1. Introduction
The design and construction of low-carbon and energy-efficient houses can have significant challenges during various phases of the project, especially in regions where the concept is still relatively new and unfamiliar (Souaid, C., Van der Heijden, H., Elsinga, M., 2022), and where the design and construction involves a unique set of considerations, such as finding qualified and motivated engineers, complying with regulatory frameworks, managing the material and supply chain, and dealing with the special construction requirements for these types of building (Pitts A. , 2017).
The purpose of this research paper is to shed light on these barriers, and to provide insights into the experience of the stakeholders engaged in the design and permitting of the Everly House, also known as the Caja House, in Fayetteville Arkansas, which has been designed as a multi-story multi-generational low-carbon Passive House. By examining these barriers and their potential solutions, this study seeks to contribute to the development of strategies and recommendations that can facilitate the design and permitting process for future Passive House projects in a similar context.
2. Literature Review
The Passivhaus standard is generally defined as a low-energy building that achieves indoor thermal comfort (Dequaire, 2012). This concept was developed in Europe by the end of 1988 by Wolfgang Feist from Germany and Bo Adamson from Sweden (Moreno-Rangel, 2021). The design of the first Passivhaus was established in 1991 resulting in a super-insulated building (Christina J. Hopfe, Robert S. McLeod, 2015). The concept was formulated according to Passivhaus standards that are reviewed through the Passivhaus Institute (PHI,) an internationally recognized research institution that was established in 1996 to provide the guidance, design, and certification of houses meeting the performance standards (Pitts A. , 2017). In North America, the Passive House Institute (US PHIUS) also provides certification and requires the use of PHIUS Standards for building energy modeling. Originally part of PHI, PHIUS was established to tailor the standards to North America Climate. A break in the agreement resulted in the two institutions providing for separate Passive House certification in North America ( Pierson, R., Paquin-Béchard, C, 2021) with differences in criteria for heating and cooling, air tightness, energy, and the energy modeling tools (AUROSGroup, n.d.). For the modeling tool, PHIUS uses Wärme Und Feuchte Instationär (WUFI) Passive while PHI uses the Passive House Planning Package (PHPP) as an informing tool for project certification. The decision to choose one of these options for the Passive House certification solely depends on the architect, engineer, and owner.
The US Department of Energy (DOE) defines an NZE building as an energy-efficient edifice that generates as much or more energy than it consumes over a year through onsite renewable energy sources (ASHRAE, 2018), resulting in a net zero balance of energy use and emissions (Marszal, A. J., & Heiselberg, P., 2009). The design of a NZE building demands the implementation of specific energy performance strategies, design concepts, and technologies (Shambalid Ahady, Nirendra Dev, Anubha Mandal, 2019)The measurement and classification of NZE performance varies, contributing to common challenges and barriers encountered during the implementation of NZE building projects (Heffernan, Emma Elizabeth; Pan, Wei; Liang, Xi; and De Wilde, Pieter, 2013). These challenges result from multidimensional factors that are related to technical knowledge and expertise of professionals, efficient project management, project cost implications, policies and regulatory requirements and dealing with market barriers (Hafez, F. et al., 2023).
Research conducted in both developed and developing countries have identified many challenges in implementing sustainable building practices that are related to cost, timing, regulations, knowledge gap, and lack of incentives and support (Darko, A., Chan, A., 2017). For instance, a recent study conducted in New Zealand about the slowdown in construction of NZE buildings concluded that legislations and policies are the main challenges in incentivizing and encouraging the adoption of these types of buildings while the impact of financial and technical challenges are limited (Daryl Cielo, Alison Subiantoro, 2021). The challenges, however, can be different among countries, cities, and states. For example, study conducted in Nigeria found that the main challenges to adopting sustainable construction practices are related to the lack of experience among professionals, lack of clear strategies to promote sustainable constructions, and lack of demand among different stakeholders to adopt sustainable construction (Daniel, E I, Oshineye, O and Oshodi, O, 2018).
As other examples, a study conducted in southern Europe has highlighted technical and social challenges in implementing Nearly Zero-Energy Buildings (NZEB) (Attia, S. et al., 2017), and, -a study in Portugal found that the main obstacles to implementing the Passive House concept were related to a lack of knowledge among building industry technicians and key actors (Figueiredo, A., Rebelo, F. et al., 2020).
The literature review highlights eight categories of barriers and challenges that affect the project implementation phases. The first phase is comprised of the issues arising during the project inception period and includes cultural and social constraints and project management (Hafez, 2023; Daniel, 2018). The second phase, or preconstruction phase, covers design and permitting, and includes the technical challenges, knowledge gap, legislative and regulatory barriers, and financial constraints (Attia,2017; Daniel,2020; Fiueuredo,2020; Karji,2020). During the last phase or the construction work, delays are caused by barriers arising from knowledge gaps and project management (Hakkinen,2011; Karji,2020).
Results of the literature review highlighting the common barriers and challenges (CBC) to sustainable buildings including Passive Houses and NZE buildings are summarized in the
Table 1.
3. Methodology
Everly Passive House is the case study under investigation for the specific challenges and barriers faced during the preconstruction phase. The triangulated approach combines the use of data from multiple sources, among them the literature review, direct observations, and open-ended interviews (Turner, S., Cardinal, L., Burton, R., 2017). These collections of data enhance the validity and reliability of the findings by corroborating information across multiple sources.
