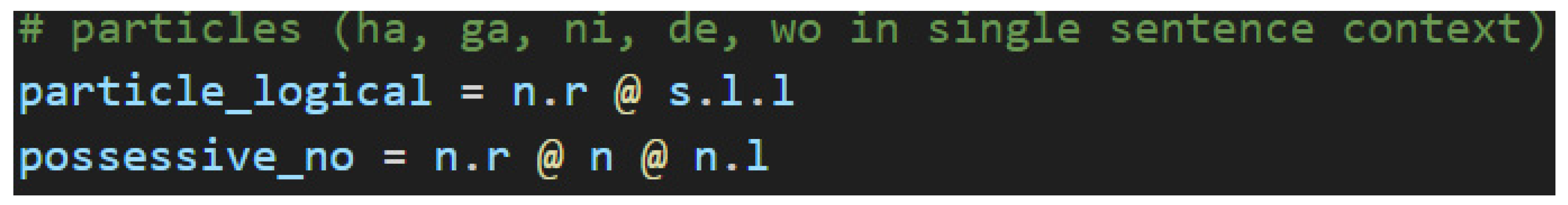
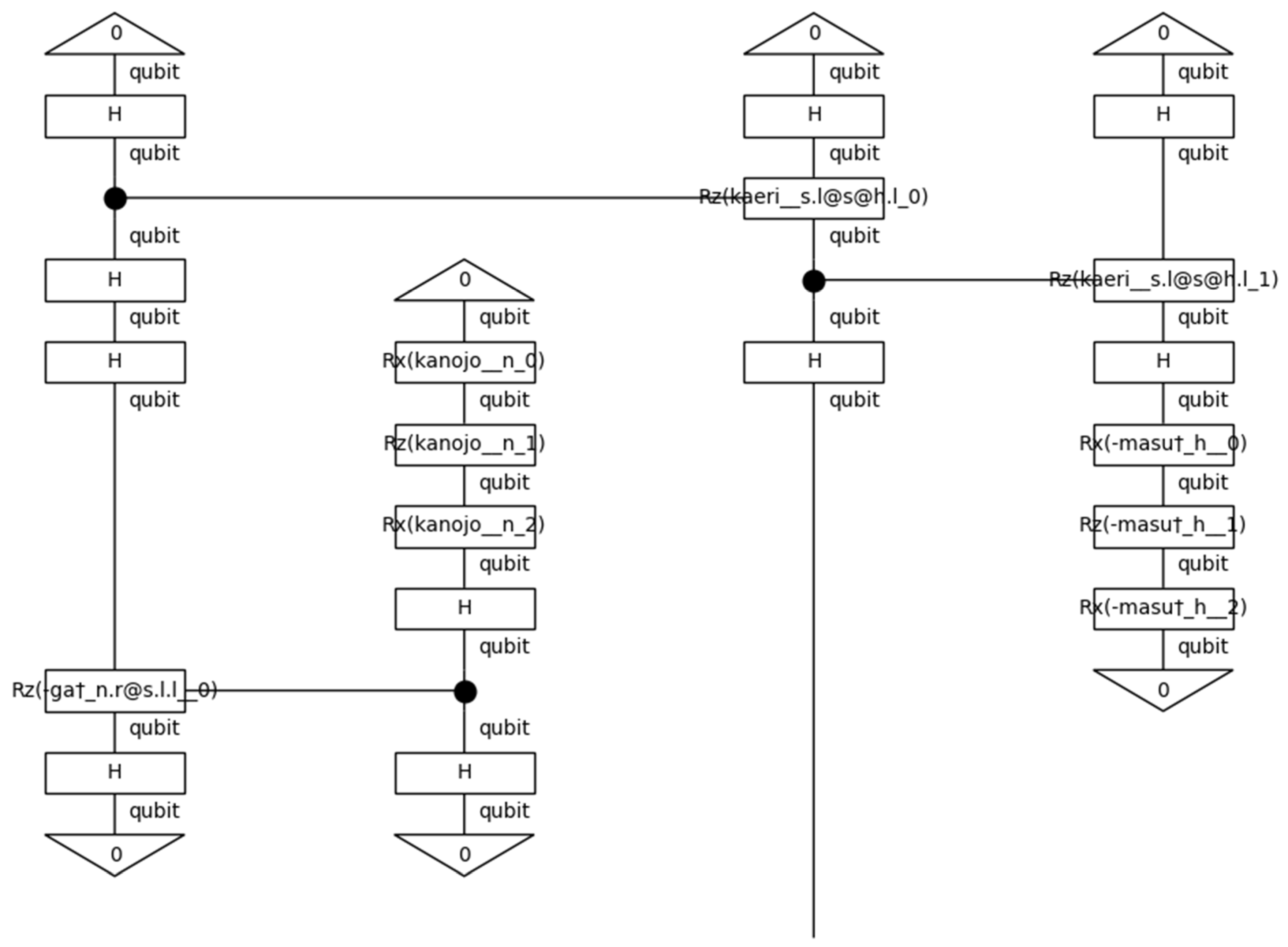
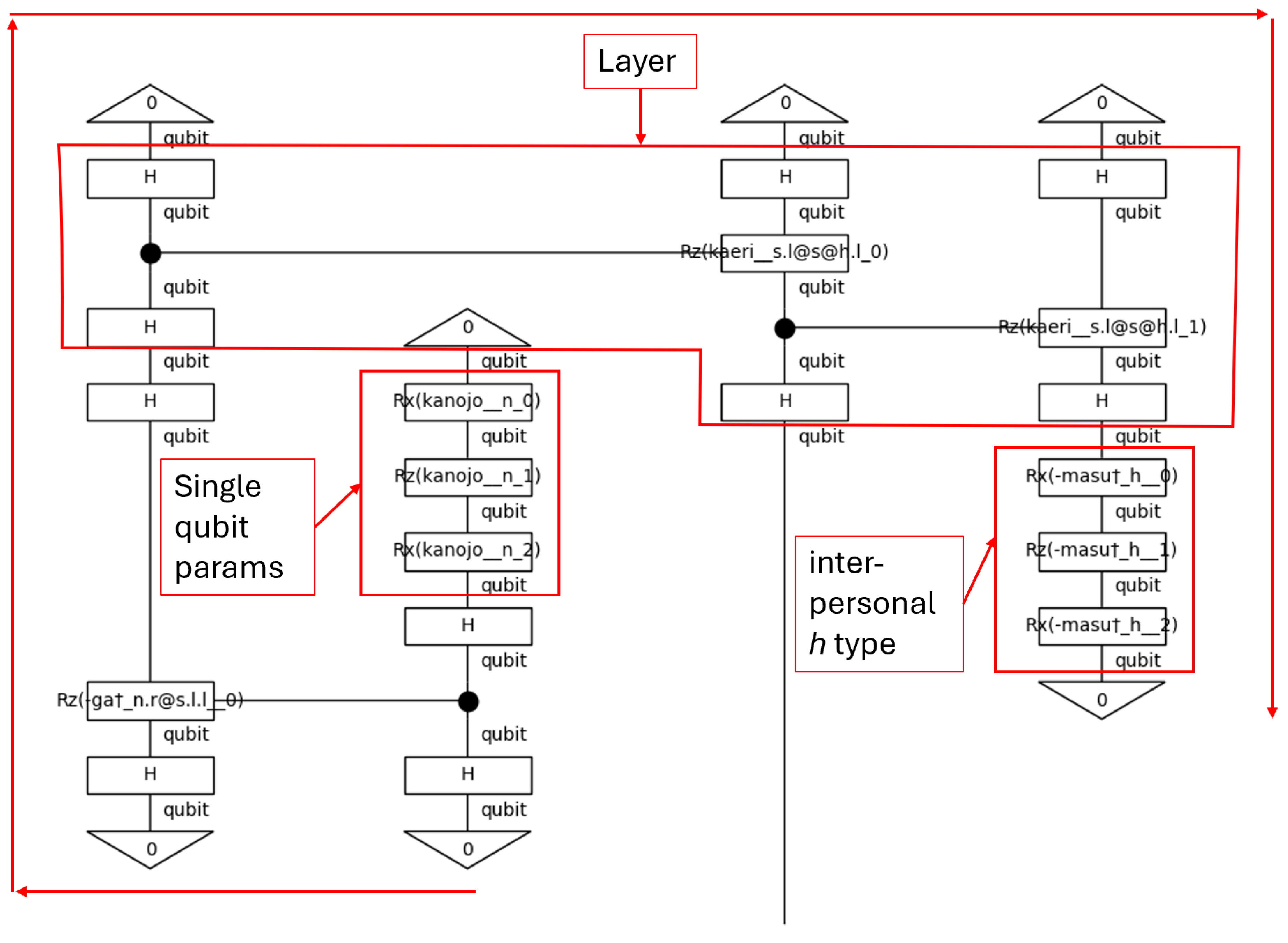
2.6.2. Code: Define Types and Grammar
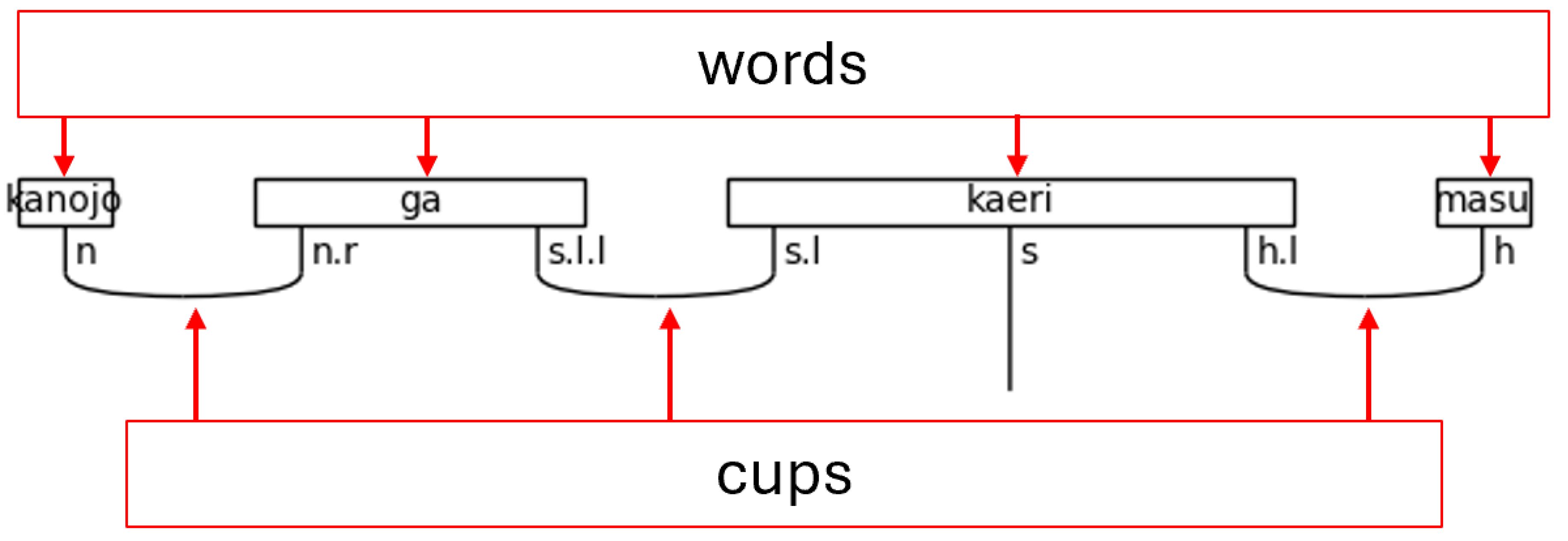
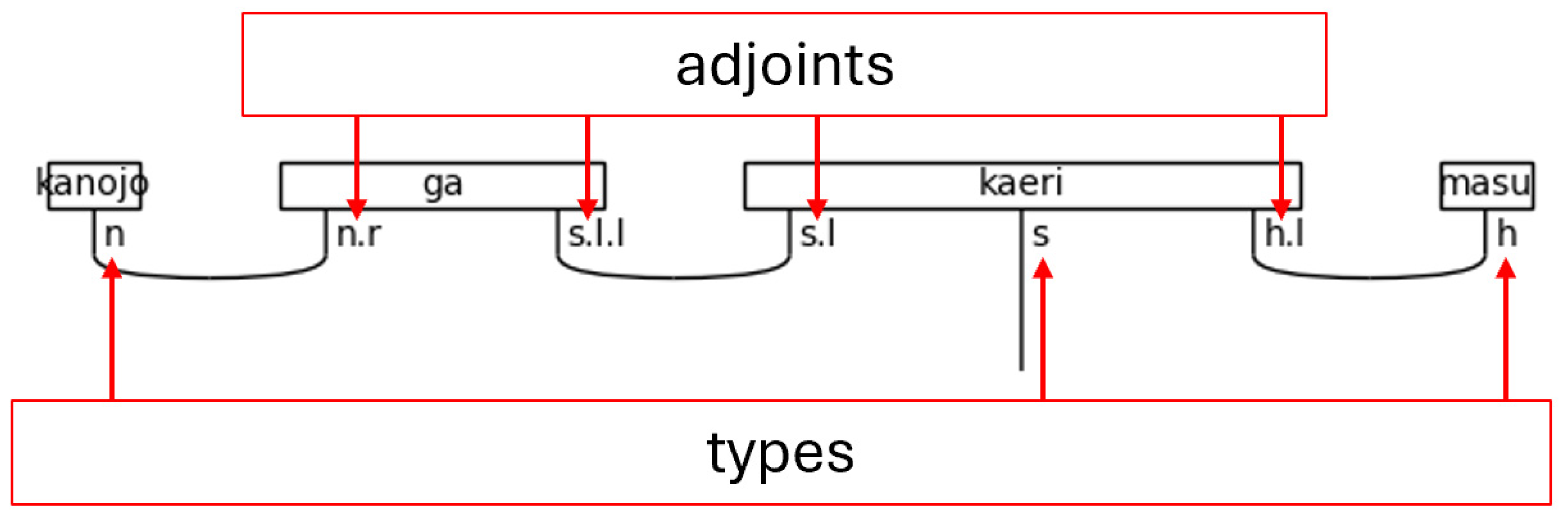
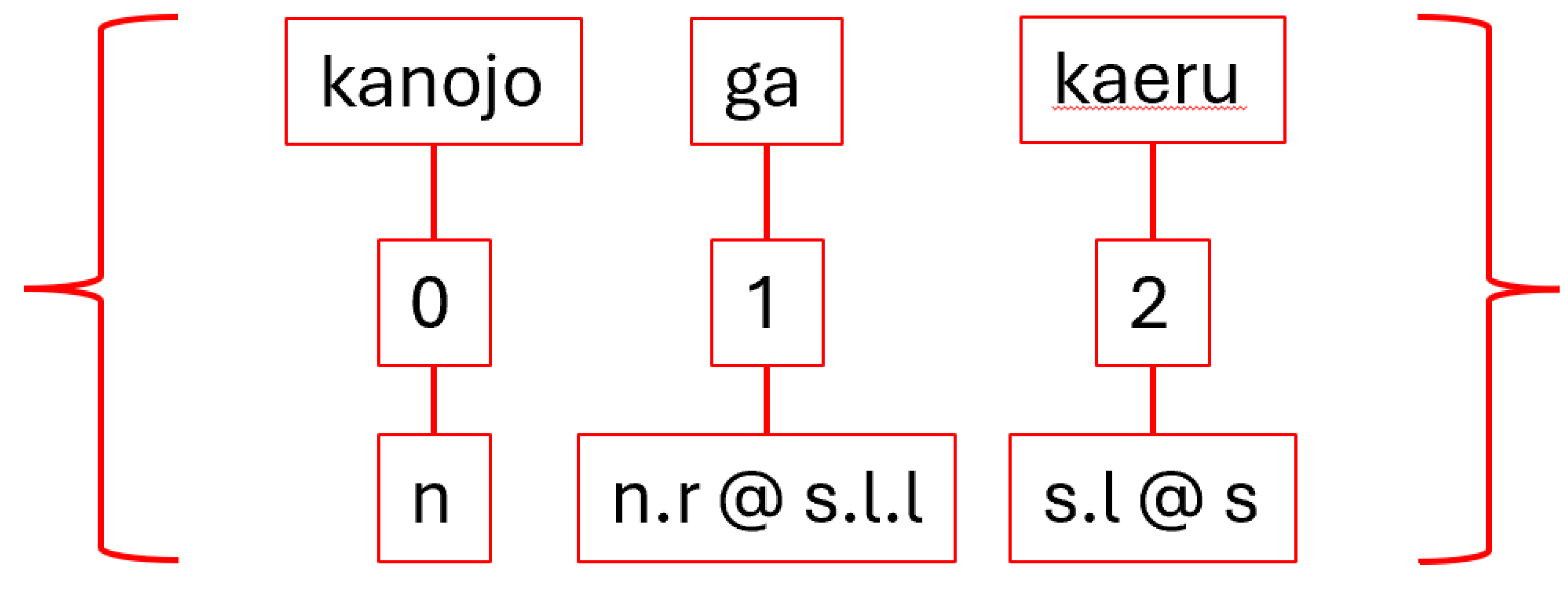
The process of creating a quantum circuit without using the BobcatParser in lambeq begins with defining types, also known as simple types. Combinations of types—called complex types—are assigned to words. After the definition of simple types, the connectivity of the grammar is specified by pairing the simple types with their left or right-adjoints. For example, the type s has a left-adjoint called s.l and a right-adjoint called s.r. The left and right nomenclature can be remembered by the adjoints relative position to the noun. The right-adjoint, for example, will always be written to the right of the non-adjoint, simple type (the base type)—i.e., n.r will always be found to the right of n. Adjoints can be chained, like s.l.l (the left-adjoint of the left-adjoint), which simply means that the s.l.l is to the left of an s.l type that completes the pair. Lastly, the grammar connections of the words are joined together using cups, resulting in a type of string diagram known as a pregroup diagram.
Figure 3.
Words and Cups in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 3.
Words and Cups in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 4.
Types and Adjoints in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 4.
Types and Adjoints in a Pregroup Diagram.
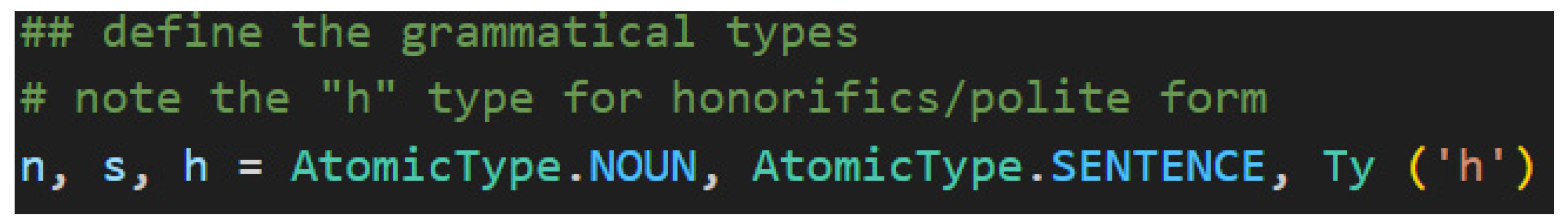
For this project, the type definitions have been separated into their own file named
jp_grammar_model.py to honor the software engineering principle of
separation of concerns. Because the sentence type
s and the noun type
n are standard types, lambeq provides them as enumerations. The honorific type
h is a custom implementation. The instantiation of these types is found in
Figure 5.
Now that these basic types are defined, they are combined into complex types to grammatically type words in a sentence. The remainder of the contents of jp_grammar_model.py contain the complex types necessary to model very basic Japanese grammar along with honorifics. The most critical of these complex types are those found in the predicate, particles, and honorific titles, which are attached to names or otherwise used to transform a noun into a name.
