Submitted:
09 May 2024
Posted:
10 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
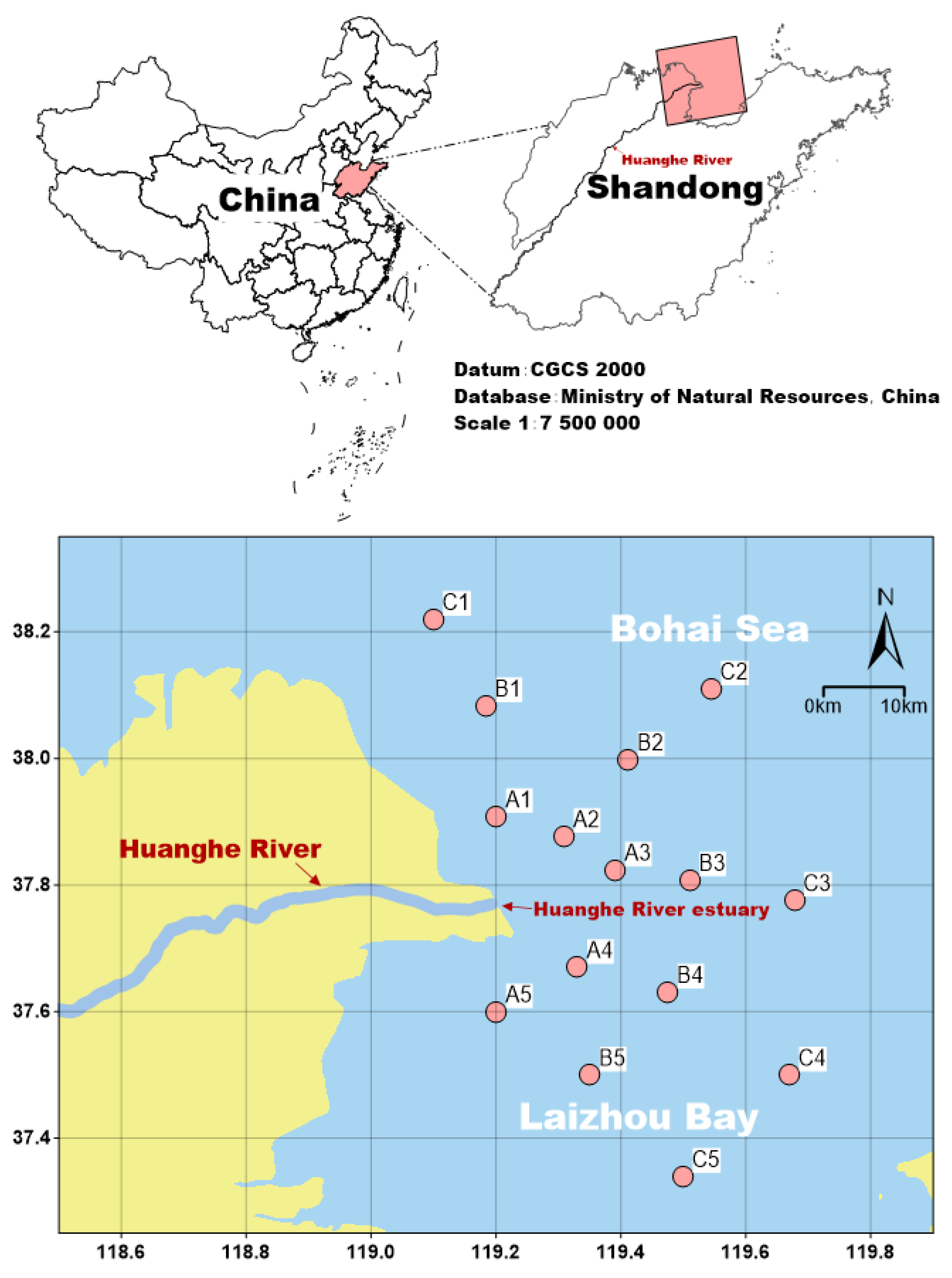
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Functional Traits
2.2.2. Functional alpha-diversity
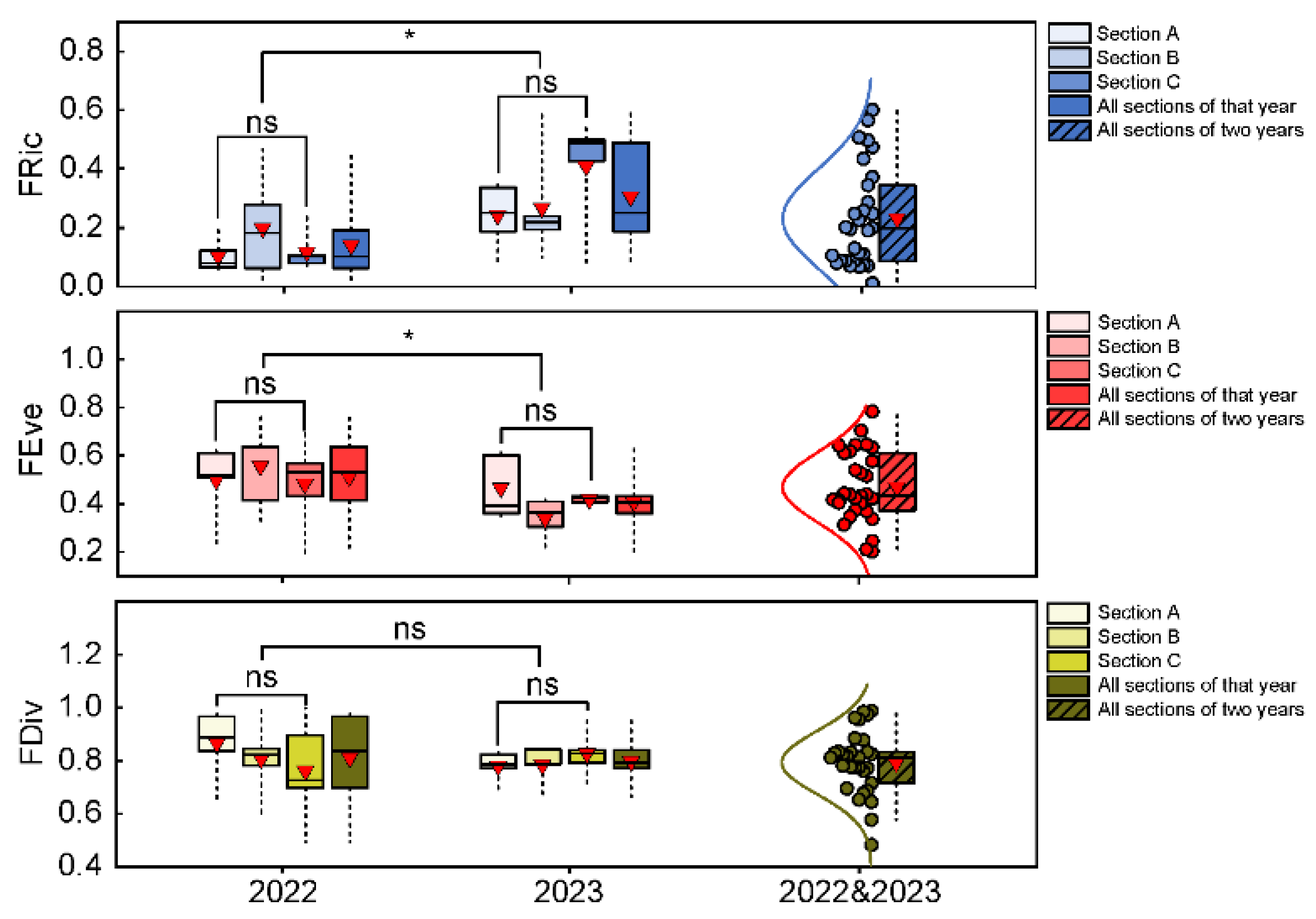
- Functional richness, FRic, quantifies the size of the ecological space occupied by a species within a community, reflecting the stability of the community and its ability to buffer environmental disturbances and resist ecological invasion [48]. FRic was calculated as follows. First, a species with an extreme character value was identified and used as the end point of the smallest convex shape in the N-dimensional character space. Then, the endpoints were connected to form a minimum convex polygon. Finally, the area or volume of the minimum convex polygon was calculated [46].
