Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Fundamental Characteristics of the Sample Examined
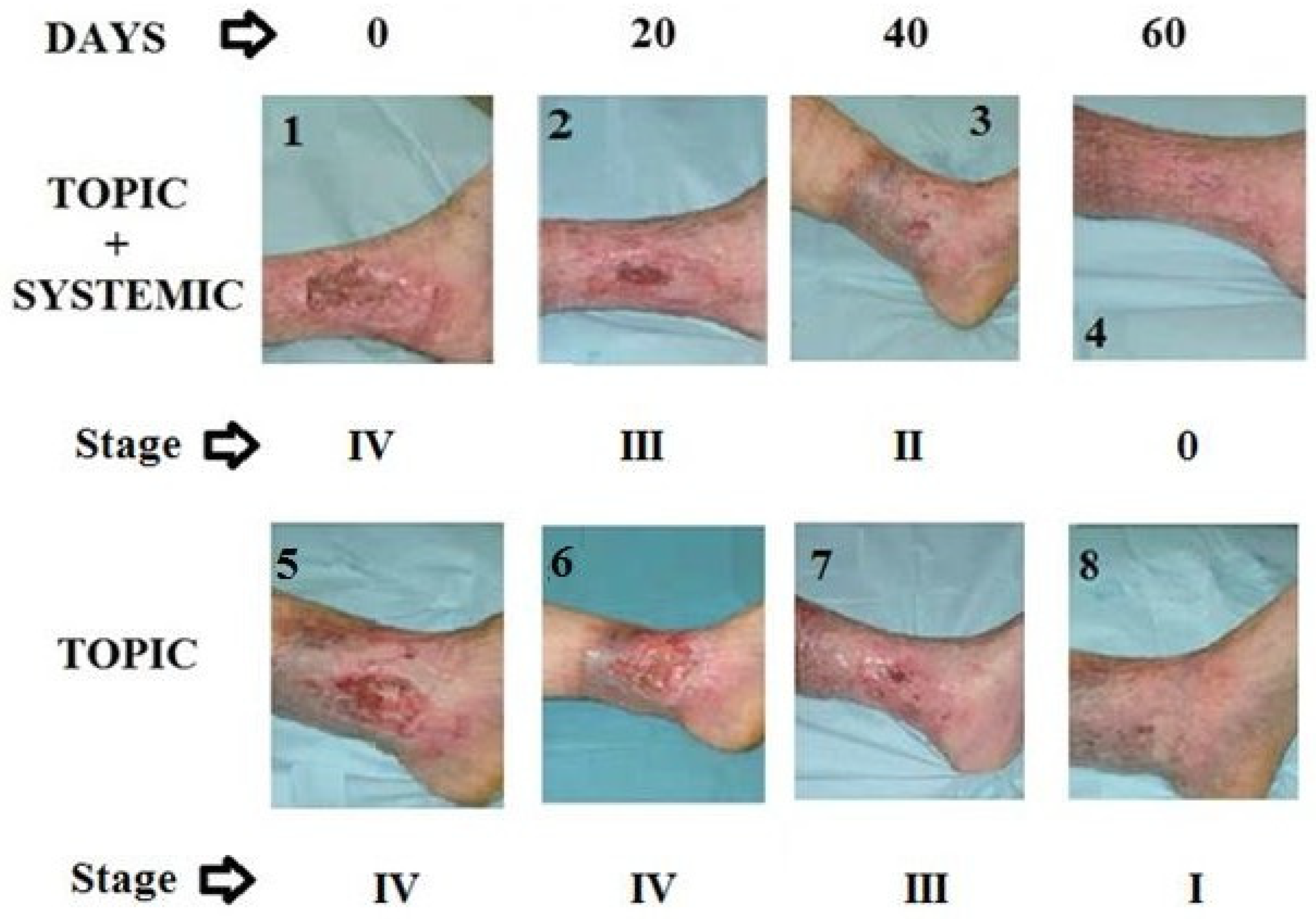
