Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
21 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Review Approach
2.2. Research Questions
- What are the facilitators influencing routine vaccination uptake in Nigeria?
- What are the specific barriers contributing to missed and zero doses children in Nigeria's vaccination programs?
- What variations exist at state and regional levels regarding barriers and facilitators of vaccination uptake in Nigeria?
2.3. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.4. Study Selection
2.4.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.4.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Study Identification
2.6. Data Extraction
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Ethical Consideration
3. Results
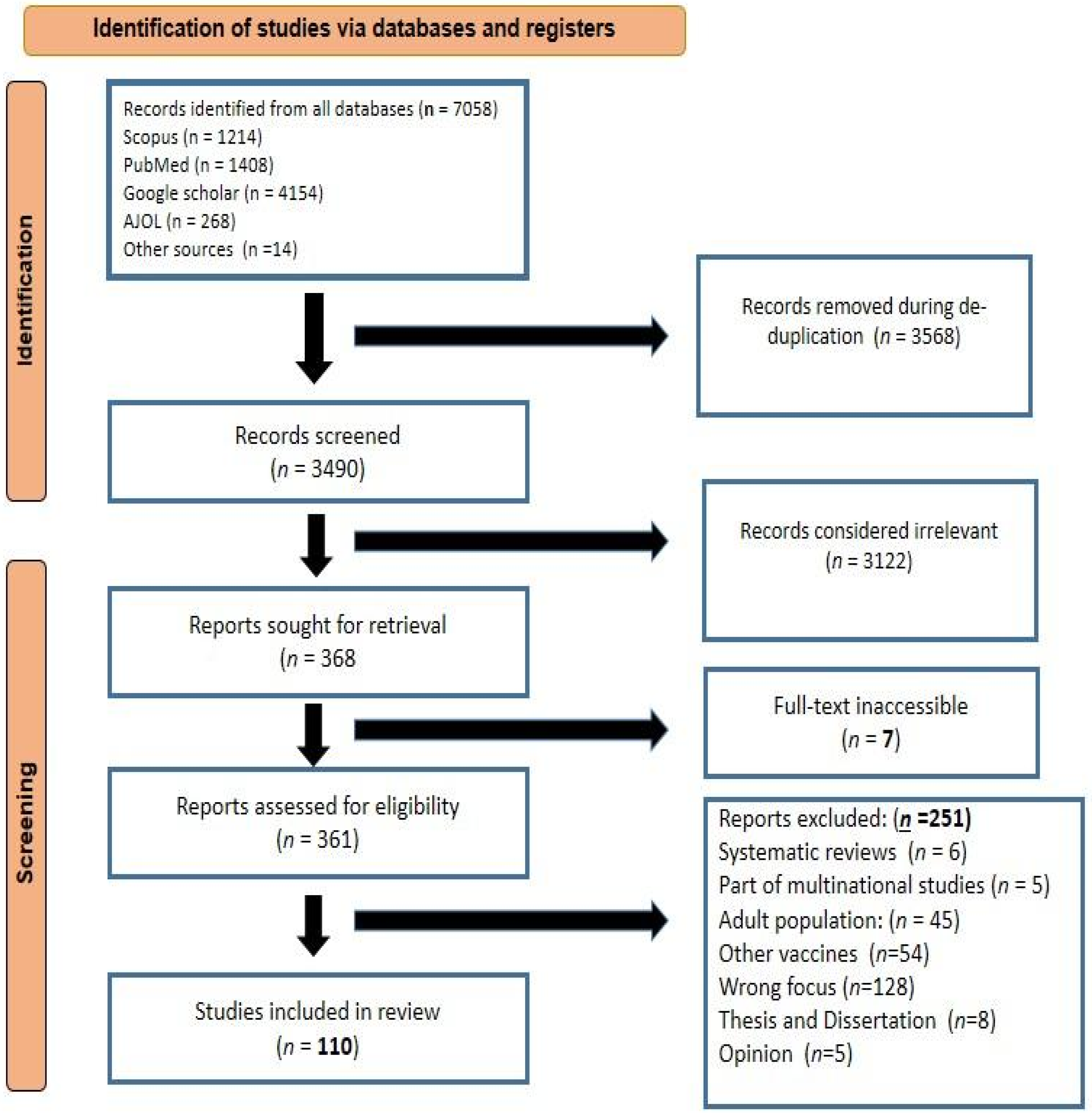
3.1. Study Selection and Inclusion Process
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
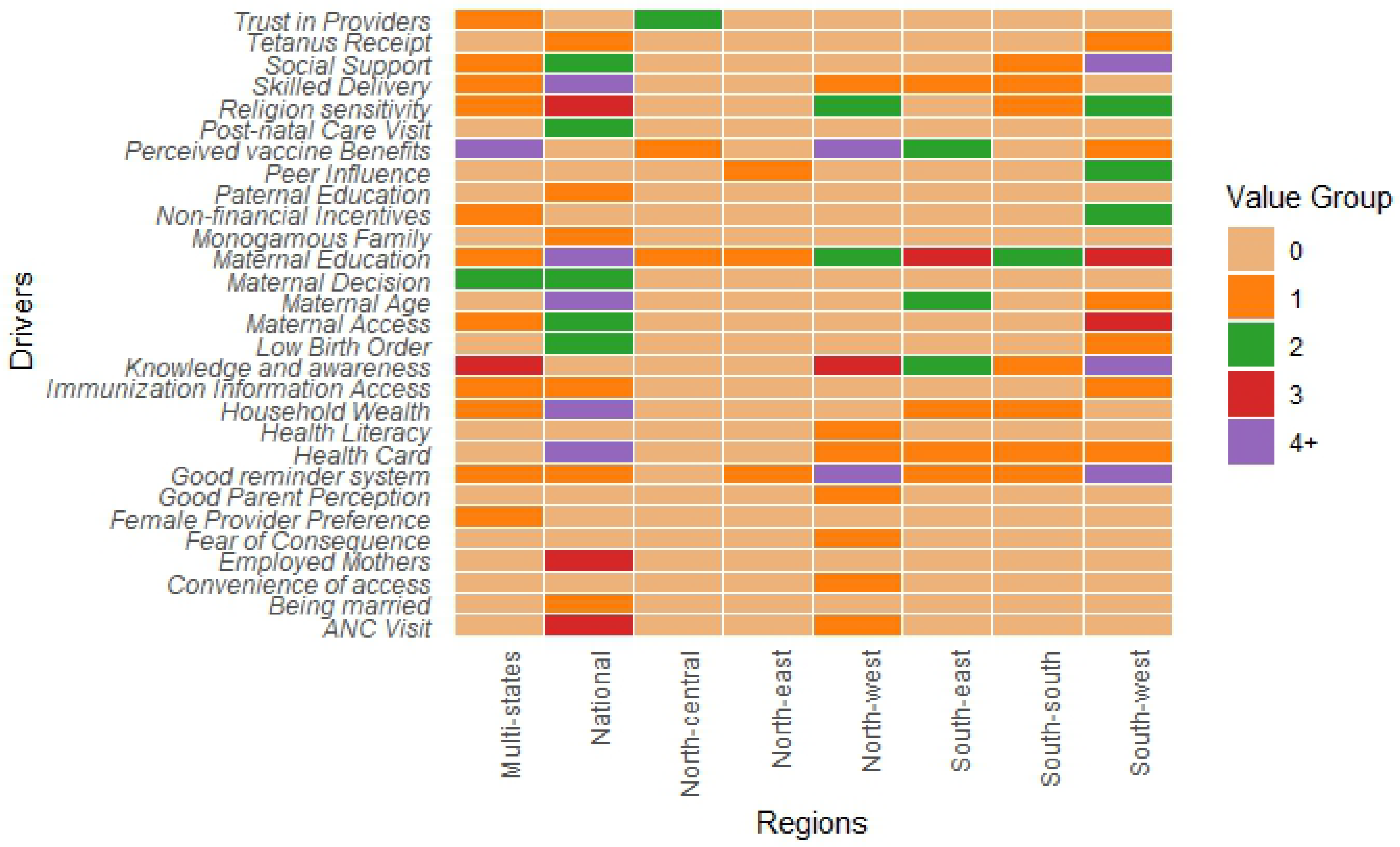
3.3 Facilitators of Routine Immunization in Nigeria
3.3.1. Caregiver-Related Drivers
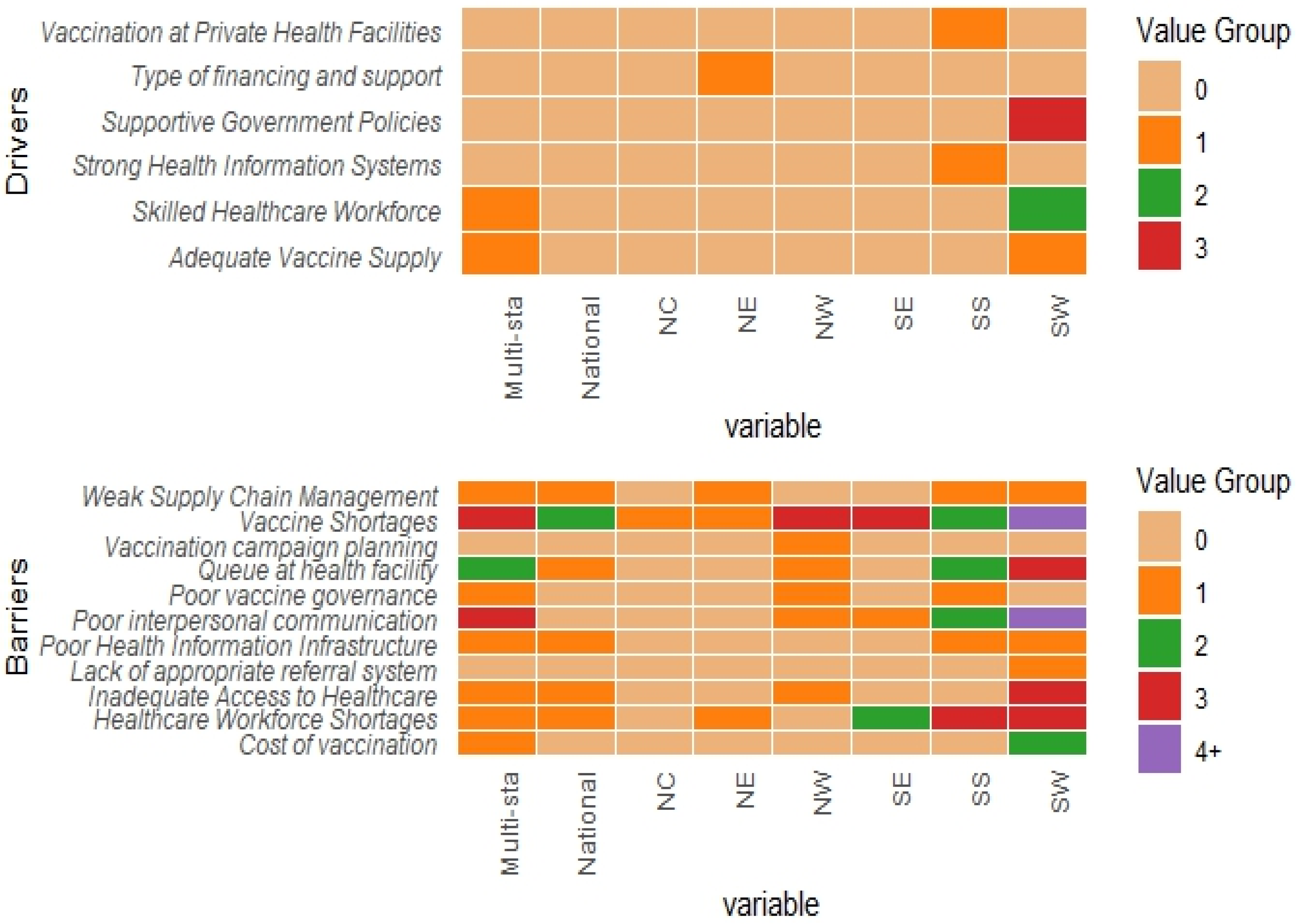
3.3.2. Health-System Related Drivers
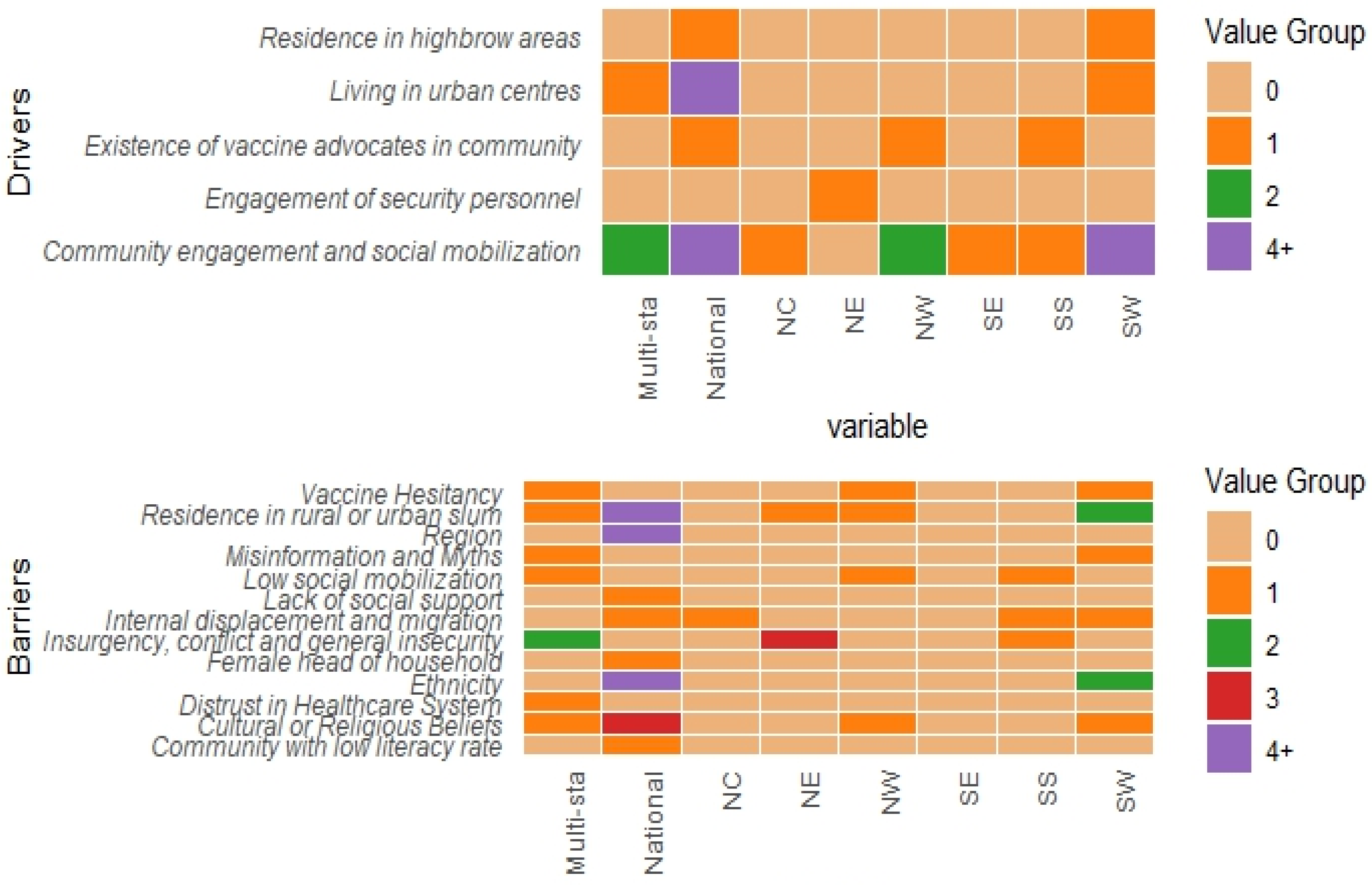