- Functional evenness, FEve, quantifies the evenness of the abundance of functional traits of species within a community that is distributed in functional space, reflecting the overall utilization of resources by species [48]. FEve was calculated as follows:where a to m represented the 16 functional traits of species i and j in a multidimensional trait space, dist(i, j) was the Euclidean distance between species i and j, EWl was the branch length, wi and wj were the relative abundances of species i and j, PEWl was the branch length weight, and S was the number of species.
- Functional divergence, FDiv, quantifies the dispersion of species functional trait abundance within the community in the functional space, reflecting the degree of niche differentiation and resource competition among species within the community [48]. FDiv was calculated as follows:where xik was the value of trait k for species I, gk was the centroid of trait k, S was the number of species, T was the number of traits, was the average distance between species i and the centroid, Δd was the dispersion weighted by abundance, and wi was the relative abundance of species i. The usage conditions were S>T.
- Community-weighted mean, CWM, quantifies the weighted average of functional traits of species within a community, reflecting the changes in dominant trait values of fish communities. CWM is very important for evaluating community dynamics [10]. CWM was calculated as follows:where pi represented the relative abundance of species i, traiti was the trait value of species i, and S was the number of species in the community.
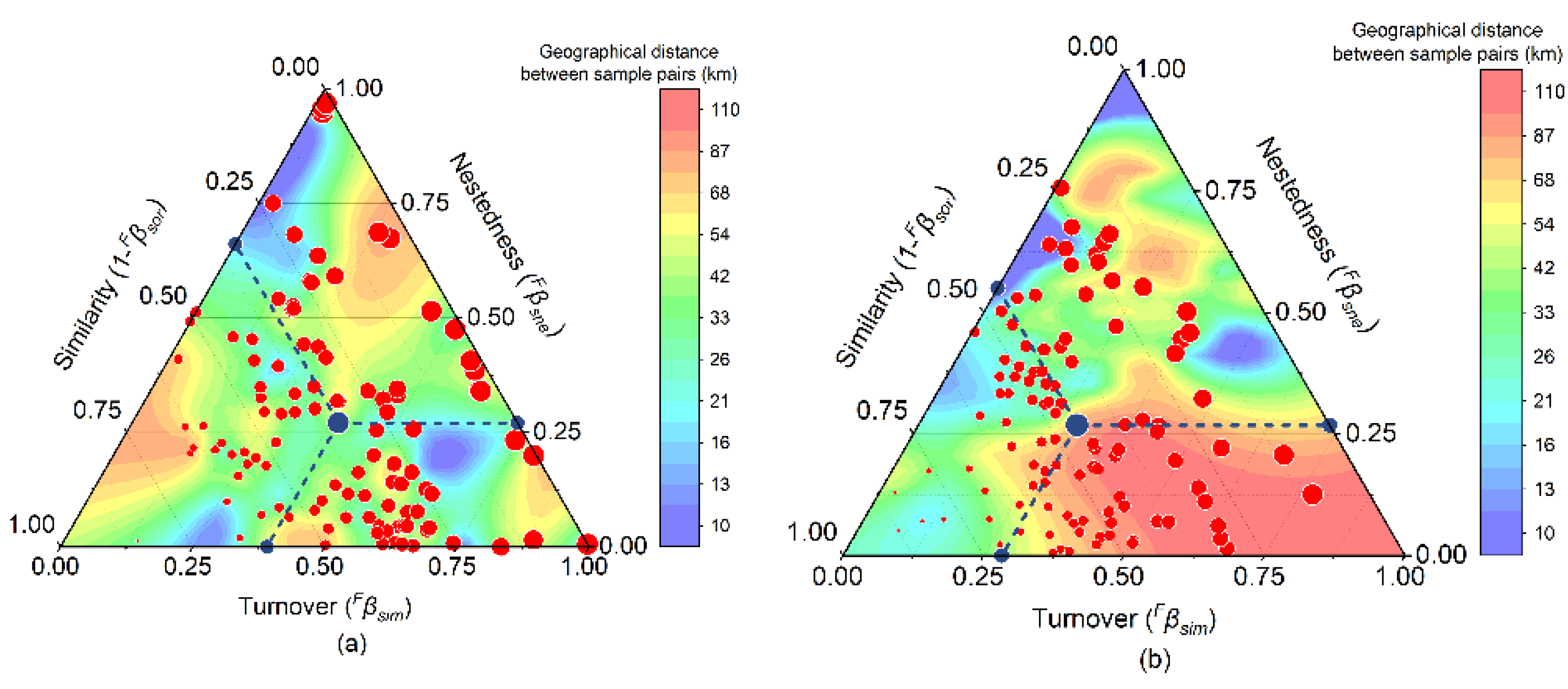
2.2.3. Functional Beta-Diversity
2.2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
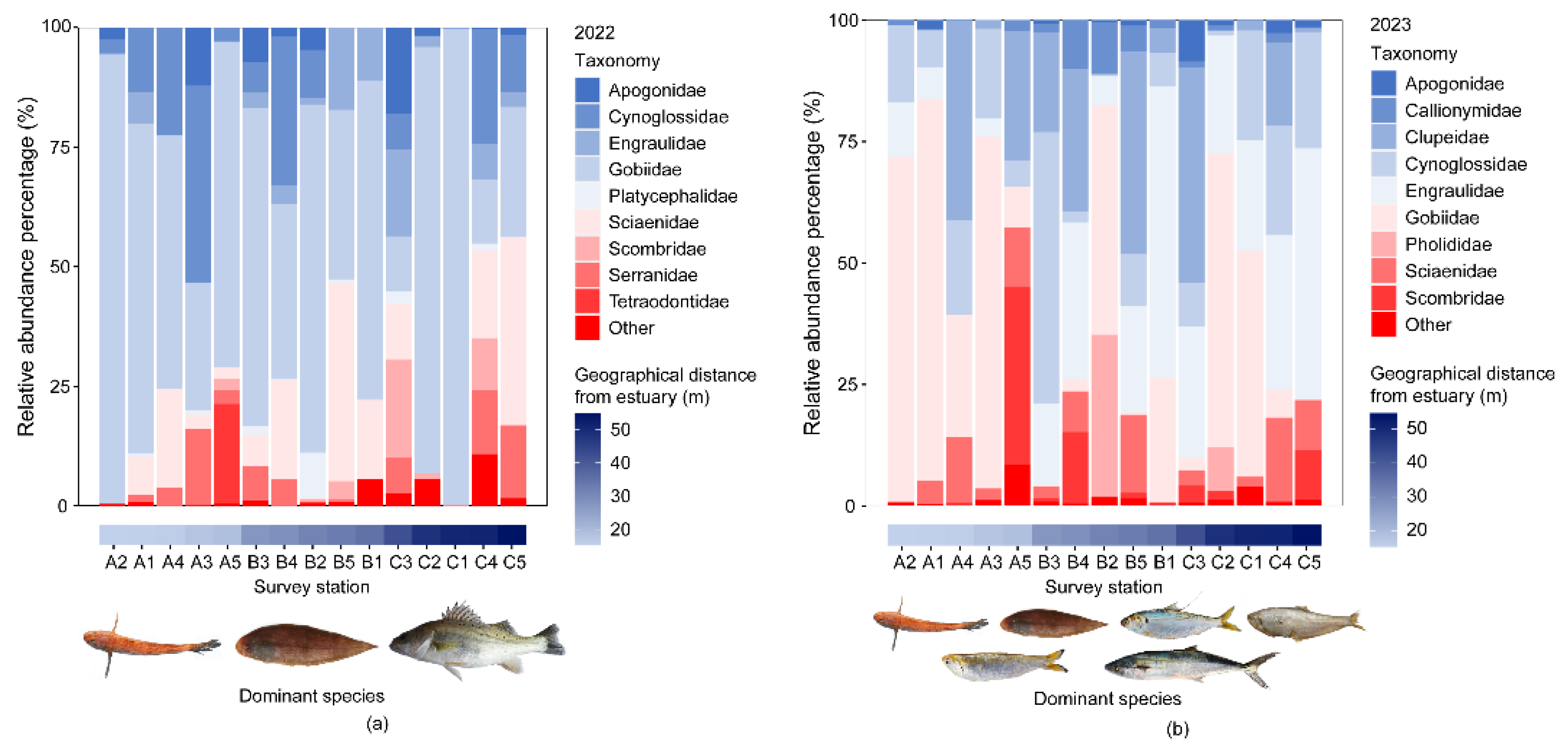
3.1. Fish Species Composition in the Huanghe River Estuary and Adjacent Seas
3.2. Functional Alpha-Diversity and Dominant Community Trait Composition of Fishes in the Huanghe River Estuary and Adjacent Seas
3.3. Functional Beta-Diversity of Fishes in the Huanghe River Estuary and Adjacent Seas
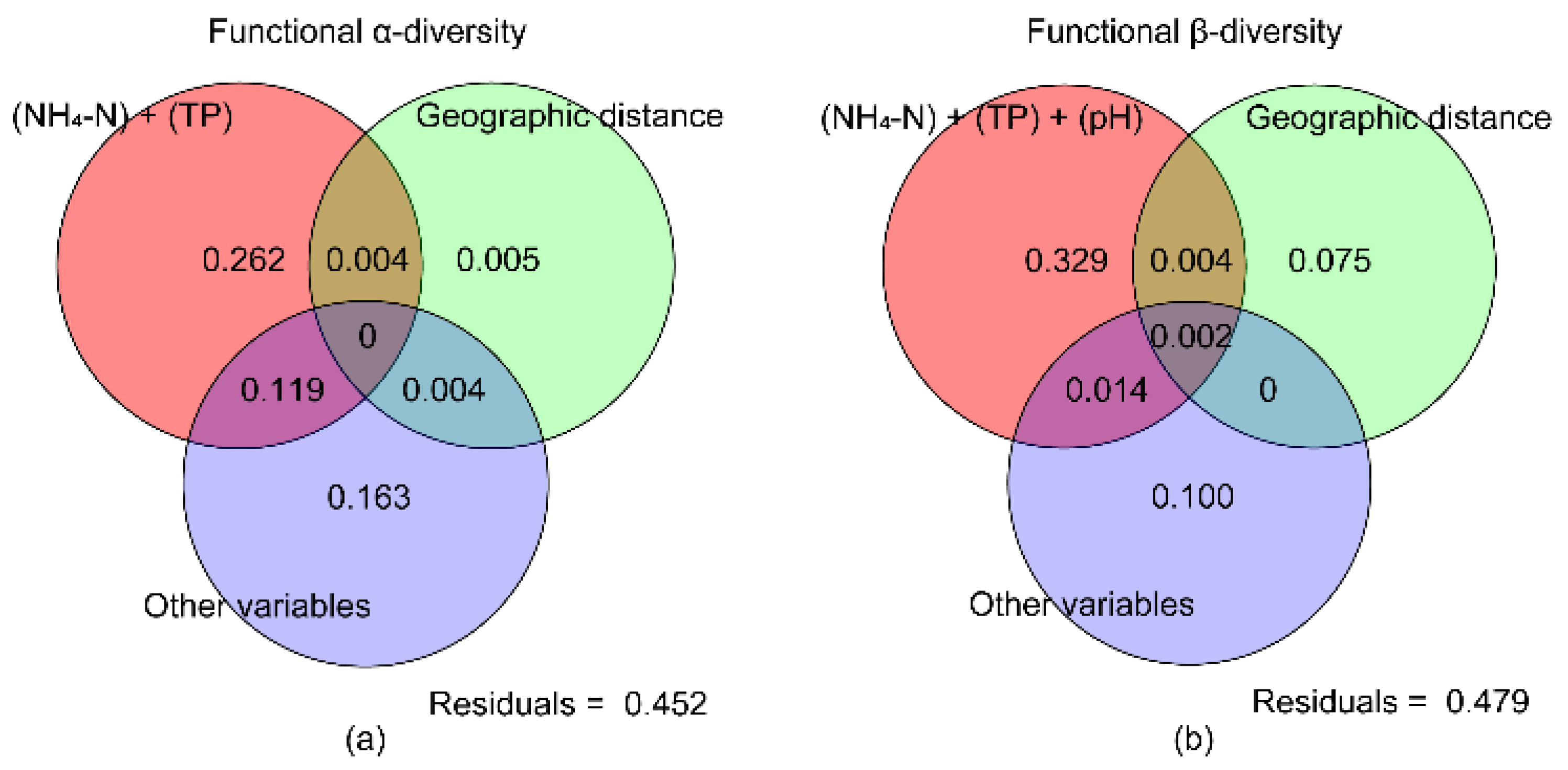
3.4. Relationship between Functional Diversity of Fishes and Environmental Factors in the Huanghe River Estuary and Adjacent Seas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Family | Species | Feeding habit | Mouth position | Mouth relative size | Trophic Level | Habitat | Migration type | Body shape | Maximum body length (cm) | Body length at first sexual maturity (cm) | Age at first sexual maturity (a) | Generation time (a) | Ecological type of eggs | Growth coefficient (k) | Vulnerability | Resilience | Thermo-phily |
| Apogonidae | Apogon lineatus | B | Front | CB | 3.7 | De | OM | 2 | 9.00 | 6.8 | 0.8 | 1.0 | PAE | 0.50 | 12 | Hr | WW |
| Callionymidae | Callionymus beniteguri | B | Front | S | 3.3 | De | ST | 3 | 13.96 | - | - | - | PE | 0.52 | 13 | Hr | T |
| Clupeidae | Konosirus punctatus | H | Front | CS | 2.9 | Pe | OM | 2 | 32.00 | 18.1 | 2.9 | 3.2 | PE | 0.65 | 36 | Hr | T |
| Sardinella zunasi | P | Front | CS | 3.4 | Pe | OM | 2 | 18.00 | 11.0 | 1.0 | 2.2 | PE | 0.50 | 22 | Hr | T | |
| Cottidae | Trachidermus fasciatus | B-N | Front | B | 3.0 | De | OM | 10 | 17.00 | 10.9 | 1.0 | - | DAE | - | 10 | Lr | CT |
| Cynoglossidae | Cynoglossus joyeri | B | Lower | S | 4.3 | De | CM | 5 | 24.00 | 17.2 | 3.8 | 4.1 | PE | 0.20 | 40 | Mr | T |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | B | Lower | S | 3.7 | De | CM | 5 | 61.10 | 34.6 | 2.8 | 3.8 | PE | 0.26 | 44 | Mr | T | |