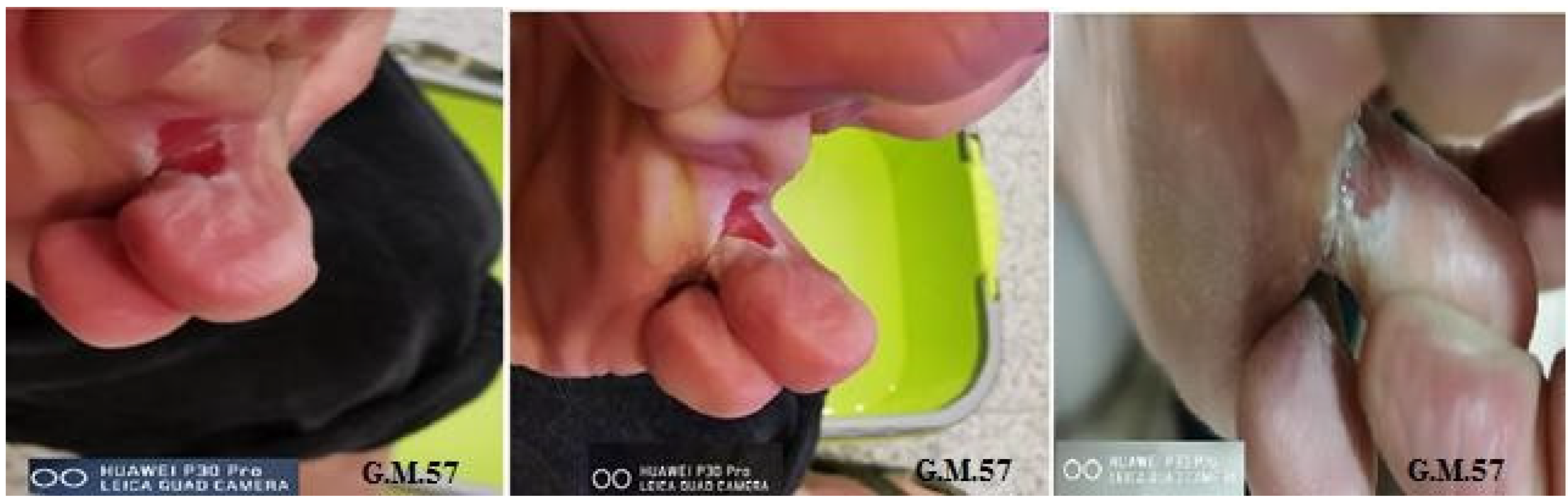
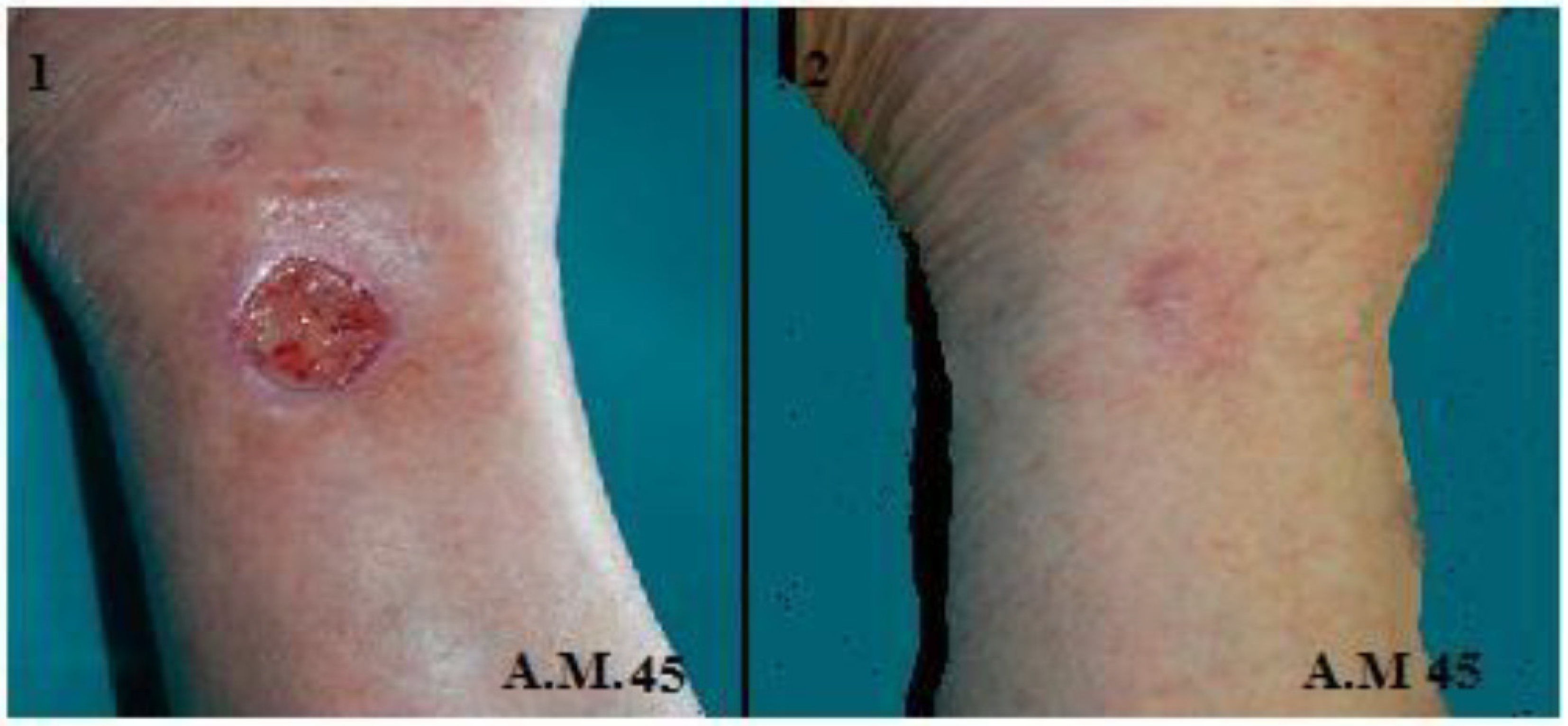
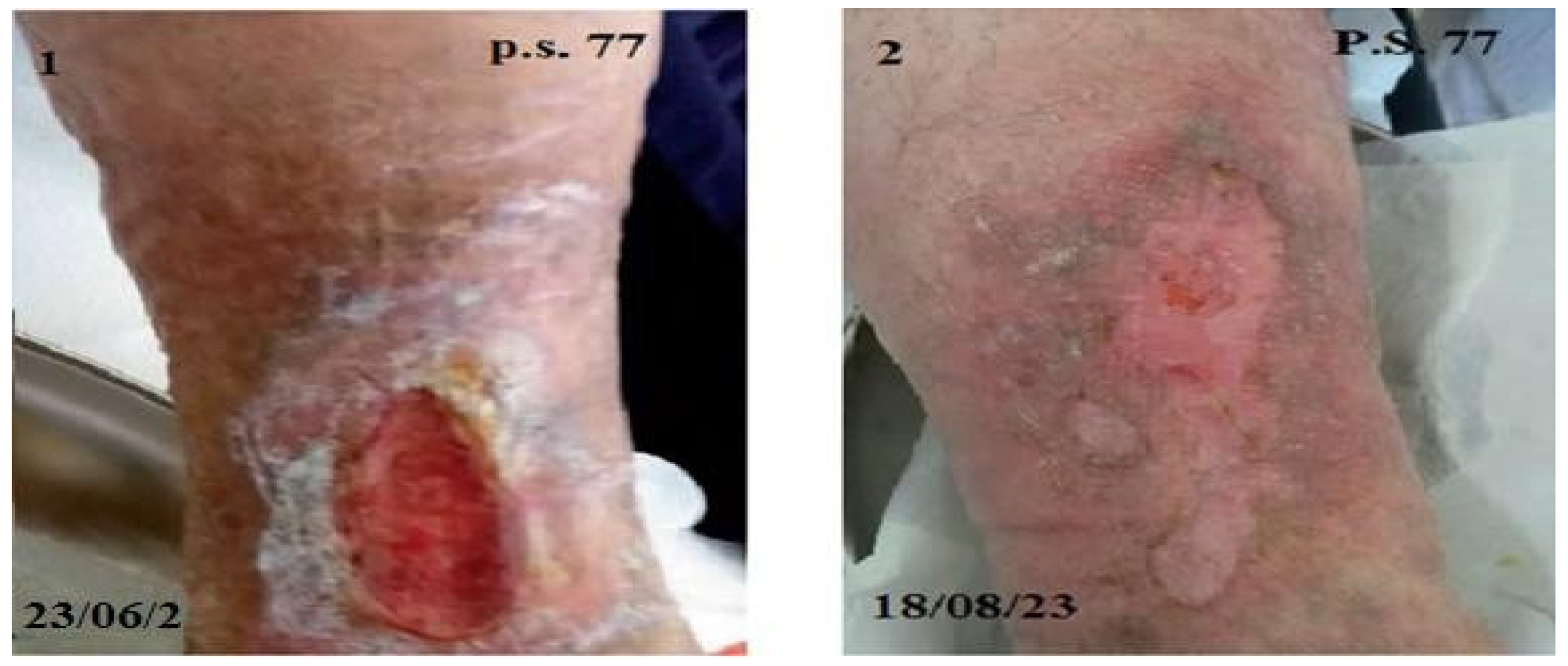
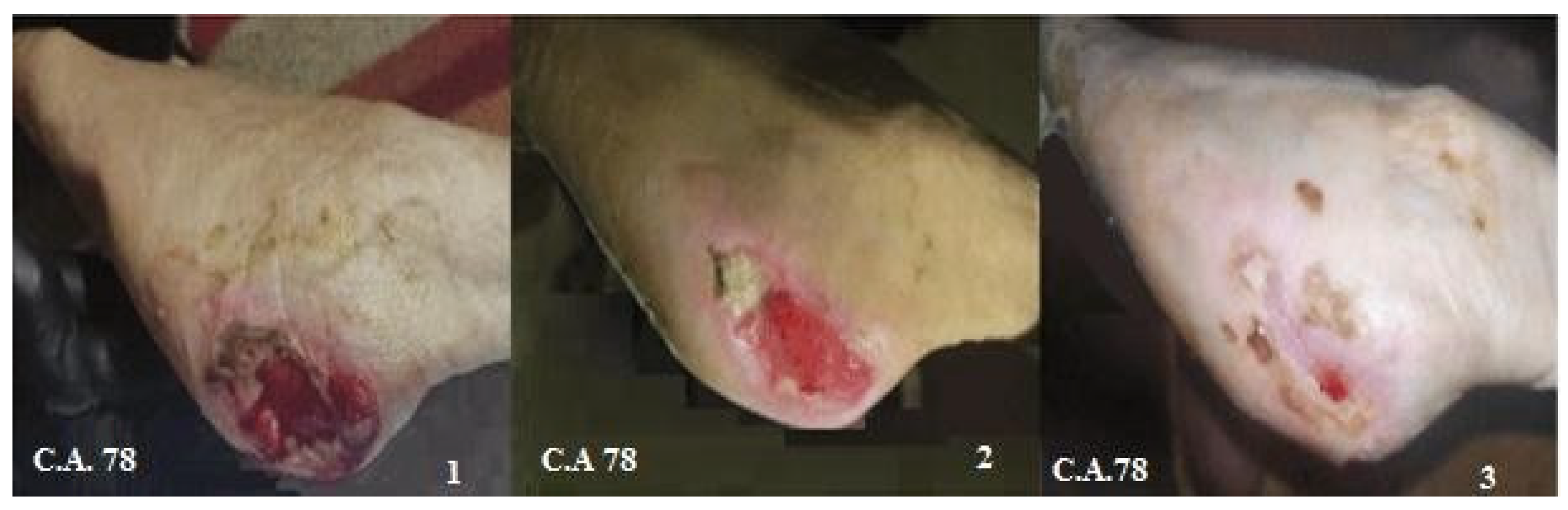