3.3.3. Community/Social Context Related Drivers
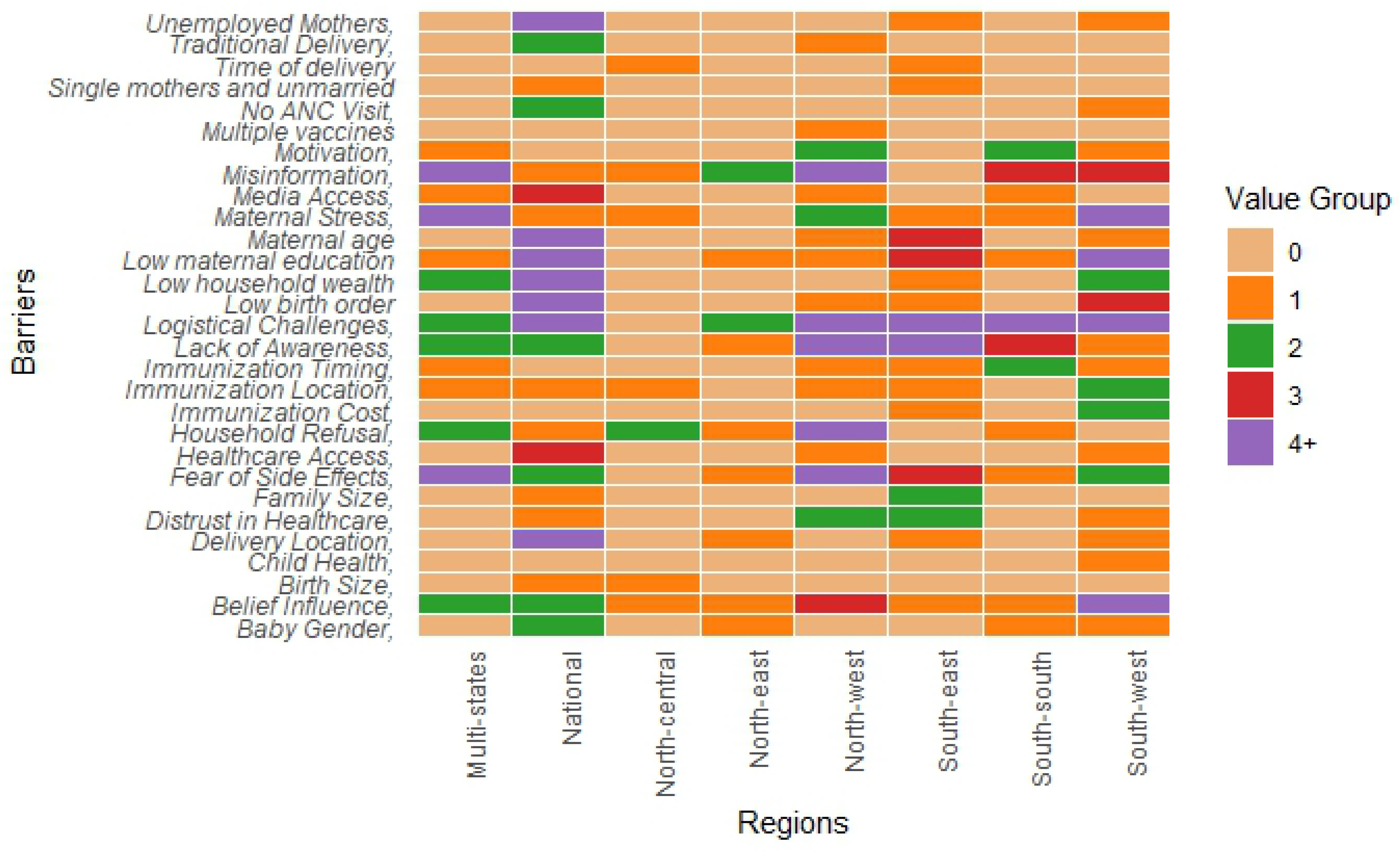
3.4. Barriers of Routine Immunization in Nigeria
3.4.1. Caregiver-Related Barriers
3.4.2. Health System-Related Barriers
3.4.3. Community/Social Context Related Barriers
3.5. Regional Insights into Childhood Immunization Dynamics in Nigeria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
7. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Immunization. WHO Reg Off Afr 2023. https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/immunization (accessed September 23, 2023).
