Submitted:
05 May 2024
Posted:
06 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Competing Interest
Availability of data and material
Acknowledgments
Consent for Publication
Data availability
Authors' contribution
References
- Sigrist, R.M.S.; Liau, J.; Kaffas, A.E.; Chammas, M.C.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound Elastography: Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1303–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantisani, V.; De Silvestri, A.; Scotti, V.; Fresilli, D.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Polti, G.; Guiban, O.; Polito, E.; Pacini, P.; Durante, C.J.F.i.o. US-elastography with different techniques for thyroid nodule characterization: systematic review and meta-analysis. 2022, 12, 845549.
- Cantisani, V.; David, E.; Barr, R.G.; Radzina, M.; de Soccio, V.; Elia, D.; De Felice, C.; Pediconi, F.; Gigli, S.; Occhiato, R.J.U.i.d.M.-E.J.o.U. US-elastography for breast lesion characterization: prospective comparison of US BIRADS, strain elastography and shear wave elastography. 2021, 42, 533–540.
- Ginat, D.T.; Destounis, S.V.; Barr, R.G.; Castaneda, B.; Strang, J.G.; Rubens, D.J.J.R. US elastography of breast and prostate lesions. 2009, 29, 2007–2016.
- Ryu, J.; Jeong, W.K.J.U. Current status of musculoskeletal application of shear wave elastography. 2017, 36, 185.
- Correas, J.-M.; Tissier, A.-M.; Khairoune, A.; Khoury, G.; Eiss, D.; Hélénon, O.J.D.; imaging, i. Ultrasound elastography of the prostate: state of the art. 2013, 94, 551–560.
- Pedersen, M.R.; Sloth Osther, P.J.; Nissen, H.D.; Vedsted, P.; Møller, H.; Rafaelsen, S.R. Elastography and diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with testicular microlithiasis, normal testicular tissue, and testicular cancer: an observational study. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden : 1987) 2019, 60, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.l.; Ding, H.; Fu, T.t.; Peng, S.y.; Chen, S.y.; Luo, J.j.; Wang, W.p.J.H.R. Portal hypertension in hepatitis B-related cirrhosis: diagnostic accuracy of liver and spleen stiffness by 2-D shear-wave elastography. 2019, 49, 540–549.
- Pawluś, A.; Inglot, M.; Chabowski, M.; Szymańska, K.; Inglot, M.; Patyk, M.; Słonina, J.; Caseiro-Alves, F.; Janczak, D.; Zaleska-Dorobisz, U.J.T.B.J.o.R. Shear wave elastography (SWE) of the spleen in patients with hepatitis B and C but without significant liver fibrosis. 2016, 89, 20160423.
- Chang, J.M.; Moon, W.K.; Cho, N.; Yi, A.; Koo, H.R.; Han, W.; Noh, D.-Y.; Moon, H.-G.; Kim, S.J.J.B.c.r. ; treatment. Clinical application of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases. 2011, 129, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, L.J.M. Diagnostic potential of real-time elastography (RTE) and shear wave elastography (SWE) to differentiate benign and malignant thyroid nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis. 2017, 96. 96.
- Ferraioli, G.; Tinelli, C.; Dal Bello, B.; Zicchetti, M.; Filice, G.; Filice, C.; Hepatology, L.F.S.G.J. Accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study. 2012, 56, 2125–2133.
- Mancini, M.; Salomone Megna, A.; Ragucci, M.; De Luca, M.; Marino Marsilia, G.; Nardone, G.; Coccoli, P.; Prinster, A.; Mannelli, L.; Vergara, E.J.P.o. Reproducibility of shear wave elastography (SWE) in patients with chronic liver disease. 2017, 12, e0185391.
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Ong, M.F.; Martens, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Bojunga, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Herrmann, E. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G.; Wilson, S.R.; Rubens, D.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ferraioli, G.J.R. Update to the society of radiologists in ultrasound liver elastography consensus statement. 2020, 296, 263–274.
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.-M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.J.U.i.m.; et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. 2003, 29, 1705–1713.