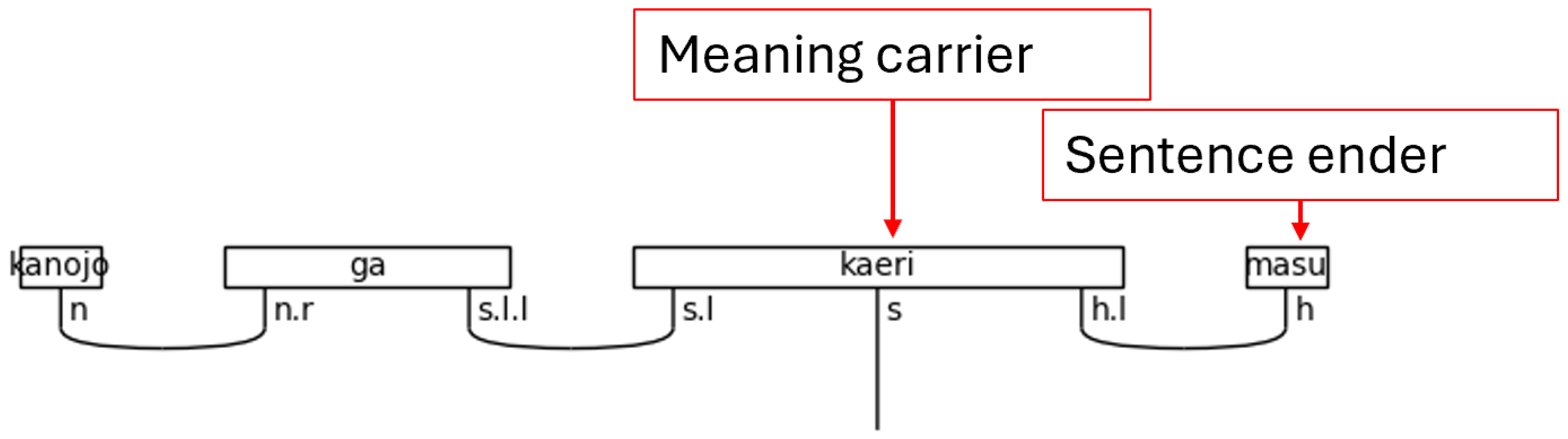
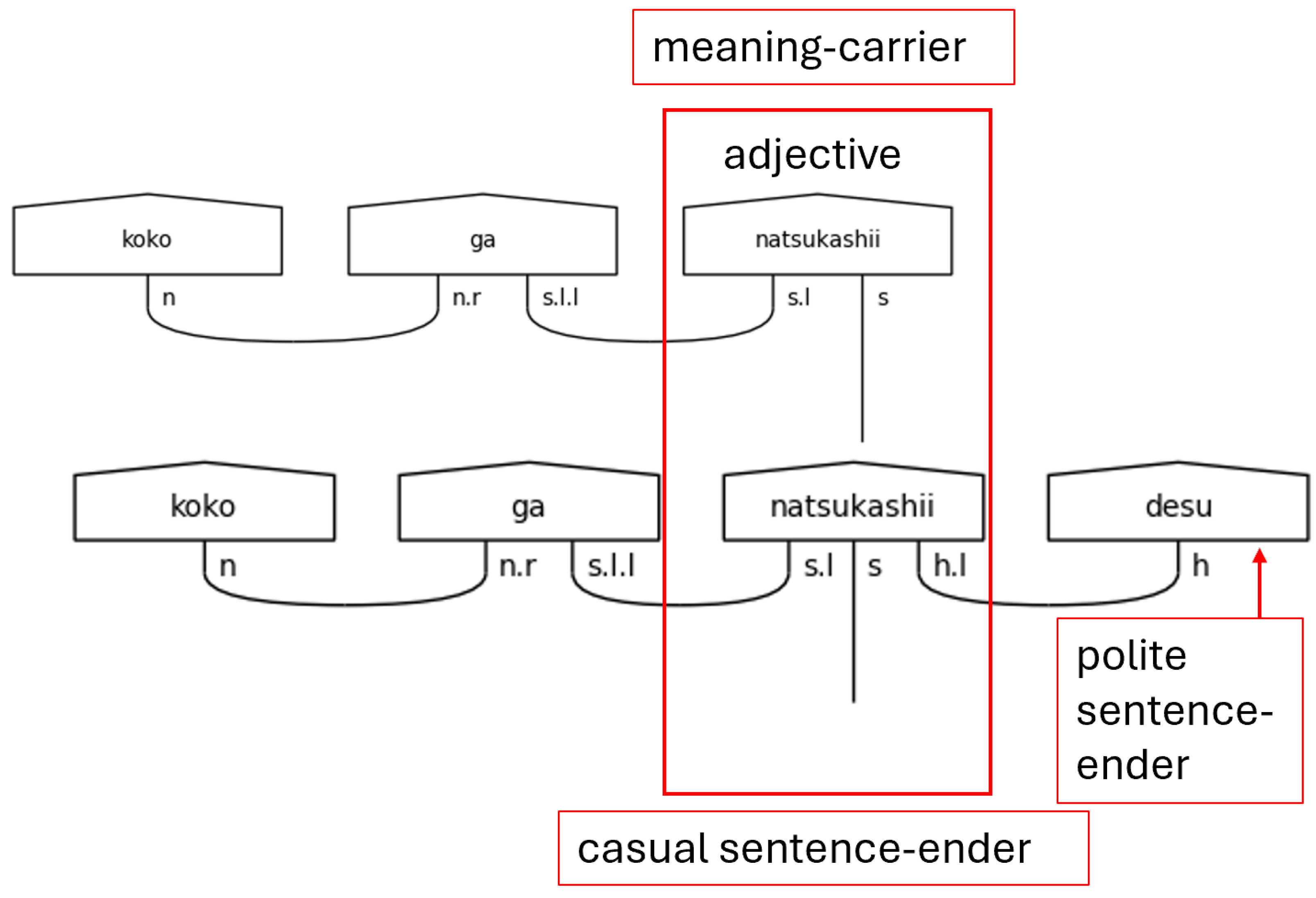
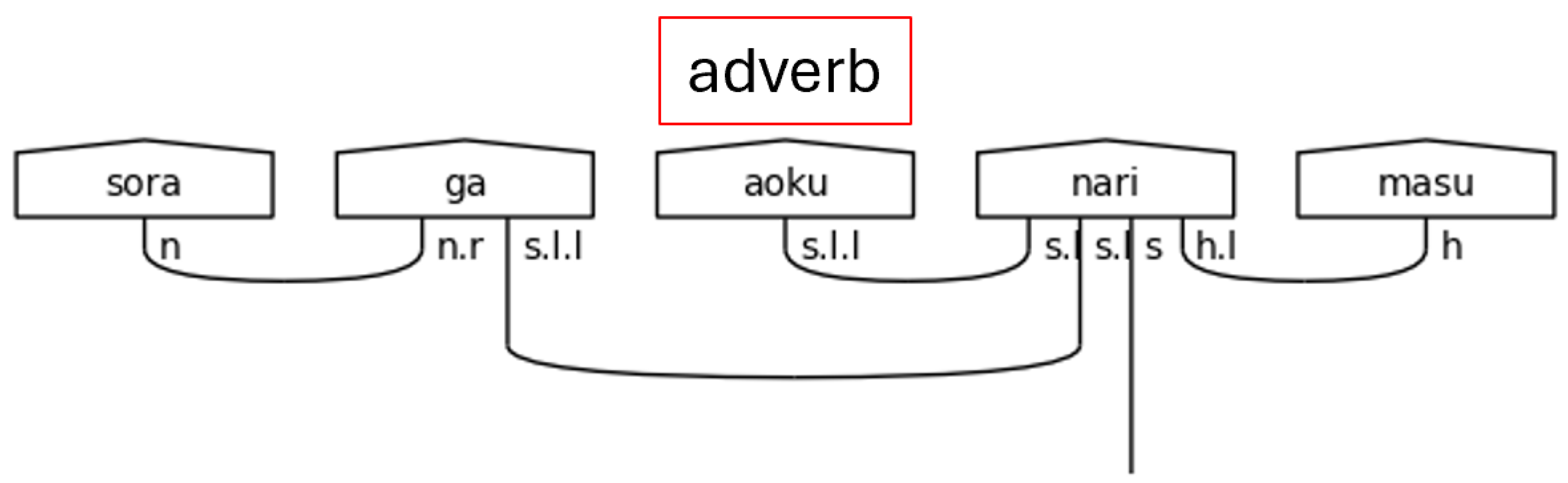
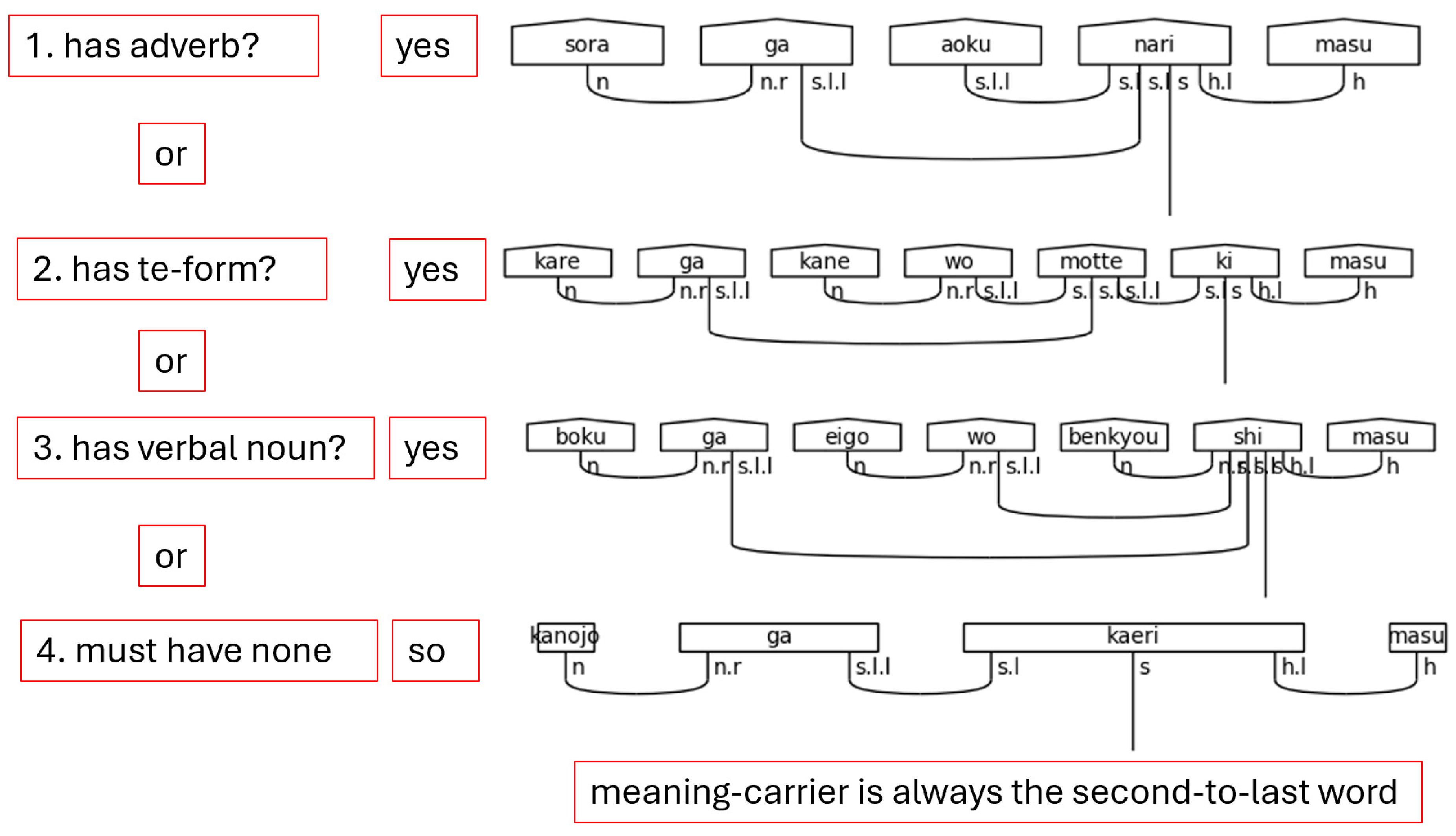
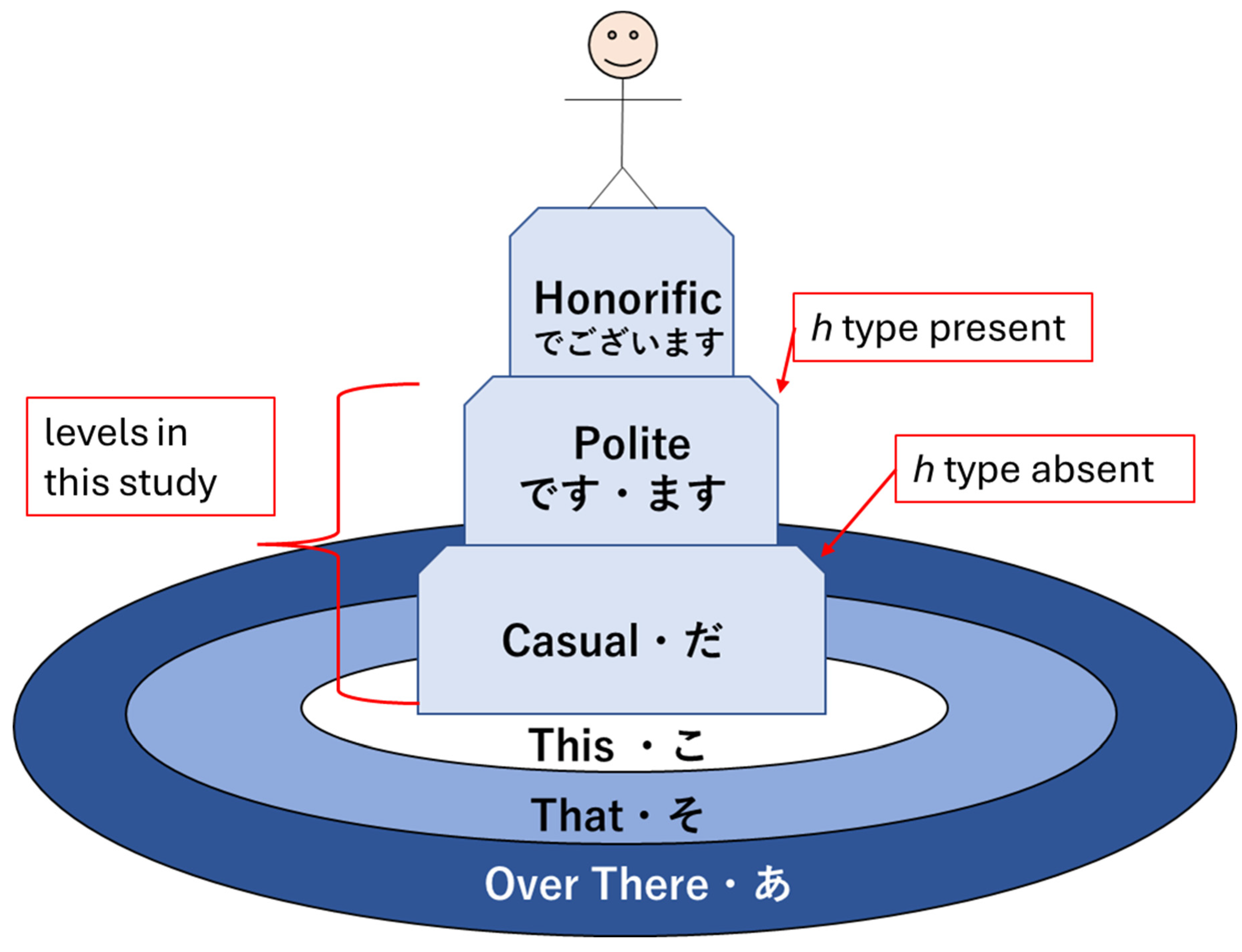
Japanese is often said to obey a subject-object-verb, or SOV, word order. This is not strictly true as the particles determine the logical, grammatical relationships between the words in the sentence. Regardless, the SOV order is often used in textbooks, and there is no flexibility in the placement of the verb or the copula in a simple sentence; therefore, SOV or OSV is possible, but a sentence will always end in with V. Specifically, in a casual sentence that is taken in isolation—topic-comment level discourse, marked with the particle は[ha], is left for future research—the final word in the sentence always carries the sentence type—carries the meaning (Dvorak & Walton, 2014). When the polite form is used, the final word instead, or additionally depending on the situation, adds in the vertical dimension of meeting—the politeness level. This means that the final word does not always carry the textual meaning of the sentence. Therefore, the grammar model must account for this when considering the predicate at large. In the discussion that follows, any grammatical type that can end a sentence is simply referred to as a sentence-ender. This is shorthand for verbs, the copula, and politeness markers. Whenever the sentence-ender does not carry the textual meaning of the sentence, the word that does will be referred to as the meaning-carrier. Again, this is a shorthand to identify the word that will include the s simple type as a part of its complex type definition.
There is one more crucial note to make regarding the meaning-carrier before continuing. The meaning-carrier is the changeling in the sentence. While it will always have an s core, the number of particles, the presence of adverbs, other verbs, or even the presence of nouns in some cases will persuade the meaning-carrier to adopt a different typing. In other words, the meaning-carrier is very much influenced by the company it keeps.
Figure 6.
Sentence-ender and Meaning-carrier in a Polite Sentence.
Figure 6.
Sentence-ender and Meaning-carrier in a Polite Sentence.
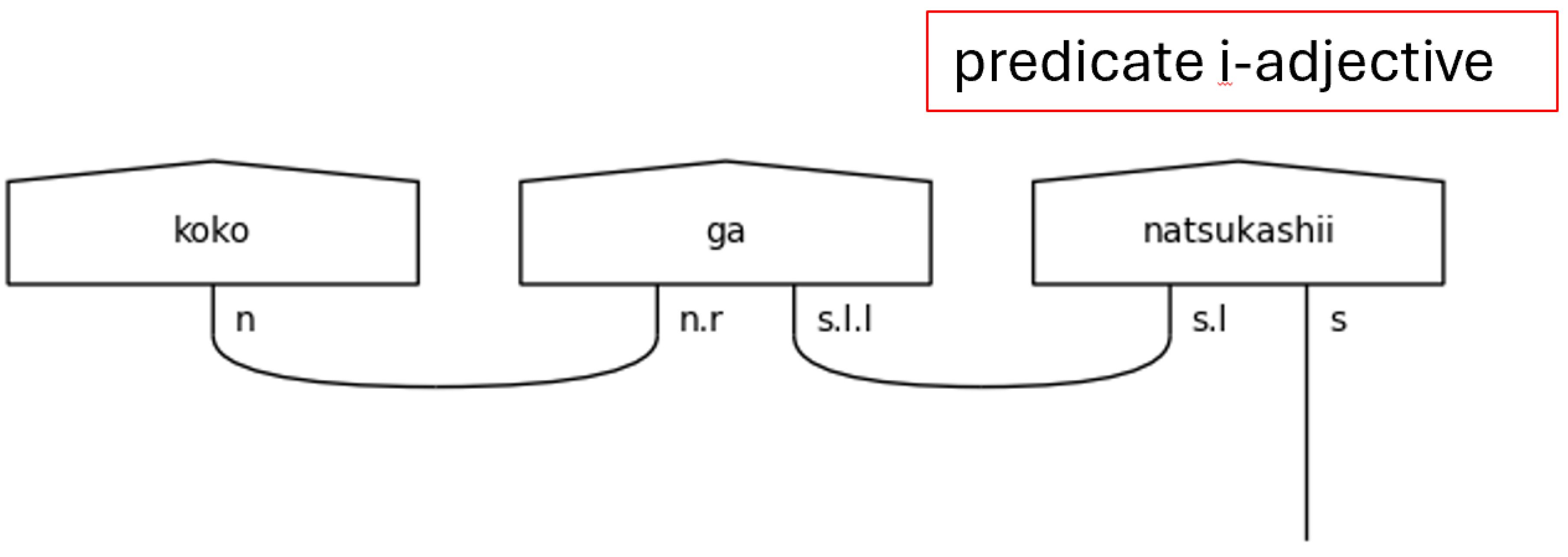
Consider first the casual predicate types found in
Figure 7. These complex types, and those that follow, are used in the string diagram building algorithm, named
diagramizerin
jp_grammar_utilities.py. There will be more on that algorithm starting with the Beginning with Diagrams section that follows.
