Submitted:
30 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Overview of Muscular Dystrophy
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Muscle Damage and Inflammation in DMD
2. Physiological Role of Adiponectin in Non-Dystrophic Models
2.1. Cellular Properties and Structural Features
2.2. Multi-Organ and Inflammatory Regulation of ApN
3. Synthetic Adiponectin Receptor Agonists
3.1. AdipoRon
3.2. ALY688
4. Pre-Clinical Development of Adiponectin-Receptor Agonists for DMD
5. Conclusion and Future Directions
Funding
Competing interests
Author contributions
References
- Nigro, G.; Comi, L.I.; Limongelli, F.M.; Giugliano, M.A.M.; Politano, L.; Petretta, V.; Passamano, L.; Stefanelli, S. Prospective Study of X-linked Progressive Muscular Dystrophy in Campania. Muscle Nerve 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisafulli, S.; Sultana, J.; Fontana, A.; Salvo, F.; Messina, S.; Messina, S.; Trifirò, G. Global Epidemiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; den Dunnen, J.T. Phenotype Predictions for Exon Deletions/Duplications: A User Guide for Professionals and Clinicians Using Becker and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy as Examples. Hum. Mutat. 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, A.; Raguènès-Nicol, C.; Yaou, R. Ben; Hir, S.A. Le; Chéron, A.; Vié, V.; Claustres, M.; Leturcq, F.; Delalande, O.; Hubert, J.F.; et al. Becker Muscular Dystrophy Severity Is Linked to the Structure of Dystrophin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzer, C.; Meaney, F.J.; Andrews, J.; Ciafaloni, E.; Fox, D.J.; James, K.A.; Lu, Z.; Miller, L.; Pandya, S.; Ouyang, L.; et al. Disparities in the Diagnostic Process of Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy. Genet. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, R.; Street, N.; Conway, K.C.; James, K.; Cunniff, C.; Oleszek, J.; Fox, D.; Ciafaloni, E.; Westfield, C.; Paramsothy, P. Secondary Conditions among Males with Duchenne or Becker Muscular Dystrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirski, K.T.; Crawford, T.O. Motor and Cognitive Delay in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Implication for Early Diagnosis. J. Pediatr. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrizaila, N.; Kinnear, W.J.M.; Wills, A.J. Respiratory Involvement in Inherited Primary Muscle Conditions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006. [CrossRef]
- Chey, Y.C.J.; Arudkumar, J.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Adikusuma, F.; Thomas, P.Q. CRISPR Applications for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: From Animal Models to Potential Therapies. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, S.; Marks, R.M.; Rok, M.J.; Perillat, L.; Ivakine, E.A.; Cohn, R.D. Advances in CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing for the Treatment of Muscular Dystrophies. Hum. Gene Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilton-Clark, H.; Yokota, T. Biological and Genetic Therapies for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escolar, D.M.; Hache, L.P.; Clemens, P.R.; Cnaan, A.; McDonald, C.M.; Viswanathan, V.; Kornberg, A.J.; Bertorini, T.E.; Nevo, Y.; Lotze, T.; et al. Randomized, Blinded Trial of Weekend vs Daily Prednisone in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neurology 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.M.; Zaidman, C.M.; Golumbek, P.T.; Cradock, M.M.; Flanigan, K.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Finkel, R.S.; McDonald, C.M.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Anand, P.; et al. Twice-Weekly Glucocorticosteroids in Infants and Young Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Muscle and Nerve 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrocelli, M.; Zelikovich, A.S.; Jiang, Z.; Peek, C.B.; Demonbreun, A.R.; Kuntz, N.L.; Barish, G.D.; Haldar, S.M.; Bass, J.; McNally, E.M. Pulsed Glucocorticoids Enhance Dystrophic Muscle Performance through Epigenetic-Metabolic Reprogramming. JCI Insight 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, E.; Brassington, R.; Kuntzer, T.; Jichi, F.; Manzur, A.Y. Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Samra, M.; Lecompte, S.; Schakman, O.; Noel, L.; Many, M.C.; Gailly, P.; Brichard, S.M. Involvement of Adiponectin in the Pathogenesis of Dystrophinopathy. Skelet. Muscle 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Samra, M.; Selvais, C.M.; Boursereau, R.; Lecompte, S.; Noel, L.; Brichard, S.M. AdipoRon, a New Therapeutic Prospect for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecompte, S.; Abou-Samra, M.; Boursereau, R.; Noel, L.; Brichard, S.M. Skeletal Muscle Secretome in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Pivotal Anti-Inflammatory Role of Adiponectin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursereau, R.; Abou-Samra, M.; Lecompte, S.; Noel, L.; Brichard, S.M. Downregulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Adiponectin Rescues Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. BMC Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, N.; Versele, R.; Davis-López de Carrizosa, M.A.; Selvais, C.M.; Noel, L.; Planchon, C.; Van den Bergh, P.Y.K.; Brichard, S.M.; Abou-Samra, M. The Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, ALY688: A Promising Therapeutic for Fibrosis in the Dystrophic Muscle. Cells 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissimo, C.A.; Gandhi, S.; Castellani, L.N.; Murugathasan, M.; Delfinis, L.J.; Thuhan, A.; Garibotti, M.C.; Seo, Y.; Rebalka, I.A.; Hsu, H.H.; et al. The Slow-Release Adiponectin Analog ALY688-SR Modifies Early-Stage Disease Development in the D2.Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Am. J. Physiol. - Cell Physiol. [CrossRef]
- Fruebis, J.; Tsao, T.S.; Javorschi, S.; Ebbets-Reed, D.; Erickson, M.R.S.; Yen, F.T.; Bihain, B.E.; Lodish, H.F. Proteolytic Cleavage Product of 30-KDa Adipocyte Complement-Related Protein Increases Fatty Acid Oxidation in Muscle and Causes Weight Loss in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin Stimulates Glucose Utilization and Fatty-Acid Oxidation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Nat. Med. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular Adiponectin Increases GLUT4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake but Reduces Glycogen Synthesis in Rat Skeletal Muscle Cells. Diabetologia 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.B.; McAinch, A.J.; Macaulay, S.L.; Castelli, L.A.; O’Brien, P.E.; Dixon, J.B.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Kemp, B.E.; Steinberg, G.R. Impaired Activation of AMP-Kinase and Fatty Acid Oxidation by Globular Adiponectin in Cultured Human Skeletal Muscle of Obese Type 2 Diabetics. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Turdi, S.; Park, T.; Morris, N.J.; Deshaies, Y.; Xu, A.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin Corrects High-Fat Diet-Induced Disturbances in Muscle Metabolomic Profile and Whole-Body Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin Action in Skeletal Muscle. In Proceedings of the Best Practice and Research: Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marette, A.; Liu, Y.; Sweeney, G. Skeletal Muscle Glucose Metabolism and Inflammation in the Development of the Metabolic Syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ervasti, J.M.; Campbell, K.P. A Role for the Dystrophin-Glycoprotein Complex as a Transmembrane Linker between Laminin and Actin. J. Cell Biol. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrof, B.J.; Shrager, J.B.; Stedman, H.H.; Kelly, A.M.; Sweeney, H.L. Dystrophin Protects the Sarcolemma from Stresses Developed during Muscle Contraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, K.; Liang, F.; Giordano, C.; Lemaire, C.; Danialou, G.; Okazaki, T.; Bourdon, J.; Rafei, M.; Galipeau, J.; Divangahi, M.; et al. Inflammatory Monocytes Promote Progression of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Can Be Therapeutically Targeted via CCR 2. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.S.; Puig, M.; Nagaraju, K.; Hoffman, E.P.; Villalta, S.A.; Rao, V.A.; Wakefield, L.M.; Woodcock, J. Immune-Mediated Pathology in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Tulangekar, A.; Sztal, T.E. Inflammation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy–Exploring the Role of Neutrophils in Muscle Damage and Regeneration. Biomedicines 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Karpati, G. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Plasma Membrane Loss Initiates Muscle Cell Necrosis Unless It Is Repaired. Brain 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidball, J.G.; Welc, S.S.; Wehling-Henricks, M. Immunobiology of Inherited Muscular Dystrophies. Compr. Physiol. 2018.
- Land, W.G. The Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Human Diseases: Part I - Promoting Inflammation and Immunity. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2015.
