1. Introduction
Supraglottic airway devices (SADs) offers an alternative airway management to traditional tracheal intubation with potential beneficial effects, including ease of placement and less airway disruption [
1].
One of the first SADs to come on the market was the Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA), a term coined over forty years ago by its inventor, Dr Archie Brain, who revolutionised airway management [
2]. We have witnessed the continuous development of SADs, their improvement and the emergence of new models and technology.
The most widely used classification of SADs is that published by Timmemann et al. in 2011 [
3]. He divides them into first-generation devices which have only a breathing tube and second-generation devices which have a breathing tube and a gastric channel to protect against aspiration, resulting in better sealing pressures. Van Zunderck proposed classifying third generation SADs as those with built-in video [
4].
We now know that proper head and neck position is essential to achieve adequate visualisation of the larynx during direct laryngoscopy, a concept that was first described by Kirstein in 1895[
5]. In 1913 Chevalier Jackson described his method of laryngoscopy while his assistant Boyce supported the patient's head and neck in an elevated position (Boyce-Jackson position) [
6]. Ivan Magill recommended in 1936 to place a pillow under the occiput to achieve the best laryngeal exposure, being the first to describe the optimal head position for direct laryngoscopy [
7]. In 1944 Bannister and Macbeth [
8] introduced the 3-axis alignment theory to explain the anatomical reasons for the superiority of the sniffing position and it has since become the "golden rule" of airway management. Horton et al. [
9] measured the angle of neck flexion and head extension that results in the best laryngeal exposure, determining that the average value of neck flexion is 35° and the plane of the face in extension is 15° to the horizontal. The elevation of the head in the sniffing position needs to be reproduced and may vary between individuals depending on the length of the neck, the anterior posterior diameter of the thorax and the size and shape of the head in relation to the thorax. Therefore, the height of the pillow to be used depends on the patient's anatomy [
10]. There is no standard pillow that works for all patients.
Lee et al. [
11] found that the laryngeal view improves significantly with a 25° position achieved with the operating table compared to the supine position. They achieved an increase in the POGO (percentage of glottic opening) score from 42.2% to 66.8% with this position. A POGO score of 100% is the visualisation of the entire glottic opening, defined in the anterior region by the anterior commissure and in the posterior region by the presence of the interarytenoid notch [
12].
El-Orbany et al. [
13] performed direct laryngoscopy with three different head positions: no elevation, sniffing position with a 6 cm elevation (neck flexion of approximately 35°) and sniffing position with a 10 cm pillow elevation of the occiput (neck flexion ≥ 35°), finding an incidence of difficult laryngoscopy of 8.3% when the head was not elevated, 2.39% when the sniffing position was used and 1.19% when the head elevation was higher.
The optimal position for the neck and head during direct laryngoscopy is the sniffing position, which aligns the ear lobe and sternal fork. This has been extensively studied and established in literature. But so far, little is known about the association of head elevation degree and LMA insertion [
14]. Changes in head and neck position may significantly affect the performance of SAD by altering the pharyngeal structure [
15].
Brain recommended extension of the head and flexion of the neck for the standard insertion method of the LMA [
16]. Brimacombe and Berry reported that there was no significant difference in the success rate of insertion when they compared the sniffing position with neutral position[
17].
Most studies assess whether the SADs achieve ideal anatomical position, with clinical parameters or using laryngoscopy [
18,
19]. videolaryngoscopy [
20] o fibroscopy [
21,
22,
23] However, all of these alternatives can delay and complicate the procedure because of the additional time required.
Within the clinical parameters, the oropharyngeal leak pressure (OPLP) [
24,
25] is commonly measured during LMA insertion to evaluate the degree of airway protection [
26]. Kim et al [
19] considered that OPLP indicates clinical performance or function of the LMA better than the fiberoptic score system does.
Improper placement may result in partial or complete obstruction of the airway. On the other hand, excessive LMA cuff pressure may exceed the capillary tissue perfusion pressure. The manufacturer recommends not to exceed a pressure of 60 cm H2O (44 mmHg) when using these devices.
Until recently the placement of a SAD was a blind procedure and contrary to the belief that its placement led to proper positioning, the literature suggests that despite suggested clinical tests to verify proper placement, in 50 to 80% its placement is deficient [
20]. Blind insertion of a SAD can lead to errors.
The Cormack Lehane classification, published in 1984, is the gold standard for describing laryngeal visualisation in clinical practice and is used in airway research studies for direct laryngoscopy. The classification is as follow:
Grade 1: Most of the glottis is visible.
Grade 2: At best almost half of the glottis is seen at worst only the posterior tip of the arytenoids is seen.
Grade 3: Only the epiglottis is visible.
Grade 4: No laryngeal structures are visible.
There is no universally accepted definition in literature for difficult intubation using direct laryngoscopy. In most studies, difficult intubation was defined as a Cormack Lehane grade 3 and 4 [
27].
In 1993, Brimacombe and Berry introduced a fibre-optic scoring system to standardise the assessment of SAD position and has been the most widely used since then [
28]. The score is:
4:Only vocal cords are visible. This is the optimal position.
3: Vocal cords plus the posterior epiglottis are seen.
2: Vocal cords plus the anterior epiglottis are seen.
1: No vocal cords are visible, but function is adequate.
0: Device failure occurs.
