1. Introduction
Global environmental concerns are on the rise, prompting countries to develop sustainable development programs aimed at tackling climate change. In China, as economic transformation progresses, the concept of green development is gaining traction, with enterprises playing a pivotal role in promoting sustainability. In recent years, the Chinese government has implemented a series of policies to promote ecological civilization and green development. In alignment with these efforts, the ESG evaluation system has gained increasing attention. Regulators have issued policies to integrate ESG elements into the oversight of listed companies, encouraging ESG information disclosure and enhancing supervision. Meanwhile, the export ratio of enterprises, a crucial economic indicator, significantly influences corporate performance and long-term development, especially in achieving the 'dual carbon' goal. Given the unique dynamics of the Chinese economy, it is clear that domestic demand is paramount. However, leveraging exports for growth is also indispensable. Thus, factoring in the export rate allows for a holistic assessment of a company's economic robustness and sustainability, offering broader insights for achieving the "double carbon" goal.
Despite numerous empirical studies analyzing the link between ESG and corporate financial performance, findings vary and can be categorized into two main perspectives: one suggests a negative correlation between ESG and corporate financial performance, while the other proposes a positive correlation. ESG is thought to enhance corporate financial performance [
1,
2,
3]. Moreover, ESG initiatives can boost firms' financial performance by bolstering investor confidence and fostering innovation [
4]. Different industries place different emphasis on environmental, social and governance ( ESG ) factors. For example, the automotive industry places more emphasis on governance (G) [
5], and European firms prioritize social factors (S) [
6]. Some studies suggest that prioritizing environmental performance may negatively affect firms, resulting in increased expenditures on disclosing ESG information and decreased financial performance [
7]. ESG controversies may somewhat weaken corporate performance [
8]. Other studies have found no significant relationship between ESG performance and corporate financial performance, suggesting that ESG policies may have a limited short-term impact on corporate financial performance [
9]. Emphasizing environmental factors alone in ESG may not enhance corporate performance. Additionally, the relationship between ESG and financial performance may be insignificant for certain enterprises, such as those not primarily engaged in pollution monitoring or high-tech industries [
10]. Many scholars tend to concentrate on the influence of individual ESG factors on firms' financial performance, often overlooking the significance of other interconnected factors. Although the impact of ESG strategies and operations on corporate financial performance has been a hot topic in modern academic and business research, there is still a relative lack of research in the ESG literature on the impact of ESG ratings of carbon-intensive companies on their financial performance. Additionally, the export activities of listed firms play a crucial role in economic development [
11]. However, research on firms' export ratios remains limited from this perspective. Carbon-intensive industries play a crucial role in ecological sustainability [
12]. Sixteen carbon-intensive industries, including coal, mining, textile, tannery, paper, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, chemical, metallurgy, and thermal power, are categorized as carbon-intensive enterprises [
13]. Given the nature of their operations, carbon-intensive listed companies are significant contributors to carbon emissions. Consequently, these companies face stringent regulations and social pressure from environmental protection agencies [
14]. Therefore, understanding the correlation between ESG activities and financial performance in carbon-intensive industries is imperative. In summary, the main issues identified in this study are as follows: Do ESG ratings of Chinese listed companies affect their financial performance? Does the ESG rating of Chinese listed companies affect their export ratio? What is the impact of E, S, and G factors on a firm's financial performance? Which factor has the greatest influence? What is the impact of export ratio, a key indicator of corporate development, on company performance? Does the presence of carbon-intensive firms impact financial performance? These questions constitute the focal point of this study. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to study the impact of ESG rating on corporate financial performance and its specific impact paths, to provide more guidance and practice for Chinese enterprises to create long-term sustainable earnings, and to provide policy reference suggestions for the sustainable development of China's economy. Building on the background, this study focuses on manufacturing enterprises listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges from 2009 to 2022. Its objective is to delve into the influence of ESG factors on corporate financial performance. The contributions of this paper are outlined below:
This study confirms the influence of ESG performance on corporate financial performance. Unlike previous studies that predominantly examine the impact of individual ESG factors on corporate financial performance, this study explores the independent effects of environmental (E), social (S), and governance (G) factors separately. Furthermore, this study validates the influence of the firm's export ratio as an additional factor, enhancing the understanding of elements affecting firms' financial performance. Lastly, this study examines the moderating effects of significant carbon-intensive firms in China on the relationship between ESG and corporate financial performance. Through these validations, this study aims to provide more guidance and practical experience for Chinese firms to create long-term sustainable profitability, as well as to provide reference suggestions for the formulation of related policies.