- Giuffrè, M.; Macor, D.; Masutti, F.; Abazia, C.; Tinè, F.; Patti, R.; Buonocore, M.R.; Colombo, A.; Visintin, A.; Campigotto, M.; et al. Evaluation of spleen stiffness in healthy volunteers using point shear wave elastography. Annals of Hepatology 2019, 18, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Kirnake, V.; Tyagi, P.; Bansal, N.; Singla, V.; Kumar, A.; Arora, A.J.O.j.o.t.A.C.o.G. ; ACG. Spleen stiffness in patients with cirrhosis in predicting esophageal varices. 2013, 108, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Rewisha, E.; Elsabaawy, M.; Alsebaey, A.; Elmazaly, M.; Tharwa, E.J.o. Evaluation of the Role of Liver and Splenic Transient Elastography in Chronic Hepatitis C Related Fibrosis. J Liver Disease Transplant 5: 3. 2016, 5, 35–06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batur, A.; Alagoz, S.; Durmaz, F.; Baran, A.I.; Ekinci, O.J.U.Q. Measurement of spleen stiffness by shear-wave elastography for prediction of splenomegaly etiology. 2019, 35, 153–156.
- GIBIINO, G.; Garcovich, M.; Ainora, M.; Zocco, M.J.E.R.f.M.; Sciences, P. Spleen ultrasound elastography: state of the art and future directions-a systematic review. 2019, 23. 23.
- Webb, M.; Zimran, A.; Dinur, T.; Shibolet, O.; Levit, S.; Steinberg, D.M.; Salomon, O. Are transient and shear wave elastography useful tools in Gaucher disease? Blood cells, molecules & diseases 2018, 68, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Bhatia, H.; Saxena, A.K.; Lal, S.B.; Sodhi, K.S. Shear wave elastography of the spleen using elastography point quantification: stiffness values in healthy children. Abdominal Radiology 2022, 47, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, K.; Demir, B.Ç.J.A.R. Spleen stiffness measurement by shear wave elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse in predicting the etiology of splenomegaly. 2021, 46, 609–615.
- Barr, R.G.; Wilson, S.R.; Rubens, D.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ferraioli, G. Update to the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Liver Elastography Consensus Statement. 2020, 296, 263–274. [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.W.; Li, K.N.; Yi, A.J.; Wang, B.; Wei, Q.; Wu, G.G.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound elastography. Endoscopic ultrasound 2022, 11, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, R.; Celmer, M.; Silicki, J.; Hołownia, D.; Pozowski, P.; Międzybrodzki, K. Clinical applications of spleen ultrasound elastography - a review. Journal of ultrasonography 2018, 18, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, L.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Guo, H.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Zheng, R.J.R. Liver stiffness measured with two-dimensional shear-wave elastography is predictive of liver-related events in patients with chronic liver disease due to hepatis B viral infection. 2020, 295, 353–360.
- Kim, H.Y.; Jin, E.H.; Kim, W.; Lee, J.Y.; Woo, H.; Oh, S.; Seo, J.-Y.; Oh, H.S.; Chung, K.H.; Jung, Y.J.J.M. The role of spleen stiffness in determining the severity and bleeding risk of esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients. 2015, 94. 94.
- Rozario, R.; Ramakrishna, B.J.J.o.h. Histopathological study of chronic hepatitis B and C: a comparison of two scoring systems. 2003, 38, 223–229.
- Uchida, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Shigeta, T.; Matsunami, M.; Sasaki, K.; Kanazawa, H.; Fukuda, A.; Kanamori, Y.; Miyasaka, M.J.J.o.p.s. The degree of spleen stiffness measured on acoustic radiation force impulse elastography predicts the severity of portal hypertension in patients with biliary atresia after portoenterostomy. 2015, 50, 559–564.
- Benedetti, E.; Tavarozzi, R.; Morganti, R.; Bruno, B.; Bramanti, E.; Baratè, C.; Balducci, S.; Iovino, L.; Ricci, F.; Ricchiuto, V.; et al. Organ Stiffness in the Work-Up of Myelofibrosis and Philadelphia-Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Journal of clinical medicine 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, R.; Celmer, M.; Silicki, J.; Hołownia, D.; Pozowski, P.; Międzybrodzki, K.J.J.o.u. Clinical applications of spleen ultrasound elastography–a review. 2018, 18, 37–41.