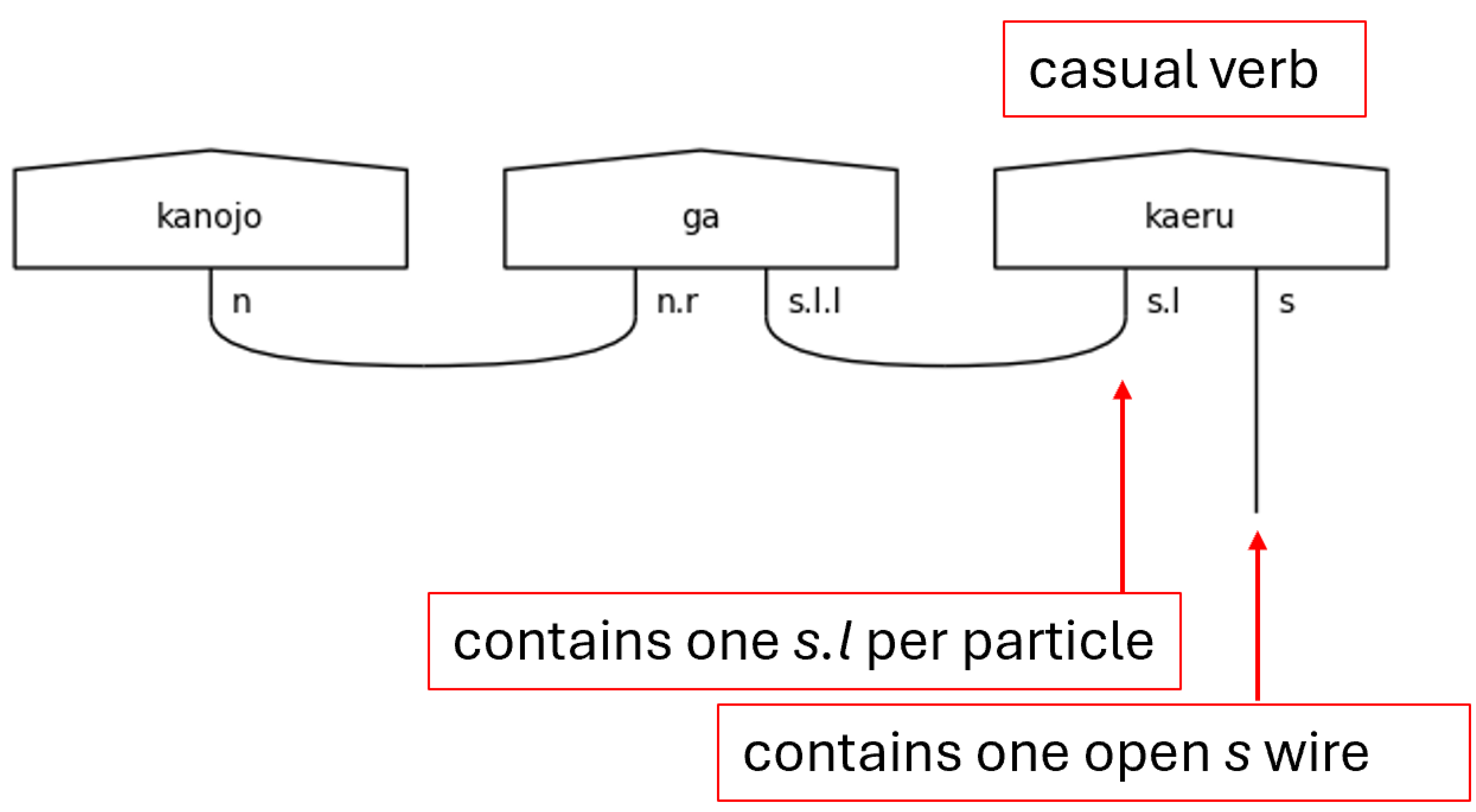
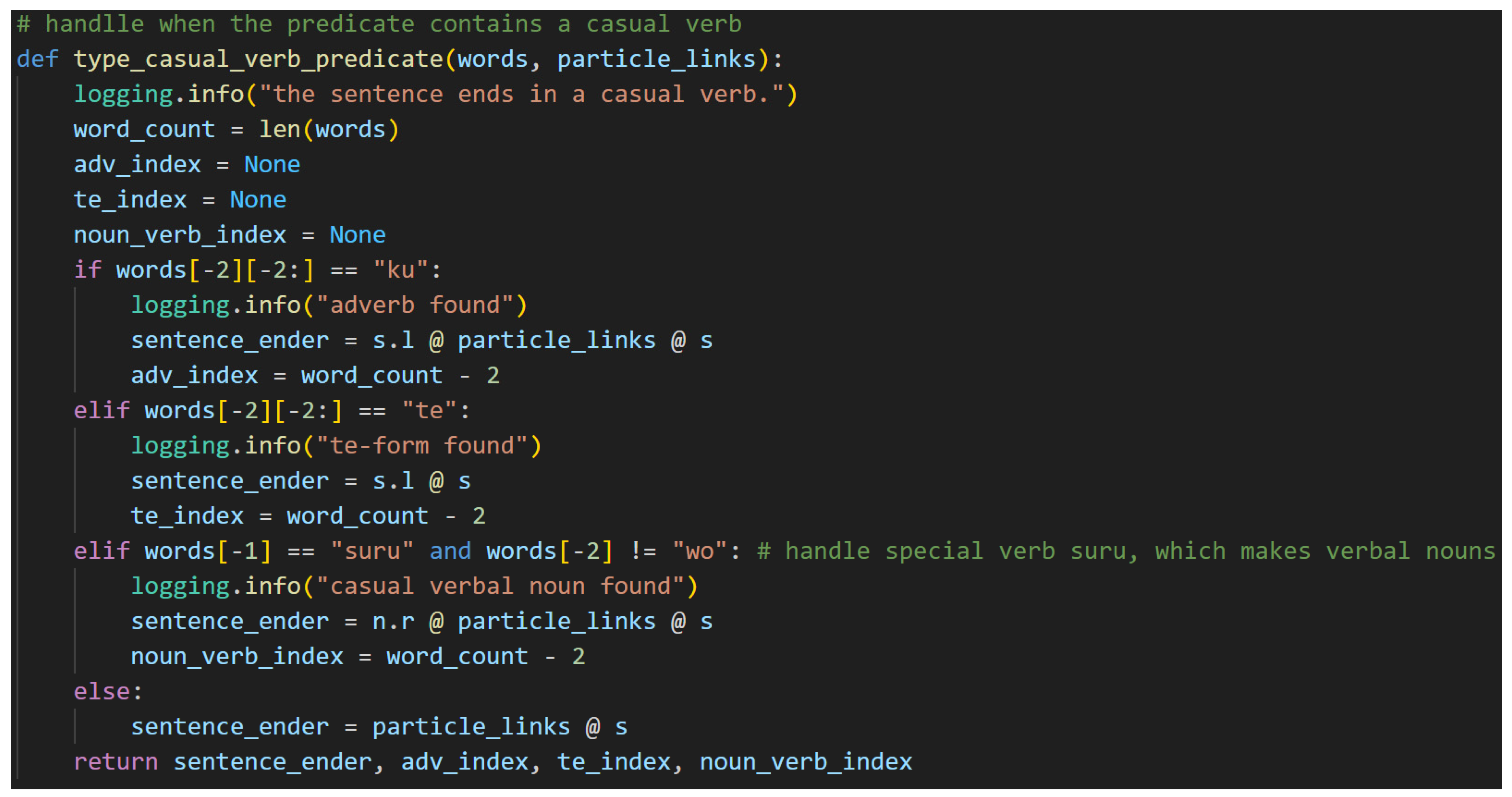
Now, the casual level of language has no honorifics, so its type definitions are the simplest. The fundamental type here is that of the casual verb, named
verb_casual, because its core is none other than the
s type itself. It is also worthy of note that the い[i]-adjective type is nothing more than a casual verb when it is the sentence-ender. That is shown in
Figure 4 by the variable
adj_i_s, where “
s” means the sentence type
s. Adjectives that are not found in the predicate,
adj_i, modify nouns, as would be expected. They are included in
Figure 4 for completeness. The presence of particles will cause the
s type core of the sentence-ender to expand with one
s.l type for each particle present. This is because the particle specifies the relationship between the noun to which it is joined and the sentence-ender in the casual case.
Figure 8.
Casual Verb Sentence-ender in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 8.
Casual Verb Sentence-ender in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 9.
Predicate Adjectives are Casual Verbs.
Figure 9.
Predicate Adjectives are Casual Verbs.
Figure 10.
Particles in Pregroup Diagrams of with Casual Japanese Verbs.
Figure 10.
Particles in Pregroup Diagrams of with Casual Japanese Verbs.
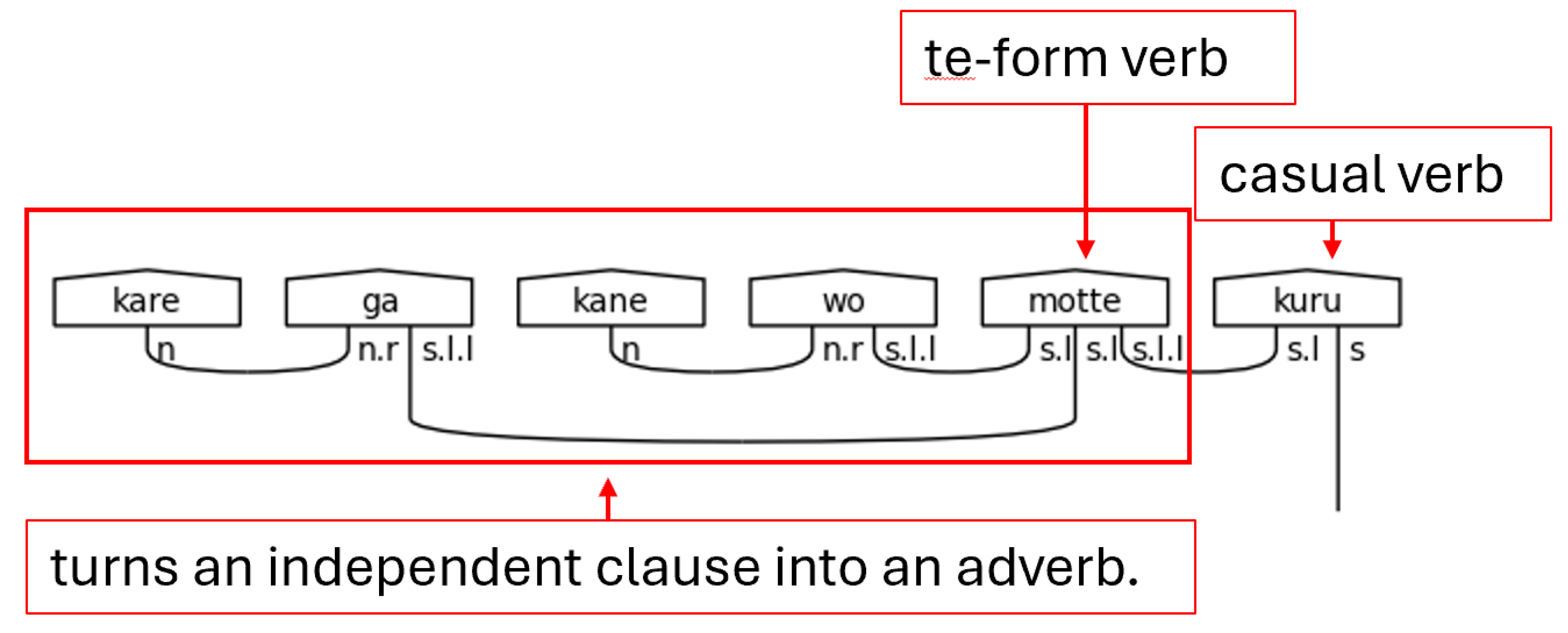
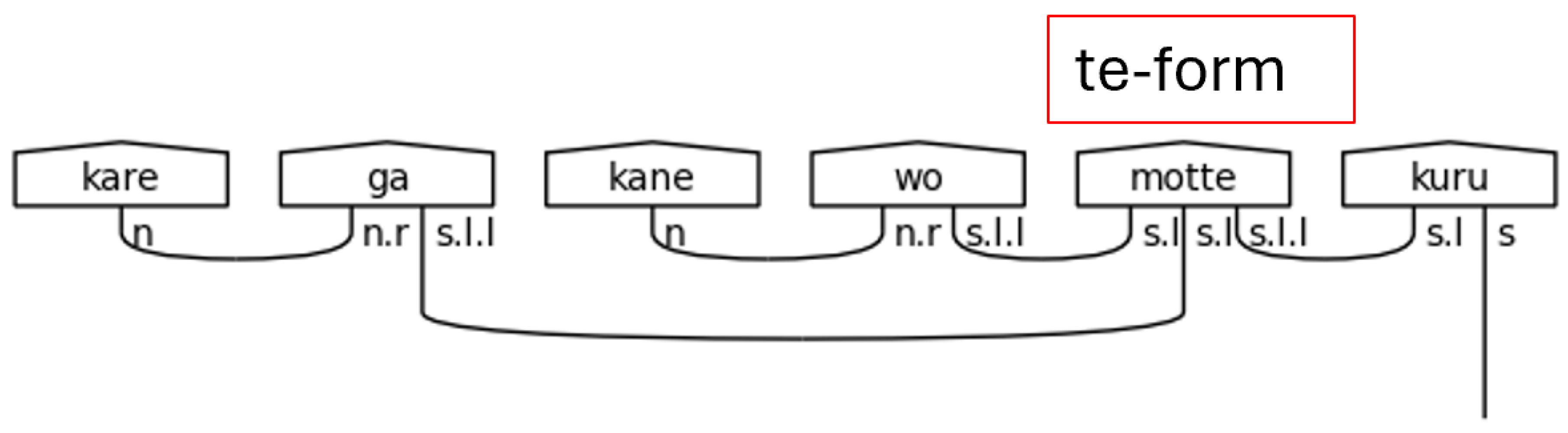
The て[te]-form is a special form of a Japanese verb that allows its meaning to directly modify the verb that succeeds it. It, in effect, allows an entire verbal clause to modify another verb. Therefore, it allows a verb to function adverbially—as a standalone s.l.l type in this grammar model. When it does this, the particle links, the s.l types, of the sentence are paired to the て[te]-form, and the て[te]-form verb itself expects another verb to succeed it and bear the sentence type.
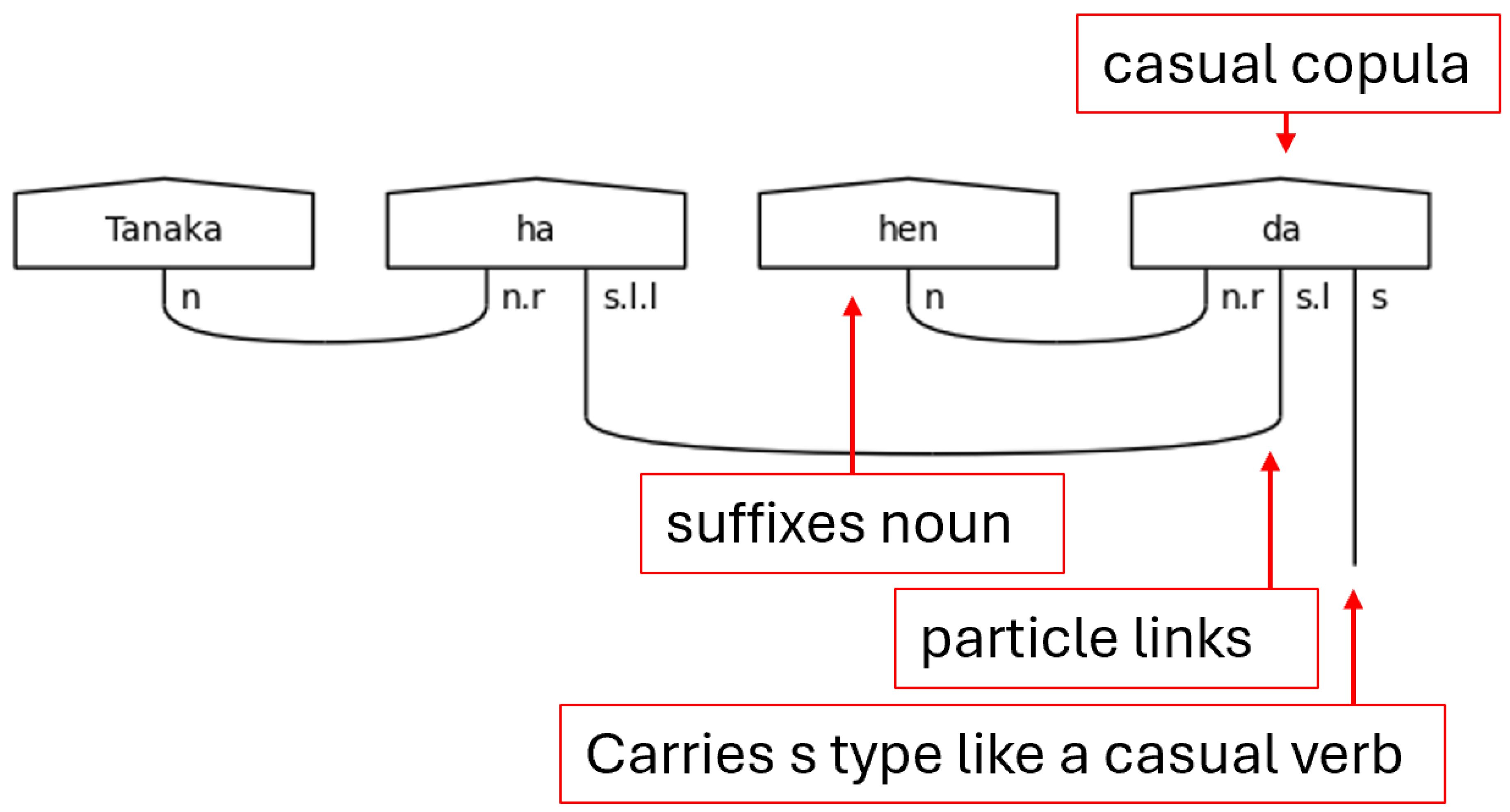
Lastly for the casual predicate section is the copula だ[da]. The copula functions strangely, at least to the native English-speaker, in that it is a statement of the equivalence of two things but is not a statement of their being. In other words, it bears the fundamental meaning of “is” without any implication of existence. The copula, then, can be thought of as an equal sign (=). Practically speaking, this means that the copula must suffix a noun like a particle, hence the n.r type on the left-side of the copula’s complex type. Otherwise, it functions like a verb. The s.l here is a stand-in for any number of particle links needed to carry the meaning.
Figure 11.
て[te]-form in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 11.
て[te]-form in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 12.
The Casual Copula in a Pregroup Diagram.
Figure 12.
The Casual Copula in a Pregroup Diagram.
With casual sentences, there is a simple pattern. The connections flow from the left to the right. In the casual sentence-ender, any noun terms, as in the case of だ[da], are defined on the leftmost side of the assignment. The particle links follow next, and the final term will always be the s term. This order always holds and will become crucial for the implementation of the diagramizer algorithm.
Consider next the polite predicate types found in
Figure 13.
Everything that was true about casual verbs is also true here with two notable exceptions, both of which are caused by the inclusion of the h type. The first exception is the inclusion of the honorific type’s left-adjoint, h.l, on the left-side of s types in the connective—polite form stemmed—verb, verb_connective. The second is the inclusion of the h type on the left-side of the n.r type in the case of the polite copula です[desu], desu_n.
First, regarding the use of h.l, verbs in the polite form anticipate the helper verb ます[masu] to succeed them. ます[Masu] always has the type h. This, then, is the first and archetypal example of a sentence ending word that does not carry the meaning. When ます[masu]is present, the meaning is always carried by the connective form verb that precedes it. The same is also true of the predicate use of the adjective. There is no difference in the assigned types between polite verbs and predicate adjectives paired with です[desu].
Figure 14.
Polite and Casual Juxtaposition of the Same Sentence.
Figure 14.
Polite and Casual Juxtaposition of the Same Sentence.
Figure 15.
Polite Sentence with a Predicate い[i]-Adjective.
Figure 15.
Polite Sentence with a Predicate い[i]-Adjective.
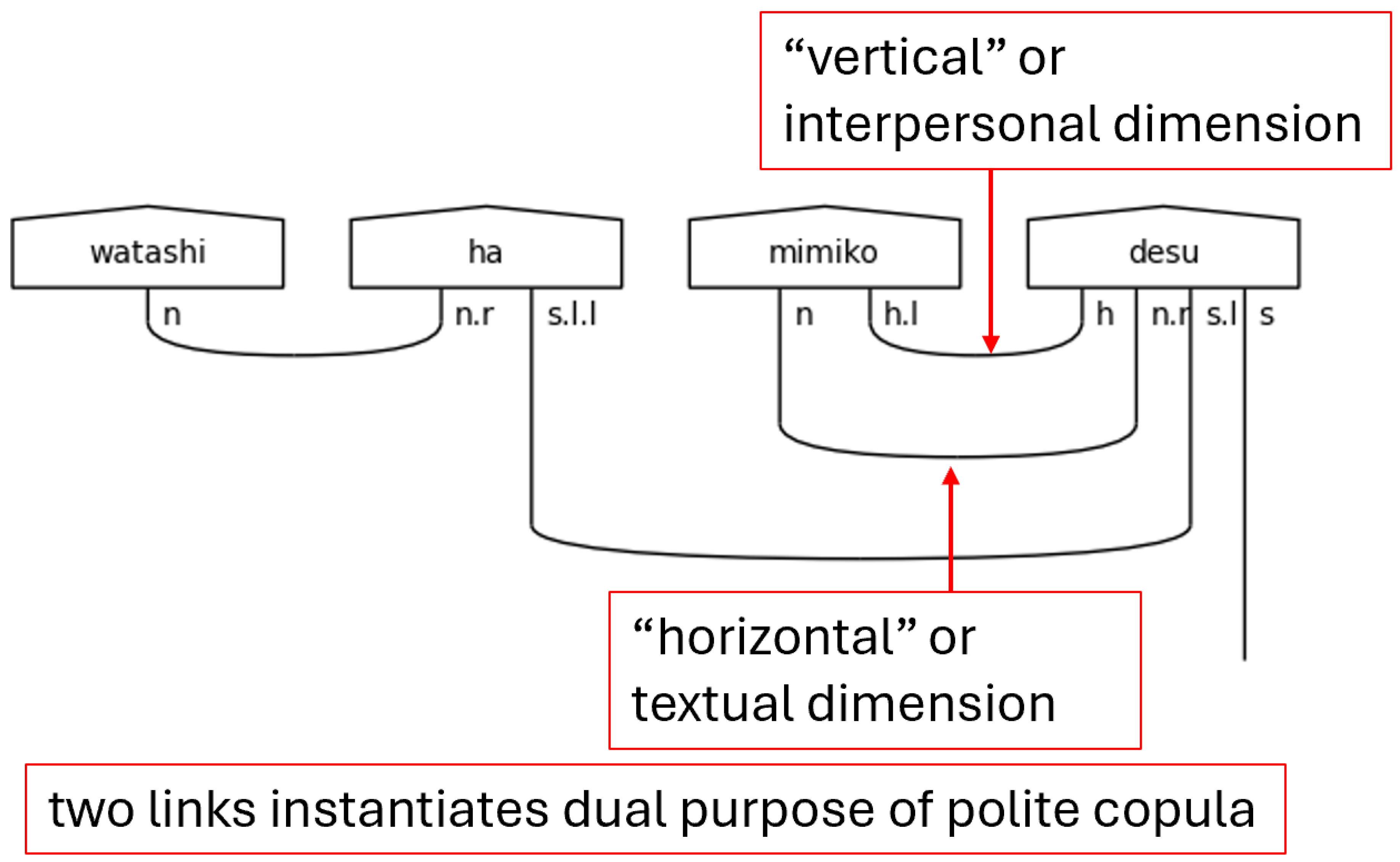
Second, the h on the left-side of n.r is a special case that occurs only with the aforesaid です[desu] in this grammar model. The result of this h is that the predicate noun that precedes です[desu]is expecting two links, resulting in the special type assigned to pred_polite_n. The use of this type means that two cups will be drawn between the predicate noun and です[desu]. The reason for this is that です[desu]is serving two purposes in the sentence. The first of these is that of the copula—the textual case of equivalence. The second of these is to mark the sentence as polite—the interpersonal case of honorifics. This dual purpose of a single word is a great example of the two-dimensional nature encoded into Japanese utterances.
Figure 16.
A Special Case: Predicate-Noun Usage of です[desu].
Figure 16.
A Special Case: Predicate-Noun Usage of です[desu].