2.3. Metric Measurements and Photographic Monitoring
2.4. Percent Rate of Wound Contraction and Calculation of Linear Growth (Re-Epithelialization)
2.5. Citozym® Treatment Protocol
2.6. Re-Epithelialization
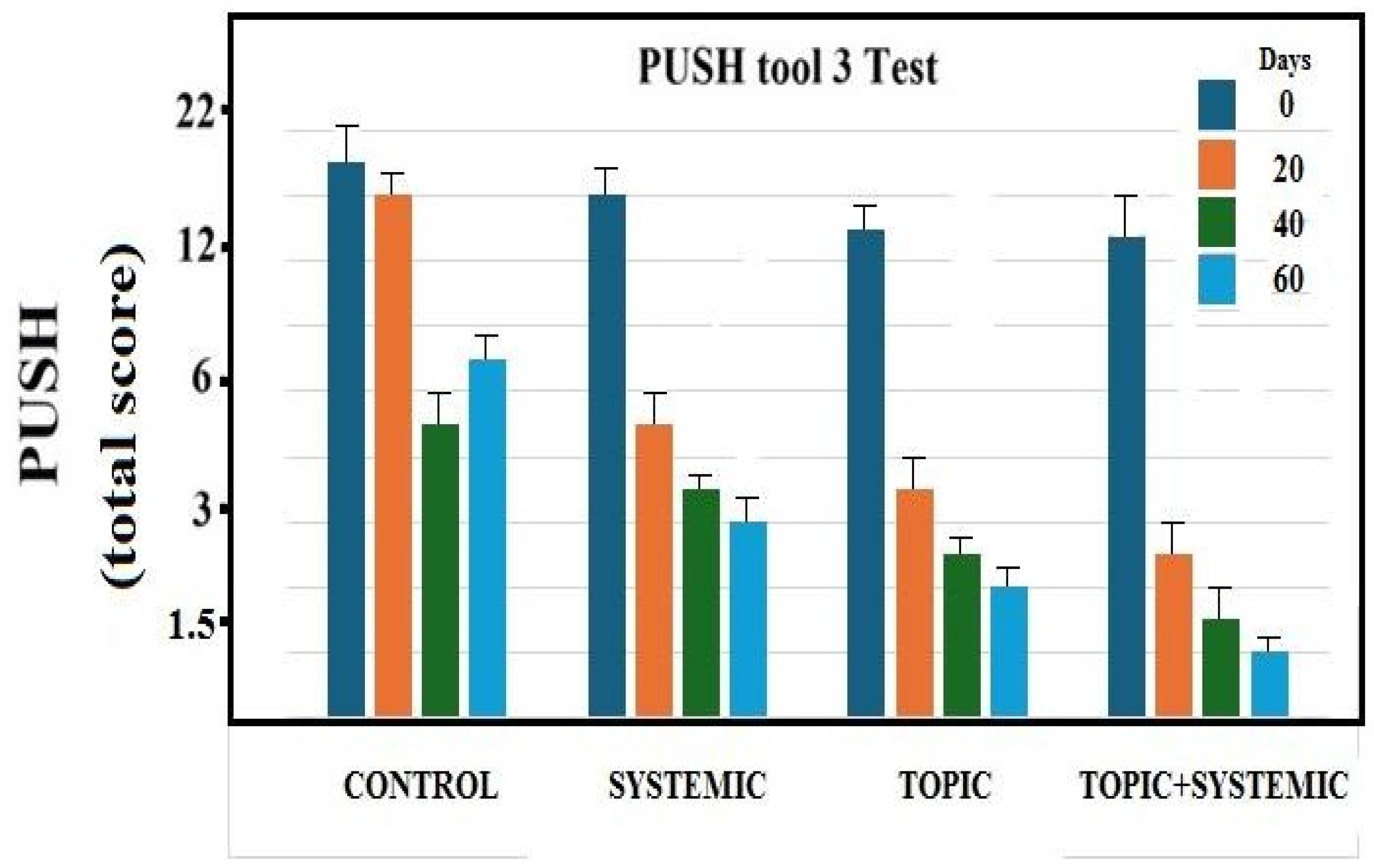
2.7. The Push Tool Test 3
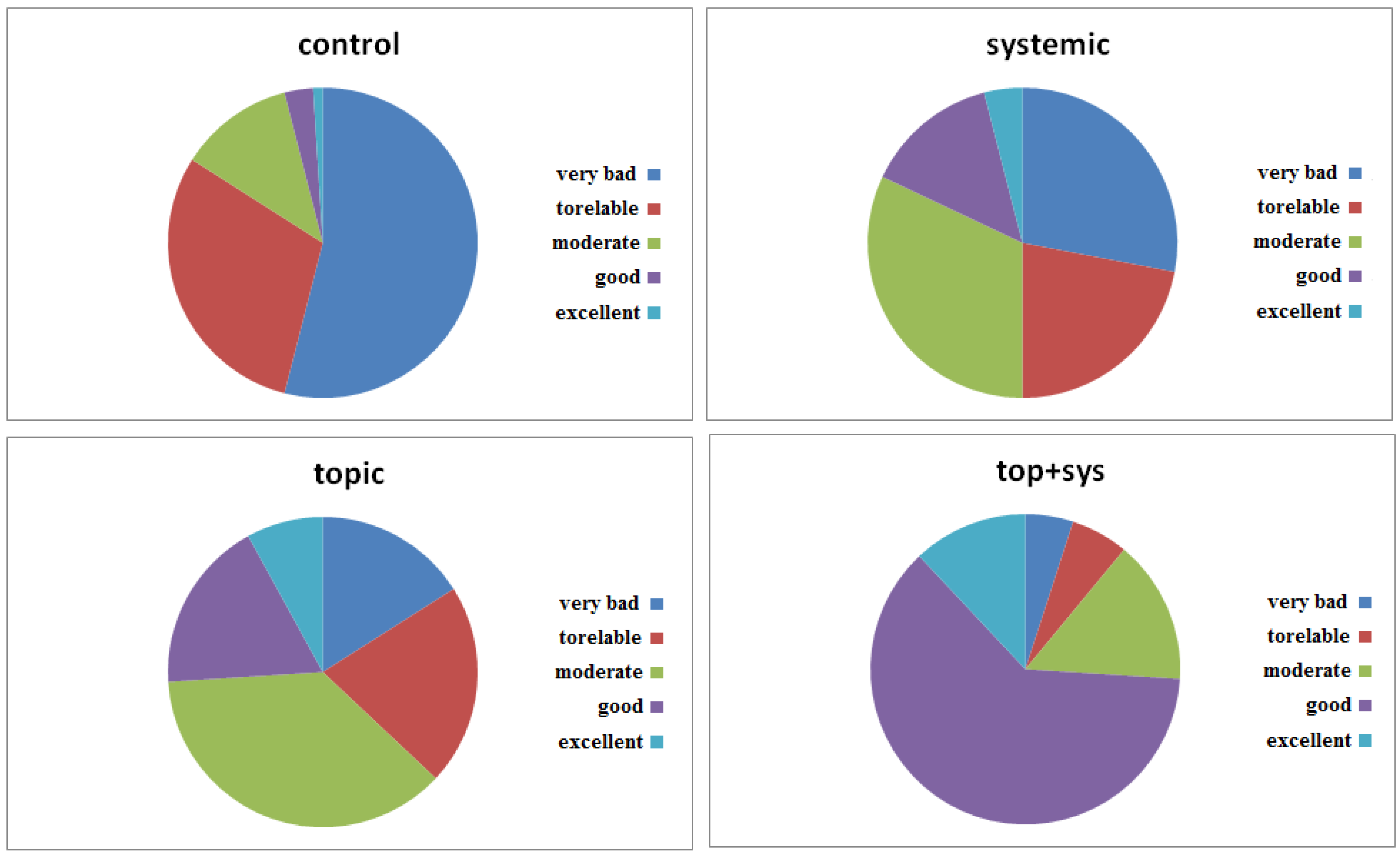
