Submitted:
08 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
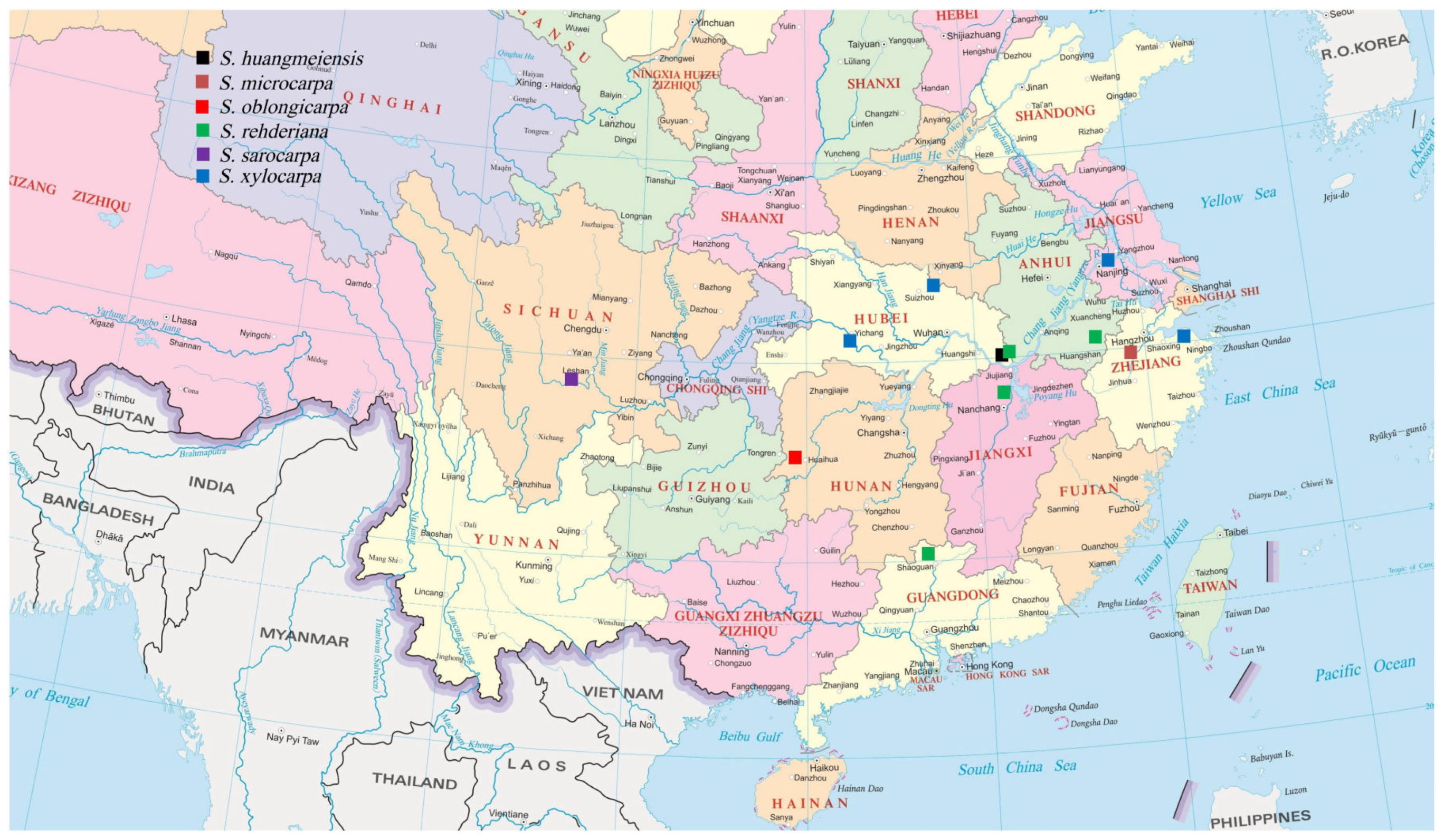
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Assembly
2.2. Plastome Annotation
2.3. Comparative Analyses of Plastomes
2.4. Codon Usage Pattern Analyses
2.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.6. Divergence Time Estimate
2.7. Biogeographic Analyses
2.8. Ancestor State Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Complete Plastome of S. Oblongicarpa and Comparison with Its Congeneric Species
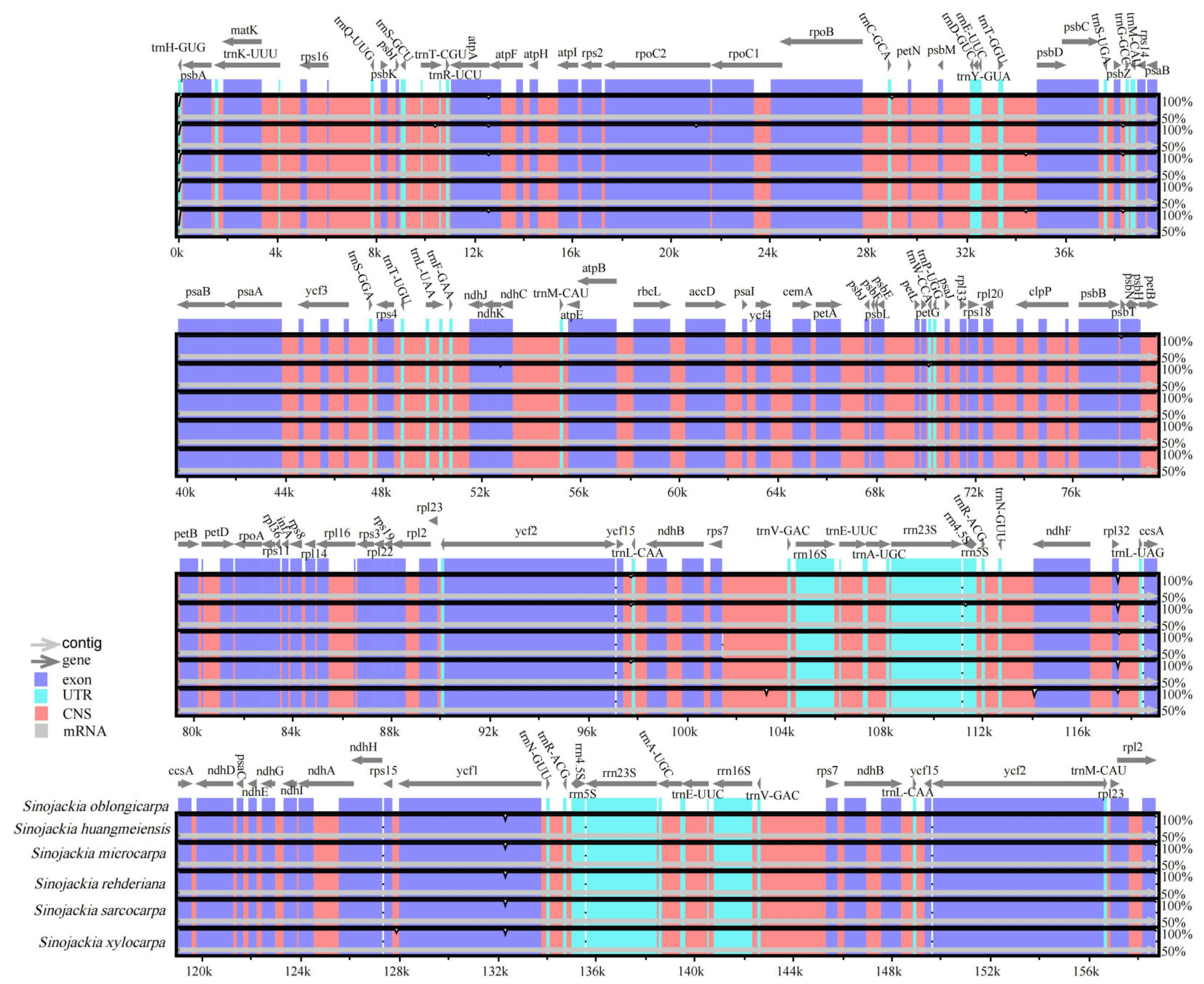
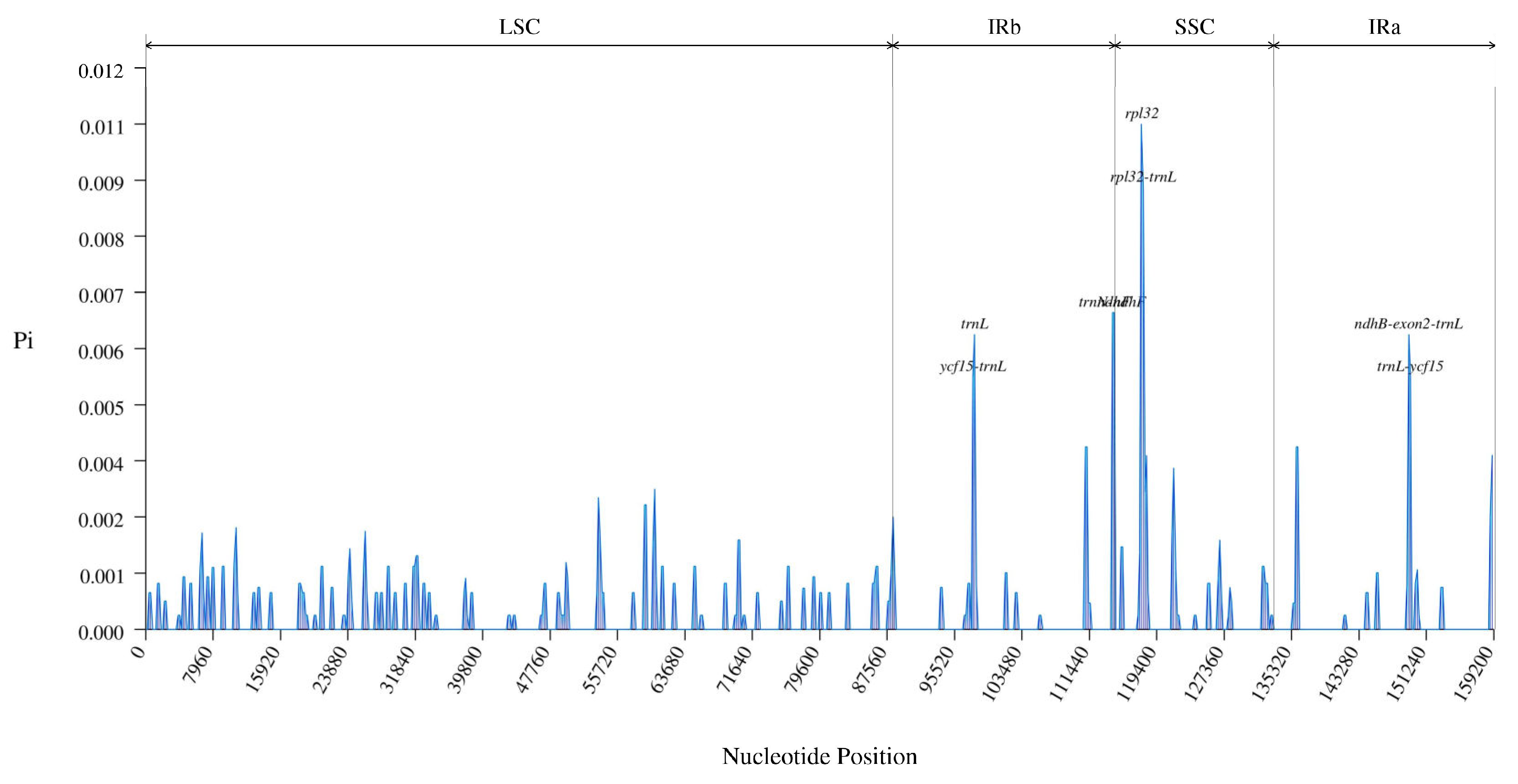
3.2. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Divergence Hotspot Regions
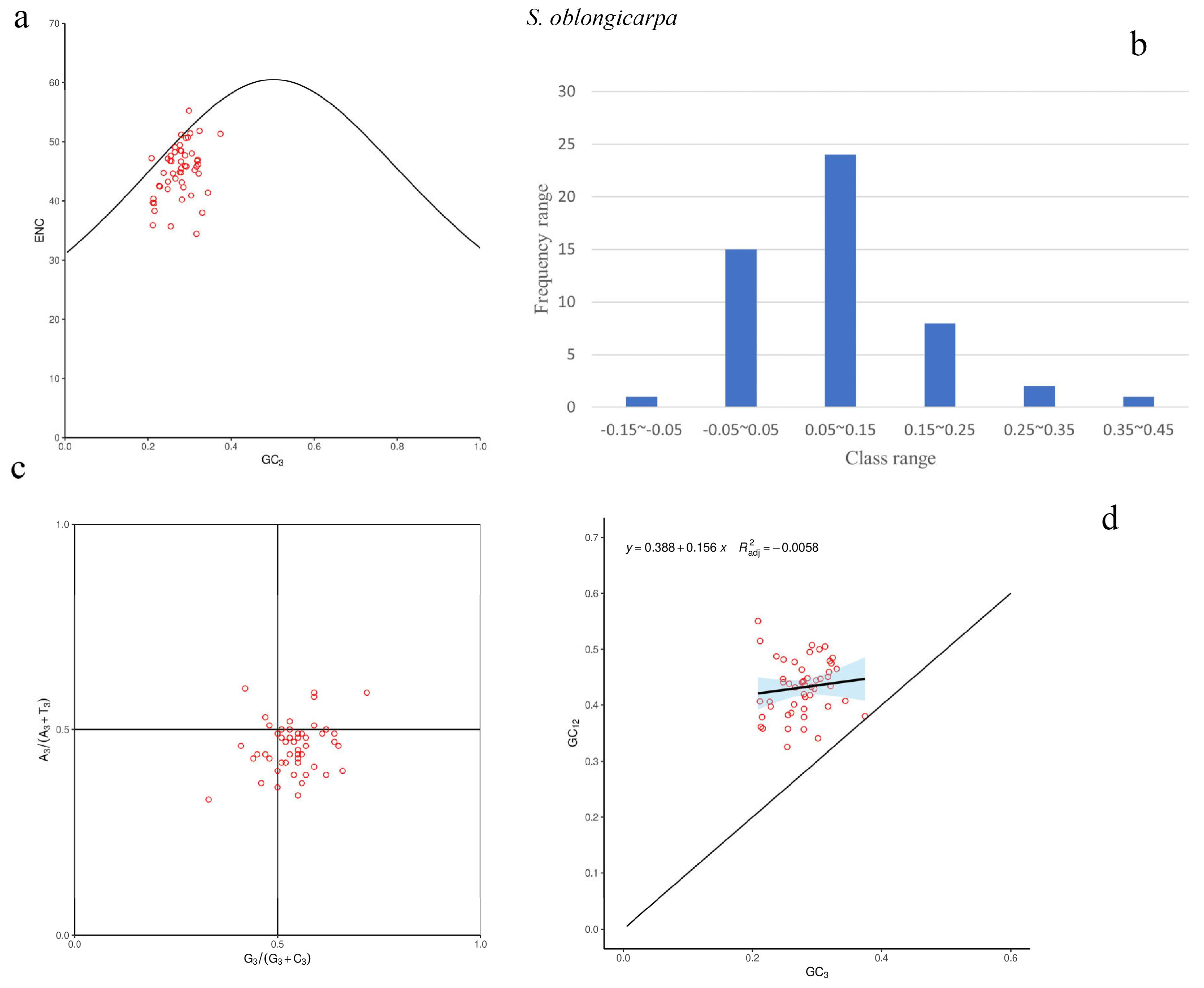
3.3. Codon Usage Pattern Analyses
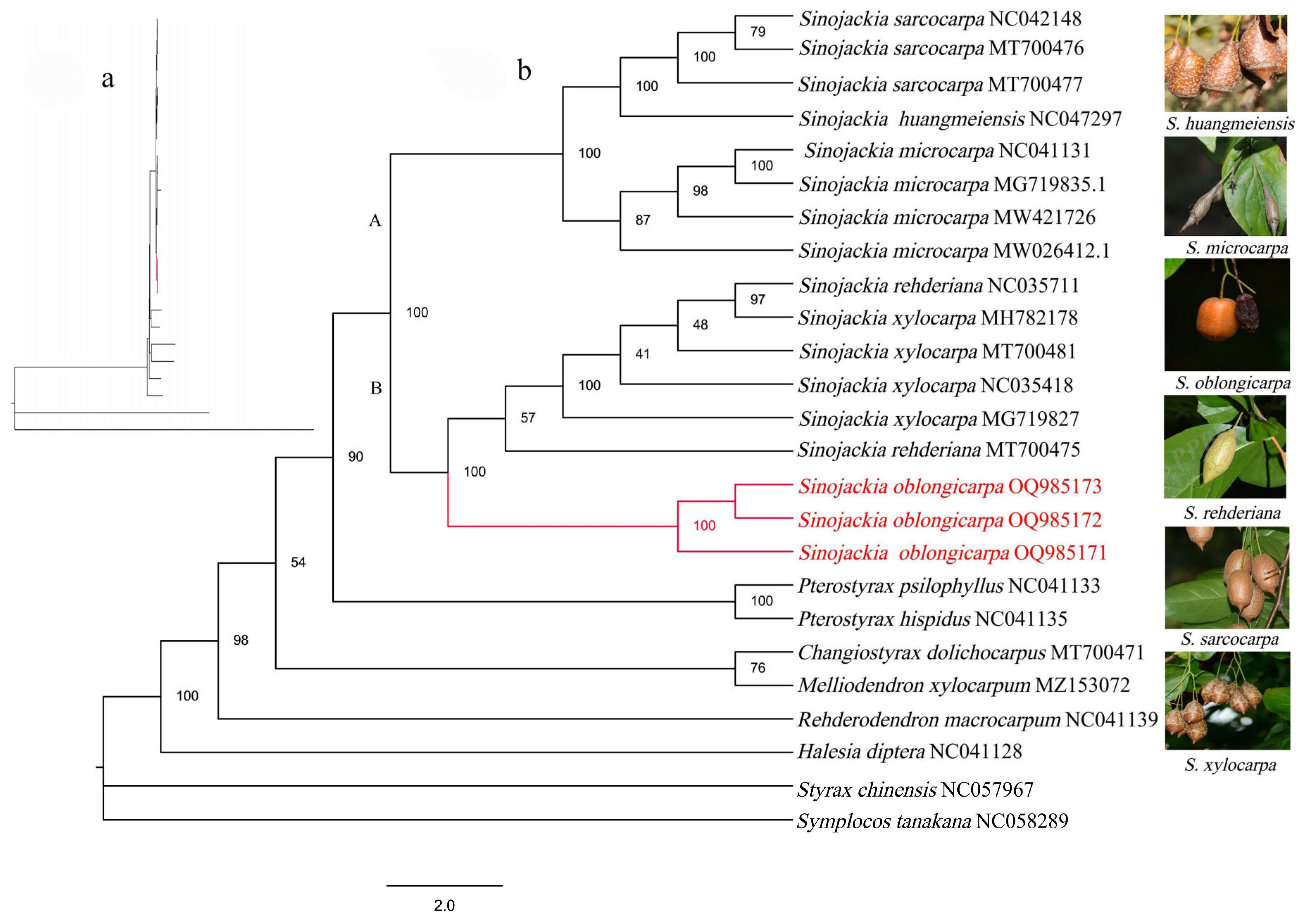
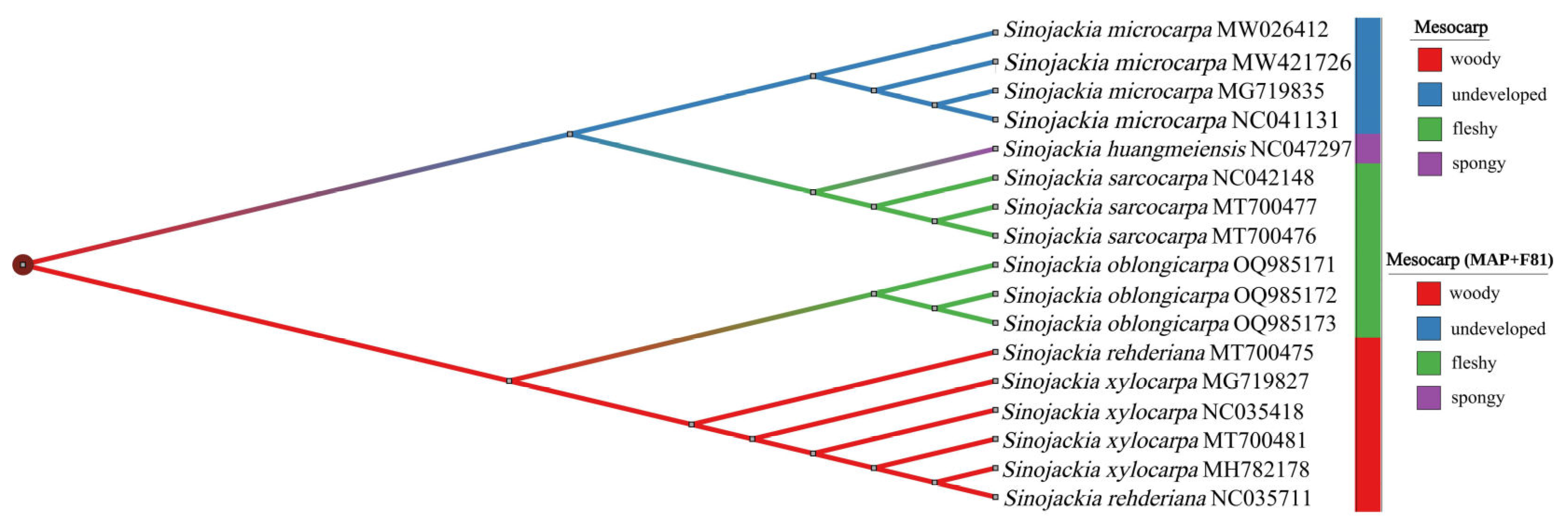
3.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
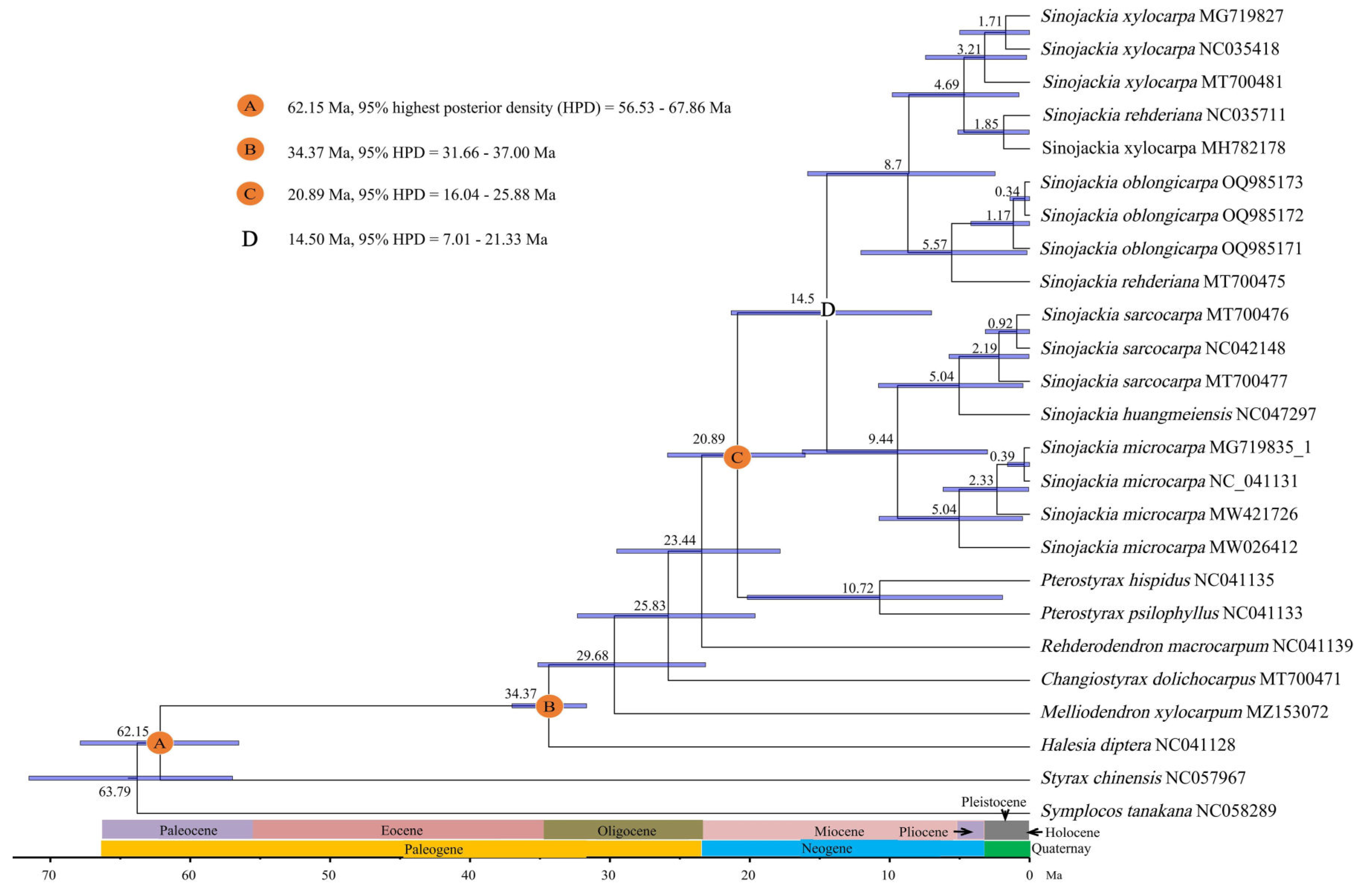
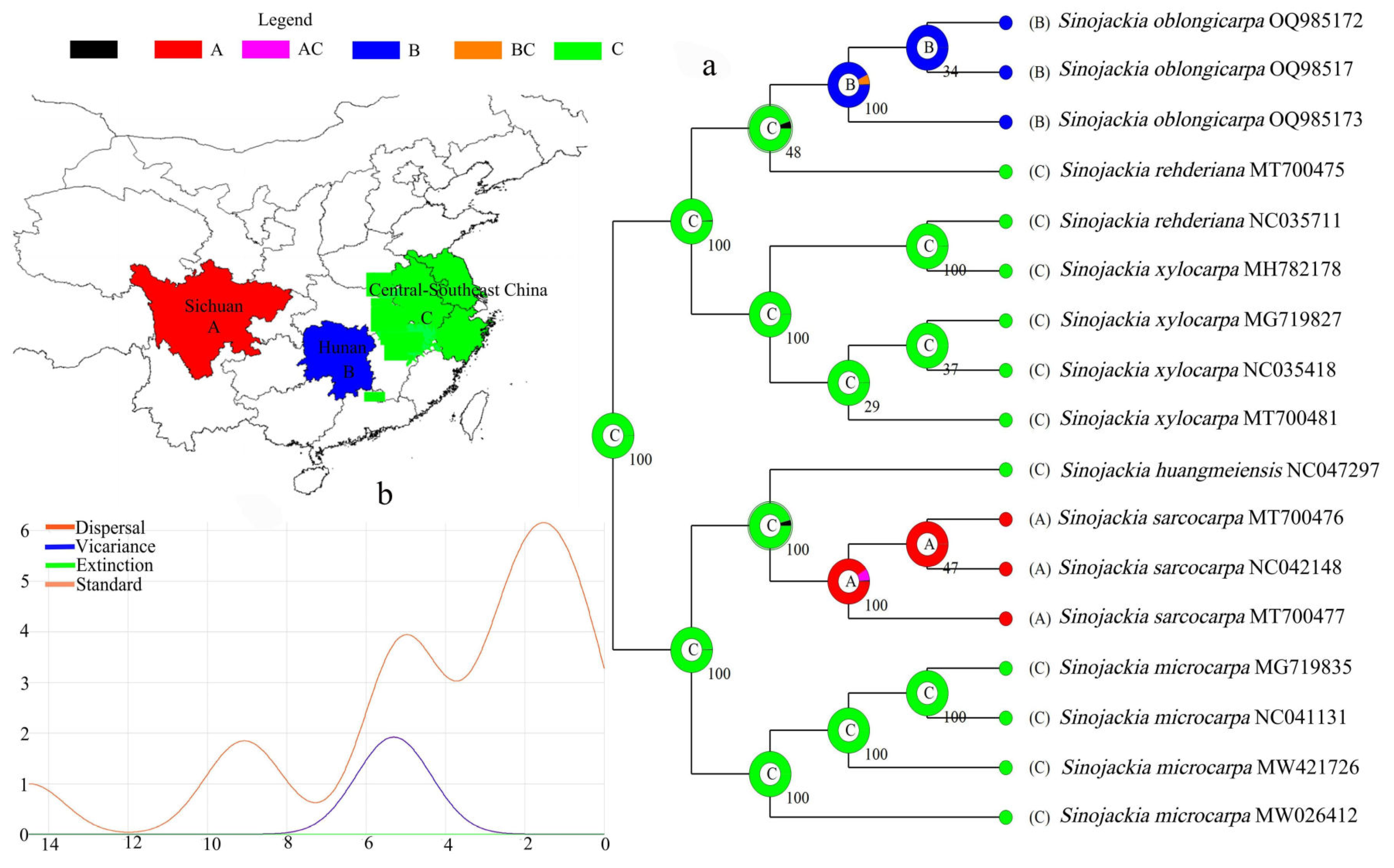
3.5. Evolutionary History Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Plastome Structure and Sequence Variation
4.2. Analysis of Factors Influencing Codon Bias
4.3. Interspecific Phylogenetic Relationships
4.4. Evolutionary History Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, J.; Döring, E.; Hilu, K.W.; Röser, M. Phylogenetic Structure of the Grass Subfamily Pooideae Based on Comparison of Plastid MatK Gene-3’trnK Exon and Nuclear ITS Sequences. Taxon 2009, 58, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orton, L.M.; Barberá, P.; Nissenbaum, M.P.; Peterson, P.M.; Quintanar, A.; Soreng, R.J.; Duvall, M.R. A 313 Plastome Phylogenomic Analysis of Pooideae: Exploring Relationships among the Largest Subfamily of Grasses. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 159, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, A.; Baltisberger, M. Extensive Intraspecific Chloroplast DNA (CpDNA) Variation in the Alpine Draba Aizoides L. (Brassicaceae): Haplotype Relationships and Population Structure. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.C.; Wang, W.K.; Peng, C.I.; Chiang, T.Y. Phylogeography and Conservation Genetics of Hygrophila Pogonocalyx (Acanthaceae) Based on AtpB-RbcL Noncoding Spacer CpDNA. J. Plant Res. 2005, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.S.; Soltis, P.S. Intraspecific Phylogeny Analysis Using ITS Sequences: Insights from Studies of the Streptanthus Glandulosus Complex (Cruciferae). Syst. Bot. 1999, 24, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Ma, P.F.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.Z.; Guo, Z.H. Phylogenomic Analyses of Nuclear Genes Reveal the Evolutionary Relationships within the BEP Clade and the Evidence of Positive Selection in Poaceae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.V.; Clark, L.G.; Triplett, J.K.; Grennan, C.P.; Duvall, M.R. Biogeography and Phylogenomics of New World Bambusoideae (Poaceae), Revisited. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attigala, L.; Wysocki, W.P.; Duvall, M.R.; Clark, L.G. Phylogenetic Estimation and Morphological Evolution of Arundinarieae (Bambusoideae: Poaceae) Based on Plastome Phylogenomic Analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 101, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.X.; Dong, C.C.; Niu, Y.T.; Lu, L.M.; Xu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhou, S.L.; Lu, A.M.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wen, J.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny and Species Delimitation of Stachyuraceae: Advocating a Herbarium Specimen-Based Phylogenomic Approach in Resolving Species Boundaries. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; He, J.; Lyu, R.; Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Yao, M.; Pei, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Xie, L. Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of 13 Species in Epilobium, Circaea, and Chamaenerion and Insights Into Phylogenetic Relationships of Onagraceae. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgung, J.; Do, H.D.K.; Kim, C.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, J. -H Complete Chloroplast Genomes Shed Light on Phylogenetic Relationships, Divergence Time, and Biogeography of Allioideae (Amaryllidaceae). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.B.S.; Giulietti, A.M.; Prado, J.; Vasconcelos, S.; Watanabe, M.T.C.; Pinangé, D.S.B.; Oliveira, R.R.M.; Pires, E.S.; Caldeira, C.F.; Oliveira, G. Plastome-Based Phylogenomics Elucidate Relationships in Rare Isoëtes Species Groups from the Neotropics. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 161, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.M.; Grimes, J. Sinojackia. In Flora of China; Wu, C.Y., Raven, P., Eds.; Science Press/Missouri Botanical Garden Press: Beijing/St. Louis, 1996; pp. 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L. A New Synonym in the Genus Sinojackia (Styracaceae). Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2005, 43, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. New Taxa, Nomenclature, and Chromosome Report. J. Syst. Evol. 2011, 49, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.H.; Ye, Q.G.; Ge, J.W.; Ming, K.; Huang, H.W. A New Species of Sinojackia (Styracaceae) from Hubei, Central China. Novon 2007, 17, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Gao, P.; Yao, X. Genetic Footprints of Habitat Fragmentation in the Extant Populations of Sinojackia (Styracaceae): Implications for Conservation. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 170, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, R.; Chen, C. Cultivation Technology and Application of Sinojackia. Contemp. Hortic. 2015, 294, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, Z. Study on the Bacteriostatic Action of the Extracts from the Leaves of Sinojackia Sarcocarpa. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 36, 9599–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhuo, J.; Chen, D.; Vasupalli, N.; Chu, J.; Qian, Q. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Sinojackia Microcarpa (Styracaceae): Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis. Biologia (Bratisl). 2021, 76, 3891–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.K.; Jin, J.M. China Plant Red Data Book–Rare and Endangered Plants; Science Press: Beijing, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y. China Species Red List; Higher Education Press: Beijing, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X. Geographic Distribution and Current Status of the Endangered Genera Sinojackia and Changiostyrax. Biodivers. Sci. 2005, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H. Sinojackia, a New Genus of Styracaceae from Southeastern China. J. Arnold Arbor. 1928, 9, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C. A New Species of Styracaceae from Hunan. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1981, 19, 526–528. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Li, G. A New Species of Sinojackia Hu (Styracaceae) from Zhejiang, East China. NOVON 1997, 7, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cao, T. A New Species of Sinojackia Hu ( Styracaceae) from Hunan, South Central China. Edinburgh J. Bot. 1998, 55, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H. Notulae Systematicae Ad Floram Sinensem, II. J. Arnold Arbor. 1930, 11, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. A New Species of Sinojackia from Sichuan. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1992, 31, 78–79. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L. Sinojackia Xylocarpa Var Leshanensis (Styracaceae) a New Variety from Sichuan, China. Bull. Bot. Res. 2005, 25, 260–261. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, E.D. Miscellanea Sinensia. Sunyatsenia 1937, 3, 246–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Ye, Q.; Fritsch, P.W.; Cruz, B.C.; Huang, H. Phylogeny of Sinojackia (Styracaceae) Based on DNA Sequence and Microsatellite Data: Implications for Taxonomy and Conservation. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Changiostyrax, a New Genus of Styracaceae from China. Guihaia 1995, 15, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, P.W. Phylogeny and Biogeography of the Flowering Plant Genus Styrax (Styracaceae) Based on Chloroplast DNA Restriction Sites and DNA Sequences of the Internal Transcribed Spacer Region. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 19, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Fritsch, P.W.; Moore, M.J.; Feng, T.; Meng, A.; Yang, J.; Deng, T.; Zhao, C.; Yao, X.; Sun, H.; et al. Plastid Phylogenomics Resolves Infrafamilial Relationships of the Styracaceae and Sheds Light on the Backbone Relationships of the Ericales. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 121, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.L.; Landis, J.B.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, Z.X.; Wang, H.F. Plastome Structure and Phylogenetic Relationships of Styracaceae (Ericales). BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Luo, Y.; Huang, M.; Liang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, M. Analysis of RDNA-ITS Molecular Identification, Seed Morphology and Breeding on the Endangered Sinojackia Sarcocarpa in Sichuan. Genomics Appl. Biol. 2015, 34, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, J. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Sinojackia Huangmeiensis (Styracaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2020, 5, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Fu, Q.C.; Liang, Z. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Sinojackia Sarcocarpa, an Endemic Plant in Southwest China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2019, 4, 1350–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Genomic Plant DNA Preparation from Fresh Tissue-CTAB Method. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A Fast and Versatile Toolkit for Accurate de Novo Assembly of Organelle Genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive Visualization of de Novo Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an Integrated Plastome Sequence Annotator and Analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W65–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq - Versatile and Accurate Annotation of Organelle Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) Version 1.3.1: Expanded Toolkit for the Graphical Visualization of Organellar Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT Online Service: Multiple Sequence Alignment, Interactive Sequence Choice and Visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Gan, H.; Liang, X. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias in Potato Virus M and Its Adaption to Hosts. Viruses 2019, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.-L.; Ma, L.-B.; Khan, M.S.; Zhang, X.-X.; Xu, S.-Q.; Xie, J.-Y. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Hirudinaria Manillensis Reveals a Preference for GC-Ending Codons Caused by Dominant Selection Constraints. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Su, K.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Sun, J. Analysis of Codon Usage in the Chloroplast Genome of Medicago Truncatula. Acta Prataculturae Sin 2015, 24, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, B.; Ning, Z. Comprehensive Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Patterns and Influencing Factors of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An Integrated and Scalable Desktop Platform for Streamlined Molecular Sequence Data Management and Evolutionary Phylogenetics Studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R.; Teeling, E. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, M.E.J. The Lower Tertiary Floras of Southern England. II. Flora of the Pipe-Clay Series of Dorset (Lower Bagshot); British Museum (Natural History): London, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- MacGinitie, H.D. Fossil Plants of the Florissant Beds, Colorado; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, J.P.; Kleist, T.J.; Löfstrand, S.D.; Drew, B.T.; Schönenberger, J.; Sytsma, K.J. Phylogeny, Historical Biogeography, and Diversification of Angiosperm Order Ericales Suggest Ancient Neotropical and East Asian Connections. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 122, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Luebert, F.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Rees, M.; Frohlich, M.W.; Qi, J.; Weigend, M.; et al. Asterid Phylogenomics/Phylotranscriptomics Uncover Morphological Evolutionary Histories and Support Phylogenetic Placement for Numerous Whole-Genome Duplications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 3188–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, D.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. A New Record Species of Styracaceae from Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Blair, C.; He, X. RASP 4: Ancestral State Reconstruction Tool for Multiple Genes and Characters. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.A.; Zhukova, A.; Iwasaki, W.; Gascuel, O.; Pupko, T. A Fast Likelihood Method to Reconstruct and Visualize Ancestral Scenarios. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2069–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, X.-F.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Jiang, L.-S.; Li, X.; Deng, H.-N.; Liao, M.; Xu, B. Complete Chloroplast Genomes Provide Insights Into Evolution and Phylogeny of Campylotropis (Fabaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 895543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Teng, K.; Zhang, H.; Gao, K.; Wu, J.; Duan, L.; Yue, Y.; Fan, X. Chloroplast Genomes of Four Carex Species: Long Repetitive Sequences Trigger Dramatic Changes in Chloroplast Genome Structure. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; He, N.; Peng, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. Comparative Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Chinese Lacquer Tree (Toxicodendron Vernicifluum, Anacardiaceae): East-West Divergence within Its Range in China. Forests 2023, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. The Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Primula Obconica Provide Insight That Neither Species nor Natural Section Represent Monophyletic Taxa in Primula (Primulaceae). Genes (Basel). 2022, 13, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Grover, C.E.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Nie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Molecular Evolution of the Plastid Genome during Diversification of the Cotton Genus. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 112, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.; Hashem, A.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Al-Harrasi, A. Gene Loss and Evolution of the Plastome. Genes (Basel). 2020, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, L.; Quan, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Lan, X. Comparative Analyses of Chloroplast Genomes from Six Rhodiola Species: Variable DNA Markers Identification and Phylogenetic Relationships within the Genus. BMC Genomics 2022, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, H.M.W.; Cavalcanti, A.R.O. Factors Influencing Codon Usage Bias in Genomes. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, S.T.; Udayasuriyan, V.; Bhadana, V. Codon Usage Bias. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, J. Codon Usage Patterns across Seven Rosales Species. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Guo, K.; Zhao, L.; Meng, F.; Xiao, J.; Niu, Y.; Sun, Y. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Chloroplast Genomes of Ten Epimedium Species. BMC Genomic Data 2023, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, B.R. The Role of Context-Dependent Mutations in Generating Compositional and Codon Usage Bias in Grass Chloroplast DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quax, T.E.F.; Claassens, N.J.; Söll, D.; van der Oost, J. Codon Bias as a Means to Fine-Tune Gene Expression. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Lee, W.; Hottes, A.K.; Shapiro, L.; McAdams, H.H. Codon Usage between Genomes Is Constrained Genome-Wide Mutational Processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. A Code within the Genetic Code: Codon Usage Regulates Co-Translational Protein Folding. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.-L.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Xia, R.