Fibre-optic scores of 2, 3 and 4 are considered anatomically acceptable placements and 1 is considered a poor placement [
29]. Different studies find an incidence of score 1 of 9.4% [
30,
31]
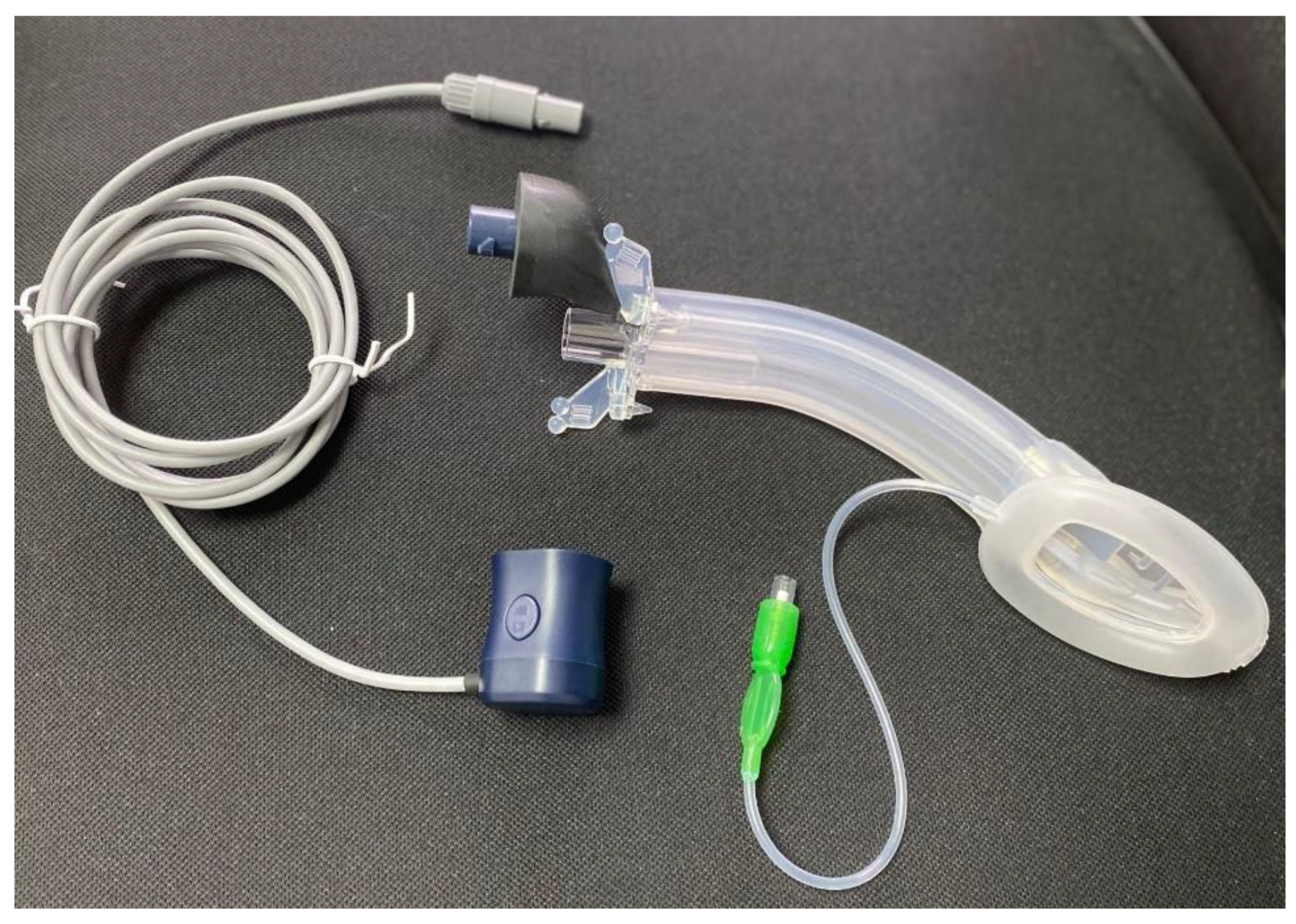
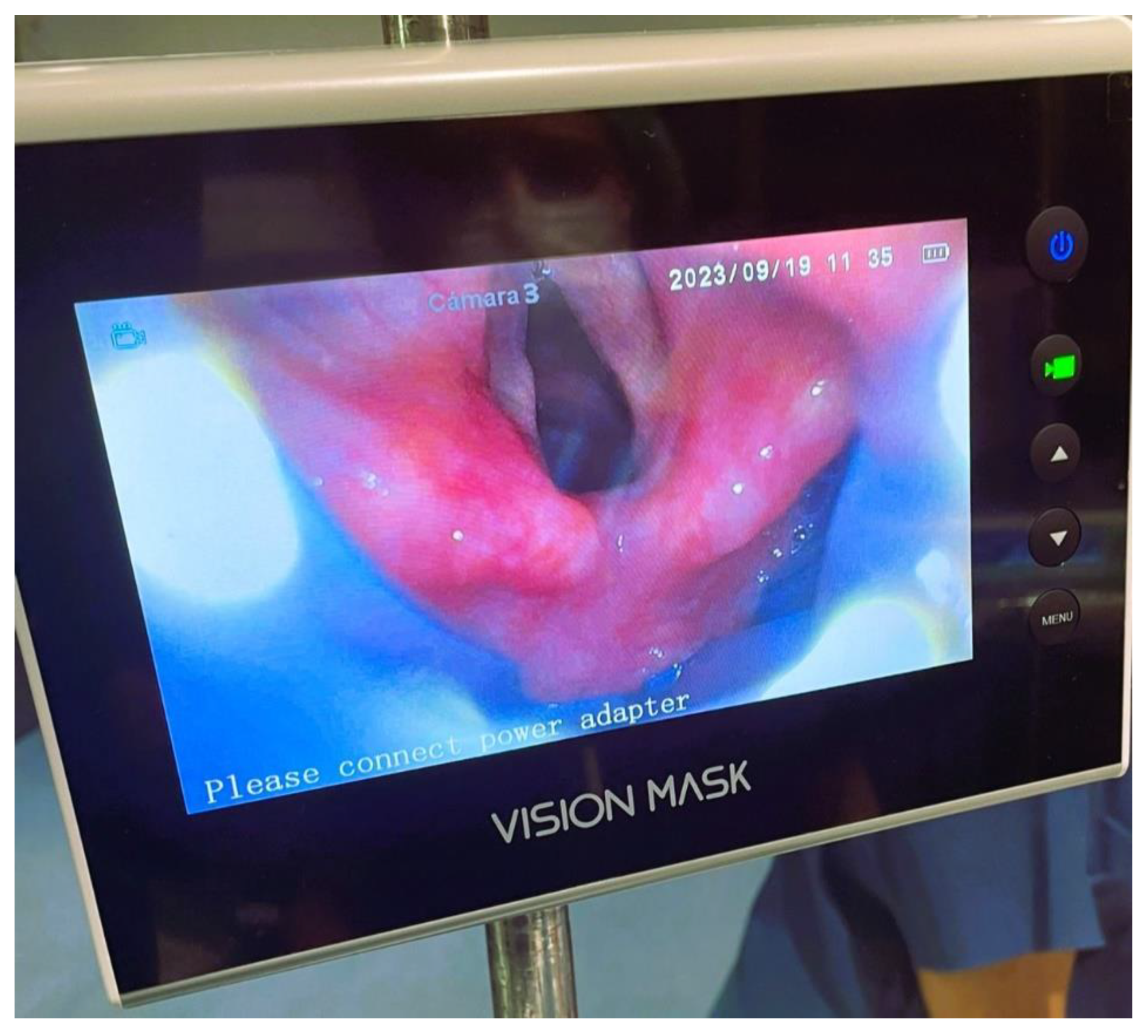
Vision Mask is a video laryngeal mask system, with continuous vision and 5 accesses developed by Pedro Acha MD, the inventor of Airtraq and Totaltrack. Was presented for the first time in the world at the Anaesthesia Service of the University Hospital Complex of Cartagena, Murcia – Spain and we have been using it since then. These devices combine the advantages of an integrated video laryngoscope incorporated into a second-generation SAD.