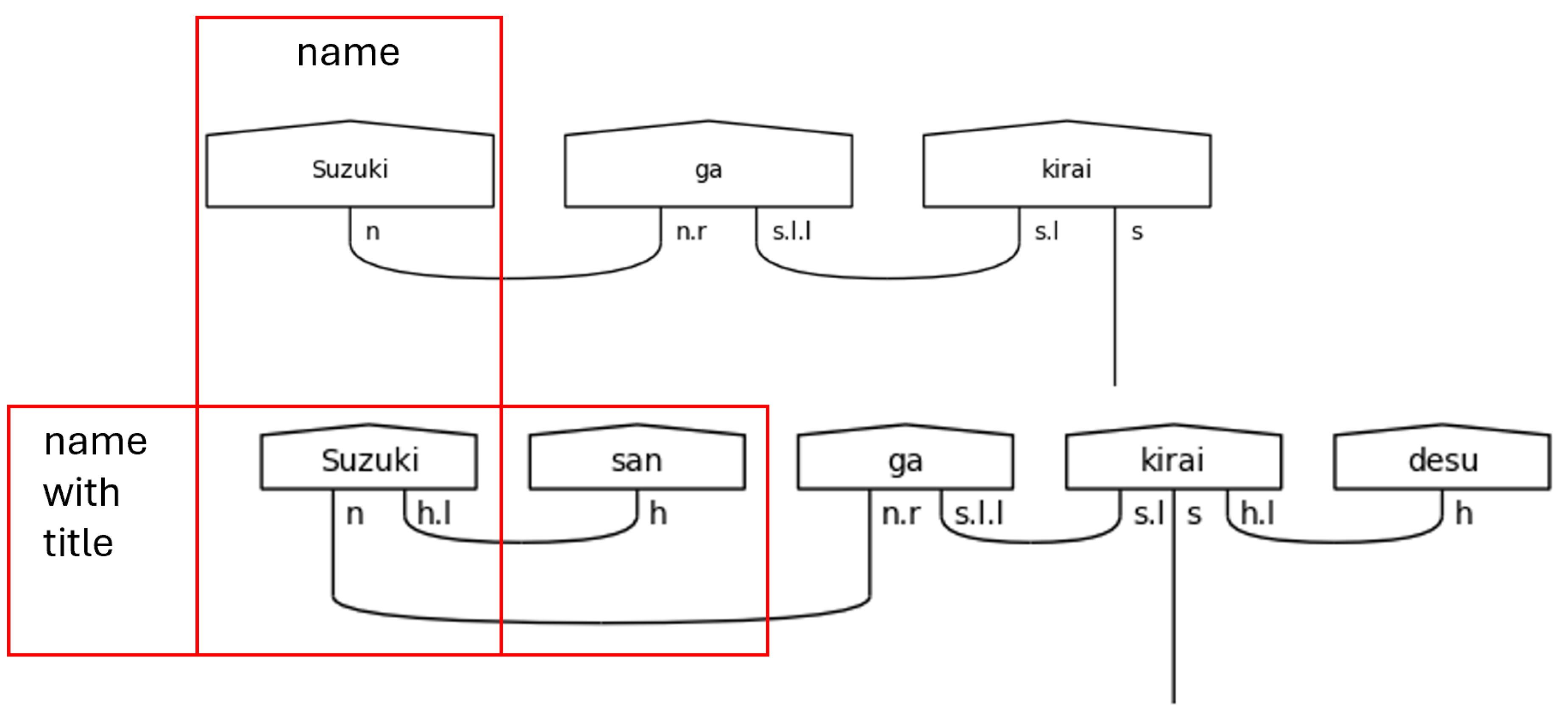
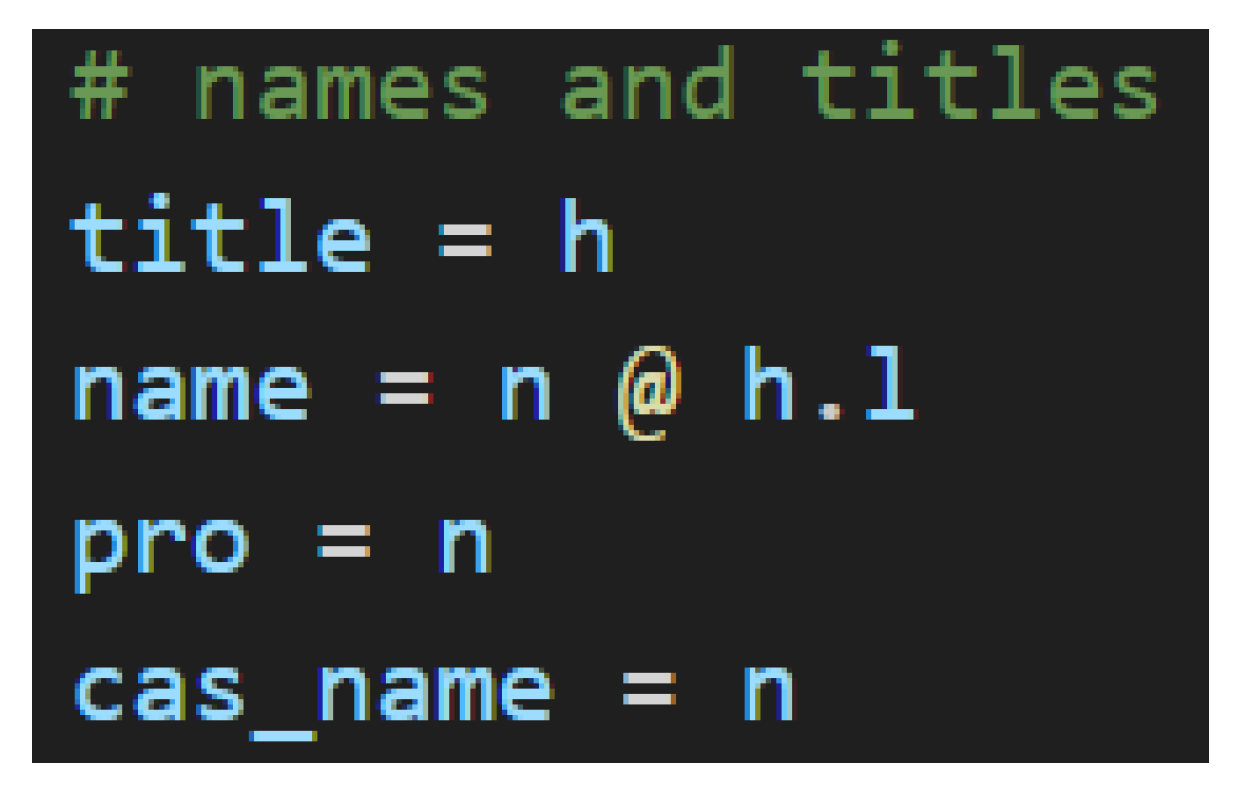
There are two more portions of the grammar model that deserve attention here. The first of these is titles, and the second is particles. In the simplest sense, titles in Japanese approximate the English titles that have fallen out of fashion in contemporary parlance. The use of the most universally recognized title, さん[san], as a suffix can be translated as “Mr.”, “Mrs.”, “Ms.”, “Miss”, or any other related term. It specifies no sex or marital status. Instead, it simply elevates the use of a name in politeness. Since this is its function, it modifies the type of the name or noun to which it is fixed.
Figure 17 shows the variable assignments for titles and names.
Modification, of course, makes no sense unless there is some baseline from which to modify. In this case, that baseline is the casual name—cas_name. A name is nothing more than a highly exclusive and specific noun. It’s counterpart, the pronoun, is itself a noun that is, on the other hand, inclusive of a larger category of people and completely general. Nevertheless, these are all nouns in this grammar model because they link to other parts of speech in the same way. It is the polite name—name—that stands out as something more. While it remains a noun, it also bears an h.l, so it anticipates the title suffix that follows, and because it anticipates, it is changed. This change that the presence of the title brings on makes it a special word—a word that determines types of other words—to which the diagramizer algorithm pays special attention.
Figure 18.
Comparison of a Casual Name and a Polite Name with a Title.
Figure 18.
Comparison of a Casual Name and a Polite Name with a Title.
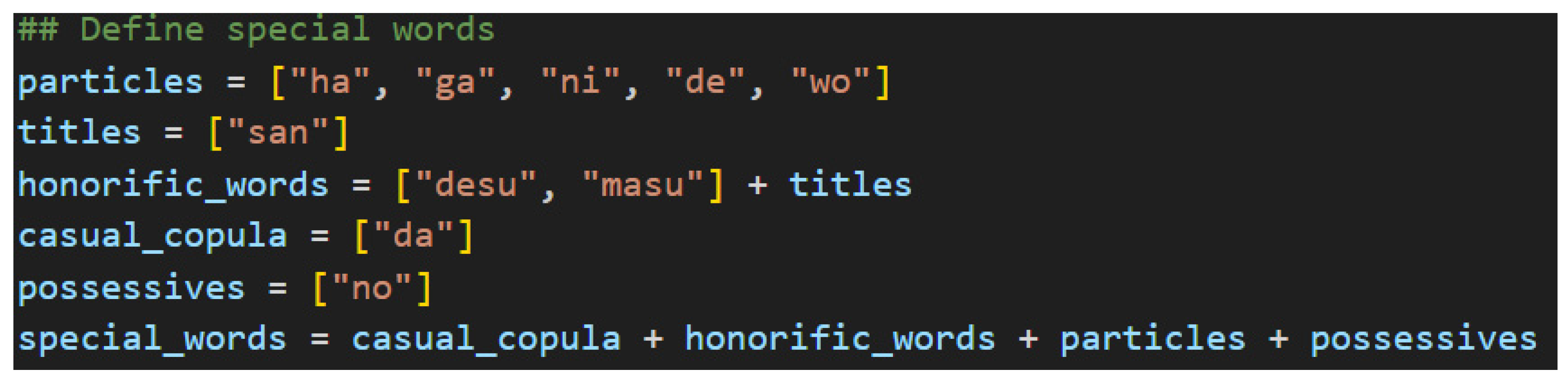
Speaking of special words, now is a good time to introduce the others.
Figure 19 shows them. This list is by no means comprehensive for Japanese, but it is sufficient for a first iteration of the grammar model to handle a functional variety of simple sentences.
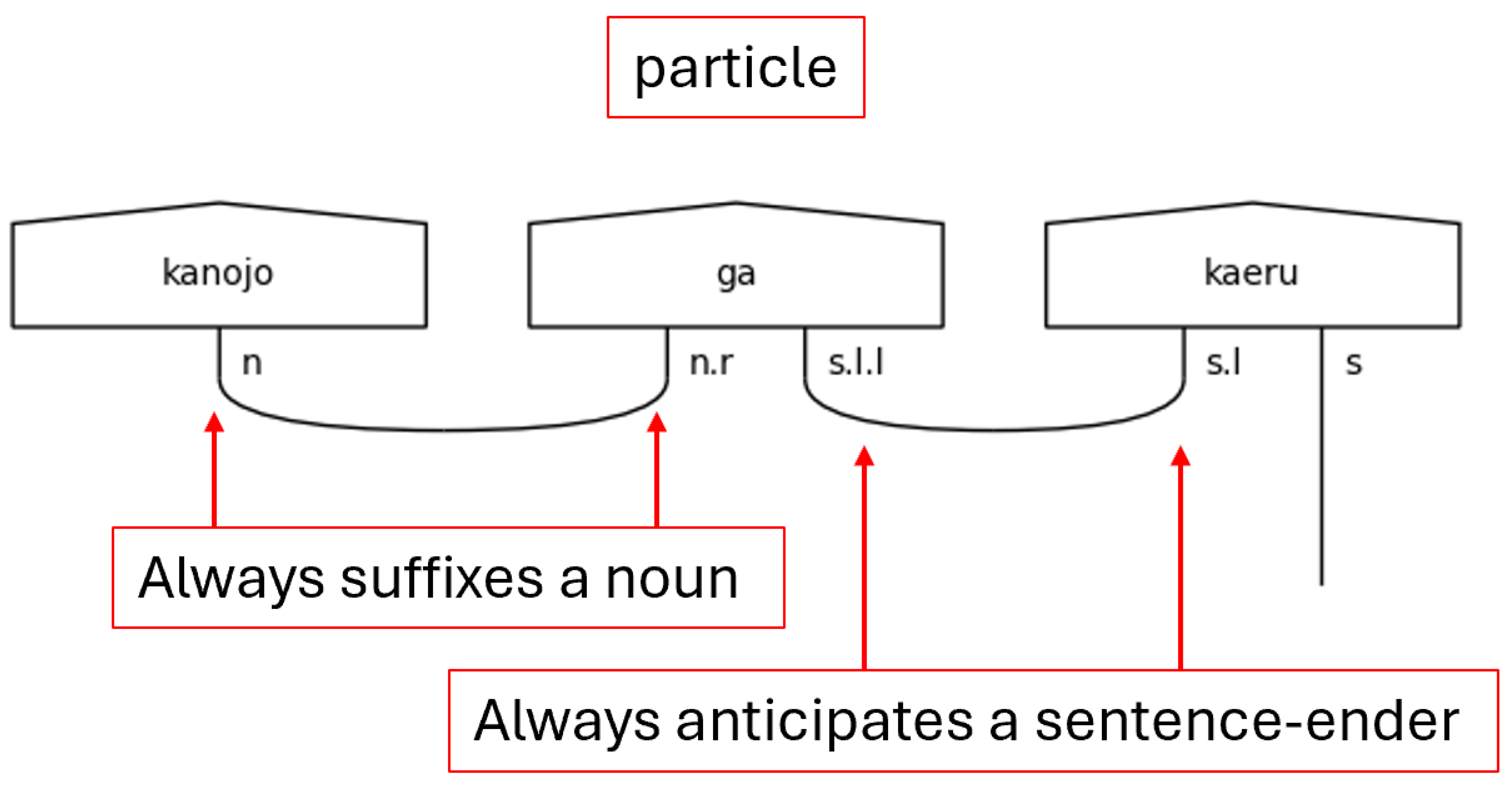
The honorific words, titles, and copula make their appearances again here in python lists, which will be used for list comprehension tasks later. For now, the new part of speech to consider is the particles, which are found in the particles list and the possessives list. In Japanese, particles can be thought of as utterances that suffix nouns and specify the relationship of the noun to the action of the verb. To use terminology familiar with English speakers, particles are words that explicitly define the subject, object, indirect object, and so on of a sentence. They also, therefore, give Japanese its flexibility regarding word order. Since their essential function is to suffix nouns and link to verbs, their position in the sentence—their indices in the ordered list of words—will be of great importance later.
Figure 20 shows their type assignments.
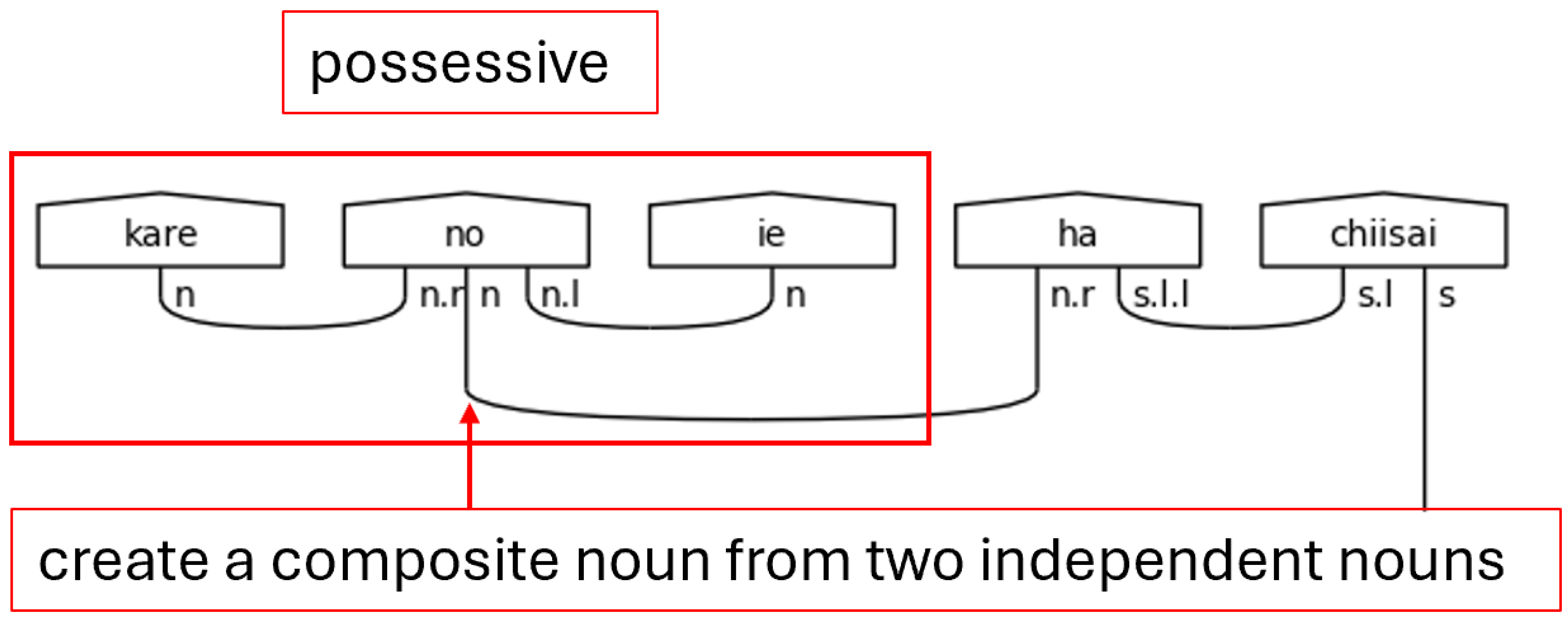
The possessive, or genitive, particle の[no] will always link two nouns together, so it is expecting a noun on its left and on its right. The simple noun type in the middle, then, remains to connect to suffixed particles. There are other uses of the particle の[no] that are not considered here as it is one of the more overloaded particles in the Japanese language. Handling the different types of の[no] in this model is an avenue of future research. The rest of the particles will always link the noun to the verb, so they carry the
s.l.l type. Again, each particle in the sentence will persuade the verb to include another
s.l to pair with it as in
Figure 10.
Figure 21.
The Genitive Use of の[no].
Figure 21.
The Genitive Use of の[no].
2.6.3. Beginning with Diagrams
Having defined the grammar model in
jp_grammar_model.py, it is time to discuss the
diagramizer algorithm found in
jp_grammar_utilities.py. The purpose of this algorithm is to parse a simple, proper Japanese sentence that has been tokenized into the format presented in
Figure 22 and create a string diagram. That string diagram can subsequently be converted into a quantum circuit.
A note on tokenization. Tokenization is, of course, an art as well as a science. This tokenization follows the convention of using whole words separated by white space to tokenize input data for QNLP tasks, which results in diagrams with cups drawn between whole words. It also relies on romaji, which is the anglicized spelling of Japanese words. This is due to the tkinter library, on which lambeq relies in part for drawing diagrams, lacking support for properly displaying kanji and kana—hiragana and katakana—characters even when a file is encoded with UTF-8. Instead of developing a potentially time-consuming work around, the decision was made to work with romaji to avoid the issue as the display format of the text does not impact the core of the diagramizer algorithm. While the decision to use romaji makes certain tokenization decisions a little simpler, it does make it more difficult to handle certain adjectives that phonetically end with an “i” sound (pronounced like “ea” in “eagle”) with total accuracy. This will be discussed in greater detail when discussing い[i]-adjectives in Step 1.
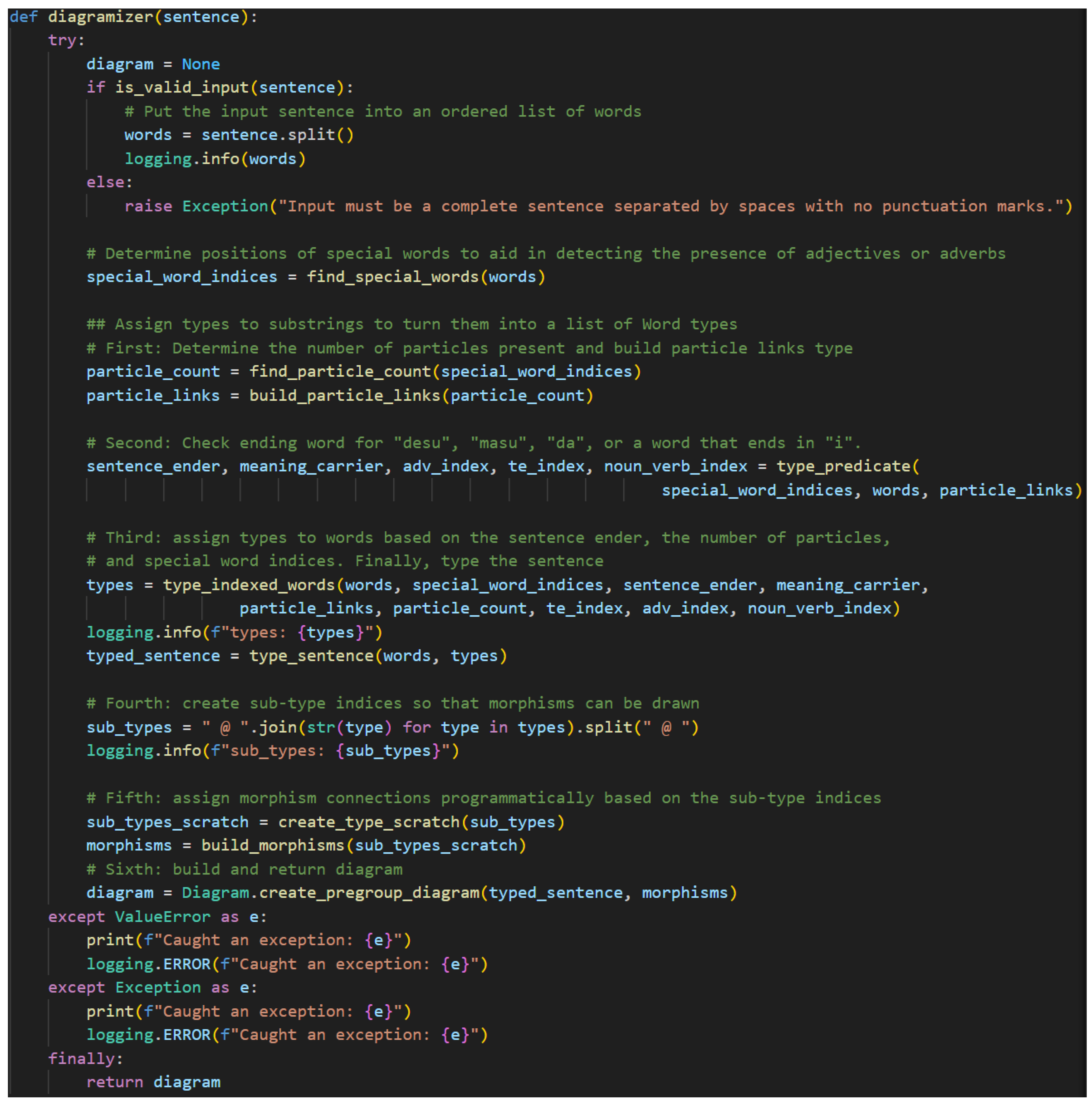
The pseudocode. The diagramizer algorithm consists of eight essential steps.
- 5.
Receive and validate the input.
- 6.