2.8. Quality of Life (QL)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
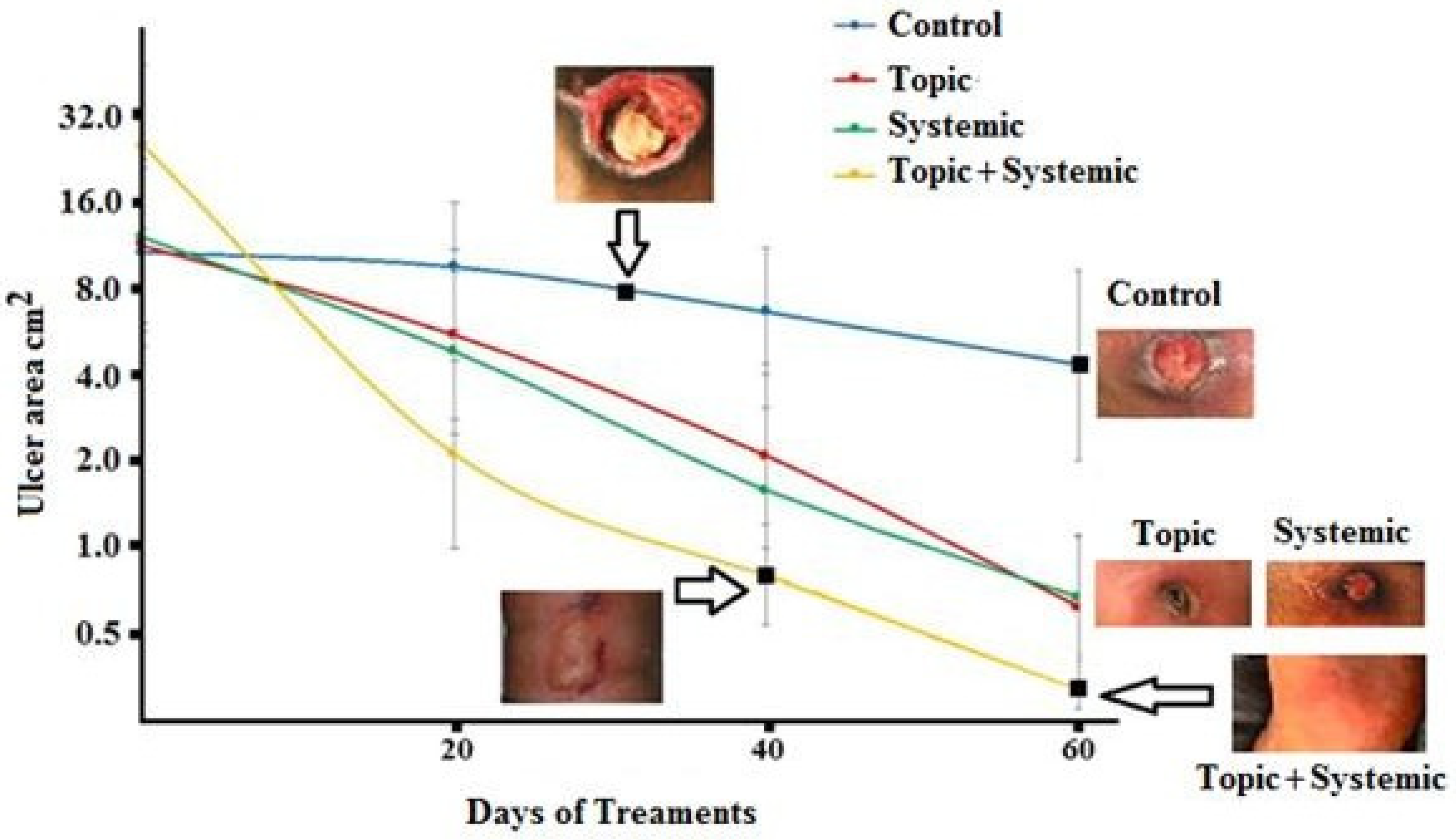
3.1. Re-Epithelialization
3.2. PUSH Score
3.3. Quality of Life (QL)
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klugarová J, Pokorná A, Hussain S, Vrbová T, Slezáková S, Búřilová P, Saibertová S, Dolanová D, Klugar M. Economic evaluations of interventions for the prevention and treatment of PU: an umbrella review protocol. JBI Evid Synth. 2022, 20(2):633-639.