Figure 1. This device solves the problem that all laryngeal masks on the market have which do not permit vision, this SAD with vision guidance system in its placement allows evaluation of the larynx, allows objectifying the spasm of the vocal cords, bronchial aspiration, is a visual aid to intubation and allows standard ventilation.
It consists of five access points:
An access point which allows measurement with a manometer to determine the pressure inside the laryngeal mask in cm H2O, where the pressure ranges from 10 to 20 mmHg.
A video stylus hole with connection. A left side access point is available for its camera stylet, which can be connected to a reusable 2.8-inch and 7-inch portable monitor with image/video recording capabilities.
Figure 2. The channel is open at one end and closed at the other end, and never comes into contact with the patient.
Its central access allows gas inlet and outlet, plus the introduction of an endotracheal tube (ETT) for rescue intubation or fibro or a video bronchoscope, with 15 mm connection.
The lower right-side access has gastric access. It has an open channel at both ends. Suction catheter number 12 French or lower can be use in Vision Mask size 3 and suction catheter number 14 or lower can be use in Vision Mask size 4.
An upper right-side access point for a free gas outlet from the interior when using CPAP ventilation.
Airway management is an area of ongoing research, and video laryngeal mask system is a technology that is here to stay.
In this study, we aimed to evaluate the hypothesis that sniffing position allows for better placement/positioning of the Vision Mask device and better vision of the glottic area when compared to the neutral position. Secondary objectives were to compare the number of placement attempts, additional manoeuvres in device placement, haemodynamic response and complications arising during the procedure.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Santa Lucia Hospital. Murcia. Spain. Informed written consent was obtained from each patient. A prospective, observational, transversal, analytical study was performed. We prospectively included 72 consecutive patients. Inclusion criteria were body mass index (BMI) ≤ 40 kg/m2, American Society of Anaesthesiologists I-III (ASA) physical status, 18 years or older undergoing a variety of surgical interventions were enrolled in the study and attended by the main investigator, with more than 30 uses of the device at the beginning of the investigation.
Exclusion criteria were patients who had gastroesophageal symptomatic reflux, hiatus hernia, gastric bands, presence of a difficult intubation, BMI greater than 40 kg/m2, pregnancy, respiratory or cardiac disease severe, patients undergoing head and neck surgery, urgent surgery, mouth opening less than 2.5 cm, unstable teeth and allergy to any of the drugs used during the procedure.
Preoperative evaluation of the patient included: age, height, weight, ASA physical status class, Mallampatti classification scored 1 to 4 (obtained with the patient in the sitting position, tongue out without phonation); thyromental distance (measured with the patient in the sitting position) being classified as easy when ≥ 6 cm and difficult was < 6 cm, with head in extension; interincisor distance, easy was ≥ 4 cm and difficult was < 4 cm and neck circumference. Neck circumference was measured with the head in a neutral position, at the level of the thyroid cartilage, and it was considered as easy when it was < 45 cm and difficult when ≥ 45 cm and type of surgery.
In the same patient, laryngeal vision will first be assessed with the head and neck in the sniffing position (the external auditory meatus and the sternal notch were horizontally aligned with blankets) and then with the head in the neutral position (head on the operating table). Procedures were filmed and performed by the same investigator.
Assessment of the laryngeal view was performed using two classifications: Cormack-Lehane classification and Brimacombe classification. Device placement was considered adequate when the Cormack-Lehane rating was scored from 1 to 2 and the Brimacombe rating was from 2 to 4. Evaluation of the quality of the laryngeal vision was carried out independently by another researcher.
Secondary outcomes variables were number of attempts, manoeuvres necessary during insertion to get a better view of the glottic area (external laryngeal manipulation, jaw thrust), hemodynamic response and complications (incidence of airway trauma: lip or oral mucosa trauma, bleeding into the device at the time of removal, dental trauma, and others).
Three attempts were allowed before a failure of insertion was recorded. If the SADs could not achieve a satisfactory airway within three insertion attempts, an endotracheal tube was inserted for airway management.
2.1. Study Procedure
After the patients were admitted to premedication area, a peripheral 18G venous access was placed in upper limb and 4-5 ml/kg Ringer’s lactate solution was infused (ideal weight). As part of the procedure, all patients were premedicated with omeprazole 40 mg, dexamethasone 0.1 mg/kg, paracetamol 1 gr and midazolam 1 or 2 mg depending on their needs.
Standard monitoring devices were attached before induction of anaesthesia, including the following: II-lead electrocardiography, non-invasive blood pressure, pulse oximetry, end-tidal carbon dioxide and bispectral index. Prior to pre-oxygenation, patients were placed first in sniffing position and after neutral head position to obtain laryngeal vision with the SAD Vision Mask. Patients were preoxygenated with 100% oxygen with a tight face mask. Induction was initiated when the end tidal of oxygen was more than 90%.
Anaesthesia was induced with 1mg/kg lidocaine, 2mg/kg propofol, fentanyl 1 µg/kg and rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg ideal weight and after target-controlled infusion (TCI) of propofol on the Marsh model: 2 µg/ml during the study and optionally atropine 0.5mg as required.
