Submitted:
22 May 2024
Posted:
22 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Software and Statistical Methods
2.4. Variable Selection and TreeBagger Model Construction
3. Results
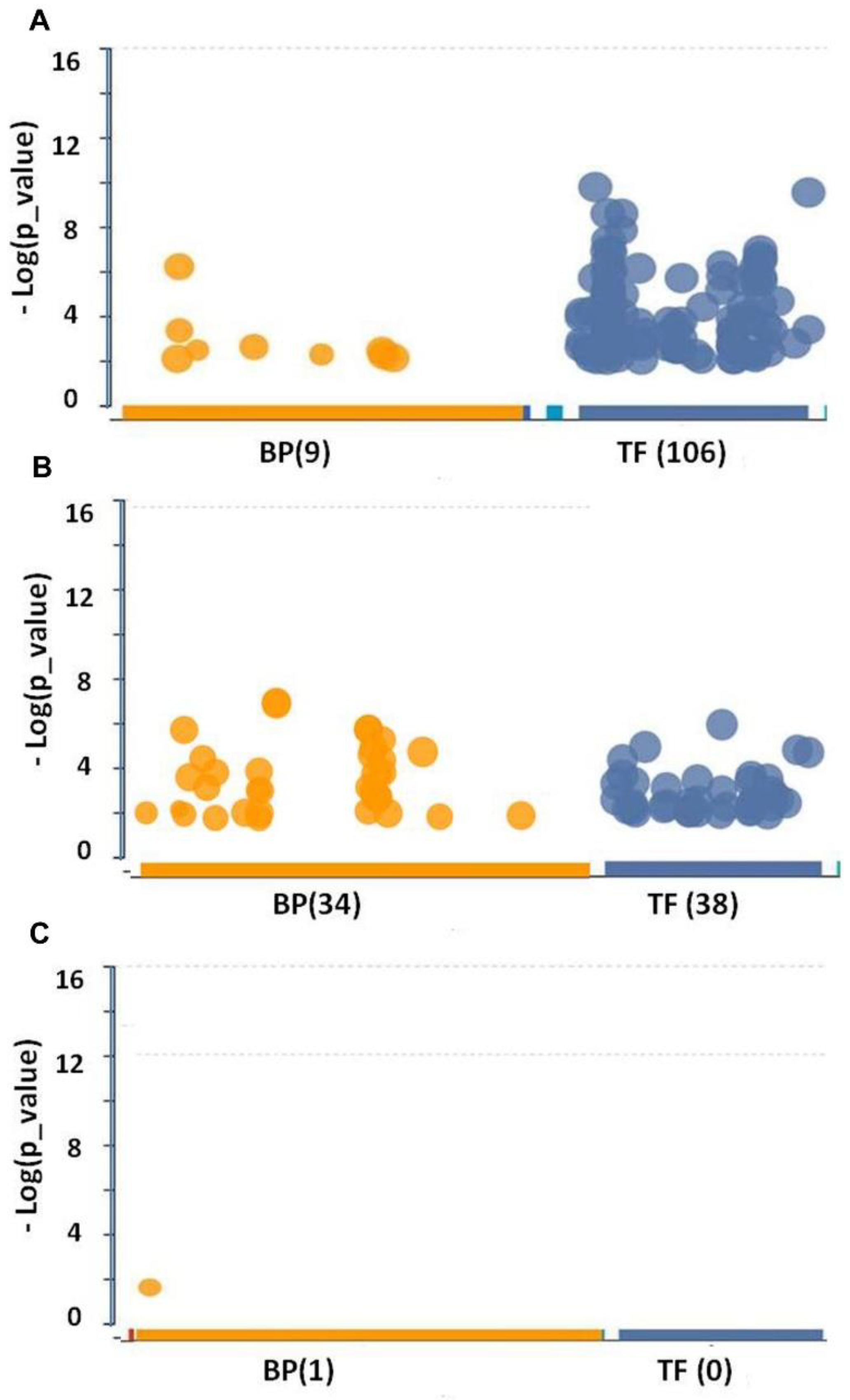
3.1. Differential Transcription Factor Expression in Bevacizumab-Responsive Glioblastoma Post-BVZ Treatment
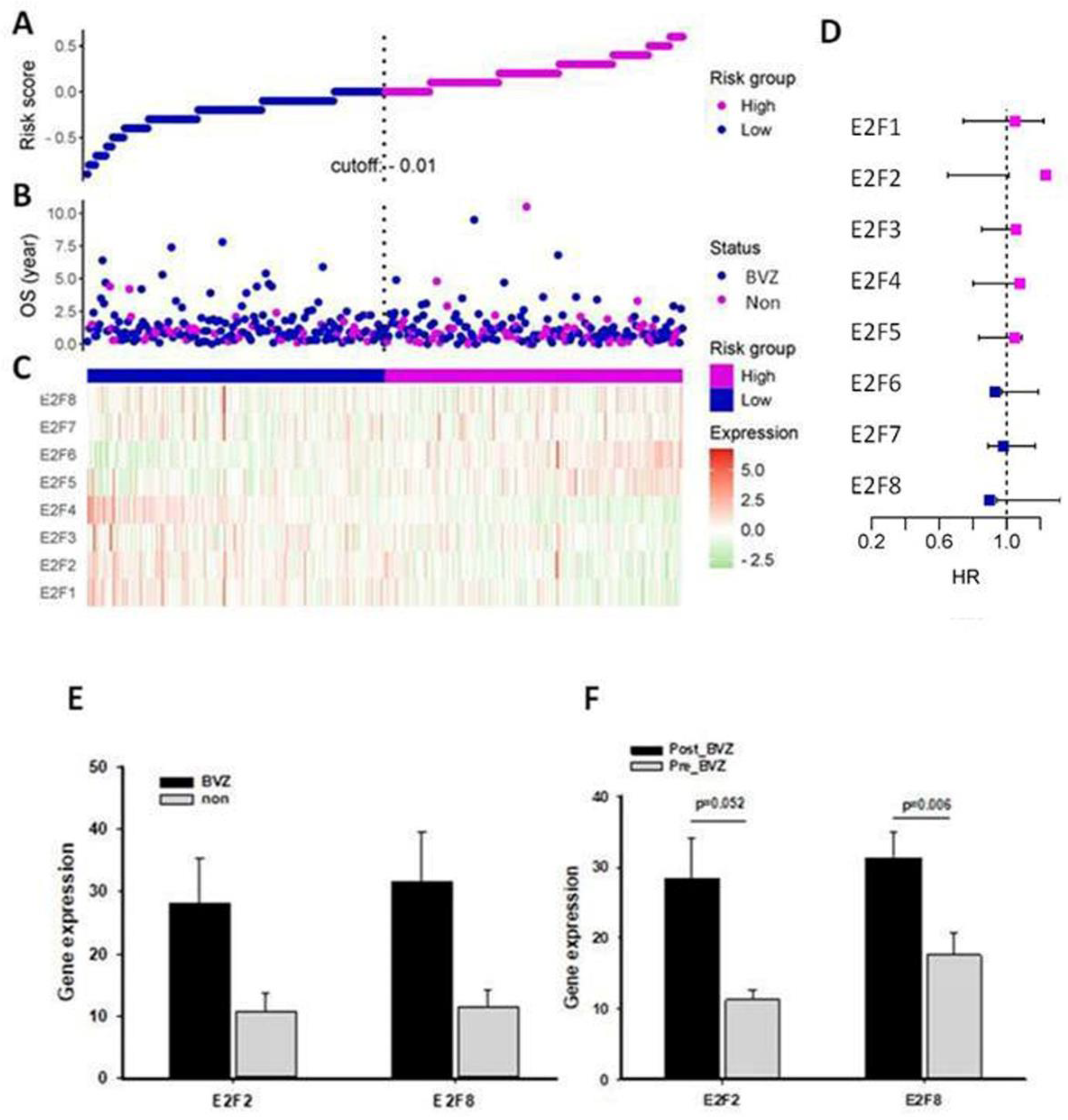
