Submitted:
11 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Different Abiotic Stressors Impact on Cotton Plants
2.1. Impact of Salinity Stress on Cotton
| Abiotic stress factor | Impact on cotton plant development and traits | Growth impact | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat stress | Leaves: wilting | +++ | [257] |
| Reduced photosynthesis | --- | [258] | |
| Fiber quality | --- | [259] | |
| Leaf number | --- | [24] | |
| Stomatal density | --- | [260] | |
| Trichome density | +++ | [261] | |
| Flowering | --- | [262] | |
| Bolls: boll size | --- | [263] | |
| Root length | --- | [258] | |
| Shoot length | --- | [264] | |
| Premature boll opening | [265] | ||
| Drought | Leaf rolling, | +++ | [266] |
| Leaf growth, | --- | [267] | |
| Leaf area | --- | [268] | |
| Fiber quality | --- | [269] | |
| Root length | --- | [270] | |
| Shoot length | --- | [271] | |
| Stomatal density | +++ | [272,273] | |
| Trichome density | +++ | [274] | |
| Flowering | ---- | [119] | |
| Leaf number | ---- | [275] | |
| Bolls size | --- | [276] | |
| Premature bolls opening | +++ | [119] | |
| Salinity | Root length | --- | [277] |
| Leaf necrosis | +++ | [278] | |
| Nutrient absorption, | --- | [116] | |
| Fiber quality | --- | [279] | |
| Stomatal density | +++ | [280] | |
| Bolls size | --- | [281] | |
| Premature bolls opening | +++ | [282] | |
| Leaves: leaf rolling | +++ | [283] | |
| Leaf area | --- | [284] | |
| Root length | --- | [285] | |
| Shoot length | --- | [286] | |
| Trichome density | --- | [287] | |
| Flowering delay | +++ | [288] | |
| Leaf number | --- | [289] | |
| Heavy metal toxicity | Shoot length | --- | [290] |
| Leaf chlorosis, necrosis | +++ | [291] | |
| Leaf rolling | +++ | [292] | |
| Leaf area | --- | [291] | |
| Fiber quality | --- | [293] | |
| Root length | --- | [290] | |
| Stomatal density | +++ | [291] | |
| Flowering | --- | [294] | |
| Leaf number | --- | [295] | |
| Bolls size | --- | [296] | |
| Premature bolls opening | --- | [296] | |
| Water logging | Nutrient deficiency | +++ | [297] |
| Leaves: chlorosis | +++ | [298] | |
| Shoot length, | --- | [299] | |
| Leaf area | --- | [300] | |
| Fiber quality | --- | [301] | |
| Root length | --- | [302] | |
| Stomatal density | --- | [303] | |
| Trichome density | +++ | [303] | |
| Flowering | --- | [300] | |
| Leaf number | [304] | ||
| Bolls size | --- | [303] | |
| Premature bolls opening | +++ | [305] |
2.2. Impact of Drought Stress on Cotton
2.3. Impact of Heat Stress on Cotton
3. Effects of Abiotic Stress on Cotton Plants
3.1.1. Physiological Changes in Response to Abiotic Stress in Cotton
| Biochemical raits | Effects on biochemical traits | Explant source | Screening method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proline accumulation | Increased under drought stress, indicative of osmotic adjustment | Leaf tissue | High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) | [306,307] |
| Chlorophyll content | Decreased under heat stress, indicating photoinhibition | Leaf tissue | HPLC | [308,309] |
| Antioxidant enzyme activity | Enhanced activity under oxidative stress, protecting against damage | Leaf tissue | Enzyme Assays | [310,311] |
| Ion homeostasis | Alterations in nutrient uptake, essential for plant growth | Root tissue | Ion Analysis | [312] |
| Heat shock protein expression | Induced expression under high temperatures, aiding protein stability | Leaf tissue | Protein Analysis | [131,314] |
| Peroxidase (pod) activity | Changes in metabolic pathways, impacting plant growth and development | Root tissue | Enzyme Assays | [315,316] |
| Lipid peroxidation | Increased levels indicate membrane damage under stress conditions | Leaf tissue | Thiobarbituric Acid Assay | [317,318] |
| Soluble sugar content | Accumulation acts as an osmoprotectant, maintaining cellular integrity | Leaf tissue | Spectrophotometry | [317,319] |
| Total phenolic content | Elevated levels contribute to antioxidant defense against stress | Leaf tissue | Spectrophotometry | [320,321] |
| Malondialdehyde (mda) content | Elevated levels indicate lipid peroxidation and cellular damage | Leaf tissue | Spectrophotometry | [322,323] |
| Superoxide dismutase (sod) activity | Increased activity under oxidative stress, scavenging superoxide radicals | Leaf tissue | Enzyme Assays | [324,325] |
| Catalase (cat) activity | Enhanced activity under oxidative stress, decomposing hydrogen peroxide | Leaf tissue | Enzyme Assays | [326] |
| Carotenoid content | Decreased levels impact photosynthetic efficiency under stress | Leaf tissue | HPLC | [327] |
| Flavonoid content | Increased synthesis contributes to stress tolerance mechanisms | Leaf tissue | Spectrophotometry | [328] |
| Ascorbic acid content | Decreased levels affect antioxidant capacity and stress tolerance | Leaf tissue | Titration Method | [329] |
| Glutathione content | Altered levels impact oxidative stress response and redox regulation | Leaf tissue | Enzymatic Assay | [330] |
| Polyphenol oxidase activity | Enhanced activity in response to stress, leading to tissue browning | Leaf tissue | Enzyme Assay | [4] |
3.1.2. Morphological Changes in Response to Abiotic Stress in Cotton
3.1.3. Yield Reduction in Response to Abiotic Stress in Cotton
3.2. Mechanisms of Cotton Plants in Response to Abiotic Stress
3.2.1. Stress Signaling Pathways
3.2.2. Stress-Responsive Genes and Proteins
| Sr.no | Genes | Abiotic stress | Plant part | Impact on gene expression | Regulation | Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | GhHSP70, GhHSP90 | High Temperature | Leaves | Upregulation of heat shock proteins (HSPs) | Upregulated | qRT-PCR | [331,332] |
| 2. | GhRD29A, GhDREB1A | Drought | Roots | Activation of genes related to osmotic regulation | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [333,334] |
| 3. | GhSOS1, GhNHX1 | Salinity | Roots | Altered expression of ion transport genes | Upregulated | Microarray | [335,336] |
| 4. | GhMT1, GhPCS | Heavy Metal Toxicity | Roots | Induction of metal detoxification genes | Upregulated | qPCR | [174,196,337] |
| 5. | GhUVR8, GhCOP1 | UV-B Radiation | Leaves | Activation of genes involved in UV protection | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [338,339] |
| 6. | GhAPX, GhSOD | Oxidative Stress | Leaves | Upregulation of antioxidant enzyme genes | Upregulated | qRT-PCR | [340,341] |
| 7. | GhLEA, GhRAB | Waterlogging | Roots | Induction of genes related to waterlogging tolerance | Upregulated | Microarray | [342,343] |
| 8. | GhPIP, GhTIP | Drought | Leaves | Regulation of aquaporin genes involved in water transport | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [344,345,346] |
| 9. | GhMYB, GhbZIP | Heat Stress | Leaves | Activation of transcription factor genes | Upregulated | qPCR | [347] |
| 10. | GhNAC, GhWRKY | Salt Stress | Roots | Modulation of stress-responsive transcription factor genes | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [348,349,350,351] |
| 11. | GhPAL, GhCHS | UV-B Radiation | Leaves | Regulation of genes involved in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | Upregulated | qRT-PCR | [352–355] |
| 12. | GhCAT, GhPOD | High Temperature | Leaves | Induction of antioxidant enzyme genes | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [356,357] |
| 13. | GhP5CS, GhBADH | Drought | Leaves | Activation of genes involved in proline biosynthesis | Upregulated | qPCR | [358] |
| 14. | GhHKT1, GhNHX2 | Salinity | Roots | Alteration in ion homeostasis-related gene expression | Upregulated | RNA-Seq | [359,360] |
| 15. | GhDHN, GhERF | Cold Stress | Leaves | Modulation of genes related to cold response | Upregulated | qRT-PCR | [361,362] |
4. Breeding and Biotechnological Approaches to Improve Abiotic Stress Tolerance to Overcome in Cotton
4.1. Breeding for Stress Tolerance
4.2. Transgenic Approaches
4.3. CRISPR/Cas in Cotton: Challenges and Solutions
5. Future Prospects and Challenges
5.1. Advanced Biotechnological Interventions in Mitigating Abiotic Stress
5.2. Genes Pyramiding Approach to Improve Multi-Stress Tolerance in Crops
5.3. Challenges in Mitigating Abiotic Stress in Cotton
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopecká, R.; Kameniarová, M.; Černý, M.; Brzobohatý, B.; Novák, J. Abiotic Stress in Crop Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawar Jabran, Sami Ul-Allah, Bhagirath Singh Chauhan, An Introduction to Global Production Trends and Uses, History and Evolution, and Genetic and Biotechnological Improvements in Cotton, Cotton Production. Chapter 18 2020, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.; Wang, L. Mechanism of Cotton Resistance to Abiotic Stress, and Recent Research Advances in the Osmoregulation Related Genes. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Recent Advances of Polyphenol Oxidases in Plants. Molecules 2023, 28, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emine Karademir Cetin Karademir, E.B. Cotton Production Under Abiotic Stress; 2021; ISBN 9786258061703.
- Voora, V.; Bermudez, S.; Farrell, J.J.; Larrea, C.; Luna, E. Cotton Prices and Sustainability Market Overview; 2023. 2023.