| Engraulidae | Engraulis japonicus | P | Lower | B | 3.6 | Pe | OM | 2 | 18.00 | 10.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | PE | 0.79 | 10 | Hr | T |
| Setipinna taty | P | Lower | B | 3.6 | Pe | OM | 2 | 22.20 | 12.4 | 1.0 | - | PE | 0.57 | 17 | Hr | WW | |
| Thrissa kammalensis | P | Lower | B | 3.4 | Pe | OM | 2 | 18.00 | 8.9 | 2.4 | 3.3 | PE | 0.56 | 32 | Mr | T | |
| Thrissa mystax | P | Lower | B | 3.6 | Pe | OM | 2 | 19.00 | 13.0 | 1.0 | - | PE | 0.56 | 11 | Hr | WW | |
| Gobiidae | Acanthogobius ommaturus | B | Front | CB | 3.4 | De | ST | 8 | 50.00 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | AE | 0.20 | 50 | Lr | T |
| Amblychaeturichthys hexanema | B | Front | S | 3.4 | De | ST | 4 | 17.40 | 11.4 | 1.9 | 2.5 | AE | 0.70 | 10 | Mr | T | |
| Amoya pflaumi | B | Front | CS | 3.1 | De | ST | 8 | 12.00 | 8.9 | 1.0 | 1.4 | AE | 0.44 | 10 | Hr | WW | |
| Chaeturichthys stigmatias | B | Front | S | 3.8 | De | ST | 4 | 28.20 | 11.8 | 2.7 | 2.9 | AE | 0.45 | 18 | Mr | T | |
| Ctenotrypauchen chinensis | B | Front | S | 3.8 | De | ST | 2 | 19.20 | - | - | - | AE | - | 13 | Mr | T | |
| Myersina filifer | B | Front | CS | 3.4 | De | ST | 2 | 13.20 | - | - | - | AE | - | 10 | Hr | WW | |
| Odontamblyopus lacepedii | B | Front | CB | 3.9 | De | ST | 4 | 33.40 | 20.3 | 3.7 | 4.2 | AE | 0.19 | 31 | Mr | WW | |
| Tridentiger barbatus | B | Front | S | 3.5 | De | ST | 8 | 10.40 | 7.3 | 1.5 | 2.0 | AE | 0.56 | 14 | Hr | T | |
| Hexagrammidae | Hexagrammos otakii | P-B | Front | S | 3.8 | De | OM | 2 | 57.00 | 11.6 | 2.0 | 2.9 | AE | 0.36 | 34 | Mr | CT |
| Mugilidae | Liza haematocheila | P | Lower | S | 2.5 | De | ST | 11 | 80.00 | 48.0 | 2.5 | 8.1 | PE | 0.31 | 58 | Mr | T |
| Paralichthyidae | Paralichthys olivaceus | N | Front | M | 4.5 | De | CM | 5 | 103.00 | 40.0 | 2.0 | 7.3 | PE | 0.24 | 60 | Mr | T |
| Pholididae | Enedrias fangi | P-B | Front | M | 3.2 | De | CM | 9 | 16.80 | 11.2 | 1.1 | 1.5 | O | 0.61 | 10 | Hr | CT |
| Platycephalidae | Platycephalus indicus | B-N | Front | M | 3.6 | De | OM | 3 | 100.00 | 45.7 | 1.8 | 2.5 | PE | 0.30 | 35 | Mr | WW |
| Pleuronectidae | Kareius bicoloratus | B | Front | S | 3.7 | De | CM | 5 | 50.00 | 31.6 | 3.7 | 4.8 | PE | 0.18 | 46 | Lr | CT |
| Sciaenidae | Collichthys niveatus | P-B | Front | CS | 3.6 | De | CM | 2 | 17.00 | 8.8 | 1.0 | 4.0 | PE | 0.42 | 17 | Hr | T |
| Johnius belengerii | B | Lower | CS | 3.3 | De | OM | 2 | 30.00 | 12.5 | 1.3 | 1.5 | PE | 0.53 | 20 | Hr | WW | |
| Larimichthys polyactis | B-N | Front | M | 3.7 | De | OM | 2 | 40.00 | 18.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | PE | 0.45 | 27 | Mr | T | |
| Pennahia argentata | B | Lower | M | 4.1 | De | OM | 2 | 40.00 | 11.1 | 1.6 | 2.0 | PE | 0.42 | 34 | Hr | T | |
| Scombridae | Scomberomorus niphonius | N | Front | CB | 4.8 | Pe | DM | 1 | 113.00 | 37.0 | 1.0 | 8.5 | PE | 0.53 | 34 | Mr | T |
| Serranidae | Lateolabrax maculatus | N | Upper | M | 4.7 | De | CM | 2 | 102.00 | 52.7 | 2.0 | 5.2 | PE | 0.42 | 52 | Mr | T |
| Sillaginidae | Sillago sihama | B | Front | S | 3.4 | De | OM | 6 | 31.00 | 16.7 | 1.4 | 1.5 | PE | 0.80 | 24 | Hr | WW |
| Stromateidae | Pampus argenteus | P | Front | S | 3.3 | Pe | DM | 2 | 60.00 | 25.3 | 1.3 | 1.5 | PE | 0.56 | 31 | Mr | WW |