The main text is structured as follows: The introductory section provides background information on ESG research and underscores the critical importance of ESG for Chinese manufacturing enterprises. The second part gives a comprehensive introduction to the literature review and then presents the hypotheses of this study. The third part is the research model, variable definitions, and research methodology of this study. The fourth part is the analysis results of the empirical study. Finally, the fifth part, as the conclusion part, summarizes the results of the study and its managerial and theoretical significance, and makes suggestions for future research.
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
- (1)
ESG ratings and corporate financial performance
ESG is Environmental, Social and Governance and its various sub-factors [
15]. ESG is considered to have a significant impact on the sustainability and long-term value of a company by minimizing the negative impacts that a company may have on the environment and society and maximizing the effectiveness of corporate governance [
16]. ESG contains a wide range of information related to the environment, society, and dominance structure, and therefore can be an important indicator for firms to consider along with financial results when making decisions [
17]. If a firm has a high level of ESG, it can effectively deal with various risks including market, policy and financial risks, which can help to improve its business performance [
18]. According to existing studies, there is a close relationship between ESG and firms' financial outcomes [
19]. For example, some studies found that firms' non-financial and ESG efforts negatively impacted liquidity and efficiency but ultimately improved profitability and cash generation [
18]. Han et al. (2016) analyzed the relationship between ESG ratings and firm performance and confirmed that there was a significant effect between the two [
20]. In a study utilizing the ESG index of the Korea Domination Constructing Institute, ESG outcomes and the financial outcomes or corporate value of the firms were largely positively correlated [
21]. These studies confirm that there is a close relationship between non-financial and ESG and corporate outcomes or business results.
As listed companies that form the backbone of China's economy, ESG issues are crucial to China's economic development in the national strategy [
22]. Listed companies, as leaders of enterprise development, should pay more attention to ESG, reduce environmental, social and governance structure risks through ESG improvement, improve risk response-ability, promote sustainable development, and ultimately improve enterprise efficiency [
23]. Therefore, listed companies should pay more attention to ESG rating for sustainable development. From the above perspective, ESG ratings help to reduce the negative impacts of environmental, social and governance structure issues encountered by firms in their business activities, improve operational efficiency, and positively affect corporate performance. Based on this, the following assumptions can be made.
Hypothesis 1: ESG ratings have a positive impact on firms' financial performance.
- (2)
E ratings and corporate financial performance
Increasing environmental pressures and natural deterioration have become a major obstacle for mankind. Sustainable development and environmental issues are increasingly emphasized by the international community, academia and industry, and these issues directly affect the business activities of enterprises and their financial performance [
24]. At the same time, research on environmental issues has been actively carried out, and the impact of environmental issues has been explored from different perspectives, such as resource depletion and industrial waste emissions. Different enterprises encounter different environmental problems in their production processes, and therefore the environmental strategies they choose are also diverse. In Europe, firms' environmental strategies play an important role in the regulation of environmental and economic performance, especially for firms adopting shareholder value-oriented strategies [
24]. Countries are in the process of developing environmental policies and rules that are appropriate to their circumstances, and China is no exception. China requires firms to manage their production in accordance with established environmental regulations and to publish environmental information on a regular basis [
25]. Strict environmental regulations promote competition among firms, which ultimately improves firms' efficiency, encourages lower production costs, and increases consumer satisfaction and sales, thereby improving firms' profitability. Firms with high environmental levels tend to publish environmental information more frequently and with greater transparency. From the standpoint of a company, publishing environmental information about its own company may have an impact on the stock price. Negative news reports related to the environment may have a negative impact on the stock price, while positive reports may have a positive impact [
26]. Therefore, to enhance corporate value, companies may comply with environmental laws and regulations, proactively prevent undesirable environmental activities, and proactively publicize environmental information. These environmental efforts may adversely affect corporate effectiveness in the short term, but in the long term, they are more conducive to sustainable development and ultimately improve corporate performance [
27].
Existing studies have analyzed the correlation between environmental outcomes and business outcomes. The results show that there is a significant correlation between the environmental investment index and the price-earnings ratio, and there is a close relationship between environmental performance and corporate financial performance [
28]. Enterprises with high environmental performance not only significantly improve their external reputation but also increase their business performance. In addition, previous studies have shown that the level of environmental business activities of enterprises has a positive impact on enterprise value [
29]. Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed in this study.