- Bita, C.; Gerats, T. Plant Tolerance to High Temperature in a Changing Environment: Scientific Fundamentals and Production of Heat Stress-Tolerant Crops. Front Plant Sci 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bita, C.E.; Gerats, T. Plant Tolerance to High Temperature in a Changing Environment: Scientific Fundamentals and Production of Heat Stress-Tolerant Crops. Front Plant Sci 2013, 4, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastain, D.R.; Snider, J.L.; Choinski, J.S.; Collins, G.D.; Perry, C.D.; Whitaker, J.; Grey, T.L.; Sorensen, R.B.; van Iersel, M.; Byrd, S.A.; et al. Leaf Ontogeny Strongly Influences Photosynthetic Tolerance to Drought and High Temperature in Gossypium Hirsutum. J Plant Physiol 2016, 199, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, R.; Dong, H.; Abid, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Potassium Fertilizer Improves Drought Stress Alleviation Potential in Cotton by Enhancing Photosynthesis and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Environ Exp Bot 2017, 137, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, R.; Zhao, W.; Abid, M.; Dong, H.; Zhou, Z. Title: Potassium Application Regulates Nitrogen Metabolism and Osmotic Adjustment in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Functional Leaf under Drought Stress. J Plant Physiol 2017, 215, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Snider, J.L.; Bhattarai, A.; Collins, G. Economic Penalties Associated with Irrigation during High Rainfall Years in the Southeastern United States. Agric Water Manag 2022, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, G.A.; Bange, M.P. The Yield Potential of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Field Crops Res 2015, 182, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, C.; Snider, J.L.; Sobolev, V.; Chastain, D.R.; Sorensen, R.B.; Meeks, C.D.; Massa, A.N.; Walk, T.; Singh, B.; Earl, H.J. Assessing Stomatal and Non-Stomatal Limitations to Carbon Assimilation under Progressive Drought in Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea L.). J Plant Physiol 2018, 231, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, A.; Adams, N.; Zhang, J. Effects of Drought on Agronomic and Fiber Quality in an Introgressed Backcross Inbred Line Population of Upland Cotton under Field Conditions. Field Crops Res 2020, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.C.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Gonias, E.D. Exogenous Application of Putrescine Ameliorates the Effect of High Temperature in Gossypium Hirsutum l. Flowers and Fruit Development. J Agron Crop Sci 2010, 196, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, J.L.; Collins, G.D.; Whitaker, J.; Perry, C.D.; Chastain, D.R. Electron Transport Through Photosystem II Is Not Limited By A Wide Range of Water Deficit Conditions In Field-Grown Gossypium Hirsutum. J Agron Crop Sci 2014, 200, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao W, Dong H, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Hu W. Potassium (K) application alleviates the negative effect of drought on cotton fiber strength by sustaining higher sucrose content and carbohydrates conversion rate. Plant physiology and biochemistry 2020, 157, 105–113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju F, Pang J, Sun L, Gu J, Wang Z, Wu X, Ali S, Wang Y, Zhao W, Wang S, Zhou Z. Integrative transcriptomic, metabolomic and physiological analyses revealed the physiological and molecular mechanisms by which potassium regulates the salt tolerance of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) roots. Industrial Crops and Products 2023, 193, 116177. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Hu, W.; Loka, D.A.; Snider, J.L.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Carbon Assimilation and Distribution in Cotton Photosynthetic Organs Is a Limiting Factor Affecting Boll Weight Formation under Drought. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Hao, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Yan, Y.; Guo, X. A Raf-like MAPKKK Gene, GhRaf19, Negatively Regulates Tolerance to Drought and Salt and Positively Regulates Resistance to Cold Stress by Modulating Reactive Oxygen Species in Cotton. Plant Science 2016, 252, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Shi, G.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Hua, J. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals That Distinct Metabolic Pathways Operate in Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Upland Cotton Varieties Subjected to Salinity Stress. Plant Science 2015, 238, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Zahoor, R.; Chen, B.; Meng, Y. Soil Water and Salt Affect Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Photosynthesis, Yield and Fiber Quality in Coastal Saline Soil. Agric Water Manag 2017, 187, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loka, D.A.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Baxevanos, D.; Noulas, C.; Hu, W. Single and Combined Effects of Heat and Water Stress and Recovery on Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Leaf Physiology and Sucrose Metabolism. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2020, 148, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Qiao, W.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Yan, G.; Huang, Q. Relative Contribution of Na+/K+ Homeostasis, Photochemical Efficiency and Antioxidant Defense System to Differential Salt Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Cultivars. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2017, 119, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Abdelraheem, A.; Wedegaertner, T. Genetic Variation of Waterlogging Tolerance in Pima (Gossypium Barbadense) Cotton and Glanded and Glandless Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) under Field Conditions. Ind Crops Prod 2019, 129, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.-K. Proline Accumulation and Salt-Stress-Lnduced Gene Expression in a Salt-Hypersensitive Mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology 1997, 114, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, I.; Aleem, S.; Farooq, J.; Rizwan, M.; Younas, A.; Sarwar, G.; Chohan, S.M. Salinity Stress in Cotton: Effects, Mechanism of Tolerance and Its Management Strategies. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants 2019, 25, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, K.; Mondal, S.; Gorai, S.; Singh, A.P.; Kumari, A.; Ghosh, T.; Roy, A.; Hembram, S.; Gaikwad, D.J.; Mondal, S.; et al. Impacts of Salinity Stress on Crop Plants: Improving Salt Tolerance through Genetic and Molecular Dissection. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Roles of Glycine Betaine and Proline in Improving Plant Abiotic Stress Resistance. Environ Exp Bot 2007, 59, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelake RM, Kadam US, Kumar R, Pramanik D, Singh AK, Kim JY. Engineering drought and salinity tolerance traits in crops through CRISPR-mediated genome editing: Targets, tools, challenges, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 2022, 3. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative Physiology of Salt and Water Stress. Plant Cell Environ 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.C.; Oelmüller, R. Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Signaling in Plants. Plant Signal Behav 2012, 7, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekmen, A.H.; Ozgur, R.; Uzilday, B.; Turkan, I. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Capacities of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) Cultivars under Combined Drought and Heat Induced Oxidative Stress. Environ Exp Bot 2014, 99, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.A.; Oliva, M.A.; Martinez, C.A.; Cambraia, J. Photosynthesis and Activity of Superoxide Dismutase, Peroxidase and Glutathione Reductase in Cotton under Salt Stress. Environmental and experimental botany 2003, 49, 69–76, Rajguru, S.N.; Banks, S.W.; Gossett, D.R.; Lucas, M.C.; Fowler, T.E.; Millhollon, E.P.; Rajguru, S.N.; Banks, S.W.; Gossett, D.R.; Lucas, M.C.; et al. PHYSIOLOGY Antioxidant Response to Salt Stress During Fiber Development in Cotton Ovules; J Cotton Sci. 1999, 10;3(1):11-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Shulaev, V.; Mittler, R. Reactive Oxygen Signaling and Abiotic Stress. Physiol Plant 2008, 133, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki, S. A., Wagh, S. G., Sul, R. S., Pawar, K. R., & Harke, S. N. Comparative Studies among Different Genotypes of Soybean (Glycine max L.) against Salinity Stress. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology 2020, 91–100. [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Shah, N.A.; Zeeshan, M.; Abraham, G. Differential Response of Antioxidant Enzymes to Salinity Stress in Two Varieties of Azolla (Azolla Pinnata and Azolla Filiculoides). Environ Exp Bot 2006, 58, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Shams, M. Some Agronomic and Physiological Aspects of Salt Tolerance in Cotton {Gossypium Hirsutum L.). J. Agronomy & Crop Science 1997, 179, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamer, Z.; Chaudhary, M.T.; Du, X.; Hinze, L.; Azhar, M.T. Review of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Defense Mechanisms in Gossypium Hirsutum L. in Response to Extreme Abiotic Conditions. Journal of Cotton Research 2021, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Harish; Singh, R.K.; Verma, K.K.; Sharma, L.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Meena, M.; Gour, V.S.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; et al. Recent Developments in Enzymatic Antioxidant Defence Mechanism in Plants with Special Reference to Abiotic Stress. Biology 2021, 10, 267. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Lu, X.; Tao, Y.; Guo, H.; Min, W. Comparative Ionomics and Metabolic Responses and Adaptive Strategies of Cotton to Salt and Alkali Stress. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinze, L.L.; Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Wilson, I.W.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Spriggs, A.; Fang, D.D.; Ulloa, M.; Burke, J.J.; et al. Diversity Analysis of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Germplasm Using the CottonSNP63K Array. BMC Plant Biol 2017, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Abudurezikekey, A.K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Z. Effect of Shading on Cotton Yield and Quality on Different Fruiting Branches. Crop Sci 2013, 53, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, R.C. Osmoregulation in Cotton in Response to Water Stress’ III. Effects Of Phosphorus Fertility. Plant physiology, 1985; 77, 309–312, Shinde, H., Dudhate, A., Sathe, A., Paserkar, N., Wagh, S. G., & Kadam, U. S. Gene Coexpression Analysis Identifies Genes Associated with Chlorophyll Content and Relative Water Content in Pearl Millet. Plants 2023, 12(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, C.; Snider, J.L.; Sobolev, V.; Chastain, D.R.; Sorensen, R.B.; Meeks, C.D.; Massa, A.N.; Walk, T.; Singh, B.; Earl, H.J. Assessing Stomatal and Non-Stomatal Limitations to Carbon Assimilation under Progressive Drought in Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea L.). J Plant Physiol 2018, 231, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Snider, J.L.; Bhattarai, A.; Collins, G. Economic Penalties Associated with Irrigation during High Rainfall Years in the Southeastern United States. Agric Water Manag 2022, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, A.; Adams, N.; Zhang, J. Effects of Drought on Agronomic and Fiber Quality in an Introgressed Backcross Inbred Line Population of Upland Cotton under Field Conditions. Field Crops Res 2020, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Tan, Q.; Li, L.; Shi, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, X. Drought Stress Tolerance Mediated by Zinc-Induced Antioxidative Defense and Osmotic Adjustment in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Acta Physiol Plant 2015, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, B.; Briantais, J.; Bravo Vieira Silva, J. DA Effects of Drought on Primary Photosynthetic Processes of Cotton Leaves’. Plant Physiology 1987, 83, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response Mechanism of Plants to Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, T.; Chaudhary, M.T.; Majeed, S.; Rana, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Elansary, H.O.; Moussa, I.M.; Sun, S.; Azhar, M.T. Exploitation of Various Physio-Morphological and Biochemical Traits for the Identification of Drought Tolerant Genotypes in Cotton. BMC Plant Biol 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, J.H.; Brandão, Z.N.; Rodrigues, J.I.D.S.; Sofiatti, V. Cotton Response to Water Deficits at Different Growth Stages. Revista Caatinga 2017, 30, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Drought Coping Strategies in Cotton: Increased Crop per Drop. Plant Biotechnol J 2017, 15, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Pandey, A.K.; Ranjan, S.; Mishra, A.; Singh, R.; Sharma, Y.K.; Shirke, P.A.; Pandey, V. Physiological and Proteomic Responses of Cotton (Gossypium Herbaceum L.) to Drought Stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2012, 53, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreen, S.; Athar, H.; Ashraf, M.; Bot, P.J.; Ur, H.; Athar, R. Interactive Effects of Watering Regimes and Exogenously Applied Osmoprotectants on Earliness Indices and Leaf Area Index in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Crop. Pak. J. Bot 2013, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, S.; Rana, I.A.; Mubarik, M.S.; Atif, R.M.; Yang, S.-H.; Chung, G.; Jia, Y.; Du, X.; Hinze, L.; Azhar, M.T. Heat Stress in Cotton: A Review on Predicted and Unpredicted Growth-Yield Anomalies and Mitigating Breeding Strategies. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, A.A.; Anwar, M.; Javwad, M.U.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; Salama, E.A.A.; Ahmed, M.A.A. Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Responses under Heat Stress in Cotton: Overview. Biotechnology Reports, 2023; 40, Zafar, M.M.; Chattha, W.S.; Khan, A.I.; Zafar, S.; Subhan, M.; Saleem, H.; Ali, A.; Ijaz, A.; Anwar, Z.; Qiao, F.; et al. Drought and Heat Stress on Cotton Genotypes Suggested Agro-Physiological and Biochemical Features for Climate Resilience. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14, doi:10.3389/fpls.2023.1265700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koevoets, I.T.; Venema, J.H.; Elzenga, J.T.M.; Testerink, C. Roots Withstanding Their Environment: Exploiting Root System Architecture Responses to Abiotic Stress to Improve Crop Tolerance. Front Plant Sci 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, Y.M.; Moreno, L.P.; Barragán, E. Predictive Models of Drought Tolerance Indices Based on Physiological, Morphological and Biochemical Markers for the Selection of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Varieties. J Integr Agric 2022, 21, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmalatha, K.V.; Dhandapani, G.; Kanakachari, M.; Kumar, S.; Dass, A.; Patil, D.P.; Rajamani, V.; Kumar, K.; Pathak, R.; Rawat, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Transcriptomic Analysis of Cotton under Drought Stress Reveal Significant down-Regulation of Genes and Pathways Involved in Fibre Elongation and up-Regulation of Defense Responsive Genes. Plant Mol Biol 2012, 78, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Pan, X.; Najeeb, U.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Fahad, S.; Zahoor, R.; Luo, H. Coping with Drought: Stress and Adaptive Mechanisms, and Management through Cultural and Molecular Alternatives in Cotton as Vital Constituents for Plant Stress Resilience and Fitness. Biol Res 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Hao, X.; Zhou, H.; Ding, R. An Integrated Strategy for Improving Water Use Efficiency by Understanding Physiological Mechanisms of Crops Responding to Water Deficit: Present and Prospect. Agric Water Manag 2021, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Basit, A.; Mohamed, H.I.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Kamel, E.A.R.; Shalaby, T.A.; Ramadan, K.M.A.; Alkhateeb, A.A.; Ghazzawy, H.S. Mulching as a Sustainable Water and Soil Saving Practice in Agriculture: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Waraich, E.A.; Skalicky, M.; Hussain, S.; Zulfiqar, U.; Anjum, M.Z.; Habib ur Rahman, M.; Brestic, M.; Ratnasekera, D.; Lamilla-Tamayo, L.; et al. Adaptation Strategies to Improve the Resistance of Oilseed Crops to Heat Stress Under a Changing Climate: An Overview. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ton, P. Cotton & Climate Change: Impacts and Options to Mitigate and Adapt; International Trade Centre 2011:1-7.