- Unicef undefined. Levels and trends in child mortality report 2017 2017.
- Yamey G, Garcia P, Hassan F, Mao W, McDade KK, Pai M, et al. It is not too late to achieve global covid-19 vaccine equity. BMJ 2022;376:e070650. [CrossRef]
- WHO/UNICEF. Progress and Challenges with achieving Universal Immunization Coverage: 2022 Estimates of National Immunization coverage. 2022.
- Hosseinpoor AR, Bergen N, Schlotheuber A, Gacic-Dobo M, Hansen PM, Senouci K, et al. State of inequality in diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis immunisation coverage in low-income and middle-income countries: a multicountry study of household health surveys. Lancet Glob Health 2016;4:e617–26. [CrossRef]
- Khetsuriani N, Mosina L, Van Damme P, Mozalevskis A, Datta S, Tohme RA. Progress Toward Hepatitis B Control - World Health Organization European Region, 2016-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1029–35. [CrossRef]
- Mahachi K, Kessels J, Boateng K, Jean Baptiste AE, Mitula P, Ekeman E, et al. Zero- or missed-dose children in Nigeria: Contributing factors and interventions to overcome immunization service delivery challenges. Vaccine 2022;40:5433–44. [CrossRef]
- Akwataghibe NN, Ogunsola EA, Broerse JEW, Popoola OA, Agbo AI, Dieleman MA. Exploring Factors Influencing Immunization Utilization in Nigeria—A Mixed Methods Study. Front Public Health 2019;7.
- Ataguba JE, Ojo KO, Ichoku HE. Explaining socio-economic inequalities in immunization coverage in Nigeria. Health Policy Plan 2016;31:1212–24.
- Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth 2020;18:2119. [CrossRef]
- Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 2005;8:19–32. [CrossRef]
- Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018;169:467–73. [CrossRef]
- Bedford H, Attwell K, Danchin M, Marshall H, Corben P, Leask J. Vaccine hesitancy, refusal and access barriers: The need for clarity in terminology. Vaccine 2018;36:6556–8. [CrossRef]
- Olaniyan A, Isiguzo C, Hawk M. The Socioecological Model as a framework for exploring factors influencing childhood immunization uptake in Lagos state, Nigeria. BMC Public Health 2021;21:867. [CrossRef]
- Omoleke SA, Tadesse MG. A pilot study of routine immunization data quality in Bunza Local Government area: causes and possible remedies. Pan Afr Med J 2017;27. [CrossRef]
- Abad N, Uba BV, Patel P, Barau DN, Ugochukwu O, Aliyu N, et al. A rapid qualitative assessment of barriers associated with demand and uptake of health facility-based childhood immunizations and recommendations to improve immunization service delivery in Sokoto State, Northwest Nigeria, 2017. Pan Afr Med J 2021;40:10. [CrossRef]
- Odinaka. Acceptance of mobile phone short message service for childhood immunisation reminders by Nigerian mothers n.d. https://www.phmj.org/article.asp?issn=0795-3038;year=2018;volume=12;issue=3;spage=127;epage=130;aulast=Odinaka (accessed October 5, 2023).
- Michael CA, Team OCMCS, Ashenafi S, Team OCMCS, Ogbuanu IU, Team OCMCS, et al. An evaluation of community perspectives and contributing factors to missed children during an oral polio vaccination campaign–Katsina State, Nigeria. J Infect Dis 2014;210:S131–5.
- Uwaibi N, Erah F. Assessment of healthcare worker’s implementation of childhood routine immunization in primary healthcare centers in Edo State, Nigeria: A mixed method survey. Ann Clin Biomed Res 2021;2. [CrossRef]
- Danjuma SD, Ibrahim AI, Shehu NY, Diala MU, Pam CV, Ogbodo CO. At-birth vaccination timeliness: An analysis of inborns in the highlands of Jos, North-Central Nigeria. Niger Postgrad Med J 2020;27:209–14. [CrossRef]
- Ekhaguere OA, Oluwafemi RO, Badejoko B, Oyeneyin LO, Butali A, Lowenthal ED, et al. Automated phone call and text reminders for childhood immunisations (PRIMM): a randomised controlled trial in Nigeria. BMJ Glob Health 2019;4:e001232. [CrossRef]
- Akaba GO, Dirisu O, Okunade KS, Adams E, Ohioghame J, Obikeze OO, et al. Barriers and facilitators of access to maternal, newborn and child health services during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria: findings from a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 2022;22:611. [CrossRef]
- Freeland C, Kanu F, Mohammed Y, Nwokoro UU, Sandhu H, Ikwe H, et al. Barriers and facilitators to hepatitis B birth dose vaccination: Perspectives from healthcare providers and pregnant women accessing antenatal care in Nigeria. PLOS Glob Public Health 2023;3:e0001332.
- Olaniyan A, Isiguzo C, Agbomeji S, Akinlade-Omeni O, Ifie B, Hawk M. Barriers, facilitators, and recommendations for childhood immunisation in Nigeria: perspectives from caregivers, community leaders, and healthcare workers. Pan Afr Med J 2022;43.
- Nasiru S-G, Aliyu GG, Gasasira A, Aliyu MH, Zubair M, Mandawari SU, et al. Breaking community barriers to polio vaccination in northern Nigeria: the impact of a grass roots mobilization campaign (Majigi). Pathog Glob Health 2012;106:166–71. [CrossRef]
- Adekunle L. Child immunization—What are the impediments for reaching desired goals in a transitional society? Soc Sci Med Part Med Psychol Med Sociol 1978;12:353–7. [CrossRef]
- McGavin ZA, Wagner AL, Carlson BF, Power LE, Eboreime E, Boulton ML. Childhood full and under-vaccination in Nigeria, 2013. Vaccine 2018;36:7294–9. [CrossRef]
- Uthman OA, Adedokun ST, Olukade T, Watson S, Adetokunboh O, Adeniran A, et al. Children who have received no routine polio vaccines in Nigeria: Who are they and where do they live? Hum Vaccines Immunother 2017;13:2111–22. [CrossRef]
- Babalola S. COMMUNITY AND SYSTEMIC FACTORS AFFECTING THE UPTAKE OF IMMUNISATION IN NIGERIA: A QUALITATIVE STUDY IN FIVE STATES 2023.
- McArthur-Lloyd A, McKenzie A, Findley SE, Green C, Adamu F. Community Engagement, Routine Immunization, and the Polio Legacy in Northern Nigeria. Glob Health Commun 2016;2:1–10. [CrossRef]
- Itimi K, Dienye PO, Ordinioha B. Community participation and childhood immunization coverage: a comparative study of rural and urban communities of Bayelsa State, south-south Nigeria. Niger Med J J Niger Med Assoc 2012;53:21.