Hypothesis 2: E ratings have a positive impact on firms' financial performance.
- (3)
S ratings and corporate financial performance
Corporate social responsibility is a hot topic in current academic research. Academics have launched extensive research on social responsibility. The business objectives of enterprises should pursue both the maximization of a single benefit and the maximization of the overall well-being of stakeholders. From this perspective,
social responsibility can be defined as a company's efforts to maximize corporate value by strengthening ethical management [
30]. Research confirms that corporate social responsibility positively affects financial performance [
31].
By engaging in social responsibility activities, companies can improve their social reputation, increase consumer confidence, attract investors, and ultimately promote sustainable development. Prior studies have shown that in the literature examining the relationship between CSR activities and firm value, there is empirical evidence that excessive corporate social involvement can improve brand image, employee satisfaction, and customer loyalty and positively affect firm performance [
32]. In other words, if a company can actively participate in social activities, corporate value and business results will rise. Actively fulfilling social responsibility helps to reduce the adverse social and environmental risks faced by enterprises, reduce negative social impacts, increase social awareness, and avoid some potential lawsuits and industry regulatory issues, thus reducing corporate risks [
33]. Employees who work in companies with positive social impacts feel a greater sense of fulfillment, which helps to improve employee performance and creativity. Positive corporate social responsibility often helps to build a favorable corporate image and enhance corporate reputation [
34]. These positive images help to build trusting relationships with stakeholders such as shareholders, employees, and customers, which in turn improves the firm's position in the market. Some investors and shareholders are increasingly focusing on corporate social responsibility performance. A high level of social responsibility can attract more socially responsible investors and increase the share price and market value of a company [
35].
Listed companies, as an important part of Chinese enterprises, should actively participate in social activities. The active participation of enterprises in social responsibility activities is usually due to their long-term planning for sustainable development. This long-term perspective facilitates enterprises to better cope with changes and uncertainties and improve their long-term performance. That is, the more a firm engages in social activities, the higher the financial results of its operations [
36]. Therefore, the following hypothesis is formulated.
Hypothesis 3: S ratings has a positive impact on firms' financial performance.
- (4)
G ratings and corporate financial performance
Unstable external factors have a negative impact on business operations. Compared to the uncertainty of the external environment, firms pay more attention to the management and improvement of the internal environment. To reduce the uncertainty of internal environment, firms should strengthen their own control structure [
37].
By measuring various factors such as shareholders' rights, board of directors, outside directors, share concentration, public disclosure system, ownership consistency, etc., corporate dominance structure is proved to be a determinant factor affecting the value of the firm [
38]. Therefore, firms can mitigate the dominance structure problem by improving various dominance structure subordinate factors such as extra-social director ratio, board size, institutional investor share rate, and operator share rate [
39]. Current research on the relationship between corporate governance structure and corporate performance is quite extensive. For example, the results of research on the relationship between corporate dominance structure and firm value show that firm value increases with the increase in the operator's shares, and the higher the rate of out-of-society directorships and the shares of institutional investors, the higher the value of the firm [
40]. The dominant structure activities of the firm can increase the transparency of the financial information of the firm [
41]. In terms of economic outcomes, higher levels of dominance structure are associated with higher business outcomes [
42,
43].
In domestic and international studies on the relationship between corporate dominance structure and firm value, Korean scholars utilized the corporate dominance structure index of the Corporate Domination Structure Institute. They found that the higher the dominance structure index, the higher the financial outcome and firm value of the firm. A study of the relationship between dominant structure and firm value in Korea revealed a meaningful positive relationship between the dominant structure index and firm value [
44]. A study of the relationship between corporate governance structure and firm performance in the United States measured corporate governance structure indices. It confirmed a positive correlation between the indices and firm value [
38]. In addition, using the level of shareholders' equity of the top 1500 firms in the 1990s, the stronger the dominance structure, the better the firm value and operating results [
43]. In other words, if firms pursue a better and healthy dominance structure, they can increase firm value and operating results. Previous research on Chinese dominance structure suggests that there is a defined correlation between dominance structure and return on assets for Chinese firms [
45]. For Chinese firms, there is a considerably defined relationship between dominance structure and firm value, which proves that for every 1% increase in the level of dominance structure, firm value increases by 0.01%. Based on these findings, this study aims to clarify the relationship between the level of governance and corporate financial performance of listed companies in China and, therefore, proposes the following hypotheses on the basis of previous studies.