- Petrof, B. The Role of Innate Immunity in Dystrophic Diaphragm Pathology. FASEB J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbelet, S.; Rodenbach, A.; De Paepe, B.; De Bleecker, J.L. Anti-Inflammatory and General Glucocorticoid Physiology in Skeletal Muscles Affected by Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Exploration of Steroid-Sparing Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharyya, S.; Villalta, S.A.; Bakkar, N.; Bupha-Intr, T.; Janssen, P.M.L.; Carathers, M.; Li, Z.W.; Beg, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Sahenk, Z.; et al. Interplay of IKK/NF-ΚB Signaling in Macrophages and Myofibers Promotes Muscle Degeneration in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Clin. Invest. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, S.; Li, Q.; Ding, J.; Liang, F.; Gusev, E.; Lapohos, O.; Fonseca, G.J.; Kaufmann, E.; Divangahi, M.; Petrof, B.J. TLR4 Is a Regulator of Trained Immunity in a Murine Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.; Shimizu-Motohashi, Y.; Takeda, S.; Aoki, Y. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Focus on Skeletal Muscle-Releasing Factors. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016.
- Henriques-Pons, A.; Yu, Q.; Rayavarapu, S.; Cohen, T. V.; Ampong, B.; Cha, H.J.; Jahnke, V.; Van der meulen, J.; Wang, D.; Jiang, W.; et al. Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Dystrophin-Deficient Skeletal and Heart Muscle. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heier, C.R.; Damsker, J.M.; Yu, Q.; Dillingham, B.C.; Huynh, T.; Van der Meulen, J.H.; Sali, A.; Miller, B.K.; Phadke, A.; Scheffer, L.; et al. VBP15, a Novel Anti-Inflammatory and Membrane-Stabilizer, Improves Muscular Dystrophy without Side Effects. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, S.M.; Walsh, G.S.; Balazsi, K.; Seale, P.; Sandoz, J.; Hierlihy, A.M.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Chamberlain, J.S.; Miller, F.D.; Megeney, L.A. Activation of JNK1 Contributes to Dystrophic Muscle Pathogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuru, S.; Inukai, A.; Kato, T.; Liang, Y.; Kimura, S.; Sobue, G. Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Regenerating Muscle Fibers in Inflammatory and Non-Inflammatory Myopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, L.; Berardinelli, M.G.; Forcina, L.; Spelta, E.; Rizzuto, E.; Nicoletti, C.; Camilli, C.; Testa, E.; Catizone, A.; De Benedetti, F.; et al. Increased Levels of Interleukin-6 Exacerbate the Dystrophic Phenotype in Mdx Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moresi, V.; Adamo, S.; Berghella, L. The JAK/STAT Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Pathophysiology. Front. Physiol. 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, L.; Berardinelli, M.G.; De Pasquale, L.; Nicoletti, C.; D’Amico, A.; Carvello, F.; Moneta, G.M.; Catizone, A.; Bertini, E.; De Benedetti, F.; et al. Functional and Morphological Improvement of Dystrophic Muscle by Interleukin 6 Receptor Blockade. EBioMedicine 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, S.A.; Deng, B.; Rinaldi, C.; Wehling-Henricks, M.; Tidball, J.G. IFN-γ Promotes Muscle Damage in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Suppressing M2 Macrophage Activation and Inhibiting Muscle Cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, S.A.; Nguyen, H.X.; Deng, B.; Gotoh, T.; Tidbal, J.G. Shifts in Macrophage Phenotypes and Macrophage Competition for Arginine Metabolism Affect the Severity of Muscle Pathology in Muscular Dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burelle, Y.; Khairallah, M.; Ascah, A.; Allen, B.G.; Deschepper, C.F.; Petrof, B.J.; Des Rosiers, C. Alterations in Mitochondrial Function as a Harbinger of Cardiomyopathy: Lessons from the Dystrophic Heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.C.; Ramos, S. V.; Turnbull, P.C.; Edgett, B.A.; Huber, J.S.; Polidovitch, N.; Schlattner, U.; Backx, P.H.; Simpson, J.A.; Perry, C.G.R. Impairments in Left Ventricular Mitochondrial Bioenergetics Precede Overt Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodelling in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Physiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dort, J.; Fabre, P.; Molina, T.; Dumont, N.A. Macrophages Are Key Regulators of Stem Cells during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Diseases. Stem Cells Int. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.F.; Souza, L.S.; Almeida, C.F.; Ishiba, R.; Fernandes, S.A.; Guerrieri, D.A.; Santos, A.L.F.; Onofre-Oliveira, P.C.G.; Vainzof, M. Muscle Satellite Cells and Impaired Late Stage Regeneration in Different Murine Models for Muscular Dystrophies. Sci. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharraz, Y.; Guerra, J.; Pessina, P.; Serrano, A.L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Understanding the Process of Fibrosis in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Biomed Res. Int. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.R.; Robb, C.T.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G. The Role of Neutrophils in Inflammation Resolution. Semin. Immunol. 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehling, M.; Spencer, M.J.; Tidball, J.G. A Nitric Oxide Synthase Transgene Ameliorates Muscular Dystrophy in Mdx Mice. J. Cell Biol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrill, J.R.; Duong, M.N.; Turner, R.; Le Guiner, C.; Boyatzis, A.; Kettle, A.J.; Grounds, M.D.; Arthur, P.G. Levels of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress, and a Role for Taurine in Dystropathology of the Golden Retriever Muscular Dystrophy Dog Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Redox Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grounds, M.D.; Terrill, J.R.; Al-Mshhdani, B.A.; Duong, M.N.; Radley-Crabb, H.G.; Arthur, P.G. Biomarkers for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Myonecrosis, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. DMM Dis. Model. Mech. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arecco, N.; Clarke, C.J.; Jones, F.K.; Simpson, D.M.; Mason, D.; Beynon, R.J.; Pisconti, A. Elastase Levels and Activity Are Increased in Dystrophic Muscle and Impair Myoblast Cell Survival, Proliferation and Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtesad, S.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Little, S.R.; Clemens, P.R. Rapamycin Ameliorates Dystrophic Phenotype in Mdx Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Mol. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyn, D.; Kuswanto, W.; Kolodin, D.; Shadrach, J.L.; Cerletti, M.; Jang, Y.; Sefik, E.; Tan, T.G.; Wagers, A.J.; Benoist, C.; et al. XA Special Population of Regulatory T Cells Potentiates Muscle Repair. Cell 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling-Henricks, M.; Lee, J.J.; Tidball, J.G. Prednisolone Decreases Cellular Adhesion Molecules Required for Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Dystrophin-Deficient Skeletal Muscle. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.K.K.; Cuello, C.; Bertouch, J. V.; Roberts-Thomson, P.J.; Ahern, M.J.; Smith, M.D.; Youssef, P.P. Effects of Pulse Methylprednisolone on Macrophage Chemotactic Protein-1 and Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α in Rheumatoid Synovium. J. Rheumatol. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdman, R.M.; Church, J.A. Immunologic and Virologic Effects of Glucocorticoids on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Children: A Preliminary Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauber, H.P.; Gotfried, M.; Newman, K.; Danda, R.; Servi, R.J.; Christodoulopoulos, P.; Hamid, Q. Effect of HFA-Flunisolide on Peripheral Lung Inflammation in Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors in the Integrated Regulation of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Obes. 2008. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted Disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Causes Abrogation of Adiponectin Binding and Metabolic Actions. Nat. Med. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turer, A.T.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications. Diabetologia 2012. [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A Novel Serum Protein Similar to C1q, Produced Exclusively in Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Sidossis, L.S. Recent Advances in the Measurement of Adiponectin Isoform Distribution. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007. [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Lam, K.S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Xu, A. Adiponectin and Cardiovascular Health: An Update. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, T.S.; Tomas, E.; Murrey, H.E.; Hug, C.; Lee, D.H.; Ruderman, N.B.; Heuser, J.E.; Lodish, H.F. Role of Disulfide Bonds in Acrp30/Adiponectin Structure and Signaling Specificity: Different Oligomers Activate Different Signal Transduction Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiaschi, T.; Giannoni, E.; Taddei, M.L.; Chiarugi, P. Globular Adiponectin Activates Motility and Regenerative Traits of Muscle Satellite Cells. PLoS One 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Kita, S.; Ito, Y.; Hada, Y.; Uchida, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Takekawa, S.; Kadowaki, T. Generation of Globular Fragment of Adiponectin by Leukocyte Elastase Secreted by Monocytic Cell Line THP-1. Endocrinology 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda-Murakami, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kawamata, S.; Saito, K.; Choi-Miura, N.H.; Tomita, M. Change in Expression of GBP28/Adiponectin in Carbon Tetrachloride-Administrated Mouse Liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaigle, A.M.; Jonas, J.C.; Bauche, I.B.; Cornu, O.; Brichard, S.M. Induction of Adiponectin in Skeletal Muscle by Inflammatory Cytokines: In Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Endocrinology 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J. V.; Abraheem, A.; Dotsenko, O.; Creamer, J.; Gunning, M.; Hughes, E.A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Circulating Serum Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Relationship to Atherosclerotic Burden and Cardiac Function. J. Intern. Med. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Carbone, F.; Rocca, C. La; Formisano, L.; Matarese, G. Role of Adipokines Signaling in the Modulation of T Cells Function. Front. Immunol. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Berner, H.S.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Spahr, A.; Monjo, M.; Thommesen, L.; Drevon, C.A.; Syversen, U.; Reseland, J.E. Adiponectin and Its Receptors Are Expressed in Bone-Forming Cells. Bone 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Wang, M.Y.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Deja, S.; Chen, S.; Balzer, M.S.; Kim, D.S.; Sun, X.; An, Y.A.; Field, B.C.; et al. Endogenous Renal Adiponectin Drives Gluconeogenesis through Enhancing Pyruvate and Fatty Acid Utilization. Nat. Commun. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. CDNA Cloning and Expression of a Novel Adipose Specific Collagen-like Factor, ApM1 (Adipose Most Abundant Gene Transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Cheng, K.K.Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A. Vascular Effects of Adiponectin: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Intervention. Clin. Sci. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.I.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical Decrease of an Adipose-Specific Protein, Adiponectin, in Obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Schraw, T.D.; Wang, Z. V.; Kim, J.Y.; Yi, J.; Hamilton, M.P.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Scherer, P.E. Systemic Fate of the Adipocyte-Derived Factor Adiponectin. Diabetes 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Vu, V.; Sweeney, G. Examining the Potential of Developing and Implementing Use of Adiponectin-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2019. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Yang, H.J. Long-Term Central Infusion of Adiponectin Improves Energy and Glucose Homeostasis by Decreasing Fat Storage and Suppressing Hepatic Gluconeogenesis without Changing Food Intake. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Deepa, S.S.; Etzler, J.C.; Ryu, J.; Mao, X.; Fang, Q.; Liu, D.D.; Torres, J.M.; Jia, W.; Lechleiter, J.D.; et al. Adiponectin Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Muscle Cells via APPL1/LKB1-Dependent and Phospholipase C/Ca2+/Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase-Dependent Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Endogenous Glucose Production Is Inhibited by the Adipose-Derived Protein Acrp30. J. Clin. Invest. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awazawa, M.; Ueki, K.; Inabe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Bardeesy, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin Suppresses Hepatic SREBP1c Expression in an AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK Dependent Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients 2021. [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.K.; Mitchell, P.L.; Gross, S.; Marette, A.; Sweeney, G. ALY688 Elicits Adiponectin-Mimetic Signaling and Improves Insulin Action in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Am. J. Physiol. - Cell Physiol. [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.R.; Mertz, V.A.