specificity. A combined criterion of the minimal axial diameter larger than 8 mm and spotted or peripheral pattern increased the accuracy to 82% and sensitivity to 77% but specificity decreased to 86%. | |
| The significance of immunohistochemically demonstrated nodal micrometastases in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck | 2002 | Rhee D, Wenig B, Smith R | Laryngoscope | 10.1097/00005537-200211000-00011 | 10 patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck without conventional histological evidence of nodal metastases | HNSCC | Nodal specimens | Occult micrometastases were found in the lymph nodes 5 of 10 patients examined. There was no association between the site of primary tumor, or T stage, and the presence of occult metastases. | |
| Expression of E-cadherin in squamous cell carcinomas of the supraglottic larynx with correlations to clinicopathological features | 2002 | Rodrigo J, Domínguez F, Alvarez C et al. | European Journal of Cancer | 10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00399-9 | 101 primary carcinomas | Squamous cell carcinomas of the supraglottic larynx | Tissue samples | There was a significant correlation between decreased E-cadherin expression and the presence of nodal metastases | P=0.007 |
| Clinical and histopathological correlates of the proliferative activity in squamous cell laryngeal carcinoma. | 2002 | Bayazit Y, Bakir K, Ucak R et al. | Revue de laryngologie - otologie - rhinologie | 28 patients who were treated for LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples | There was no association between the mean values of the proliferative markers, and N stage and T stage of the patients as well as laryngeal site of involvement | p > 0.05 | |
| Detection of occult cervical micrometastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell cancer | 2003 | Barrera J, Miller M, Said S et al. | Laryngoscope | 10.1097/00005537-200305000-00022 | 50 patients treated between 1992 and 2001 | HNSCC | 1012 lymph nodes | H&E-stained and cytokeratin-stained sections revealed occult nodal micrometastases in 3.8% of NO and 5% of N1 cases. Overall, 26 micrometastases were identified in NO and N1 patients, causing 29% of N0 patients and 45% of N1 patients to be upstaged. | |
| Multivariate Predictors of Occult Neck Metastasis in Early Oral Tongue Cancer | 2004 | Sparano A, Weinstein G, Chalian A et al. | Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery | 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.04.008 | 45 clinically determined N0 patients (T1/T2) | Oral tongue cancer | Tissue samples | Independent correlates of positive occult neck metastasis included greater tumor thickness, greater depth of muscle invasion, T2 stage, poorly differentiated tumors, infiltrating-type invasion front, presence of perineural invasion, and presence of angiolymphatic invasion. | Greater tumor thickness (P = 0.01)Depth of muscle invasion (P = 0.01) T2 stage (P = 0.01)Poorly differentiated tumors (P = 0.007),Infiltrating-type invasion front (P = 0.03)Presence of perineural invasion (P = 0.001)Presence of angiolymphatic invasion (P = 0.005) |
| Clinical relevance of circulating tumour cells in the bone marrow of patients with SCCHN | 2004 | Wollenberg B, Walz A, Kolbow K et al. | Onkologie | 10.1159/000079088 | 176 patients suffering from SCCHN | HNSCC | Bone marrow aspirates | Single CK19-expressing tumour cells could be detected in the bone marrow of 30.7% of the patients. | |
| Clinical evaluation of a new molecular method for detection of micrometastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 2004 | Shores C, Yin X, Funkhouser W et al. | Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery | 10.1001/archotol.130.8.937 | 35 consecutive patients | HNSCC | 153 cervical lymph nodes | Of 35 HNSCCs, 33 expressed CK 14 RNA, and 15 lymph nodes with routine pathologically positive metastasis were also positive for CK 14 RNA. 4 lymph nodes that were pathologically negative nodes were positive for CK 14 RT-PCR, with 2 containing metastases detected by semi-step sectioning. | |
| Basic and clinical studies on quantitative analysis of lymph node micrometastasis in oral cancer. | 2004 | Onishi A, Nakashiro K, Mihara M et al. | Oncology reports | 10 patients with oral cancer | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | 115 lymph nodes using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based on the expression of squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) and cytokeratin 13 (CK13) | Of 108 histologically metastasis-negative LNs, 19 (17.6%) expressed SCCA mRNA levels higher than the cut-off value. CK13 mRNA is not a suitable marker for the real-time PCR since it was detected frequently even in the control LNs | ||
| Cyclin D1 gene numerical aberration is a predictive marker for occult cervical lymph node metastasis in TNM Stage I and II squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity | 2005 | Myo K, Uzawa N, Miyamoto R et al. | Cancer | 10.1002/cncr.21491 | 45 patients with previously untreated TNM Stage I and II (T1-2N0M0) disease who had not undergone elective cervical lymph node dissection | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), using a BAC clone specific for CCND1, was performed on OSCC specimens obtained by fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy | CCND1 numerical aberrations were observed in 15 of the 45 patients and were significantly associated with the presence of occult lymph node metastases | P < 0.001 |
| Amplification of Cyclin L1 is associated with lymph node metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). | 2005 | Sticht C, Hofele C, Flechtenmacher C et al. | British journal of cancer | 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602400 | 280 primary paraffin-embedded HNSCC | 124 oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC);96 pharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (PSCC);60 laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas (LSCC) | HNSCCs biopsies mounted on a tissue microarray were analysed for copy number changes of CCNL1, SNO, PIK3CA and TP73L by fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH). | A significant association of CCNL1 gains and the presence of lymph node metastases was found, which was independent of anatomical site and T-stage of the primary tumour. | P=0.049 |
| Predictive value of p53 and PCNA expression for occult neck metastases in patients with clinically node-negative oral tongue cancer | 2006 | Keum K, Chung E, Koom W et al. | Otolaryngology–head and neck surgery | 10.1016/j.otohns.2006.02.011 | 37 clinically N0 patients who underwent neck dissection | Oral tongue cancer | p53 or proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunoreactivities on deparaffinized sections of the primary tumor | Although tumor differentiation and tumor size were significantly correlated with occult neck metastases of oral tongue cancer by univariate analysis, no correlation was found between p53 or PCNA and the presence of occult neck metastasis | P = 0.03 |
| Detection of occult carcinomatous diffusion in lymph nodes from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using real-time RT-PCR detection of cytokeratin 19 mRNA | 2006 | Tao L, Lefèvre M, Ricci S et al. | British Journal of Cancer | 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603073 | 31 patients treated between 2004 and 2005 | HNSCC | A total of 1328 lymph nodes were prospectively evaluated by routine haematoxylin-eosin-safran (HES) staining, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and real-time Taqman reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (real-time RT-PCR) assay. Amplification of cytokeratin 19 (CK19) mRNA transcripts using real-time RT-PCR was used to quantify cervical micrometastatic burden | The cervical lymph node metastatic rates determined by routine HES staining and real-time RT-PCR assay were 16.3 and 36.0%, respectively,Moreover, CK19 mRNA expression values in histologically positive lymph nodes were significantly higher than those observed in histologically negative lymph nodes. | P<0.0001 |
| Cyclin B1 is useful to predict occult cervical lymph node metastases in tongue carcinoma. | 2006 | Harada H, Omura K, Nakajima Y et al. | Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research | 40 oral tongue squamous cell carcinomas | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinomas | immunohistochemical expression of cyclin B1 in a series of tissue samples | Cyclin B1 overexpression was positively correlated with occult cervical lymph node metastases and the number of mitotic cells. In addition, there was a positive relationship between labeling indices of cyclin B1 and Ki-67. | ||