- Saini, D.K.; Impa, S.M.; McCallister, D.; Patil, G.B.; Abidi, N.; Ritchie, G.; Jaconis, S.Y.; Jagadish, K.S.V. High Day and Night Temperatures Impact on Cotton Yield and Quality—Current Status and Future Research Direction. Journal of Cotton Research 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tao, X.; Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Luo, H. Biomass Accumulation, Photosynthetic Traits and Root Development of Cotton as Affected by Irrigation and Nitrogen-Fertilization. Front Plant Sci 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, T.B.; Ribas, A.F.; de Souza, S.G.H.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Physiological Responses to Drought, Salinity, and Heat Stress in Plants: A Review. Stresses 2022, 2, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Zhou, M.; Shabala, S. How Does Stomatal Density and Residual Transpiration Contribute to Osmotic Stress Tolerance? Plants 2023, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudahe, K.; Sheshukov, A.Y.; Aguilar, J.; Djaman, K. Irrigation-Water Management and Productivity of Cotton: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10070, Plant Breeding for Climate Resilience: Strategies and Genetic Adaptations. Trends in Animal and Plant Sciences 2024, 3, 20–30, doi:10.62324/taps/2024.023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadau, S.B.; Liu, Z.; Ninkuu, V.; Guan, L.; Sun, X. DREB Transcription Factors Are Crucial Regulators of Abiotic Stress Responses in Gossypium Spp. Plant Stress 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.; Li, J.; Gong, B.; Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; Lü, G.; Gao, H. Drought Stress Tolerance in Vegetables: The Functional Role of Structural Features, Key Gene Pathways, and Exogenous Hormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13876, Zahid, K.R.; Ali, F.; Shah, F.; Younas, M.; Shah, T.; Shahwar, D.; Hassan, W.; Ahmad, Z.; Qi, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Response and Tolerance Mechanism of Cotton Gossypium Hirsutum L. To Elevated Temperature Stress: A Review. Front Plant Sci 2016, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W. Potassium (K) Application Alleviates the Negative Effect of Drought on Cotton Fiber Strength by Sustaining Higher Sucrose Content and Carbohydrates Conversion Rate. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2020, 157, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Dong, H.; Li, C. Waterlogging Stress in Cotton: Damage, Adaptability, Alleviation Strategies, and Mechanisms. Crop Journal 2021, 9, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Leng, Y.-N.; Zhu, F.-Y.; Li, S.-E.; Song, T.; Zhang, J. Water-Saving Techniques: Physiological Responses and Regulatory Mechanisms of Crops. Advanced Biotechnology 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, K. R., Wagh, S. G., Sonune, P. P., Solunke, S. R., Solanke, S. B., Rathod, S. G., & Harke, S. N. . Analysis of Water Stress in Different Varieties of Maize (Zea mays L.) at the Early Seedling Stage. Biotechnol. Jour. Inter 2020, 15–24. [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, R.C. Osmoregulation in Cotton in Response to Water Stress’ II. Leaf Carbohydrate Status In Relation To Osmotic Adjustment; 1981; Vol. 67.
- Chen, W.; Feng, C.; Guo, W.; Shi, D.; Yang, C. Comparative Effects of Osmotic-, Salt- and Alkali Stress on Growth, Photosynthesis, and Osmotic Adjustment of Cotton Plants. Photosynthetica 2011, 49, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Hou, Z. Growth, Ionic Homeostasis, and Physiological Responses of Cotton under Different Salt and Alkali Stresses. Sci Rep 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamullah; Isoda, A. Adaptive Responses of Soybean and Cotton to Water Stress: I. Transpiration Changes in Relation to Stomatal Area and Stomatal Conductance. Plant Prod Sci 2005, 8, 16–26. [CrossRef]
- Loka, D.A.; Oosterhuis, D.M. Water Stress And Reproductive Development In Cotton; Flowering and Fruiting in Cotton. Cordova: The Cotton Foundation. 2012:51-8.
- Argyrokastritis, I.G.; Papastylianou, P.T.; Alexandris, S. Leaf Water Potential and Crop Water Stress Index Variation for Full and Deficit Irrigated Cotton in Mediterranean Conditions. Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2015, 4, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim M, Li X, Anjum S, Shahzad K, Ahmad F, Ali M, Zulfiar U, Muhammad M, Zeng F.Potassium Silicate improves drought tolerance in Cotton by modulating growth, gas exchange and antioxidant activities. Research Square 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, H.; Zahoor, R.; Zhou, Z.; Snider, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wang, Y. Ameliorative Effects of Potassium on Drought-Induced Decreases in Fiber Length of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Are Associated with Osmolyte Dynamics during Fiber Development. Crop Journal 2019, 7, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; Conley, M.M.; Herritt, M.T.; Thorp, K.R. Response of Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Leaf Chlorophyll Content to High Heat and Low-Soil Water in the Arizona Low Desert. Photosynthetica 2022, 60, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Wang, X.; Ahmar, S.; Abdullah, M.; Iqbal, M.S.; Rana, R.M.; Yasir, M.; Khalid, S.; Javed, T.; Mora-Poblete, F.; et al. Genetic Potential and Inheritance Pattern of Phenological Growth and Drought Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; et al. Leaf Anatomical Alterations Reduce Cotton’s Mesophyll Conductance under Dynamic Drought Stress Conditions. Plant Journal 2022, 111, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakma, S.P.; Chileshe, S.M.; Thomas, R.; Krishna, P. Cotton Seed Priming with Brassinosteroid Promotes Germination and Seedling Growth. Agronomy 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A. Water Stress Mediated Changes in Morphology and Physiology of Gossypium Arboreum (Var FDH-786). Journal of Plant Sciences (Science Publishing Group) 2014, 2, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, S.; Reddy, K.R. Reproductive and Fiber Quality Responses of Upland Cotton to Moisture Deficiency. Agron J 2014, 106, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Dagaonkar, V.S.; Phalak, M.S.; Umalkar, G. V.; Aurangabadkar, L.P. Alterations in Photosynthetic Pigments, Protein and Osmotic Components in Cotton Genotypes Subjected to Short-Term Drought Stress Followed by Recovery. Plant Biotechnol Rep 2007, 1, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Ul-Allah, S.; Naeem, M.; Ijaz, M.; Sattar, A.; Sher, A. Response of Cotton Genotypes to Water and Heat Stress: From Field to Genes. Euphytica 2017, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ishaque, W.; Farid, M.; Mahmood, K.; Iqbal, Z. Cadmium Stress in Cotton Seedlings: Physiological, Photosynthesis and Oxidative Damages Alleviated by Glycinebetaine. South African Journal of Botany 2016, 104, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Badgujar, G.; Reddy, V.R.; Fleisher, D.H.; Bunce, J.A. Carbon Dioxide Diffusion across Stomata and Mesophyll and Photo-Biochemical Processes as Affected by Growth CO2 and Phosphorus Nutrition in Cotton. J Plant Physiol 2013, 170, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.U. Genetic Analysis of Stomatal Conductance in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) under Contrasting Temperature Regimes. Journal of Agricultural Science 2005, 143, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, C.; Pusadkar, P.; Shilpa, B.; N, C.C.; Pratik, P. Evaluation of Physiological and Morphological Responses Associated with Cotton Subjected to Drought Stress Conditions. Res. J. Biotech 2015, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Snider, J.L.; Bai, H.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z. Drought Effects on Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Fibre Quality and Fibre Sucrose Metabolism during the Flowering and Boll-Formation Period. J Agron Crop Sci 2020, 206, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Bakhsh, A.; Zubair, M.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Shahzad, A.; Nayab, S.; Khan, M.; Anum, W.; Akhtar, R.; Kanwal, N.; et al. Effects of Water Stress on Cotton (Gossypium Spp.) Plants and Productivity. Egyptian Journal of Agronomy 2021, 0, 0–0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Z.; Dong, H.; Li, C. Fine Root and Root Hair Morphology of Cotton under Drought Stress Revealed with RhizoPot. J Agron Crop Sci 2020, 206, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Han, Y.; Xing, F.; Feng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, B.; Fan, Z.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, S.; et al. Plant Density Influences Reproductive Growth, Lint Yield and Boll Spatial Distribution of Cotton. Agronomy 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Gao, K.; Hu, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z. Foliar and Seed Application of Plant Growth Regulators Affects Cotton Yield by Altering Leaf Physiology and Floral Bud Carbohydrate Accumulation. Field Crops Res 2019, 231, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.R.; Bhale, V.M. Abscission of Fruiting Structures in Bt and Non-Bt Cotton in Relation to Abiotic Factors and Agronomic Intervention under Rainfed Condition. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 2019, 8, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanai, Y.; Tissue, D.T.; Bange, M.P.; Braunack, M. V.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Interactive Effects of Elevated CO2, Temperature and Extreme Weather Events on Soil Nitrogen and Cotton Productivity Indicate Increased Variability of Cotton Production under Future Climate Regimes. Agric Ecosyst Environ 2017, 246, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, W. Quantifying Individual and Interactive Effects of Elevated Temperature and Drought Stress on Cotton Yield and Fibre Quality. J Agron Crop Sci 2021, 207, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, R.; Basbağ, S.; Karademir, E.; Karademir, Ç. The Effects Of High Temperature Stress On Some Agronomic Characters In Cotton. Pak. J. Bot. 2017, 49, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, T.; Tabassum, B.; Yousaf, S.; Sarwar, G.; Qaisar, U. Consequences of Drought Stress Encountered During Seedling Stage on Physiology and Yield of Cultivated Cotton. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, Y.; Chen, J.; Lv, F.; Ma, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Oosterhuis, D.M. Effect of Late Planting and Shading on Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality Formation. Field Crops Res 2015, 183, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M., Ed.; Agronomic Crops Volume 3: Stress Responses and Tolerance, Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 978-981-15-0024-4.