3.2. E2F Expression and Bevacizumab-Responsive Subtypes of Glioblastoma
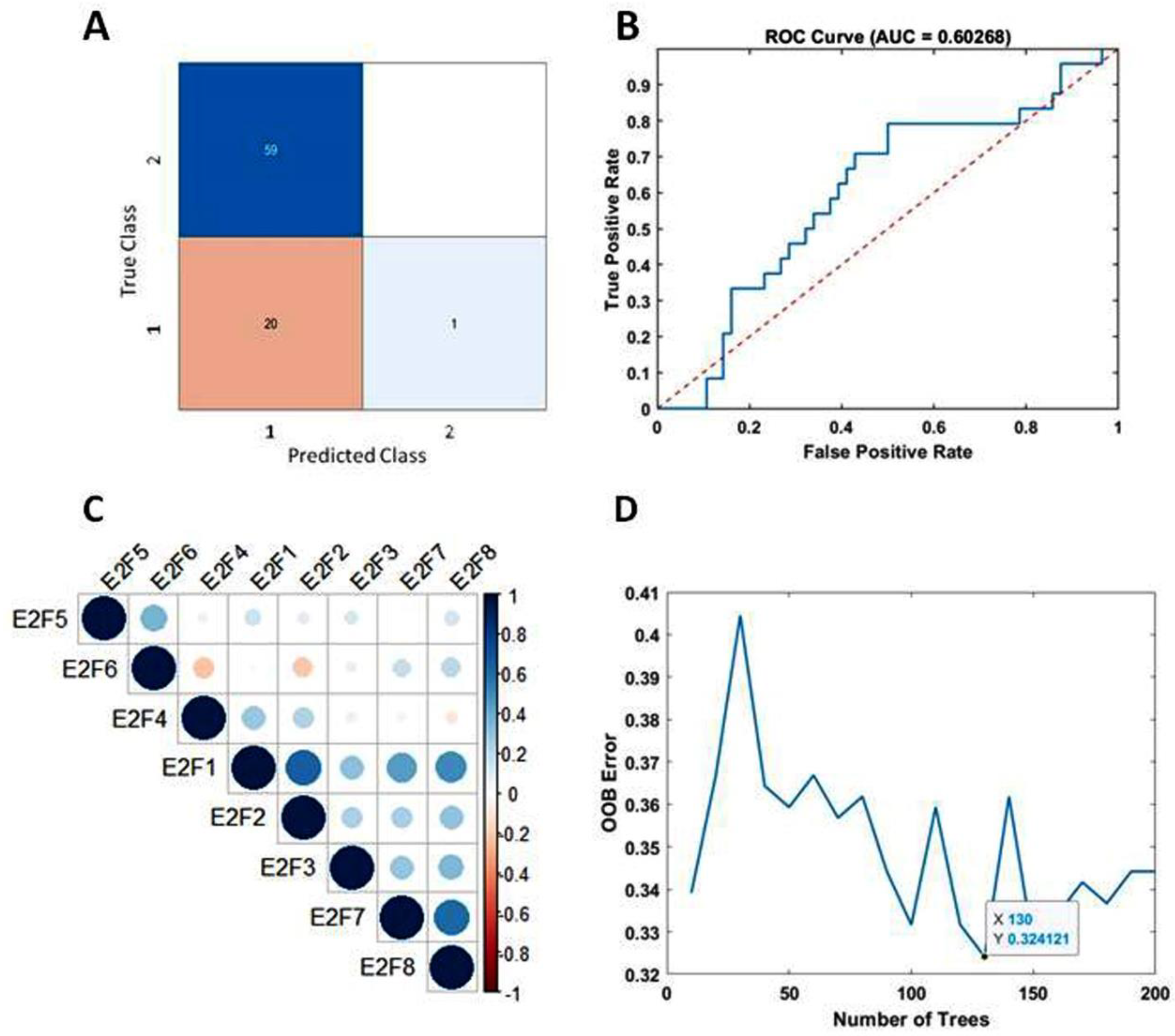
3.3. Predicting Survival in Bevacizumab-Responsive Subtypes of Glioblastoma Using TreeBagger Analysis
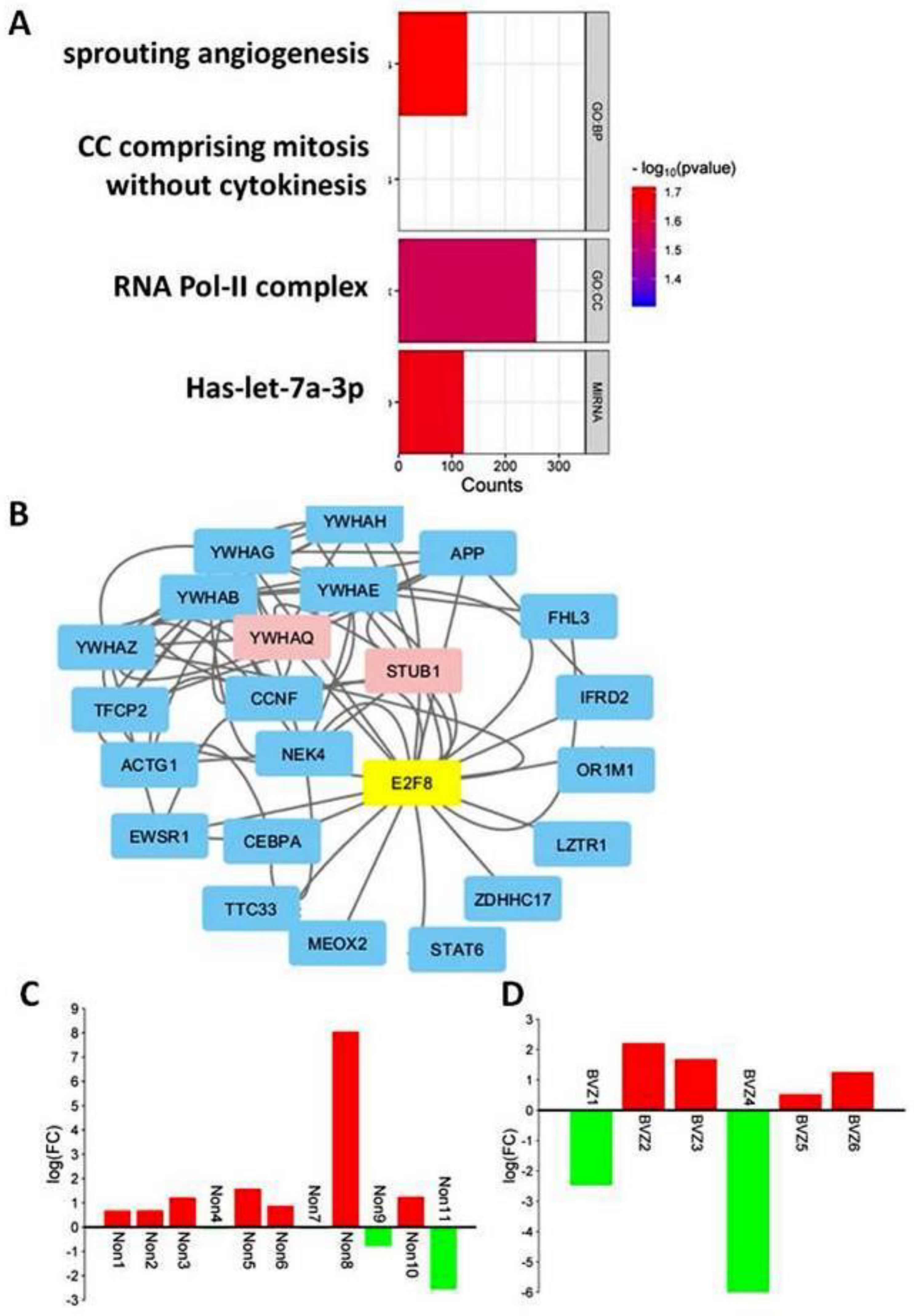
3.4. Post-Treatment Functional Analysis of E2Fs on GBM BVZ Response Subtypes
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- Kent, L.N. and G. Leone, The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019. 19(6): p. 326-338. [CrossRef]
- Kent, L.N., et al., E2f8 mediates tumor suppression in postnatal liver development. J Clin Invest, 2016. 126(8): p. 2955-69. [CrossRef]
- Xie, D., et al., Emerging Role of E2F Family in Cancer Stem Cells. Front Oncol, 2021. 11: p. 723137. [CrossRef]
- Shats, I., et al., Expression level is a key determinant of E2F1-mediated cell fate. Cell Death Differ, 2017. 24(4): p. 626-637. [CrossRef]
- Schaal, C., S. Pillai, and S.P. Chellappan, The Rb-E2F transcriptional regulatory pathway in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res, 2014. 121: p. 147-182.