- Nalley JC, Maduka O. Completeness and timeliness of immunization among children aged 12 to 23 months in South-South Nigeria. J Community Med Prim Health Care 2019;31:22–31. [CrossRef]
- Onyeneho N, Igwe I, I’Aronu N, Okoye U. Compliance With Regimens of Existing Vaccines in Orumba North Local Government Area of Anambra State, Nigeria. Int Q Community Health Educ 2015;35:120–32. [CrossRef]
- Duru JI, Usman S, Adeosun O, Stamidis KV, Bologna L. Contributions of volunteer community mobilizers to polio eradication in Nigeria: the experiences of non-governmental and civil society organizations. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2019;101:74.
- Kawakatsu Y, Adesina AO, Kadoi N, Aiga H. Cost-effectiveness of SMS appointment reminders in increasing vaccination uptake in Lagos, Nigeria: a multi-centered randomized controlled trial. Vaccine 2020;38:6600–8.
- Nwangwu CC, Chike AE, Eucharia Ijeoma IO. Cross-sectional Survey on Parental Perception and Attitude on Measles Vaccine: Low Hospital Measles Case Presentation in Rural Area in Enugu Nigeria. J Clin Diagn Res 2021;15.
- Obi-Jeff C, Garcia C, Onuoha O, Adewumi F, David W, Bamiduro T, et al. Designing an SMS reminder intervention to improve vaccination uptake in Northern Nigeria: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 2021;21:844. [CrossRef]
- Konwea PE, David FA, Ogunsile SE. Determinants of compliance with child immunization among mothers of children under five years of age in Ekiti State, Nigeria. J Health Res 2018;32:229–36. [CrossRef]
- Alhassan NH, Hamza AM, Bala U, Kaugama BM. Determinants of Immunization Coverage in Children 12-23 Months in Miga Local Government Area, Jigawa State Nigeria. South Am J Public Health 2016:1–13.
- Gidado S, Nguku P, Biya O, Waziri N, Mohammed A, Nsubuga P. Determinants of routine immunization coverage in Bungudu, Zamfara state, northern Nigeria, may 2010. Pan Afr Med J. 2014; 18 n.d.
- Babalola S. Determinants of the Uptake of the Full Dose of Diphtheria–Pertussis–Tetanus Vaccines (DPT3) in Northern Nigeria: A Multilevel Analysis. Matern Child Health J 2009;13:550–8. [CrossRef]
- Fatiregun AA, Etukiren EE. Determinants of uptake of third doses of oral polio and DTP vaccines in the Ibadan North Local Government Area of Nigeria. Int Health 2014;6:213–24.
- Olumuyiwa O Odusanya. Determinants of vaccination coverage in rural Nigeria | BMC Public Health | Full Text n.d. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2458-8-381 (accessed October 14, 2023).
- Sato R. Differential determinants and reasons for the non-and partial vaccination of children among Nigerian caregivers. Vaccine 2020;38:63–9.
- IPSOS. Drivers And Barriers To Uptake And Completion Of Early Years Vaccination: Early Insights n.d.
- Sato R. Effect of armed conflict on vaccination: evidence from the Boko haram insurgency in northeastern Nigeria. Confl Health 2019;13:49. [CrossRef]
- Balogun FM, Bamidele OS, Bamgboye EA. Effect of intensive training in improving older women’s knowledge and support for infant vaccination in Nigerian urban slums: a before-and-after intervention study. BMC Public Health 2021;21:266. [CrossRef]
- Brown VB, Oluwatosin OA, Akinyemi JO, Adeyemo AA. Effects of Community Health Nurse-Led Intervention on Childhood Routine Immunization Completion in Primary Health Care Centers in Ibadan, Nigeria. J Community Health 2016;41:265–73. [CrossRef]
- Dougherty L, Abdulkarim M, Ahmed A, Cherima Y, Ladan A, Abdu S, et al. Engaging traditional barbers to identify and refer newborns for routine immunization services in Sokoto, Nigeria: a mixed methods evaluation. Int J Public Health 2020;65:1785–95. [CrossRef]
- Afolabi RF, Salawu MM, Gbadebo BM, Salawu AT, Fagbamigbe AF, Adebowale AS. Ethnicity as a cultural factor influencing complete vaccination among children aged 12-23 months in Nigeria. Hum Vaccines Immunother 2021;17:2008–17. [CrossRef]
- Fagbamigbe AF, Lawal TV, Atoloye KA. Evaluating the performance of different Bayesian count models in modelling childhood vaccine uptake among children aged 12–23 months in Nigeria. BMC Public Health 2023;23:1197. [CrossRef]
- Balogun FM, Omotade OO. Facilitators and barriers of healthcare workers’ recommendation of HPV vaccine for adolescents in Nigeria: views through the lens of theoretical domains framework. BMC Health Serv Res 2022;22:824. [CrossRef]
- Taiwo L, Idris S, Abubakar A, Nguku P, Nsubuga P, Gidado S, et al. Factors affecting access to information on routine immunization among mothers of under 5 children in Kaduna State Nigeria, 2015. Pan Afr Med J 2017;27.
- Oku A, Oyo-Ita A, Glenton C, Fretheim A, Eteng G, Ames H, et al. Factors affecting the implementation of childhood vaccination communication strategies in Nigeria: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2017;17:1–12.
- Ghani NA, Dalhatu S, Adam MF, Ghazalli FSM. Factors Associated with Polio Immunization Resistivityin Kano State, Nigeria. Env Sci 2015.
- Sadoh AE, Sadoh WE, Uduebor J, Ekpebe P, Iguodala O. Factors contributing to delay in commencement of immunization in Nigerian infants. Tanzan J Health Res 2013;15.
- Rahji FatimaR. Factors Influencing Compliance with Immunization Regimen among Mothers in Ibadan, Nigeria. IOSR J Nurs Health Sci 2013;2:01–9. [CrossRef]
- Antai D. Gender inequities, relationship power, and childhood immunization uptake in Nigeria: a population-based cross-sectional study. Int J Infect Dis 2012;16:e136–45.
- Tobin-West CI, Alex-Hart BA. Identifying Barriers and Sustainable Solution to Childhood Immunization in Khana Local Government Area of Rivers State, Nigeria. Int Q Community Health Educ 2012;32:149–58. [CrossRef]
- Adedire EB, Ajayi I, Fawole OI, Ajumobi O, Kasasa S, Wasswa P, et al. Immunisation coverage and its determinants among children aged 12-23 months in Atakumosa-west district, Osun State Nigeria: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2016;16:905. [CrossRef]
- Fajola A, Chidozie B. Immunization Completion Rates in a Cottage Hospital in the Niger Delta Area of Nigeria 2018;Volume 8:51–3.