- Li, T.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, C.; Dong, H. Topical Shading Substantially Inhibits Vegetative Branching by Altering Leaf Photosynthesis and Hormone Contents of Cotton Plants. Field Crops Res 2019, 238, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhou, Z. Guo; Guo, L. Tao; Xu, W. Zheng; Zhao, W. Qin; Chen, B. Lin; Meng, Y. Li; Wang, Y. hua Susceptible Time Window and Endurable Duration of Cotton Fiber Development to High Temperature Stress. J Integr Agric 2017, 16, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Zuo, W.; Lei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhang, W. Characters in Light-Response Curves of Canopy Photosynthetic Use Efficiency of Light and N in Responses to Plant Density in Field-Grown Cotton. Field Crops Res 2017, 203, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.F.; Raza, M.A.S.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, I.H.; Shahid, A.M. Understanding and Mitigating the Impacts of Drought Stress in Cotton- A Review. Pak J Agric Sci 2016, 53, 609–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Du, M.; Xu, D.; Lu, H.; Tian, X.; Li, Z. Effect of Planting Date and Plant Density on Cotton Traits as Relating to Mechanical Harvesting in the Yellow River Valley Region of China. Field Crops Res 2016, 198, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Luo, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; WeiTang; Dong, H. Effects of Deficit Irrigation and Plant Density on the Growth, Yield and Fiber Quality of Irrigated Cotton. Field Crops Res 2016, 197, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. zheng; Luo, X. jiao; Nie, Y. chun; Zhang, X. long Effects of Plant Density on Yield and Canopy Micro Environment in Hybrid Cotton. J Integr Agric 2014, 13, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ge, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, G.; Chen, E.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SnRK2 Gene Family in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). BMC Genet 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Cui, X.; Lin, S.; Gan, S.; Xing, H.; Dou, D. GmCYP82A3, a Soybean Cytochrome P450 Family Gene Involved in the Jasmonic Acid and Ethylene Signaling Pathway, Enhances Plant Resistance to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadallah, M.A.A. Effect of Water Stress, Abscisic Acid and Proline on Cotton Plants. Journal of arid environments 1995, 30, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Shariq Iqbal, M.; Singh, S.P.; Buaboocha, T. Ca2+/Calmodulin Complex Triggers CAMTA Transcriptional Machinery Under Stress in Plants: Signaling Cascade and Molecular Regulation. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Cai, C.; Guo, W. Genome-Wide Identification of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Gene Family in Gossypium Raimondii and the Function of Their Corresponding Orthologs in Tetraploid Cultivated Cotton. BMC Plant Biol 2014, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mi, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Guo, W. Identification on Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Cascades by Integrating Protein Interaction with Transcriptional Profiling Analysis in Cotton. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, H.; Philippe, F.; Domon, J.-M.; Gillet, F.; Pelloux, J.; Rayon, C. Cell Wall Metabolism in Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants 2015, 4, 112–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, G.; Song, X.; Hussein Ibrahim, M.E.; Ibrahim Salih, E.G.; Hussain, S.; Younas, M.U. Pivotal Role of Phytohormones and Their Responsive Genes in Plant Growth and Their Signaling and Transduction Pathway under Salt Stress in Cotton. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.M.; Zhang, H.; Ge, P.; Iqbal, M.S.; Muneeb, A.; Pervaiz, A.; Maqsood, J.; Sarfraz, Z.; Kassem, H.S.; Ismail, H.; et al. Exploiting Morphophysiological Traits for Yield Improvement in Upland Cotton under Salt Stress. Journal of Natural Fibers 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Song, G.; Yue, Z.; Cong, L.; Shang, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The Draft Genome of a Diploid Cotton Gossypium Raimondii. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L. Ling; Guo, Y. Ning; Ondati, E.; Pang, C. You; Wei, H. Ling; Song, M. Zhen; Fan, S. Li; Yu, S. Xun Identification and Expression Analysis of Group III WRKY Transcription Factors in Cotton. J Integr Agric 2016, 15, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Jia, H.; Chen, X.; Hao, L.; An, H.; Guo, X. The Cotton WRKY Transcription Factor GhWRKY17 Functions in Drought and Salt Stress in Transgenic Nicotiana Benthamiana through Aba Signaling and the Modulation of Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Plant Cell Physiol 2014, 55, 2060–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Liu, D.; Hao, L.; Wu, C. ai; Guo, X.; Li, H. GhWRKY39, a Member of the WRKY Transcription Factor Family in Cotton, Has a Positive Role in Disease Resistance and Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 2014, 118, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, J.; Niu, E.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, W. Genome-Wide Association Studies Reveal Genetic Variation and Candidate Genes of Drought Stress Related Traits in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum l.). Front Plant Sci 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of Allotetraploid Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L. Acc. TM-1) Provides a Resource for Fiber Improvement. Nat Biotechnol 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Afridi, M.Z.; Luo, H.; Tung, S.A.; Ajab, M.; Fahad, S. Nitrogen Fertility and Abiotic Stresses Management in Cotton Crop: A Review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2017, 24, 14551–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; He, C.Q.; Ding, N.Z. Abiotic Stresses: General Defenses of Land Plants and Chances for Engineering Multistress Tolerance. Front Plant Sci 2018, 9, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. WRKY Proteins: Signaling and Regulation of Expression during Abiotic Stress Responses. Scientific World Journal 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, S.; Ye, N.; Jiang, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J. WRKY Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Stresses. J Integr Plant Biol 2017, 59, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY Transcription Factors. Trends Plant Sci 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenare, S., Arun Daspute, A., Raut, V., Babar, N., Ganpatrao Wagh, S., Sonar, S., Thole, S., Vitekar, V., & Harke, S.. Suppression of bacterial wilt in susceptible scion of tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.) and brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) using Solanum. torvum as resistant rootstock. Curr. Hort. 2023, 48–52. [CrossRef]
- Wagh, S. G., Kobayashi, K., Yaeno, T., Yamaoka, N., Masuta, C., & Nishiguchi, M.. Rice necrosis mosaic virus, a fungal transmitted Bymovirus: complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNAs and subgrouping of bymoviruses. Journal of General Plant Pathology 2016, 82, 38–42. [CrossRef]
- Wagh, S. G., Alam, M. M., Kobayashi, K., Yaeno, T., Yamaoka, N., Toriba, T., Hirano, H. Y., & Nishiguchi, M.. Analysis of rice RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 6 (OsRDR6) gene in response to viral, bacterial and fungal pathogens. Journal of General Plant Pathology 2016, 82, 12–17. [CrossRef]
- Wagh, S. G., Daspute, A. A., Akhter, S. M., Bhor, S. A., Kobayashi, K., Yaeno, T., & Nishiguchi, M.. Relationship between Resistance to Rice necrosis mosaic virus and the Expression Levels of Rice RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 6 (OsRDR6) in Various Rice Cultivars. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly 2021, 55, 127–135, Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Regulation of Specialized Metabolism by WRKY Transcription Factors. Plant Physiol 2015, 167, 295–306, doi:10.1104/pp.114.251769. [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Tian, R.; Ma, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, C. Comparative Transcriptome Study Provides Insights into Acquisition of Embryogenic Ability in Upland Cotton during Somatic Embryogenesis. Journal of Cotton Research 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.P.; Sun, S.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Q.H.; Xue, F.; Sun, J. GhWRKY70D13 Regulates Resistance to Verticillium Dahliae in Cotton Through the Ethylene and Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathways. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Yu, F.; Gao, Z.; An, H.; Cao, X.; Guo, X. GhWRKY3, a Novel Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) WRKY Gene, Is Involved in Diverse Stress Responses. Mol Biol Rep 2011, 38, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, A.; Vlad, F.; Sirichandra, C.; Redko, Y.; Jammes, F.; Valon, C.; Frei Dit Frey, N.; Leung, J. An Update on Abscisic Acid Signaling in Plants and More ⋯. Mol Plant 2008, 1, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Sunita, K.; Giri, S.N.; Reddy, K.R. Influence of High Temperature and Breeding for Heat Tolerance in Cotton: A Review. Advances in Agronomy 2007, 93, 313–385. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.M.U.; Ma, F.; Prodhan, Z.H.; Li, F.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Molecular and Physio-Biochemical Characterization of Cotton Species for Assessing Drought Stress Tolerance. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelraheem, A.; Esmaeili, N.; O’Connell, M.; Zhang, J. Progress and Perspective on Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance in Cotton. Ind Crops Prod 2019, 130, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.; Li, F.; Yang, Z. Regulatory Network of Cotton Genes in Response to Salt, Drought and Wilt Diseases (Verticillium and Fusarium): Progress and Perspective. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhao, J.; Deng, X.; Gu, A.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; et al. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping and Identification of Candidate Genes for Resistance to Fusarium Wilt Race 7 Using a Resequencing-Based High Density Genetic Bin Map in a Recombinant Inbred Line Population of Gossypium Barbadense. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.P.; Tiwari, G.J.; Joshi, B.; Song-Beng, K.; Tamta, S.; Boopathi, N.M.; Jena, S.N. GBS-SNP and SSR Based Genetic Mapping and QTL Analysis for Drought Tolerance in Upland Cotton. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants 2021, 27, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, J.; Du, X. Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Yield-Related Traits of Upland Cotton Revealed by Genome-Wide Association Analysis under Drought Conditions. BMC Genomics 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Kanwal, H.H.; Hussain, Q.; Riaz, M.W.; Sajjad, M.; Rong, J.; Jiang, Y. Status and Prospects of Genome-Wide Association Studies in Cotton. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryum, Z.; Luqman, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, S.M.U.D.; Wang, B.; Ditta, A.; Khan, M.K.R. An Overview of Salinity Stress, Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance and Strategies for Its Management in Cotton. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerson RC, Krieg DR. Stomatal and nonstomatal regulation of water use in cotton, corn, and sorghum. Plant Physiology 1977, 60, 850–853. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluoch, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Khan, M.K.R.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; et al. QTL Mapping for Salt Tolerance at Seedling Stage in the Interspecific Cross of Gossypium Tomentosum with Gossypium Hirsutum. Euphytica 2016, 209, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, J.I.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, J. A Comprehensive Meta QTL Analysis for Fiber Quality, Yield, Yield Related and Morphological Traits, Drought Tolerance, and Disease Resistance in Tetraploid Cotton. BMC Genomics 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. bei; Yu, D. wei; Zhao, F. li; Pang, C. you; Song, M. zhen; Wei, H. ling; Fan, S. li; Yu, S. xun Genome-Wide Analysis of the Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase Gene Family in Gossypium Raimondii. J Integr Agric 2015, 14, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Malik, W.; Yan, R.; Lwin, K.M.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhou, T.; et al. GhABF2, a BZIP Transcription Factor, Confers Drought and Salinity Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Sci Rep 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Jin, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, X. Overexpression of Rice NAC Gene SNAC1 Improves Drought and Salt Tolerance by Enhancing Root Development and Reducing Transpiration Rate in Transgenic Cotton. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Q.; Lian, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Overexpression of an H+-PPase Gene from Thellungiella Halophila in Cotton Enhances Salt Tolerance and Improves Growth and Photosynthetic Performance. Plant Cell Physiol 2008, 49, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, W.F. Effects of Water Stress and Rewatering on Photosynthesis, Root Activity, and Yield of Cotton with Drip Irrigation under Mulch. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddula, Y.; Singh, K. Progression of Drip Irrigation and Fertigation in Cotton across the Globe and Its Future Perspectives for Sustainable Agriculture: An Overview. Appl Water Sci 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Zhang, J.; Valle, P. Del, Growth Responses of an Interspecific Cotton Breeding Line and Its Parents to Controlled Drought Using an Automated Irrigation System. The Journal of Cotton Science 2015, 19, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Tu, L.; Yang, X.; Tan, J.; Deng, F.; Hao, J.; Guo, K.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X. The Calcium Sensor GhCaM7 Promotes Cotton Fiber Elongation by Modulating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production. New Phytologist 2014, 202, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Yu, X.; Zhou, G.; Sun, D.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, N.; Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; et al. GhCDPK60 Positively Regulates Drought Stress Tolerance in Both Transgenic Arabidopsis and Cotton by Regulating Proline Content and ROS Level. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.S.; Picchioni, G.A.; Steiner, R.L.; Hughs, S.E.; Jones, D.C.; Zhang, J. Genetic Variation in Salt Tolerance during Seed Germination in a Backcross Inbred Line Population and Advanced Breeding Lines Derived from Upland Cotton × Pima Cotton. Crop Sci 2013, 53, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-A.; Yang, G.-D.; Meng, Q.-W.; Zheng, C.-C. The Cotton GhNHX1 Gene Encoding a Novel Putative Tonoplast Na + /H + Antiporter Plays an Important Role in Salt Stress. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2004; 45, 600–607, Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Tan, Q.; Li, L.; Shi, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, X. Drought Stress Tolerance Mediated by Zinc-Induced Antioxidative Defense and Osmotic Adjustment in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Acta Physiol Plant 2015, 37, doi:10.1007/s11738-015-1919-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Alayafi, A.A. Overexpression of StDREB2 Transcription Factor Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Barbadense L.). Genes (Basel) 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.J.; Wei, Q.; Liao, Y.; Song, H.L.; Li, X.; Xiang, C. Bin; Kuai, B.K. Ectopic Overexpression of AtHDG11 in Tall Fescue Resulted in Enhanced Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stress. Plant Cell Rep 2009, 28, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhanokho, H.K.; Zipf, A.; Rajasekaran, K.; Saha, S.; Sharma, G.C.; Chee, P.W. Somatic Embryo Initiation and Germination in Diploid Cotton (Gossypium Arboreum L. ). In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology—Plant 2004, 40, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Uribe, L.; Higbie, S.M.; Stewart, J.M.D.; Wilkins, T.; Lindemann, W.; Sengupta-Gopalan, C.; Zhang, J. Identification of Salt Responsive Genes Using Comparative Microarray Analysis in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Plant Science 2011, 180, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, J. Glycinebetaine and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Plant Signal Behav 2011, 6, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.J.; Chen, J. Enhancement of Reproductive Heat Tolerance in Plants. PLoS One 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, H.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Kong, X. Increased Glycine Betaine Synthesis and Salinity Tolerance in AhCMO Transgenic Cotton Lines. Molecular Breeding 2009, 23, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasapula, V.; Shen, G.; Kuppu, S.; Paez-Valencia, J.; Mendoza, M.; Hou, P.; Chen, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Expression of an Arabidopsis Vacuolar H+-Pyrophosphatase Gene (AVP1) in Cotton Improves Drought- and Salt Tolerance and Increases Fibre Yield in the Field Conditions. Plant Biotechnol J 2011, 9, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J Bot 2012, 2012, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant Responses to Drought, Salinity and Extreme Temperatures: Towards Genetic Engineering for Stress Tolerance. Planta 2003, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasapula, V.; Shen, G.; Kuppu, S.; Paez-Valencia, J.; Mendoza, M.; Hou, P.; Chen, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Expression of an Arabidopsis Vacuolar H+-Pyrophosphatase Gene (AVP1) in Cotton Improves Drought- and Salt Tolerance and Increases Fibre Yield in the Field Conditions. Plant Biotechnol J 2011, 9, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, L.H.; Becker, S.R.; Cruz, V.M. V.; Byrne, P.F.; Dierig, D.A. Root Traits Contributing to Plant Productivity under Drought. Front Plant Sci 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Lan, H.; Wood, A.J.; Wang, J. Overexpression of ScALDH21 Gene in Cotton Improves Drought Tolerance and Growth in Greenhouse and Field Conditions. Molecular Breeding 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; et al. Overexpression of a Myb Family Gene, Osmyb6, Increases Drought and Salinity Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Rice. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.M.; Shangguan, X.X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.F.; Chao, L.M.; Yang, C.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zeng, Y. Da; Guo, W.Z.; et al. Control of Cotton Fibre Elongation by a Homeodomain Transcription Factor GhHOX3. Nat Commun 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Salt and Drought Stress Signal Transduction in Plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yan, J.; Shen, G.; Fu, L.; Holaday, A.S.; Auld, D.; Blumwald, E.; Zhang, H. Expression of an Arabidopsis Vacuolar Sodium/Proton Antiporter Gene in Cotton Improves Photosynthetic Performance under Salt Conditions and Increases Fiber Yield in the Field. Plant Cell Physiol 2005, 46, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Sharoni, A.M.; Kikuchi, S. Roles of NAC Transcription Factors in the Regulation of Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants. Front Microbiol 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillo, E.H.; Kimotho, R.N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P. Transcription Factors Associated with Abiotic and Biotic Stress Tolerance and Their Potential for Crops Improvement. Genes 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibo, N.J.M.; Lourenço, T.; Oliveira, M.M. Transcription Factors and Regulation of Photosynthetic and Related Metabolism under Environmental Stresses. Ann Bot 2009, 103, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. CRISPR/Cas Genome Editing Improves Abiotic and Biotic Stress Tolerance of Crops. Front Genome Ed 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.A.; Zaidi, S.S.E.A.; Gaba, Y.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Dhankher, O.P.; Li, X.; Mansoor, S.; Pareek, A. Engineering Abiotic Stress Tolerance via CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Genome Editing. J Exp Bot 2020, 71, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil AM, Wagh SG, Janvale GB, Pawar BD, Daspute AA. Viral delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing for rapid crop improvement: A promising approach to enhance crop resilience against biotic and abiotic stresses. IJABR, 2024; SP-8, 782–796. [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Long, L.; Tian, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Singh, P.K.; Botella, J.R.; Song, C. Genome Editing in Cotton with the CRISPR/Cas9 System. Front Plant Sci 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiaz, S.; Khan, S.A.; Younas, A.; Shahzad, K.; Ali, H.; Noor, M.A.; Ashraf, U.; Nadeem, F. Application of CRISPR/Cas System for Genome Editing in Cotton. In CRISPR and RNAi Systems: Nanobiotechnology Approaches to Plant Breeding and Protection: A Volume in Nanobiotechnology for Plant Protection; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 277–301.