Hypothesis 4: G ratings have a positive impact on firms' financial performance.
- (5)
ESG ratings, firm export ratios and firm financial performance
More studies are needed on enterprise ESG rating evaluation and enterprise export ratio. As the concept of sustainable development penetrates all aspects of enterprise development, ESG-related concepts and systems are being improved. Most of the existing studies believe that an enterprise's ESG performance can improve its financial performance and operational performance in terms of environment, society, and corporate governance, and from the perspective that ESG performance unilaterally supports exports, thus enhancing the competitive advantage of exporting enterprises in the international market and promoting their exports [
46].
Generally speaking, enterprises with high ESG not only have good management ability and financial performance but also pay attention to the sustainable development of the enterprise, which is characterized by solid risk resistance, high credit quality, etc. On the one hand, it reduces the cost of capital acquisition, which can improve the performance of the environment, social responsibility, and corporate governance. On the other hand, it improves the market competitiveness of the enterprise's products through a good reputation, which has a positive exporting impact [
47].
First, according to stakeholder theory, high ESG performance of enterprises is more likely to attract the attention of relevant stakeholders in the market, so that export enterprises can benefit from the advantages of low cost and high market share [
48].; second, for the government, the government and relevant administrative units can introduce ESG-related policies and guiding measures, so that enterprises pay attention to the green development and the concept of sustainable development, which is conducive to the good and stable development of the whole economy. Enterprises with strong business management ability and high social influence are important handholds for the government to promote ESG development. Enterprises with high ESG performance are more likely to establish a good relationship with the government and obtain a better development environment. As the government plays an important resource allocation role in economic development, enterprises with high ESG performance can play a "leading role" and enjoy corresponding financial support and policy preferences, which is conducive to promoting exports and giving exporters more advantages in terms of policies and costs [
49]. Third, from the perspective of consumers, enterprises with high ESG performance have high levels of business management and produce high quality products [
50]. Through effective communication and active social participation, consumers' awareness and satisfaction with products can be increased, making them more inclined to purchase products from firms with high ESG performance [
51]. On the other hand, firms with high ESG performance indicate that the firms are performing well in environmental protection and corporate social responsibility, and since environmental protection awareness is deeply rooted in people's minds, firms with high ESG performance can attract environmentalist consumers to buy the products they produce [
52]. Therefore, high ESG performance can increase a firm's operating profit and market share, and positively affect the firm's exports. Based on this, we propose the following hypothesis.
