Submitted:
18 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. The Study Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
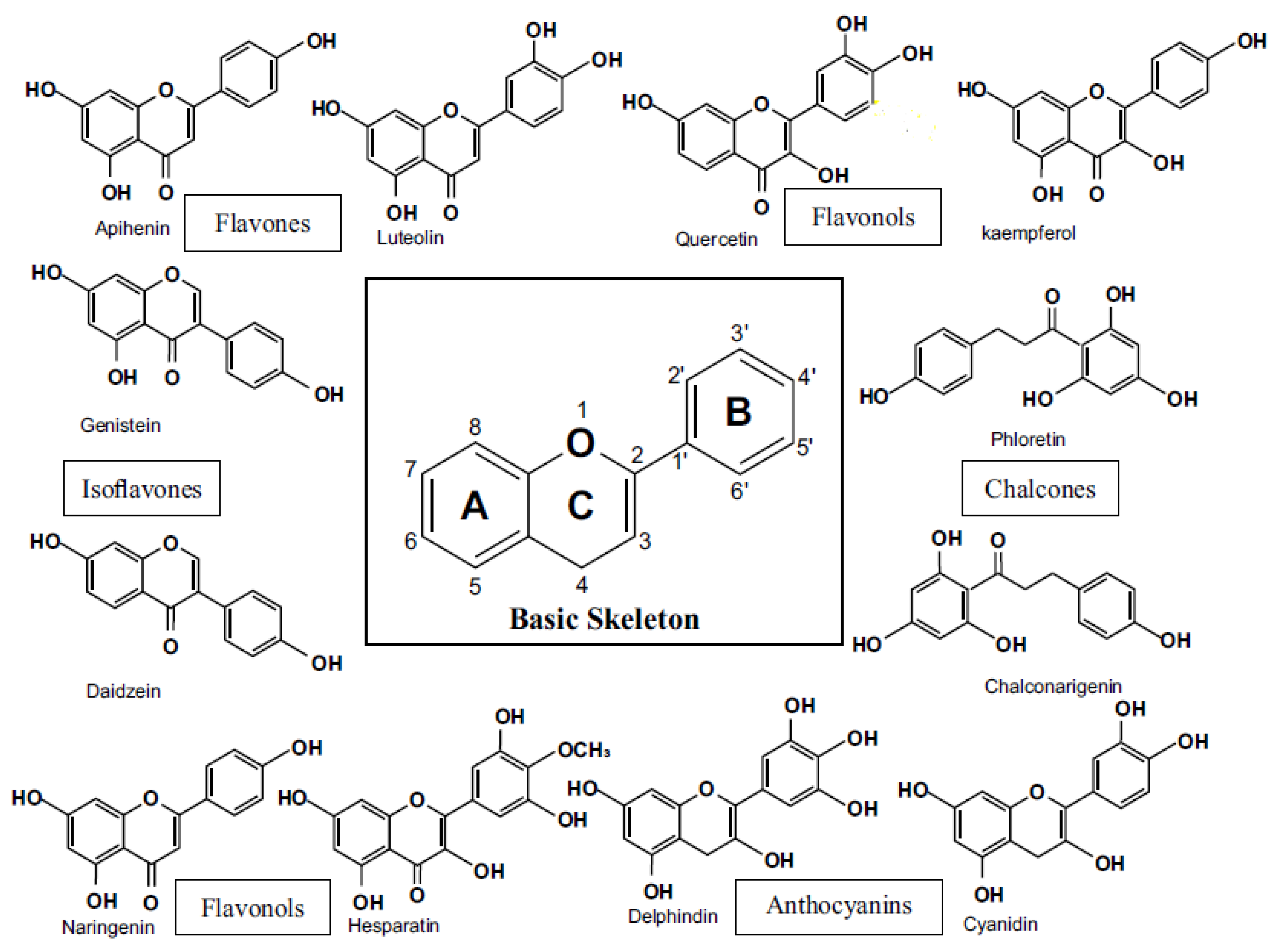
2. Treatment of Sepsis Flavonoids
2.1. Flavanoids
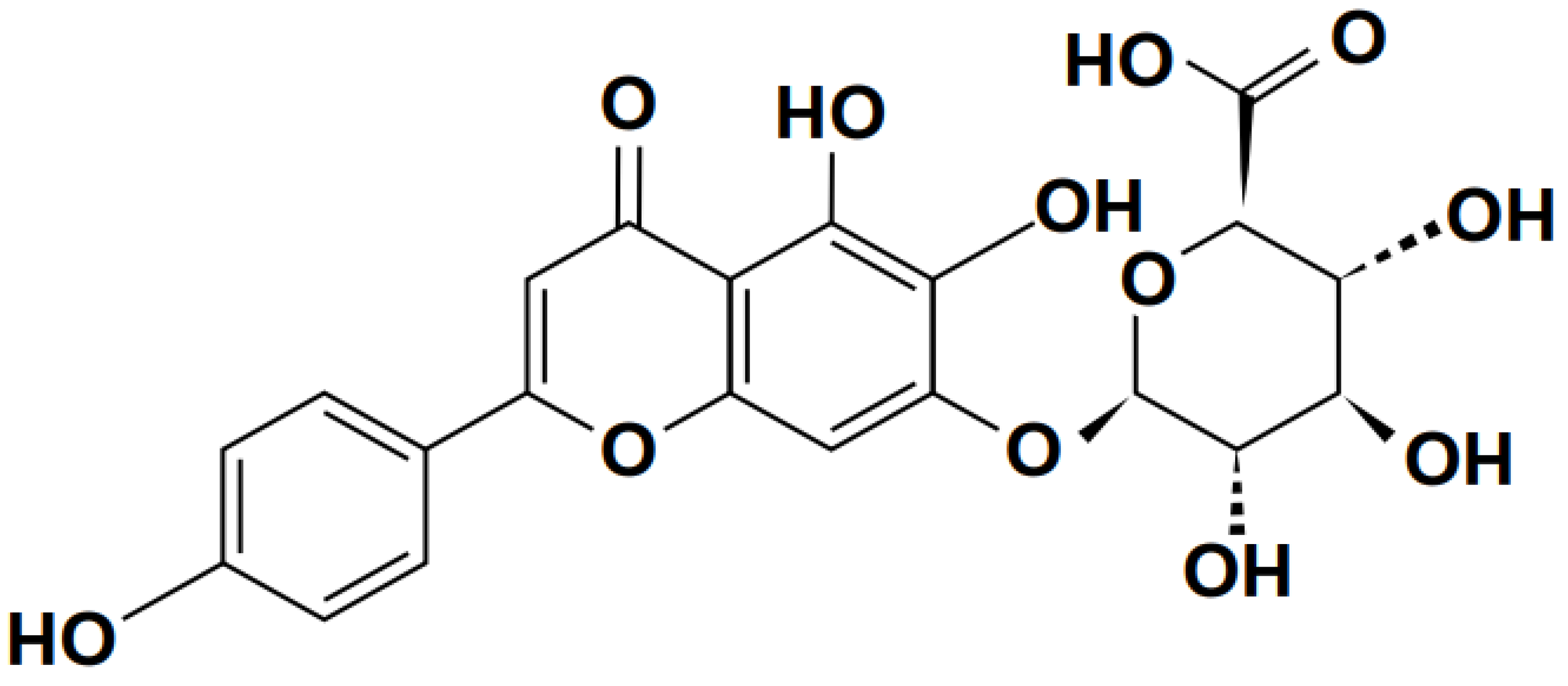
2.1.1. Baicalin
2.1.2. Scutellarin
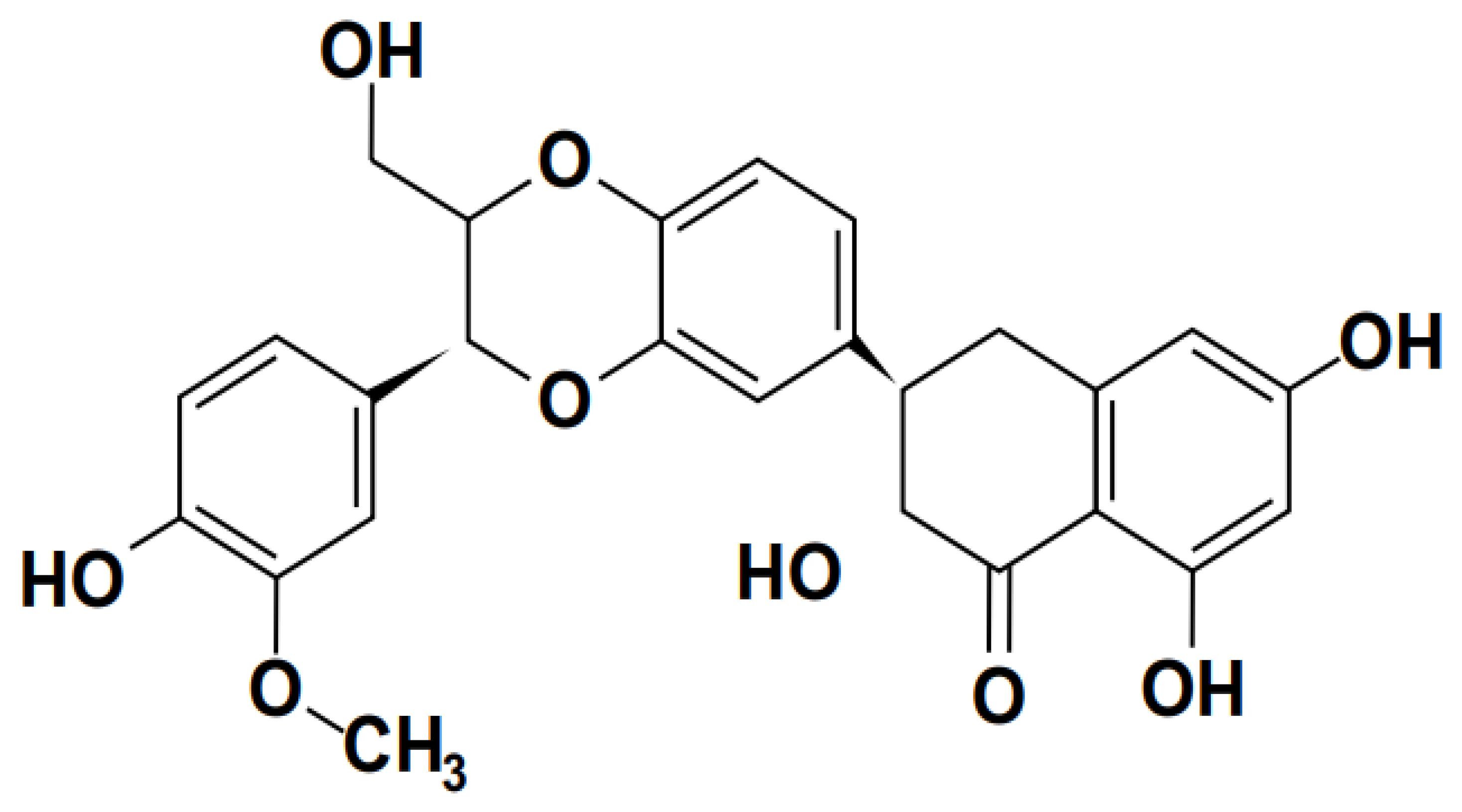
3.1.3. Silymarin
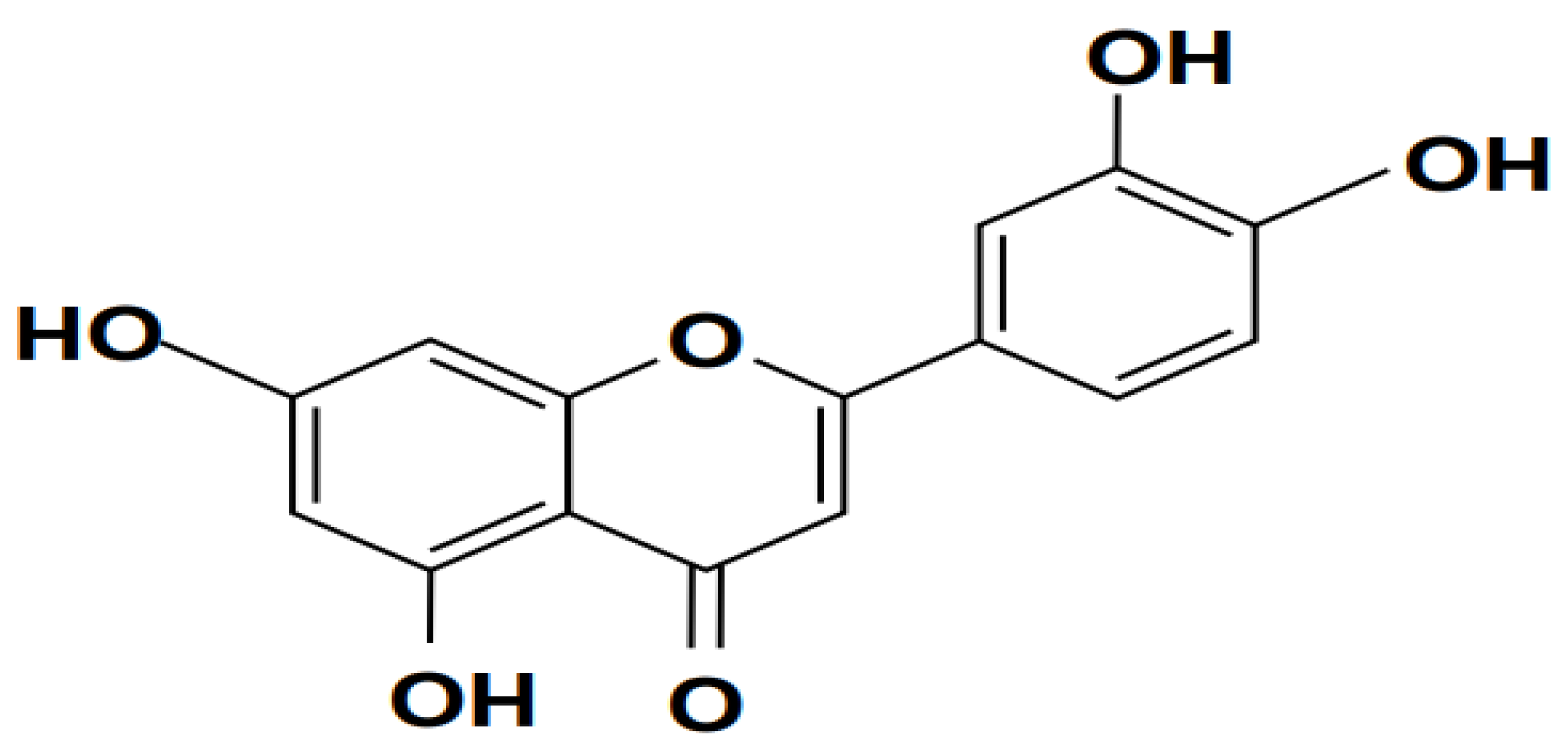
3.1.4. Luteolin
3.2. Flavonol
3.2.1. Quercetin
3.2.2. Isorhamnetin
3.2.3. Fisetin
3.2.4. Myricetin
3.3. Flavan
3.3.1. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)
3.4. Immune Response in Sepsis
3.4.1. Natural Killer (NK)
- Cytokine Therapy: Administration of cytokines such as interleukin-15 (IL-15) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) may help enhance NK cell activity and promote their proliferation and function in sepsis (Carson et al., 1995).
- Immunomodulatory Agents: Drugs that target immune checkpoints, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors, could potentially enhance NK cell-mediated immune responses during sepsis (Chen et al., 2013).
- Adoptive NK Cell Therapy: Infusion of ex vivo expanded and activated NK cells may offer a promising approach to augment NK cell function and improve immune surveillance in septic patients (Romee et al., 2016).
- Targeted Immunotherapy: Monoclonal antibodies directed against inhibitory receptors on NK cells, such as killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), may unleash the cytotoxic potential of NK cells and enhance their antitumor and antiviral activities (Vey et al., 2012).
- Immunomodulatory Strategies: Adjunctive therapies that modulate the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), could help restore immune homeostasis and improve outcomes in septic patients (Hotchkiss et al., 2013).
3.4.2. T Cells
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Drugs targeting immune checkpoint molecules such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) may help alleviate T cell exhaustion and restore their effector functions in sepsis (Hotchkiss et al., 2013).
- Cytokine Therapy: Administration of cytokines such as interleukin-7 (IL-7) and interleukin-15 (IL-15) can promote T cell proliferation, survival, and effector functions, potentially enhancing immune responses in septic patients (Zagorulya, 2023).
- Adoptive T Cell Therapy: Infusion of ex vivo expanded and activated T cells, such as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) or T cell receptor (TCR)-engineered T cells, may augment T cell-mediated immune responses and improve host defense mechanisms during sepsis (Lynn et al., 2019).
- Targeted Immunomodulation: Therapies targeting specific T cell subsets, such as regulatory T cells (Tregs) or memory T cells, could help rebalance the immune response and mitigate excessive inflammation in sepsis(Duffy & Crown, 2019)
- Immunomodulatory Agents: Small molecules or biologics that modulate T cell signaling pathways, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors or nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitors, may offer novel approaches to regulate T cell activation and function in septic patients(Angioni et al., 2021).
- Supportive Therapies: Supportive care measures, including early and appropriate antibiotic therapy, fluid resuscitation, and organ support, remain crucial in managing sepsis and preventing further T cell dysfunction and immune compromise (Shankar-Hari et al., 2016).
3.4.3. B Cells
- Immunomodulatory Therapies: Immunomodulatory agents, such as corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG), and monoclonal antibodies, are being investigated for their potential to modulate B cell function and attenuate the inflammatory response in sepsis. For example, IVIG therapy has shown promise in improving outcomes in septic patients by enhancing antibody-mediated immunity and mitigating immune dysregulation (Alejandria et al., 2013).
- B Cell-Targeted Therapies: Emerging therapies targeting B cells, such as anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (e.g., rituximab), aim to deplete B cell populations and suppress aberrant antibody production in sepsis. These targeted approaches hold potential for modulating B cell responses and restoring immune homeostasis in septic patients (Fowler et al., 2014).
- Cytokine Modulation: Therapies aimed at modulating cytokine levels and inflammatory signaling pathways may indirectly influence B cell function and immune responses in sepsis. For instance, agents targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), may attenuate B cell activation and dampen the systemic inflammatory response associated with sepsis(Cohen et al., 2015).