The choice of mask size and insertion technique was made in accordance with the recommendations of the manufacturer. The posterior surface of the SAD was well lubricated with a water-soluble lubricant. It was left in place and used for the surgical procedure or only for evaluation purposes before the patient was intubated.
Two minutes after the neuromuscular blocking agent was administered, the SAD Vision Mask was placed, the laryngeal view was filmed and haemodynamic parameters were recorded one minute before and one minute after the device was placed. After filming the larynx in the sniffing position, the Vision Mask device was removed, and the patient's head and neck were repositioned and filmed in the neutral position.
Adequate ventilator status of the device in situ were confirmed by bilateral chest movement, auscultation and by a normal square wave on the capnogram.
A specific chart was recorded for each patient during the entire procedure.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
The distributions by fiberoptic scoring of each insertion technique group were compared using the Chi-squared test and Fisher exact test when the expected values in any of the cells of a contingency table are below 5 in Chi-squared test. In the same way secondary outcomes variables. P value <0, 05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
A total of 72 patients consented to participate in the study. The patient characteristics are shown in
Table 1.
In 72 eligible patients, the median age was 53.74 years (range 23 to 82), height 165.33 cm (range 146-192) and weight were 75.66 kg (range 42-129) respectively. The male: female ratio was 19/53. Most were women.
In the assessment of the glottis using the Cormack Lehane classification for fiberoptic view, laryngeal visibility was adequate in 64 (88.89%) patients in the neutral position and in 65 (90,28%) patients in the sniffing position with no statistically significant difference.
Table 2.
In the fiberoptic view of the glottis assessed using the Brimacombe classification, laryngeal visibility was adequate in 68 (93%) patients in the neutral position and in 69 (95%) patients in the sniffing position, with no statistically significant difference.
Table 3.
There was no statistically significant difference in the rate of success between the sniffing position (70 patients, 97.22% success rate) and the neutral position (67 patients, 93.06% success rate) during the first insertion attempt. In cases where the first attempt was unsuccessful, success was achieved in the second attempt for all patients. Two patients required a second attempt in the sniffing position, while five patients required a second attempt in the neutral position.
Table 4
More than 50% of patients did not require any airway interventions to improve device placement. Jaw thrust was the most used airway manoeuvre. When used, in 20% of cases of sniffing position and 17% of cases of neutral position, this manoeuvre did not improve vision in all cases.
Table 4.
Upper airway trauma, as evaluated by the presence of blood staining of the devices after their removal was the most frequent complication.
Table 5. The presence of blood was noted on 13 patients in sniffing position and 15 patients in neutral position following LMA removal. There was no statistically significant difference when comparing the presence of complications. There was no correlation by comparing Mallampati score, tryromental distance, intercisor gap, neck circumference and fiberoptic scoring. All patients-maintained oxygen saturation ≥99%. Gastric tube insertion was successful in all patients. Gastric distension did not occur in either group.
Vision Mask insertion-related variations in heart rate and blood pressure are shown in
Table 5, 15 patients (20,83%) developed variation of mean blood pressure more than ≥ 20% and variation of heart rate more than ≥ 20% in 8 patients (11,11%).
4. Discussion
The primary objectives of this study were to compare the better glottic vision in two head and neck positions with Vision Mask a laryngeal mask video system. For this purpose, a standard pillow was not used to reach the sniffing position, the position was reproduced by placing blankets under the head to align a horizontal between the external auditory meatus with the sternal recess. The sniffing position has been recommended for conventional LMA insertion but the height of the head in the sniffing position depends on the patient's anatomy (neck length, the anterior posterior diameter of the thorax and the size and shape of the head in relation to the thorax). In many studies, the sniffing position is employed with varying head and neck angles.
In this study it was not found that the sniffing position allows a better view of the glottic area using the Vision Mask device. Both neutral and sniffing positions equally allowed adequate positioning of the video laryngeal mask. There was a group of patients who did not achieve adequate positioning of the device, but the device still allowed them to be well ventilated. When evaluated using the Cormack-Lehane classification, only the epiglottis was seen in 9.72% and the laryngeal structures were not seen in 1.39% in neutral position. In sniffing position, these figures were 6.94% and 2.78%, respectively. Using the Brimacombe classification, the vocal cords were not visible in 5.56% of patients in the neutral position and 4.17% of patients in the sniffing position.
Other studies have found the same result with first and second generation SADs. They have done this by passing a fiberscope through a SAD and have been able to have a frontal view. This is the first study to evaluate with a SAD with video system the glottic area in real time. The Vision Mask has a continuous and lateral field of view while the mask is in place and connected.
Guanghui et al. [
32], assessed the impact of head position and the use of muscle relaxant on the insertion and ventilation of the LMA classic in 132 patients. These researchers concluded that the sniffing position and use of a muscle relaxant had no effects on placement of the LMA, the fiberoptic score or the ventilation parameters of the LMA.
Brimacombe and Berry [
17] reported there were no significant difference in the success rate of insertion and no significant differences in scores as assessed by fiberoptic bronchoscopy when they compared the sniffing position with the neutral position in 80 patients.
Keller and Brimacombe [
33] compared in four head and neck positions (neutral, flexion, extension and rotation), oropharyngeal leak pressure and fiberoptic position with the Flexible and the Standard LMA. Fiberoptic position was similar between devices and was unchanged by head and neck position.
Lim et al [
34] did not observed differences in glottis views between the supine and ramped positions. In this study a partial or full glottic views were observed in 78.6% of patients in both positions. In this research glottic view assessment was based on the Cormack Lehane laryngeal view classification.
Multiple studies have shown that different head positions during laryngeal mask insertion does not seem to impact the fiberoptic score, ventilation parameters and the success rate of LMA placement. [
32,
34] It has been found that a difficult airway and head position do not affect the ease of insertion of a LMA Proseal (PLMA) and fiberoptic score [
22].
Traditionally, there has been a belief that extraglottic devices are well placed if they have adequate ventilation. However, recent literature suggests that this is not always the case and ventilation is often suboptimal.
In the study, LMA Vision Masks were successfully positioned in the neutral position 93% of the time and in the sniffing position 97% of the time on the first attempt. The success rate for insertion at the first attempt in the LMA Classic has been reported to be between 77% and 97% [
23] depending on the experience of the anaesthesiologist and suboptimal positioning of the LMA occurs in 30-66% of cases [
35] and in 50-80% of cases [
20] according to different authors.
