Submitted:
04 May 2024
Posted:
06 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Algal Cultures
Lipid Extraction
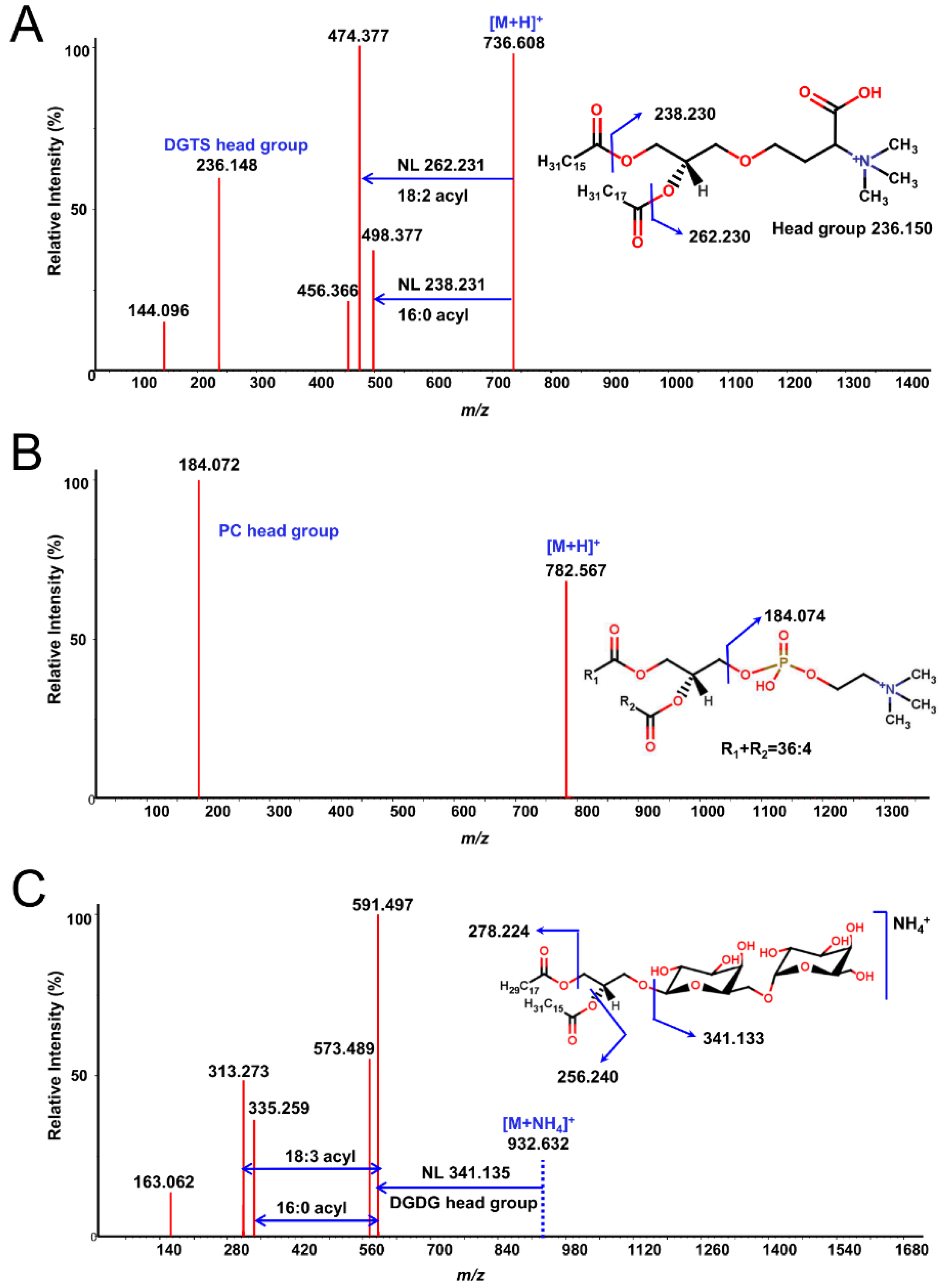
Analytical Separation by 2D-TLC and LC-MS/MS
Data Processing and Annotation of Lipid Species
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tietel, Z.; Hammann, S.; Meckelmann, S.W.; Ziv, C.; Pauling, J.K.; Wölk, M.; Würf, V.; Alves, E.; Neves, B.; Domingues, M.R. An overview of food lipids toward food lipidomics. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety 2023, 22, 4302–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züllig, T.; Köfeler, H.C. High resolution mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Mass spectrometry reviews 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2014, 61, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.; Süß, R.; Teuber, K.; Eibisch, M.; Schiller, J. Lipid analysis by thin-layer chromatography—A review of the current state. Journal of Chromatography A 2011, 1218, 2754–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Benning, C. Arabidopsis thaliana polar glycerolipid profiling by thin layer chromatography (TLC) coupled with gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, R.M.; Benning, C. Two enzymes of diacylglyceryl-O-4′-(N, N, N,-trimethyl) homoserine biosynthesis are encoded by btaA and btaB in the purple bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2001, 98, 5910–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, G.; Schwack, W. Coupling of planar chromatography to mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2010, 29, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Xin, G.-z.; So, P.-K.; Yao, Z.-P. Thin layer chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for direct analysis of raw samples. Journal of Chromatography A 2015, 1415, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, M.; Hasan, N.; Wu, H.-F. Rapid detection of haloarchaeal carotenoids via liquid–liquid microextraction enabled direct TLC MALDI-MS. Talanta 2013, 107, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R. Algae: the world’s most important “plants”—an introduction. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Change 2013, 18, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guschina, I.A.; Harwood, J.L. Lipids and lipid metabolism in eukaryotic algae. Progress in Lipid Research 2006, 45, 160–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudière, L.; Michaud, M.; Petroutsos, D.; Rébeillé, F.; Falconet, D.; Bastien, O.; Roy, S.; Finazzi, G.; Rolland, N.; Jouhet, J.; et al. Glycerolipids in photosynthesis: Composition, synthesis and trafficking. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2014, 1837, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, S.A.; Leblond, J.D. Betaine lipids in chlorarachniophytes. Phycological Research 2010, 58, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armada, I.; Hachero-Cruzado, I.; Mazuelos, N.; Ríos, J.L.; Manchado, M.; Cañavate, J.P. Differences in betaine lipids and fatty acids between Pseudoisochrysis paradoxa VLP and Diacronema vlkianum VLP isolates (Haptophyta). Phytochemistry 2013, 95, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, G.; Woznica, M.; Gfeller, H.; Müller, C.; Stämpfli, A.A.; Jenny, T.A.; Eichenberger, W. 1(3),2-Diacylglyceryl-3(1)-O-2′-(hydroxymethyl)(N,N,N,-trimethyl)-β-alanine (DGTA): A novel betaine lipid from Ochoromonas danica (Chrysophyceae). Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 1990, 52, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, B.T.; Nobles, D.; Ma, Y.; Wikoff, W.; Kind, T.; Fiehn, O.; Brand, J.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Informatics for improved algal taxonomic classification and research: A case study of UTEX 2341. Algal Research 2015, 12, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochaix, J.-D. Chlamydomonas, a model system for studying the assembly and dynamics of photosynthetic complexes. FEBS letters 2002, 529, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siaut, M.; Cuiné, S.; Cagnon, C.; Fessler, B.; Nguyen, M.; Carrier, P.; Beyly, A.; Beisson, F.; Triantaphylidès, C.; Li-Beisson, Y. Oil accumulation in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: characterization, variability between common laboratory strains and relationship with starch reserves. BMC biotechnology 2011, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Bhatnagar, M.; Chinnasamy, S.; Das, K. Chlorella minutissima—a promising fuel alga for cultivation in municipal wastewaters. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology 2010, 161, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yang, J.; Li, B. Optimization of the biomass production of oil algae Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Bioresource technology 2011, 102, 9128–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, B.T.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Effects of Escherichia coli on Mixotrophic Growth of Chlorella minutissima and Production of Biofuel Precursors. PloS one 2014, 9, e96807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J biol chem 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, S.F.; Yao, A.I.; Tietel, Z.; Kind, T.; Facciotti, M.T.; Parikh, A.N. Role of squalene in the organization of monolayers derived from lipid extracts of Halobacterium salinarum. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7922–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouser, G.; Kritchevsky, G.; Yamamoto, A. Column chromatographic and associated procedures for separation and determination of phosphatides and glycolipids. Lipid chromatographic analysis 1967, 1, 99–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Kind, T.; Yang, D.; Leon, C.; Fiehn, O. MS2Analyzer – a software for small molecule substructure annotations from accurate mass MS/MS spectra. Analytical chemistry 2014, 86, 10724–10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Liu, K.H.; Lee do, Y.; DeFelice, B.