- Supportive Care: In addition to targeted therapies, supportive care measures play a crucial role in managing sepsis-associated complications and optimizing patient outcomes. Supportive interventions, including fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and mechanical ventilation, aim to stabilize hemodynamics, maintain organ perfusion, and support vital organ function during the acute phase of sepsis(Rhodes et al., 2017).
3.4.4. Cytokines
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abenavoli, L.; Capasso, R.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Milk thistle in liver diseases: Past, present, future. Phytotherapy Research 2010, 24, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abotaleb, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Kubatka, P.; Liskova, A.; Büsselberg, D. Flavonoids in cancer and apoptosis. Cancers 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achuthan, M.; Werschler, N. A Novel Approach to CFTR Gene Editing through CRISPR-Cas9 Technology in Cystic Fibrosis. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, S.; Kondo, S.; Sato, Y.; Yoshizawa, F.; Yagasaki, K. Anti-hyperuricemic effect of isorhamnetin in cultured hepatocytes and model mice: Structure–activity relationships of methylquercetins as inhibitors of uric acid production. Cytotechnology 2019, 71, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandria, M.M.; Lansang, M.A. D.; Dans, L.F.; Mantaring III, J.B. Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2013; 9, https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD001090.pub2/abstract. [Google Scholar]
- Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Gong, M.N.; Fan, E.; Oczkowski, S.; Levy, M.M.; Derde, L.; Dzierba, A. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Medicine 2020, 46, 854–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadi, A.; Ahmed, A.-S.; El-Tahawy, N.F. G.; Khalifa, M.M. A.; El-Daly, M. Silymarin protects against sepsis-induced acute liver and kidney injury via anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms in the rat. Journal of Advanced Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 3, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Potential Therapeutic Targets of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG), the Most Abundant Catechin in Green Tea, and Its Role in the Therapy of Various Types of Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, Article 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrubayyi, A.; Ogbe, A.; Moreno Cubero, E.; Peppa, D. Harnessing natural killer cell innate and adaptive traits in HIV infection. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2020, 10, 395, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00395/full. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Viola, A.; Molon, B. TGF-β in cancer: Metabolic driver of the tolerogenic crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 401, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/3/401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoce, A.O.; Stockley, C. An overview of the implications of wine on human health, with special consideration of the wine-derived phenolic compounds. AgroLife Sci J 2019, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, M.-J.; Hong, S.-G.; Lee, J.-W.; Jeong, W.-S. Red ginseng marc oil inhibits iNOS and COX-2 via NFκB and p38 pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Molecules 2012, 17, 13769–13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Ma, Y.; Liang, M.; Sun, X.; Ju, X.; Yong, Y.; Liu, X. Research progress on pharmacological effects and new dosage forms of baicalin. Veterinary Medicine and Science 2022, 8, 2773–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berretta, A.A.; Silveira, M.A. D.; Capcha, J.M. C.; De Jong, D. Propolis and its potential against SARS-CoV-2 infection mechanisms and COVID-19 disease: Running title: Propolis against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 131, 110622. [Google Scholar]
- Bhan, C.; Dipankar, P.; Chakraborty, P.; Sarangi, P.P. Role of cellular events in the pathophysiology of sepsis. Inflammation Research 2016, 65, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharrhan, S.; Chopra, K.; Arora, S.K.; Toor, J.S.; Rishi, P. Down-regulation of NF-κB signalling by polyphenolic compounds prevents endotoxin-induced liver injury in a rat model. Innate Immunity 2012, 18, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; To, K.; Chang, K.C.; Takasu, O.; Osborne, D.F.; Walton, A.H.; Bricker, T.L.; Jarman, S.D.; Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. Jama 2011, 306, 2594–2605, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/1104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, F.J.; Shao-Nong, C. (2013). HiFSA Fingerprinting Applied to Isomers with Near-Identical NMR Spectra: The Silybin/Isosilybin Case.