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Dyck, D.J. The Stimulatory Effect of Globular Adiponectin on Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake and Fatty Acid Oxidation Is Impaired in Skeletal Muscle from Obese Subjects. Diabetes 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Sweeney, G. Direct Effects of Adipokines on the Heart: Focus on Adiponectin. In Proceedings of the Heart Failure Reviews; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Palanivel, R.; Cresser, J.; Schram, K.; Ganguly, R.; Thong, F.S.L.; Tuinei, J.; Xu, A.; Abel, E.D.; Sweeney, G. An APPL1-AMPK Signaling Axis Mediates Beneficial Metabolic Effects of Adiponectin in the Heart. Am. J. Physiol. - Endocrinol. Metab. [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Parker, J.L.; Ouchi, N.; Higuchi, A.; Vita, J.A.; Gokce, N.; Pedersen, A.A.; Kalthoff, C.; Tullin, S.; Sams, A.; et al. Adiponectin Promotes Macrophage Polarization toward an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin Induces the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in Human Leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Oritani, K.; Takahashi, I.; Ishikawa, J.; Matsuyama, A.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Tenner, A.J.; Tomiyama, Y.; et al. Adiponectin, a New Member of the Family of Soluble Defense Collagens, Negatively Regulates the Growth of Myelomonocytic Progenitors and the Functions of Macrophages. Blood 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Quan, A.; Szmitko, P.E.; Singh, K.K.; Shukla, P.C.; Gupta, M.; Chan, L.; Al-Omran, M.; Teoh, H. Adiponectin Primes Human Monocytes into Alternative Anti-Inflammatory M2 Macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. - Hear. Circ. Physiol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajuwon, K.M.; Spurlock, M.E. Adiponectin Inhibits LPS-Induced NF-ΚB Activation and IL-6 Production and Increases PPARγ2 Expression in Adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. - Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, M. Adiponectin: A Versatile Player of Innate Immunity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ramírez, P.; Malmhäll, C.; Tliba, O.; Rådinger, M.; Bossios, A. Adiponectin/AdipoR1 Axis Promotes IL-10 Release by Human Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xue, C.; Li, J.; Feng, K.; Zeng, P.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Han, J.; et al. Adiponectin Agonist ADP355 Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Decreasing Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, L.; Haspinger, E.; La Russa, F.; Maspero, F.; Graziano, P.; Kovalszky, I.; Lovas, S.; Nama, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Knappe, D.; et al. Design and Development of a Peptide-Based Adiponectin Receptor Agonist for Cancer Treatment. BMC Biotechnol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Lau, W.B.; Yuan, Y.X.; Liang, B.; Li, R.; Gao, E.H.; Koch, W.J.; Ma, X.L.; et al. AdipoRon, the First Orally Active Adiponectin Receptor Activator, Attenuates Postischemic Myocardial Apoptosis through Both AMPK-Mediated and AMPK-Independent Signalings. Am. J. Physiol. - Endocrinol. Metab. [CrossRef]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.I.