Studies looking for the best head position to facilitate the placement of a SAD have used pillows of different heights in different populations: ≤ 6 cm [
36], 7 cm [
37,
38], 8 cm [
22,
32] o 14 cm [
14].
Yun et al [
36] compared between 3 vs 6 cm in PLMA insertion and suggested that the appropriate head position to facilitate LMA insertion is achieved by 3 cm head elevation, which facilitates successful LMA placement and rapid ventilation in emergency situations.
Park et al [
14] found that high head elevation of 14 cm increased the fiberoptic bronchoscopic grade compared with conventional head elevation of 7 cm height. These results suggest that high head elevation can be an effective option for successful insertion of an LMA.
A meta-analysis shows that the flexed neck position significantly improves airway sealing but adversely affects ventilation and the fiberoptic view with most SADs. Although neck extension significantly reduced airway sealing, it did not affect ventilation or the fiberoptic view. [
15]
In this study we used a fiberoptic scoring system for standardized evaluation of the LMA position following its insertion into the hypopharynx proposed by Brimacombe and Berry and compared the glottic view with that found with the Cormack Lehane classification, which is used with direct laryngoscopy. Most studies use the Brimacombe score [
39,
40,
41] and very few the Cormack and Lehane laryngeal view classification. [
34] When the two classifications were compared, the glottic view was found to be consistent in 88-89% of cases using the Cormack-Lehane classification and in 93-95% of cases using the Brimacombe classification. Device placement was considered optimal when the fiberoptic score with Brimacombe was grade 2 to 4 or Cormack Lehane 1 or 2. In both situations, the vocal cords are visible, either fully or partially.
The vocal cords could not be visualised in 3 patients (4.17%) in the sniffing position and 4 (5.56%) in the neutral position using the Brimacombe classification, but in all these patients ventilation was adequate, confirming the findings of a previous report that there is no correlation between adequacy of ventilation and a low fiberoptic score. [
38]
The proper placement and functioning of the laryngeal mask has been evaluated through clinical tests and using different equipment that allowed visualisation of the glottic area to confirm that the procedure was well performed. By moving from a blind procedure to visualisation of the anatomy, we assume that it increases safety in airway management, although this visualisation of the glottic area is not directly related to the sealing device. The efficacy of the seal or tightness may vary depending on the individual patient’s laryngopharyngeal anatomy, in addition to the anatomical placement of the LMA.
Campbell et al [
18] used fiberoptic examination to compare the traditional blind insertion technique of LMA placement with direct visual placement using a laryngoscope. They reported that the appropriate positioning of the LMA had been achieved in 91.5% of patients in the direct visual placement group, compared with 42% in the blind insertion group. However other researchers indicate that laryngoscope guided insertion is not superior to blind insertion in terms of achieving proper anatomical placement of the LMA, since the fiberoptic position scores were similar for both techniques. [
19] Chandal et al[
42] concludes that if the blind insertion is easier and simpler method for insertion of LMA and has a reasonable success during insertion, so it is recommended to be used.
Visualisation of the glottis during insertion of the Vision Mask allows immediate detection and correction of inadequate cuff inflation, incorrect device size, glottis distortion or epiglottis within the cuff. Any problems can be resolved by adjusting the head position, changing the MLA or using an additional manoeuvre. However, it is important to note that this method may not be successful in all cases.
In a meta-analysis [
43] to quantify the potential advantage that the LMA Supreme may offer over the LMA ProSeal on oropharyngeal leak pressures in adult patients. Three RCTs assessed the correct placement of the LMA by fiberoptic bronchoscopy. An FOB view of the full glottis was obtained more often in the LMA Proseal group than in the LMA Supreme group.
In our study, the frequency of a fiberoptic score of more than 2 (suboptimal anatomic position) was 11,11% in the neutral position and 9,72% in the sniffing position with Cormack Lehane classification and the frequency of a fiberoptic score less than 2 (suboptimal position) was 5,56% in the neutral position and 4,17% in the sniffing position with Brimacombe classification (using neuromuscular relaxation with 0.6 mg/kg de Rocuronio). In a study conducted by Brimacombe and Keller it was found that poor vision was present in 1 out of 60 patients with LMA and in 4 out of 60 patients with PLMA. The study used vecuronium at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg [
44].
Other studies find a higher percentage of inadequate LMA position assessed with fibroscopy. Jun et al [
35] in 148 patients who had successful PLMA insertion, 77 patients (52%) were found to have suboptimal position (fiberoptic score < 3), similar to the results of Brimacombe et al. (50.3%)[
45]. In the latter two studies, the neuromuscular relaxation dose was low (rocuronium 0.3mg/kg) or the patients were not relaxed.
Jun et al [
22] have found that changing the head position after Proseal insertion did not significantly change the fiberoptic score. In this study, the frequency of vocal cord visibility (a fiberoptic score ≥ 2) was 87.2-93.9% in all groups, which was similar to the results of Brimacombe and Keller [
37] (93.3%) and with our results 93 % with neutral head position and 95% with sniffing position.
Different studies have found that the position of the head and neck did not change fiberoptic assessment of the view of the vocal cords through LMA, but flexion of the head and neck adversely affects ventilation. [
21] A difficult airway, and the head position had no influence on the ease of PLMA insertion and the fiberopic score. [
22]
Somri et al [
38] comparing the laryngeal tube suction disposable and the supreme laryngeal mask airway and despite the high percentage of the manoeuvres necessary to optimize the position of the device, the success rate after two insertion attempts was 100 % reflecting the excellent clinical effectives of both devices. Cook et al[
46] reported 30 manoeuvres necessary to optimize the airway patency in 24 patients. In this study, it was necessary to perform 28-29 airway manoeuvres to improve glottic vision using Vision Mask in 72 patients.
Jaw thrust was the most frequently used manoeuvre, with this manoeuvre the epiglottis is raised and increased the distance between the posterior aspect of the tongue and posterior pharyngeal wall. There were no significant differences in the number of manipulations between both positions.