| What is important for ultrasound evaluation of occult metastatic lymph nodes in laryngeal cancer: size, shape, vascularity or cytological findings? | 2007 | Cvorović L, Milutinović Z, Strbac M et al. | ORL; journal for oto-rhino-laryngology and its related specialties | 10.1159/000099227 | 60 patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma without enlarged neck nodes on CT scan. | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 144 lymph nodes | Fifty-two of 144 lymph nodes were involved with metastasis on histopathological examination. Respective values for ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology (USg FNAC) showed high sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and accuracy | |
| Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue is associated with down-regulation of epidermal fatty acid binding protein (E-FABP). | 2007 | Uma R, Naresh K, D’Cruz A et al. | Oral oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.12.024 | 54 cases of squamous carcinoma of the oral tongue; stages: T1, T2 or T3 | Oral tongue carcinoma | About 100 mg of fresh tissue from the primary tumour, a grossly metastatic lymph node and a non-metastatic lymph node were collected from each surgical procedure. | Gene FABP5, coding for Epidermal fatty acid binding protein (E-FABP) expression was up to 4-fold higher in the primary tumours (67%) as compared to the corresponding metastatic lymph nodes by northern blot analysis. | |
| Focal adhesion kinase and E-cadherin as markers for nodal metastasis in laryngeal cancer | 2007 | Rodrigo J, Dominguez F, Suárez V et al. | Archives of otolaryngology–head & neck surgery | 10.1001/archotol.133.2.145 | 95 previously untreated men with squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottic larynx. | Squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottic larynx. | Samples of tissue from surgical resection of the tumor and bilateral neck dissection | Decreased E-cadherin expression was correlated with the presence of nodal metastases. The combination of E-cadherin and FAK expression resulted in a superior accuracy in assessing nodal metastasis. | P=0.006P=0.001 |
| Determination of lymph node micrometastases in patients with supraglottic carcinoma | 2007 | Xu Y, Zhao X, Guan M et al. | Acta Oto-Laryngologica | 10.1080/00016480701200327 | 20 patients with supraglottic cancer | Supraglottic cancer | Twenty samples from supraglottic cancer and 182 lymph nodes from neck dissections were examined by LOH comparing immunohistochemical (IHC) staining using cytokeratin 19 (CK19), and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. | The frequency of LOH was 37.4% of lymph nodes and all of the primary tumors. Occult micrometastases were present in 9 of 20 cases; 23.6% of lymph nodes were positive for CK19 by IHC; 16.5% of lymph nodes were positive by H&E. | |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor a and proliferation marker in prediction of lymph node metastasis in oral and pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 2008 | Boonkitticharoen V, Kulapaditharom B, Leopairut J et al. | Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery | 10.1001/archotol.134.12.1305 | A total of 147 previously untreated patients with different stages of HNSCC | Oral cavity SCC; Pharyngeal SCC;Laryngeal SCC | Lymph nodes samples | Regarding nodal status, Ki-67 expression was a significant risk factor for N+ in all tumors, whereas VEGF-A expression was related to N+ in oral and pharyngeal SCC only. Analytically, Ki-67 expression alone in oral and pharyngeal SCC was associated with a relative risk of N+ of 3.83,and additional expression of VEGF-A raised the value to 6.12. Moreover, the combined expression of both markers was 3.25 times more effective in predicting N+ for T1,2 tumor compared with T3,4 tumor. | Ki-67 expression in all tumors (P< 0,009);Ki-67 expression alone in oral and pharyngeal SCC (P=0.009);VEGF-A expression was related to N+ in oral and pharyngeal SCC only (P<0.03);Ki-67 associated with VEGF-A expression in oral and pharyngeal SCC (P<0,001) |
| Histologic identification of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related squamous cell carcinoma in cervical lymph nodes: A reliable predictor of the site of an occult head and neck primary carcinoma | 2008 | El-Mofty S, Zhang M, Davila R | Head and Neck Pathology | 10.1007/s12105-008-0066-1 | 93 cases of SCC metastatic to the neck from known primary tumors were classified morphologically into conventional keratinizing SCC (KSCC) and non-keratinizing SCC (NKCa) | 32 oropharyngeal, 35 oral, and 26 arose in the laryx/hypopharynx | In situ hybridization (ISH) for high risk HPV as well as immunostaining for p16 were performed on all metastsatic and primary tumors | Twenty-three cases were found to be HPV+ by ISH, of which 22/23 had oropharyngeal origin, with 95.7% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity. Twenty-one of these HPV+ oropharyngeal tumors were NKCa. The remaining case showed overlapping NKCa/KSCC hybrid morphology. All NKCa were HPV+ and stained diffusely and strongly with p16 antibodies. | P<0.0001 |
| Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C does not predict occult lymph-node metastasis in early oral squamous cell carcinoma. | 2008 | Faustino S, Oliveira D, Nonogaki S et al. | International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery | 10.1016/j.ijom.2007.11.021 | 87 patients with primary OSCC arising in the tongue or floor of mouth, clinically T1N0M0 or T2N0M0, with (pN+) and without (pN0) occult lymph-node metastases | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Occult lymph-node metastases were analyzed for VEGF-C expression by malignant cells | Independently of VEGF-C expression, lymph-node metastasis (pN+) was the most significant prognostic factor for overall survival of patients with OSCC | P=0.030 |
| Expression of MAGE-A12 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. | 2008 | Mollaoglu N, Vairaktaris E, Nkenke E et al. | Disease markers | 10.1155/2008/359840 | Total of 57 specimens from OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Total of 57 tissue samples obtained from patientswith OSCC and 20 normal oral mucosal (NOM) probesof otherwise healthy volunteers | No expression of MAGE-A12 was observed in the non-neoplasticNOM tissues. MAGE-A12 was expressed in 49.1% of the investigated tumor samples. The correlation between malignant lesion and MAGE-A12 detection was significant | P<0.001 |
| Detection of metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using the relative expression of tissue-specific mir-205 | 2008 | Fletcher A, Heaford A, Trask D | Translational Oncology | 10.1593/tlo.08163 | 12 patients with primary HNSCC | HNSCC | Snap-frozen tissue from 12 surgically removed, pathologically confirmed, primary HNSCC samples from various subsites in the head and neck and 7 benign mucosal tissue samples derived from the oral cavity or oropharynx were collected. A total of eight histologicallydetermined HNSCC-positive lymph nodes were included in thisstudy. Using a quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction-based assay, we examined the expression of microRNA-205 (mir-205) across tissues. | mir-205 is abundantly expressed in squamous epithelial cells and that this expression remains relatively constant as these tissues transition from normal to neoplastic. Significantly, mir-205 is not expressed in normal lymph node tissue, allowing for the use of whole-lymph node processing and quantitative analysis by PCR to detect this biomarker | |
| Pathologic evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes in oral squamous cell carcinoma | 2010 | Trivedi N, Ravindran H, Sundram S et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/hed.21345 | 80 patients with primary HNSCC | HNSCC | Frozen section, imprint-cytology, hematoxylin-eosin staining, serial step sectioning (SSS) with hematoxylin-eosin, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) | SSS upstaged the disease in a further 7 patients (9%). Frozen section detected macrometastasis in 7 of 8 cases but failed to detect smaller metastases | |