- Nkwogu L, Shuaib F, Braka F, Mkanda P, Banda R, Korir C, et al. Impact of engaging security personnel on access and polio immunization outcomes in security-inaccessible areas in Borno state, Nigeria. BMC Public Health 2018;18:1311. [CrossRef]
- Walker J-A, Hashim Y, Oranye N. Impact of Muslim opinion leaders’ training of healthcare providers on the uptake of MNCH services in Northern Nigeria. Glob Public Health 2019;14:200–13. [CrossRef]
- Gooding E, Spiliotopoulou E, Yadav P. Impact of vaccine stockouts on immunization coverage in Nigeria. Vaccine 2019;37:5104–10.
- Obi-Jeff C, Garcia C, Adewumi F, Bamiduro T, David W, Labrique A, et al. Implementing SMS reminders for routine immunization in Northern Nigeria: a qualitative evaluation using the RE-AIM framework. BMC Public Health 2022;22:2370. [CrossRef]
- Yau IB, Mustapha MZ, Nwaze E, Nobila O, Maigoro A, Abdullah A, et al. Improving the timeliness and completeness of childhood vaccination through color-coded bracelets: a pilot study among Fulani tribe populations in Nigeria. J Public Health Afr 2023.
- Adedokun ST, Uthman OA, Adekanmbi VT, Wiysonge CS. Incomplete childhood immunization in Nigeria: a multilevel analysis of individual and contextual factors. BMC Public Health 2017;17:236. [CrossRef]
- Oleribe O, V K, A A-O, Sd T-R. Individual and socioeconomic factors associated with childhood immunization coverage in Nigeria. Pan Afr Med J 2017;26. [CrossRef]
- Adeiga A, Omilabu SA, Audu RA, Sanni FA, Lakehinde GF, Balogun O, et al. Infant immunization coverage in difficult-to-reach area of Lagos metropolis. Afr J Clin Exp Microbiol 2005;6:227–31. [CrossRef]
- Korave J, Bawa S, Ageda B, Ucho A, Bem-Bura DM, Onimisi A, et al. Internal displacement; an impediment to the successful implementation of planned measles supplemental activities in Nigeria, a case study of Benue State. Vaccine 2021;39:C76–81.
- Limaye RJ, Sara AB, Siddique AR, Vivas C, Malik S, Omonoju K. Interpersonal and community influences affecting childhood vaccination decision-making among Nigerian caregivers: Perceptions among frontline workers in Nigeria. J Child Health Care 2019;23:403–14. [CrossRef]
- Umoke PCI, Umoke M, Nwalieji CA, Igwe FO, Umoke UG, Onwe RN, et al. Investigating Factors Associated with Immunization Incompletion of Children Under Five in Ebonyi State, Southeast Nigeria: Implication for Policy Dialogue. Glob Pediatr Health 2021;8:2333794X2199100. [CrossRef]
- Sibeudu FT, Uzochukwu BSC, Onwujekwe OE. Investigating socio-economic inequity in access to and expenditures on routine immunization services in Anambra state. BMC Res Notes 2017;10:78. [CrossRef]
- Mangal TD, Aylward RB, Mwanza M, Gasasira A, Abanida E, Pate MA, et al. Key issues in the persistence of poliomyelitis in Nigeria: a case-control study. Lancet Glob Health 2014;2:e90–7.
- Adegbenro CA, Olowookere SA, Fehintola FO, Adegbenro PA, Orioke OT. Knowledge about and preventive practices against neonatal tetanus among young Nigerian women. Tzu-Chi Med J 2019;31:154.
- M Shuaibu F, Birukila G, Usman S, Mohammed A, Galway M, Corkum M, et al. Mass immunization with inactivated polio vaccine in conflict zones – Experience from Borno and Yobe States, North-Eastern Nigeria. J Public Health Policy 2016;37:36–50. [CrossRef]
- Fatiregun AA, Okoro AO. Maternal determinants of complete child immunization among children aged 12–23 months in a southern district of Nigeria. Vaccine 2012;30:730–6. [CrossRef]
- Okenwa UJ, Dairo MD, Bamgboye E, Ajumobi O. Maternal knowledge and infant uptake of valid hepatitis B vaccine birth dose at routine immunization clinics in Enugu State – Nigeria. Vaccine 2020;38:2734–40. [CrossRef]
- Okenwa UJ, Dairo MD, Uba B, Ajumobi O. Maternal reasons for non-receipt of valid Hepatitis B birth dose among mother-infant pairs attending routine immunization clinics, South-east, Nigeria. Vaccine 2019;37:6894–9.
- Chidiebere ODI, Uchenna E, Kenechi OS. Maternal sociodemographic factors that influence full child immunisation uptake in Nigeria. South Afr J Child Health 2014;8:138–42.
- Okafor IP, Chukwudi CL, Igwilo UU, Ogunnowo BE. “Men are the head of the family, the dominant head”: A mixed method study of male involvement in maternal and child health in a patriarchal setting, Western Nigeria. PLOS ONE 2022;17:e0276059. [CrossRef]
- Antai D. Migration and child immunization in Nigeria: individual- and community-level contexts. BMC Public Health 2010;10:116. [CrossRef]
- Fatiregun AA, Lochlainn LN, Kaboré L, Dosumu M, Isere E, Olaoye I, et al. Missed opportunities for vaccination among children aged 0–23 months visiting health facilities in a southwest State of Nigeria, December 2019. PLOS ONE 2021;16:e0252798. [CrossRef]
- MRITE. Momentum Routine Immunization Transformation and Equity : Baseline Assessment of Routine Immunization Services Performance. n.d.
- Adegboye OA, Kotze D, Adegboye OA. Multi-year trend analysis of childhood immunization uptake and coverage in Nigeria. J Biosoc Sci 2014;46:225–39.
- Aheto JMK, Pannell O, Dotse-Gborgbortsi W, Trimner MK, Tatem AJ, Rhoda DA, et al. Multilevel analysis of predictors of multiple indicators of childhood vaccination in Nigeria. Plos One 2022;17:e0269066.
- Oladepo O, Dipeolu IO, Oladunni O. Nigerian rural mothers’ knowledge of routine childhood immunizations and attitudes about use of reminder text messages for promoting timely completion. J Public Health Policy 2019;40:459–77. [CrossRef]
- Obanewa OA. Optimising childhood immunisation in Nigeria. phd. University of Southampton, 2019.
- Oku A, A O-I, C G, A F, H A, A M, et al. Perceptions and experiences of childhood vaccination communication strategies among caregivers and health workers in Nigeria: A qualitative study. PloS One 2017;12. [CrossRef]
- Etokidem A, Nkpoyen F, Ekanem C, Mpama E, Isika A. Potential barriers to and facilitators of civil society organization engagement in increasing immunization coverage in Odukpani Local Government Area of Cross River State, Nigeria: an implementation research. Health Res Policy Syst 2021;19:1–12.
