Submitted:
09 May 2024
Posted:
09 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
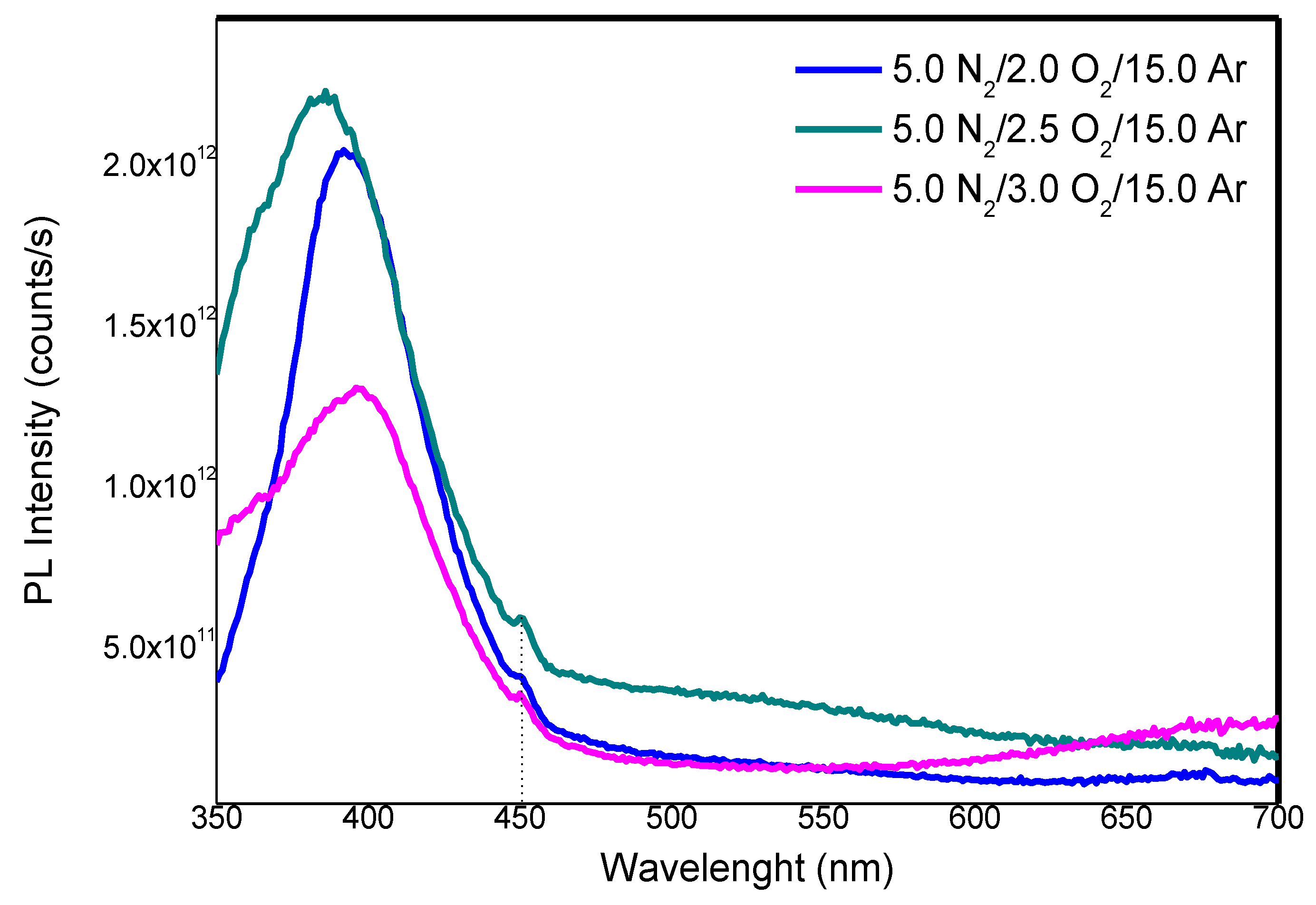
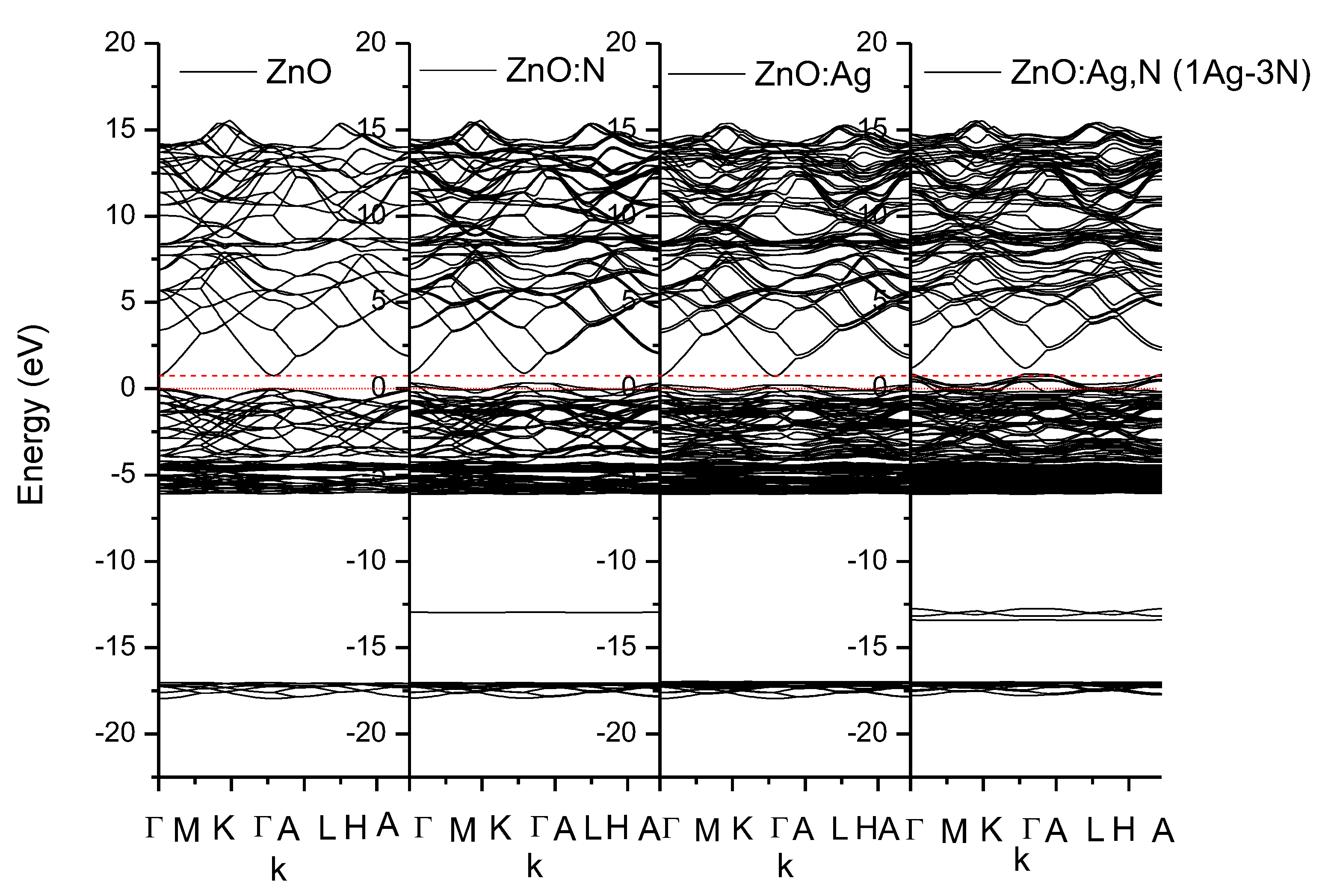
3. Results
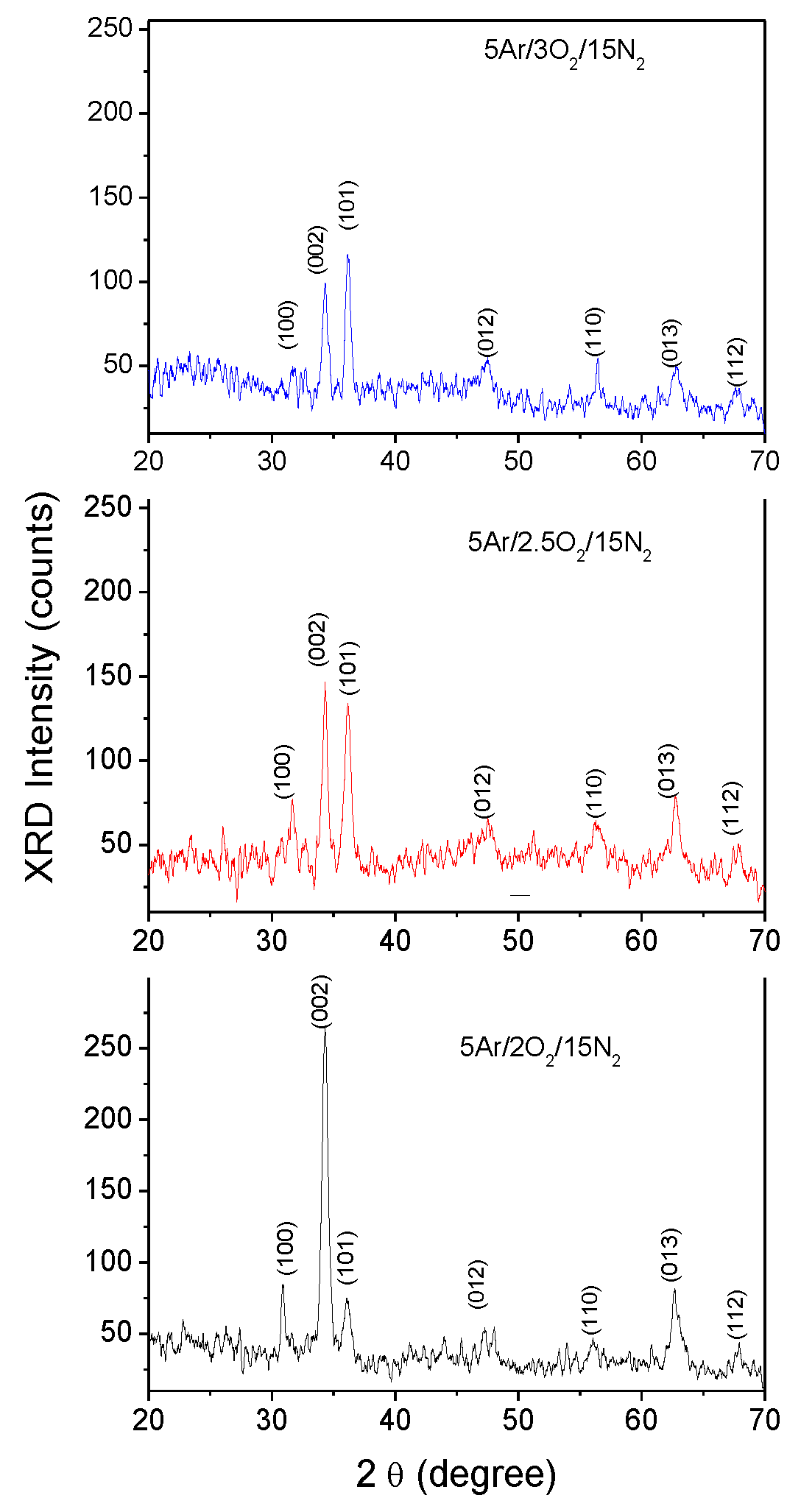
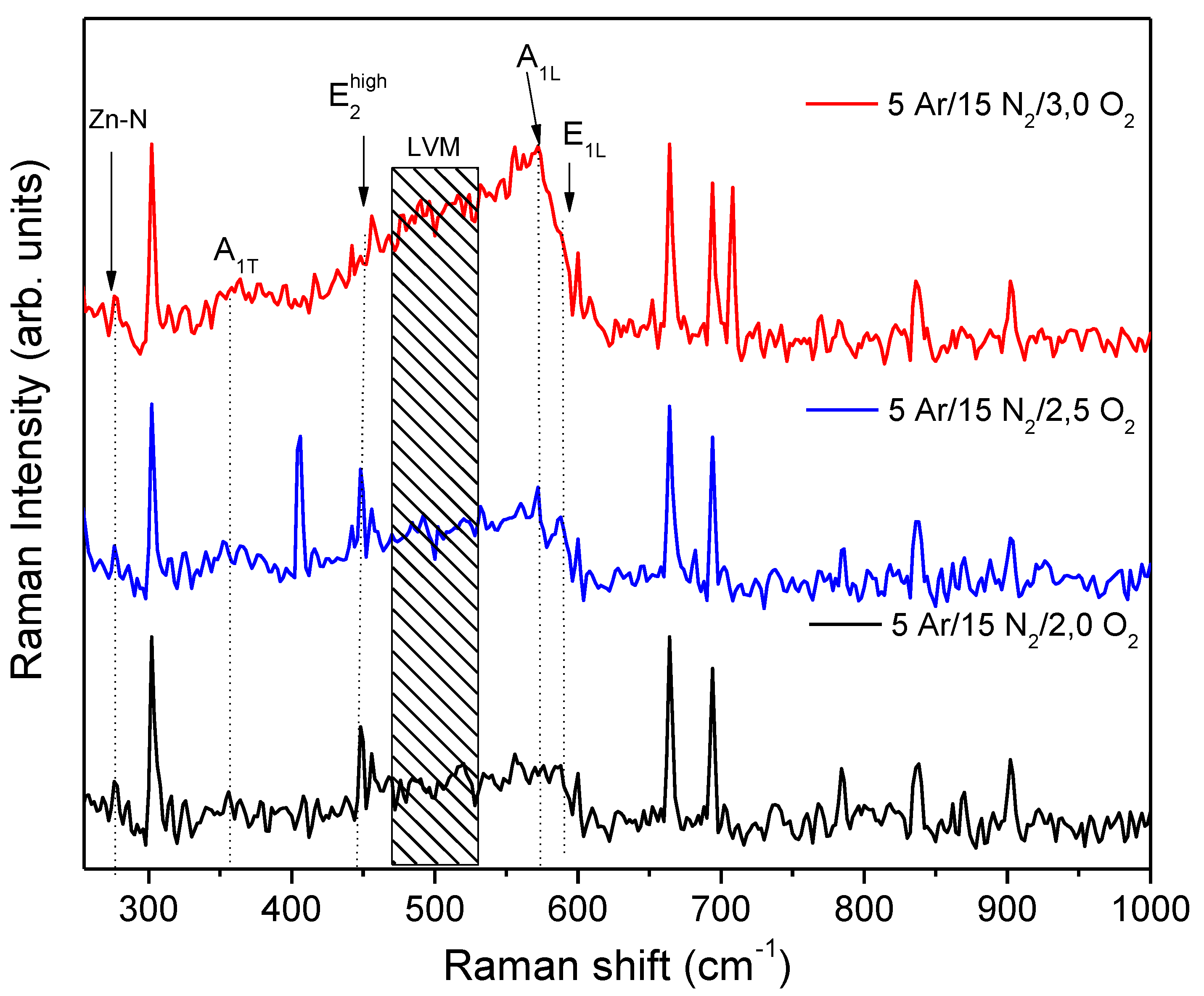
3.1. Elemental Composition
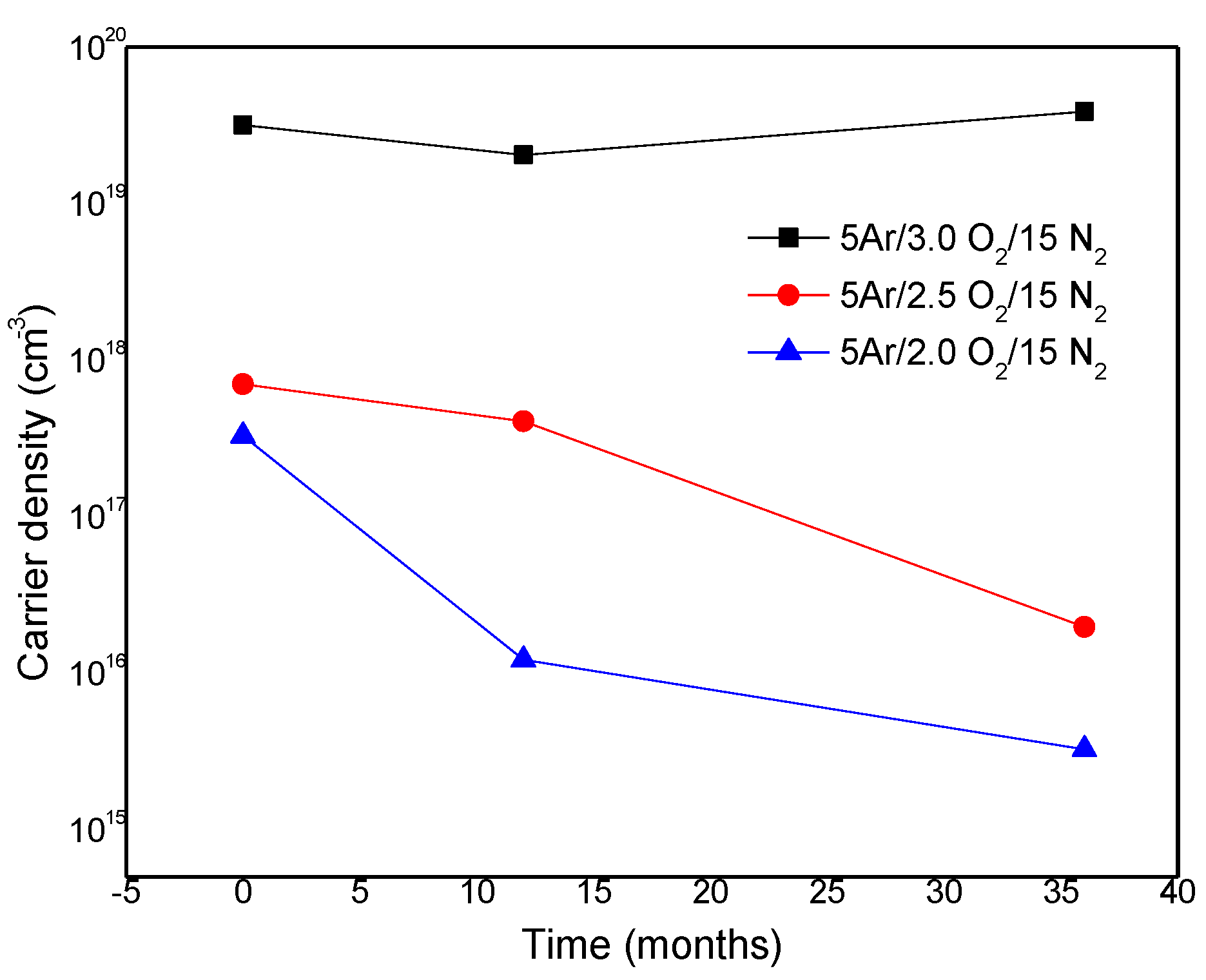
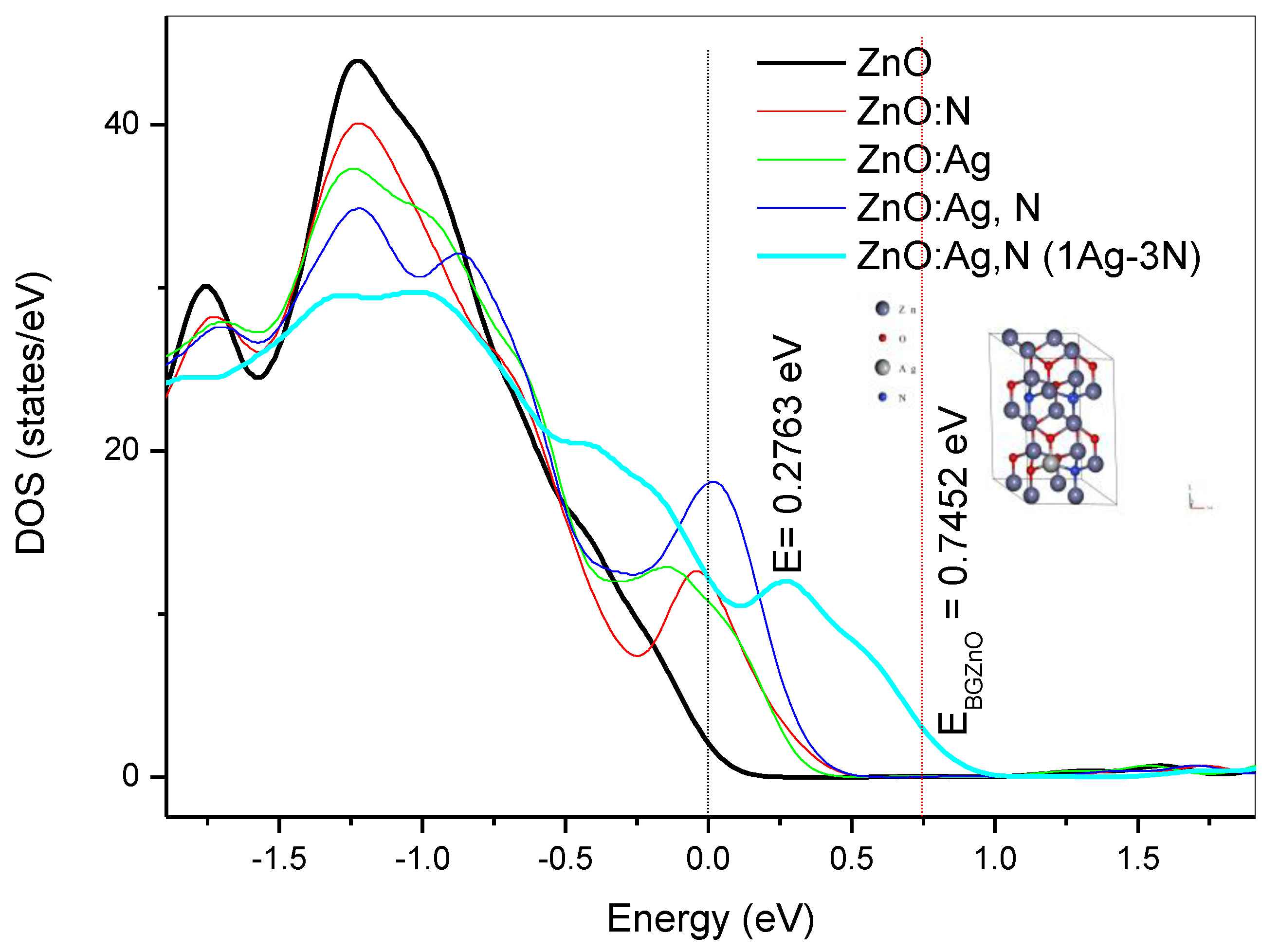
4. Conclusions
Declaration of interest statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Ozgur, U.; Ya. I; Alivov, C; et al.; A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys, 2005, 98, 041301. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.K; Oh, M. S; Lim, J. H; and Park, S. J; ZnO thin films and light-emitting diodes, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys, 2007, 40, R387–R412. [CrossRef]
- Rekha, S. M; Neelamana, H. V; and Bhat, S. Recent Advances in Solution-Processed Zinc Oxide Thin Films for Ultraviolet Photodetectors, ACS Applied Electronic Materials. 2023; 5, 4051–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, K; Overberg, M.E; Heo, Y. W; et al.; Hydrogen incorporation, diffusivity and evolution in bulk ZnO, Solid-State Electron. 2003, 47, 2255–2259. [CrossRef]