- Araki, K., et al., Mitochondrial protein E2F3d, a distinctive E2F3 product, mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in cancer cells. Commun Biol, 2019. 2: p. 3. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., et al., Early 2 factor (E2F) transcription factors contribute to malignant progression and have clinical prognostic value in lower-grade glioma. Bioengineered, 2021. 12(1): p. 7765-7779. [CrossRef]
- Lan, W., et al., E2F signature is predictive for the pancreatic adenocarcinoma clinical outcome and sensitivity to E2F inhibitors, but not for the response to cytotoxic-based treatments. Sci Rep, 2018. 8(1): p. 8330. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A., et al., E2F8 as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Lung Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2015. 107(9). [CrossRef]
- Hollern, D.P., et al., The E2F transcription factors regulate tumor development and metastasis in a mouse model of metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol, 2014. 34(17): p. 3229-43. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y., et al., Emerging role of E2F8 in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2023. 1869(6): p. 166745. [CrossRef]
- Shi, J., Machine learning and bioinformatics approaches for classification and clinical detection of bevacizumab responsive glioblastoma subtypes based on miRNA expression. Sci Rep, 2022. 12(1): p. 8685. [CrossRef]
- Fu, M., et al., Use of Bevacizumab in recurrent glioblastoma: a scoping review and evidence map. BMC Cancer, 2023. 23(1): p. 544. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, S., et al., Bevacizumab changes vascular structure and modulates the expression of angiogenic factors in recurrent malignant gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol, 2016. 33(2): p. 129-36. [CrossRef]
- Al-Holou, W.N., et al., Subclonal evolution and expansion of spatially distinct THY1-positive cells is associated with recurrence in glioblastoma. Neoplasia, 2023. 36: p. 100872. [CrossRef]
- Luo, X., et al., High gene expression levels of VEGFA and CXCL8 in the peritumoral brain zone are associated with the recurrence of glioblastoma: A bioinformatics analysis. Oncol Lett, 2019. 18(6): p. 6171-6179. [CrossRef]
- Shi, J., Mizuma A, Huang SW, Mueller S., Treatment-Altered VEGF-Associated Network in GBM BVZ-Responsive Subtypes: Bioinformatics Case Studies. Annals of Case Reports, 2023. 8(2): p. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Network, C.G.A.R., Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature, 2008. 455(7216): p. 1061-8.
- Bolger, A.M., M. Lohse, and B. Usadel, Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 2014. 30(15): p. 2114-20. [CrossRef]
- Urup, T., et al., Transcriptional changes induced by bevacizumab combination therapy in responding and non-responding recurrent glioblastoma patients. BMC Cancer, 2017. 17(1): p. 278. [CrossRef]
- Tang, N., et al., Blood Markers Show Neural Consequences of LongCOVID-19. Cells, 2024. 13(6). [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W., et al., DoSurvive: A webtool for investigating the prognostic power of a single or combined cancer biomarker. iScience, 2023. 26(8): p. 107269. [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, G., et al., A Machine-Learning Approach for Detection and Quantification of QRS Fragmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2019. 23(5): p. 1980-1989. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M., et al., Glioblastoma as an age-related neurological disorder in adults. Neurooncol Adv, 2021. 3(1): p. vdab125. [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T., et al., The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a "state of the science" review. Neuro Oncol, 2014. 16(7): p. 896-913. [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.I., et al., NRG Oncology/RTOG1205: A Randomized Phase II Trial of Concurrent Bevacizumab and Reirradiation Versus Bevacizumab Alone as Treatment for Recurrent Glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol, 2023. 41(6): p. 1285-1295. [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Fernández, M. and M. Malumbres, An Atypical Oncogene Within the Atypical E2Fs. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2015. 107(9).