Locate the indices of special words in the sentence.
- 7.
Count the number of particles to aid in determining the sentence-ender’s type.
- 8.
Type the predicate by identifying the sentence-ender and, if necessary, other special words found in the predicate.
- 9.
Type all the indexed special words and then the rest of the sentence via pregroup grammar rules.
- 10.
Create a list of sub-types to allow referencing the simple types directly.
- 11.
Copy this list and mark paired sub-types so the algorithm will not attempt to pair previously paired sub-types again. Paired sub-types share a cup at this stage.
- 12.
Draw the diagram.
Figure 23 shows the code. Steps of interest will be discussed in more detail as the functions performing them are introduced.
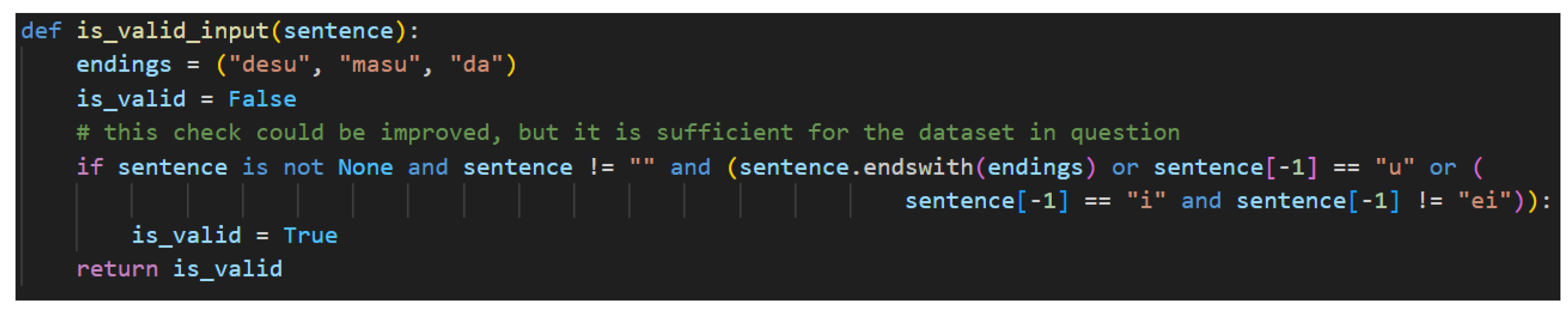
Step 1. In Step 1, input validation focuses on ensuring grammatical expectations are met rather than attempting to address every possible edge case. The grammatical expectations for a Japanese sentence rest primarily on the sentence-ender, so attention is focused there.
Figure 24 shows the function.
The endings variable is assigned a tuple of valid sentence-enders in the Japanese grammar model. These only catch whole words at the end of the sentence strings, so if です[desu], ます[masu], or だ[da] is present, the sentence is assumed to be valid. This is generally true as the copula implies the subject based on the context and ます[masu] is only used in conjunction with a polite verb preceding it. That preceding verb will also imply a subject, so it will produce a valid utterance. The other validation checks are looking for the non-past verb ending “u” or the い[i]-adjective ending “i”. In the former case, the “u” could be preceded by any of the consonantal sound in Japanese and still yield a valid verb (i.e., う[u], く[ku], す[su], る[ru], etc.). In this case, romaji makes the validation check easier since checking for the “u” sound catches all the casual non-past verbal endings. The latter case requires a little more processing to ensure that the ending “i” character is not a common な[na]-adjective like 綺麗[kirei] and 有名[yuumei] by checking for “ei”. While this is not a perfect solution, as this also does not address common names, it is sufficient to handle most sentences. In this case, kanji and kana characters would be more useful as the い[i]-adjective must end with the hiragana い, which is transliterated as “i”. There is no way to detect this with complete accuracy without using the kanji or splitting the “i” off い[i]-adjectives and treating it as a separate token. Investigating these approaches is left to future work.
Table 1.
Sentence-ender Candidates and Their Validity.
Table 1.
Sentence-ender Candidates and Their Validity.
| Japanese |
Transliteration |
Part of Speech |
Translation |
Valid? |
| 嫌い |
kirai |
い[i]-adjective |
“dislike”, “hate” |
yes |
| 綺麗 |
kirei |
noun or な[na]-adjective |
“beautiful”, “clean” |
no |
| ます |
masu |
verb |
None
polite verb ender |
yes |
| 持つ |
motsu |
verb |
“hold” |
yes |
| 源治 |
Genji |
noun |
Nonename |
no |
| だ |
da |
copula |
“is”, “am”, “are”
casual |
yes |
| です |
desu |
copula |
“is”, “am”, “are”
polite |
yes |
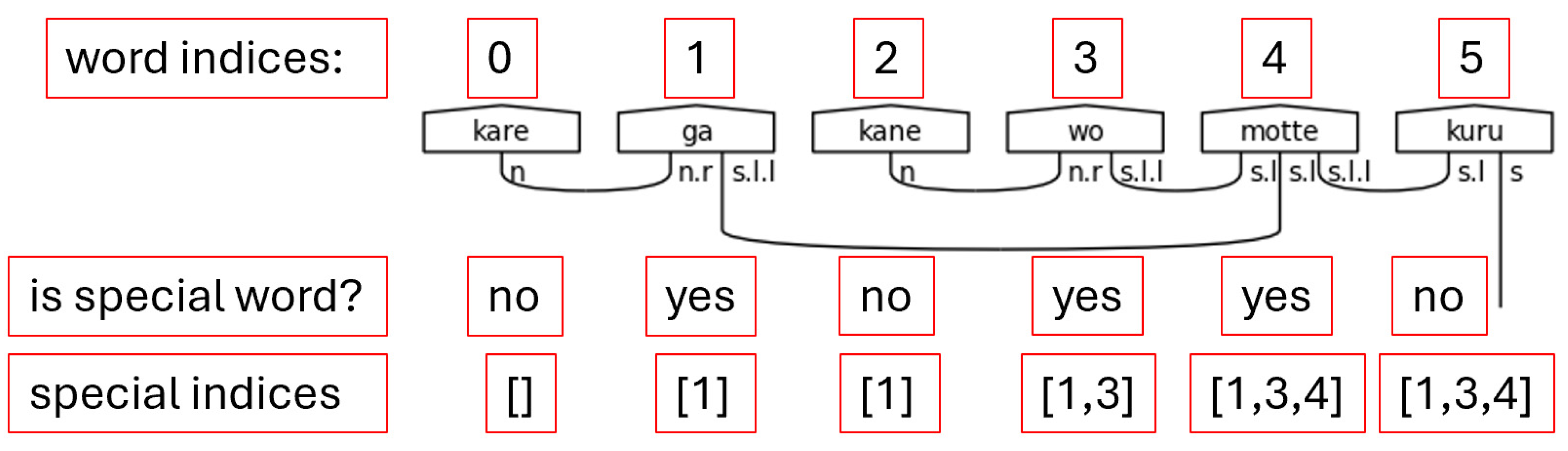
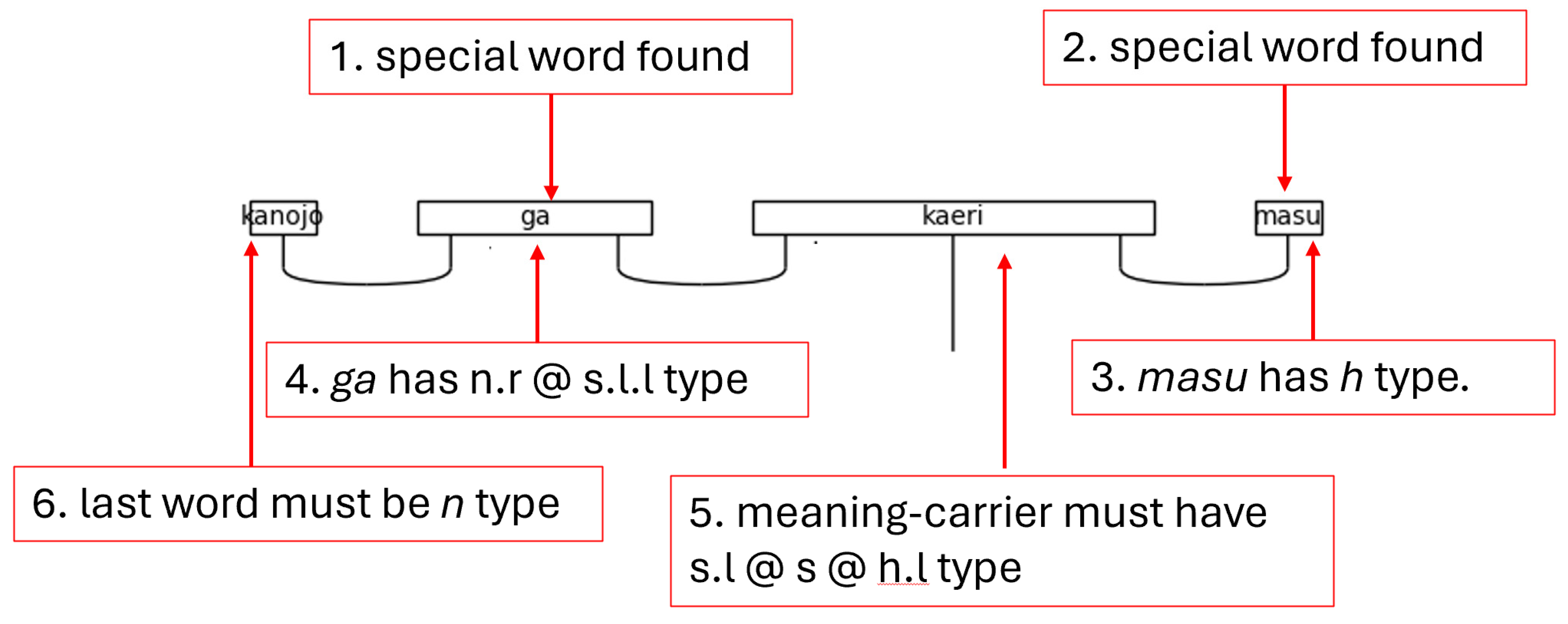
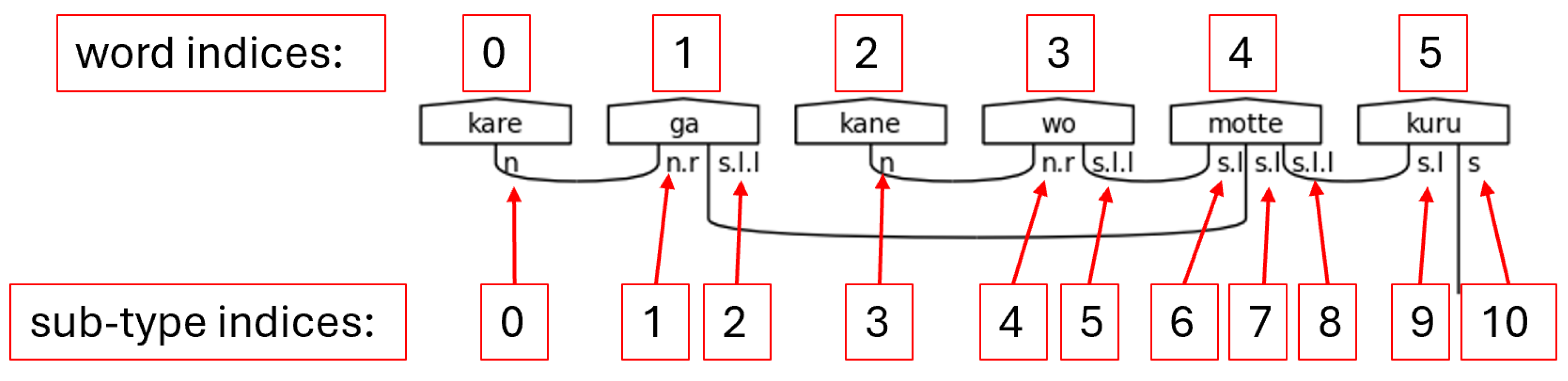
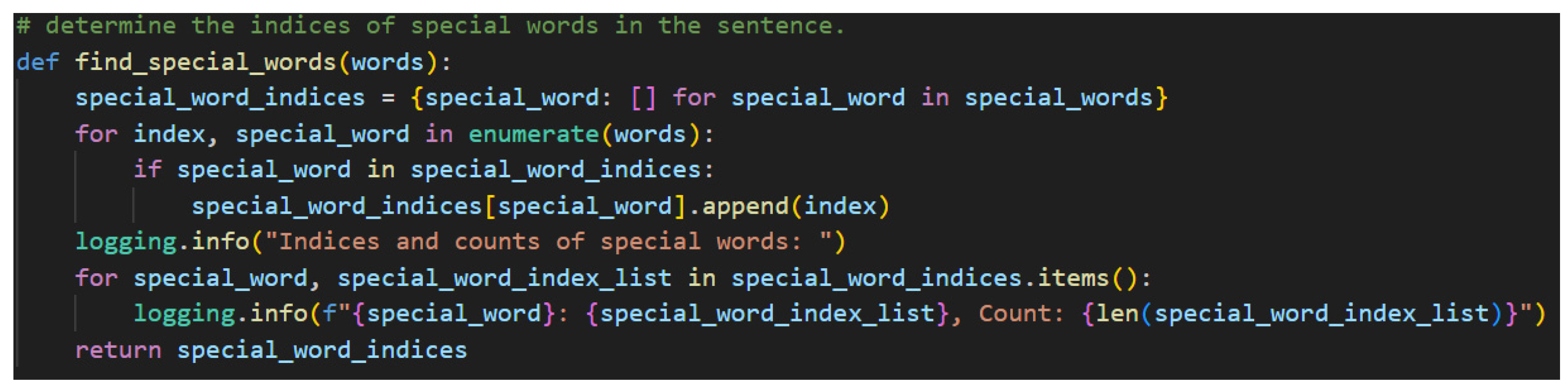
Step 2. Locating the indices of special words in the sentence is the second crucial step. While it is true that to truly understand the grammatical structure of a Japanese sentence that one must begin at the ending, it is also equally true that the ending is dependent on the presence of certain special words, namely particles, honorific words, and the copula.
Figure 25 shows the function that accomplishes Step 2.
The indices are appended to lists which are themselves stored in a dictionary using the special words as keys. Each word is then enumerated, which creates a tuple of with the first element being an index and the second element being the word. If the word is found to be one of the keys—one of the special words—in the special word dictionary, the index is appended to the list associated with said key. This approach is concise and flexible enough to handle multiple occurrences of the same word in different places of the initial word list. This flexibility is required for adequately handling natural language.
Figure 26.
Finding Special Word Indices Note. The special indices are a list of lists in the code. They are shown here as a flat list for visual simplicity.
Figure 26.
Finding Special Word Indices Note. The special indices are a list of lists in the code. They are shown here as a flat list for visual simplicity.
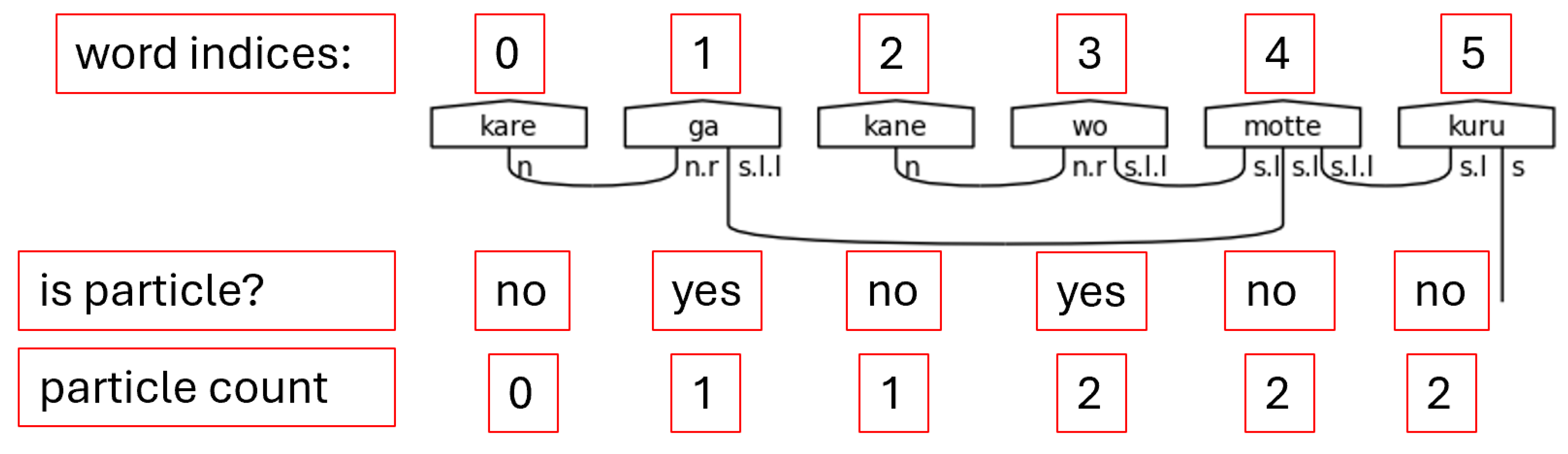
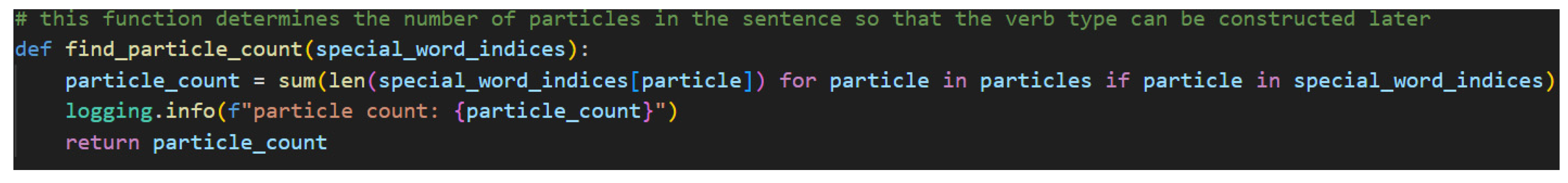
Step 3. Because the number of particles can vary significantly, it is impossible to adequately type the predicate without first counting the number of particles in the sentence. Python’s list comprehension capability, as demonstrated in
Figure 27 is well suited for this task.
Given the dictionary of special words and their associated lists of indices, list comprehension allows for an easy way to calculate the sum of all the lengths of the special words that were identified as particles in the grammar model. If the special word is a particle, then length of its list is added to the accumulating sum. The final sum, then, returns the count of all particles found in the sentence.
Figure 28.
Counting Particles.
Figure 28.
Counting Particles.
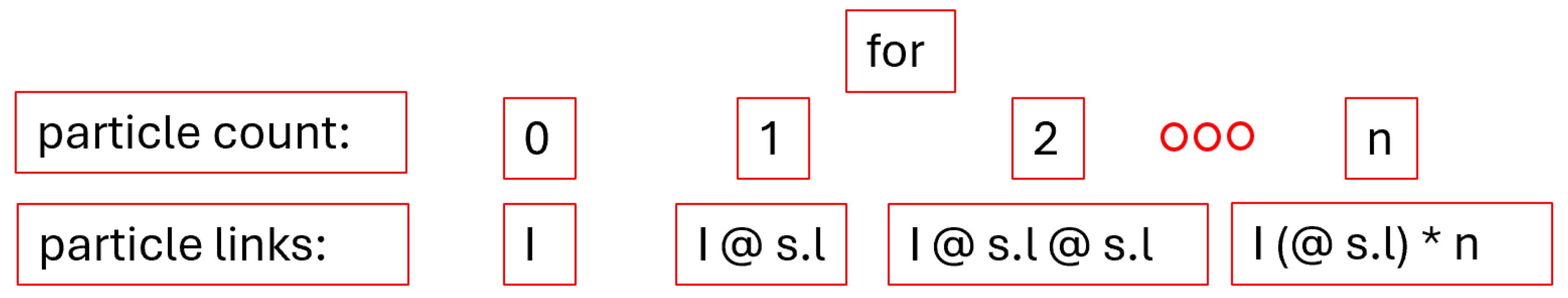
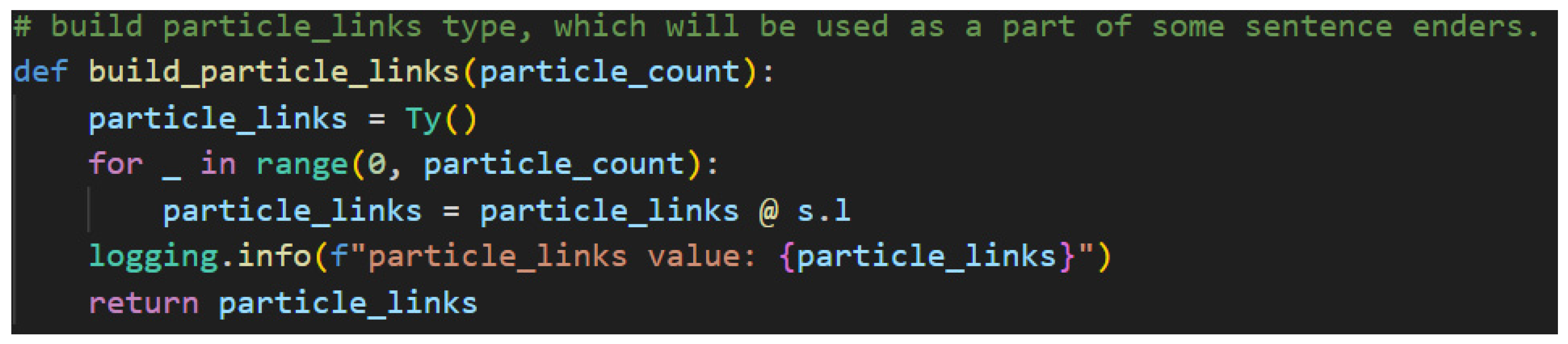
The particle count is used to build the portion of the meaning-carrier’s type called the particle links.
Figure 29 shows how.