- Janotti A; de Walle, C.G.V; Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 126501. [CrossRef]
- Yang, R; Wang, F; Lu, J; et al. ; ZnO with p-Type Doping: Recent Approaches and Applications ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2023, 5, 4014–4034. [CrossRef]
- Brauer, G; Kuriplach, J; Ling C.C; Djurisic, A. B; Activities towards p-type doping of ZnO, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser, 2011, 265, 012002. [CrossRef]
- Regalado-Contreras, A.; Farías, M.H.; De La Cruz, W. Room temperature deposition of stable p-type ZnO:N thin films through chemical species modulation using reactive pulsed laser deposition. Applied Surface Science, 2023; 640, 158393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, ALC; Vargas, LMB; Peres, ML; et al. ; Exploring Na Doping in ZnO Thin Films: Electrical and Optical Insights. Coatings. 2024, 14, 510. [CrossRef]
- Çavdar, Ş; Şahin, V; Turan; N; et al; Structural and electrical characterization of Cd-doped ZnO thin films produced on p-type Si substrate by SILAR technique. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 2023, 34, 1787.
- Ellmer and Bikowski, A. ; Intrinsic and extrinsic doping of ZnO and ZnO alloys, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys, 2016, 49, 413002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessadaluk, S.; Khemasiri, N.; Kayunkid, N.; et al. ; Influence of Antimony Species on Electrical Properties of Sb-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Pulsed Laser Deposition. Nanomaterials, 2023, 13, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J. G.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Ye, Z. Z.; et al. ; Low resistivity, stable p-type ZnO thin films realized using a Li and N dual acceptor doping method, Appl. Phys. Lett, 2006, 88, 222114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.Y.; Yao, R. H. ; and Zhao; Y. J., The mechanism of Li,N dual-acceptor co-doped p-type ZnO, Appl. Phys. A, 2008, 91, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A; Basak, D, Ed.; Mechanism