LMA is associated with lower complication rates. Severe traumatic complications occur rarely. However, it is important to note that extraglottic airway devices can cause esophageal perforations, as well as tracheal and other injuries. [
47,
48]
The study found that the most frequent complication was the presence of blood in the Vision Mask, which was observed on removal, 18,05% in patients in sniffing position and 20,83% in patients in neutral position. Additionally, lip lesions were observed in one patient from each different position. Although the reported complications are not frequent and not very serious, a significantly higher blood staining on the mask has been noted with Vision Mask. The total adverse event rate was 22, 22% in patients in neutral position and 19,44% in patients in sniffing position, and no severe complications were observed.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials comparing the LMA Supreme and the LMA Pro-Seal revealed that the incidence of bloodstaining on the LMA was reported in six of seven studies. Additionally, the incidence of adverse events in groups not using neuromuscular relaxant was higher than in those using muscle relaxant. Other adverse events reported in these patients were: vomiting, sore throat, dysphagia, dysphonia and laryngospasm. [
43]
5. Limitations
Our study has some limitations. It is important to note that the sample size is not large enough and therefore inadequately powered. Despite this, we were still able to detect no difference in glottis view in neutral position versus sniffing position.
The data collection was carried out by observers who were not blinded which might have caused some bias in the results. To obtain an adequate sniffing position, the principal investigator positioned the head and neck of all patients. All Vision Mask devices were done by only one author, so the results express the author’s experience with this device.
Our results may not be applicable to patients with spontaneous ventilations.
In summary
Clinical tests have traditionally been used to evaluate the correct placement of the SAD. However, with the use of a SAD with vision, we can now evaluate the correct placement of the device in real-time during placement and reposition it if necessary. This allows us to evaluate the glottis area when the surgery requires changing the position of the head and neck, reducing the time taken for evaluation compared to using a laryngoscope, VLP or fiberscope. The use of a video SAD eliminates the need for a blind procedure.
In this study, we evaluated glottic views using two different head-neck positions: the sniffing position and a neutral position with Vision Mask. We found that an adequate sniffing position did not result in a better glottic view, and the number and type of additional maneuvers were equal in both positions.
Therefore, the head and neck position when placing a SAD can be selected based on the individual patient's situation.
Table 1.
Patients Characteristics (n = 72).
Table 1.
Patients Characteristics (n = 72).
| Male/Female (n, %) |
19 |
26,39% |
53 |
73,61% |
| Age (years) |
53,74 |
(23-82) |
D.S. |
13,21 |
| Height (cm) |
165,33 |
(146-192) |
D.S. |
9,56 |
| Weight (kg) |
75,66 |
(42-129) |
D.S. |
17,18 |
| ASA physical status |
|
|
|
|
| I |
15 |
20,83% |
|
|
| II |
44 |
61,11% |
|
|
| III |
13 |
18,06% |
|
|
| Body mass index (kg/m2) |
27,55 |
(16,00-37,42) |
D.S. |
5,10 |
| BMI < 30 |
44 |
61,11% |
|
|
| BMI 30 - <35 |
21 |
29,17% |
|
|
| BMI ≥ 35 - <40 |
7 |
9,72% |
|
|
| Mallampati classification |
|
|
|
|
| I |
6 |
8% |
|
|
| II |
37 |
51% |
|
|
| III |
27 |
38% |
|
|
| IV |
2 |
3% |
|
|
| Tryromental distance (cm) |
|
|
|
|
| ≥ 6 cm |
59 |
82% |
|
|
| < 6 cm |
13 |
18% |
|
|
| Intercisor gap (cm) |
|
|
|
|
| ≥ 4 cm |
66 |
92% |
|
|
| < 4 cm |
6 |
8% |
|
|
| Neck circumference (cm) |
|
|
|
|
| ≤ 40 cm |
54 |
75% |
|
|
| 41-59 cm |
18 |
25% |
|
|
| ≥ 60 cm |
0 |
0% |
|
|
| Size Vision Mask |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
54 |
75% |
|
|
| 4 |
18 |
25% |
|
|
| SAD used |
|
|
|
|
| To evaluation |
43 |
60% |
|
|
| To anesthesia |
29 |
40% |
|
|
| Type of surgery |
|
|
|
|
| General Surgery |
29 |
40% |
|
|
| Gynecolgy |
19 |
26% |
|
|
| Orthopedic |
2 |
3% |
|
|
| Urology |
12 |
17% |
|
|
| Other |
10 |
14% |
|
|
Table 2.
Fiberoptic view of the glottis with Cormarck Lehane Classification. (n=72) .
Table 2.
Fiberoptic view of the glottis with Cormarck Lehane Classification. (n=72) .
| Grade |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
p-value |
| n |
% |
n |
% |
| 1 |
42 |
58,33% |
43 |
59,72% |
|
| 2 |
22 |
30,56% |
22 |
30,56% |
|
| 3 |
7 |
9,72% |
5 |
6,94% |
|
| 4 |
1 |
1,39% |
2 |
2,78% |
|
| Total |
72 |
100,00% |
72 |
100,00% |
0,8783 |
| Laryngeal view |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
p-value |
| n |
% |
n |
% |
| Adequate |
64 |
88,89% |
65 |
90,28% |
|
| No adequate |
8 |
11,11% |
7 |
9,72% |
|
| Total |
72 |
100,00% |
72 |
100,00% |
0,785 |
Table 3.
Fiberoptic view of the glottis with Brimacombe Classification. (n=72) .
Table 3.
Fiberoptic view of the glottis with Brimacombe Classification. (n=72) .
| Score |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
p-value |
| n |
% |
n |
% |
| 4 |
40 |
55,56% |
39 |
54,17% |
|
| 3 |
18 |
25,00% |
18 |
25,00% |
|
| 2 |
10 |
13,89% |
12 |
16,67% |
|
| 1 |
4 |
5,56% |
3 |
4,17% |
|
| Total |
72 |
100,00% |
72 |
100,00% |
0,817 |
| Laryngeal view |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
p-value |
| n |
% |
n |
% |
| Adequate |
68 |
94,44% |
69 |
95,83% |
|
| No adequate |
4 |
5,56% |
3 |
4,17% |
|
| Total |
72 |
100,00% |
72 |
100,00% |
0,6984 |
Table 4.