- Ogbuabor DC, Chime AC. Prevalence and predictors of vaccine hesitancy among expectant mothers in Enugu metropolis, South-east Nigeria. J Public Health Policy 2021;42:222–35. [CrossRef]
- Victoria TO, Ogunleye A, Abubakar MA, Abacha M, Okijiola SO, Adediji PO. Routine Immunization Compliance among Nursing Mothers in Ibadan North East Local Government, Oyo State, Nigeria. Eur J Mod Med Pract 2023;3:82–93.
- Gunnala R, Ogbuanu IU, Adegoke OJ, Scobie HM, Uba BV, Wannemuehler KA, et al. Routine Vaccination Coverage in Northern Nigeria: Results from 40 District-Level Cluster Surveys, 2014-2015. PLOS ONE 2016;11:e0167835. [CrossRef]
- Antai D. Rural-urban inequities in childhood immunisation in Nigeria: The role of community contexts. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med 2011;3:1–8.
- Nwokocha EE, Obioma C. Social and cultural factors influencing immunization of children in rural Abia State, Nigeria. Int J Child Youth Fam Stud 2016;7:404–22.
- Monguno AK. Socio cultural and geographical determinants of child immunisation in Borno State, Nigeria. J Public Health Afr 2013;4.
- Oluwatosin OA. Socio-demographic factors associated with childhood immunization uptake in Akinyele Local Government Area, Oyo State, Nigeria. Afr J Med Med Sci 2012;41:161–7.
- Ilusanya T, Oladosun M. Socio-Economic Factors Influencing Health Behavior of Women and Immunization Status of Children in Nigeria. 2017.
- Okoro JC, Ojinnaka NC, Ikefuna AN, Onyenwe NE. Sociodemographic influences on immunization of children with chronic neurological disorders in Enugu, Nigeria. Trials Vaccinol 2015;4:9–13.
- Lawal TV, Atoloye KA, Adebowale AS, Fagbamigbe AF. Spatio-temporal analysis of childhood vaccine uptake in Nigeria: a hierarchical Bayesian Zero-inflated Poisson approach. BMC Pediatr 2023;23:493. [CrossRef]
- Korir C, Shuaib F, Adamu U, Bawa S, Musa A, Bashir A, et al. Targeting the last polio sanctuaries with Directly Observed Oral Polio Vaccination (DOPV) in northern Nigeria, (2014–2016). BMC Public Health 2018;18:1314. [CrossRef]
- Babakura B, Nomhwange T, Baptiste AEJ, Dede O, Taiwo L, Abba S, et al. The challenges of insecurity on implementing vaccination campaign and its effect on measles elimination and control efforts: A case study of 2017/18 measles campaign in Borno state, Nigeria q 2021.
- Sato R, Belel A. The effect of performance-based financing on child vaccinations in northern Nigeria. Vaccine 2020;38:2209–15.
- Anichukwu OI, Asamoah BO. The impact of maternal health care utilisation on routine immunisation coverage of children in Nigeria: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2019;9:e026324.
- Sato R. The impacts of quantity and quality of health clinics on health behaviors and outcomes in Nigeria: analysis of health clinic census data. BMC Health Serv Res 2019;19:377. [CrossRef]
- Oluwadare C. The Social Determinants of Routine Immunisation in Ekiti State of Nigeria. Stud Ethno-Med 2009;3:49–56. [CrossRef]
- Masresha B, Nwankwo O, Bawa S, Igbu T, Oteri J, Tafida H, et al. The use of WhatsApp group messaging in the coordination of measles supplemental immunization activity in Cross Rivers State, Nigeria, 2018. Pan Afr Med J 2020;35.
- Adeyanju GC, Sprengholz P, Betsch C. Understanding drivers of vaccine hesitancy among pregnant women in Nigeria: A longitudinal study. Npj Vaccines 2022;7:96.
- Taylor S, Khan M, Muhammad A, Akpala O, van Strien M, Morry C, et al. Understanding vaccine hesitancy in polio eradication in northern Nigeria. Vaccine 2017;35:6438–43.
- Ijarotimi IT, Fatiregun AA, Adebiyi OA, Ilesanmi OS, Ajumobi O. Urban–rural differences in immunisation status and associated demographic factors among children 12-59 months in a southwestern state, Nigeria. PLoS One 2018;13:e0206086.
- Ozawa S, Wonodi C, Babalola O, Ismail T, Bridges J. Using best-worst scaling to rank factors affecting vaccination demand in northern Nigeria. Vaccine 2017;35:6429–37. [CrossRef]
- Akwataghibe NN, Ogunsola EA, Popoola OA, Agbo AI, Dieleman MA. Using participatory action research to improve immunization utilization in areas with pockets of unimmunized children in Nigeria. Health Res Policy Syst 2021;19:88. [CrossRef]
- Adamu AA, Uthman OA, Gadanya MA, Cooper S, Wiysonge CS. Using the theoretical domains framework to explore reasons for missed opportunities for vaccination among children in Kano, Nigeria: a qualitative study in the pre-implementation phase of a collaborative quality improvement project. Expert Rev Vaccines 2019;18:847–57. [CrossRef]
- Tagbo BN, Eke CB, Omotowo BI, Onwuasigwe CN, Onyeka EB, Mildred UO. Vaccination Coverage and Its Determinants in Children Aged 11 - 23 Months in an Urban District of Nigeria. World J Vaccines 2014;04:175–83. [CrossRef]
- Ignis IO, Tomini S. Vaccination Coverage: Vaccine-Related Determinants & Anthropometric Measures in Children Resident in a Rural Community in Nigeria. Curr Drug Saf 2022;17:199–210. [CrossRef]
- Obi-Jeff C, Rakhshani NS, Bello-Malabu JI, Nwangwu C, Nwaononiwu E, Eboreime E, et al. Vaccine indicator and reminder band to improve demand for vaccination in Northern Nigeria: A qualitative evaluation of implementation outcomes. Vaccine 2020;38:4191–9.
- Murele B, Vaz R, Gasasira A, Mkanda P, Erbeto T, Okeibunor J. Vaccine perception among acceptors and non-acceptors in Sokoto State, Nigeria. Vaccine 2014;32:3323–7. [CrossRef]
- Olorunsaiye CZ, Degge H. Variations in the Uptake of Routine Immunization in Nigeria: Examining Determinants of Inequitable Access. Glob Health Commun 2016;2:19–29. [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft A, Usman MU, Nyamucherera OF, Emori H, Duke B, Umar NA, et al. Why children are not vaccinated against measles: a cross-sectional study in two Nigerian States. Arch Public Health 2014;72:48. [CrossRef]
- Musa A, Mkanda P, Manneh F, Korir C, Warigon C, Gali E, et al. Youth group engagement in noncompliant communities during supplemental immunization activities in Kaduna, Nigeria, in 2014. J Infect Dis 2016;213:S91–5.