Clearly, the particle count will be the loop controller variable as each particle must connect to the meaning-carrier. A dangling particle would not provide any textual meaning to the sentence. The less obvious logic here is how to build the links programmatically. The answer is to rely on the fact that the definition of an empty Ty—the same lambeq class that was used to define the custom h type—is the identity value for types. So, by defining particle_links with an empty Ty, the calculation can be created by performing matrix multiplications—as represented by the python “@” operator—iteratively. This allows for a programmatic construction of particle links of a variable length, which in turn provides the missing information required to type the predicate of the sentence.
Figure 30.
Building Particle Links Block Visualization. Note. The “* n” operator represents repetition of the “@ s.l” string in the figure n times.
Figure 30.
Building Particle Links Block Visualization. Note. The “* n” operator represents repetition of the “@ s.l” string in the figure n times.
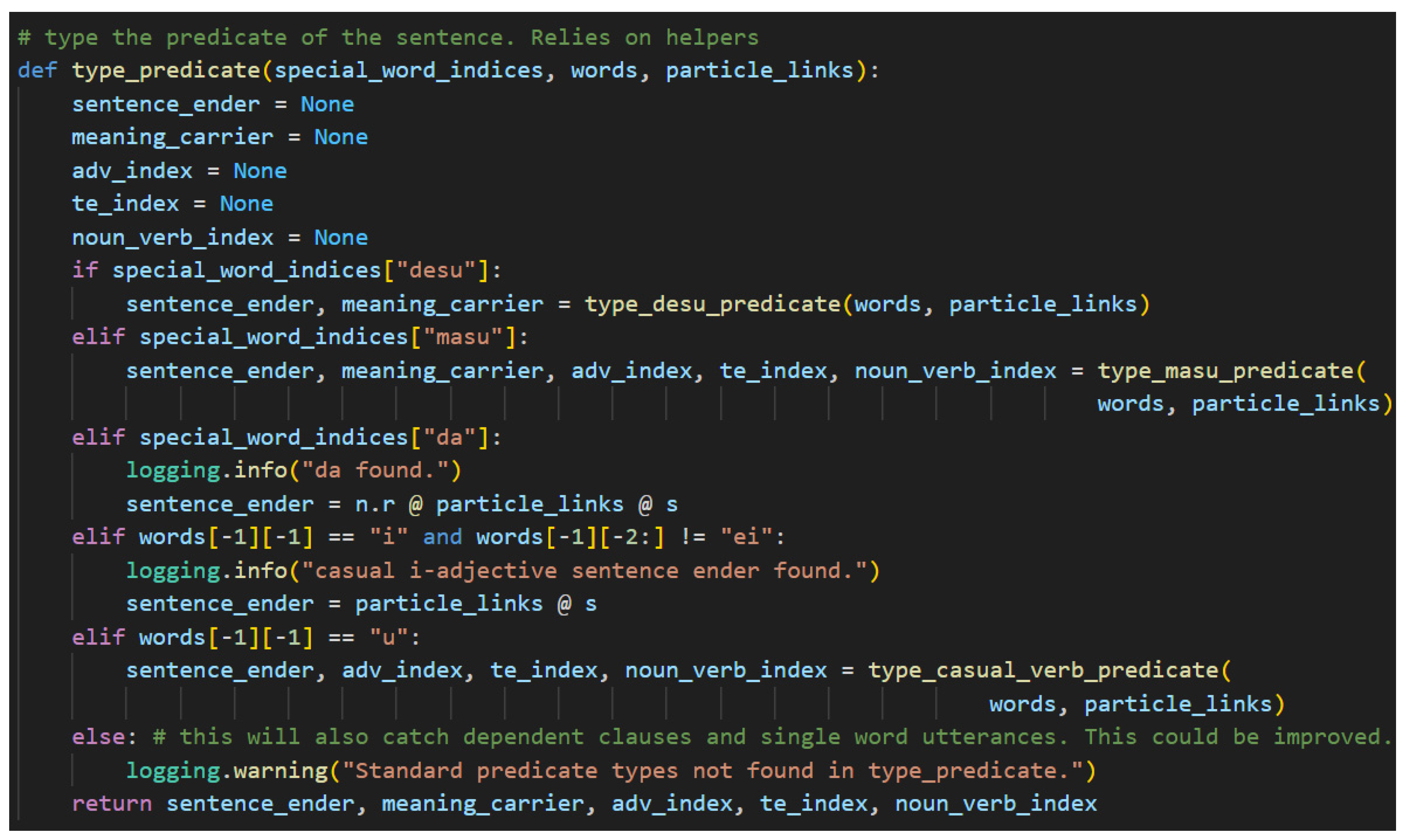
Step 4. Typing the predicate is a moderately complicated NLP task that relies on different helper functions depending on which sentence-ender was found in the sentence. The presence of the sentence-ender is determined by identifying which special word key returns a non-empty list as is shown in
Figure 31.
The structure of the predict will differ depending on the found sentence-ender. Because of this, more complicated predicate types have been separated into an additional level of helper functions. The helper functions require the list of words and the particle links as inputs. They also leverage python’s capability to return multiple variables for readability. If there is no index for a return variable, its value will remain None.
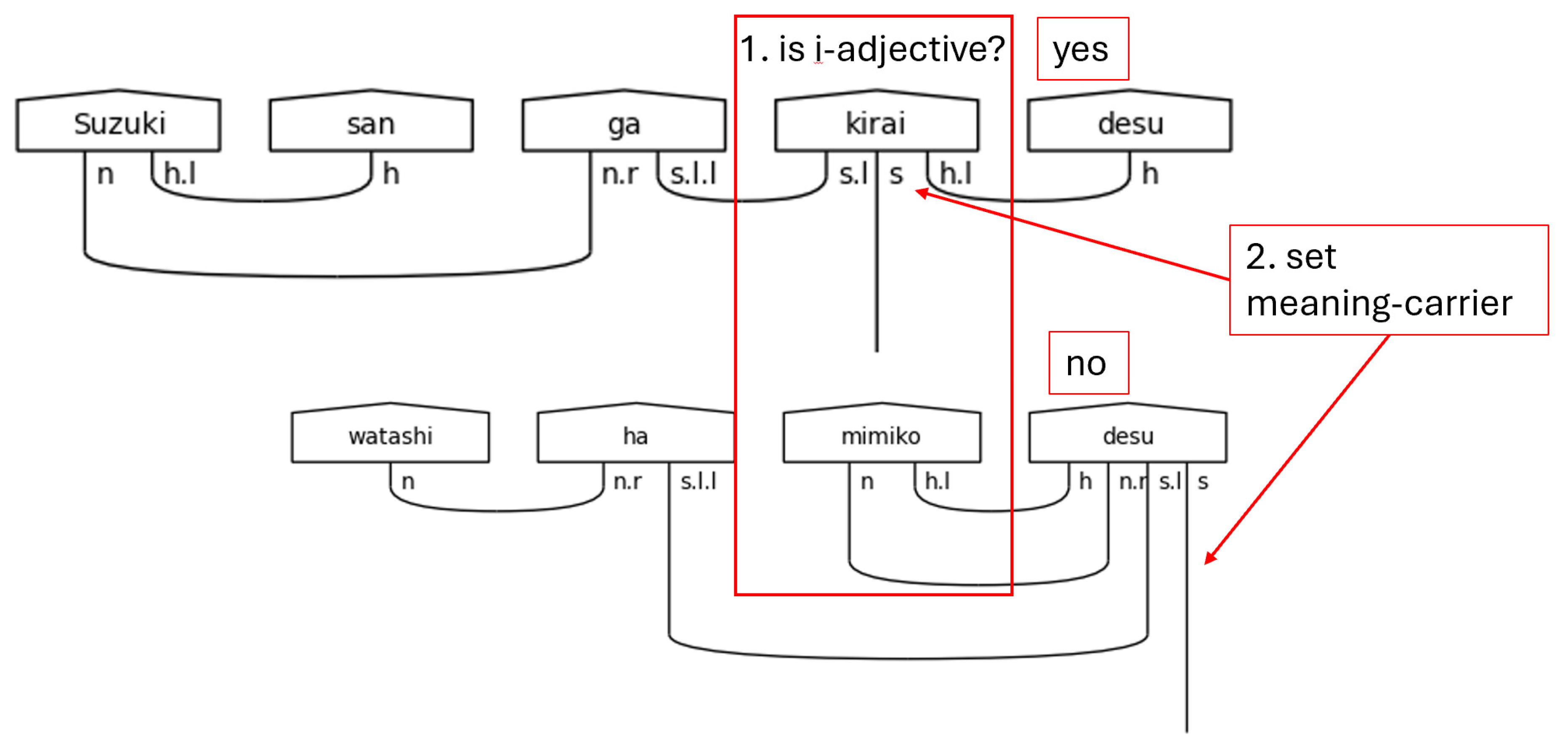
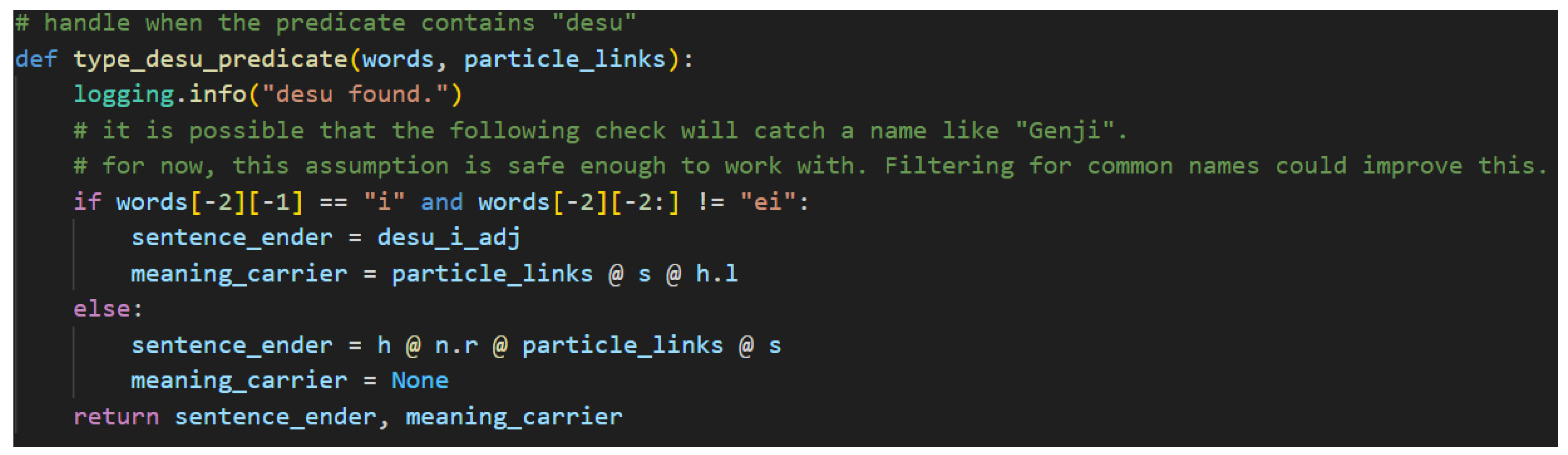
In the case that です[desu] is found, the predicate may include a sentence-ender and a meaning-carrier. A ます[masu] can result in a much more complicated structure that includes a sentence-ender, a meaning-carrier, adverbs, て[te]-form verbs, and even verbal nouns. The casual copula だ[da] is a simple case, so no helper function is needed. It simply uses matrix multiplication to add in the particle links between the n.r and the s type. The casual い[i]-adjective case is also simple. It behaves as a casual verb but ignores the possibility of adverbs and て[te]-form verbs in this model. Both the だ[da] case and the い[i]-adjective case do not require a meaning-carrier as the sentence-ender itself will carry the s type. Lastly, the case of non-past casual verbs requires its own helper method. It returns the same values as the ます[masu] predicate except it does not require a meaning-carrier. This is a common pattern. The polite versions of sentences typically have a meaning-carrier that is distinct from the sentence-ender—with the notable exception of です[desu] used with a predicate noun. Casual sentences do not distinguish between the two. Again, this is evidence of the vertical dimension of language because of the dual functionality of です[desu].
Beginning with です[desu], the helper functions are listed in the following figures and discussed in the following paragraphs.
Figure 32, then, is first.
It is first worth noting that this helper method shares the same limitations as the input validation code found in
Figure 24, and it also ignores names. One possible way of adding in support for names is to create a list of common names and use it as a filter. Since that is beyond the scope of this initial version of the model, properly handling names is left to future work. The if-statement here is designed to determine whether the です[desu] is preceded by an い[i]-adjective or a predicate noun by using two-dimensional list syntax on the list of words. The left set of brackets is selecting the second to last word in the list. The right set of brackets is selecting either the last character or a slice of the word containing its last two characters. The logic here is an excellent example of how です[desu] functions in both the honorific sense and in the logical sense. In the case of an い[i]-adjective, です[desu] functions purely honorifically. It carries only
h type just as ます[masu] does. The direct consequence of this is that the meaning-carrier is the い[i]-adjective that precedes です[desu] in the sentence. Now, in the case where the preceding word is not an い[i]-adjective, it will be a predicate noun. In this case, です[desu] will carry the meaning—carry the
s type. This is the one case in this model where it does not hold that the cup count will be word count minus one. In this singular case, the cup count will equal the word count.
Figure 33.
Typing です[desu] Visualization.
Figure 33.
Typing です[desu] Visualization.
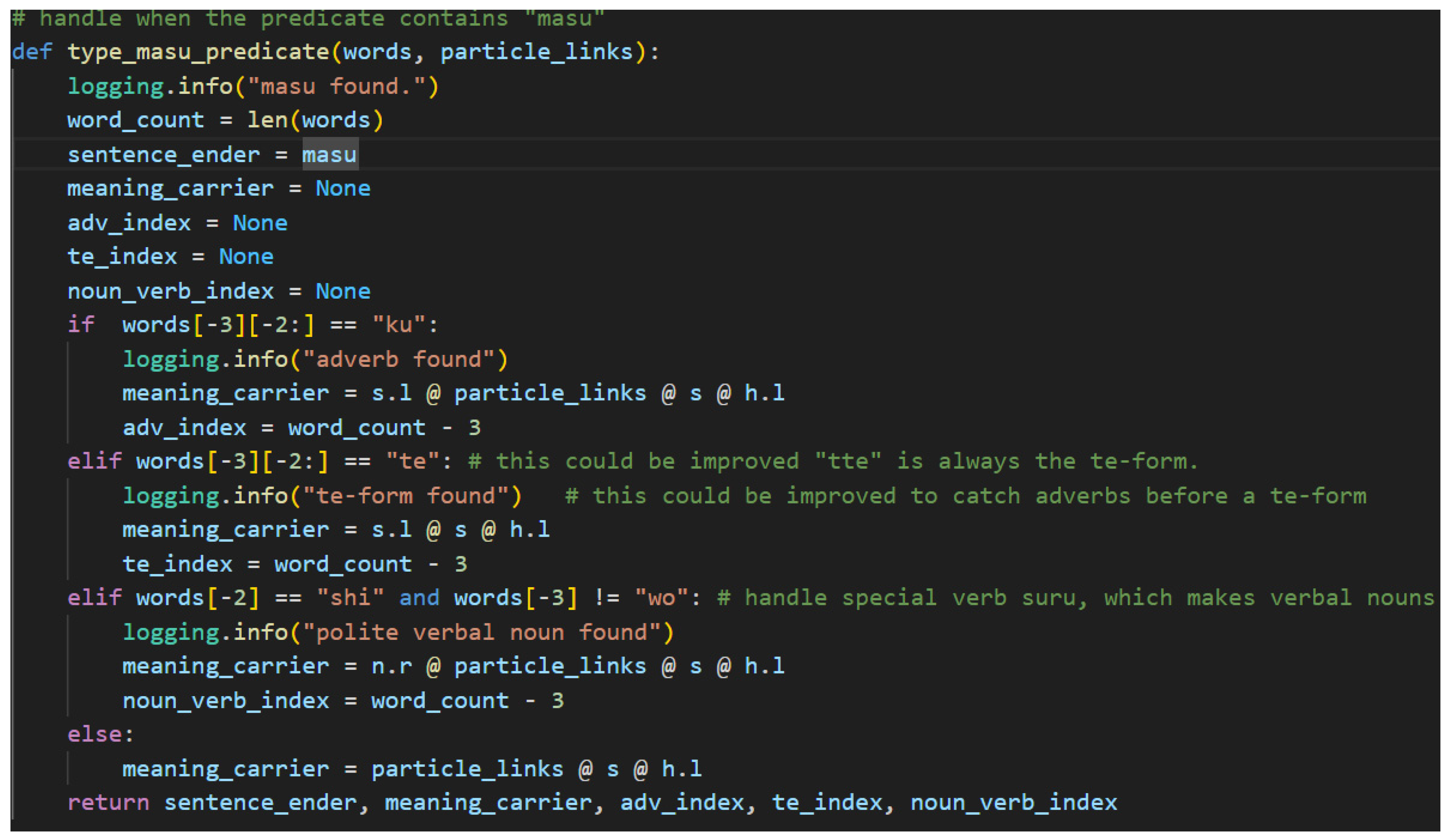
Figure 34 shows the code used for typing a ます[masu] predicate.
The function accepts the list of words and the particle links and begins its work with calculating the word count. The word count is then assigned to a variable and used to find indices for discovered adverbs and て[te]-form verbs in the predicate. The next step is to assign the sentence-ender as ます[masu]. The primary work of the method then is to determine what type the meaning-carrier word should have based on the textual clues of its preceding neighbor.
Japanese adverbs come primarily in two forms. The first is akin to the な[na]-adjective in that it is a noun suffixed with another word, in this case the に[ni] particle. Fortunately, this case is already handled in this model by the generic particle typing. Since に[ni] is a particle, the noun will be linked to the verb and no extra processing is required. The second is derived from い[i]-adjectives by changing the い[i] ending to く[ku]. This is a very regular part of the language, so finding a “ku” in the third to last position of a sentence in standard SOV order means finding an adverb. The algorithm assigns the meaning-carrier’s type with an additional s.l to resolve the adverb, and then it marks the adverb’s index so that it may be typed later.
Figure 35.
Japanese Adverb in a Polite Predicate.
Figure 35.
Japanese Adverb in a Polite Predicate.
The て[te]-form is a specialized verb form that is used for a variety of reasons in Japanese. The grammar model presented here handles when the て[te]-form functions adverbially, meaning the entire clause that links to the て[te]-form verb is subsequently linked to the meaning-carrier verb. This has the notable effect of removing the particle links from the meaning-carrier onto the て[te]-form verb, which gives the effect of modifying the meaning of a verb by an entire clause.
Figure 36.
て[te]-form in a Polite Predicate.
Figure 36.
て[te]-form in a Polite Predicate.
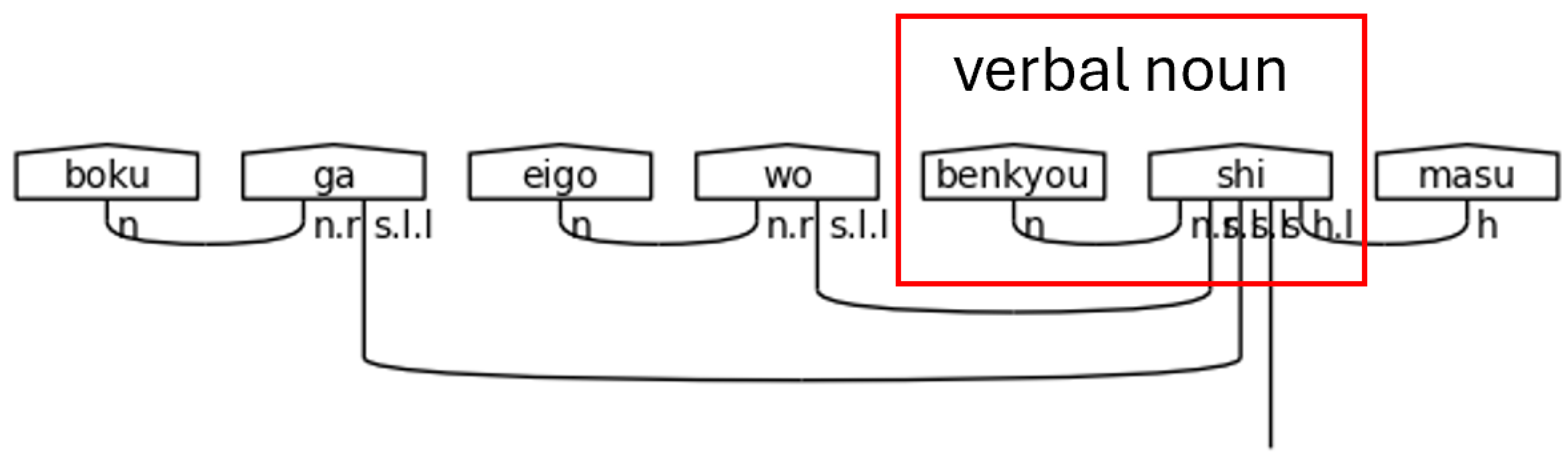
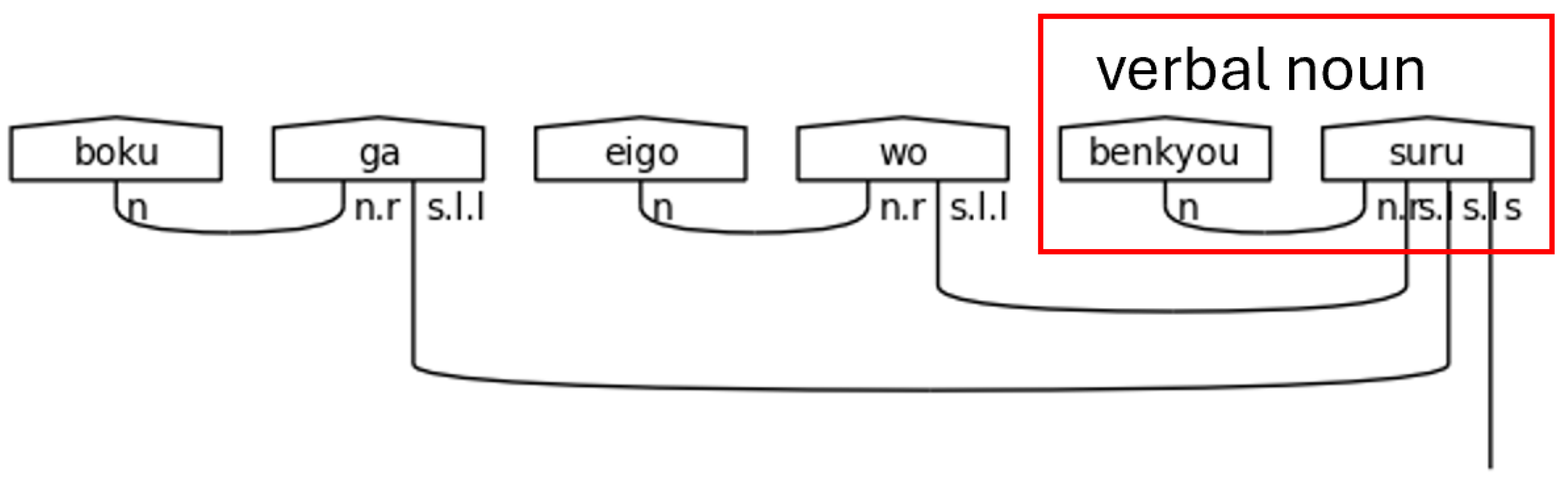
Verbal nouns, or noun-verbs, refer to nouns that receive a verb directly suffixed onto them without having a particle as a buffer. In polite Japanese, the most common of these verbs is します[shi-masu], meaning “do” or “will do” in the non-past form. By suffixing します[shi-masu] to a noun, it simply means doing the action of the noun. Verbal nouns require an n.r type in the meaning-carrier since there is no other particle present to link the noun to the meaning-carrier し[shi].