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O. LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nature methods 2013, 10, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietel, Z.; Wikoff, W.R.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Fiehn, O. Hyperosmotic stress in Chlamydomonas induces metabolomic changes in biosynthesis of complex lipids. European Journal of Phycology 2020, 55, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieler, A.; Wilhelm, C.; Goss, R.; Süß, R.; Schiller, J. The lipid composition of the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and the diatom Cyclotella meneghiniana investigated by MALDI-TOF MS and TLC. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2007, 150, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, W.G.; Yoder, T.F.; Ericson, L.; Pratum, T.; Winget, R.R. The characterisation and cyclic production of a highly unsaturated homoserine lipid in Chlorella minutissima. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Lipids and Lipid Metabolism 1996, 1299, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Meissen, J.; Yang, D.; Nocito, F.; Vaniya, A.; Cheng, Y.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O. Qualitative analysis of algal secretions with multiple mass spectrometric platforms. J Chromatogr A 2012, 1244, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, S.; Vacula, R.; Krajcovic, J.; Proksch, P.; Martin, W. Variability of wax ester fermentation in natural and bleached Euglena gracilis strains in response to oxygen and the elongase inhibitor flufenacet. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 2010, 57, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences-Guzmán, M.Á.; Guan, Z.; Bermúdez-Barrientos, J.R.; Geiger, O.; Sohlenkamp, C. Agrobacteria lacking ornithine lipids induce more rapid tumour formation. Environmental microbiology 2013, 15, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
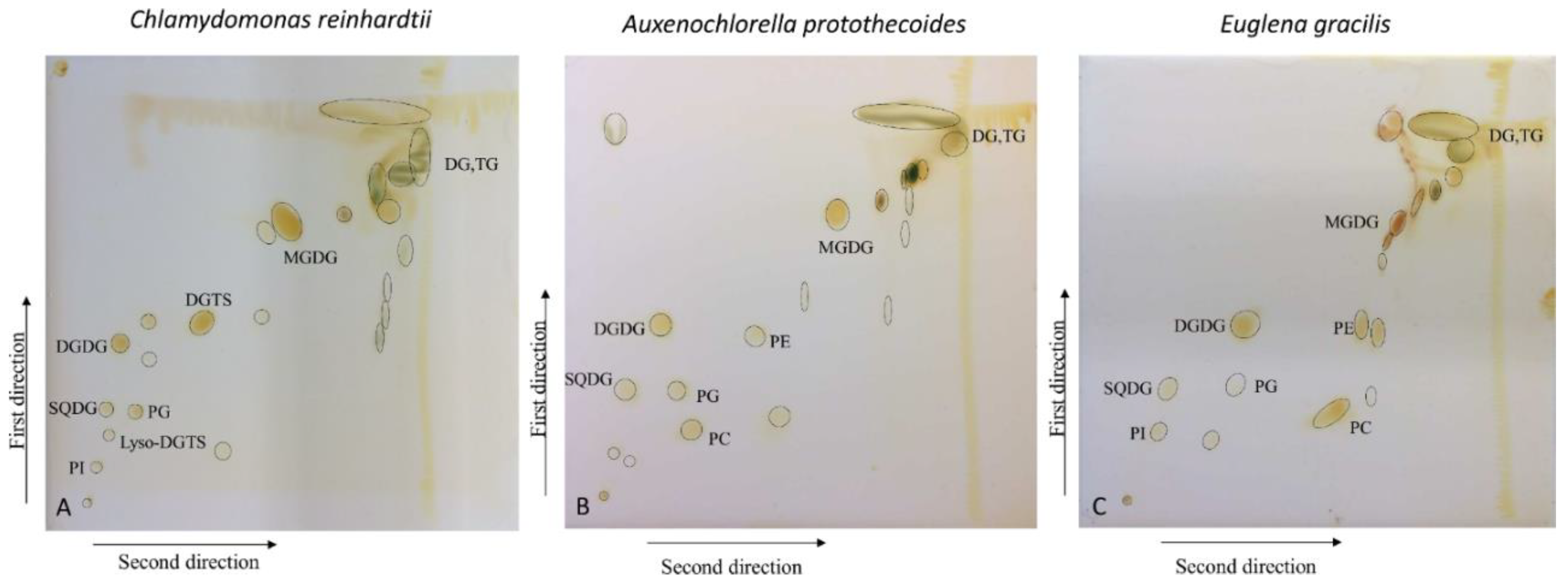
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Auxenochlorella protothecoides | Euglena gracilis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| DGDG | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| DGTS | 10 | ND | ND* |
| LysoDGTS | 3,10 | ND | ND* |
| DG | 21 | 19 | 13 |
| TG | 19,20,21 | 19,20 | 17 |
| PA | ND | ND | ND* |
| PC | ND | 4 | 6 |
| lysoPC | ND | ND* | 6 |
| PE | ND* | 9 | 9 |
| plasmenyl-PE | ND | ND | 9 |
| LysoPE | ND | ND* | 9 |
| PI | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| SQDG | 4 | 7 | 5 |
| PG | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| TOTAL | 123 | 158 | 212 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