| Overexpression of cornulin in histologically normal adjacent tissue predicts occult nodal metastases in head and neck | 2010 | Weinberger P, Merkley M, Jackson L et al. | Cancer Research | 10.1158/1538-7445.AM10-3286 | A cohort of 7 cN0 HNSCC patients who subsequently underwent planned neck dissection as part of their treatment was selected | HNSCC | Snap frozen tissue was enriched for tumor and adjacent normal tissue by laser capture microdissection. Total protein was extracted and separated by saturation-labeling 2D difference in-gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE). | There were 31 proteins underexpressed in occult metastases patients, with the top candidate being 11.9 fold lower in the occult metastasis group. There were 29 proteins overexpressed, with the top candidate being 6.6 fold higher in the occult metastasis group. This protein was identified as Cornulin, a novel HNSCC biomarker. | P < 0.001 |
| Usefulness of 18F-FDG PET/CT examination in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer - Preliminary results | 2010 | Kuźmińska M, Osuch-Wójcikiewicz E, Fronczewska-Wieniawska K et al. | Otolaryngologia Polska | 10.1016/S0030-6657(11)70704-1 | 41 patients diagnosed with head and neck cancer | HNSCC | 45 PET/CT examinations were performed in 41 patients | Based on PET/CT imaging the recurrent disease was diagnosed in 9 patients, cervical lymph node metastases - in 12 patients, distant metastases - in 6 patients, possible primary tumour localization - in 3 patients. In 7 cases additional foci of increased FDG uptake were revealed outside the head and neck. | |
| Relationships between metastasis-associated protein (MTA) 1 and lymphatic metastasis in tonsil cancer. | 2011 | Park J, Jung C, Sun D et al. | European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology | 10.1007/s00405-010-1478-6 | 43 clinical N0 patients with tonsillar cancer | Tonsillar cancer | Immunohistochemical analysis of 43 tonsillar neoplasm tissues was performed using antibodies raised to MTA1. | There was a significant correlation between the expression of MTA1 and lymph node metastasis | P = 0.034 |
| Podoplanin expression correlates with sentinel lymph node metastasis in early squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx. | 2011 | Huber G, Fritzsche F, Züllig L et al. | International journal of cancer | 10.1002/ijc.25795 | 120 patients with HNSCC of the oral cavity and oropharynx undergoing a SLN biopsy were enrolled | Oral cavity and oropharynx squamous cell carcinoma | Cancer cell-expressed podoplanin was determined by immunohistochemistry using tissue microarrays | SLN examination revealed occult metastasis in 45 patients (37.5%). Twenty-nine of 120 (24.2%) primary HNSCC showed podoplanin expression. Podoplanin expression correlated significantly with SLN metastasis and remained a significant predictor for lymph node status even after controlling for tumor stage | p = 0.029 |
| Muscle invasion in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma as a predictor of nodal status and local recurrence: just as effective as depth of invasion? | 2011 | Chandler K, Vance C, Budnick S et al. | Head and neck pathology | 10.1007/s12105-011-0296-5 | 61 cases of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma stage T1 | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples were examined histologically to assess muscle invasion and DOI | Cases with muscle invasion had a 23.3% PPV of occult lymph node metastasis. Cases with DOI of greater than 3 mm had a 29.7% PPV of occult lymph node metastasis. | |
| Human papillomavirus type 16 oropharyngeal cancers in lymph nodes as a marker of metastases | 2011 | Mirghani H, Moreau F, Lefèvre M et al. | Archives of otolaryngology–head & neck surgery | 10.1001/archoto.2011.141 | 11 patients with HPV-16(+) OSCC and 3 control patients with HPV-16(-) OSCC. | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Viral load quantification using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was retrospectively performed in primary tumors and in cervical lymph nodes, originating from levels IIa, IIb, and III. A total of 45 lymph node levels were analyzed. | The viral load value was significantly higher in metastatic lymph nodes than in tumor-free lymph nodes | P < 0.001 |
| Down regulation of e-cadherin (ECAD) - a predictor for occult metastatic disease in sentinel node biopsy of early squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx | 2011 | Huber G, Züllig L, Soltermann A et al. | BMC Cancer | 10.1186/1471-2407-11-217 | 120 patients | Oral cavity SCC (n = 110) (91.7%; mostly tongue);Oropharyngeal SCC (n=10) (8.3%). | E-Cadherin expression in tumour tissue with microarray technique | Differentiation grade and down regulation of E-Cadherin expression significantly correlate with positive lymph node status in univariate and multivariate analysis. | Differentiation grade (p = 0.018);Down regulation of E-Cadherin expression (p = 0.005) |
| Detection of occult lymph node metastasis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | 2011 | Suresh A, Jeevan M, Trivedi N et al. | Oral Oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.06.290 | 44 patients (126 nodes) with oral tongue cancer | Oral tongue SCC | 126 samples of lymph nodes analyzed by quantitative PCR (QPCR). The detection efficacies were compared to pathological evaluation by frozen sections, serial step sectioning (SSS) with H&E as well as cytokeratin immunohistochemistry (IHC); | An evaluation using two markers (CK14 and DSG3) further increased the efficacy, while a combined evaluation identified all the patients with occult metastasis. | Sensitivity: 0.88; specificity: 0.85;Combined evaluation sensitivity: 1. |
| Can a metastatic gene expression profile outperform tumor size as a predictor of occult lymph node metastasis in oral cancer patients? | 2011 | Méndez E, Lohavanichbutr P, Fan W et al. | Clinical cancer research | 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0175 | 187 recruited subjects with primary OSCC or dysplasia | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Affymetrix U133 2.0 plus arrays was used to compare the tumor genome-wide gene expression of 73 node-positive OSCC with 40 node-negative (≥18 months) OSCC | Regression identified a four-gene model (MYO5A, RFN145, FBXO32 and CTONG2002744) as the most predictive of nodal metastasis. | p = 0.011 |
| Nuclear BMI-1 expression in laryngeal carcinoma correlates with lymph node pathological status | 2012 | Allegra E, Puzzo L, Zuccalà V et al. | World Journal of Surgical Oncology | 10.1186/1477-7819-10-206 | 64 previously untreated patients who underwent surgical excision of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma with neck dissection were included in this study. | Laryngeal SCC | The expression of B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus integration site 1 (BMI-1) was examined immunohistochemically on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded primary tissue specimens. | High cBMI-1 expression correlated significantly withdistant metastasis | p < 0.05 |
| LINE-1 and alu methylation patterns in lymph node metastases of head and neck cancers | 2012 | Kitkumthorn N, Keelawat S, Rattanatanyong P et al. | Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention | 10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4469 | 61 lymph nodes from patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | 61 lymph nodes were divided into 3 groups: 1) non-metastatic head and neck cancer (NM);2) histologically negative for tumor cells of cases with metastatic head and neck cancer (LN);3) histologically positive for tumor cells (LP). | LINE-1 methylation of both LN and LP was altered.The LINE-1 methylation changes in LN have the same pattern as that in LP. This epigenomic change may be due to the presence of occult metastatic tumor in LN cases. | Lower LINE-1 methylation levels (p<0.001);Higher percentage of mCuC (p<0.01);Lower percentage of uCmC (p<0.001);Higher percentage of uCuC (p<0.001) |
| Loss of NKX3-1 as a potential marker for an increased risk of occult lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. | 2012 | Miyaguchi K, Uzawa N, Mogushi K et al. | International journal of oncology | 10.3892/ijo.2012.1373 | 60 OSCC patients | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Genomic DNAs from 60 OSCC patients using Affymetrix mapping arrays | Quantitative RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses also showed significantly lower expression of NKX3-1 in the cases with occult LNM | |