Success, airways manoeuvres and complication.
Table 4.
Success, airways manoeuvres and complication.
| |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
| Successful placement |
72 |
100% |
72 |
100% |
| Number of attemps |
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
67 |
93,06% |
70 |
97,22% |
| 2 |
5 |
6,94% |
2 |
2,78% |
| Airways maneuvers |
|
|
|
|
| No one |
43 |
59,72% |
41 |
56,94% |
| ELM* |
1 |
1,39% |
1 |
1,39% |
| Jaw thrust |
27 |
37,50% |
29 |
40,28% |
| Recolocation |
1 |
1,39% |
1 |
1,39% |
| Improve |
23 |
82,14% |
24 |
80,00% |
| No improve |
5 |
17,86% |
6 |
20,00% |
| Complications |
Neutral position |
Sniffing position |
| ∙ No one |
56 |
58 |
| ∙ Lips trauma |
1 |
1 |
| ∙ Blood of SAD at time of removal |
15 |
13 |
| ∙ Dental trauma |
0 |
0 |
| Total, n |
16 |
14 |
| Incidence, % |
22,22% |
19,44% |
Table 5.
Variation in heart rate and blood pressure before and after colocation of Vision Mask. Type of adverse events encountered.
Table 5.
Variation in heart rate and blood pressure before and after colocation of Vision Mask. Type of adverse events encountered.
| Type of adverse events |
n |
% |
|
| Variation of mean blood pressure (mmHg) |
|
| ≥ 20% |
15 |
20,83% |
|
| < 20% |
57 |
79,17% |
|
| Variation of heart rate (bpm) |
|
|
|
| ≥ 20% |
8 |
11,11% |
|
| < 20% |
64 |
88,89% |
|
References
- Cochrane Database Systematic Reviews. Dispositivos Supraglóticos versus intubación traqueal para el tratamiento de las vías respiratorias durante la anestesia general en pacientes con obesidad. [CrossRef]
- Brain AI. The laryngeal mask-a new concept in airway management. Br J Anaesth.1983; 55(8):801-5.
- Timmermann, A. Supraglottic airways in difficult airway management: successes, failures, use and misuse. Anaesthesia 2011, 66, 45–56. [CrossRef]
- Van Zundert, A.A.J.; Kumar, C.M.; Van Zundert, T.C.R.V.; Gatt, S.P.; Pandit, J.J. The case for a 3rd generation supraglottic airway device facilitating direct vision placement. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2021, 35, 217–224. [CrossRef]
- Levitan, R.M.; Mechem, C.; Ochroch, E.; Shofer, F.S.; Hollander, J.E. Head-elevated laryngoscopy position: Improving laryngeal exposure during laryngoscopy by increasing head elevation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2003, 41, 322–330. [CrossRef]
- Greenland, K.B. A proposed model for direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 156–161. [CrossRef]
- El-Orbany, M.; Woehlck, H.; Salem, M.R. Head and Neck Position for Direct Laryngoscopy. Obstet. Anesthesia Dig. 2011, 113, 103–109. [CrossRef]
- Banister FB, Oxfd MA, Lpool MD, Macbeth RG. Direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. Lancet 1944;244, Issue 6325:651-654.
- Horton WA, Fahy L, Charters P. Defining a standard intubating position using “angle finder”. Br J Anaesth. 1989;62(1):6-12.
- Castillo-Monzón, C.G.; Marroquín-Valz, H.A.; Gigante, S.M. Manejo de la Vía Aérea ¿Qué Sabemos? Madrid. Editorial Ergon 2016. Password: castillo2015. Available online: http://ergon.es/manejo-de-la-via-aerea-que-sabemos/.
- Lee BJ, Kang JM, Kim DO. Laryngeal exposure during laryngoscopy is better in the 25º back-up position than in the supine position. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 99(4):581-6.
- Ochroch EA, Hollander JE, Kush S, Shofer FS, and Levitan RM. Assessment of laryngeal view: Percentage of glottis opening score vs Cormack and Lehane grading. Can J Anaesth. 1999; 46(10):987-90.
- El-Orbany, M.I.; Getachew, Y.B.; Joseph, N.J.; Salem, M.R.; Friedman, M. Head elevation improves laryngeal exposure with direct laryngoscopy. J. Clin. Anesthesia 2015, 27, 153–158. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yu, J.; Hong, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Kim, Y. Head elevation and laryngeal mask airway Supreme insertion: A randomized controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 65, 343–350. [CrossRef]
- Kim MS, Jin JH, Lee KY , Choi SH , Jung HH , Kim JH, Lee B. Influence of head and neck position on the performance of supraglottic airway devices: A systematic review and meta-analysis . PLoS One. 2019 9; 14(5):e0216673.
- Aoyama, K.; Takenaka, I.; Sata, T.; Shigematsu, A. The triple airway manoeuvre for insertion of the laryngeal mask airway in paralyzed patients. Can. J. Anaesth. 1995, 42, 1010–1016. [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe J and Berry A. Laryngeal mask airway insertion. A comparison of the standard versus neutral position in normal patients with a view to its use in cervical spine instability. Anaesthesia 1993, 4(8)8:670-1.
- Campbell, R.L.; Biddle, C.; Assudmi, N.; Campbell, J.R.; Hotchkiss, M. Fiberoptic assessment of laryngeal mask airway placement: Blind insertion versus direct visual epiglottoscopy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1108–1113. [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, Y.R.; Park, E.J.; Park, S.Y. Conditions for laryngeal mask airway placement in terms of oropharyngeal leak pressure: a comparison between blind insertion and laryngoscope-guided insertion. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- van Zundert, A.A.J.; Wyssusek, K.H.; Pelecanos, A.; Roets, M.; Kumar, C.M. A prospective randomized comparison of airway seal using the novel vision-guided insertion of LMA-Supreme® and LMA-Protector®. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 34, 285–294. [CrossRef]
- Sanuki, T.; Uda, R.; Sugioka, S.; Daigo, E.; Son, H.; Akatsuka, M.; Kotani, J. The influence of head and neck position on ventilation with the i-gel airway in paralysed, anaesthetised patients. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 28, 597–599. [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.H.; Baik, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Chang, R.-N. Comparison of the ease of laryngeal mask airway ProSeal insertion and the fiberoptic scoring according to the head position and the presence of a difficult airway. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2011, 60, 244–249. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Nam, S.B.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, J.E. Randomized Comparison of Actual and Ideal Body Weight for Size Selection of the Laryngeal Mask Airway Classic in Overweight Patients. J. Korean Med Sci. 2015, 30, 1197–1202. [CrossRef]
- Moser B, Keller C, Audigé L, Bruppacher HR. Oropharyngeal leak pressure of the LMA Protector™ vs the LMA Supreme™; a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2019; 63(3):322-28.