of converting n-type to p-type conductivity in ZnO nanorods array films co-implanted with nitrogen and lithium ions, Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2023, 298, 116860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Zapien, J.A. ; et. al.; Conversion of n-type to p-type conductivity in ZnO by incorporation of Ag and Ag-Li, Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33, 104278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Nurul, H.L.; Abu Kalam, M. F. ; Md Kamruzzaman; et.al.;Dual acceptor (N, Cu) doping effects on the electronic and optical properties of ZnO. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 242, 122463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, W; Yue, Z; Jiahua, M; et al. ; Ag N dual accept doping for the fabrication of p-type ZnO. Appl. Phys. A, 2009, 94, 715–718. [CrossRef]
- Swapna, R; Santhosh-Kumar, MC; Deposition of the low resistive Ag N dual acceptor doped p-type ZnO thin films, Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1799–1806. [CrossRef]
- Swapna, R; Amiruddin, R; Santhosh-Kumar, MC; Aging and annealing effects on properties of Ag-N dual acceptor doped ZnO thin films. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 15, 682. [CrossRef]
- Jing-Wei, W; Ji-Ming, B; Hong-Wei, L; et al. ; Enhanced p-Type ZnO Films through Nitrogen and Argentum Codoping Grown by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 3400. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z, Ma, Y, Deng, P; et al. ; Ag, N doped ZnO film and its p-n junction fabricated by ion beam assisted deposition, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 2289–2292. [CrossRef]
- Duan, L; Zhang, W; Yu, X; et al. ; Stable p-type ZnO films dual-doped with silver and nitrogen. Sol. State. Commun. 2013, 157, 45–48. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcón, RI; Rodríguez-Canto, PJ; Abargues-Lopez, R; et al. ; Nitrogen effect on spin-coated ZnO-based p–n homojunction: structural, optical and electrical characteristics, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron., 2018, 29, 12690. [CrossRef]