| Identification of novel molecular markers for detecting lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma | 2012 | Oka R, Nakashiro K, Goda H et al. | Cancer Research | 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2012-720 | 7 patients with OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | The gene expression profiles in 7 metastatic lymph nodes from patients with OSCC, 1 benign lymph node, and 5 salivary gland tissues from non-cancerous patients by microarray analysis. The overexpression of 36 genes in all metastatic lymph nodes but not in benign lymph node and salivary glands was examinated in newly 15 metastatic lymph nodes and 9 benign lymph nodes by real-time quantitative RT-PCR method | Among the 36 genes, the expression of annexin A8-like 2 (ANXA8L2) and desmoglein 3 (DSG3) was commonly detected in metastatic lymph nodes at much higher level but not in benign lymph nodes at all. | |
| Expression of chemokine receptor CCR7 in oral squamous cell carcinoma with and without cervical metastasis | 2012 | Lourenc¸o S, Silami M, Camisasca D et al. | European Journal of Cancer | 10.1016/S0959-8049(12)71708-2 | 41 patients with OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Paraffin embedded samples from both the tumor and cervical lymph nodes. Semi-seriated H&Estained sections and immunohistochemical reaction using anti-cytokeratin AE1/AE3 antibody were performed in metastasis-free cervical lymph nodes. | There was a significant association between pathological stage and cervical metastasis. A trend for an association with CCR7 expression in tumors was noted in relation to cervical metastasis and tumor thickness | pathological stage and cervical metastasis p = 0.00;CCR7 expression and cervical metastasis (p = 0.058) and tumor thickness (p = 0.051) |
| DSG3 as a biomarker for the ultrasensitive detection of occult lymph node metastasis in oral cancer using nanostructured immunoarrays | 2013 | Patel V, Martin D, Malhotra R et al. | Oral Oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.08.001 | 317 HNSCC cases | HNSCC | Multiple general cancer- and HNSCC-tissue microarrays (TMAs), in negative and positive HNSCC metastatic cervical lymph nodes, and in a variety of HNSCC and control cell lines | DSG3 is highly expressed in all HNSCC lesions and their metastatic cervical lymph nodes, but absent in non-invaded lymph nodes. | |
| Proteomic markers in early buccal mucosa squamous cell cancers | 2013 | Nair S, Malgundkar S, Patil A et al. | European Journal of Cancer | 10.1016/S0959-8049(13)70161-8 | 90 patients with early stage (T1/T2) buccal mucosa cancers | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue microarrays was prepared and the sectons stained with antibodies for 19 markers | Higher expression of SFN and TCTP are associated with lower risk of nodal metastasis | p = 0.003 |
| Oropharyngeal cancers: significance of HPV16 detection in neck lymph nodes. | 2013 | Mirghani H, Ferchiou M, Moreau F et al. | Journal of clinical virology | 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.02.009 | 11 patients with HPV16-positive OPSCC and 3 patients with HPV16-negative OPSCC | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | HP16-viral load (VL) was quantified by real-time-polymerase-chain reaction in primary tumours and neck LNs | All metastatic LNs from HPV16-positive OPSCC had a high VL and the viral DNA was located within tumoural cells | |
| E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in well-differentiated and moderately-differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma: Relations with clinical variables | 2013 | Rosado P, Lequerica-Fernández P, Fernández S et al. | British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | 10.1016/j.bjoms.2012.03.018 | 69 patients who had been operated on for oral SCC. | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples of oral squamous cell carcinomas were examined immunohistochemically | E-cadherin was significantly associated with histological grade and alcohol consumption, and β-catenin was significantly associated with nodal stage, TNM stage, and E-cadherin expression. | E-cadherin with histological grade (p = 0.002)alcohol consumption (p = 0.05); β-catenin with nodal stage (p = 0.02), TNM stage (p = 0.009), and E-cadherin expression (p = 0.01). |
| Discovery of DNA methylation markers that predict nodal metastases in oral squamous cell carcinoma | 2013 | Clausen M, Melchers L, De Bruin L et al. | Oral Oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.03.011 | 6 oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) with nodal metastas es (N+) and 6 OSCC without nodal metastases (N0) | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Global methylation levels on DNA extracted from 6 oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) with nodal metastas es (N+) and 6 OSCC without nodal metastases (N0) by MethylCap -Seq. | The most promising methylation markers will be further validated on a N-status validation cohort containing 463 cases for which complete clinicopathological and follow-up data are available | |
| Activin A immunoexpression is useful to predict occult lymph node metastasis and overall survival in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | 2013 | Coletta R, Rodrigues P, Kelner N et al. | Virchows Archiv | 10.1007/s00428-013-1444- | 110 patients with primary TSCC | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Clinicopathological features and immunohistochemical detection of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and activin A | Activin A high expression was significantly associated with presence of occult lymph node metastasis | p=0.006 |
| Staging of cervical lymph nodes in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Adding ultrasound in clinically lymph node negative patients may improve diagnostic work-up | 2014 | Norling R, Buron B, Therkildsen M et al. | PLoS ONE | 10.1371/journal.pone.0090360 | 51 patients with OSCC classified as cN0 by CT/MRI | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | US prior to sentinel node biopsy or selective neck dissection | Short axial diameter was the best size criterion for detection of metastases. The number of patients with occult metastases decreased from 16 out of 51 (31%) to 9 out of 51 (18%). | |
| Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 and E-cadherin expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 2014 | Ahmed R, Shawky A, Hamed R | Pathology and Oncology Research | 10.1007/s12253-014-9741-6 | 75 patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Tumor tissue sampleswere examined for cyclin D1 and E-cadherin expression by immunohistochemistry. | Cyclin D1 was found to be a significant independent prognostic factor of lymph node metastasis | p = 0.001 |
| Significance of myofibroblast appearance in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity on the occurrence of occult regional metastases, distant metastases, and survival. | 2015 | Luksic I, Suton P, Manojlovic S et al. | International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery | 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.05.009 | 52 patients with cT1-T3N0 OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | The frequency of myofibroblasts within the tumour stroma was assessed immunohistochemically and compared with other clinical and histopathological factors in surgical resection specimens | An increased presence of myofibroblasts in the tumour stroma was significantly correlated with T stage, the presence of occult neck metastasis, regional recurrence, and distant metastasis | Myofibroblasts with T stage P=0.019, occult neck metastasis P<0.001, regional recurrence P=0.037, and distant metastasis P=0.008 |
| Does SPECT/CT offer incremental benefit over planar lympho-scintigraphy in sentinel node biopsies in oral cavity squamous cell carcinomas? | 2015 | Chandra P, Dhake S, Agrawal A et al. | Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 44 patients with clinically node negative oral cavity SCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | 99mTc-labelled Human Serum Albumin Nanocolloid was injected at 2-4 sites on the edge of the tumour 3-6 hours before surgery. Static lymphoscintigraphy in two planes followed by SPECT/CT (low mA) was done. | PL revealed 77 hotspots with a mean of 1.75 per patient and SPECT revealed 92 hotspots with a mean of 2.5 per patient. Additional hotpots were identified in 8 patients on SPECT/CT, including 3 patients, where PL didn’t detect any nodes. | ||