- Hill JE, Edney S, Hamer O, Williams A, Harris C. Interventions for the treatment and prevention of PU.Br J Community Nurs. 2022 ;27(Sup6):S28-S36.
- Lyu Y, Huang YL, Li ZY, Lin F. Interventions and strategies to prevent medical device-related pressure injury in adult patients: A systematic review. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32(19-20):6863-6878.
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure Ulcers: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(4):881-890.
- Headlam J, Illsley A. Pressure Ulcers: an overview.Br J Hosp Med (London). 2020:2;81(12):1-9.
- Rajkumar J, Chandan N, Lio P, Shi V. The Skin Barrier and Moisturization: Function, Disruption, and Mechanisms of Repair. Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;36(4):174-185.
- Jaul E. Assessment and management of PU in the elderly: current strategies. Drugs Aging. 2010;27(4):311-325.
- Palmieri B, Vadalà M, Laurino C. Nutrition in wound healing: investigation of the molecular mechanisms, a narrative review. J Wound Care. 2019 ;28(10):683-693.
- Brunner S, Mayer H, Qin H, Breidert M, Dietrich M, Müller Staub M Interventions to optimise nutrition in older people in hospitals and long-term care: Umbrella review. Scand J Caring Sci. 2022;36(3):579-598.
- Kremer M, Burkemper N. Aging Skin and Wound Healing. Clin Geriatr Med. 2024;40(1):1-10.
- Ferorelli P., Antonelli F., Shevchenko A., Mischiati C., Doepp M., Lenzi S., Borromeo I. Feriotto G., Beninati S. Reduction in fatigue symptoms following the administration of nutritional supplements in patients with multiple sclerosis. Med Sci (Basel). 2021;9(3):52-58.
- Gardner SE, Hillis SL, Frantz RA.J A prospective study of the PUSH tool in diabetic foot ulcers. Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2011;38(4):385-393.
- Haraldstad K, Wahl A, Andenæs R, Andersen JR, Andersen MH, Beisland E, et al.; A systematic review of quality of life research in medicine and health sciences. LIVSFORSK network. Qual Life Res. 2019;28(10):2641-2650.
- Hyun S., X. Li, Vermillion B., Newton C., Fall M., Kaewprag P., Moffatt-Bruce S., MD, and Lenz E.R. Body Mass Index and Pressure Ulcers: Improved Predictability of Pressure Ulcers in Intensive Care Patients. Am J Crit Care. 2014,23(6): 494–501.
- Butcher N.J, Monsour A., Mew E.J., et al. Guidelines for Reporting Outcomes in Trial Protocols: The CONSORT-Outcomes 2022 Extension. jama. 2022;328(22):2252-2264.
- Butcher NJ, Monsour A, Mew EJ, Chan AW, Moher D, Mayo-Wilson E, Terwee CB, et al.. Statement of the European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel--pressure ulcer classification: differentiation between PU and moisture lesions. JAMA. 2022;328(23):2345-2356.
- Edsberg LE, Black JM, Goldberg M, McNichol L, Moore L, Sieggreen M. Revised National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel Pressure Injury Staging System: J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2016 Nov/Dec;43(6):585-597.
- Bártolo I, Reis RL, Marques AP, Cerqueira MT. Keratinocyte Growth Factor-Based Strategies for Wound Re-Epithelialization.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Jun;28(3):665-676.
- Pastar I., Stojadinovic O., Yin, N.C. et al. Epithelialization in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. 2014, 3(7):445-464.
- Felce D, Perry J. Quality of life:its definition and measurement. Res. Dev. Disa. 1995,16(1):51-57.
- Rodrigues M, Kosaric N, Bonham CA, Gurtner GC. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):665-706.
- Gould L.J., Jenny Alderden J., Rummana Aslam R. et al. WHS guidelines for the treatment of pressure ulcers-2023 update. Wound Repair Regen. 2024. 32(1):6-33.
- Marhoffer W, Stein M, Mäser E, Federlin K. Reduced phagocytic capacity of circulating granulocytes in diabetes mellitus. Immun Infekt. 1992;20(1):10-2.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