- Kumar CM, Van Zundert TC, Seet E, Van Zundert AA. Time to consider supraglottic airway device oropharyngeal leak pressure measurement more objectively. Editorial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2021; 65(2): 142-45.
- Buckham, M.; Brooker, M.; Brimacombe, J.; Keller, C. A Comparison of the Reinforced and Standard Laryngeal Mask Airway: Ease of Insertion and the Influence of Head and Neck Position on Oropharyngeal Leak Pressure and Intracuff Pressure. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care 1999, 27, 628–631. [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Gutiérrez, D.; Ruíz-Villa, J.; Rincón-Valenzuela, D.; Feliciano-Alfonso, J. Multivariable prediction models for difficult direct laryngoscopy: Systematic review and literature metasynthesis. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2022, 69, 88–101. [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe J, Berry A. A proposed fiber optic scoring system to standardize the assessment of laryngeal mask airway position. Anesth Analg 1993;76(2):457.
- Joshi, S.; Sciacca, R.R.; Solanki, D.; Young, W.L.; Mathru, M.M. A Prospective Evaluation of Clinical Tests for Placement of Laryngeal Mask Airways. Anesthesiology 1998, 89, 1141–1146. [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, J.; Berry, A. The laryngeal mask airway - anatomical and physiological implications. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1996, 40, 201–209. [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, J.; Berry, A. NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCK AND INSERTION OF THE LARYNGEAL MASK AIRWAY. Br. J. Anaesth. 1993, 71, 166–167. [CrossRef]
- An G, Fang B, Wang Z. Comparing the insertion and ventilation of laryngeal mask airway according to the patient’s head position and muscle relaxation use: A prospective clinical trial. Saudi Med J. 2019; 40(7): 687–93.
- Keller C and Brimacombe J. The influence of head and neck position on oropharyngeal leak pressure and cuff position with the flexible and the standard laryngeal mask airway. Anesth Analg 1999;88(4):913-6.
- Lim WY, Fook-Chong S, Wong P. Comparison of glottis visualization through supraglottic airway device (SAD) using bronchoscope in the ramped versus supine “sniffing air” position: A pilot feasibility study. Indian J Anaesth 2020;64(8):681-7.
- Jun JH, Kim HJ, Baik HJ, Kim YJ, and Yun DG. Analysis of predictive factors for difficult ProSeal laryngeal mask airway insertion and suboptimal positioning. Anesth Pain Med 2013; 8(4):271-8.
- Yun, M.-J.; Hwang, J.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Hong, H.-J.; Jeon, Y.-T.; Park, H.-P. Head elevation by 3 vs. 6 cm in ProSeal laryngeal mask airway insertion: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015, 16, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe J, Keller C. The ProSeal laryngeal mask airway: A randomized, crossover study with the standard laryngeal mask airway in paralyzed, anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology. 2000; 93(1):104-9.
- Somri, M.; Vaida, S.; Fornari, G.G.; Mendoza, G.R.; Charco-Mora, P.; Hawash, N.; Matter, I.; Swaid, F.; Gaitini, L. A randomized prospective controlled trial comparing the laryngeal tube suction disposable and the supreme laryngeal mask airway: the influence of head and neck position on oropharyngeal seal pressure. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015, 16, 87. [CrossRef]
- Keller C, Brimacombe J, Pühringer. A fiberoptic scoring system to assess the position of laryngeal mask airway devices. Interobserver variability and a comparison between the standard, flexible and intubating laryngeal mask airway. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther 2000; 35(11):692-4.
- Mishra, S.K.; Nawaz, M.; Satyapraksh, M.V.S.; Parida, S.; Bidkar, P.U.; Hemavathy, B.; Kundra, P. Influence of Head and Neck Position on Oropharyngeal Leak Pressure and Cuff Position with the ProSeal Laryngeal Mask Airway and the I-Gel: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesthesiol. Res. Pr. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Salman JM. Comparison of standard versus a new technique for classic laryngeal mask insertion. Anaesth. pain intensive care 2021;25(5):569-74:.
- Chandan, S.N.; Sharma, S.M.; Raveendra, U.S.; Prasad, B.R. Fiberoptic assessment of laryngeal mask airway placement: a comparison of blind insertion and insertion with the use of a laryngoscope. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2009, 8, 95–98. [CrossRef]
- Maitra S, Khanna P, Baidya DK. Comparison of laryngeal mask airway Supreme and laryngeal mask airway Pro-Seal for controlled ventilation during general anaesthesia in adult patients: systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014; 31(5):266-73.
- Brimacombe J, Keller C. The Proseal laryngeal mask airway. Anesthesiology 2000;93:104-9.
- Brimacombe J, Keller C, Fullekrug B, Agrò F, Rosenblatt W, Dierdorf SF et al. A multicenter study comparing the ProSeal and Classic laryngeal mask airway in anesthetized, nonparalyzed patients. Anesthesiology 2002; 96(2):289-95.
- Cook TM, Gatward JJ, Handel J, Hardy R, Thompson C, Srivastava R, Clarke PA. Evaluation of the LMA Supreme in 100 non-paralysed patients. Anaesthesia. 2009;64(5):555-62.
- Castillo-Monzón, C.G.; Gaszyński, T.; Marroquín-Valz, H.A.; Orozco-Montes, J.; Ratajczyk, P. Supraglottic Airway Devices with Vision Guided Systems: Third Generation of Supraglottic Airway Devices. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5197. [CrossRef]
- Michalek, P.; Donaldson, W.; Vobrubova, E.; Hakl, M. Complications Associated with the Use of Supraglottic Airway Devices in Perioperative Medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–13. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).