| Clinical relevance of copy number profiling in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 2015 | van Kempen P, Noorlag R, Braunius W et al. | Cancer Medicine | 10.1002/cam4.499 | 191 oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (OPSCC) and 164 oral cavity squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) | Oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Copy number status in 36 common oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes correlated with human papillomavirus (HPV) status in OPSCC, with occult lymph node status in OSCC and with patient survival. | In clinically lymph node-negative OSCC (Stage I-II), gain of the 11q13 region was significantly correlated with occult lymph node metastases | Negative predictive value of 81% |
| Activin A regulates cell interactions in the microenvironment of oral squamous cell carcinomas | 2015 | Coletta R, Bufalino A, Sobral L et al. | Cancer Research | 10.1158/1538-7445 | 115 OSCC patients | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Immunohistochemical analysis of 115 OSCC samples | Increased activin A expression is significantly correlated with presence of regional metastasis | p=0.034 |
| Activin A immunoexpression as predictor of occult lymph node metastasis and overall survival in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. | 2015 | Kelner N, Rodrigues P, Bufalino A et al. | Head & neck | 10.1002/hed.23627 | 110 patients with primary oral tongue SCC | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Immunohistochemical detection of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and activin A on tissue samples | Only high immunohistochemical expression of activin A was significantly associated with presence of occult lymph node metastasis | p =0 .006 |
| Accuracy of microRNAs as markers for the detection of neck lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | 2015 | de Carvalho A, Scapulatempo-Neto C, Maia D et al. | BMC medicine | 10.1186/s12916-015-0350-3 | 161 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | The most differentially expressed microRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR in two independent cohorts: i) 48 FFPE lymph node samples, and ii) 113 FNA lymph node biopsies. | Seven microRNAs highly expressed in metastatic lymph nodes from the discovery set were validated in FFPE lymph node samples. MiR-203 and miR-205 identified all metastatic samples | |
| Prediction of occult lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and the oropharynx using peritumoral Prospero homeobox protein 1 lymphatic nuclear quantification. | 2016 | Mermod M, Bongiovanni M, Petrova T et al. | Head & neck | 10.1002/hed.24452 | Oral cavity and the oropharynx squamous cell carcinoma | Staining of the specific lymphatic endothelial cells nuclear marker, PROX1, as an indicator of lymphatic vessel density was determined by counting the number of positive cells in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the oral cavity and the oropharynx with clinically negative necks | Peritumoral PROX1 lymphatic nuclear count significantly correlated with the detection of OLNM in multivariate analysis | p < 0.005 | |
| Determining the potential of desmoglein 3 as a sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for the detection of micrometastasis in patients with primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. | 2016 | Nagvekar S, Spadigam A, Dhupar A | Contemporary oncology | 10.5114/wo.2016.64596 | 10 patients who underwent neck dissection for primary OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Forty-seven lymph node specimens were immunostained with DSG3 | DSG3 positivity was noted in the six positive lymph nodes. However, when using DSG3 as an immunohistochemical marker, no additional micrometastatic deposits were evident in the histologically negative nodes | |
| Detection of cervical lymph node micrometastasis and isolated tumor cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma using immunohistochemistry and serial sectioning. | 2016 | Dhawan I, Sandhu S, Bhandari R et al. | Journal of oral and maxillofacial pathology | 10.4103/0973-029X.190946 | 10 patients treated with radical neck dissection for primary OSCC. | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | 133 LNs were subjected to SS at 100 μm intervals. The sections were stained with routine H&E staining, pan-CK and analyzed for MM and ITC | The application of combination of SS and IHC using pan-CK (AE1/AE3) revealed the presence of MM and ITC in 2.25% of the LNs diagnosed as negative on routine H&E examination | |
| Clinical significance of three-dimensional measurement of tumour thickness on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. | 2016 | Kwon M, Moon H, Nam S et al. | European radiology | 10.1007/s00330-015-3884-z | 53 OTSCC patients | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tumour thickness measured on axial, coronal, and sagittal views was compared to that in pathologic specimens. | TT in all three planes was significantly correlated with lymph node (LN) metastasis. Occult LN metastasis was found in 15 of 39 (38.5%) patients | |
| Worst Pattern Of Invasion and occult cervical metastases for oral squamous carcinoma | 2017 | Velosa C, Shi Q, Stevens T et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/hed.24754 | 323 patients with T1T2cNo oral cavity squamous carcinoma | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | The resection specimens were examined for worst pattern of invasion, perineural invasion, and lymphocytic host responses | High-risk classification is significantly associated with decreased time to local recurrence and regional metastasis. For patients undergoing END, 31 (20%) had occult-positive lymph nodes. WPOI-5 is significantly predictive of occult cervical metastases | Local recurrence (p = .0128) and regional metastasis (p = .052). WPOI-5 (p 0< .0001). |
| Predictive Significance of Tumor Depth and Budding for Late Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Clinical N0 Early Oral Tongue Carcinoma | 2017 | Hori Y, Kubota A, Yokose T et al. | Head and neck pathology | 10.1007/s12105-017-0814-1 | 48 patients with early oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Associations between the histopathological factors and late lymph metastasis were analyzed | High-grade tumor budding is an independent predictive factor for neck recurrenc | p < 0.01 |
| Positron emission tomography-CT prediction of occult nodal metastasis in recurrent laryngeal cancer. | 2017 | Rosko A, Birkeland A, Shuman A et al. | Head & neck | 10.1002/hed.24719 | 46 clinically and radiographically N0 patients with recurrent laryngeal cancer | Laryngeal SCC | PET-CT examination before salvage laryngectomy with neck dissection | Two patients (16.7%) had true-positive PET-CT results, whereas 10 patients (83.3%) had false-negative scans, 1 patient (2.9%) had a false-positive result and 33 patients (97.1%) had a true-negative PET-CT. | |
| Molecular marker based intra-operative diagnostic assay for detection of lymph node metastasis in hnscc | 2017 | James B, Kontharaman S, Kumar M et al. | Head and Neck | 24 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | positive (17) and negative (7) lymph nodes metastases | Sandwich ELISA indicated the best combination of antibodies and the Lateral Flow test (LFT) assays developed with combination for DSG-3, showed a sensitivity of 72.5% and specificity of 55.6% in detecting positive lymph node samples (11 positive & 9 negative lymph nodes) | ||
| MFAP5 and TNNC1: Potential markers for predicting occult cervical lymphatic metastasis and prognosis in early stage tongue cancer | 2017 | Yang X, Wu K, Li S et al. | Oncotarget | 10.18632/oncotarget.12446 | 12 patients underwent surgical resection for TSCC and selective neck dissection | Oral tongue SCC | Microarray in TSCC fresh tumor and normal tissue specimens with CLNM (n = 6) compared to those without CLNM (n = 6). | Over-expression of MFAP5 and TNNC1 were correlated with CLNM, metastasis relapse-free survival and overall survival | p < 0.001 |
| Immunohistochemical detection of lymph node-DTCs in patients with node-negative HNSCC | 2017 | Sproll C, Freund A, Hassel A et al. | International Journal of Cancer | 10.1002/ijc.30617 | 50 pN0-HNSCC patients | HNSCC | A total of 1.137 exactly mapped LNs. Three immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays using antibodies directed against CK5/14 and CD44v6 | 7 micrometastases (MM) in five patients and 31 disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) in 12 patients. | |