- Brinkworth, J.F.; Shaw, J.G. On race, human variation, and who gets and dies of sepsis. American Journal of Biological Anthropology 2022, 178, 230–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, G.; Xie, J. Immune dysregulation in sepsis: Experiences, lessons and perspectives. Cell Death Discovery 2023, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Svabek, C.; Vazquez-Guillamet, C.; Sato, B.; Rasche, D.; Wilson, S.; Robbins, P.; Ulbrandt, N.; Suzich, J.; Green, J.; Patera, A.C.; Blair, W.; Krishnan, S.; Hotchkiss, R. Targeting the programmed cell death 1: Programmed cell death ligand 1 pathway reverses T cell exhaustion in patients with sepsis. Critical Care 2014, 18, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, H. Immune intervention in sepsis. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021, 12, 718089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-H.; Wang, S.-F.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Wang, M.-L.; Chiou, S.-H.; Chang, Y.-L. Pharmacological development of the potential adjuvant therapeutic agents against coronavirus disease 2019. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 2020, 83, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, H.S.; Cai, Y.; Hakim, I.A.; Crowell, J.A.; Shahi, F.; Brooks, C.A.; Dorr, R.T.; Hara, Y.; Alberts, D.S. Pharmacokinetics and safety of green tea polyphenols after multiple-dose administration of epigallocatechin gallate and polyphenon E in healthy individuals. Clinical Cancer Research 2003, 9, 3312–3319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuammitri, P.; Srikok, S.; Saipinta, D.; Boonyayatra, S. The effects of quercetin on microRNA and inflammatory gene expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bovine neutrophils. Veterinary World 2017, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CİHAN, B.; YARAT, A.; AKBAY, T.T.; ŞENER, G. Investigation of the effect of silymarin on the liver in experimental sepsis. Marmara Pharmaceutical Journal 2015, 19, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Vincent, J.-L.; Adhikari, N.K.; Machado, F.R.; Angus, D.C.; Calandra, T.; Jaton, K.; Giulieri, S.; Delaloye, J.; Opal, S. Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2015, 15, 581–614, https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(15)70112-X/fulltext. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, M.L.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Giribone, L.; Demartini, A.; Sartini, M. Epidemiology and prevention of healthcare-associated infections in geriatric patients: A narrative review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Hu, G.; Peng, J.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; Qiao, L. Quercetin exerted protective effects in a rat model of sepsis via inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and downregulation of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein expression. Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research 2019, 25, 5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, X.; Li, Y. Quercetin and quercitrin protect against cytokine-induced injuries in RINm5F β-cells via the mitochondrial pathway and NF-κB signaling. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2013, 31, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.S.; Ferreira, D.; Paige, E.; Gedye, C.; Boyle, M. Infectious Complications of Biological and Small Molecule Targeted Immunomodulatory Therapies. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2020, 33, e00035–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.G. M.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Pimentel, G.D.; Mota, J.F. Nuts and human health outcomes: A systematic review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DGI, G.R. B. R. C.; Role, J.P. K. Z. P. Of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.; Dinda, S.; DasSharma, S.; Banik, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Dinda, M. Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 131, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditlevsen, K.; Sandøe, P.; Lassen, J. Healthy food is nutritious, but organic food is healthy because it is pure: The negotiation of healthy food choices by Danish consumers of organic food. Food Quality and Preference 2019, 71, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyakolu, S.; Chikkala, R.; Ratnakar, K.S.; Sritharan, V. Hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus—An update on their biology, role in pathogenesis and as targets for anti-virulence therapy. Advances in Infectious Diseases 2019, 9, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, G.; Luo, Y. Protective effect of isorhamnetin on oxidative stress induced by H2O2 in H9C2 cells. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull 2015, 3, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; Dos Santos, K.C.; da Silva, P.B.; de Toledo, L.G.; Marena, G.D.; Rodero, C.F.; de Camargo, B.A. F.; Fortunato, G.C.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnological strategies for systemic microbial infections treatment: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2020, 589, 119780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Crown, J. Biomarkers for predicting response to immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients. Clinical Chemistry 2019, 65, 1228–1238, https://academic.oup.com/clinchem/article-abstract/65/10/1228/5608308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElTanbouly, M.A.; Noelle, R.J. Rethinking peripheral T cell tolerance: Checkpoints across a T cell’s journey. Nature Reviews Immunology 2021, 21, 257–267, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41577-020-00454-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Guo, Q.; Shen, J.; Zheng, K.; Lu, C.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; He, X. The effect of triptolide in rheumatoid arthritis: From basic research towards clinical translation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, M.R.; Maugeri, A.; De Sarro, G.; Navarra, M.; Barreca, D. Molecular Pathways Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Flavonols: A Focus on Myricetin and Kaempferol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, Article 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Rudd, K. Challenges of assessing the burden of sepsis. Medizinische Klinik - Intensivmedizin Und Notfallmedizin 2023, 118, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.A.; Mittmann, N.; Geerts, W.; Heels-Ansdell, D.; Gould, M.K.; Guyatt, G.; Krahn, M.; Finfer, S.; Pinto, R.; Chan, B. Cost-effectiveness of dalteparin vs unfractionated heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in critically ill patients. Jama 2014, 312, 2135–2145, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/1921813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, B.; Jeannet, R.; Daix, T.; Walton, A.H.; Shotwell, M.S.; Unsinger, J.; Monneret, G.; Rimmelé, T.; Blood, T.; Morre, M. Interleukin-7 restores lymphocytes in septic shock: The IRIS-7 randomized clinical trial. JCI Insight, 2018; 3, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5922293/. [Google Scholar]
- Fürst, R.; Zündorf, I. Plant-derived anti-inflammatory compounds: Hopes and disappointments regarding the translation of preclinical knowledge into clinical progress. Mediators of Inflammation 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarin, R.S.; Li, M.; Zimmel, P.A.; Marshall, J.C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Intracellular and extracellular lipopolysaccharide signaling in sepsis: Avenues for novel therapeutic strategies. Journal of Innate Immunity 2021, 13, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, N.M. S.; Bohmwald, K.; Pacheco, G.A.; Andrade, C.A.; Carreño, L.J.; Kalergis, A.M. Type I Natural Killer T Cells as Key Regulators of the Immune Response to Infectious Diseases. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gažák, R.; Svobodová, A.; Psotová, J.; Sedmera, P.; Přikrylová, V.; Walterová, D.; Křen, V. Oxidised derivatives of silybin and their antiradical and antioxidant activity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2004, 12, 5677–5687. [Google Scholar]
- Gerin, F.; Sener, U.; Erman, H.; Yilmaz, A.; Aydin, B.; Armutcu, F.; Gurel, A. The effects of quercetin on acute lung injury and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in the rat model of sepsis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D.I.; Le Nours, J.; Andrews, D.M.; Uldrich, A.P.; Rossjohn, J. Unconventional T cell targets for cancer immunotherapy. Immunity 2018, 48, 453–473, https://www.cell.com/immunity/pdf/S1074-7613(18)30085-2.pdf. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhou, S.; Luan, X.; Zhang, H. Isorhamnetin: A review of pharmacological effects. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 128, 110301. [Google Scholar]
- González-Arceo, M.; Gomez-Lopez, I.; Carr-Ugarte, H.; Eseberri, I.; González, M.; Cano, M.P.; Portillo, M.P.; Gómez-Zorita, S. Anti-Obesity Effects of Isorhamnetin and Isorhamnetin Conjugates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 24, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, A.; Frias, I.; Neves, A.R.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Therapeutic potential of epigallocatechin gallate nanodelivery systems. BioMed Research International 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grollino, M.G.; Raschellà, G.; Cordelli, E.; Villani, P.; Pieraccioli, M.; Paximadas, I.; Malandrino, S.; Bonassi, S.; Pacchierotti, F. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and gene expression changes elicited by exposure of human hepatic cells to Ginkgo biloba leaf extract. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2017, 109, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Demchuk, O.M. New perspectives for fisetin. Frontiers in Chemistry 2019, 7, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Patil, N.K.; Luan, L.; Bohannon, J.K.; Sherwood, E.R. The biology of natural killer cells during sepsis. Immunology 2018, 153, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Ajmal, M.; Ahsan, R.; Rahaman, M.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Arshad, M.; Khushtar, M. Current pharmacological trends on myricetin. Drug Research 2020, 70, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Khan, Z.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Khan, M.A.; Moni, M.A.; Rahman, M.H. In silico molecular docking and ADME/T analysis of Quercetin compound with its evaluation of broad-spectrum therapeutic potential against particular diseases. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2022, 29, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, J. Studies on Quercetin and its derivatives, treatise VII. Monatshefte Für Chemie 1891, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, P.C.; Katan, M.B. Health effects and bioavailability of dietary flavonols. Free Radical Research 1999, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, P.H.; Katan, M.B. Dietary flavonoids: Intake, health effects and bioavailability. Food and Chemical Toxicology 1999, 37, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Richel, A.; Blecker, C. Valorization of the green waste parts from sweet potato (Impoea batatas L.): Nutritional, phytochemical composition, and bioactivity evaluation. Food Science & Nutrition 2020, 8, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2013, 13, 260–268, https://www.thelancet.com/journals/a/article/PIIS1473-3099(13)70001-X/fulltext. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Webster, D.; Cao, J.; Shao, A. The safety of green tea and green tea extract consumption in adults–results of a systematic review. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2018, 95, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhong, T.; Wu, H. Experimental research quercetin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Archives of Medical Science 2015, 11, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.-W.; Tsai, S.-C.; Peng, S.-F.; Lin, M.-W.; Chiang, J.-H.; Chiu, Y.-J.; Fushiya, S.; Tseng, M.T.; Yang, J.-S. Kaempferol induces autophagy through AMPK and AKT signaling molecules and causes G2/M arrest via downregulation of CDK1/cyclin B in SK-HEP-1 human hepatic cancer cells. International Journal of Oncology 2013, 42, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Saeed, F.; Hussain, G.; Imran, A.; Mehmood, Z.; Gondal, T.A.; El-Ghorab, A.; Ahmad, I.; Pezzani, R.; Arshad, M.U. Myricetin: A comprehensive review on its biological potentials. Food Science & Nutrition 2021, 9, 5854–5868. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Umair Arshad, M.; Khan, H. Kaempferol: A key emphasis to its anticancer potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishola, I.O.; Osele, M.O.; Chijioke, M.C.; Adeyemi, O.O. Isorhamnetin enhanced cortico-hippocampal learning and memory capability in mice with scopolamine-induced amnesia: Role of antioxidant defense, cholinergic and BDNF signaling. Brain Research 2019, 1712, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackie Oh, S.; Han, S.; Lee, W.; Lockhart, A.C. Emerging immunotherapy for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2016, 25, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Croft, K.; Ashida, H. Quercetin and its metabolite isorhamnetin promote glucose uptake through different signalling pathways in myotubes. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, S. Anti-tumor effects and associated molecular mechanisms of myricetin. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 120, 109506. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, R.A. Cosuppression, flower color patterns, and metastable gene expression states. Science 1995, 268, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppagounder, V.; Arumugam, S.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Sreedhar, R.; Giridharan, V.V.; Watanabe, K. Molecular targets of quercetin with anti-inflammatory properties in atopic dermatitis. Drug Discovery Today 2016, 21, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Deb, P.K.; Priya, S.; Medina, K.D.; Devi, R.; Walode, S.G.; Rudrapal, M. Dietary flavonoids: Cardioprotective potential with antioxidant effects and their pharmacokinetic, toxicological and therapeutic concerns. Molecules 2021, 26, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-E.; Lee, D.