Figure 37.
Verbal Noun Condition in a Polite Predicate.
Figure 37.
Verbal Noun Condition in a Polite Predicate.
The final path in the code for the ます[masu] ending is the simple case. There are no additional words that modify the meaning-carrier or any special endings. The particle links, sentence type, and h.l type are assigned to the meaning-carrier and the algorithm proceeds on to the next step.
Figure 38.
Logic Visualization for Typing a ます[masu] Predicate.
Figure 38.
Logic Visualization for Typing a ます[masu] Predicate.
Next,
Figure 39 contains the logic for typing a casual sentence, which mirrors that of a polite sentence.
Figure 39.
Typing a Predicate with a Casual Verb. Note that it follows the same flow as the ます[masu] predicate without the added dimension of the honorific type. Additionally, since the word ます[masu] is not present in casual sentences, the sentence-ender and meaning-carrier are always the same word—the final word in the sentence. This causes the word list indices to be incremented by one in the casual case shown in
Figure 39. Adverbs, て[te]-forms, and the casual verbal noun する[suru] are all accounted for. Extending this implementation to account for more complex predicates and generic verbal nouns is left to future work.
Figure 39.
Typing a Predicate with a Casual Verb. Note that it follows the same flow as the ます[masu] predicate without the added dimension of the honorific type. Additionally, since the word ます[masu] is not present in casual sentences, the sentence-ender and meaning-carrier are always the same word—the final word in the sentence. This causes the word list indices to be incremented by one in the casual case shown in
Figure 39. Adverbs, て[te]-forms, and the casual verbal noun する[suru] are all accounted for. Extending this implementation to account for more complex predicates and generic verbal nouns is left to future work.
Figure 40.
Verbal Noun Condition in a Casual Sentence.
Figure 40.
Verbal Noun Condition in a Casual Sentence.
Step 5. The fifth step consists of typing the indexed special words, including any adverbs, て[te]-form verbs, and verbal nouns, along with the rest of the sentence. The first four steps have been preparing for this one. After this step, the entire sentence will be typed. The code for this step is larger, so the typing of particles and other indexed words are separated.
Figure 41 covers the former case, and
Figure 42 covers the latter.
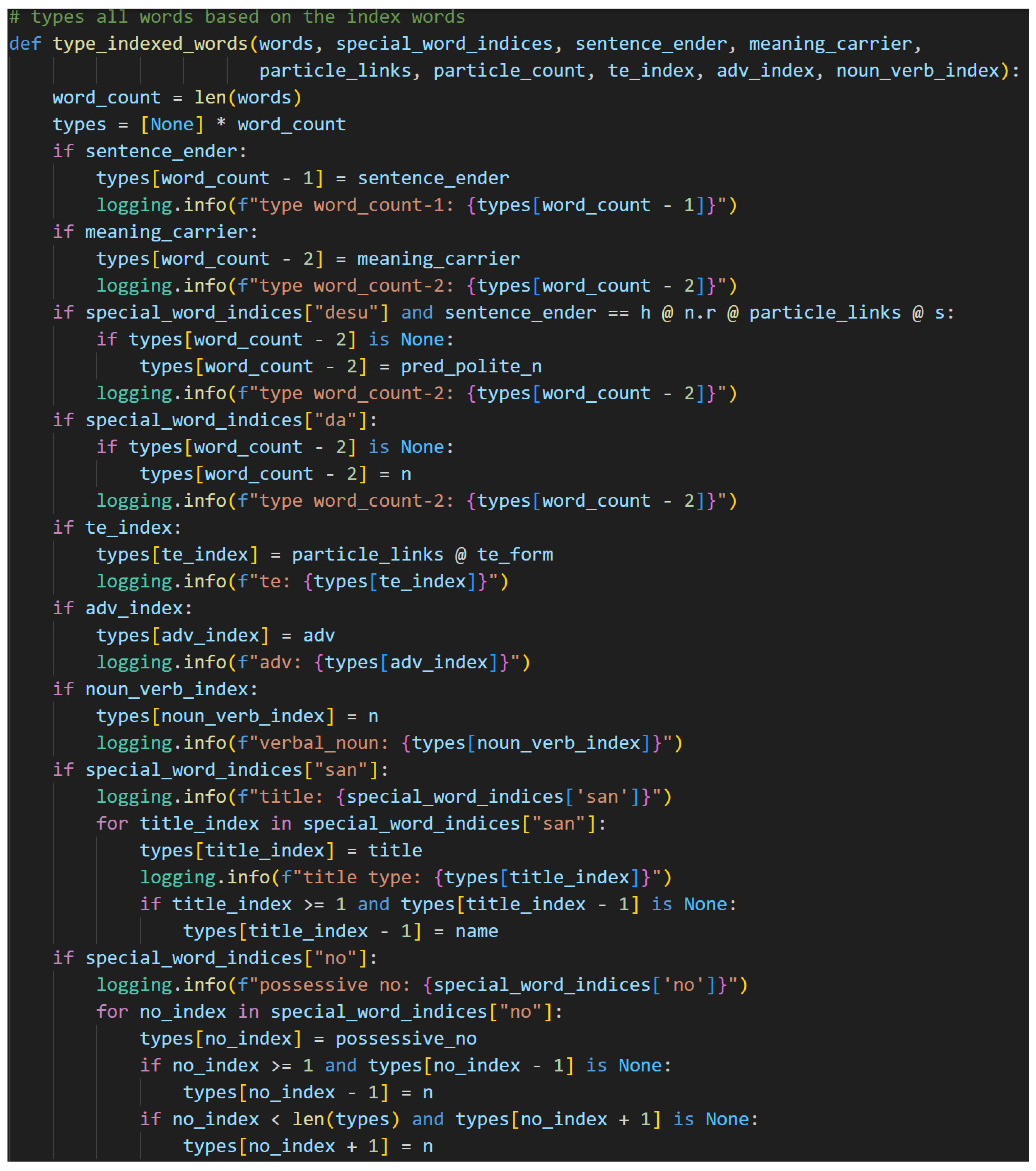
Note that the order of assignment of types in the algorithm is intentional. Like all things in Japanese, the assignment of types begins at the end. The words that are directly linked to the sentence-ender—the meaning-carrier, if present, or predicate nouns—are typed next. The rest of the predicate follows. Titles and names are handled next, followed by the possessive particle の[no]. The final portion handles the particles. This order allows for the appropriate assignment of types without overwriting. More details follow as the specific if-statements in the algorithm are addressed.
The function begins by calculating the word count and then defining a new list filled with
Nones that is the same length as the word count. This new list is called
types, and it will hold all of the types of the words in the original input sentence such that the word and type are matched by common index, i.e.,
words[
1]’s typing is stored in
types[
1]. As types are assigned, therefore, they will be added into the
types list.
The first two checks in the logic look at the sentence-ender and the meaning-carrier. If either is assigned, or not None, then the type generated during the typing of the predicate is assigned to the appropriate index in the types list. Otherwise, the assignment is skipped. These checks rely on None being “falsy” in python, meaning that None evaluates to False in a Boolean context.
The predicate noun usage of です[desu] follows. The if-statement specifically checks not only that there is a です[desu] present but also that the predicate noun version of です[desu]’s type is in the sentence_ender variable. Now, this check is the first instance of an indexed special word being used to type a word that is grammatically linked to it, meaning the index of the sentence-ender is decremented by one to point at the predicate noun. Its type, then, is assigned as an offset from the special word です[desu]’s index. The inner if-statement here is confirming that the word has not been previously typed. It, therefore, prevents later type assignments from inadvertently overwriting previous ones. This is critical for assigning the types of the non-indexed words and is a recurring pattern. The index of the casual copula, だ[da], is used to type the noun to which it is suffixed in the same—though simpler since no h.l type is required—way.
て[Te]-form verbs, adverbs, and verbal nouns are special words, so their types are assigned directly in this function. They are critical for typing the predicate, but they are not useful for discerning the types of any words in the subject. It is worthy of note here that the て[te]-form verb is assigned the particle links during this step, if present.
If titles are present, they are handled next. These can appear in the predicate but are more often found in the subject. Regardless, the algorithm here handles both cases. First, it assigns the title type to each indexed title. It then performs a list boundary check to ensure that the title is not the first word in the sentence. This should not occur since it is not proper Japanese, but safety checks are always preferred. While checking for the list boundary, the code also confirms that the title’s preceding word type is currently None to prevent overwriting. If both of those checks pass, then the preceding word type is assigned as a name, which is an n @ h.l. It is a noun that expects to be suffixed with an honorific.
The possessive particle の[no] is next. This is a unique case in that it turns a noun into an adjective while remaining a separate word. This means that the の[no] is expecting a noun on the left and a noun on the right. It, therefore, assumes the type n.r @ n.l. This, then, will link to nouns together so that the first noun modifies the second. This assignment is done by using the special word index of の[no] and offsetting to type the other two nouns. Because this is a unique case, the if-statement must check for bounds and None on both the preceding and succeeding word. When one of these cases pass, then it is assigned the type n.
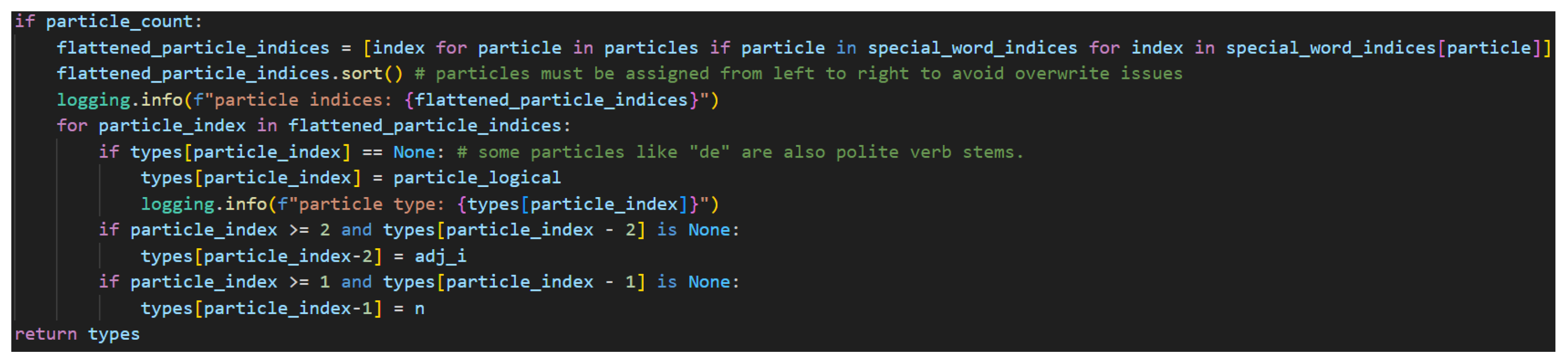
Lastly, the particles are handled in
Figure 42.
Figure 42.
Typing Indexed Words and Their Grammatically Related Words, Part Two.
Figure 42.
Typing Indexed Words and Their Grammatically Related Words, Part Two.
If particles are present, there will be a particle count, so that check is used to control this code. Particles require unique processing since the code has been written to track each particle in the model independently. While this is not strictly required, it is more extensible for those desiring to explore more complex typing that differentiates between the particles since they accomplish different things and serve different purposes in Japanese grammar. This code then, must flatten the particles into a one-dimensional list from the list of lists. List comprehension allows for a concise way to flatten the lists by checking for all the non-empty lists and returning their index values into a new list.
The diagramizer algorithm relies heavily on the fact that assignments must be made from left to right. This is a hard and fast rule. If assignments are done out of order, there are many instances where typing will fail to produce the correct result. Therefore, this flattened list must be sorted so that particles are typed in ascending order by index. After sorting the list, the algorithm checks to confirm that the particle index is a None type to confirm that the particle has not already be assigned another value. This is because some particles, like で[de] are also polite verb stems—meaning-carriers. This guarantees that a polite verb stem will not be overwritten with the particle type of n.r @ s.l.l.
Next comes the assignment of offset words. The particle check is reserved to the last place because it also determines which words are adjectives. It is clear from the typing of the particle that the preceding word is a noun, so it will assign that type. The, perhaps, less obvious trick here is that if there are still unassigned types at this point in the processing, they must be adjectives. Therefore, by decrementing the particle index by two, adjective types may also be assigned. The model, then, can account for adjectivally modified nouns that are suffixed with a logical particle. At this point, the function returns with a filled and ordered list of sentence types.
Figure 43.
Example of Typing Sentences Based on Special Word Indices.
Figure 43.
Example of Typing Sentences Based on Special Word Indices.
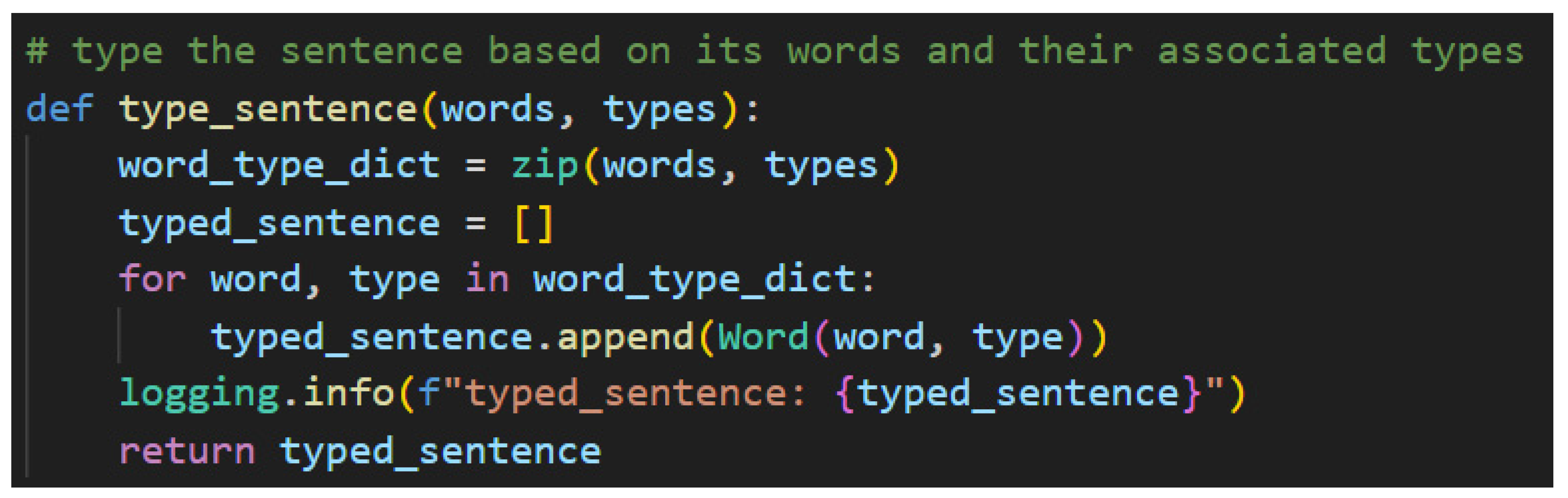
All that remains of Step 5, then, is to type the completed sentence. Recall that the list of
types and the list of
words are aligned so that words in the word list and types in the type list share a common index value. This fact is leveraged in the sentence typing function shown in
Figure 44.
To this point, the word and type values have been assigned to lists. Now, this function takes those lists assignments and instantiates them as lambeq Words as follows. Python’s zip function takes two lists that share a common index logically and concretizes them into a dictionary—a map. This makes that logically shared index a real and actionable hook in the code. The function then iterates through each word and type, instantiates the lambeq Word, and then appends those values into a new list of lambeq Words. Once the Words have been instantiated, they can be associated with one another using morphisms, which will enable the building of string diagrams. More on that process follows beginning in Step 6.
Figure 45.
Using a Dictionary to Map Words to Types Via Common Indices.Note. The casual version of this sentence is shown for simplicity. Also, to clarify, the indices are shown in the middle row between the words (top) and types (bottom).
Figure 45.
Using a Dictionary to Map Words to Types Via Common Indices.Note. The casual version of this sentence is shown for simplicity. Also, to clarify, the indices are shown in the middle row between the words (top) and types (bottom).
Step 6. After the lengthy, complicated indexing and list building activities of Step 5, Step 6 is a walk in the park. Be that as it may, it is critical to the success of the algorithm and easy to overlook. Based on the types appended into the
types list, a new list of sub-types,
sub_types, must be created.
Figure 46 shows this line of code.
This single line of code is concisely combining three separate operations before assigning the sub-types into the new list. The first of these operations is casting the type as a string. This allows for the second step, which is joining the strings together into one long string using the python matrix multiplication operator—@—surrounded by spaces via the join method. This join symbol is used because it is the same symbol that is joining all the sub-types in the complex type held in each list item. By joining with this same symbol, then, the larger string will have a uniform separator between all sub-types. The third and final step, then, is to split the newly built string of all types separated by the matrix multiplication operator into a new list made up entirely of simple types. This list enables the construction of morphisms, or cups, in Step 7, which is the second major processing step of the diagramizer algorithm.
Figure 47.
Sub-type Indices Visualization.
Figure 47.
Sub-type Indices Visualization.
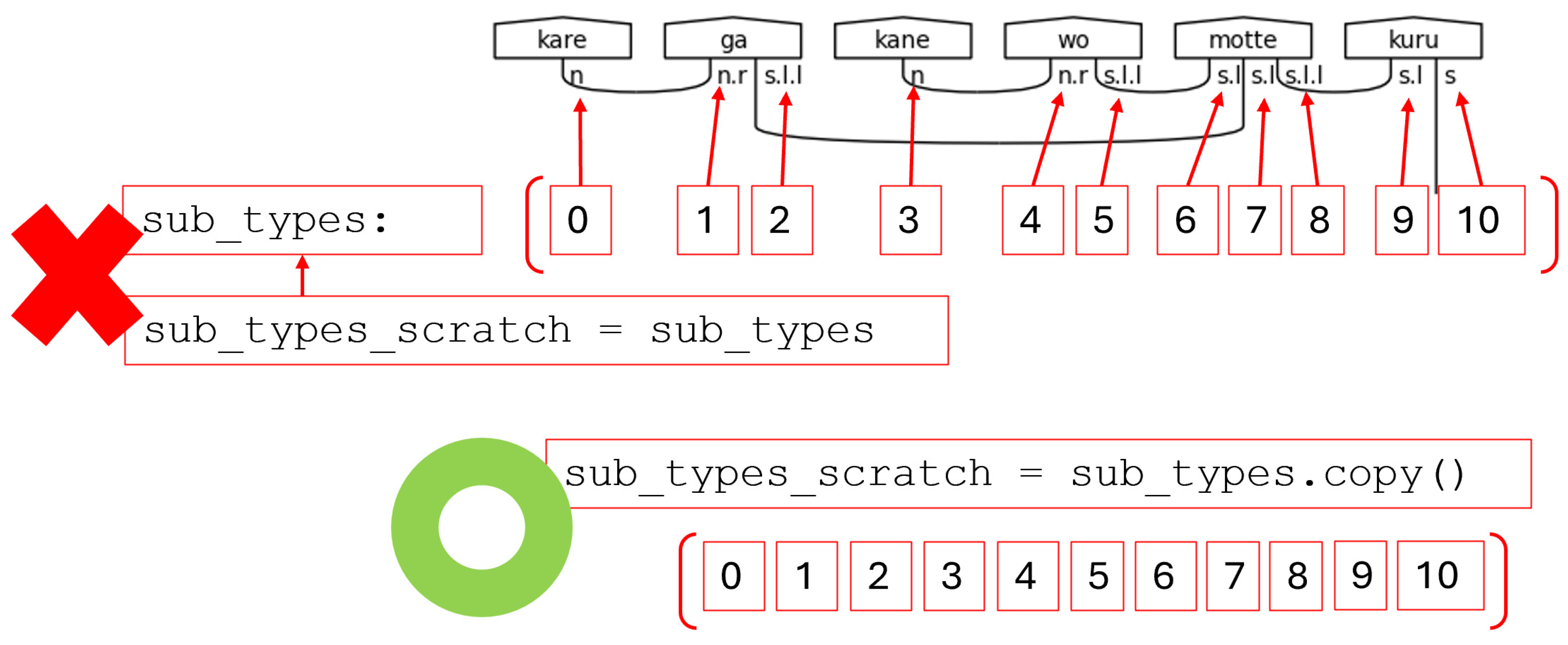
Step 7. The seventh step begins with copying the newly created sub-type list. It then proceeds to connect sub-types with cups and to mark completed pairs as matched. This work is split into two main functions. The first of which is shown in
Figure 48.