-
a)
Literature Review
A systematic approach is followed to ensure a rigorous and comprehensive literature review. The review process is focused on the discovery of scientific documents that specifically identify the challenges faced during the preconstruction and construction of sustainable buildings. These documents are then screened based on relevance to the research topic and included for detailed analysis. Next, the identified challenges are categorized and segregated according to recurring themes. A combination of keyword searches and database filters are used to identify relevant articles. The search criteria include terms such as "barriers to sustainable building design", "challenges in sustainable building permitting", "obstacles in sustainable construction," and related variations.
-
b)
Interviews
Interviews were conducted (see Appendix A for interview questions) and the key barriers are identified and categorized, and themes are analyzed based on the frequency of response including the issues that are consistently reported by multiple stakeholders-based categories and themes (Bryman, 2015). T hemes are weighted based on their observed impact on project time and goals, and the elements represent the factors contributing to each identified barrier. Selected comments and quotations from the interviews are included in the analysis to provide a richer understanding of the identified barriers. These direct quotes serve as supporting evidence and offer firsthand perspectives and insights from the respondents (Lorelei Lingard, Christopher Watling, 2021). The comments and quotations are selected to represent a range of perspectives and to highlight the challenges faced during the preconstruction phase.
The interviews are directed at city officials, engineers, and architects engaged in the Everly house preconstruction phase, as well as the owner. The interviewees include the structural and mechanical engineers (E1 and E2), two architects from the architectural firm (A1 and A2), and two official representatives from the city of Fayetteville (R1 and R2), in addition to the owner who also acts as the main contractor of the house. Follow-up questions are also shared with some participants for clarification and requesting additional information for the study. The interview questions are conceived to capture the interviewees’ viewpoints and experience on the design and permitting of this house as well as their experience as professional bodies and regulatory agencies on the challenges and barriers to implementing sustainable buildings in fast-growing cities.
-
c)
Direct observation
In addition, the research is based on direct observation to gain insights into the process of developing similar projects as well as to understand common challenges faced during the preconstruction of Everly House. The observation period spanned from August 2022 to May 2023. During this period, the author closely observed the design and permitting process through direct engagement with the project owner. This engagement consisted of weekly meetings, recorded in written meeting notes, which included progress updates, decisions made, and discussions.
Additionally, a collaboration folder between the owner and the architectural firm is shared by the project owner with the author. . The folder includes project architectural, mechanical, and structural design plans and material data sheets. This folder serves as an essential source for project documents during the follow-up period and represents a primary source of data for analysis.
Relevant documents, such as mechanical design reports, structural design calculation notes, WUFI Energy simulation reports, permit draft documents, and relevant regulations such as Energy Fayetteville, AR Code of Ordinances, are reviewed to supplement the observation data.
4. Results
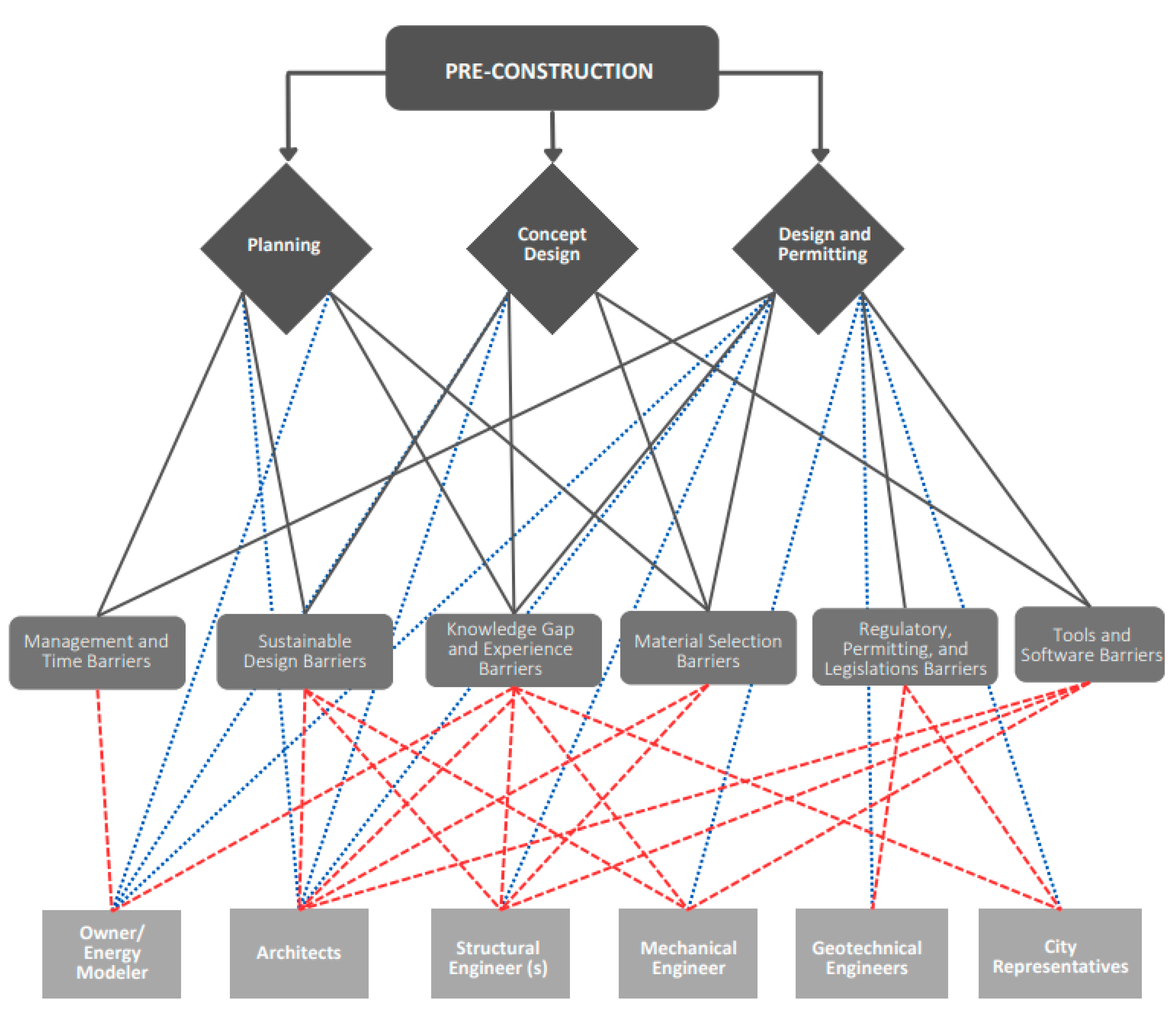
The barriers can be summarized into six main categories, which were highlighted by the interviewees and observed during the follow-up period. The six categories include 20 barriers faced at different stages, where each barrier is represented as a theme, themes are related to elements representing factors causing these challenges depending on the nature of the barrier, these elements are used to develop recommendations to overcome these barriers.