-X.; Qin, L. Comprehensive Analysis of Codon Usage in Quercus Chloroplast Genome and Focus on PsbA Gene. Genes (Basel). 2022, 13, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Nandhini, M.B.; Monalisha, E.; Murugan, K.; Nagarajan, S.; Surya, N.; Rao, P.; Ganesh, D. Synonymous Codon Usage in Chloroplast Genome of Coffea Arabica. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, L. Analysis of Codon Usage Bias of Chloroplast Genomes in Gynostemma Species. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2021, 27, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Ye, Q.G.; Yao, X.H.; Huang, H.W. Spontaneous Interspecific Hybridization and Patterns of Pollen Dispersal in Ex Situ Populations of a Tree Species (Sinojackia Xylocarpa) That Is Extinct in the Wild: Contributed Paper. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Luozhong, T. Basic Characteristic and Dormancy Mechanism of Sinojackia Xylocarpa Fruit and Seed. J. southwest For. universty 2021, 41, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, W.Q.; Hu, H.; Shen, Y.B. Mechanical Constraints in the Endosperm and Endocarp Are Major Causes of Dormancy in Sinojackia Xylocarpa Hu (Styracaceae) Seeds. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, K.; Chave, J. Evolutionary Patterns of Range Size, Abundance and Species Richness in Amazonian Angiosperm Trees. PeerJ 2016, 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Yi, T.S.; Gao, L.M.; Ma, P.F.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.B.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Cai, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Origin of Angiosperms and the Puzzle of the Jurassic Gap. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, K. Late Miocene and Pliocene Floras in Central Honshu, Japan; Bulletin of Kanagawa Prefectural Museam Natural Science: Yokohama, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Z. The Geographical Distribution of Styracaceae. Bull. Bot. Res. 1996, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Currano, E.D.; Wilf, P.; Wing, S.L.; Labandeira, C.C.; Lovelock, E.C.; Royer, D.L. Sharply Increased Insect Herbivory during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInerney, F.A.; Wing, S.L. The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum: A Perturbation of Carbon Cycle, Climate, and Biosphere with Implications for the Future. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 39, 489–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, H. Is the East Asian Flora Ancient or Not? Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Valdes, P.J.; Farnsworth, A.; Davies-Barnard, T.; Su, T.; Lunt, D.J.; Spicer, R.A.; Liu, J.; Deng, W.Y.D.; Huang, J.; et al. Orographic Evolution of Northern Tibet Shaped Vegetation and Plant Diversity in Eastern Asia. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.J. Phylogeographic History of Broad-Leaved Forest Plants in Subtropical China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5894–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Tian, S.; Li, B.; Fan, D.; Chen, Y.; Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S.; Zhang, Z. The Antiquity of Cyclocarya Paliurus (Juglandaceae) Provides New Insights into the Evolution of Relict Plants in Subtropical China since the Late Early Miocene. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Chen, C.; Dobeš, C.; Fu, C.X.; Koch, M.A. Phylogeography of a Living Fossil: Pleistocene Glaciations Forced Ginkgo Biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae) into Two Refuge Areas in China with Limited Subsequent Postglacial Expansion. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Shao, J.W.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X.P.; Qiu, Y.X. Chloroplast Phylogeography of a Temperate Tree Pteroceltis Tatarinowii (Ulmaceae) in China. J. Syst. Evol. 2012, 50, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Comes, H.P.; Cao, Y.N.; Guo, R.; Mao, Y.R.; Qiu, Y.X. Quaternary Climate Change Drives Allo-Peripatric Speciation and Refugial Divergence in the Dysosma Versipellis-Pleiantha Complex from Different Forest Types in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-S.; Chen, Y.; Tamaki, I.; Sakaguchi, S.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Takahashi, D.; Li, P.; Isaji, Y.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Y.-X. Pre-Quaternary Diversification and Glacial Demographic Expansions of Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) in Temperate Forest Biomes of Sino-Japanese Floristic Region. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 143, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
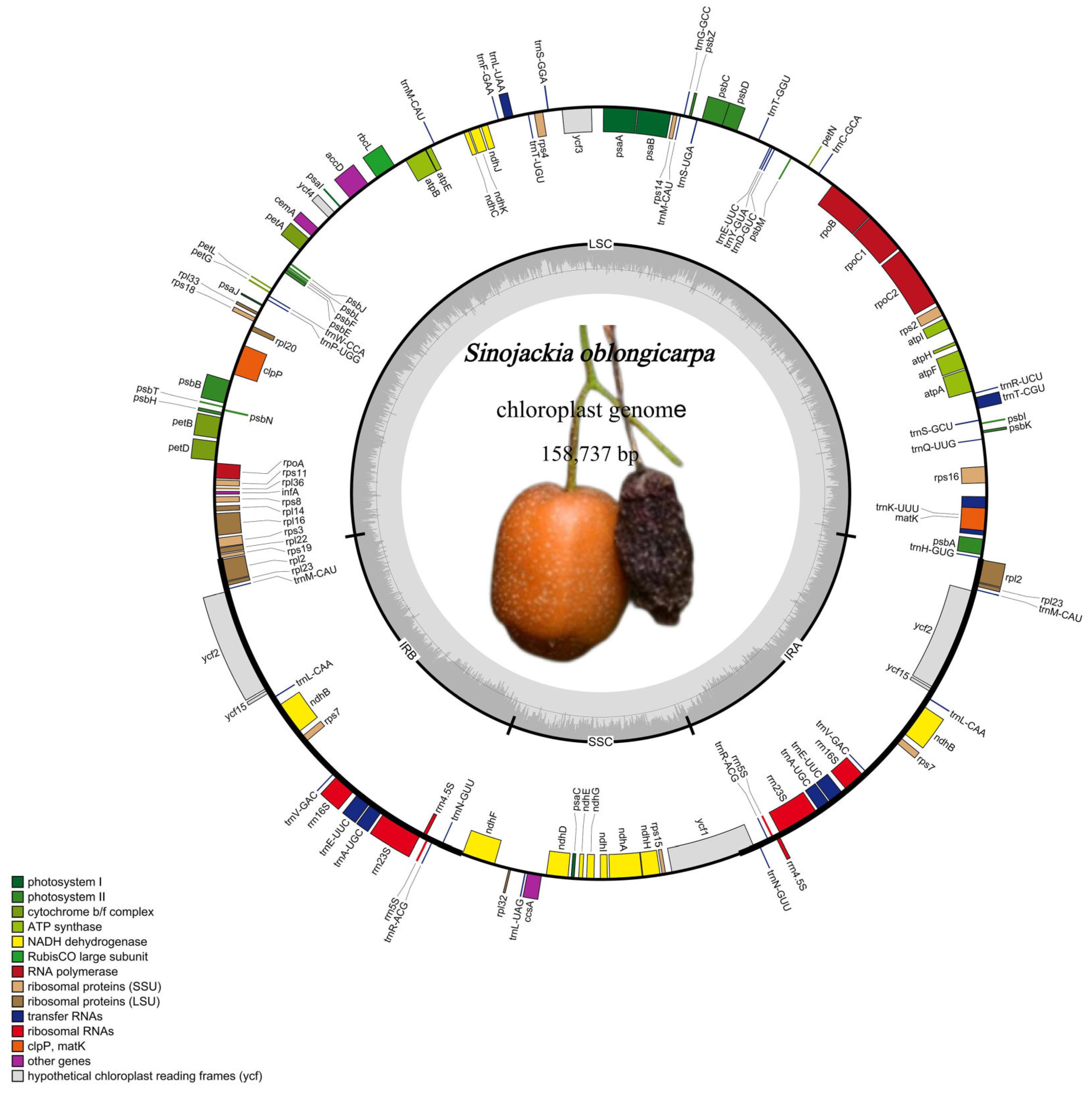

| Species | Length (bp) | LSC (bp) | SSC (bp) | IR (bp) | GC content (%) | Number of Gene | CDS | tRNA | rRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. oblongicarpa | 158,737 | 87,955 | 18,562 | 26,090 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
| S. xylocarpa | 158,725 | 87,994 | 18,551 | 26,090 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
| S. sarcocarpa | 158,737 | 88,002 | 18,555 | 26,090 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
| S. rehderiana | 158,760 | 87,974 | 18,586 | 26,100 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
| S. microcarpa | 158,739 | 88,002 | 18,553 | 26,092 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
| S. huangmeiensis | 158,758 | 88,023 | 15,555 | 26,090 | 37.3 | 113 | 79 | 30 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