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A Small-Molecule AdipoR Agonist for Type 2 Diabetes and Short Life in Obesity. Nature 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio, L.; Nigro, E.; Ragone, A.; Salzillo, A.; Illiano, M.; Spina, A.; Polito, R.; Daniele, A.; Naviglio, S. AdipoRon Affects Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Proliferation in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. J. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, L. Potential Adiponectin Receptor Response Modifier Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, L.; Knappe, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Kovalszky, I.; Olah, J.; Hewitson, T.D.; Stawikowska, R.; Stawikowski, M.; Cudic, P.; Lin, F.; et al. Development of Second Generation Peptides Modulating Cellular Adiponectin Receptor Responses. Front. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Smith, T.; Rahman, K.; Thorn, N.E.; Anania, F.A. Adiponectin Agonist ADP355 Attenuates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice. PLoS One 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; La Gahu, Z.; Xue, Z.; Da, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Adiponectin-Derived Active Peptide ADP355 Exerts Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrotic Activities in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Injury. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Dadson, K.; Sung, H.K.; Ayansola, O.; Mirzaesmaeili, A.; Noskovicova, N.; Zhao, Y.; Cheung, K.; Radisic, M.; Hinz, B.; et al. Cardioprotection by the Adiponectin Receptor Agonist ALY688 in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, Y.; Liang, C.; Ogundele, M.; Xu, G.; Tawalbeh, S.M.; Dang, U.J.; Hoffman, E.P.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Conklin, L.S.; van den Anker, J.N.; et al. Disease-Specific and Glucocorticoid-Responsive Serum Biomarkers for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelikovich, A.S.; Quattrocelli, M.; Salamone, I.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; McNally, E.M. Moderate Exercise Improves Function and Increases Adiponectin in the Mdx Mouse Model of Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Sato, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Funata, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Namiki, S.; Nakayama, R.; Tabata, M.; et al. Adiponectin and AdipoR1 Regulate PGC-1α and Mitochondria by Ca 2+ and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juban, G.; Saclier, M.; Yacoub-Youssef, H.; Kernou, A.; Arnold, L.; Boisson, C.; Ben Larbi, S.; Magnan, M.; Cuvellier, S.; Théret, M.; et al. AMPK Activation Regulates LTBP4-Dependent TGF-Β1 Secretion by Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages and Controls Fibrosis in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Cell Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Turpin-Nolan, S.; Febbraio, M.A. IL-6 Family Cytokines as Potential Therapeutic Strategies to Treat Metabolic Diseases. Cytokine 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
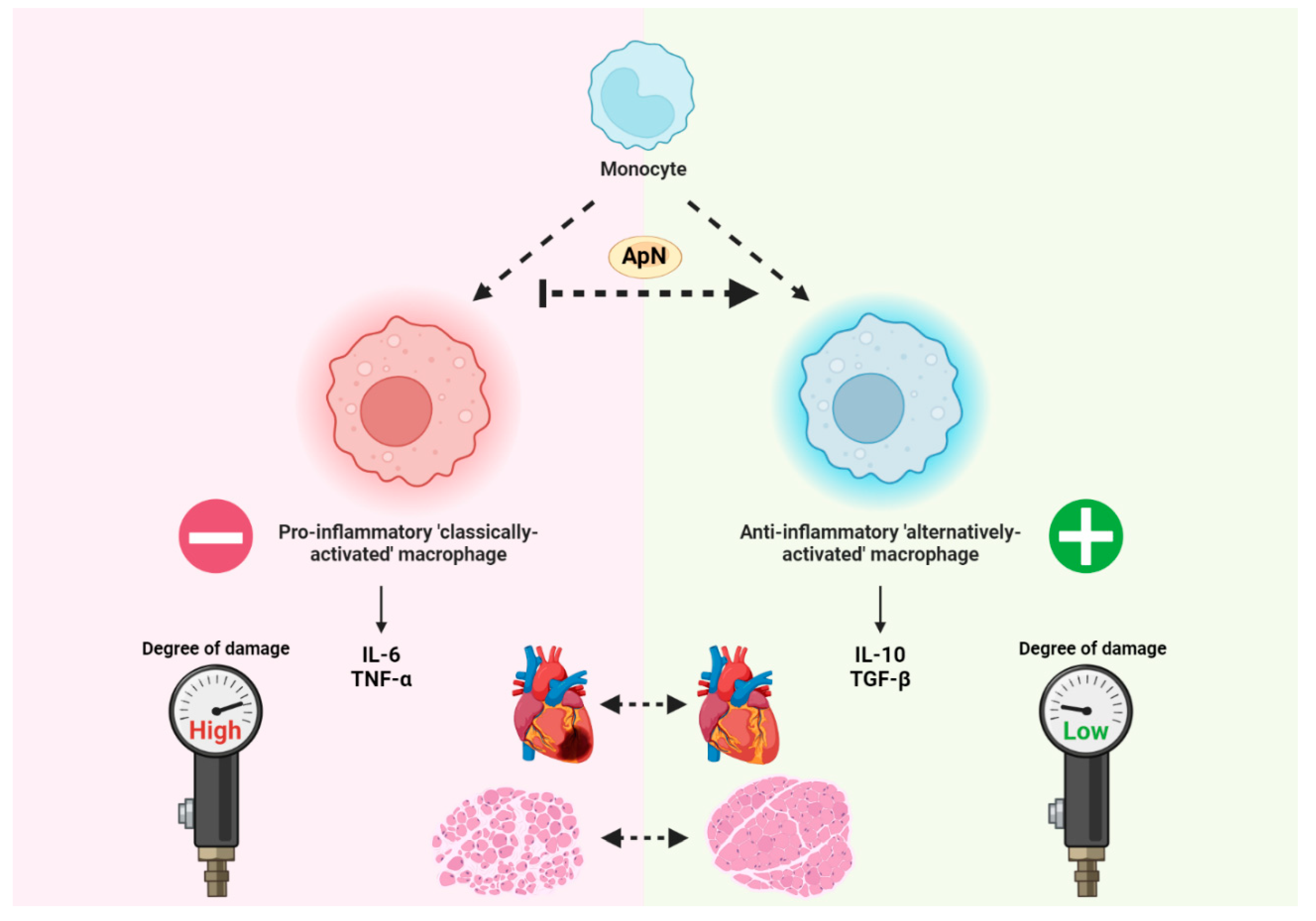
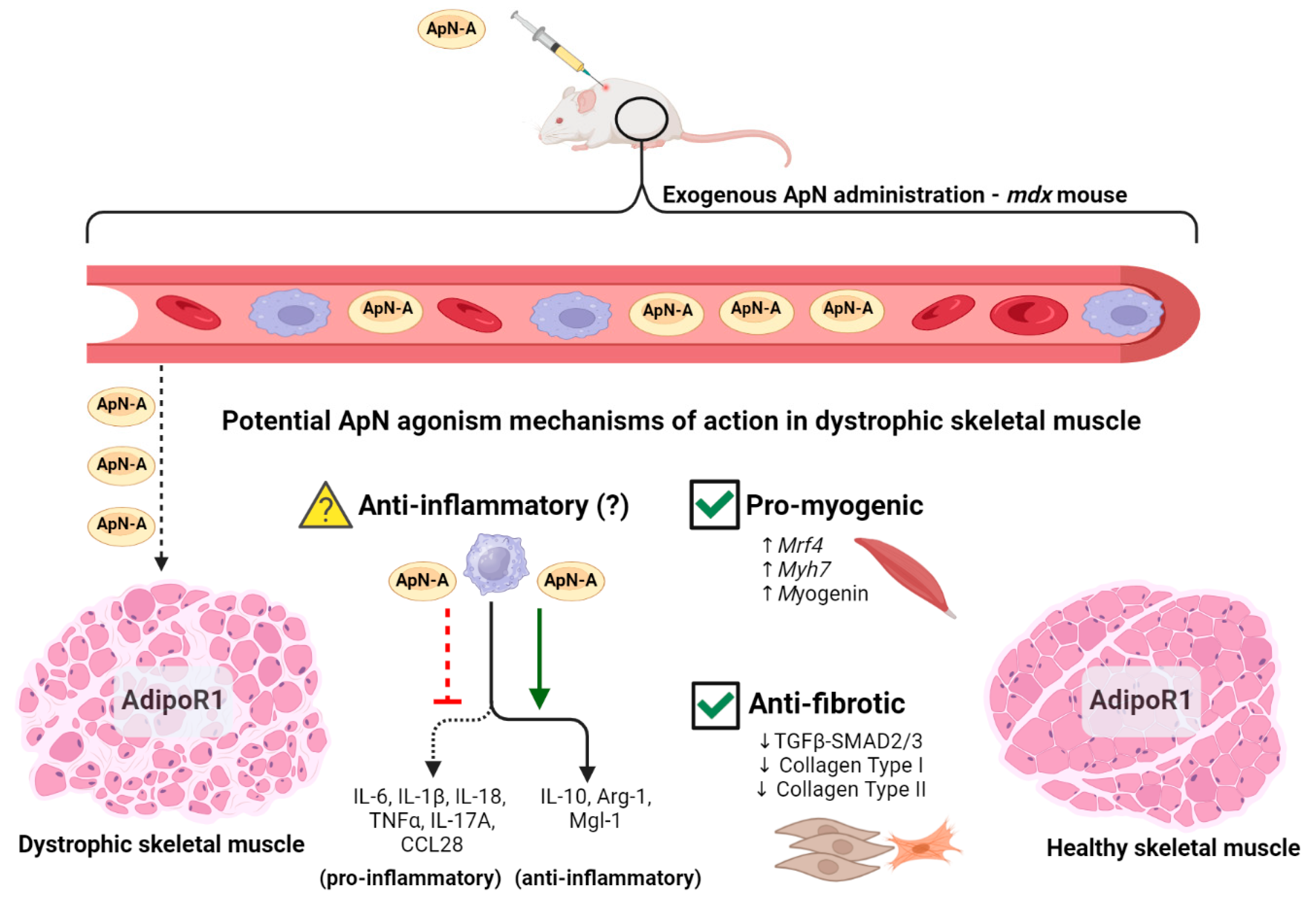
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