Table 2 is a summary of the categories, themes, and elements along with weighing these barriers based on their impact on the project timeline ranking from low to high impact barriers., and the frequency of times it is mentioned in the interviews.
The preconstruction phase of the Everly project has three main stages: planning, conceptual design development, detailed design and permitting (Widjaja, 2016). The barriers are not isolated to one stage but do rather overlap, interact, and result from the difficulties or gaps encountered by the various stakeholders involved in the project. To provide an understanding of the relationship between project participants, project stages, and identified barriers, a diagram has been developed (
Figure 1). This diagram briefly explains the relationship between project participants, the three main stages during the preconstruction phase, and the main barriers encountered in these stages.
5. Management and Time Barriers
“A lot of changes came but not all at one time so there were many iterations which made us constantly need to reevaluate how we are meeting the standards, “said A1, a sentiment echoed by E1, “One should get a schematic plan in front of the permitting people as early as possible and to get everyone on board as early as possible."
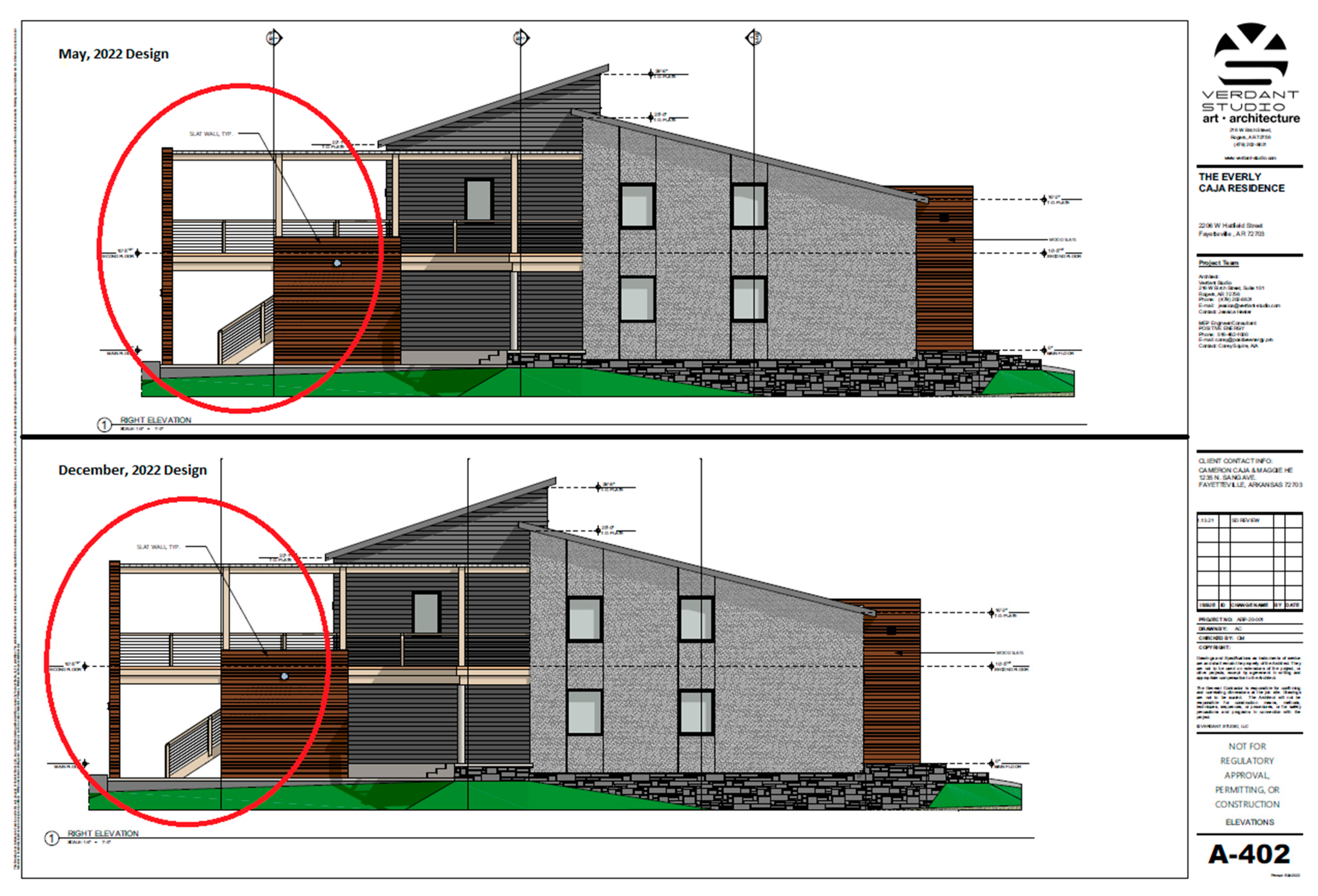
For example, the design of the Everly House changed substantially in response to the discovery of zoning requirements for property in a flood plain that required raising the residential quarters a minimum of 0.6 m from the surface (
Figure 2). Moreover, WUFI modeling of the original design revealed the need for additional shading and insulation to meet Passive House energy goals (
Figure 2).