- Shelake, R.M., Pramanik, D. and Kim, J.Y., CRISPR base editor-based targeted random mutagenesis (BE-TRM) toolbox for directed evolution. BMB reports 2024, 57, 30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.; Guo, X. CRISPR/Cas9 for Genome Editing: Progress, Implications and Challenges. Hum Mol Genet 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladinovic, D.; Antunes, D.; Yildirim, K.; Bakhsh, A.; Cvejić, S.; Kondić-Špika, A.; Marjanovic Jeromela, A.; Opsahl-Sorteberg, H.G.; Zambounis, A.; Hilioti, Z. Targeted Plant Improvement through Genome Editing: From Laboratory to Field. Plant Cell Rep 2021, 40, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, D.; Pereira, A.M.; Lopes, A.L.; Coimbra, S. The Best CRISPR/Cas9 versus RNA Interference Approaches for Arabinogalactan Proteins’ Study. Mol Biol Rep 2020, 47, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K.; Mandal, S.; Tiwari, A.; Monachesi, C.; Catassi, G.N.; Srivastava, A.; Gatti, S.; Lionetti, E.; Catassi, C. Current Status and Perspectives on the Application of CRISPR/Cas9 Gene-Editing System to Develop a Low-Gluten, Non-Transgenic Wheat Variety. Foods 2021, 10, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-Based Methods for Genome Engineering. Trends Biotechnol 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelake, R.M., Pramanik, D., Waghunde, R.R., Kim, JY. Plant Mutagenesis Tools for Precision Breeding: Conventional CRISPR/Cas9 Tools and Beyond. In: Penna, S., Jain, S.M. (eds) Mutation Breeding for Sustainable Food Production and Climate Resilience. Springer, Singapore 2023. [CrossRef]
- Javaid, D.; Ganie, S.Y.; Hajam, Y.A.; Reshi, M.S. CRISPR/Cas9 System: A Reliable and Facile Genome Editing Tool in Modern Biology. Mol Biol Rep 2022, 49, 12133–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Song, G.; Yue, Z.; Cong, L.; Shang, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The Draft Genome of a Diploid Cotton Gossypium Raimondii. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Guo, D.D.; Gao, W.; Yang, W.W.; Hou, L.P.; Ma, X.N.; Miao, Y.C.; Botella, J.R.; Song, C.P. Optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing in Cotton by Improved SgRNA Expression. Plant Methods 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Unver, T.; Zhang, B. A High-Efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 System for Targeted Mutagenesis in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, M.R.; Campbell, L.A.M.; Rathore, K.S. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Plant Mol Biol 2017, 94, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Liang, S.; Deng, J.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tu, L.; et al. High Efficient Multisites Genome Editing in Allotetraploid Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) Using CRISPR/Cas9 System. Plant Biotechnol J 2018, 16, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Shu, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Guo, L.; Ye, W. Targeted Mutagenesis in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., He Z., Zhang, G., Jiao, H., Sang, Y., Ma, P., CRISPR/Cas9 Targeted Editing of GhNAC3 in Cotton. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2023, 43, 1834–1841. [CrossRef]
- Xia L, Sun S, Han B, Yang X. NAC domain transcription factor gene GhNAC3 confers drought tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol. and Biochem. 2023, 195, 114–123. [CrossRef]
- Shelake, R.M., Pramanik, D. and Kim, J.Y., CRISPR base editor-based targeted random mutagenesis (BE-TRM) toolbox for directed evolution. BMB reports 2024, 57, 30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L., Li, J., Wang, Q., Xu, Z., Sun, L., Alariqi, M., Manghwar, H., Wang, G., Li, B., Ding, X. and Rui, H., High-efficient and precise base editing of C• G to T• A in the allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) genome using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant biotechn. Jour. 2020, 18, 45–56. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G., Xu, Z., Wang, F., Huang, Y., Xin, Y., Liang, S., Li, B., Si, H., Sun, L., Wang, Q. and Ding, X.,. Development of an efficient and precise adenine base editor (ABE) with expanded target range in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). BMC biology, 2022; 20, 45. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G., Wang, F., Xu, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Hui, F., Yang, X., Nie, X., Zhang, X. and Jin, S.,. Precise fine-turning of GhTFL1 by base editing tools defines ideal cotton plant architecture. Genome Biology 2024, 25, 59. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Miao, K.; Botella, J.R.; Song, C.P.; Miao, Y. A Transient Transformation System for Gene Characterization in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Plant Methods 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Han, L.H.; Zhou, W.; Tao, M.; Hu, Q.Q.; Zhou, Y.N.; Li, X.B.; Li, D. Di; Huang, G.Q. GhEIN3, a Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) Homologue of AtEIN3, Is Involved in Regulation of Plant Salinity Tolerance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2019, 143, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Wu, A.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of the Early Flowering 4 (ELF4) Gene Family in Cotton and Silent GhELF4-1 and GhEFL3-6 Decreased Cotton Stress Resistance. Front Genet 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Kong, Z.; Li, S.; Lu, L.; Nosheen kabir; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Qanmber, G.; Liu, Z. Identification of GhLOG Gene Family Revealed That GhLOG3 Is Involved in Regulating Salinity Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2021, 166, 328–340. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Fu, X.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, S. Genome-Wide Identification of NF-YA Gene Family in Cotton and the Positive Role of GhNF-YA10 and GhNF-YA23 in Salt Tolerance. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 165, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, P.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; You, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Efficient Virus-Mediated Genome Editing in Cotton Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.; Alariqi, M.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jin, S.; Min, L.; Zhang, X. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Pooled-SgRNAs Assembly Accelerates Targeting Multiple Genes Related to Male Sterility in Cotton. Plant Methods 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chang, L.; Fang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lv, F.; Wu, H.; Si, Z.; et al. Sequence-Based Ultra-Dense Genetic and Physical Maps Reveal Structural Variations of Allopolyploid Cotton Genomes. Genome Biol 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, B.P.; Malla, S. Improving Horticultural Crops via Crispr/Cas9: Current Successes and Prospects. Plants 2020, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopan Ganpatrao Wagh, & Manoj Baliram Pohare.. Current and Future Prospects of Plant Breeding with CRISPR/Cas. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology 2019, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Makarova, S.S.; Khromov, A. V.; Spechenkova, N.A.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. Application of the CRISPR/Cas System for Generation of Pathogen-Resistant Plants. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2018, 83, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zafar, N.; Ali, Q.; Manghwar, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, L.; Ding, X.; Ding, F.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.; et al. CRISPR/Cas Genome Editing Technologies for Plant Improvement against Biotic and Abiotic Stresses: Advances, Limitations, and Future Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Unver, T.; Zhang, B. CRISPR/Cas: A Powerful Tool for Gene Function Study and Crop Improvement. J Adv Res 2021, 29, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Guo, D.D.; Gao, W.; Yang, W.W.; Hou, L.P.; Ma, X.N.; Miao, Y.C.; Botella, J.R.; Song, C.P. Optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing in Cotton by Improved SgRNA Expression. Plant Methods 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, R.; Pal, R.; Dutta, S. Chloroplast Engineering: Fundamental Insights and Its Application in Amelioration of Environmental Stress. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2023, 195, 2463–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Clemente, R.M.; Vives, V.; Zandalinas, S.I.; López-Climent, M.F.; Muñoz, V.; Gómez-Cadenas, A. Biotechnological Approaches to Study Plant Responses to Stress. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Khan, S.; Wani, I.A.; Gupta, R.; Verma, S.; Alam, P.; Alaklabi, A. Unravelling the Role of Epigenetic Modifications in Development and Reproduction of Angiosperms: A Critical Appraisal. Front Genet 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Approaches to Enhancing Antioxidant Defense in Plants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Wani, K.I.; Naeem, M.; Khan, M.M.A.; Aftab, T. Cellular Responses, Osmotic Adjustments, and Role of Osmolytes in Providing Salt Stress Resilience in Higher Plants: Polyamines and Nitric Oxide Crosstalk. J Plant Growth Regul 2023, 42, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, C.; Franco, O.L. Pathogenesis-Related Proteins (PRs) with Enzyme Activity Activating Plant Defense Responses. Plants 2023, 12, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, M.; Cai, X.; Han, Z.; Si, J.; Chen, D. Jasmonate Signaling Pathway Modulates Plant Defense, Growth, and Their Trade-Offs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.D.; Félix, M.d.R.; Patanita, M.; Materatski, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Varanda, C. Defense Strategies: The Role of Transcription Factors in Tomato–Pathogen Interaction. Biology 2022, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykiel, M.; Gietler, M.; Fidler, J.; Prabucka, B.; Rybarczyk-Płońska, A.; Graska, J.; Boguszewska-Mańkowska, D.; Muszyńska, E.; Morkunas, I.; Labudda, M. Signal Transduction in Cereal Plants Struggling with Environmental Stresses: From Perception to Response. Plants 2022, 11, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, V.; Cervero, R.; Gamir, J. The Simultaneous Perception of Self- and Non-Self-Danger Signals Potentiates Plant Innate Immunity Responses. Planta 2022, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushanov, F.N.; Turaev, O.S.; Ernazarova, D.K.; Gapparov, B.M.; Oripova, B.B.; Kudratova, M.K.; Rafieva, F.U.; Khalikov, K.K.; Erjigitov, D.S.; Khidirov, M.T.; et al. Genetic Diversity, QTL Mapping, and Marker-Assisted Selection Technology in Cotton (Gossypium Spp.). Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwando, E.; Han, Y.; Angessa, T.T.; Zhou, G.; Hill, C.B.; Zhang, X.Q.; Li, C. Genome-Wide Association Study of Salinity Tolerance During Germination in Barley (Hordeum Vulgare L.). Front Plant Sci 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Joung, Y.H. CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Genome Editing for Crop Improvement: Current Applications and Future Prospects. Plant Biotechnol Rep 2019, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shen, L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roychowdhury, R.; Das, S.P.; Gupta, A.; Parihar, P.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Sarker, U.; Kumar, A.; Ramrao, D.P.; Sudhakar, C. Multi-Omics Pipeline and Omics-Integration Approach to Decipher Plant’s Abiotic Stress Tolerance Responses. Genes 2023, 14, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Z. Overexpression of the Cotton Trihelix Transcription Factor GhGT23 in Arabidopsis Mediates Salt and Drought Stress Tolerance by Binding to GT and MYB Promoter Elements in Stress-Related Genes. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihad, S.A.I.; Hasan, M.A.I.; Anik, T.R.; Rashid, M.M.; Khan, M.A.I.; Islam, M.R.; Latif, M.A. Pyramiding of Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes in Premium Quality Rice Variety, BRRI Dhan63 through Marker-Assisted Breeding Approach. Euphytica 2024, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, M.; Ling, B.; Cao, T.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Tang, W.; Chen, K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Overexpression of the Autophagy-Related Gene SiATG8a from Foxtail Millet (Setaria Italica L.) in Transgenic Wheat Confers Tolerance to Phosphorus Starvation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2023, 196, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, T.; Sirk, S.J.; Shui, S.L.; Liu, J. Genome-Editing Technologies: Principles and Applications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndudzo, A.; Sibanda Makuvise, A.; Moyo, S.; Bobo, E.D. CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing in Crop Breeding for Climate Change Resilience: Implications for Smallholder Farmers in Africa. J Agric Food Res 2024, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Anee, T.I.; Parvin, K.; Nahar, K.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M. Regulation of Ascorbate-Glutathione Pathway in Mitigating Oxidative Damage in Plants under Abiotic stress. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Abiotic Stress: Revisiting the Crucial Role of a Universal Defense Regulator. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 681. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birrer, K.F.; Conaty, W.C.; Cottee, N.S.; Sargent, D.; Francis, M.E.; Cahill, D.M.; Long, R.L. Can Heat Stress and Water Deficit Affect Cotton Fiber Wax Content in Field-Grown Plants? Ind Crops Prod 2021, 168. [CrossRef]
- Carmo-Silva, A.E.; Gore, M.A.; Andrade-Sanchez, P.; French, A.N.; Hunsaker, D.J.; Salvucci, M.E. Decreased CO 2 Availability and Inactivation of Rubisco Limit Photosynthesis in Cotton Plants under Heat and Drought Stress in the Field. Environ Exp Bot 2012, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kato, N.; Ndathe, R.; Thyssen, G.N.; Jones, D.C.; Ratnayaka, H.H. Evidence for Thermosensitivity of the Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Immature Fiber (Im) Mutant via Hypersensitive Stomatal Activity. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, R.; Sun, F.; Qu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q. Identification of Exogenous ABA and Heat Stress Tolerance in Various Cotton Genotypes. Plant Genetic Resources: Characterisation and Utilisation 2020, 18, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Khan, Z.; Nazeer, W.; Arshad, S.F.; Ahmad, F. Effect of Drought on Trichome Density and Length in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Journal of Bioresource Management 2021, 8, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echer, F.R.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Loka, D.A.; Rosolem, C.A. High Night Temperatures during the Floral Bud Stage Increase the Abscission of Reproductive Structures in Cotton. J Agron Crop Sci 2014, 200, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten TK. Heat unit accumulation to determine boll maturity and the impact upon fiber properties and lint yield of cotton. Texas A&M University; 2003.264. Ahmad, S.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Cotton Production and Uses: Agronomy, Crop Protection, and Postharvest Technologies; Springer Singapore, 2020; ISBN 9789811514722.
- Oosterhuis, D.M.; Snider, J.L. High Temperature Stress On Floral Development And Yield Of Cotton. Stress physiology in cotton 2011, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.; Khalid, S.; Abdullah, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Shah, M.K.N.; Ghafoor, A.; Du, X. Insights into Drought Stress Signaling in Plants and the Molecular Genetic Basis of Cotton Drought Tolerance. Cells 2020, 9, 105. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamatha K, Jaybhaye P. Impact of Drought Weather Condition on Bt Cotton Growth, Development and Yield. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci 2018, 2332–2338.
- ÖDEMİŞ, B.; KAZGÖZ CANDEMİR, D. The Effects of Water Stress on Cotton Leaf Area and Leaf Morphology. Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi Tarım ve Doğa Dergisi 2023, 26, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karademir, C.; Karademir, E.; Ekinci, R.; Berekatoǧlu, K. Yield and Fiber Quality Properties of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) under Water Stress and Non-Stress Conditions. Afr J Biotechnol 2011, 10, 12575–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Chen, T.T.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhang, S.P.; Liu, S.D.; Dong, H.L.; Feng, L.; Yu, S.X. Effect Of Drought Stress On Lipid Peroxidation And Proline Content In Cotton Roots. JAPS: Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences 2014, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Gondal, M.R.; Saleem, M.Y.; Rizvi, S.A.; Riaz, A.; Naseem, W.; Muhammad, G.; Hayat, S.; Iqbal, M. Assessment of Drought Tolerance in Various Cotton Genotypes under Simulated Osmotic Settings. Asian Journal of Agriculture and Biology 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Response of Leaf Stomata and Photosynthetic Parameters to Short-Term Drought Stress in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture 2019, 27, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.J.; Reddy, V.R. Transpiration Response of Cotton to Vapor Pressure Deficit and Its Relationship with Stomatal Traits. Front Plant Sci 2018, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Sangwan, R.S.; Sabir, F.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sangwan, N.S. Effect of Prolonged Water Stress on Specialized Secondary Metabolites, Peltate Glandular Trichomes, and Pathway Gene Expression in Artemisia Annua L. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2014, 74, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alishah, O., Ahmadikhah, A. The Effects of Drought Stress on Improved Cotton Varieties in Golesatn Province of Iran. International Journal of Plant Production 2012, 3, 17–26. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ji, S.; Zhang, P.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z. Drought Effects on Cotton Yield and Fiber Quality on Different Fruiting Branches. Crop Sci 2016, 56, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.X.; Tian, C.Y.; Li, C.J. Soil Salinity Dynamics under Drip Irrigation and Mulch Film and Their Effects on Cotton Root Length. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 2013, 44, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühling KH, Läuchli A. Effect of salt stress on growth and cation compartmentation in leaves of two plant species differing in salt tolerance. Journal of plant physiology 2002, 159, 137–46. [CrossRef]
- Munawar, W.; Hameed, A.; Khan, M.K.R. Differential Morphophysiological and Biochemical Responses of Cotton Genotypes Under Various Salinity Stress Levels During Early Growth Stage. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnoli, E.; Lauteri, M. Effects of Salinity on Stomatal Conductance, Photosynthetic Capacity, and Carbon Isotope Discrimination of Salt-Tolerant (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) and Salt-Sensitive (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) C3 Non-Halophytes. Plant physiology, 1991; 95, 628–635, Razaji, A.; Paknejad, F.; Moarefi, M.; Mahdavi Damghani, A.; Nabi Ilkaee, M. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Salinity Stress on Cotton (Gossypium Spp.) Growth and Yield in Iran. Tarim Bilimleri Dergisi 2020, 26, 94–103, doi:10.15832/ankutbd.489187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W. Effects of Different Salt Stress on Physiological Growth and Yield of Drip Irrigation Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Intelligent Automation and Soft Computing 2020, 26, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, A.; Terzi, R.; Saruhan, N.; Saglam, A. Current Advances in the Investigation of Leaf Rolling Caused by Biotic and Abiotic Stress Factors. Plant Science 2012, 182, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagaraj G, Manikandan K, Desingh R. Growth and carbohydrate metabolism of two cotton varieties under salinity stress. Plant Archives 2009, 9, 413–415.
- Bernstein, N.; Kafkafi, U. 44 Root Growth Under Salinity Stress; CRC Press, 2002. 1222-1250.
- Chaudhary, M.T.; Shakeel, A.; Rana, I.A.; Azhar, M.T. Evaluation of Morpho-Physiological and Biochemical Attributes of Cotton under Salt Stress. Int J Agric Biol 2020, 24, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Medina, T.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Sosenski, P.; Grandi, L.; Cervera, J.C.; Moreira, X.; Abdala-Roberts, L. Effects of Soil Salinity on the Expression of Direct and Indirect Defences in Wild Cotton Gossypium Hirsutum. Journal of Ecology 2021, 109, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, I.; Aleem, S.; Farooq, J.; Rizwan, M.; Younas, A.; Sarwar, G.; Chohan, S.M. Salinity Stress in Cotton: Effects, Mechanism of Tolerance and Its Management Strategies. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants 2019, 25, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Dong, H.Z.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, D.M. Effects of Soil Salinity and Plant Density on Yield and Leaf Senescence of Field-Grown Cotton. J Agron Crop Sci 2012, 198, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajjak Shaikh, I.; Rajjak Shaikh, P.; Ahmed Shaikh, R.; Abdulla Shaikh, A. Phytotoxic Effects of Heavy Metals (Cr, Cd, Mn and Zn) on Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Seed Germination and Seedlings Growth in Black Cotton Soil of Nanded, India. J Res J Chem Sci 2013, 2231, 606X.