| Feasibility of panitumumab-IRDye800 for metastatic lymph node identification in patients with head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma | 2017 | Van Den Berg N | Molecular Imaging and Biology | 10.1007/s11307-01-017-1138-y | 10 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | Excised LN samples evaluated on high-sensitivity fluorescence systems and histopathotologically evaluated (including hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and EGFR staining) and unstained paraffin-embedded sections) | Fluorescence imaging of panitumumab-IRdye800 predicted the LN status correctly in all cases with 164 true negative nodes, 8 true positive nodes, 0 false-positive nodes and 0 false-negative nodes | |
| Cytokeratin 19 expression in early oral squamous cell carcinoma and their metastasis: Inadequate biomarker for one-step nucleic acid amplification implementation in sentinel lymph node biopsy procedure | 2017 | Noorlag R, van Es R, de Bree R et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/hed.24847 | 207 patients with OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Immunohistochemical CK19 expression was done in 65 cases of paired nodal metastases. | CK19 was expressed in 65% of all OSCC and even less in early OSCC (56%), with poor correlation between primary tumor and (occult) nodal metastasis. | |
| Clinical application of bio-markers for detection of nodal metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 2017 | Kothandaraman S, James B, Raghavan N et al. | Head and Neck | HNSCC | A retrospective (from tissue repository) and prospective (lymph node sample collection) validation of markers ). The validation of these markers will be done by IHC | Using antibodies to desmoglein-3 (DSG-3), with 17 positive and negative lymph node samples, a sensitivity of 72.5% and specificity of 55.6% was achieved for the detection of nodal metastasis using a Lateral Flow Test assay system | |||
| Amplification and protein overexpression of cyclin D1: Predictor of occult nodal metastasis in early oral cancer | 2017 | Noorlag R, Boeve K, Witjes M et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/hed.24584 | 158 patients with early tongue and floor of mouth (FOM) squamous cell carcinomas | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Both CCND1 amplification and cyclin D1, FADD, and cortactin protein expression were correlated with occult nodal metastases from tissue samples | CCND1 amplification and cyclin D1 expression correlated with occult nodal metastases. | |
| Tumor budding is a predict marker of occult node metastasis and prognosis in patients with cT2N0 TSCC | 2018 | Yamana K, Sakata J, Yoshida R et al. | Cancer Science | A total 100 patients with clinical T2N0 TSCC. | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples | OCLNM was significantly associated with endophytic growth pattern, depth of invasion (> 3.3mm) and tumor budding (> 4) in univariate analysis. Multivariate analysis revealed that the tumor budding (> 4) was independently associated with the OCLNM. | ||
| Tumor budding as a novel predictor of occult metastasis in cT2N0 tongue squamous cell carcinoma | 2018 | Sakata J, Yamana K, Yoshida R et al. | Human Pathology | 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.12.021 | 97 patients with cT2N0 TSCC who underwent surgical resection of their primary lesion | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tumor budding using immunohistochemical staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3 and hematoxylin and eosin staining (HE). | Tumor budding score ≥4 is a significant independent predictive factor for the occurrence of occult neck metastasis, which in turn is a significant independent prognostic factor. | |
| Prognostic implication of NOTCH1 in early stage oral squamous cell cancer with occult metastases. | 2018 | Wang S, Fan H, Xu J et al. | Clinical oral investigations | 10.1007/s00784-017-2197-9 | 144 patients with early stage (cT1T2N0) OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples analyzed for the impact of the immunohistochemical expression of CD133, NANOG, and NOTCH1 | CD133, NANOG, and NOTCH1 were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis | CD133: p = 0.035; NANOG: p = 0.024, NOTCH1: p = 0.043 |
| Pre-treatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a predictor for occult cervical metastasis in early stage (T1-T2 cN0) squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. | 2018 | Abbate V, Dell’Aversana Orabona G, Salzano G et al. | Surgical oncology | 10.1016/j.suronc.2018.06.002 | 110 patients suffering from early stage OTSCC | Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples analyzed for Neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in predicting occult cervical metastasis in stage I and II OTSCC | A statistically significant relationship between high levels of pre-treatment NLR and probability rate for neck occult metastases has been found | p = 0.000496 |
| MYO5A inhibition by miR-145 acts as a predictive marker of occult neck lymph node metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 2018 | Zhao X, Zhang W, Ji W | OncoTargets and Therapy | 10.2147/OTT.S164597 | 132 patients with LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | MYO5A and miR-145 expression was analyzed in tissue samples | Downregulation of miR-145 in LSCC, which was negatively correlated with MYO5A suppression of LSCC progression and metastasis. MiR-145 directly regulated MYO5A expression in vitro and suppressed LSCC proliferation and invasion while promoting apoptosis by inhibiting MYO5A. | |
| Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Occult Primary HPV+ Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OPSCC): Comparison of the Primary Tumor and Regional Lymph Node Metastases | 2019 | Lukens J, Pustylnikov S, Montone K et al. | International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics | 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.1539 | 14 patients presenting with initially occult primary HPV+ OPSCC managed with trans-oral robotic surgery (TORS) and neck dissection, with a final TNM stage of pT1 N2b | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on paired specimens from the primary site and involved nodes for CD3, CD8, FOXP3, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 | Occult primary tumors had a higher percentage of CD3+ and CD8+ TILs compared to tumor in lymph nodes. There was a higher concentration of FOXP3+ TILs in primary tumors compared to nodal tumor and a trend towards a higher percentage of CTLA-4+ cells | CD3+ (p = 0.006), CD8+ T cells (p = 0.01). FOXP3+ TILs (p = 0.01), CTLA-4+ cells (p = 0.09) |
| Selected molecular markers as indicators of clinical profile, tumor characteristics and treatment outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx | 2019 | Iype E, Balakrishnan L | Journal of Clinical Oncology | 10.1200/jco.2019.37.15_suppl.e17522 | 72 cases of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Samples from patients who underwent laryngectomy were taken and analyzed prospectively. Immunoreactivity in tissue sections was evaluated as negative when no positive cells were observed within the tumor, weak (1+) , moderate (2+) , and strong or intense (3+) | Proliferation markers EGFR, Cyclin D1 and Ki 67, individually and collectively were predictive of extracapsular spread and perineural spread of tumour. The significant expression of Cox-2 was highly predictive of Node positivity. Markers of aggressiveness were identified as p53, Bcl-2 Cox-2. Markers of invasiveness were EGFR, Cyclin D1 and Ki 67. Markers predicting survival were p53, BCl-2, Cyclin D1 and Ki 67. | |
| Prediction of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Head and Neck Cancer with CD31 Vessel | 2019 | Mermod M, Bongiovanni M, Petrova T et al. | Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (United States) | 10.1177/0194599818791779 | 56 cases of squamous cell carcinoma | Oral cavity SCC (n = 50);Oropharyngeal SCC (n = 6) | Intra- and peritumoral microvascular density values | Peritumoral CD31 microvascular density was significantly associated with occult LNM in multivariate analysis | P< 0.01 |
| Immunohistochemical quantification of partial-EMT in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma primary tumors is associated with nodal metastasis | 2019 | Parikh A, Puram S, Faquin W et al. | Oral Oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104458 | 99 OCSCC patients (47 with low volume T2 disease, 52 with high volume T4 disease, and ∼50% in each group with nodal metastasis) | Oral cavity SCC | Tissue microarrays (TMA) were created using 2 mm cores from patients | There were associations of p-EMT scores with higher grade, PNI, and node positivity, including occult node positivity | p-EMT scores with higher grade (p = 0.04), PNI (p = 0.003), and node positivity (p = 0.02), including occult node positivity (p = 0.005) |