Challenges associated with management and time are common among sustainable building projects across the construction project phases (
Table 1, e.g., Timing and Managerial Constraints). The Everly House faced similar challenges during the preconstruction phase, and one key barrier that had the highest impact on this project was the lack of an integrated design approach among architectural, structural, geotechnical, mechanical, and sustainable building designs that resulted in multiple design revisions. The inadequacy of coordination was mentioned several times by the design professionals during their interviews, indicating a recurrent theme. A1, for example, noted the multifaceted nature of design alterations stemming from diverse factors such as project location, structural modifications, and regulatory requisites.
To overcome this barrier, it is important to establish clear lines of communication and coordination between architects, structural engineers, geotechnical experts, mechanical engineers, and sustainable building designers from the very early stages of planning. Regular project meetings coupled with the comprehensive documentation of decisions foster alignment amongst all stakeholders with the overarching project vision and objectives. Ultimately, this approach can reduce the number of design revisions, and reduce the project timeline.
6. Sustainable Design Barriers
"We seemed to be looking at the design process from two different directions, “said the owner. In parallel, E2 pointed out that "The impact of design decisions and assumptions is greater than that of any specific tool in Mechanical Engineering and Plumbing (MEP) systems. These systems have historically been oversized due to outdated rules of thumb and dynamic design conditions.”
For example, there is a difference between conventional design and Passive House design assumptions for the thermostat settings. The conventional thermostat setting, initially used in the design of the Everly Passive House is set between 21 and 24 degrees Celsius (70- and 75-degrees Fahrenheit), however, the Passive House paradigm mandates a much wider range of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). The indoor design temperature assumption affects the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, leading to oversizing due to disparities in thermal requirements, where heating transmission load increases and cooling transmission load decreases when increasing indoor design temperature (Ozel, 2016). for the final design (?), the heating load estimated through WUFI was approximately 17,141 Btu/hr while the estimated value through Hourly Analysis Program (HAP) was 14,321 Btu/hr, while the cooling load estimated through WUFI was approximately 7,737 Btu/hr, and the estimated sensible and latent cooling loads calculated in HAP were 21,991 Btu/hr and 1640 Btu/hr, respectively.
Designers and engineers, by and large, prefer conventional design and material over sustainable design approaches (
Table 1, Development and Evaluation and Technical Challenges). The common barrier illustrated in the above example is the lack of alignment between design decisions and the project vision and objectives, which results in suboptimal or incompatible design solutions.
Another barrier stems from the lack of integration between architectural design, HVAC systems, and structural design, hindering the quest for optimal energy efficiency. For example, Passive House design (?) assumes the infiltration in the HVAC design in all zones to be negligible due to tight construction, however, real-world observations reveal a significant disparity between this assumption and the physical setting, where infiltration occurs through cracks in building envelopes and through natural ventilation caused by opening doors and windows, which allows outdoor air to enter. (K. Gowri,D. Winiarski, R. Jarnagin, 2009). These examples emphasize how such differences in design assumptions can lead to significant effects on system efficiency and energy consumption.
7. Regulatory, Permitting, and Legislations Barriers
"Additionally the house design doesn’t meet the typical design requirements stated in the fire code for single house, and it was considered a Triplex that requires additional modification to meet standards,” said R1, and "The codes are not written to address Passive [House] design explicitly,” according to R2, who also noted that "The State of Arkansas does not give us much ability to regulate building materials for single-family homes in our zoning codes."
Even though adopted regulations and policies related to sustainable building design differ among countries, states, and cities (Daniel, E I, Oshineye, O and Oshodi, O, 2018), regulatory barriers remain common among different projects. The analysis identified several barriers related to regulatory frameworks, permitting processes, and legislative aspects. The inadequate integration of energy efficiency, carbon reduction, and sustainable building design standards within building codes and urban planning regulations emerged as a critical barrier. As highlighted by R1, this barrier of code non-compliance causes design modifications and delays in permitting. Even though these codes are not directly related to energy or carbon reduction, they, however, affect the shape and physical layout of the house originally decided based on sustainable design principles such as building orientation, number of floors, and internal loads, in addition to carbon reduction and ecological footprint principles that are related to the type of foundation, structural design, type of material used in addition to the building layout.
The absence of specific and clear guidance on sustainable building design requirements in the existing building codes can lead to uncertainty among project designers to integrate sustainable building practices into their projects and can also result in lack of interest in designing for energy saving and carbon reduction. This gap highlights the need to advocate for adopting updated building energy codes and provide consistency and standardization through including clear requirements and guidance to make informed decision and align the design with code requirements as well as sustainable building practices (Darko, A., Chan, A., 2017).
8. Knowledge Gap and Experience Barriers
"The lack of literature and experts who knew about these systems made our task more complex," said E2, and A2 pointed out, "Most of the challenges faced during this [preconstruction] phase is primarily rooted in a general lack of experience in this region with Passive House design and the technologies being used in this house.”