- Ozyigit, I.I.; Vardar, F.; Yasar, U.; Akinci, S. Long-Term Effects of Aluminum and Cadmium on Growth, Leaf Anatomy, and Photosynthetic Pigments of Cotton. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 2013, 44, 3076–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barce, J.; Poschenrieder, C. Plant Water Relations as Affected by Heavy Metal Stress: A Review. J Plant Nutr 1990, 13, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Ren, P. Advances in Cotton Tolerance to Heavy Metal Stress and Applications to Remediate Heavy Metal-Contaminated Farmland Soil. Phyton (B Aires) 2020, 90, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Ghosh, R. Monitoring Effects of Heavy Metal Stress on Biochemical and Spectral Parameters of Cotton Using Hyperspectral Reflectance. Environ Monit Assess 2023, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.J.; Wang, H.J.; Fan, H.; Ippolito, J.A.; Meng, C.; Yulian, E.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Wei, C. Effects of Modifiers on the Growth, Photosynthesis, and Antioxidant Enzymes of Cotton Under Cadmium Toxicity. J Plant Growth Regul 2019, 38, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G.; Bachir L, D.M. Effect of Cadmium on Uptake and Translocation of Three Microelements in Cotton. J Plant Nutr 2005, 27, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, P.J., Reicosky, D.C. & Meyer, W.S. Effects of intermittent waterlogging on the mineral nutrition of cotton. Plant Soil 1987, 101, 211–221. [CrossRef]
- Bange, M.P.; Milroy, S.P.; Thongbai, P. Growth and Yield of Cotton in Response to Waterlogging. Field Crops Res 2004, 88, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaddar, U.; Mia, S.; Khalil, M.I.; Sarker, U.K.; Uddin, M.R.; Kaysar, M.S.; Chaki, A.K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; et al. Effect of Reproductive Stage-Waterlogging on the Growth and Yield of Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Plants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W. Effect of Water Logging Stress on Cotton Leaf Area Index and Yield. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering; 2012; Vol. 28, pp. 202–209. [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.; Truong, V.; Bheemanahalli, R.; Brand, D.; Reddy, V.; Reddy, K.R. Developing Functional Relationships between Waterlogging and Cotton Growth and Physiology-towards Waterlogging Modeling. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Guo, W. Root Recovery Development and Activity of Cotton Plants after Waterlogging. Agron J 2015, 107, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Lu, H.; Kong, X.; Eneji, A.E.; Dong, H. Physiological and Molecular Adjustment of Cotton to Waterlogging at Peak-Flowering in Relation to Growth and Yield. Field Crops Res 2015, 179, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Z. Effect of Waterlogging on Carbohydrate Metabolism and the Quality of Fiber in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Front Plant Sci 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J. The Effect of Water Deficit and Waterlogging on the Yield Components of Cotton. Crop Sci 2018, 58, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Rajkumar, B.K.; Kumar, V. Differential Responses of Antioxidants and Osmolytes in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) Cultivars Contrasting in Drought Tolerance. Plant Stress 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, H.; Ping, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Z.; Li, A.; Zhu, J.; Li, C. Exogenous Ethylene Promotes the Germination of Cotton Seeds Under Salt Stress. J Plant Growth Regul 2023, 42, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Duan, W.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Salt Tolerance of Cotton by Removing Active Oxygen and Protecting Photosynthetic Organs. BMC Plant Biol 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Min, W.; Hou, Z. Comparative Effects of Salt and Alkali Stress on Antioxidant System in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Leaves. Open Chem 2019, 17, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Wang, X.; Chang, D.; Wang, S.; Hong, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, K. Application of Compound Material Alleviates Saline and Alkaline Stress in Cotton Leaves through Regulation of the Transcriptome. BMC Plant Biol 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, A.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X.; Gui, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, M. High Nitrogen Enhance Drought Tolerance in Cotton through Antioxidant Enzymatic Activities, Nitrogen Metabolism and Osmotic Adjustment. Plants 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, S.; Guo, H.; Hou, Z. Ion Homeostasis and Na+ Transport-Related Gene Expression in Two Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Varieties under Saline, Alkaline and Saline-Alkaline Stresses. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batcho, A.A.; Sarwar, M.B.; Rashid, B.; Hassan, S.; Husnain, T. Heat Shock Protein Gene Identified from Agave Sisalana (AsHSP70) Confers Heat Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum). Theor Exp Plant Physiol 2021, 33, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Liu, N.; Yu, Y.; Bi, C.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y. The Cotton 70-KDa Heat Shock Protein GhHSP70-26 Plays a Positive Role in the Drought Stress Response. Environ Exp Bot 2021, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Dong, J.; Xu, Q.; Hu, M.; Cheng, Y.; Shen, F.; Wang, W. Mitigation of Salt Stress Response in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) by Exogenous Melatonin. J Plant Res 2021, 134, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Tandem Mass Tag-Based (TMT) Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Response of Fine Roots to Drought Stress in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). BMC Plant Biol 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yan, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Y.; Yu, R. Beneficial Effects of Abscisic Acid and Melatonin in Overcoming Drought Stress in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Physiol Plant 2021, 173, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xin, L.; Mounkaila Hamani, A.K.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Amin, A.S.; Wang, X.; Qin, A.; Gao, Y. Foliar Application of Melatonin Positively Affects the Physio-Biochemical Characteristics of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) under the Combined Effects of Low Temperature and Salinity Stress. Plants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, W.A.; He, J.; Abdalmegeed, D.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Foliar Melatonin Stimulates Cotton Boll Distribution Characteristics by Modifying Leaf Sugar Metabolism and Antioxidant Activities during Drought Conditions. Physiol Plant 2022, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, F.; Pang, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, K.; Sun, L.; Loka, D.A.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. Potassium Application Alleviates the Negative Effects of Salt Stress on Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Yield by Improving the Ionic Homeostasis, Photosynthetic Capacity and Carbohydrate Metabolism of the Leaf Subtending the Cotton Boll. Field Crops Res 2021, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.P.; Sun, S.C.; Zhu, Q.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, F.; Xue, F.; Sun, J. The Cotton Lignin Biosynthetic Gene Gh4CL30 Regulates Lignification and Phenolic Content and Contributes to Verticillium Wilt Resistance. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2021, 34, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamani, A.K.M.; Wang, G.; Soothar, M.K.; Shen, X.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, R.; Mehmood, F. Responses of Leaf Gas Exchange Attributes, Photosynthetic Pigments and Antioxidant Enzymes in NaCl-Stressed Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Seedlings to Exogenous Glycine Betaine and Salicylic Acid. BMC Plant Biol 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Q.; Iqbal, A.; Gui, H.; Kayoumu, M.; Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Ameliorative Effects of Silicon against Salt Stress in Gossypium Hirsutum L. Antioxidants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samrana, S.; Ali, A.; Muhammad, U.; Azizullah, A.; Ali, H.; Khan, M.; Naz, S.; Khan, M.D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J. Physiological, Ultrastructural, Biochemical, and Molecular Responses of Glandless Cotton to Hexavalent Chromium (Cr6+) Exposure. Environmental Pollution 2020, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; He, S.; Zhou, Q. Potassium Application Promote Cotton Acclimation to Soil Waterlogging Stress by Regulating Endogenous Protective Enzymes Activities and Hormones Contents. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2022, 185, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Snider, J.L.; Zhou, Z. Short-Term Soil-Waterlogging Contributes to Cotton Cross Tolerance to Chronic Elevated Temperature by Regulating ROS Metabolism in the Subtending Leaf. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2019, 139, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettmann, G.T.; Ratnayaka, H.H.; Molin, W.T.; Sterling, T.M. Physiological and Antioxidant Responses of Cotton and Spurred Anoda ( Anoda Cristata ) under Nitrogen Deficiency. Weed Sci 2006, 54, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Zhu, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, C.W.; Zhu, S.; Wu, F. Genotypic Differences in Leaf Secondary Metabolism, Plant Hormones and Yield under Alone and Combined Stress of Drought and Salinity in Cotton Genotypes. Physiol Plant 2019, 165, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Y.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z. Influence of Drought Stress on Pistil Physiology and Reproductive Success of Two Gossypium Hirsutum Cultivars Differing in Drought Tolerance. Physiol Plant 2020, 168, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Daud, M.K.; Basharat, A.; Khan, M.J.; Azizullah, A.; Muhammad, N.; Muhammad, N.; ur Rehman, Z.; Zhu, S.J. Alleviation of Lead-Induced Physiological, Metabolic, and Ultramorphological Changes in Leaves of Upland Cotton through Glutathione. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, 8431–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, K.; Wang, N.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yan, G. Development and Identification of Molecular Markers of GhHSP70-26 Related to Heat Tolerance in Cotton. Gene 2023, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sable, A.; Rai, K.M.; Choudhary, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Agarwal, S.K.; Sawant, S. V. Inhibition of Heat Shock Proteins HSP90 and HSP70 Induce Oxidative Stress, Suppressing Cotton Fiber Development. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Malik, W.A.; Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Cui, R.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Upland Cotton Revealed Novel Pathways to Scavenge Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Responding to Na2SO4 Tolerance. Sci Rep 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Su, J.; Ge, X.; Duan, H. Genome-Wide Identication of WRKY in Cotton and the Positive Role of GhWRKY31 in Response to Salt and Drought Stress. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, K.R.; Pabuayon, I.C.M.; Hinze, L.L.; Sweeney, M.E.; de los Reyes, B.G. Networks of Physiological Adjustments and Defenses, and Their Synergy With Sodium (Na+) Homeostasis Explain the Hidden Variation for Salinity Tolerance Across the Cultivated Gossypium Hirsutum Germplasm. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Mostafa, S.; Lu, Z.; Jin, B. Melatonin-Mediated Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S. Abscisic Acid Synthesis and Root Water Uptake Contribute to Exogenous Methyl Jasmonate-Induced Improved Tomato Drought Resistance. Plant Biotechnol Rep 2022, 16, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossi, V.E.; Regalado, J.J.; Iannicelli, J.; Laino, L.E.; Burrieza, H.P.; Escandón, A.S.; Pitta-Álvarez, S.I. Beyond Arabidopsis: Differential UV-B Response Mediated by UVR8 in Diverse Species. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xie, Z.; Xin, J.; Yuan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C. OsbZIP18 Is a Positive Regulator of Phenylpropanoid and Flavonoid Biosynthesis under UV-B Radiation in Rice. Plants 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.H.; Wang, F.L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Zhu, Q.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhu, H.G.; Sun, J. Polyamine and Its Metabolite H2O2 Play a Key Role in the Conversion of Embryogenic Callus into Somatic Embryos in Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Front Plant Sci 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, U.; Zhang, Y.; Ali, A.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Samrana, S.; Khan, S.; et al. Melatonin Reduces Cadmium Accumulation through Cell Wall Fraction Fixation Capacity in Cotton Seedlings. Plant Stress 2024, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.; Singh, S.; Tiwari, G.J.; Kumar, H.; Boopathi, N.M.; Jaiswal, S.; Adhikari, D.; Kumar, D.; Sawant, S. V.; Iquebal, M.A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Fiber Yield-Related Traits Uncovers the Novel Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes in Indian Upland Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Front Plant Sci 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Guo, W. Genome-Wide Characterization of the Rab Gene Family in Gossypium by Comparative Analysis. Bot Stud 2017, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y. The Roles of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum) Aquaporins in Cell Expansion; 2016.