- Ece, B.; Aydin, S.J.C. Can Shear Wave Elastography Help Differentiate Acute Tonsillitis from Normal Tonsils in Pediatric Patients: A Prospective Preliminary Study. 2023, 10, 704.
- Aydin, S.; Senbil, D.C.; Karavas, E.; Kadirhan, O.; Kantarci, M. Shear-wave Elastography of Palatine Tonsils: A Normative Study in Children. Journal of medical ultrasound 2023, 31, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garra, B.S.J.A.i. Elastography: history, principles, and technique comparison. 2015, 40, 680–697.
- Ormachea, J.; Parker, K.J.P.i.M. ; Biology. Elastography imaging: the 30 year perspective. 2020, 65, 24TR06. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, C.; Bogs, C.; Verlinden, W.; Thiele, M.; Möller, P.; Görtzen, J.; Lehmann, J.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Vonghia, L.; Praktiknjo, M.J.L.I. Shear-wave elastography of the liver and spleen identifies clinically significant portal hypertension: a prospective multicentre study. 2017, 37, 396–405.
- Elkrief, L.; Rautou, P.-E.; Ronot, M.; Lambert, S.; Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Francoz, C.; Plessier, A.; Durand, F.; Valla, D.; Lebrec, D.J.R. Prospective comparison of spleen and liver stiffness by using shear-wave and transient elastography for detection of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. 2015, 275, 589–598.
- Nedredal, G.I.; Yin, M.; McKenzie, T.; Lillegard, J.; Luebke-Wheeler, J.; Talwalkar, J.; Ehman, R.; Nyberg, S.L. Portal hypertension correlates with splenic stiffness as measured with MR elastography. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2011, 34, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavu, E.; Gennisson, J.L.; Couade, M.; Bercoff, J.; Mallet, V.; Fink, M.; Badel, A.; Vallet-Pichard, A.; Nalpas, B.; Tanter, M.; et al. Noninvasive in vivo liver fibrosis evaluation using supersonic shear imaging: a clinical study on 113 hepatitis C virus patients. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2011, 37, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirooka, M.; Ochi, H.; Koizumi, Y.; Kisaka, Y.; Abe, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Matsuura, B.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M.J.R. Splenic elasticity measured with real-time tissue elastography is a marker of portal hypertension. 2011, 261, 960–968.
- Jeon, S.K.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Han, J.K.J.A.r. Two-dimensional shear wave elastography with propagation maps for the assessment of liver fibrosis and clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease: a prospective study. 2020, 27, 798–806.
- Shan, Q.Y.; Liu, B.X.; Tian, W.S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.Y. Elastography of shear wave speed imaging for the evaluation of liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Hepatology research : the official journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology 2016, 46, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraquelli, M.; Conti, C.B.; Giunta, M.; Gridavilla, D.; Tosetti, G.; Baccarin, A.; Casazza, G.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Nicolini, A.; Primignani, M.J.G. Assessing spleen stiffness by point shear-wave elastography: Is it feasible and reproducible in patients with chronic liver disease? Is it useful to predict portal hypertension? 2019, 1, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, N.; Huang, W.; Lv, N.J.P.O. Imaging findings of primary splenic lymphoma: a review of 17 cases in which diagnosis was made at splenectomy. 2013, 8, e80264.