A similar observation was made by the structural engineer (E1) regarding the challenges associated with nontraditional design approaches to reduce the carbon footprint such as the limited use of concrete structures in the project, as well as vertical capacities that include the use of fiberglass composite posts instead of using traditional materials like steel and concrete, and lateral capacities that use bracing systems to enhance lateral stability or hybrid systems such as glulam beams and timber for lateral bracing. (He,M., Li, M., Li, Z. et al., 2021) (Zhang X, Xuan L, Huang W, Yuan L and Li P , 2022) .This lack of familiarity with advanced design strategies and technologies affects the delivery of design drawings in addition to several tradeoffs that increase the carbon footprint and oversize the structural beams.
Challenges associated with the knowledge and experience of professionals engaged in the design and implementation of sustainable building projects are another common barrier among similar projects (
Table 1, Knowledge Gap). One barrier identified in this study is associated with the gaps in knowledge and experience among design professionals. The lack of expertise and knowledge not only increases the pressure on designers to conduct extensive research but also affects their willingness to embrace innovative approaches during the design phase.
There have been other identified barriers associated with knowledge gaps and experience categories that had a moderate impact on the project and their effect were mainly on the project timeline, these barriers included the lack of awareness and understanding of available energy-efficient technologies such as the passive house concept and energy efficient HVAC systems and difficulty in translating theoretical knowledge into practice and was also highlighted by the architects and engineers. Addressing these barriers requires training architects and engineers on sustainable design practices, energy-efficient technologies, and best practices to enhance their knowledge and expertise and, utilizing knowledge-sharing platforms and resources to enhance designers' awareness and understanding of available energy-efficient technologies and practical design solutions.
9. Material Selection and Supply Chain Barriers:
Although material selection and supply chain are not highlighted and they are mostly associated with cost, material information and decision-making process during the design process (Akadiri, 2015).
One of the challenges that this research identified is the lack of affordable and sustainable building materials within the local market. Specifically, materials such as hemp wool, cork, and rock wool, which hold immense promise for reducing carbon footprint are not widely accessible. For example, cork was a material that had these qualities, but it was difficult to import due to supply chain disruptions and high costs. This means that the designers and owner had to spend a lot of time searching for suitable materials to meet the criteria of low carbon footprint, Passive House standards, and energy efficiency. This resulted in some compromises in the original envelope material selection and trade-off in the amount of carbon reduction and energy savings without affecting the Passive House thermal enclosure requirements for assemblies, which were thermal resistance values (R-values) of roof 11.27-15.15 m
2.K/W (64-86 hr ft² °F/Btu), above-grade walls, overhanging floors 5.64-8.46 m
2.K/W (32-48 hr ft² °F/Btu) and below grade walls and floors 2.82-4.23 m
2.K/W (16-24 hr ft² °F/Btu) (Phius, 2021).
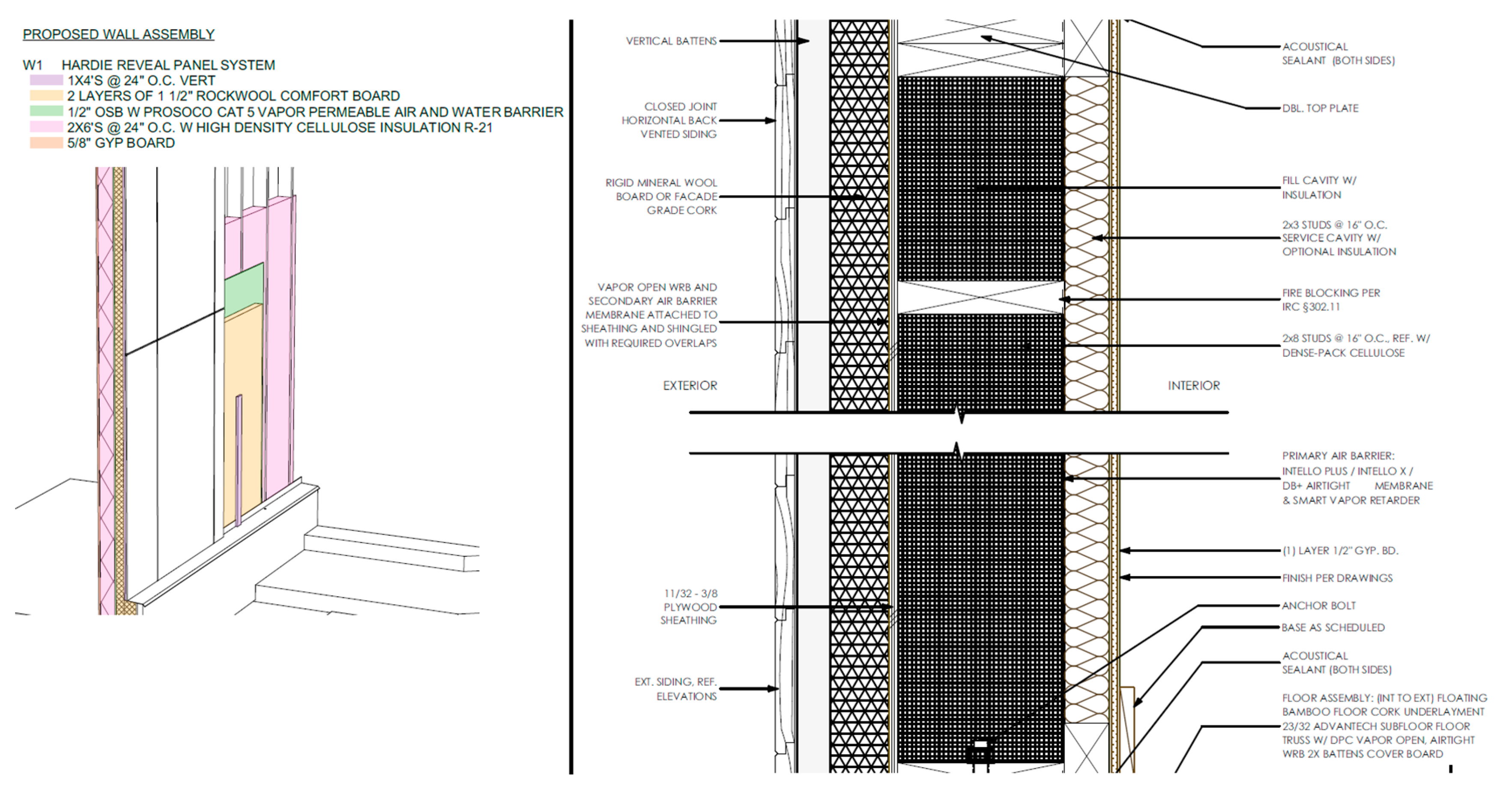
Figure 3 illustrated two wall section changes that occurred between May 2022 and August 2022 due to design changes and estimation of the carbon footprint associated with envelop assembly.