-E.; Lee, K.W.; Son, J.E.; Seo, S.K.; Li, J.; Jung, S.K.; Heo, Y.-S.; Mottamal, M.; Bode, A.M. Isorhamnetin Suppresses Skin Cancer through Direct Inhibition of MEK1 and PI3-KInhibition of Skin Cancer by Isorhamnetin. Cancer Prevention Research 2011, 4, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, T.; Müller, C.I.; Desmond, J.C.; Imai, Y.; Heber, D.; Koeffler, H.P. Scutellaria baicalensis, a herbal medicine: Anti-proliferative and apoptotic activity against acute lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma cell lines. Leukemia Research 2007, 31, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. The Scientific World Journal 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkin, V.A.; Ryzhov, V.M.; Biryukova, O.V.; Mel’nikova, N.B.; Selekhov, V.V. Interaction of milk-thistle-fruit flavanonols with Langmuir monolayers of lecithin and bilayers of liposomes. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal 2009, 43, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalitha, N.; Sadashivaiah, B.; Ramaprasad, T.R.; Singh, S.A. Anti-hyperglycemic activity of myricetin, through inhibition of DPP-4 and enhanced GLP-1 levels, is attenuated by co-ingestion with lectin-rich protein. PloS One 2020, 15, e0231543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.-W.; Liu, Y. Molecular structure and stereochemistry of silybin a, silybin B, isosilybin a, and isosilybin B, isolated from Silybum m arianum (milk thistle). Journal of Natural Products 2003, 66, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Maliakal, P.; Chen, L.; Meng, X.; Bondoc, F.Y.; Prabhu, S.; Lambert, G.; Mohr, S.; Yang, C.S. Pharmacokinetics of tea catechins after ingestion of green tea and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate by humans: Formation of different metabolites and individual variability. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention 2002, 11, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kwak, C.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Ha, S.-H.; Park, J.; Chung, T.-W.; Ha, K.-T.; Suh, S.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, H.W. Anti-inflammatory effect of ascochlorin in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells is accompanied with the down-regulation of iNOS, COX-2 and proinflammatory cytokines through NF-κB, ERK1/2, and p38 signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2016, 117, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.-K.; Bae, J.-S. Vascular barrier protective effects of orientin and isoorientin in LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Vascular Pharmacology 2014, 62, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, M.; Beara, I.; Simin, N.; Pintać, D.; Majkić, T.; Bekvalac, K.; Orčić, D.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin and its derivatives. Journal of Functional Foods 2018, 40, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Du, S. Research progress on antitumor effect and mechanism of isorhamnetin, Shanxi Med. J 2011, 40, 1215–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, C.; Wan, X. Antiviral Properties of Baicalin: A Concise Review. Revista Brasileira De Farmacognosia 2021, 31, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, A. Metabolic fingerprinting to understand therapeutic effects and mechanisms of silybin on acute liver damage in rat. Pharmacognosy Magazine 2015, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Chen, J.; Zhi, D.; Fan, Y.; Liu, W.; HE, X. Effects of isorhamnetin on human liver microsomes CYPs and rat primary hepatocytes. Drug Evaluation Research 2017, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Shen, S.-C.; Lin, C.-W.; Yang, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. Baicalein inhibition of hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via ROS-dependent heme oxygenase 1 gene expression. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 2007, 1773, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- \Lodyga-Chruscińska, E.; Pilo, M.; Zucca, A.; Garribba, E.; Klewicka, E.; Rowińska-Żyrek, M.; Symonowicz, M.; Chrusciński, L.; Cheshchevik, V.T. Physicochemical, antioxidant, DNA cleaving properties and antimicrobial activity of fisetin-copper chelates. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 2018, 180, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, C.; Wang, K.; Dai, L.; Zhang, J.; Ye, H. The effect of quercetin nanoparticle on cervical cancer progression by inducing apoptosis, autophagy and anti-proliferation via JAK2 suppression. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2016, 82, 595–605. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, R.C.; Weber, E.W.; Sotillo, E.; Gennert, D.; Xu, P.; Good, Z.; Anbunathan, H.; Lattin, J.; Jones, R.; Tieu, V. C-Jun overexpression in CAR T cells induces exhaustion resistance. Nature 2019, 576, 293–300, https://idp.nature.com/authorize/casa?redirect_uri=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1805-z&casa_token=VJ3gEm0iZVIAAAAA:_k2zyBOOMzkCOZuP0_iNOOTsKKXO05NrSOH1SPaP3NzP9lS93Gad7qwrQ3-DyLc0ZmqzF_d7SSwdQn03Zw. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalik, A.; Khan, F.A.; Mumtaz, A.; Mehmood, A.; Azhar, S.; Atif, M.; Karim, S.; Altaf, Y.; Tariq, I. Pharmacological applications of quercetin and its derivatives: A short review. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2014, 13, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, P. Fisetin acts on multiple pathways to reduce the impact of age and disease on CNS function. Frontiers in Bioscience (Scholar Edition) 2015, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Steele, E.; Popkin, B.M.; Swinburn, B.; Monteiro, C.A. The share of ultra-processed foods and the overall nutritional quality of diets in the US: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study. Population Health Metrics 2017, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Yoshie, O.; Nakayama, T. Multifaceted roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in tumor immunity. Cancers 2021, 13, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.K.; Gracias, D.T.; Croft, M. TNF activity and T cells. Cytokine 2018, 101, 14–18, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1043466616304501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Pawar, A.; Mahadik, K.; Bothiraja, C. Emerging novel drug delivery strategies for bioactive flavonol fisetin in biomedicine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018, 106, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Micek, A.; Godos, J.; Del Rio, D.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Dietary flavonoids and cardiovascular disease: A comprehensive dose–response meta-analysis. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2021, 65, 2001019. [Google Scholar]
- Momose, Y.; Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Nabetani, H. Systematic review of green tea epigallocatechin gallate in reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of humans. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 2016, 67, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Hoshino, A. Recent advances in flower color variation and patterning of Japanese morning glory and petunia. Breeding Science 2018, 68, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, A.F.; Alizadeh, M. Antioxidant properties of the flavonoid fisetin: An updated review of in vivo and in vitro studies. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2017, 70, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano, L.M. Sepsis 2018: Definitions and Guideline Changes. Surgical Infections 2018, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeva, C. Inflammation and Cell Death of the Innate and Adaptive Immune System during Sepsis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, Article 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, N.; Koh, W.-P.; Yuan, J.-M.; van Dam, R.M. Diet-quality indexes are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular, respiratory, and all-cause mortality among Chinese adults. The Journal of Nutrition 2018, 148, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Balkwill, F.; Chonchol, M.; Cominelli, F.; Donath, M.Y.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Golenbock, D.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Heneka, M.T.; Hoffman, H.M. A guiding map for inflammation. Nature Immunology 2017, 18, 826–831, https://www.nature.com/articles/ni.3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, V.; Du, J.; Charrondière, U.R. Assessment of the nutritional composition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Chemistry 2016, 193, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, J.N.; Durojaye, O.A.; Njoku, U.O.; Tanze, M.M.; Christian, N.; Orum, T.G.; Cosmas, S. Improving the Drug Bioavailability Property of Myricetin through a Structural Monosubstitution Modification Approach: An In-Silico Pharmacokinetics Study. African Journal of Biomedical Research 2019, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, K.C.; Khoo, H.-E. Biological effects of myricetin. General Pharmacology: The Vascular System 1997, 29, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, F.; Ozmen, A.; Akkaya, B.; Aliciguzel, Y.; Aslan, M. Beneficial effect of myricetin on renal functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2012, 12, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, J.; Cerwenka, A. Tricking the balance: NK cells in anti-cancer immunity. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Pearlman, R.L.; Afaq, F. Fisetin and its role in chronic diseases. Anti-Inflammatory Nutraceuticals and Chronic Diseases, 2016; 213–244. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, W.; Kan, R.; Zhu, H.; Li, D. Cardioprotective Effects and Possible Mechanisms of Luteolin for Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Evidence. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 2022, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. Journal of Nutritional Science 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, J.; Gharbi, A.; Han, H.D.; Kang, T.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, W.S.; Jung, I.D. Tamarixetin exhibits anti-inflammatory activity and prevents bacterial sepsis by increasing IL-10 production. Journal of Natural Products 2018, 81, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J.; Ahuja, A.; Vasudev, S.S.; Ahmad, S. Oil based nanocarrier for improved oral delivery of silymarin: In vitro and in vivo studies. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2011, 413, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pene, F.; Zuber, B.; Courtine, E.; Rousseau, C.; Ouaaz, F.; Toubiana, J.; Tazi, A.; Mira, J.-P.; Chiche, J.-D. Dendritic cells modulate lung response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine model of sepsis-induced immune dysfunction. The Journal of Immunology 2008, 181, 8513–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wen, L.; Shi, Q.-F.; Gao, F.; Huang, B.; Meng, J.; Hu, C.-P.; Wang, C.-M. Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and inflammation. Cell Death & Disease 2020, 11, 978. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.; Encina-Zelada, C.; Barros, L.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Cadavez, V.; Ferreira, I.C. Chemical and nutritional characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Willd (quinoa) grains: A good alternative to nutritious food. Food Chemistry 2019, 280, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Fraga, C.G. Research trends in flavonoids and health. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2018, 646, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović-Djordjević, J.B.; Kostić, A. Ž. , Rajković, M.B.; Miljković, I.; Krstić, \DJur\dja, Caruso, G.; Siavash Moghaddam, S.; Brčeski, I. Organically vs. conventionally grown vegetables: Multi-elemental analysis and nutritional evaluation. Biological Trace Element Research 2022, 200, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawira-Atmaja, M.I.; Sita, K.; Setyaningtyas, S.S. W.; Maulana, H.; Setiadi, D.; Priatni, S.; Sulaswatty, A. Perspective regulatory framework on health claim of tea-mini review. Turkish Journal of Agriculture-Food Science and Technology 2022, 10, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Angus, D.C. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: A review. Jama 2018, 319, 62–75, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2667727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Liang, M.; Fu, P. FP297 Anti-Inflammatory Flavonoid Fisetin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2019, 34 (Suppl. 1), gfz106–FP297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.N. I. M.; Hussein, Z.M.; Mustapa, F.; Azhari, H.; Sekar, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Amin, M.C. I. M. Exploring the possible targeting strategies of liposomes against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2021, 165, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, H.; Javvaji, C.K.; Malali, S.; Kumar, S.; Acharya, S.; Toshniwal, S.; Malali Jr, S.; Toshniwal, S.S. Navigating the Cytokine Storm: A Comprehensive Review of Chemokines and Cytokines in Sepsis. Cureus, 2024; 16, https://www.cureus.com/articles/219659-navigating-the-cytokine-storm-a-comprehensive-review-of-chemokines-and-cytokines-in-sepsis.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Remy, K.E.; Mazer, M.; Striker, D.A.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Walton, A.H.; Unsinger, J.; Blood, T.M.; Mudd, P.A.; Daehan, J.Y.; Mannion, D.A. Severe immunosuppression and not a cytokine storm characterizes COVID-19 infections. JCI Insight, 2020; 5, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7526441/. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, C.; Jones, T.M.; Hamad, Y.; Pande, A.; Varon, J.; O’Brien, C.; Anderson, D.J.; Warren, D.K.; Dantes, R.B.; Epstein, L. Prevalence, underlying causes, and preventability of sepsis-associated mortality in US acute care hospitals. JAMA Network Open 2019, 2, e187571–e187571, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/article-abstract/2724768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Angus, D.C.; Annane, D.; Beale, R.J.; Bellinghan, G.J.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.; … Dellinger, R.P. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Medicine 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegsecker, S.; Wiczynski, D.; Kaplan, M.J.; Ahmed, S. Potential benefits of green tea polyphenol EGCG in the prevention and treatment of vascular inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sciences 2013, 93, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Battaglini, D.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R. M. Multiple organ dysfunction in SARS-CoV-2: MODS-CoV-2. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 2020, 14, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ramírez, S.; Navarro-Hernandez, I.C.; Cervantes-Díaz, R.; Sosa-Hernández, V.A.; Acevedo-Ochoa, E.; Kleinberg-Bild, A.; Valle-Rios, R.; Meza-Sánchez, D.E.; Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; Maravillas-Montero, J.L. Innate-like B cell subsets during immune responses: Beyond antibody production. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2019, 105, 843–856, https://academic.oup.com/jleukbio/article-abstract/105/5/843/6935465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupasinghe, H.V. Special Issue “flavonoids and their disease prevention and treatment potential”: Recent advances and future perspectives. Molecules 2020, 25, 4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.A.; Symmons, D.P.; Noyce, P.R.; Ashcroft, D.M. Risks and benefits of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors in the management of psoriatic arthritis: Systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. The Journal of Rheumatology 2008, 35, 883–890, https://www.jrheum.org/content/35/5/883.short. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, B.D.; Kalvala, A.K.; Koneru, M.; Mahesh Kumar, J.; Kuncha, M.; Rachamalla, S.S.; Sistla, R. Ameliorative effect of fisetin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of NF-κB activation and antioxidant defence. PloS One 2014, 9, e105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.J.; Kissoon, N.; Alhawsawi, A.; Aljuaid, M.H.; Daniels, R.; Gorordo-Delsol, L.A.; Machado, F.; Malik, I.; Nsutebu, E.F.; Finfer, S.; Reinhart, K. World Sepsis Day: A global agenda to target a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2020, 319, L518–L522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets—an updated view. Mediators of Inflammation, 2013; 2013, https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mi/2013/165974/. [Google Scholar]
- Scott Luper, N.D. A review of plants used in the treatment of liver disease: Part 1. Alternative Medicine Review 1998, 3, 410–421. [Google Scholar]
- Shahcheraghi, S.H.; Salemi, F.; Small, S.; Syed, S.; Salari, F.; Alam, W.; Cheang, W.S.; Saso, L.; Khan, H. Resveratrol regulates inflammation and improves oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling pathway: Therapeutic and biotechnological prospects. Phytotherapy Research. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Shakoory, B.; Carcillo, J.A.; Chatham, W.W.; Amdur, R.L.; Zhao, H.; Dinarello, C.A.; Cron, R.Q.; Opal, S.M. Interleukin-1 receptor blockade is associated with reduced mortality in sepsis patients with features of the macrophage activation syndrome: Re-analysis of a prior Phase III trial. Critical Care Medicine 2016, 44, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar-Hari, M.; Phillips, G.S.; Levy, M.L.; Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Deutschman, C.S.; Angus, D.C.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Singer, M. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 2016, 315, 775–787, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2492876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Seaweeds as nutraceuticals for health and nutrition. Phycologia 2019, 58, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.; Akash, M.S. H.; Rehman, K.; Irshad, K.; Imran, I. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Association of risk factors and treatment strategies using plant-based bioactive compounds. Journal of Food Biochemistry 2020, 44, e13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, M.; Benedum, C.M.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G.; Markuzon, N. The association between autoimmune disease and 30-day mortality among sepsis ICU patients: A cohort study. Critical Care 2019, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Ren, K.; Lv, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, R.X.; Li, E. Baicalin from Scutellaria baicalensis blocks respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection and reduces inflammatory cell infiltration and lung injury in mice. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 35851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slika, H.; Mansour, H.; Wehbe, N.; Nasser, S.A.; Iratni, R.; Nasrallah, G.; Shaito, A.; Ghaddar, T.; Kobeissy, F.; Eid, A.H. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in cancer: ROS-mediated mechanisms. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 146, 112442. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.-W.; Long, J.-Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, L.-L.; Xie, Q.-X.; Chen, H.-J.; Deng, M.; Li, X.-F. Applications, phytochemistry, pharmacological effects, pharmacokinetics, toxicity of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. and its probably potential therapeutic effects on COVID-19: A review. Chinese Medicine 2020, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, M.; Ren, C.; Guo, C.; Yang, B.; Ren, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Pei, J. Myricetin: A review of the most recent research. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 134, 111017. [Google Scholar]
- Stawicki, S.P.; Jeanmonod, R.; Miller, A.C.; Paladino, L.; Gaieski, D.F.; Yaffee, A.Q.; De Wulf, A.; Grover, J.; Papadimos, T.J.; Bloem, C. The 2019–2020 novel coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) pandemic: A joint american college of academic international medicine-world academic council of emergency medicine multidisciplinary COVID-19 working group consensus paper. Journal of Global Infectious Diseases 2020, 12, 47, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7384689/. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, Y.; Suleria, H.A. R.; Martins, N.; Sytar, O.; Beyatli, A.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Seitimova, G.; Salehi, B.; Semwal, P.; Painuli, S. Myricetin bioactive effects: Moving from preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik, J.R.; Korth, M.J.; Simmons, C.P.; Farrar, J.; Martin, T.R.; Katze, M.G. Into the Eye of the Cytokine Storm. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2012, 76, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toklu, H.Z.; Akbay, T.T.; Velioglu-Ogunc, A.; Ercan, F.; Gedik, N.; Keyer-Uysal, M.; Sener, G. Silymarin, the antioxidant component of Silybum marianum, prevents sepsis-induced acute lung and brain injury. Journal of Surgical Research 2008, 145, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvrdỳ, V.; Pourová, J.; Jirkovskỳ, E.; Křen, V.; Valentová, K.; Mladěnka, P. Systematic review of pharmacokinetics and potential pharmacokinetic interactions of flavonolignans from silymarin. Medicinal Research Reviews 2021, 41, 2195–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Poll, T.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Wiersinga, W.J. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity 2021, 54, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Poll, T.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Scicluna, B.P.; Netea, M.G. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews Immunology 2017, 17, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellani, S.D.; Nigro, A.; Varatharajan, S.; Dworkin, L.D.; Creeden, J.F. Emerging Immunotherapeutic and Diagnostic Modalities in Carcinoid Tumors. Molecules 2023, 28, 2047, https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/5/2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venet, F.; Chung, C.-S.; Monneret, G.; Huang, X.; Horner, B.; Garber, M.; Ayala, A. Regulatory T cell populations in sepsis and trauma. Journal of Leucocyte Biology 2008, 83, 523–535, https://academic.oup.com/jleukbio/article-abstract/83/3/523/6975520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: When i’m calling you, will you answer too? Current Biology 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, Q.V.; Nam, P.C.; Thong, N.M.; Trung, N.T.; Phan, C.-T. D.; Mechler, A. Antioxidant motifs in flavonoids: O–H versus C–H bond dissociation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8935–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Knethen, A.; Heinicke, U.; Weigert, A.; Zacharowski, K.; Brüne, B. Histone deacetylation inhibitors as modulators of regulatory T cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Gu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, N.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Shao, C. Scutellarin Inhibits High Glucose–induced and Hypoxia-mimetic Agent–induced Angiogenic Effects in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species/Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Pathway. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2014, 64, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Lu, H.; Wu, H.; Chai, Y. Protective effect of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cell influx. Experimental Biology and Medicine 2014, 239, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, R.; Jiang, T.; Sun, G. Evaluating the Nutritional Properties of Food: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; An, Y.; Fang, G. The mechanism of anticancer action and potential clinical use of kaempferol in the treatment of breast cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 117, 109086. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Fan, B.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, H.; Kang, F.; Su, H.; Gu, D.; Li, S.; Lin, S. Scutellarin Reduce the Homocysteine Level and Alleviate Liver Injury in Type 2 Diabetes Model. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2020, 11. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.538407. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Lahni, P.M.; Hake, P.W.; Denenberg, A.G.; Wong, H.R.; Snead, C.; Catravas, J.D.; Zingarelli, B. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves systemic hemodynamics and survival in rodent models of polymicrobial sepsis. Shock 2007, 28, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Manach, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. II. Review of 93 intervention studies. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005, 81, 243S–255S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Pae, M.; Meydani, S.N. Green tea EGCG, T cells, and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 2012, 33, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-W.; Lin, L.-C.; Hung, S.-C.; Chi, C.-W.; Tsai, T.-H. Analysis of silibinin in rat plasma and bile for hepatobiliary excretion and oral bioavailability application. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2007, 45, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Developmental and Functional Control of Natural Killer Cells by Cytokines. Frontiers in Immunology 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Seok, J.; Cuschieri, J.; Cuenca, A.G.; Gao, H.; Hayden, D.L.; Hennessy, L.; Moore, E.E.; Minei, J.P. A genomic storm in critically injured humans. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2011, 208, 2581–2590, https://rupress.org/jem/article-abstract/208/13/2581/41049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Li, A.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Yu, L.; Ju, X. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a polyphenol, protects against sepsis-induced acute liver injury in rats. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Medicine, 2016; 9, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, B.; Cheng, K.-W.; Chen, F.; Wang, M. Neuroprotective potential of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) polyphenols in Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2021, 69, 11554–11571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-C.; Yang, C.-M. Chinese herbs and repurposing old drugs as therapeutic agents in the regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation in pulmonary diseases. Journal of Inflammation Research 2021, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, N. Attenuation of sepsis-induced rat liver injury by epigallocatechin gallate via suppression of oxidative stress-related inflammation. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2017, 16, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X. Effects and tolerance of silymarin (milk thistle) in chronic hepatitis C virus infection patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BioMed Research International 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarla, N.S.; Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G.; Reddanna, P.; Kalle, A.M.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Dowluru, K.S.; Chintala, R.; Duddukuri, G.R. Targeting arachidonic acid pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy. Seminars in Cancer Biology 2016, 40, 48–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Li, W.; Qin, H.; Yun, J.; Sun, X. The Use of Chinese Skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) and Its Extracts for Sustainable Animal Production. Animals : An Open Access Journal from MDPI 2021, 11, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagorulya, M. (2023). Dendritic cell dysfunction restrains cytotoxic T cell responses against cancer [PhD Thesis]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/150065.