| Syngnathidae | Syngnathus acus | P | Front | S | 3.3 | De | ST | 7 | 50.00 | 16.3 | - | - | O | - | 40 | Mr | T |
| Tetraodontidae | Takifugu niphobles | P-B | Front | S | 3.4 | De | OM | 6 | 20.00 | 11.0 | 1.0 | - | DAE | 0.31 | 44 | Mr | CT |
| Takifugu pseudommus | P-B | Front | S | 3.4 | De | OM | 6 | 35.00 | - | - | - | DAE | - | 33 | Mr | T | |
| Trichiuridae | Eupleurogrammus muticus | B | Front | CB | 4.1 | De | OM | 9 | 87.00 | - | - | - | PE | - | 48 | Hr | WW |
Appendix B
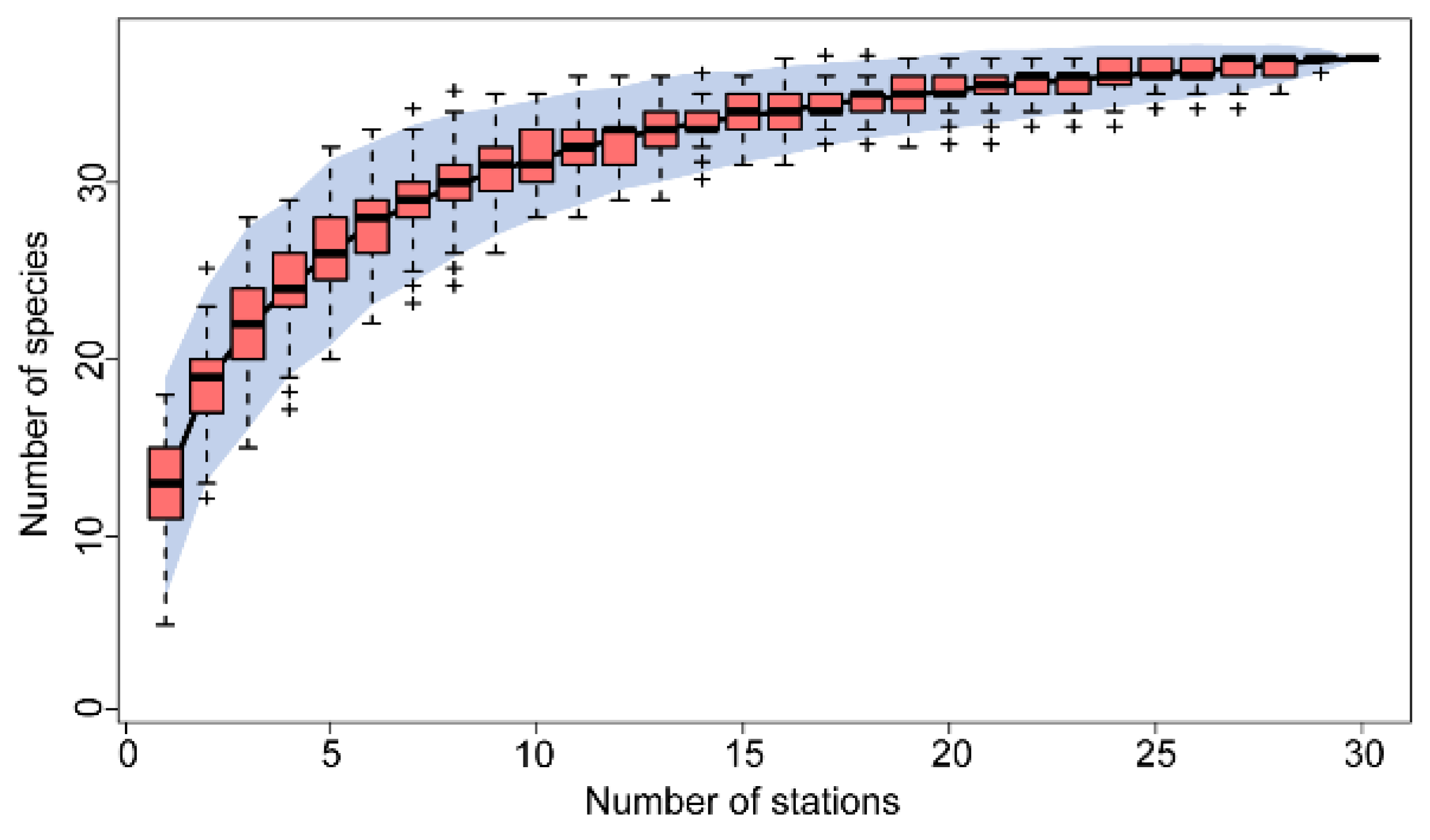
Appendix C
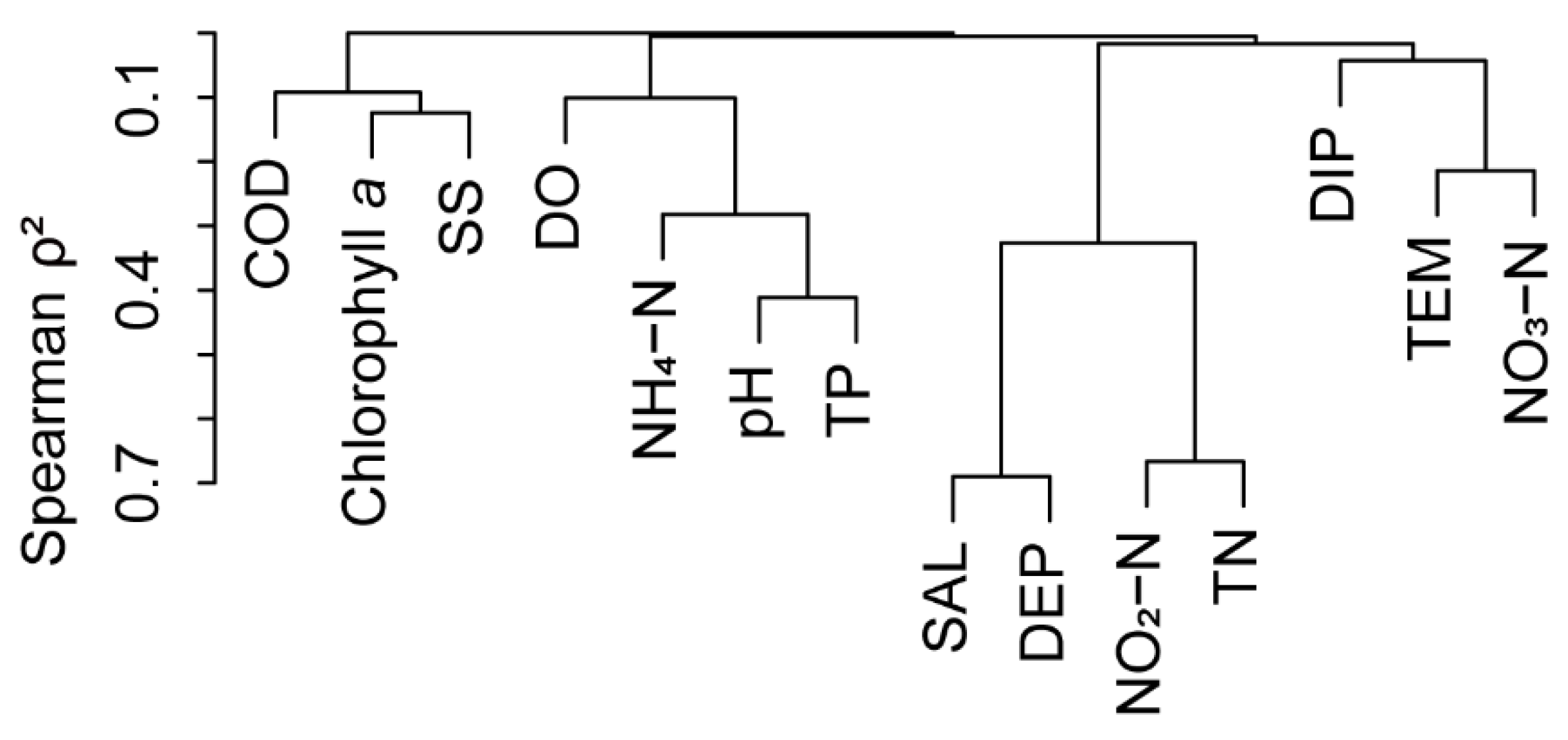
References
- Niu, K.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Shen, Z.H.; He, F.L.; Fang, J.Y. Community assembly: The relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science 2009, 17, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Xu, W.H.; Xiao, Y. A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science 2010, 18, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violle, C.; Reich, P.B.; Pacala, S.W.; Enquist, B.J.; Kattge, J. The emergence and promise of functional biogeography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2014, 111, 13690–13696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains,Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs 1960, 20, 2799–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolar, J.B.; Gilroy, J.J.; Kunin, W.E.; Edwards, D.P. How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2016, 31, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, X.F.; Zhao, Y.H.; Chen, C.W.; Ren, P.; Zeng, D.; Wu, L.B.; Ding, P. Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science 2017, 25, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureto, L.M.O.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Samia, D.S.M. Functional diversity: An overview of its history and applicability. Natureza & Conservacao 2015, 13, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, N.G.; Erickson, D.L.; Mi, X.C.; Bourg, N.A.; Forero-Montaña, J.; Ge, X.J.; Howe, R.; Lake, J.K.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, K.P.; Pei, N.C.; Thompson, J.; Uriarte, M.; Wolf, A.; Wright, S.J.; Ye, W.H.; Zhang, J.L.; Zimmerman, J.K.; Kress, W.J. Phylogenetic and functional alpha and beta diversity in temperate and tropical tree communities. Ecology 2012, 93, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, S.; Grigulis, K.; Lamarque, P.; Colace, M.P.; Garden, D.; Girel, J.; Pellet, G.; Douzet, R. Using plant functional traits to understand the landscape distribution of multiple ecosystem services. Journal of Ecology 2011, 99, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.N.; Zanden, M.J.V. What a difference a species makes: a metaanalysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 2010, 80, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villéger, S.; Grenouillet, G.; Brosse, S. Decomposing functional β-diversity reveals that low functional β-diversity is driven by low functional turnover in European fish assemblages. Global Ecology & Biogeography 2013, 22, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D.; Lee, W.G.; Wilson, J.B.; Setl, H. Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: The primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 2005, 111, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.D.; Zhang, C.L.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P. Spatio-temporal variations of functional diversity of fish communities in Haizhou Bay. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2019, 30, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, S.D.; Tang, Y.L.; Dong, X.Q.; Zhao, W.; Feng, J.; Yu, M.J. Species and functional diversity of fish communities in artificial reef area of Pipa Island Sea, Shandong. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 2023, 30, 1479–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Shan, X.J.; Bian, X.D.; Wei, C.; Zhang, W.R.; Cui, P.D. Early life resources community structure and functional diversity to the Osteichthyes in the waters adjacent to the Changdao Islands. Progress in Fishery Sciences 2023, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, N.G.; Anglada-Cordero, P.; Barone, J.A. Deterministic tropical tree community turnover: Evidence from patterns of functional beta diversity along an elevational gradient. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2011, 278, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.F.; Baselga, A.; Leprieur, F.; Song, X.; Ding, P. Selective extinction drives taxonomic and functional alpha and beta diversities in island bird assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology 2016, 85, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Ross, S.J.; Lawton, J.H. Beta diversity on geographic gradients in Britain. Journal of Animal Ecology 1992, 61, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.H. Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 1996, 263, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.J.; Koleff, P.; Greenwood, J.J.D.; Gaston, K.J. The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology 2001, 70, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, M.; Gremmen, N.J.M.; Gaston, K.J.; Chown, S.L. Nestedness of Southern Ocean island biotas: Ecological perspectives on a biogeographical conundrum. Journal of Biogeography 2005, 32, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Bao, Y.X.; Yu, M.J.; Xu, G.F.; Ding, P. Nestedness for different reasons: The distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on Islands of an inundated lake. Diversity and Distributions 2010, 16, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography 2010, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A. The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Global Ecology and Biogeography 2012, 21, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podani, J.; Ricotta, C.; Schmera, D. A general framework for analyzing beta diversity, nestedness and related community-level phenomena based on abundance data. Ecological Complexity 2013, 15, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, C.L. Variation in the β diversity of fish species in Haizhou Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 2021, 28, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Zhang, C.L. β diversity and its components of the fish community in the Haizhou Bay during autumn and the relationships with environmental factors. Haiyang Xuebao 2022, 44, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M; Su, H.X.; Li, S.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Xu, B.Q.; Li, F.; Wang, X.X. The Driving Factors of β-diversity and its Components Spatial Variation of Fish Community in Coastal Area of Yantai and Weihai. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica 2023, 54, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, H.Y. Temporal and spatial differentiation characteristics of economy in the country Yellow River Basin and its influencing factors. Yellow River 2022, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.K.; Qin, S.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Miao, C.H. Spatiotemporal differentiation and influencing factors of the coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Resources Science 2020, 42, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Yu, G.L.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Han, H.Z.; Qi, Z.H.; Wang, T.T. Terrestrial dissolved organic carbon consumption by heterotrophic bacterioplankton in the huanghe river estuary during water and sediment regulation. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 2019, 37, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Cui, T.W.; Qin, P.; Gong, J.L.; Xiao, Y.F.; Zheng, R.E. Remote sensing retrieval and temporal-spatial distribution characteristics of particulate organic carbon concentration in seawater near Yellow River estuary. Acta Optica Sinica 2017, 37, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.S.; Hua, Y.Y.; Wang, C.F.; Liao, X.L.; Tan, X.J.; Tao, W.D. Estimation of ecological water requirements based on habitat response to water level in huanghe river delta, China. Chinese Geographical Science 2010, 20, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Z.; Xu, C.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Bi, N.S.; Zhao, L.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhou, B. Response of fresh water from Yellow River to marine ecological regulation. Yellow River 2019, 41, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Longitudinal pattern and formation mechanism.in α and β diversity of taxonomic and functional of stream fish assemblages in the Xin`an River. Doctor Dissertation, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FishBase. Available online: https://fishbase.se/search.php (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Niu, M.X.; Zuo, T.; Chang, W.; Chen, R.S. Biological characteristics of Liza haematocheila in the shallow coastal waters of the Yellow River estuary. Progress in Fishery Sciences 2023, 44, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.X.; Zuo, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.S.; Zhang, J.X. Egg and larval distribution of Liza haematocheila and their relationship with environmental factors in the coastal waters of the Yellow River Estuary. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 2022, 29, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.X. Studies on the Morphology and Genetics of Trachidermus fasciatus Populations. Doctor Dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.Y.; Ji, Y.P.; Zhang, S.H.; Yuan, C.T.; Gao, T.X. Research of Fishery Biology of the Neritic Fish Synechogobius ommaturus in the Area of the Huanghe Delta. Periodical of Ocean University of China 2005, 35, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C. Study on the community structure and fishery biological characteristics of Gobioidei in Laizhou Bay. Master Dissertation, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y.; Tian, Y.J.; Ren, Y.P. The fisheries biology of the spawning stock of Scomberomorus niphonius in the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 2018, 25, 1308–71316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.Y.; Yang, G.M.M.