The following table provides detailed information on the thermal characteristics of three different envelope assemblies that were used in the WUFI Energy model of the Everly House. The name of each assembly, its thermal resistance (R-value), heat transfer coefficient (U-value), and thickness (inches) are indicated for the wall, roof, and floor/slab components. These values indicated that all selected building envelopes meet the building’s insulation requirements.
Table 3.
Thermal Performance Characteristics of Different Envelope Assemblies.
Table 3.
Thermal Performance Characteristics of Different Envelope Assemblies.
| |
Wall |
Roof |
Floor/Slab |
| Envelope Assembly 1 |
Name |
12"R22 Nexcem with 1.5"Mineral Wool |
16"TJI with DPC w 5/8 Zip, Intello+, service cavity |
4" Slab 5" Mineral wool |
| Thermal Resistance ( R-Value) |
5 m2.K/W (27.1 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
11.72/12.4m2.K/W (64.2 / 67.5 hr ft² °F/Btu ) |
1.1 m2.K/W (19.4 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
| Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-Value) |
0.2 W/ m2.K (0.036 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.06 W/ m2.K (0.015 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.2 W/m2.K (0.049 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
| Thickness |
0.34m (13.5”) |
0.47m (18.5”) |
0.23m (9”) |
| Envelope Assembly 2 |
Name |
2x8 w DPC 24"OC W 7/16 Zip Service Cavity |
16"TJI with DPC w 5/8” Zip, Intello+, service cavity |
16" 2x4 truss floor with cellulose, ¾” hardwood floor, intello |
| Thermal Resistance ( R-Value) |
5.36/6.6 m2.K/W (30.1/ 37.0 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
11.72/12.4 m2.K/W (64.2 / 67.5 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
11.77/12.08 m2.K/W (65.1 / 66.8 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
| Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-Value) |
0.05 W/m2.K (0.032 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.06 W/ m2.K (0.015 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.06 W/ m2.K (0.015 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
| Thickness |
0.3m (12”) |
0.47m (18.5)” |
0.45m (17.6”) |
| Envelope Assembly 3 |
Name |
2x8 w 7.5" DPC w 1" thermacork |
16"TJI with DPC w 5/8 Zip, Intello+, service cavity |
16" 2x4 truss floor with cellulose, 3/4 hardwood floor, intello |
| Thermal Resistance ( R-Value) |
8/8.87 m2.K/W (34.6/38.26hr ft² °F/Btu) |
11.72/12.4 m2.K/W (64.2 / 67.5 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
11.77/12.08 m2.K/W (65.1 / 66.8 hr ft² °F/Btu) |
| Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-Value) |
0.03 W/ m2.K (0.028 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.06 W/ m2.K (0.015 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
0.06 W/ m2.K (0.015 Btu/hr ft² °F) |
| Thickness |
0.3m (11.7”) |
0.47m (18.5”) |
0.45m (17.6”) |
The initial design envisioned the utilization of Nexcem blocks combined with mineral wool, and a slab-on-grade foundation, aligning with floodplain and Passive House design considerations. However, budget constraints, along with the carbon footprint associated with the Nexcem blocks and the floodplain permitting requirements for elevating the house on piles, affected the architectural design, leading to the selection of a 2x8" wall configuration, filled with cellulose insulation. While this decision was, in part, driven by the need to navigate budget constraints and logistical hurdles, it represents a tangible example of the reasons why the consequential reduction of the envelope material carbon footprint is the first to be compromised. Although, the barrier is related to many gaps from the manufacturer as well as professional knowledge, however, professionals need to have an early engagement with the supply chain to identify the whole life cycle cost as well as carbon before the design process, professionals should also understand the material physical performance, carbon footprint as well as the impact of energy efficiency to meet project goal and vision.
10. Tools and Software Barriers
"There are many tools being developed to make carbon-neutral design more achievable for designers, but there needs to be a lot more work done in this area to make it easier for architects to navigate the trade-offs involved in specifying materials and building processes for carbon-neutral buildings,” according to A2. The architect’s comments also extend to energy modeling.
For example, the drawings for the Everly House were prepared in ArchiCAD software. For the energy analysis the ArchiCAD file had to be imported into SketchUp and from SketchUp exported into WUFI. This illustrates the lack of integration and compatibility between different software platforms (Antretter, F. et al, 2017).