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, W.; Qian, F. Fisetin alleviates sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction in mice via inhibiting p38 MAPK/MK2 signaling. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2020, 41, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ning, B. Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2021, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: An overview. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2019, 570, 118642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Cardiovascular protective effect of isorhamnetin, Med. Recapitulate 2008, 15, 2321–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Tong, M.; Ou, B.; Liu, C.; Hu, C.; Yang, Y. Isorhamnetin protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2019, 43, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.T.; Choi, R.C.; Chu, G.K.; Cheung, A.W.; Gao, Q.T.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Flavonoids possess neuroprotective effects on cultured pheochromocytoma PC12 cells: A comparison of different flavonoids in activating estrogenic effect and in preventing β-amyloid-induced cell death. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2007, 55, 2438–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

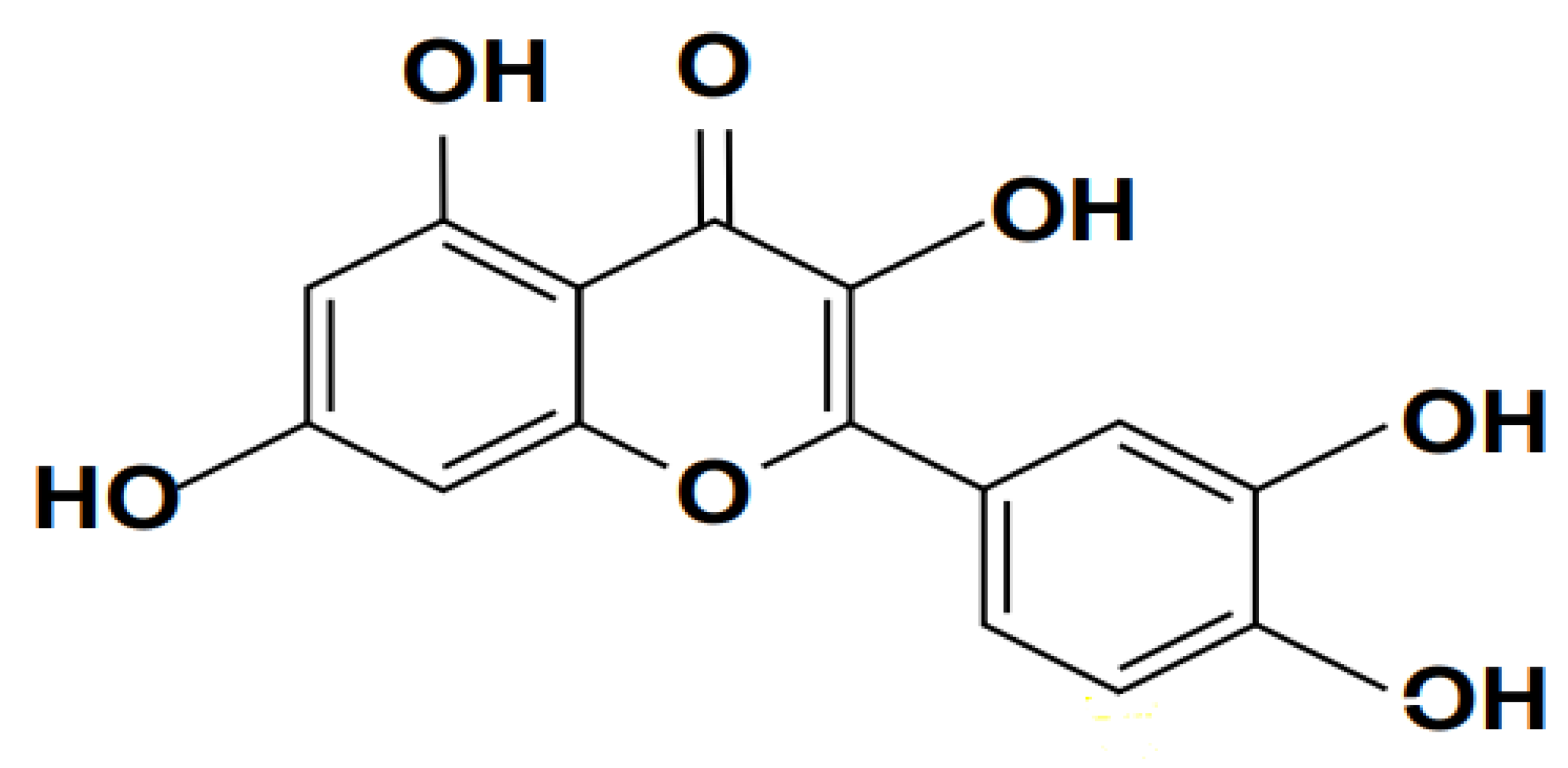
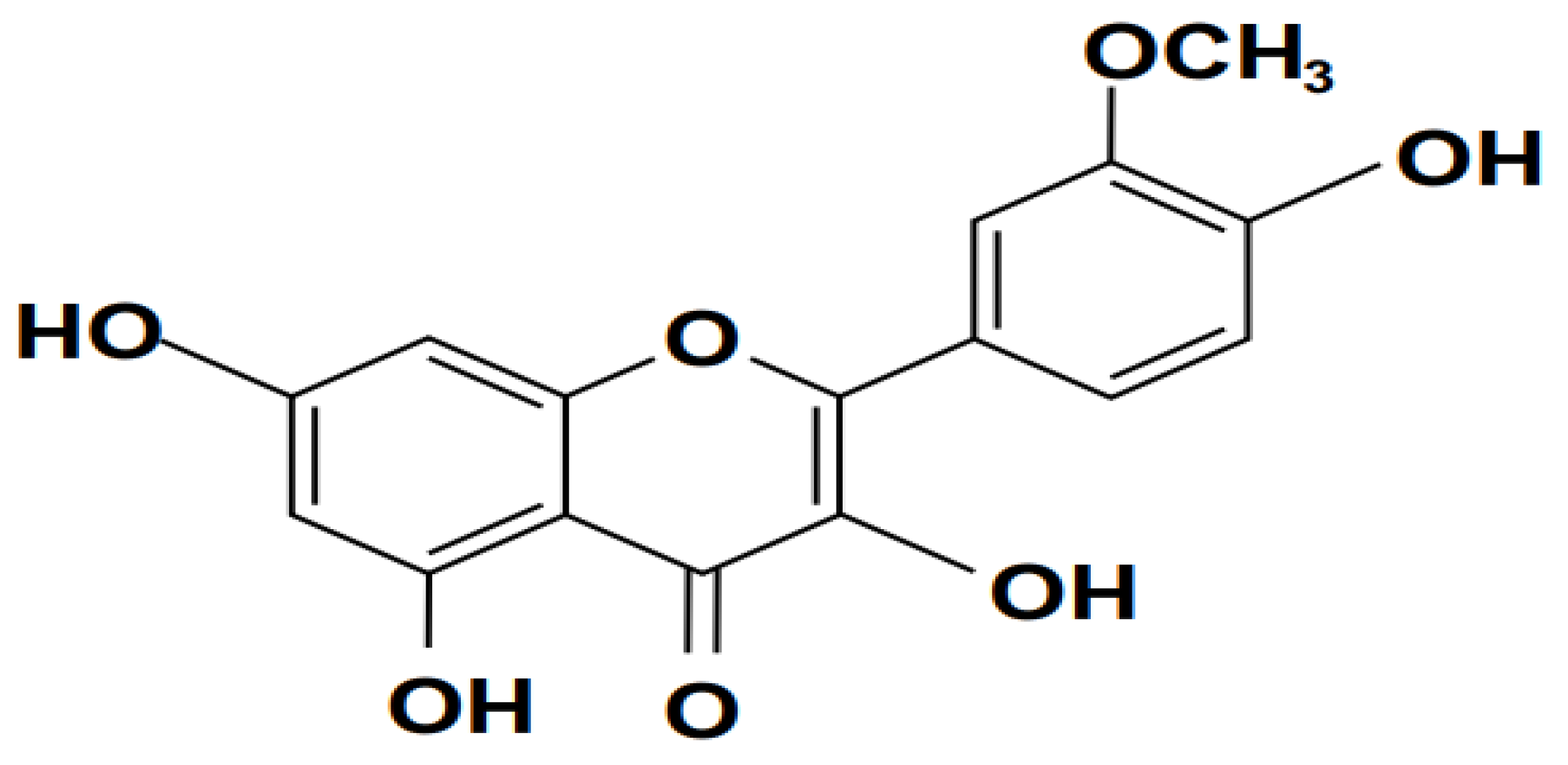
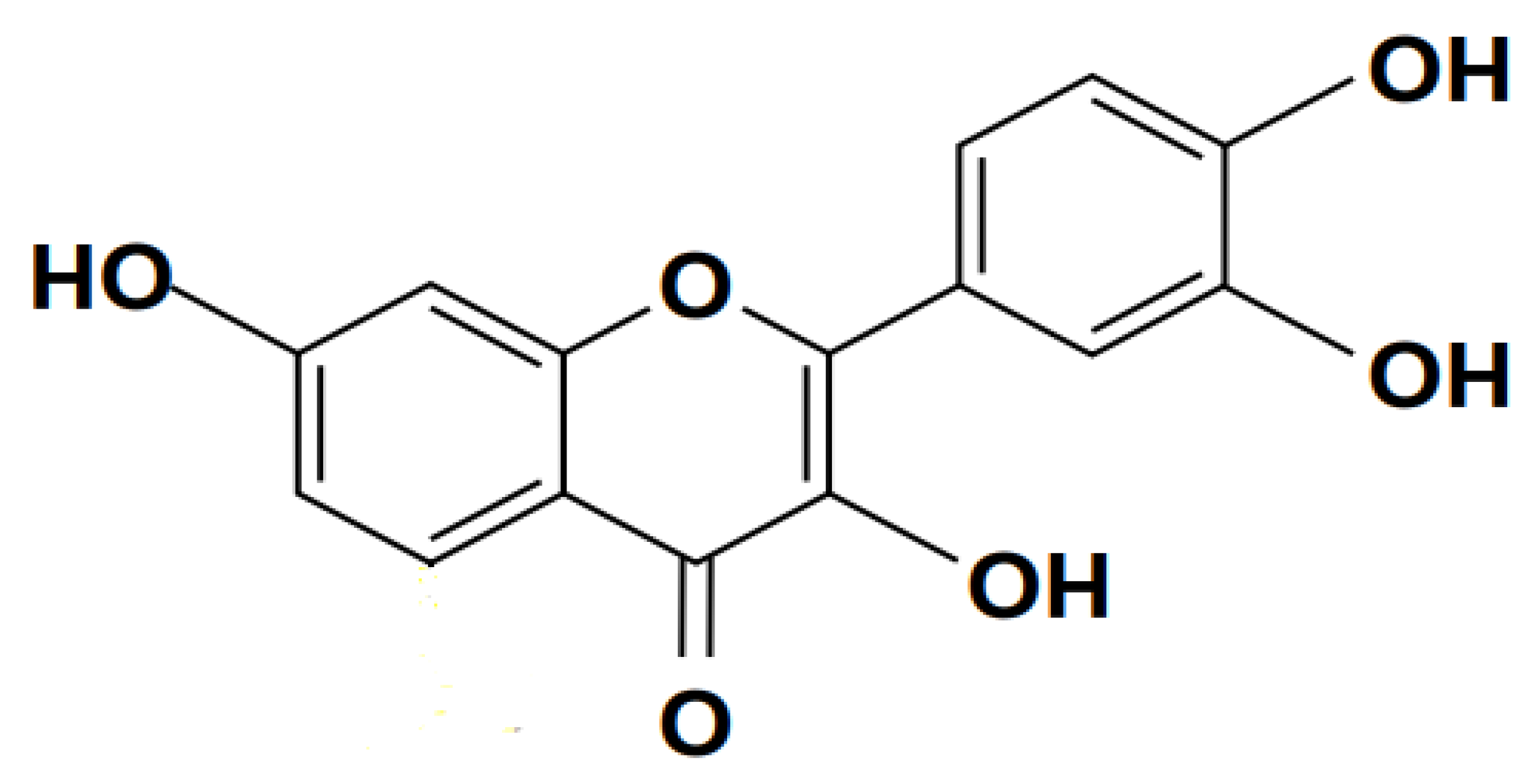
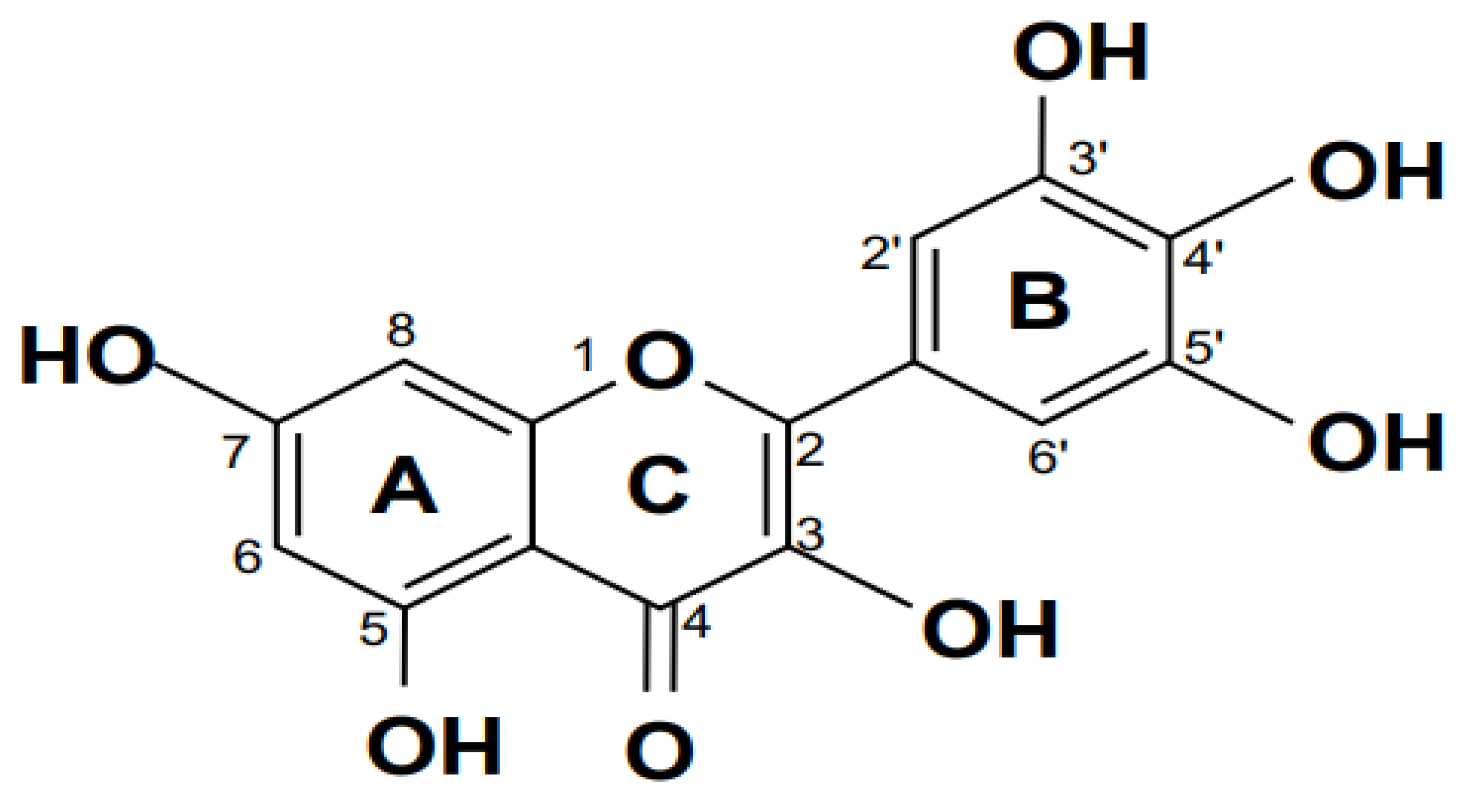
| Year | Author(s) | Title | Purpose/Objectives | Methods | Findings/Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Panche et al. | Flavonoids: An overview | To provide an overview of flavonoids, including their health benefits and potential therapeutic applications. | Review of existing literature | Flavonoids offer preventive effects against coronary heart disease, anti-inflammatory properties, and therapeutic potential for cancer and infectious diseases. |
| 2018 | Perez-Vizcaino & Fraga | Flavonoids in cardiovascular health: A review | To review the role of flavonoids in cardiovascular health, including their effects on endothelial function, blood pressure, and oxidative stress. | Review of existing literature | Flavonoids exhibit cardiovascular benefits by improving endothelial function, reducing blood pressure, and mitigating oxidative stress. |
| 2019 | Antoce & Stockley | The role of polyphenols in cardiovascular disease risk factors: A review | To examine the role of polyphenols, including flavonoids found in red wine, in mitigating cardiovascular disease risk factors. | Review of existing literature | Polyphenols, including flavonoids, found in red wine, contribute to the reduction of cardiovascular disease risk factors such as inflammation and oxidative stress. |
| 2021 | Micek et al. | Flavonoids - A Review of Their Potential Role in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus | To evaluate the potential role of flavonoids in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, including their effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. | Review of existing literature | Flavonoids demonstrate potential in managing diabetes mellitus by improving glucose metabolism and enhancing insulin sensitivity. |
| 2017 | De Souza et al. | Methods for evaluation of food and nutrient intake | To review methods for evaluating food and nutrient intake, with a focus on different approaches used in nutrition research. | Review of existing literature | Various methods, such as dietary recalls, food frequency questionnaires, and biomarkers, are employed to evaluate food and nutrient intake in nutrition research. |
| 2020 | Hong et al. | Nutritional evaluation of food: A review | To provide an overview of nutritional evaluation methods used in assessing the nutritional quality of food products. | Review of existing literature | Nutritional evaluation methods include assessing nutrient content, bioavailability, and bioactivity to determine the overall quality of food products. |
| 2016 | Martnez Steele et al. | Ultra-processed foods and added sugars in the US diet: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study | To investigate the consumption of ultra-processed foods and added sugars in the US diet and their impact on health outcomes. | Cross-sectional study using national dietary data | Consumption of ultra-processed foods and added sugars is associated with poor dietary quality and increased risk of obesity and chronic diseases. |
| 2019 | Neelakantan et al. | Association between ultra-processed food consumption and risk of mortality among middle-aged adults in France | To examine the association between ultra-processed food consumption and risk of mortality among middle-aged adults in France. | Prospective cohort study using dietary data and mortality records | Higher consumption of ultra-processed foods is associated with an increased risk of mortality among middle-aged adults in France. |
| Year | Author(s) | Title | Objectives | Methods | Findings/Results |
| 2007 | Lin et al. | Baicalin: A natural compound with potent pharmacological activities | To investigate the pharmacological activities of baicalin, the primary flavonoid glucoside of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin exhibits antiviral, bacteriostatic, anticancer, and antioxidant properties, and functions as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and neuroprotective agent. |
| 2016 | Shi et al. | Baicalin: A review of its anti-cancer effects and mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma | To review the anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of baicalin in hepatocellular carcinoma. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin demonstrates anti-cancer effects in hepatocellular carcinoma through various mechanisms, including inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. |
| 2023 | Deng et al. | Pharmacological Properties of Baicalin: A Review | To provide an overview of the pharmacological properties of baicalin, including its role as an anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anticancer agent. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin exhibits a wide range of pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anticancer effects, contributing to its therapeutic potential. |
| 2022 | Bao et al. | Baicalin as a natural product: Anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory properties | To investigate the antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory properties of baicalin. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin possesses antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory properties, indicating its potential therapeutic value in various conditions. |