This list copying function leverages python’s list and dynamic typing capabilities. First, the method copies the sub-type list. This is important because a simple assignment of the sub-type list to another variable will create a reference to the original sub-type list. Any operation, therefore, taken on the new variable is modifying the same values referenced by the original variable, which would result in an error during later processing.
Figure 49.
Passing By Reference Yields an Error. Pass By Value Instead.
Figure 49.
Passing By Reference Yields an Error. Pass By Value Instead.
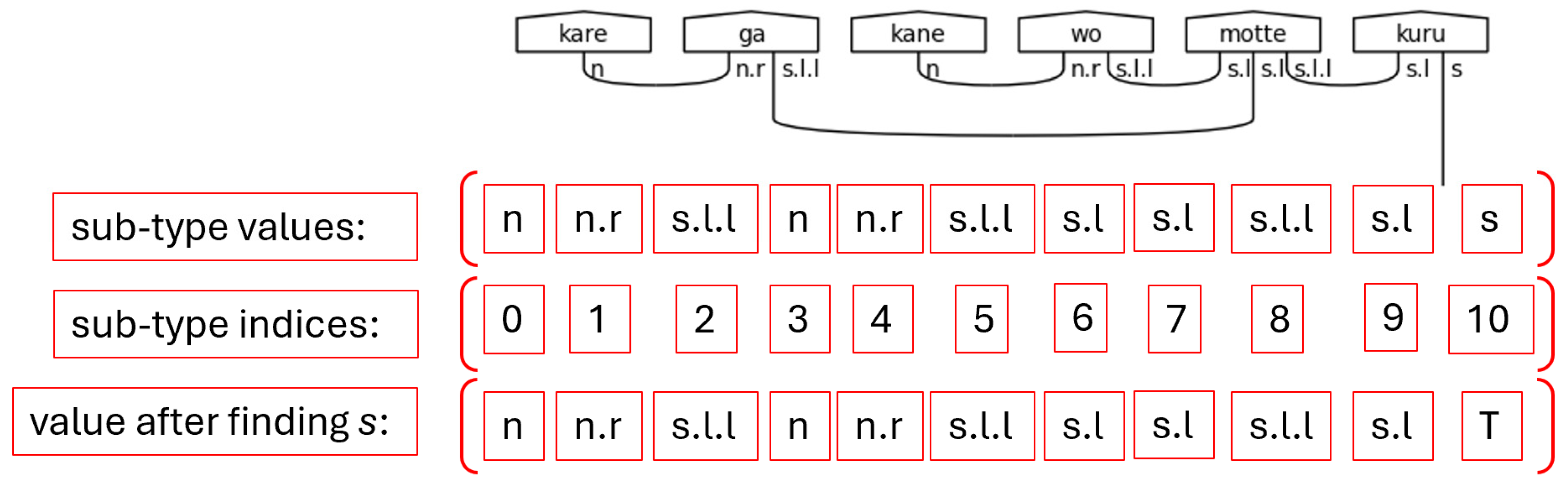
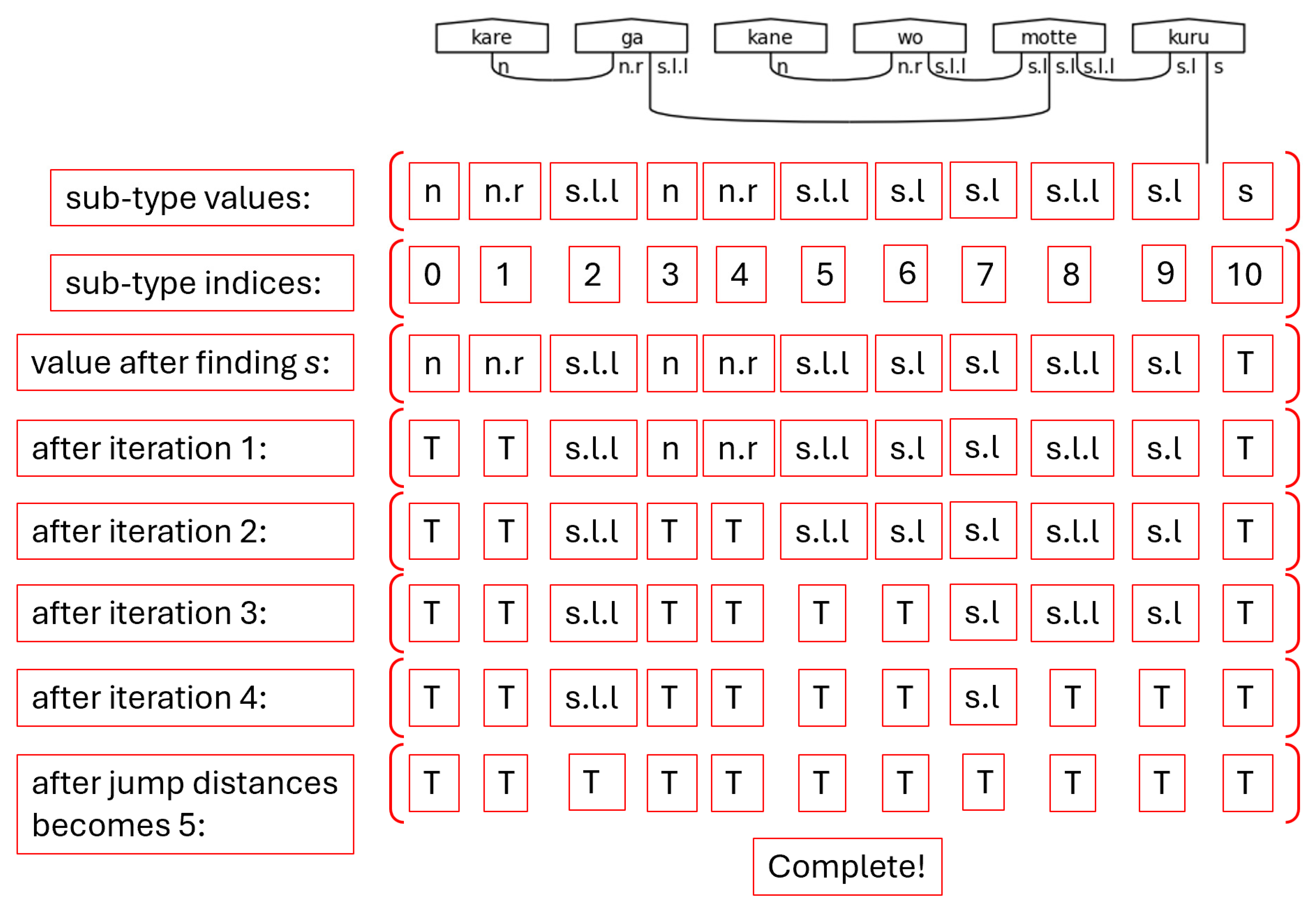
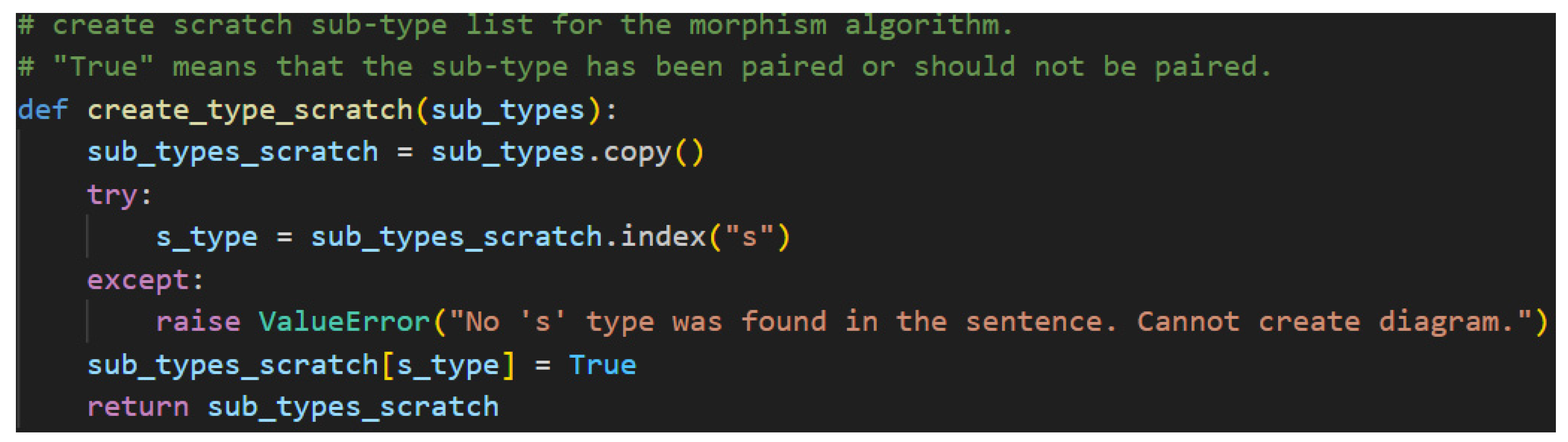
The dynamic typing capability is leveraged after attempting to find the s type in the sub-type scratch list. Once this type is found, it's value is updated to True, meaning it is considered already paired. This excludes it from the processing of the build_morphisms function. For clarity’s sake, the s type represents the only wire in a pregroup diagram that is not connected to another type with a Cup. This is the requirement for a sentence to be considered grammatically correct; therefore, it is marked True to preserve said requirement. Fortunately, the ability to reassign the value from a string to a Boolean in python allows the algorithm to mark connected pairs of sub-types logically.
Figure 50.
Sub-type Scratch Values after Marking S as True Note. Here, “T” is shorthand for python’s True Boolean value.
Figure 50.
Sub-type Scratch Values after Marking S as True Note. Here, “T” is shorthand for python’s True Boolean value.
Now that the sub-type list has been copied and the
s has been marked, it is time to begin the second major logical section of the algorithm, which is responsible for connecting the sub-types with
Cups—defining morphisms. The function is found in
Figure 51.
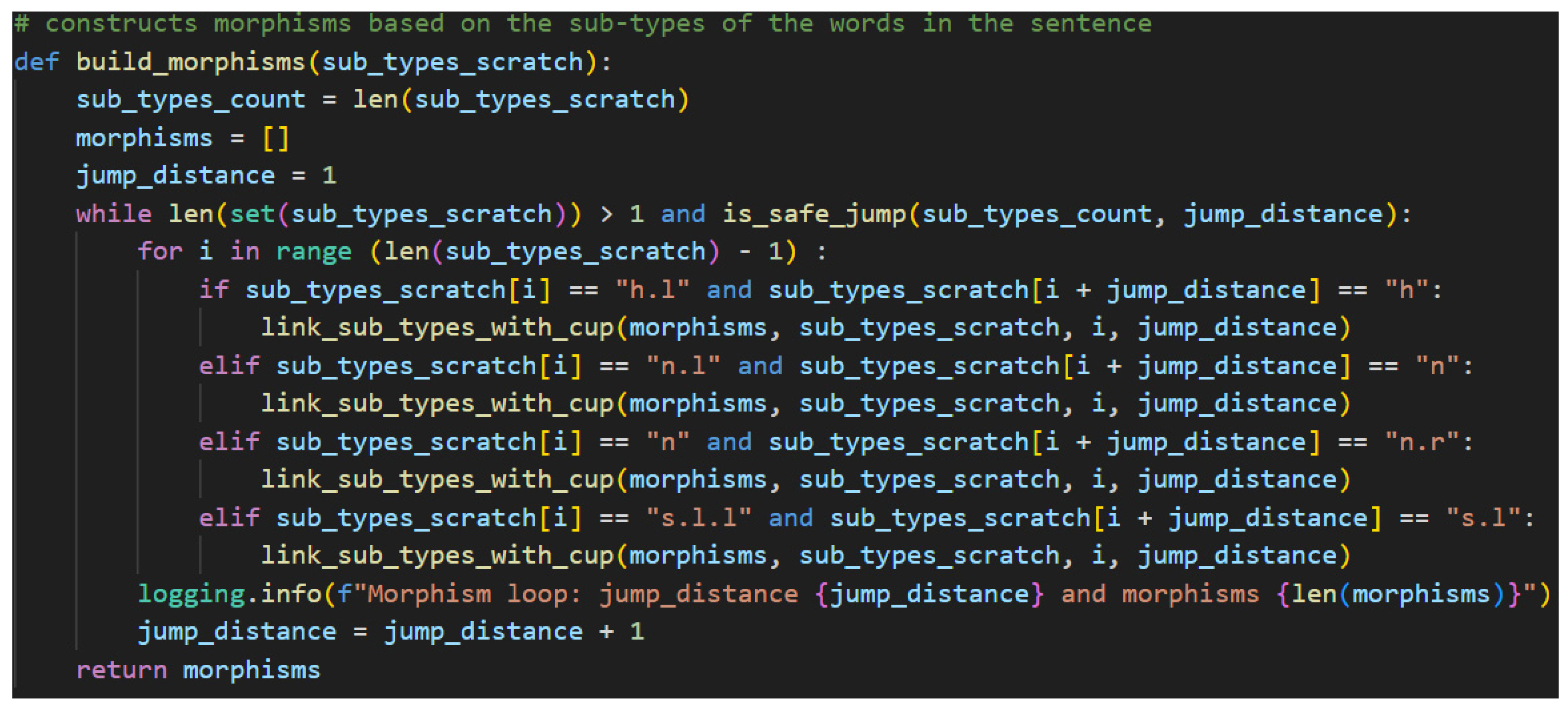
Constructing morphisms, also known as drawing cups, is the process of connecting pregroup types with their adjoints, which effectively simplifies them out of the larger calculation. In the end, again, only the s base type should remain unpaired.
The algorithm begins by collecting the length of the sub-types scratch list. It then defines a new empty list that will hold the morphisms—the
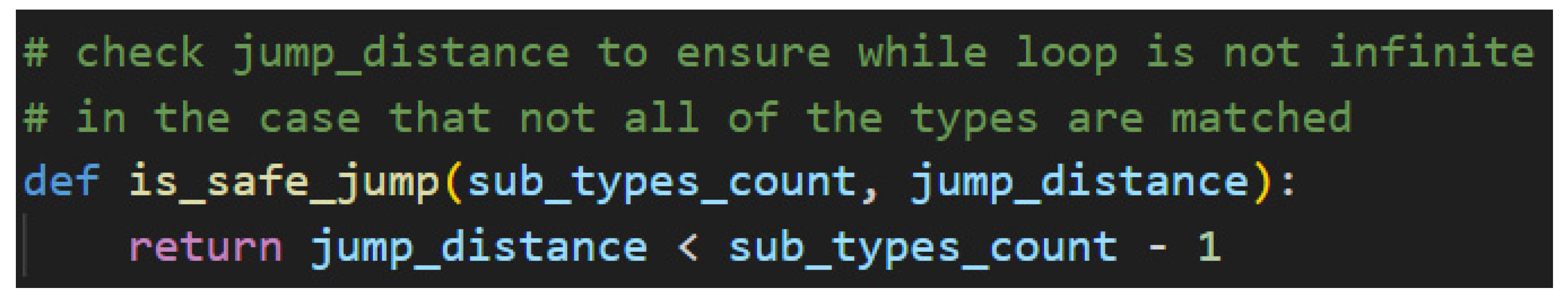
Cups in this case. The main logic of the algorithm requires nested loops, a for-loop inside of a while-loop. The outer while-loop is controlled by a counter that increments after the completion of an entire pass of the inner for-loop and by the contents of the sub-types scratch list. In the former case, the jump distance is passed to a helper function along with the sub-types count to confirm that the jump distance will not index beyond the maximum boundary of the list, as detailed in
Figure 52.
In the latter case, the contents of the sub-types scratch list case, the scratch list is passed into python’s set function, which returns the unique items of the list as a new list. In other words, it removes duplicate entries. This new list is then passed into the len function, which counts how many items are in the set. When that count is one, this means that all the sub-types have been marked True—all sub-types are either s or paired with the appropriate adjoint. This means the processing is complete.
The actual creation of the morphisms is done in the inner for-loop. For each item in the sub-types scratch list, there are several potential values the sub-type could take. Each of these is checked in an if-elif construct. Each case is controlled by the current indexed item in the scratch list, which has a value that pairs with another sub-type from the left. These, then, are either left-adjoints that pair with the base type (i.e.,
h.l to
h), base types that pair with right-adjoints (i.e.,
n to
n.r), or double left-adjoints that pair with single left-adjoints (
s.l.l to
s.l). If one of these valid pairing situations is found between the index and the index summed with the current jump distance, then a match has been found and it is time to construct a morphism. This is done with another helper method as shown in
Figure 53.
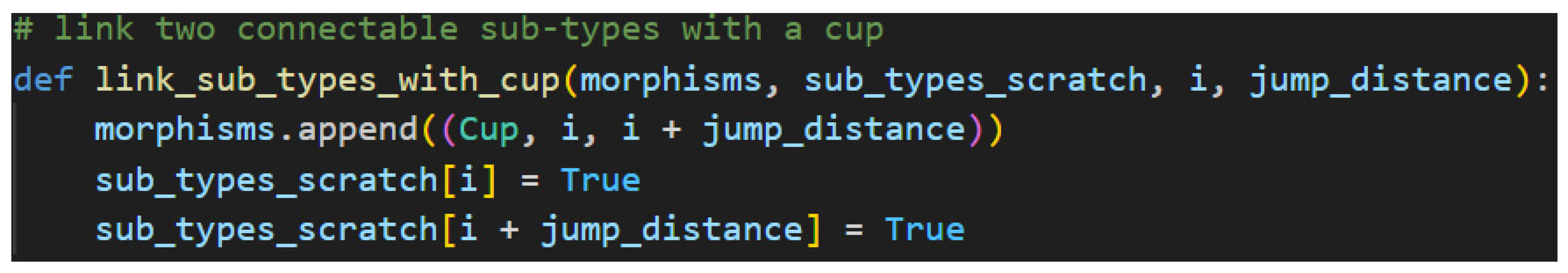
Figure 53.
Linking Sub-types with a Cup.
Figure 53.
Linking Sub-types with a Cup.
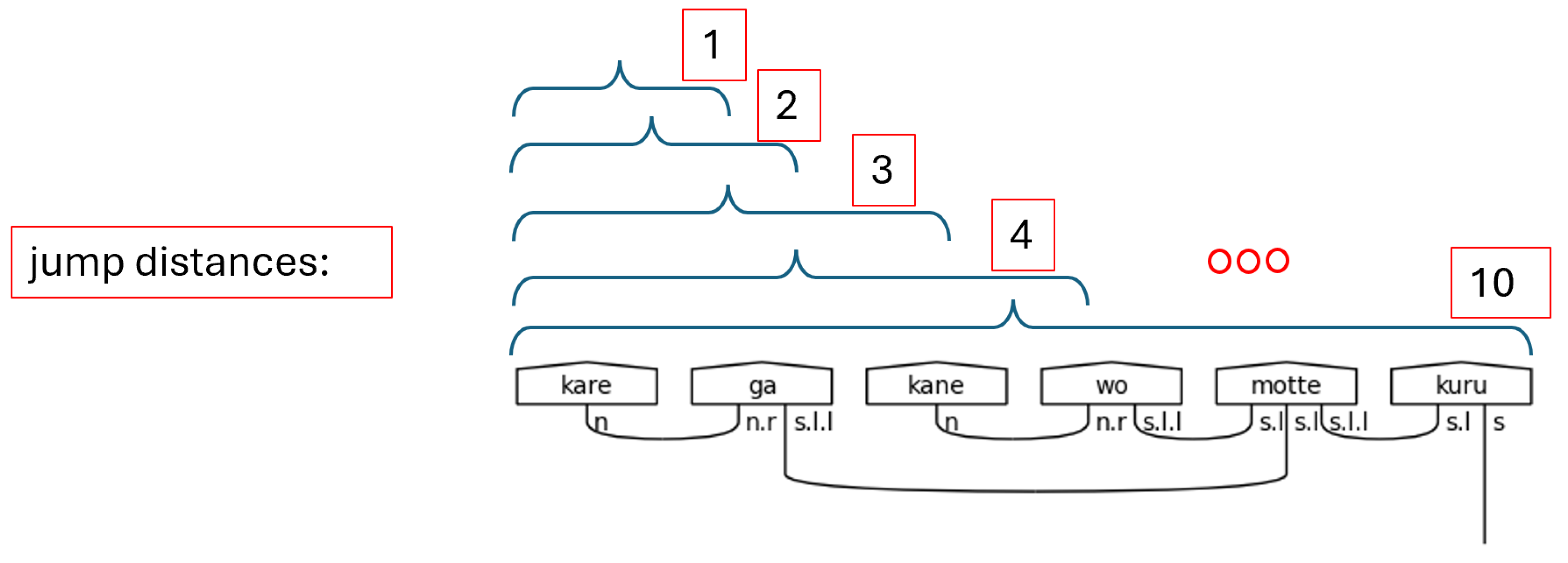
Figure 54.
Jump Distances Illustrated.
Figure 54.
Jump Distances Illustrated.
In
Figure 53, a morphism is first created using lambeq’s
Cups, the current index, and the sum of the index with the jump distance. This represents the sub-type found on the left-side of the sentence being linked to the compatible sub-type on the right-side. The newfound morphism is then appended to the morphism list, and the two linked sub-types are marked
True because they are now paired. Further iterations of the loop will ignore them. The process continues until the sub-types are all linked, which means all the necessary morphisms have been created, in worst case O(n
2) time.
Figure 55.
Sub-type Scratch Values While Passing Through the Loops of Step 7.
Figure 55.
Sub-type Scratch Values While Passing Through the Loops of Step 7.
Step 8. Now that the
Word list—the typed sentence—and the morphism list have been created and populated, all that remains is to draw the diagram. This is accomplished with a single line of code thanks to lambeq’s capabilities. That line is found in
Figure 56.
The typed sentence—a list of lambeq Words—and the morphisms—a list of lambeq Cups—are provided to create pregroup diagram static method of the Diagram class. At this point, the algorithm has fully prepared Japanese text aligned with the grammar model to be passed to lambeq, which performs all the drawing logic from here.