An attempt was initiated by the author to develop an energy model for the Everly house using EnergyPlus software, and the ArchiCAD file was also faced with similar obstacles, including gaps in translating the geometry into an analytical model that can be used by EnergyPlus. This gap affects the exchange of critical project information, which, in turn, can lead to misunderstandings, discrepancies in data interpretation, and delays in decision-making and design development.
The identified barriers in this category were of moderate to low impact on this project, however, this analysis emphasized the importance of software integration, data sharing, and collaborative workflows as key elements to address these barriers, and the respondents emphasized the relevance of software integration, data sharing, and collaborative workflows for developing energy-efficient designs.
11. Conclusions
These barriers have significant impacts on each stage of the preconstruction phase, during the planning stage, these barriers affect the feasibility and viability of the project as well as the identification of possible risks and responsibilities, on the other side these barriers may compromise the quality of the design as well as compliance with project goals, vision, codes and standards, and certification requirements. It is important to address these barriers by adopting a multidisciplinary design approach that involves integrating all relevant design disciplines (architecture, HVAC, structural engineering) to work collaboratively during the concept development and final design stages and considering energy performance and environmental impact from the outset and prioritizing sustainable design principles.
This study investigated the barriers faced during the preconstruction phase of the Everly Passive House as a case study in the south-central region in the United States, where sustainable building practices are not yet widely adopted and prioritized, both among industry professionals and within state plans and regulations. Open-ended interview discussions were conducted among professionals engaged during this phase, 7 professionals including project owner responded. A total of 20 barriers were identified through interviews and direct observation, and then were categorized in terms of management and time, design, regulatory and permitting, knowledge gap and experience, material selection, and tools and software. The findings of the study revealed multidimensional relationship between different project stakeholders and barriers categories that affect the preconstruction phase. These findings align with the literature review conducted providing scientific evidence to support these results.
In addition to that, the respondents provided valuable suggestions as solutions for problems faced, focusing on the importance of early collaboration and communication among professionals involved in the design and permitting stages, the importance of. developing knowledge and expertise of architects and engineers to implement sustainable building designs and preparing engineers and architects before graduation to incorporate sustainable approaches in their professions. These suggestions were compiled with researcher recommendations to provide a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and necessary steps to overcome them.
This research is faced with certain limitations that need to be considered. First, some respondents were reluctant to respond to the project, however, the respondents who did participate represent key professionals who exert significant influence over the design and permitting processes of the house. Second, the identified barriers are context-specific and limited to a single case study. In other words, some identified barriers provided in
Table 2 may not be relevant to other projects located in different contexts or regions where regulatory frameworks and policies prioritize and incentives similar projects, while some barriers are identified in other studies, such as design-related challenges and knowledge gaps. Third, the research methodology relies on open-ended interview discussions to capture professionals’ perspective who were directly involved in the project, and it is limited to their professional experience in this project.
Despite the limitations, the findings of this study are expected to be a valuable resource for project owners and professionals engaged in the initial stages of similar projects. The design modifications, retrofitting and changes in envelope materials are all associated with professional’s knowledge, interest and experience in Passive House design requirements and carbon reduction principles as well as the outdated and weak building energy codes and regulations that do not incorporate sustainable building design principles and doesn’t provide comprehensive guidance on energy efficient and low carbon design created confusion and challenges for architects and engineers during the concept development phase and affected the timeline of the project. These delays and modifications have affected the project budget and delayed the implementation of the project as well as finalizing the permit documents. Knowing the potential barriers, these stakeholders can utilize these recommendations and develop strategies to overcome them, to ensure successful project design and completion. Additionally, by understanding and addressing these barriers, policymakers, industry professionals, and researchers can work together to overcome these challenges and promote sustainable building typologies.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the Everly House Owners for generously sharing the project design and details and would like to thank the industry professionals who participated in this study and helped with their valuable experiences and opinions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1. Pierson, R., Paquin-Béchard, C. (2021, August 27). EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT PASSIVE HOUSE CERTIFICATION. Retrieved from Ecohome: https://www.ecohome.net/guides/2191/everything-you-need-to-know-about-passive-house/.
- Akadiri, P. (2015). Understanding barriers affecting the selection of sustainable materials in building projects. Building Engineering, 4, 86-93.
- Antretter, F. et al. (2017, June 1). WUFI®Plus3.1 Manual. WUFI®PlusManual. Fraunhofer IBP.
- ASHRAE. (2018). Residential Application. In ASHRAE, ASHRAE GreenGuide - Design, Construction, and Operation of Sustainable Buildings (5th Edition) (p. 403). American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (ASHRAE).
- Attia, S. et al. (2017). Overview and future challenges of nearly zero energy buildings (nZEB) design in Southern Europe. Energy and Buildings. [CrossRef]
- AUROSGroup. (n.d.). PHI or PHIUS? What's right for my project? Retrieved from Aurosgroup: https://www.aurosgroup.com/post/phi-or-phius-what-s-right-for-my-project#:~:text=PHI's%20airtightness%20requirement%20is%20based,pursued%20by%20a%20given%20project.
- Bryman, A. (2015). Social Research Methods (5th ed. Oxford University Press.
- Christina J. Hopfe, Robert S. McLeod. (2015). The Passivhaus Designer’s Manual: A technical guide to low and zero energy buildings. (R. S. Christina J. Hopfe, Ed.) New York: Routledge.
- Daniel, E I, Oshineye, O and Oshodi, O. (2018). Barriers to Sustainable construction Practice in Nigeria. Proceeding of the 34th ARCOM Conference (pp. 149-158). Belfast: Association of Researchers in Construction Management.