- Guo, A.; Hao, J.; Su, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, M.; Huang, Y.; Tian, B.; Shi, G.; Hua, J. Two Aquaporin Genes, GhPIP2;7 and GhTIP2;1, Positively Regulate the Tolerance of Upland Cotton to Salt and Osmotic Stresses. Front Plant Sci 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Hao, J.; Su, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, M.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Shi, G. Conserved Aquaporins in Gossypium and Silencing of Ghpip2;7 and Ghtip2;1 Decreased Salt and Osmotic Stress Tolerances in Upland Cotton. Research square 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; He, S.; Gong, W.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Xu, F.; Lu, Y.; Du, X. Comprehensive Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Transcriptional Regulation Induced by Salt Stress in Two Contrasting Cotton Genotypes. BMC Genomics 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, Q.; Ji, W.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Xu, P.; Chen, X.; Ali, W.; Wu, X.; Shen, X.; et al. Transcriptome Expression Profiling Reveals the Molecular Response to Salt Stress in Gossypium Anomalum Seedlings. Plants 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Dou, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G.; An, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. GhFB15 Is an F-Box Protein That Modulates the Response to Salinity by Regulating Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Plant Science 2024, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.Q.; Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, D. Di; Gong, S.Y.; Li, X.B. Seven Cotton Genes Encoding Putative NAC Domain Proteins Are Preferentially Expressed in Roots and in Responses to Abiotic Stress during Root Development. Plant Growth Regul 2013, 71, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, L. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Salinity Tolerance in Response to Foliar Application of β-Alanine in Cotton Seedlings. Genes (Basel) 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xue, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Molecular Analysis of Proanthocyanidins Related to Pigmentation in Brown Cotton Fibre (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). J Exp Bot 2014, 65, 5759–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianfang, G.; Li, S.; Jingli, Y.; Hongli, Z.; Quansheng, S.; Weiguang, Y.; Liqiang, Z.; Vitalis, N.E.; Sun, J.; Liping, K.; et al. Functional Analysis of GhCHS, GhANR and GhLAR in Colored Ber Formation of Gossypium Hirsutum L. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.K.; Chaudhary, B. Transcriptional Loss of Domestication-Driven Cytoskeletal GhPRF1 Gene Causes Defective Floral and Fiber Development in Cotton (Gossypium). Plant Mol Biol 2021, 107, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Shen, L.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, H.; Su, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Nnaemeka, V.E.; Sun, J.; Ke, L.; et al. Functional Analysis of GhCHS, GhANR and GhLAR in Colored Fiber Formation of Gossypium Hirsutum L. BMC Plant Biol 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Hou, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Song, C.P. Screening of Abiotic Stress-Responsive Cotton Genes Using a Cotton Full-Length CDNA Overexpressing Arabidopsis Library. J Integr Plant Biol 2020, 62, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Cao, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, W. Drought Stress and High Temperature Affect the Antioxidant Metabolism of Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) Anthers and Reduce Pollen Fertility. Agronomy 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, G.; Wang, N.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, S. A Na+/H+ Antiporter, K2-NhaD, Improves Salt and Drought Tolerance in Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Plant Mol Biol 2020, 102, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, H.; Kong, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Integrated Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Reveals Complex Regulatory Mechanism of Cotton in Response to Salt Stress. Journal of Cotton Research 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wei, H.; Cheng, S.; Hao, P.; Yu, S.; Wang, H. Silencing of GhKEA4 and GhKEA12 Revealed Their Potential Functions Under Salt and Potassium Stresses in Upland Cotton. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Qanmber, G.; Li, J.; Pu, M.; Chen, G.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Qin, W.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification and Characterization of the ERF Subfamily B3 Group Revealed GhERF13.12 Improves Salt Tolerance in Upland Cotton. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirungu, J.N.; Magwanga, R.O.; Pu, L.; Cai, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Knockdown of Gh_A05G1554 (GhDHN_03) and Gh_D05G1729 (GhDHN_04) Dehydrin Genes, Reveals Their Potential Role in Enhancing Osmotic and Salt Tolerance in Cotton. Genomics 2020, 112, 1902–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
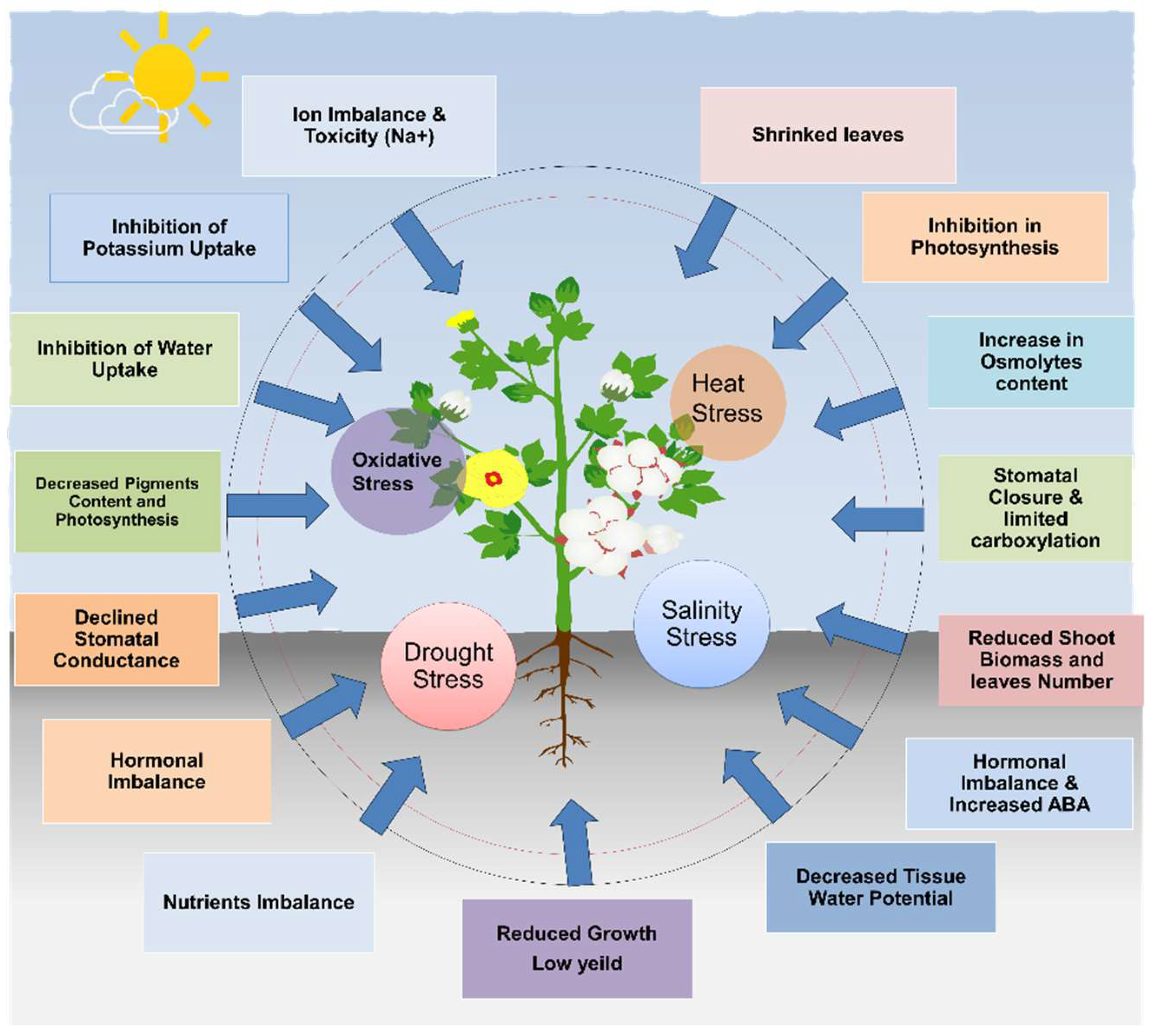
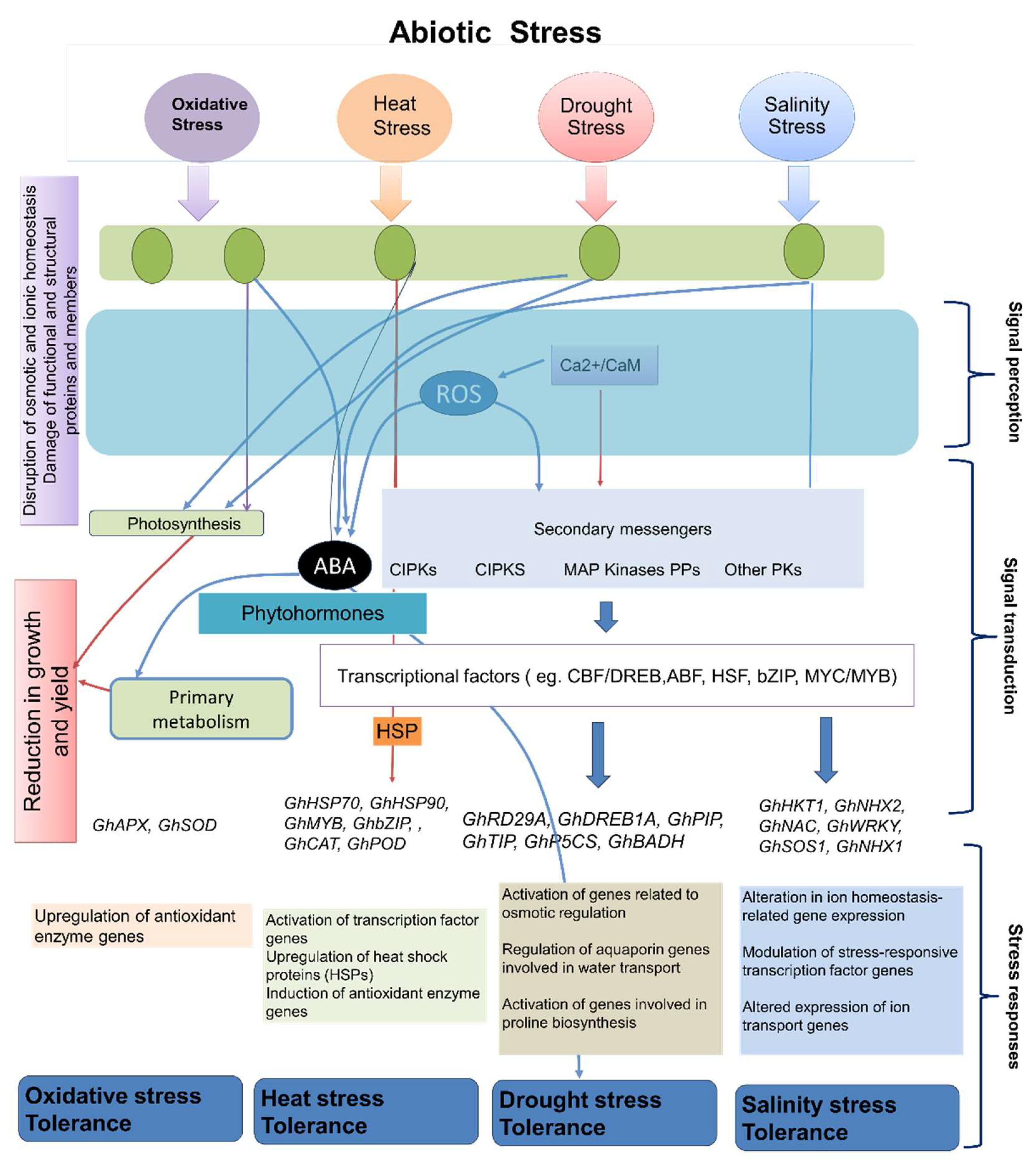
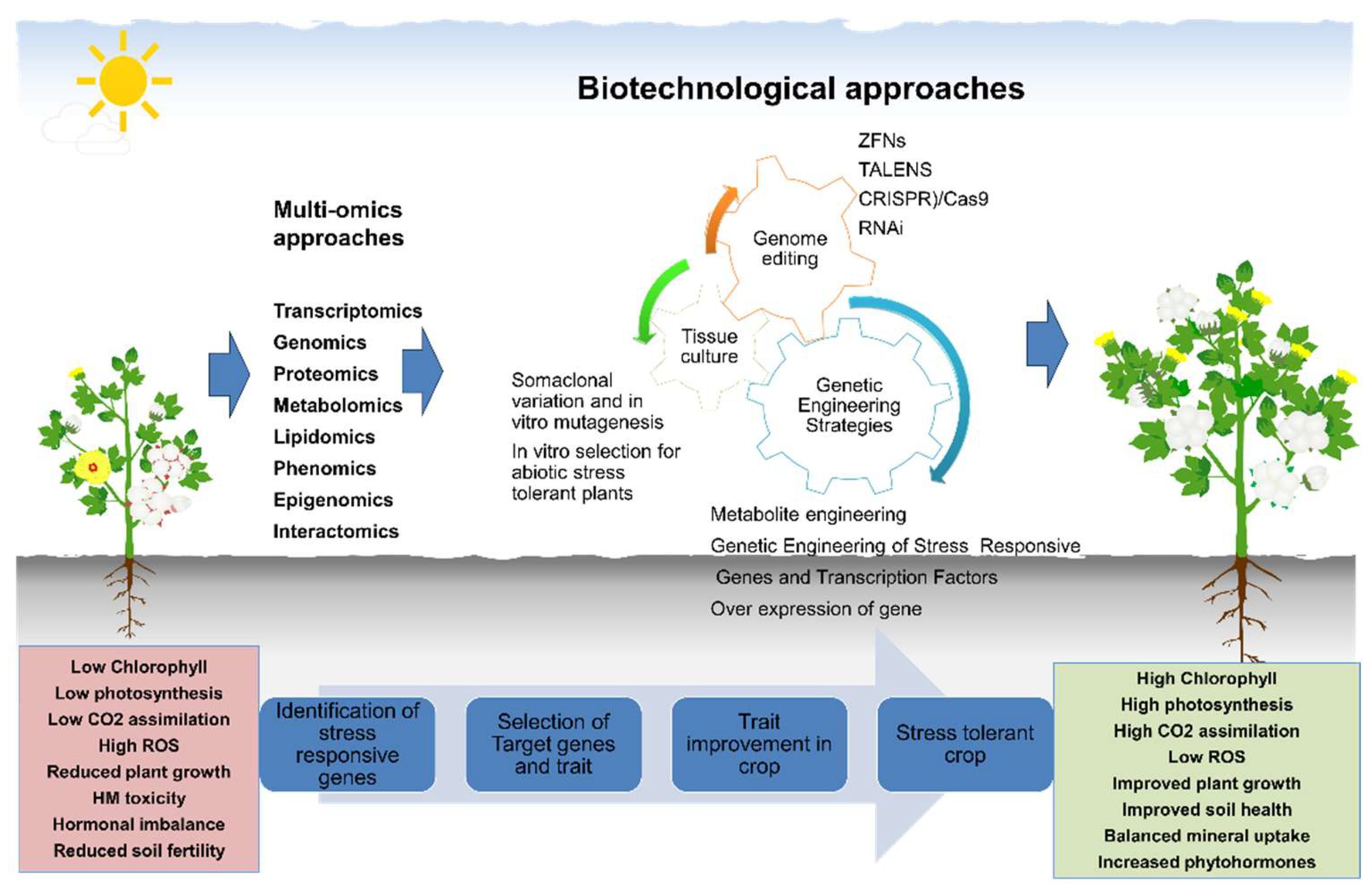
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