- Weijts, B.G.M.W., et al., Atypical E2Fs inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene, 2018. 37(2): p. 271-276. [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.F., et al., Cancer stem cells--perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res, 2006. 66(19): p. 9339-44. [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.Y. and X.A. Zhang, Knockdown of E2F8 Suppresses Cell Proliferation in Colon Cancer Cells by Modulating the NF-κB Pathway. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2019. 49(4): p. 474-480.
- Deng, Q., et al., E2F8 contributes to human hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating cell proliferation. Cancer Res, 2010. 70(2): p. 782-91. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W., et al., MicroRNAs as biomarkers for human glioblastoma: progress and potential. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2018. 39(9): p. 1405-1413. [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. and S. Huang, Comparative Insight into Microglia/Macrophages-Associated Pathways in Glioblastoma and Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2023. 25(1). [CrossRef]
- Makowska, M., B. Smolarz, and H. Romanowicz, microRNAs (miRNAs) in Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)-Recent Literature Review. Int J Mol Sci, 2023. 24(4). [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y., et al., The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells, 2021. 10(9). [CrossRef]
- Yu, F., et al., let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell, 2007. 131(6): p. 1109-23. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X., et al., Lin28/let-7 axis regulates aerobic glycolysis and cancer progression via PDK1. Nat Commun, 2014. 5: p. 5212. [CrossRef]
- Apriamashvili, G., et al., Ubiquitin ligase STUB1 destabilizes IFNγ-receptor complex to suppress tumor IFNγ signaling. Nat Commun, 2022. 13(1): p. 1923. [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.Y., et al., Derivatives of sarcodonin A isolated from Sarcodon scabrosus reversed LPS-induced M1 polarization in microglia through MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Bioorg Chem, 2022. 125: p. 105854. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P., et al., Ubiquitin ligase CHIP regulates OTUD3 stability and suppresses tumour metastasis in lung cancer. Cell Death Differ, 2020. 27(11): p. 3177-3195. [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, A., N. Kaushik, and J. de Belleroche, A 14-3-3 mRNA is up-regulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. J Neurochem, 2000. 75(6): p. 2511-20. [CrossRef]
- Mei, J., et al., YWHAZ interacts with DAAM1 to promote cell migration in breast cancer. Cell Death Discov, 2021. 7(1): p. 221. [CrossRef]
- Conklin, C.M. and T.A. Longacre, Endometrial stromal tumors: the new WHO classification. Adv Anat Pathol, 2014. 21(6): p. 383-93. [CrossRef]
| Gene | Normal | GBM | GBM/Normal | Log(FC) | Wilcoxon P-val |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2F1 | 2.42E+02 | 6.02E+02 | 2.49E+00 | 1.31E+00 | 9.99E-03 |
| E2F2 | 3.14E+00 | 1.92E+02 | 6.11E+01 | 5.93E+00 | 1.43E-04 |
| E2F3 | 4.65E+02 | 5.96E+02 | 1.28E+00 | 3.58E-01 | 4.76E-01 |
| E2F4 | 7.18E+02 | 1.05E+03 | 1.46E+00 | 5.48E-01 | 1.50E-03 |
| E2F5 | 8.48E+01 | 4.39E+02 | 5.18E+00 | 2.37E+00 | 1.43E-04 |
| E2F6 | 3.07E+02 | 5.56E+02 | 1.81E+00 | 8.57E-01 | 3.27E-04 |
| E2F7 | 4.37E+00 | 1.91E+02 | 4.37E+01 | 5.45E+00 | 1.55E-04 |
| E2F8 | 6.50E-01 | 7.65E+01 | 1.18E+02 | 6.88E+00 | 1.55E-04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