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.J. A Review of Research Advancement on Fisheries Biology of Japanese Mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius. Fisheries Science 2021, 40, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y. Study on Morphology and Genetics of Setipinna tenuifilis. Master Dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.P.; Wu, Q.; Shan, X.J.; Jin, X.S.; Su, C.C. Stock assessment of Setipinna taty in Shandong inshore waters based on lengthbased model and ensemble model. Journal of Fisheries of China 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Villeger, S.; Mason, N.W.H.; Mouillot, D. New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology 2008, 89, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Schwilk, D.W.; Ackerly, D.D. A trait-based test for habitat filtering: Convex hull volume. Ecology 2006, 87, 1465–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, F.M.; Li, X.H.; Chen, F.C.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, J.P.; Li, J.; Wu, Z. Functional diversity of freshwater fishes and methods of measurement. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2017, 37, 5228–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Sun, X.; Zhan, Q.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.M. Patterns and drivers of beta diversity of subtidal macrobenthos community on the eastern coast of Laizhou Bay. Biodiversity Science 2022, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D. Functional organization of stream fish assemblages in relation to hydrological variability. Ecology 1995, 76, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerhans, R.B.; Gifford, M.E.; Joseph, E.O. Ecological speciation in Gambusia fishes. Evolution 2007, 61, 2056–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.C. Fish Ecology; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, 1995; pp. 54–96. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.M.; Warren, M.L. Dynamics in species composition of stream fish assemblage: environmental variability and nested subsets. Ecology 2001, 82, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, D.J.; Hughes, R.M. Longitudinal zonation of Pacific Northwest (USA) fish assemblages and the species–discharge relationship. Copeia 2008, 2008, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, A.; Stefanidis, K. α- and β-diversity patterns of macrophytes and freshwater fishes are driven by different factors and processes in lakes of the unexplored Southern Balkan biodiversity hotspot. Water 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Heino, J.; Quirino, B.A.; Moresco, G.A.; Peláez, O.; Meira, B.R.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Jati, S.; Lansac-Tha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M. Differently dispersing organism groups show contrasting beta diversity patterns in a dammed subtropical river basin. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 691, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Li, F.; Lv, Q.M.; Wang, Y.B.; Yu, J.B.; Gao, Y.J.; Ren, Z.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Lv, Z.B. Impact of the water–sediment regulation scheme on the phytoplankton community in the Yellow River estuary. Journal of cleaner production 2021, 294, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.S. Decline mechanisms of fishery resources in the Bohai Sea under anthropogenic activities. Doctor Dissertation, The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tylianakis, J.M.; Klein, A.M.; Tscharntke, T. Spatiotemporal variation in the diversity of Hymenoptera across a tropical habitat gradient. Ecology 2008, 86, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