Hypothesis 5: ESG ratings have a positive impact on firm export ratios.
Hypothesis 6: Firm export ratios will mediate the relationship between ESG ratings and firms' financial performance.
- (6)
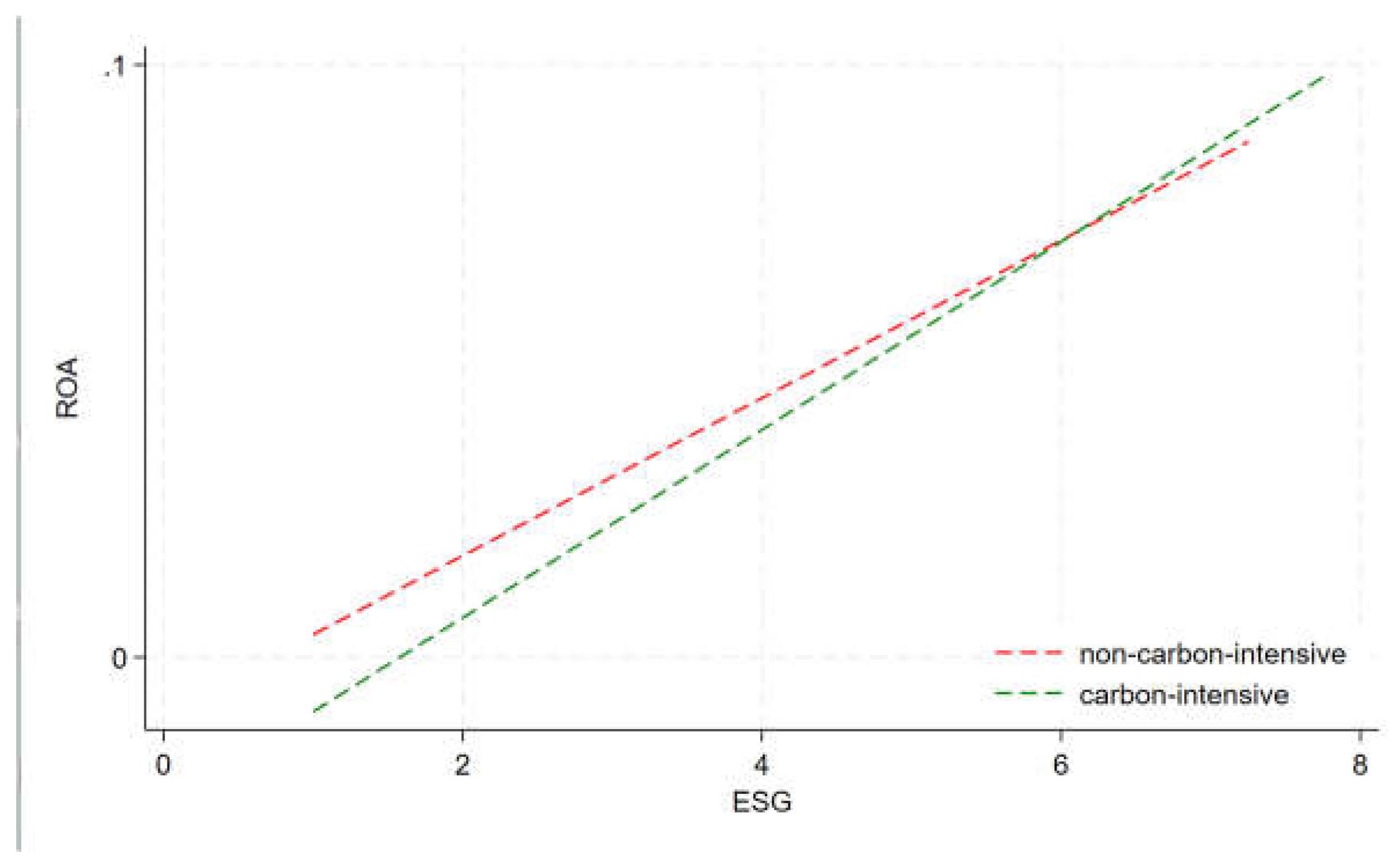
The Moderating Role of Carbon Intensive Firms
The "double carbon" goal is an inherent requirement for China to achieve high-quality and sustainable development, and China's time to achieve the "double carbon" goal is tight and the task is heavy, and the high-carbon enterprises in the eight industries of iron and steel, petroleum, electric power, and chemical industry are not only important industries for China's economic development, but also have become the focus and difficulty of China's realization of the "double carbon" goal that cannot be ignored, and it has great significance for promoting the green transformation of enterprises and realizing sustainable development [
53]. According to previous studies, 1,755 listed companies disclosed ESG-related reports in 2022, accounting for 34.32%, which also fully indicates that ESG plays the role of "booster" in the green development of enterprises [
54].
From a sustainable development perspective, ESG performance enhances enterprises' risk tolerance, boosts long-term financial performance, and increases organizational flexibility. However, listed companies, as key players in the capital market's high-quality development, may also impact the environment negatively while extracting resources for value creation [
55], with carbon-intensive enterprises being the most representative. To actively and steadily promote the realization of the "dual carbon" goal and strengthen enterprises' environmental awareness and green behaviors, local governments have introduced a series of environmental regulatory policies. Carbon-intensive enterprises with high ESG performance can timely avoid various policy barriers brought about by environmental regulation, effectively respond to the improvement of product and production standards, improve domestic and international ESG performance, reduce the risks and economic losses caused by environmental issues, and improve the long-term performance of enterprises and enhance organizational flexibility [
56]. In addition, the development of ESG requires companies to improve their production processes and replace energy-intensive technologies with green and low-carbon technologies, which obviously puts higher demands on carbon-intensive companies. High-carbon enterprises that actively improve their ESG performance have more experience in green development, which can effectively reduce the risks caused by poor management, improve organizational flexibility, and promote corporate financial performance.
From the perspective of the enterprise's own environmental pollution, carbon-intensive enterprises generally pay more attention to environmental protection and take more green sustainable development measures [
57], which not only help reduce the enterprise's operating costs such as energy and resource use, but also reduce the negative impact on the environment. Carbon-intensive enterprises optimize their production processes and use clean energy, which not only reduces environmental risks but also establishes an environmentally friendly image, which has a positive impact on financial performance.
Hypothesis 7: Carbon-intensive enterprises will moderate the relationship between ESG ratings and firms' financial performance.