- Ortega, JJ; Ortiz-Hernández, AA; Berumen-Torres, JA; et al. ; Ag-N dual acceptor doped p-type ZnO thin films by DC reactive magnetron co-sputtering. Mater. Lett. 2016, 181, 12–15. [CrossRef]
- Chun-Ying, Z; Jing, W; Yue-Lei, B; First-principles investigation of N-Ag codoping effect on electronic properties in p-type ZnO. Chin. Phys. B. 2010, 19, 047101. [CrossRef]
- Volnianska, O; Boguslawski, P; Kaminska, E; Ag and N acceptors in ZnO: An ab initio study of acceptor pairing, doping efficiency, and the role of hydrogen, Phys. Rev. B. 2012, 85, 165212. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z; He, H; Jiang, L; Co-doping: an effective strategy for achieving stable p-type ZnO thin films, Nano Energy. 2018, 52, 527–540. 52. [CrossRef]
- Yahia, SB; Znaidi, L; Kanaev, A, et al. Raman study of oriented ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel method, Spectrochim. Acta A-M., 2008, 71, 1234–1238. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gültekin, D; Akbulut, H; Raman Studies of ZnO Products Synthesized by Solution-Based Methods, Acta Phys. Pol. A. 2016, 129, 803–805. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P; Kong, C; Li, W; et al; The origin of the 274 cm−1 additional Raman mode induced by the incorporation of N dopants and a feasible route to achieve p-type ZnO:N thin films, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 327, 154–158. [CrossRef]
- Wang, LN; Hu, LZ; Zhang, HQ; et al. ; Studying the Raman spectra of Ag doped ZnO films grown by PLD. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process, 2011, 14, 274–277. [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, M; Balasubramanian K; Dopant induced local vibrational modes and Fano scattering in Ag doped ZnO microrods. Spectrochim. Acta A, 2018, 199, 322–327. [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P. et al, QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys.:Condens.Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar]
- Giannozzi, P. et al,. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with Quantum ESPRESSO. J. Phys.:Condens.Matter, 2017, 29, 465901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troullier, N.; and Martins, J. L. ; Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wavecalculations. Phys. Rev. B, 1991, 43, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troullier, N.; and Martins, J. L. ; Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. II. Operators for fast iterative diagonalization. Phys. Rev. B, 1991, 43, 8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Film | Gas flow ratio Ar/O2/N2 (sccm) |
Atomic percentage (%) Zn O N Ag |
|---|---|---|
| 1-400 | 5.0/3.0/15.0 | 36.28 57.54 4.65 1.56 |
| 2-400 | 5.0/2.5/15.0 | 37.27 58.30 3.78 0.59 |
| 3-400 | 5.0/2.0/15.0 | 39.56 55.60 3.80 1.04 |
| Film | Gas flow ratio Ar/O2/N2 (sccm) |
Initial Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier density (cm-3) | Mobility (cm2/V.s) | Resistivity (Ω.cm) | Type conductivity | ||
| 1-400 | 5.0/3.0/15.0 | 3.290E17 | 16.05 | 1.182E-01 | p-type |
| 2-400 | 5.0/2.5/15.0 | 7.008E17 | 20.46 | 4.33E-01 | p-type |
| 3-400 | 5.0/2.0/15.0 | 3.174E19 | 22.99 | 8.555E-03 | p-type |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