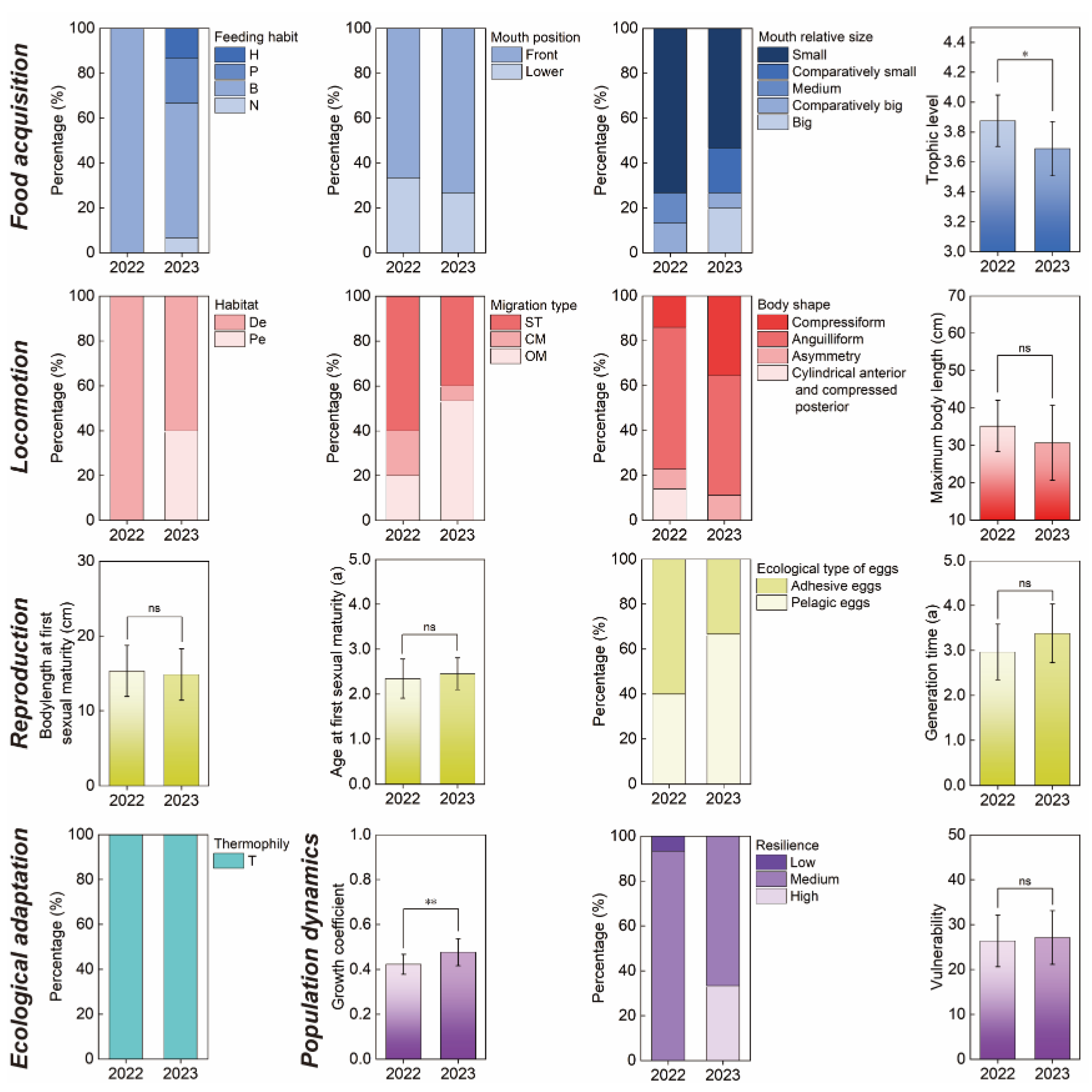
| Classification of function | Type of functional traits | Variable type | Functional trait |
| Food acquisition | Feeding habits | Ordered categorical variables | Herbivorous (H), Planktivorous (P), Planktivorous and Benthivorous (P–B), Benthivorous (B), Benthivorous and Nektivorous (B–N), Nektivorous (N) |
| Mouth position | Ordered categorical variables | Lower, Front, Upper | |
| Relative mouth size | Ordered categorical variables | Small (S), Comparatively small (CS), Medium (M), Comparatively big (CB), Big (B) | |
| Trophic level | Continuous variable | 2.5~4.8 | |
| Locomotion | Habitat | Unordered categorical variable | Demersal (De), Pelagic (Pe) |
| Migration type | Ordered categorical variables | Settlement type (ST), Coastal migratory (CM), Offshore migratory (OM), Distantly migrating (DM) | |
| Body shape | Unordered categorical variable | Fusiform (1), Compressiform (2), Depressiform (3), Anguilliform (4), Asymmetry (5), Sub-cylinder (6), Slightness (7), Cylindrical anterior part and compressed posterior part (8), Band shape (9), Depressed anterior part and compressed posterior part (10), Sub-cylindrical anterior part and compressed posterior part (11) | |
| Maximum body length (cm) | Continuous variable | 9.0~113.0 | |
| Reproduction | Body length at first sexual maturity (cm) | Continuous variable | 6.8~52.7 |
| Age at first sexual maturity (a) | Continuous variable | 0.8~3.8 | |
| Generation time (a) | Continuous variable | 1.0~8.5 | |
| Ecological type of eggs | Unordered categorical variable | Pelagic eggs (PE), Adhesive eggs (AE), Demersal adhesive eggs (DAE), Pelagic adhesive eggs (PAE), Ovoviviparous (O) | |
| Population dynamics | Growth coefficient (k) | Continuous variable | 0.18~0.80 |
| Resilience | Ordered categorical variables | Low resilience (Lr), Medium resilience (Mr), High resilience (Hr) | |
| Vulnerability | Continuous variable | 10~60 | |
| Ecological adaptation | Thermophily | Unordered categorical variable | Cold temperate (CT), Warm temperate (T), Warm water (WW) |
| Year | Normality test | T-test | |||
| Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z | P (two-tailed test) | T-value | df | P (two-tailed test) | |
| 2022 | 0.781 | 0.575 | 0.009 | 104 | 0.993 |
| 2023 | 0.895 | 0.400 | -0.016 | 104 | 0.987 |
| 2022-2023 | - | - | 4.894 | 104 | <0.001*** |
| Diversity index | Fβsor | NH4-N | TP | pH | Geographic distance | |||||
| Coefficient | P | Coefficient | P | Coefficient | P | Coefficient | P | Coefficient | P | |
| FRic | -0.1157 | 0.0001*** | -0.1550 | 0.0371* | 0.7977 | 0.0249* | - | - | - | - |
| FEve | - | - | -0.0400 | 0.0161* | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FDiv | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fβsor | - | - | 0.0317 | 0.0376* | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fβsim | - | - | - | - | - | - | -0.0393 | 0.0066** | -0.0510 | 0.046* |
| Fβsne | - | - | - | - | 0.1134 | 0.0318* | 0.0301 | 0.0379* | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