- Daniel, E I, Oshineye, O and Oshodi, O. (2018). Barriers to Sustainable Construction Practices in Nigeria. 34th ARCOM Conference (pp. 149-158.). Belfast: Association of Researchers in Construction Management.
- Darko, A., Chan, A. (2017). Review of Barriers to Green Building Adoption. Sustainable Development, 25, 167–179. [CrossRef]
- Daryl Cielo, Alison Subiantoro. (2021). Net zero energy buildings in New Zealand: Challenges and potentials reviewed against legislative, climatic, technological, and economic factors. Journal of Building Engineering.
- Dequaire, X. (2012). Passivhaus as a low-energy building standard: contribution to a typology. Energy Efficiency, 5, 377–391.
- Figueiredo, A., Rebelo, F. et al. (2020). Implementation and Challenges of the Passive House Concept in Portugal: Lessons Learnt from Successful Experience. Sustainability 12(21), 8761. [CrossRef]
- Giesekam, J., John R. Barrett, J., Taylor,P. (2016). Construction sector views on low carbon building materials. Building Research & Information, 44(4), 423-444. [CrossRef]
- Hafez, F. et al. (2023). Energy Efficiency in Sustainable Buildings: A Systematic Review with Taxonomy, Challenges, Motivations, Methodological Aspects, Recommendations, and Pathways for Future Research. Energy Strategy Reviews, 45. [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, T., & Belloni, K. (2011). Barriers and drivers for sustainable building. Building Research & Information, 39(3), 239-255. [CrossRef]
- HAP e-help. (2005, November 1). HAP e-Help 005. Carrier.
- Hap e-help. (2007, January 23). How to Import Data from Template Projects. Carrier.
- He,M., Li, M., Li, Z. et al. (2021). Mechanical performance of glulam beam-to-column connections with coach screws as fasteners. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 21(51).
- Heffernan, Emma Elizabeth; Pan, Wei; Liang, Xi; and De Wilde, Pieter. (2013). Redening zero? A critical review of denitions of zero energy buildings andzero carbon homeszero carbon homes. Faculty of Engineering andInformation Sciences - Papers: Part A.
- Honorene, J. (2017). Understanding the Role of Triangulation in Research. Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies 4(31), 91-95.
- K. Gowri,D. Winiarski, R. Jarnagin. (2009). Infiltration Modeling Guidelines for Commercial Building Energy Analysis. Oak Ridge: Pacific NorthWest national Laboratory.
- Kabeyi, M., Olanrewaju, O. (2021). Sustainable Energy Transition for Renewable and Low Carbon Grid Electricity Generation and Supply. Sustainable Energy Systems, 9. [CrossRef]
- Karji, A., Namian, M., & Tafazzoli, M. (2020). dentifying the Key Barriers to Promote Sustainable Construction in the United States: A Principal Component Analysis. Sustainability, 12(12). [CrossRef]
- Lorelei Lingard, Christopher Watling. (2021). Effective Use of Quotes in Qualitative Research. In Story, Not Study: 30 Brief Lessons to Inspire Health Researchers as Writers (pp. 34-43). Philadelphia: Springer Cham.
- Malhotra, A., Frisch, J., Treeck, C. (2019). Technical Report: Literature Review concerning IFC, gbXML and CityGML data models for Energy Performance Simulation. Institute of Energy Efficiency and Sustainable Building, RWTH Aachen University, Germany.
- Marszal, A. J., & Heiselberg, P. (2009). A Literature Review of Zero Energy Buildings (ZEB) Definitions. Department of Civil Engineering, Aalborg University. DCE Technical reports No. 78.
- Moreno-Rangel, A. (2021). Passivhaus. Encyclopedia, 1, 20-29. [CrossRef]
- Ozel, M. (2016). Effect of indoor design temperature on the heating and cooling transmission loads. Building Engineering , 46-52.
- Phius. (2021, July). Phius 2021 Passive Building Standard Certification Guidebook. Phius Certification Guidebook v3.02. Chicago, Illinois, USA: Phius.
- Pitts, A. (2017). Passive House and Low Energy Buildings: Barriers and Opportunities for Future Development within UK Practice. Sustainability, 9(2), 272. [CrossRef]
- Pitts, A. (2017). Passive House and Low Energy Buildings: Barriers and Opportunities for Future Development within UK Practice. Sustainability , 9(272). [CrossRef]
- Shambalid Ahady, Nirendra Dev, Anubha Mandal. (2019). Toward Zero Energy: Active and Passive Design Strategies to Achieve Net Zero Energy Building. International Journal of Advance Research and Innovation, 7(1), 49-61. [CrossRef]
- Souaid, C., Van der Heijden, H., Elsinga, M. (2022). Perceived Barriers to Nearly Zero-Energy Housing: Empirical Evidence from Kilkenny, Ireland. Energies, 15(7). [CrossRef]
- Turner, S., Cardinal, L., Burton, R. (2017). Research Design for Mixed Methods: A Triangulation-based Framework and Roadmap. Organizational Research Methods, 20(2), 243-267. [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, K. (2016). Sustainable design in project delivery: A discussion on current and future trends. Journal of Green Building, 11(2), 39-56.
- Wilson,J L., Tagaza, E. (2006). Green buildings in Australia: drivers and barriers. Australian Journal of Structural Engineering, 7(1), 57-63. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Xuan L, Huang W, Yuan L and Li P . (2022). Structural Design and Analysis for a Timber-Concrete Hybrid Building. Front. Mater. 9:844398. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).