| 2023 | Shahcheraghi et al. | Therapeutic potential of Baicalin in inflammation and organ damage | To explore the therapeutic potential of baicalin in inflammation and organ damage. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin exhibits therapeutic potential in inflammation and organ damage by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide production, and caspase-3 activity. |
| 2019 | Divyakolu et al. | Baicalin as an adjuvant therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection | To investigate the adjuvant therapy potential of baicalin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. | Experimental study using animal models | Baicalin shows promise as an adjuvant therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. |
| 2020 | Song et al. | Baicalin: A potent compound with multiple pharmacological activities | To explore the pharmacological activities of baicalin and its potential as a broad-spectrum antiviral drug. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin exhibits multiple pharmacological activities, including antiviral effects, suggesting its potential as a broad-spectrum antiviral drug. |
| 2020 | Chen et al. | Mechanisms of action of baicalin: A review | To elucidate the mechanisms of action of baicalin, particularly its effects on cytokines and cell pathways. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin modulates various cytokines and cell pathways, contributing to its pharmacological effects and potential as a therapeutic agent. |
| 2021 | Li et al. | Baicalin as a potential therapy for sepsis: Mechanisms and implications | To investigate the potential therapeutic effects of baicalin in sepsis and its underlying mechanisms. | Review of existing literature | Baicalin demonstrates potential as a therapy for sepsis by protecting against liver damage and increasing survival in mice with polymicrobial sepsis. |
| Year | Author(s) | Title | Purpose/Objectives | Methods | Findings/Results |
| 2007 | Zhu et al. | Neuroprotective Effects of Scutellarin | Investigate neuroprotection mechanisms of Scutellarin | Suppressed microglial activation, measured serum (TNF–α, IL–β, IL-6), lactate dehydrogenase activities, tissue glutathione levels. | Scutellarin suppresses microglial activation, reduces serum levels of inflammatory cytokines, and enhances tissue glutathione levels, indicating neuroprotective potential. |
| 2014 | Wang et al. | Scutellarin as a Potential Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy | Assess efficacy of Scutellarin in diabetic retinopathy treatment | Experimental studies on diabetic animal models, evaluation of retinal histopathology and biochemical markers. | Scutellarin shows promise in treating diabetic retinopathy by mitigating retinal histopathological changes and biochemical markers associated with the condition. |
| 2018 | Chledzik et al. | Anti-inflammatory Properties of Scutellarin | Examine anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellarin | In vitro and in vivo studies, assessment of inflammatory markers, histological analysis. | Scutellarin demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory effects both in vitro and in vivo by modulating inflammatory markers and improving tissue histology. |
| 2015 | Niu et al. | Antioxidant Activity of Scutellarin | Investigate antioxidant potential of Scutellarin | In vitro assays evaluating antioxidant capacity, measurement of ROS levels, assessment of lipid peroxidation. | Scutellarin exhibits potent antioxidant activity by scavenging ROS, reducing lipid peroxidation, and enhancing cellular antioxidant defenses. |
| 2007 | Tan et al. | Apoptotic Effects of Scutellarin on Ovarian and Breast Tumor Cells | Explore apoptotic mechanisms induced by Scutellarin in cancer cells | In vitro cell culture experiments, assessment of apoptosis markers, caspase activation assays. | Scutellarin induces apoptosis in ovarian and breast tumor cells through caspase activation, suggesting potential as an anticancer agent. |
| 2013 | Brent & Shao-Nong | Hepatoprotective Effects of Silymarin | Investigate hepatoprotective qualities and mechanisms of Silymarin | Animal models of liver injury, evaluation of liver histology, biochemical analysis of liver function parameters. | Silymarin exhibits hepatoprotective effects by preserving liver histology, reducing biochemical markers of liver injury, and inhibiting neutrophil infiltration. |
| 2018 | Fan et al. | Pharmacotoxicological Research on Silybin | Examine pharmacotoxicological aspects of Silybin, a major component of Silymarin | Pharmacokinetic studies in animals, assessment of toxicity profiles, evaluation of drug tolerance levels. | Silybin demonstrates favorable pharmacotoxicological profiles, indicating high tolerability and low toxicity levels in animals. |
| 2015 | Chan et al. | Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Silymarin | Investigate antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Silymarin | In vitro assays measuring ROS levels, assessment of inflammatory mediators, animal models of sepsis. | Silymarin exhibits potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects by scavenging ROS, reducing inflammatory mediator levels, and protecting against sepsis-induced organ damage. |
| 2020 | Al-Kadi et al. | Protective Effects of Silymarin Against Sepsis | Explore protective effects of Silymarin against sepsis-induced organ damage | Animal models of sepsis, assessment of liver and kidney function, measurement of inflammatory cytokines. | Silymarin protects against sepsis-induced liver and kidney damage by reducing inflammatory cytokine levels and preserving organ function in animal models. |
| 2017 | Chuammitri et al. | Therapeutic Properties of Luteolin | Investigate therapeutic benefits of Luteolin, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties | In vitro and animal studies, assessment of antioxidant activity, evaluation of anti-inflammatory effects, measurement of tumor growth inhibition. | Luteolin exhibits diverse therapeutic properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects, suggesting potential in various disease conditions. |
| 2022 | Pan et al. | Protective Effects of Luteolin Against Ischemia Injury | Evaluate protective effects of Luteolin against ischemia-induced tissue damage | Animal models of ischemia, assessment of tissue damage markers, measurement of ROS levels. | Luteolin protects against ischemia-induced tissue damage by reducing ROS levels, mitigating tissue damage markers, and improving tissue function in animal models. |