| Gene Expression Subtype Predicts Nodal Metastasis and Survival in Human Papillomavirus-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. | 2019 | Zevallos J, Mazul A, Walter V et al. | The Laryngoscope | 10.1002/lary.27340 | 309 OCSCC cases and 125 LSCC | Oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Clinically node-negative OCSCC cases in order to test the predictive value of gene expression subtypes in detecting occult nodal metastasis | In a subset analysis of clinically T1-2N0M0 OCSCC, we demonstrate that the mesenchymal subtype was predictive of occult nodal metastasis | (RR=3.38, 95% CI 1.08–10.69) |
| Significance of SUV Max for Predicting Occult Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Early-Stage Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. | 2020 | Xu C, Li H, Seng D et al. | Journal of oncology | 10.1155/2020/6241637 | 120 cT1-2N0 tongue SCC patients | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | The association between SUV max and occult lymph node metastasis was analyzed | In 60 patients with an SUV max >9.7, 13 patients had occult metastasis, and the difference was significant | p=0.041 |
| Pre-operative cellular dissociation grading in biopsies is highly predictive of post-operative tumour stage and patient outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | 2020 | Jesinghaus M, Steiger K, Stögbauer F et al. | British journal of cancer | 10.1038/s41416-019-0719-8 | 160 patients with HNSCC | HNSCC | CDG in n = 160 pre-therapeutic biopsies from patients who received standardised treatment following German guidelines | Pre-operative CDG was highly predictive of post-operative tumour stage, including the prediction of occult lymph node metastasis. | p < 0.001 |
| EVI1 as a marker for lymph node metastasis in HNSCC | 2020 | Idel C, Ribbat-Idel J, Kuppler P et al. | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 10.3390/ijms21030854 | Anonymized retrospective cohort of 389 patients suffering from HNSCC | Oral HNSCC n = 97;Oropharyngeal HNSCC n = 133;Hypopharyngeal HNSCC n = 48;Laryngeal HNSCC n= 111; | Tissue samples of Primary Tumors, Lymph nodes Metastasis, Distant Metastasis, and Local Recurrences | EVI1 expression in PTs that had at least one cervical lymph node metastasis (LM) was significantly higher than in those PTs that had not formed LMs yet.At the time of the first diagnosis, EVI1 expression in PT tissue could discriminate between nodal positive and nodal negative patients. | p < 0.05. |
| One-step nucleic acid amplification for detecting lymph node metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 2020 | Peigné L, Godey F, Le Gallo M et al. | Oral Oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104553 | 26 cN0 HNSCC patients | HNSCC | 157 LN were prospectively analyzed. Each node was cut into 4 equal pieces alternatively sent to pathological analysis and OSNA technique. IHC CK19 was performed on the primary tumor biopsy and RT-qPCR of CK19, PVA and EPCAM on the LN lysate of discordant cases. | SNA detected 21 metastases. There were 139 concordant LN (88.5%). | After elimination of allocation bias, false negative rate was 1.3%, sensitivity and specificity were 90% and 95.6%, PPV and NPV were 75% and 98.5%. |
| Circulating Hybrid Cells as a Marker of Nodal Metastases in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 2020 | Anderson Y, Wong M, Clayburgh D | International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics | 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.11.347 | 20 cN0 OCSCCa patients undergoing resection of the primary tumor and neck dissection for staging. | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Peripheral blood samples were obtained and it was performed immunohistochemistry on the samples to identify cells co-expressing both cytokeratin (tumor cell marker) and CD45 (macrophage marker), indicating a circulating hybrid cell | There was a statistically significant difference between CHC levels of cN0 patients who remained pN0, and those that converted to pN1+. The level of CHCs in the peripheral blood correlated with the presence of both overt and pathologically identified occult cervical nodal metastases | p = 0.005; 0.002; 0.0001 |
| Pretreatment Blood Markers in the Prediction of Occult Neck Metastasis: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. | 2021 | Ventura E, Barros J, Salgado I et al. | Cureus | 10.7759/cureus.16641 | 102 patients with early-stage OSCC of the tongue | Oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue | Role of pretreatment inflammatory blood markers in predicting occult neck metastasis. We also evaluated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) association with the depth of invasion (DOI) of the primary tumor | Significant association of NLR and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio with neck status on univariate analysis. Multivariate analysis showed that only NLR was an independent risk factor for occult metastasis among inflammatory blood markers. | p=0.001; 0.011; 0.02 |
| Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as predictors of occult cervical metastasis in clinically negative neck supraglottic and glottic cancer | 2021 | Salzano G, Perri F, Maglitto F et al. | Journal of Personalized Medicine | 10.3390/jpm11121252 | 387 patients with LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Data of patients affected by LSCC, who had been surgically treated by means of laryngectomy and END between January 2006 and January 2021, were retrospectively reviewed, using information retrieved from a database dedicated to such procedures in a single tertiary care referral institute. | A total of 27.7% of patients were found positive for neck node metastasis (the pN+ group), while 78/108 (72.3%) patients were found to be negative for the presence of neck metastasis (the pN0 group). High values of NLR, but not PLR, significantly correlated with the probability of OM, and an NLR value of 2.26 corresponds to a probability of OM of 20%. | |
| The occult nodal metastasis rate of early tongue cancer (T1–T2): A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis | 2021 | Choi K, Park S, Kim J et al. | Medicine | 10.1097/MD.0000000000024327 | 19 enrolled studies with a total of 1567 cases included. | All studies enrolled T1 and T2 oral tongue cancer patients (with clinically negative for lymph node metastasis) | Tissue samples | The occult nodal metastasis rate was not significantly affected by neither T2 ratio among T1–T2 nor reported year of the studies. | P = 0.426 and 0.921 |
| Metastatic and sentinel lymph node mapping using intravenously delivered Panitumumab- | 2021 | Krishnan G, van den Berg N, Nishio N et al. | Theranostics | 10.7150/THNO.59196 | 27 patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), 18 of whom were clinically node negative (cN0). | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Patients were infused intravenously with 50mg of Panitumumab-IRDye800CW prior to surgical resection of their primary tumour with neck dissection and/or SLNB. Lymphadenectomy specimens underwent fluorescence molecular imaging to evaluate tracer distribution to LNs. | The median MFI of metastatic LNs was significantly higher than the median MFI of benign LNs | 0.06 versus 0.02, p < 0.05 |
| Detecting head and neck lymph node metastases with white light reflectance spectroscopy; a pilot study. | 2021 | Bugter O, Aaboubout Y, Algoe M et al. | Oral oncology | 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105627 | 9 patients with a total of nineteen LNs were included. | HNSCC | Intraoperative SFR spectroscopy measurements of LNs with and without malignancies. | Three parameters, blood volume fraction (BVF), microvascular saturation (StO(2)), and Rayleigh amplitude, were significantly lower in positive LNs. They were combined into one optical parameter ‘delta’, using discriminant analysis. Delta was significantly decreased in positive LNs. | p = 0,0006 |
| Deregulation of extracellular matrix modeling with molecular prognostic markers revealed by transcriptome sequencing and validations in Oral Tongue squamous cell carcinoma. | 2021 | Thangaraj S, Shyamsundar V, Krishnamurthy A et al. | Scientific reports | 10.1038/s41598-020-78624-4 | 100 patients with Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OTSCC), | Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Transcriptome analysis of OTSCC patients identified the key genes and deregulated pathways. A panel of 26 marker genes was shortlisted and validated using real-time PCR | Up-regulation of Tenacin C (TNC) and Podoplanin (PDPN) was significantly correlated with occult node positivity. | |