- Galadima AN, Zulkefli NAM, Said SM, Ahmad N. Factors influencing childhood immunisation uptake in Africa: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 2021;21:1475. [CrossRef]
- Bangura JB, Xiao S, Qiu D, Ouyang F, Chen L. Barriers to childhood immunization in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2020;20:1108. [CrossRef]
- Nigeria: Making Reaching Every District Operational n.d.
- Amoah A, Issaka J, Ayebeng C, Okyere J. Influence of women empowerment on childhood (12–23 months) immunization coverage: Recent evidence from 17 sub-Saharan African countries. Trop Med Health 2023;51:63. [CrossRef]
- Kalaij AGI, Sugiyanto M, Ilham AF. Factors Associated With Vaccination Compliance in Southeast Asian Children: A Systematic Review. Asia Pac J Public Health 2021;33:479–88. [CrossRef]
- Anokye R, Acheampong E, Budu-Ainooson A, Edusei AK, Okyere P, Dogbe J, et al. Socio-demographic determinants of childhood immunization incompletion in Koforidua, Ghana. BMC Res Notes 2018;11:656. [CrossRef]
- Jalloh MF, Bennett SD, Alam D, Kouta P, Lourenço D, Alamgir M, et al. Rapid behavioral assessment of barriers and opportunities to improve vaccination coverage among displaced Rohingyas in Bangladesh, January 2018. Vaccine 2019;37:833–8. [CrossRef]
- Yahya M. Polio vaccines—“no thank you!” barriers to polio eradication in Northern Nigeria. Afr Aff 2007;106:185–204. [CrossRef]
- Raufu A. Polio vaccine plans may run into problems in Nigeria. BMJ 2003;327:380. [CrossRef]
- Larson HJ, Figueiredo A de, Xiahong Z, Schulz WS, Verger P, Johnston IG, et al. The State of Vaccine Confidence 2016: Global Insights Through a 67-Country Survey. eBioMedicine 2016;12:295–301. [CrossRef]
- Demographic and Health Survey 2018 n.d.
- Ojo JS, Oyewole S, Aina F. Forces of Terror: Armed Banditry and Insecurity in North-west Nigeria. Democr Secur 2023;19:319–46. [CrossRef]
- Grundy J, Biggs B-A. The impact of conflict on immunisation coverage in 16 countries. Int J Health Policy Manag 2019;8:211.
| Selection criteria | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Year of publication | All articles published from inception of the databases to 2023 | Articles published outside this period. |
| Type of publication | Peer review articles, grey literature and specific unpublished reports from stakeholders involved in vaccine administration and policy in Nigeria | Preprints, Thesis and dissertations and other publications that have not been peer reviewed. |
| Language | English | All other languages |
| Issue | Determinants of childhood vaccine uptake | Drivers and facilitators of COVID-19, influenza vaccines and other vaccines not included in the NPHDA routine immunization schedule as at October 2023 |
| Sample | Under 2 children eligible for routine immunization in accordance to the NPHCDA recommendations, their caregivers including their parents and healthcare workers administering vaccine and providing necessary logistics and administrative responsibilities. |
| Phenomenon of interest | Routine vaccination recommended by the NPHCDA |
| Design | This includes primary studies employing exploratory, observational, or experimental study designs |
| Evaluation | Behaviours towards vaccination |
| Research type | This is mainly qualitative or mixed methods |
| Characteristics | Number of studies (%), n=110 | References |
|---|---|---|
| Publication period | ||
| Before 1990 | 1 (0.9%) | [1] |
| Between 1990 and 2010 | 5 (4.5%) | [2,3,4,5,6] |
| After 2010 | 104 (94.5%) | [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109] |
| Geographical Regions | ||
| Multi-states | 11 (10.0 %) | [35,46,67,74,77,83,91,98,108] |
| National | 26 (23.6 %) | [2,5,15,19,20,22,26,34,40,41,42,46,50,56,59,60,65,71,75,76,78,84,88,90,94,107] |
| North-Central | 4 (3.6 %) | [13,61,62,97] |
| North-East | 9(8.2 %) | [16,34,54,58,86,92,93,95] |
| North-West | 17 (15.5 %) | [8,9,11,18,29,31,32,39,45,47,55,57,100,102,105,106,109] |
| South-East | 12 (10.9 %) | [10,25,28,63,64,68,69,70,89,103] |
| South-South | 10 (17.3 %) | [3,12,23,24,48,51,53,80,96,104] |
| South-West | 21 (19.1 %) | [1,4,6,7,14,17,27,30,33,37,38,43,44,49,52,72,73,82,87,99,101] |
| Research approach | ||
| Mixed Method | 44 (40.0 %) | [1,2,5,12,13,16,19,20,21,26,31,34,35,38,39,40,42,43,44,46,50,52,53,54,56,71,72,73,74,75,76,78,83,84,85,86,90,92,94,95,101,107,109] |
| Qualitative | 61 (55.5 %) | [1,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,14,15,17,18,22,23,24,25,27,28,29,30,32,33,34,35,37,41,45,46,47,48,49,51,55,57,58,60,61,62,63,64,65,67,68,69,70,77,80,81,82,87,89,91,92,93,96,97,98,99,100,102,103,104,105,106] |
| Quantitative | 5 (4.5 %) | [35,41,47,60,65] |
| Data collection methods | ||
| Combination of methods | 12 (10.9 %) | [9,35,43,73,74,83,101] |
| Analysis of secondary data | 33 (30.0 %) | [2,5,18,19,20,34,36,40,41,42,50,53,54,56,59,60,65,71,75,76,84,86,88,90,92,94,96,107,109,110,111] |
| Focus Groups | 7 (6.4 %) | [12,17,21,57,62,80,102] |
| Interviews | 18 (16.4 %) | [1,3,4,6,15,17,35,48,51,61,68,97,98,103,105,106,108] |
| Observation | 6 (5.5 %) | [14,22,27,37,58,91] |
| Questionnaire and household surveys | 34 (306 %) | [8,10,11,13,23,24,25,28,30,31,32,33,34,38,39,45,47,49,52,55,63,64,67,69,70,77,81,82,85,89,99,104] [87,100] |
| Vaccines assessed | ||
| Routine immunization | 89 (80.9 %) | [1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,17,19,21,23,24,26,29,30,31,32,34,35,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,55,56,57,58,60,62,63,64,67,68,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,93,94,95,96,97,99,100,101,102,104,105,106,107,110,111] |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTaP) Vaccine | 2 (1.8 %) | [2,33] |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTaP) Vaccine; Polio Vaccine | 1 (0.9 %) | [33] |
| Hepatitis B Vaccine | 3 (2.7 %) | [16,69,70] |
| Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine | 5 (4.5 %) | [28,61,92,108] |
| Polio Vaccine | 10 (9.1 %) | [11,20,22,54,65,91,98,103,109,112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