| 2022 | Hasan et al. | Anti-Tuberculosis Effects of Quercetin | Investigate the anti-tuberculosis properties of Quercetin | In vitro assays evaluating antimicrobial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. | Quercetin exhibits anti-tuberculosis effects by inhibiting the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
| 2018 | Lesjak et al. | Anti-inflammatory Properties of Quercetin | Examine the anti-inflammatory effects of Quercetin | In vitro studies using RAW264.7 macrophages, assessment of inflammatory marker expression, cytokine production. | Quercetin reduces LPS-induced inflammatory responses by suppressing TNF-α release and IL-1β production in RAW264.7 macrophages. |
| 2016 | Luo et al. | Anti-proliferative Effects of Quercetin | Investigate the anti-proliferative effects of Quercetin on cancer cells | In vitro cell culture experiments, assessment of cell viability, proliferation assays. | Quercetin inhibits cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. |
| 2016 | Karuppagounder et al. | Antioxidant Protection by Quercetin | Evaluate the antioxidant protective effects of Quercetin | In vitro and in vivo assays measuring antioxidant enzyme activity, lipid peroxidation levels, ROS scavenging activity. | Quercetin demonstrates potent antioxidant activity by enhancing antioxidant enzyme levels and reducing oxidative stress markers in vitro and in vivo. |
| 2015 | Huang et al. | Quercetin Pre-treatment in Sepsis | Assess the efficacy of Quercetin pre-treatment in sepsis-induced lung injury | Animal models of sepsis, evaluation of lung pathology, measurement of inflammatory cytokines, IL-10 secretion levels. | Quercetin pre-treatment attenuates lung pathology, reduces inflammatory cytokine levels, and increases IL-10 secretion in sepsis-induced lung injury. |
| 2014 | Maalik et al. | Quercetin Effects on Septic-induced Lung Damage | Investigate the effects of Quercetin on lung damage in septic-induced mice | Animal models of sepsis, assessment of lung histopathology, measurement of blood NO, MDA levels, evaluation of antioxidant enzyme activity. | Quercetin reduces lung damage in septic mice by attenuating lung histopathological changes, lowering NO and MDA levels, and enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity. |
| 2018 | Park et al. | Quercetin Suppresses HMGB1 Expression in Sepsis | Examine the effects of Quercetin on HMGB1 expression and oxidative stress in sepsis | In vivo studies using sepsis-induced animal models, assessment of HMGB1 expression, measurement of oxidative stress markers. | Quercetin suppresses HMGB1 expression, reduces oxidative stress, and improves survival outcomes in sepsis-induced animal models. |
| 2019 | Cui et al. | Quercetin Alleviates Lung Damage in Septic Mice | Investigate the protective effects of Quercetin on lung damage in septic mice | Animal models of sepsis, evaluation of lung edema, alveolar capacity, histological analysis. | Quercetin alleviates lung damage in septic mice by reducing lung edema, preserving alveolar capacity, and protecting lung tissues. |
| 2013 | Dai et al. | Quercetin Inhibition of NF-κB Activation | Examine the inhibitory effects of Quercetin on NF-κB activation | In vitro studies using LPS-stimulated macrophages, assessment of NF-κB activation, measurement of inflammatory mediator production. | Quercetin inhibits NF-κB activation and reduces the production of inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated macrophages. |
| 2012 | Bharrhan et al. | Quercetin Regulation of Oxidative Enzymes and NF-κB | Investigate the regulatory effects of Quercetin on oxidative enzymes and NF-κB signaling pathways | In vivo studies using animal models, assessment of oxidative enzyme levels, NF-κB expression analysis. | Quercetin regulates oxidative enzyme production and suppresses NF-κB signaling pathways in vivo, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. |
| 2014 | Wang et al. | Quercetin Reduces Lung Damage and Inflammatory Markers | Evaluate the effects of Quercetin on lung damage and inflammatory markers in sepsis-induced animals | Animal models of sepsis, measurement of inflammatory markers, histological analysis of lung tissues. | Quercetin reduces lung damage and inflammatory markers in sepsis-induced animals, improving survival outcomes and lung function. |
| 2012 | Ozcan et al. | Myricetin Effects on Diabetic Erythrocytes | Investigate the effects of Myricetin on oxidative stress and kidney function in diabetic erythrocytes | In vitro and in vivo studies, assessment of oxidative stress markers, measurement of kidney function parameters. | Myricetin reduces oxidative stress and improves kidney function in diabetic erythrocytes, suggesting potential therapeutic benefits in diabetes. |
| 2021 | Imran et al. | Anti-inflammatory Effects of Myricetin | Examine the anti-inflammatory effects of Myricetin on sepsis-induced inflammation | In vitro and in vivo studies using sepsis-induced animal models, assessment of inflammatory markers, NF-κB signaling analysis. | Myricetin attenuates sepsis-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-κB signaling and reducing inflammatory mediator production in vitro and in vivo. |
| 2013 | Lee et al. | Fisetin Inhibition of HMGB1 Release in Vascular Inflammation | Investigate the inhibitory effects of Fisetin on HMGB1 release and vascular inflammation | In vivo studies using animal models of vascular inflammation, measurement of HMGB1 levels, assessment of vascular function. | Fisetin inhibits HMGB1 release, reduces vascular inflammation, and improves vascular function in animal models of vascular inflammation. |
| 2020 | Zhang et al. | Fisetin Protection Against CLP-induced Organ Damage | Assess the protective effects of Fisetin against organ damage induced by CLP in sepsis | Animal models of sepsis, evaluation of organ pathology, measurement of inflammatory markers, assessment of oxidative stress. | Fisetin protects against CLP-induced organ damage in sepsis by attenuating organ pathology, reducing inflammatory markers, and alleviating oxidative stress. |
| 2019 | Grynkiewicz & Demchuk | Fisetin as a Promising Antioxidant | Investigate the antioxidant properties of Fisetin | In vitro assays evaluating antioxidant capacity, measurement of ROS levels, assessment of lipid peroxidation. | Fisetin exhibits potent antioxidant activity by scavenging ROS, reducing lipid peroxidation, and enhancing cellular antioxidant defenses. |
| 2016 | Almatroodi et al. | Pharmacological Activities of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate | Explore the pharmacological activities of EGCG | In vitro and in vivo studies, assessment of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer effects. | EGCG demonstrates diverse pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