| Circulating hybrid cells predict presence of occult nodal metastases in oral cavity carcinoma | 2021 | Henn T, Anderson A, Hollett Y et al. | Head and Neck | 10.1002/hed.26692 | 22 patients with cN0 OCSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Peripheral blood samples for CHCs with co-expression of cytokeratin (tumor) and CD45 (leukocyte) using immunofluorescence microscopy, then correlated levels with pathologic lymph node status. | CHC levels exceeded CTCs and correlated with the presence of both clinically overt and occult nodal metastases | p = 0.002; 0.006 |
| Tumor–stroma ratio can predict lymph-node metastasis in cT1/2N0 oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma independent of tumor budding grade | 2022 | Sakai T, Saito Y, Tateishi Y et al. | International Journal of Clinical Oncology | 10.1007/s10147-022-02249-y | 70 patients with cT1/2N0 OTSCC | Oral Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | BG and TSR were evaluated using hematoxylin–eosin staining and cytokeratin AE1/AE3 immunostaining. | NLM correlated with the pathological depth of invasion (pDOI), TBG and TSR in univariate analysis and pDOI and TSR in multivariate analysis. | p < 0.001, p = 0.008, p < 0.001 , p = 0.01, p = 0.02 |
| The prognostic role of the pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and tumor depth of invasion (DOI) in early-stage squamous cell carcinomas of the oral tongue. | 2022 | Salzano G, Dell’Aversana Orabona G, Abbate V et al. | Oral and maxillofacial surgery | 10.1007/s10006-021-00969-5 | 110 patients affected by early-stage (cT1-T2 cN0) OTSCC | Oral Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Tissue samples analyzed for pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and tumor depth of invasion (DOI) | A DOI greater than 5.4 mm and a NLR greater than 2.93 are associated with an increased risk of presenting occult cervical metastases | |
| Semaphorin-3F/Neuropilin-2 Transcriptional Expression as a Predictive Biomarker of Occult Lymph Node Metastases in HNSCC | 2022 | Meler-Claramonte C, Avilés-Jurado F, Vilaseca I et al. | Cancers | 10.3390/cancers14092259 | 53 patients with cN0 squamous cell carcinoma | HNSCC | Tissue samples analyzed for he transcriptional expression of SEMA3F and NRP2 | Patients with occult lymph node metastases (cN0/pN+) had significantly lower SEMA3F expression values than patients without lymph node involvement (cN0/pN0). Considering the expression of the SEMA3F-NRP2 genes, patients were classified into two groups according to the risk of occult nodal metastasis: Group 1 (n = 34), high SEMA3F/low NRP2 expression, with a low risk of occult nodal involvement (14.7% cN0/pN+); Group 2 (n = 19), low SEMA3F or high SEMA3F/high NRP2 expression, with a high risk of occult nodal involvement (78.9% cN0/pN+). | |
| Dissecting Tissue Compartment-Specific Protein Signatures in Primary and Metastatic Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. | 2022 | Sadeghirad H, Monkman J, Mehdi A et al. | Frontiers in immunology | 10.3389/fimmu.2022.895513 | 43 patients with primary tumors and 11 with nodal metastases | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Targeted spatial proteomic approaches to primary and lymph node metastasis from an oropharyngeal SCC | Overall survival (OS) analysis indicated CD25 in tumor regions of primary tumors to be associated with reduced survival, while progesterone receptor (PR) was associated with an improved OS | p = 0.003, p = 0.015 |
| Circulating tumor cells as a predictor for poor prognostic factors and overall survival in treatment naïve oral squamous cell carcinoma patients | 2022 | Qayyumi B, Bharde A, Aland G et al. | Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology | 10.1016/j.oooo.2022.02.018 | 152 patients with treatment naïve oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sensitivity analysis was performed by including 40 healthy controls. | Oral SCC | CTCs were isolated using OncoDiscover technique from presurgically obtained peripheral blood | CTCs above 20.5 were suggestive of nodal metastasis with a linear trend for detecting occult metastasis | P < 0.0001P =0.061 |
| Tumour budding-based grading as independent prognostic biomarker in HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck cancer | 2023 | Stögbauer F, Beck S, Ourailidis I et al. | British Journal of Cancer | 10.1038/s41416-023-02240-y | 331 HPV-positive and HPV-negative cases from TCGA. | HNSCC | TB and MCNS were analysed digitally in 1 and 10 high-power fields (HPF) | Analysing MCNS did not add prognostic significance to quantifying TB. CDG was a significant prognostic marker in HPV-negative and HPV-positive tumours and prognostically superior to the WHO and BG systems. High CDG was associated with clinically occult lymph-node metastases | |
| Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas | 2023 | Mizdrak I, Mizdrak M, Racetin A et al. | Genes | 10.3390/genes14020446 | 34 patients who underwent (hemi-)laryngectomy and regional lymphadenectomy due to LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Samples of tumor tissue and adjacent normal mucosa embedded in paraffin blocks were stained using the immunofluorescence method and were semi-quantitatively analyzed. | The expression of Cx37, Cx40, and Panx1 differed between cancer and adjacent normal mucosa and between histological grades, being the highest in well-differentiated (G1) cancer and low/absent in poorly differentiated (G3) cancer | p < 0.05 |
| Diagnostic performance of FDG PET/MRI for cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with clinically N0 head and neck cancer | 2023 | Cebeci S, Aydos U, Yeniceri A et al. | European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences | 10.26355/eurrev_202305_32459 | 44 patients who underwent neck dissection with the diagnosis of HNSCC | HNSCC | Clinical examinations, including ultrasonography, were performed to identify cervical metastases in HNSCC patients with preoperative cN0. A nuclear medicine specialist visually evaluated the MRI, PET, and PET/MRI results | PET/MRI was more successful in distinguishing pathological N0 and N+ patients | 83.3% sensitivity, 92.1% specificity, 97.2% NPV, 62.5% PPV and 90.9% accuracy |
| The modified Polsby-Popper score is a novel quantitative histomorphology biomarker with potential to predict lymph node positivity and cancer-specific survival in tongue squamous cell carcinoma | 2024 | Csury T, Csury A, Balk M et al. | Oncology Research and Treatment | 10.1159/000535363 | Patients with pT1-pT4a squamous cell carcinomas of the mobile tongue (TSCC) | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | A total of 100 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) primary tumor specimens | pT category, tumor grade, pNX nodal status and the presence of manifest metastatic cervical lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis were all found to be significant predictors of OS. | pT category (p = 0.044), tumor grade (p = 0.036), pNX nodal status (p = 0.004), and the presence of manifest metastatic cervical lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis (p = 0.002) |
| Predictors of Occult Metastasis and Prognostic Factors in Patients with cN0 Oral Cancer Who Underwent Elective Neck Dissection. | 2024 | Yamagata K, Fukuzawa S, Noguchi A et al. | Diseases (Basel, Switzerland) | 10.3390/diseases12020039 | 86 patients with OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Nodal nodes samples for occult metastasis and risk factors for poor prognosis after SOHND. | OS was significantly associated with pN | p = 0.015 |
| Blood Markers Predicting Clinically Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. | 2024 | Gaudioso P, Borsetto D, Polesel J et al. | ORL; journal for oto-rhino-laryngology and its related specialties | 10.1159/000534079 | 472 patients diagnosed with cN0 HNSCC who underwent up-front surgery. | HNSCC | Baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), systemic inflammatory marker (SIM), and systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) were calculated from available blood parameters. | Oro-hypopharyngeal and oral cancers, locally advanced stage were associated with an increased risk of pathological lymph node involvement. NLR, LMR, PLR, SIM, and SII were significantly associated at multivariable analysis. NLR >2.12 was the most reliable at predicting occult lymph node metastasis | OR = 5.22; 95% CI: 2.14-12.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