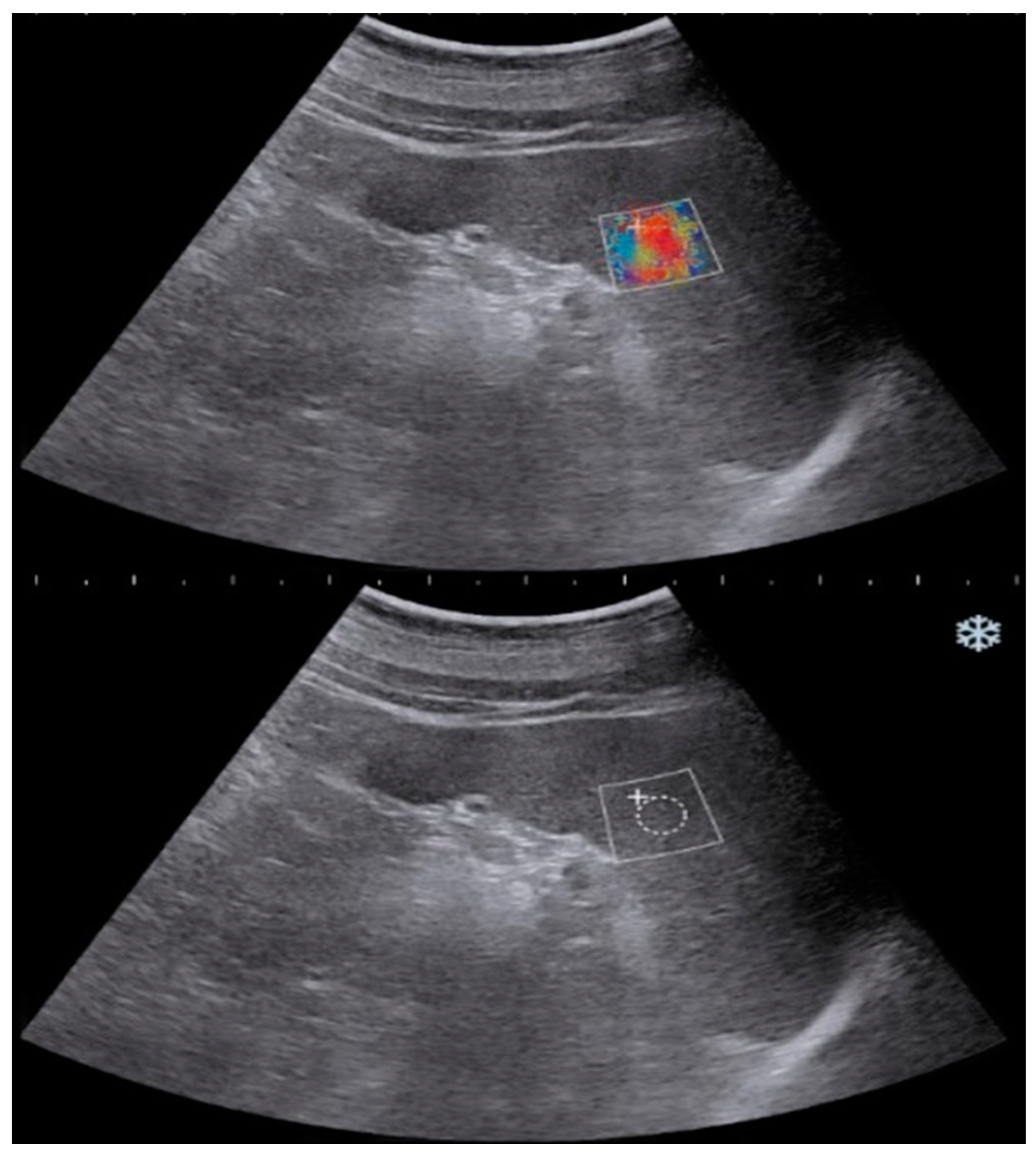
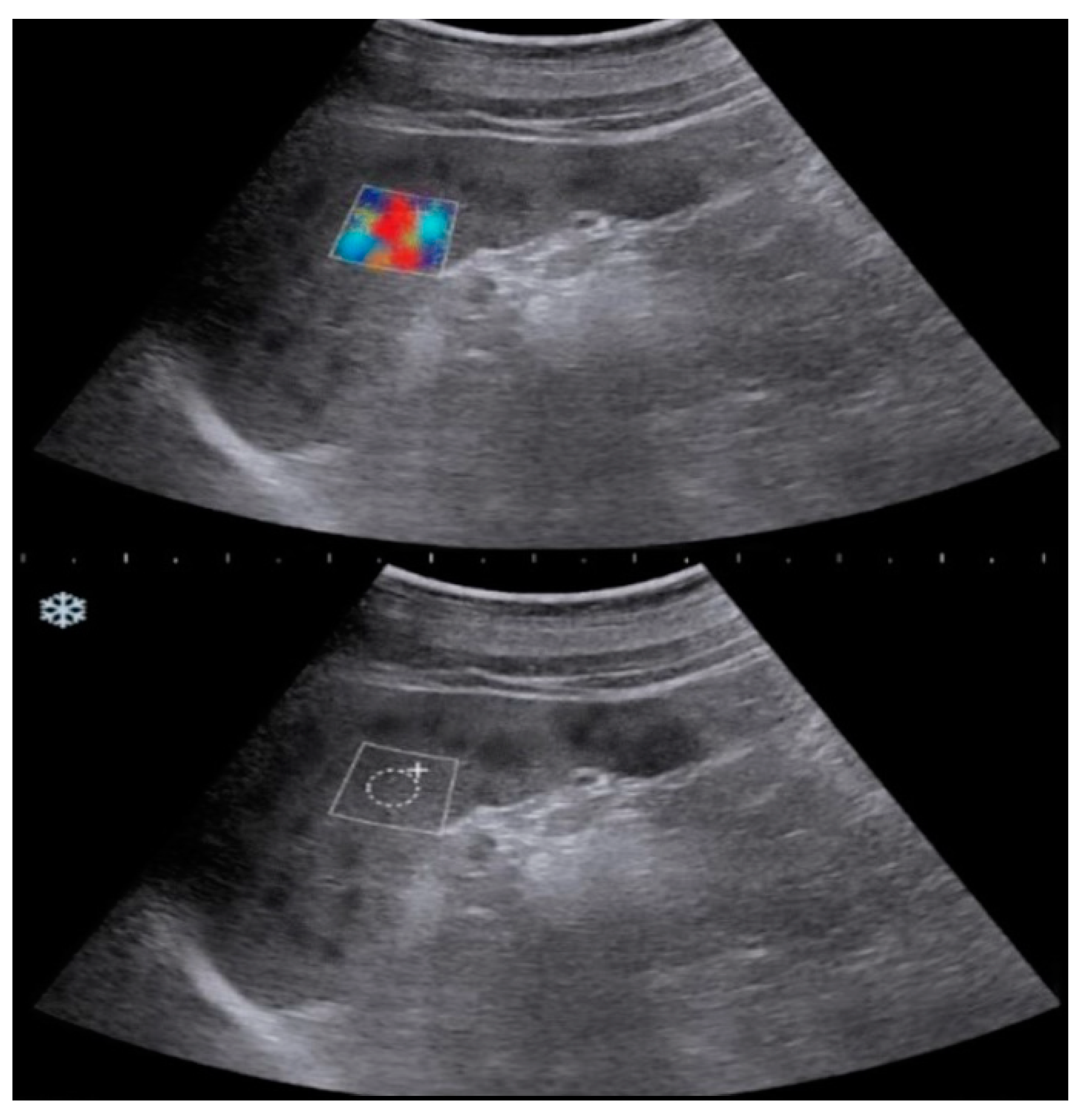
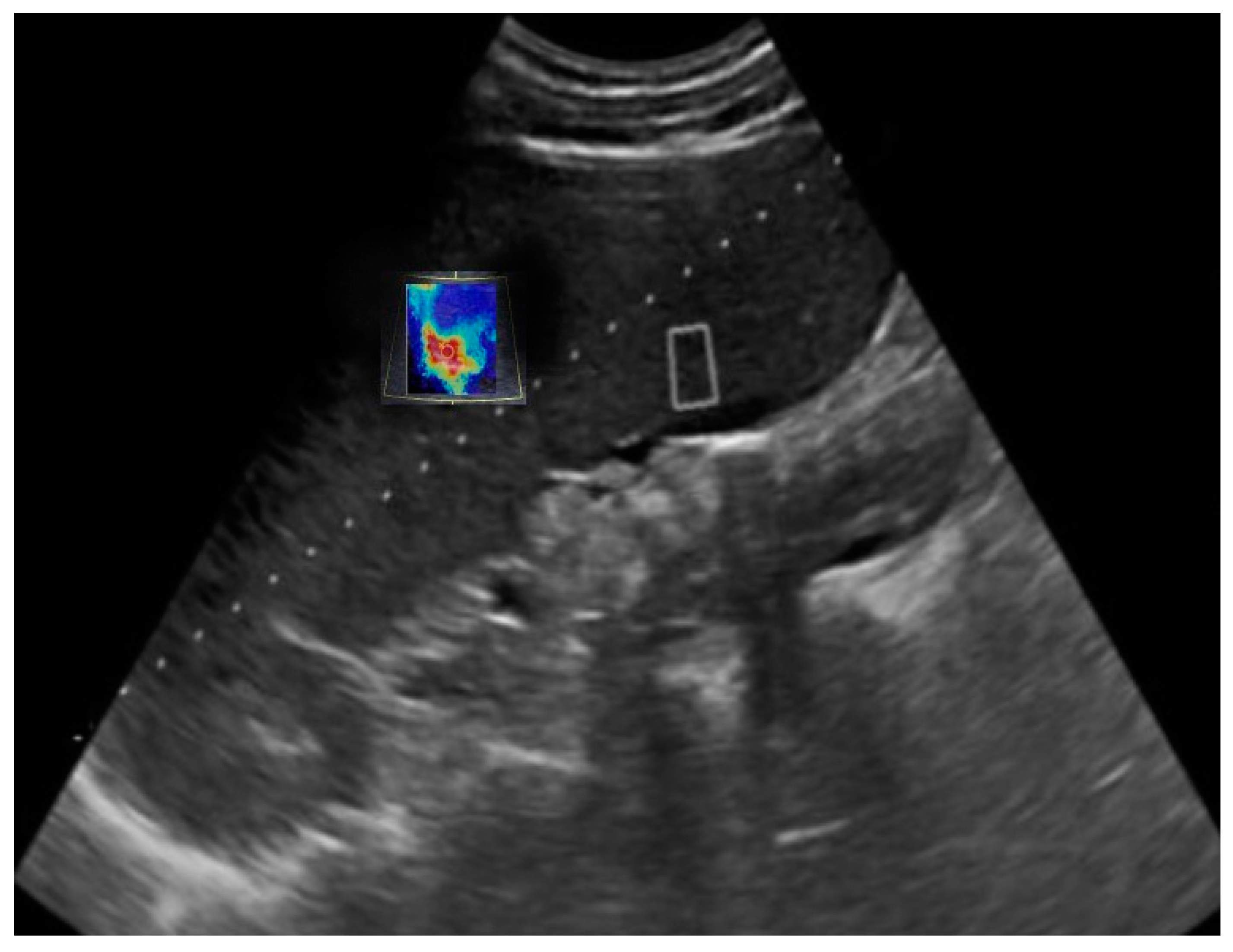
| Exclusion Criteria | n(Excluded Patients) |
|---|---|
| History of Acute Splenic İnjury | 12 |
| Splenic Surgery | 8 |
| Previous Treatment with Non-Selective Beta-Blockers | 5 |
| Shunt Placement | 4 |
| Band Ligation | 1 |
| Liver Transplantation | 3 |
| Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy | 3 |
| İntrahepatic or Extrahepatic Malignancies Other Than Lymphoid Maligninant İnfiltration | 9 |
| Portal Vein Thrombosis or Cavernous Transformation | 7 |
| Presence of Other Chronic Liver Disease | 6 |
| Male n(%) | Female n(%) | Total n(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study Group | 892 (64.6) | 487(35.3) | 1379 (100) |
|
126 (9.1) | 67 (4.8) | 193 (13.9) |
|
213 (15.4) | 144 (10.4) | 357 (25.8) |
|
553 (40.1) | 276 (20) | 829 (60.1) |
| Control Group | 779 (55.5) | 623 (44.4) | 1402 (100) |
| Groups | Mean splenic stiffness value |
|---|---|
| Control group | 13.56±3.58 kPa |
| Malignant Infiltration | 10.58±1.18 kPa |
| Portal Hypertansion | 16.63±7.73 kPa |
| Benign Lymphoid Hyperplasia | 14.11±3.91 kPa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





