Submitted:
27 May 2024
Posted:
28 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation, Labeling, and Pre-Treatment of MSCs
2.2. Experimental Animals
- Group I (control group): 0.5 ml saline intraperitoneal (I.P.) weekly
- Group II (Doxorubicin):.5 mg/kg I.P. Doxorubicin (Sigma Chemical Company; St Louis, Moment, USA) weekly [46].
- Group III (Doxorubicin and BM-MSCs): 5 mg/kg I.P. Doxorubicin weekly and one systemic injection (through the caudal vein) of stem cells (1 x 106) diluted in 0.5 ml of PBS once on day one [43].
- Group IV (Doxorubicin and L-carnitine): 5 mg/kg I.P. Doxorubicin weekly and oral L-carnitine (100 mg/kg) daily (Sigma Chemical Company; St Louis, Moment, USA) [2].
- Group V (Doxorubicin and BM-MSCs pre-treated with L carnitine): Doxorubicin and one systemic injection (through the caudal vein) of stem cells pre-treated with L carnitine (1 x 106) diluted in 0.5 ml of PBS once on day one.
2.3. Biochemical Assays
2.4. Assay of Cardiac Lipid Peroxide Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Antioxidant Enzyme Catalase
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (QRT-PCR)
2.6. Immunofluorescent Study for Ki-67
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Masson’s Trichrome Stains
2.8. Immunohistochemical Reaction
2.9. Histomorphometric Measurements
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Results
3.2. Assay of MDA and Catalase
3.3. Real-Time PCR for TNF-α and Bcl2 Gene Expression
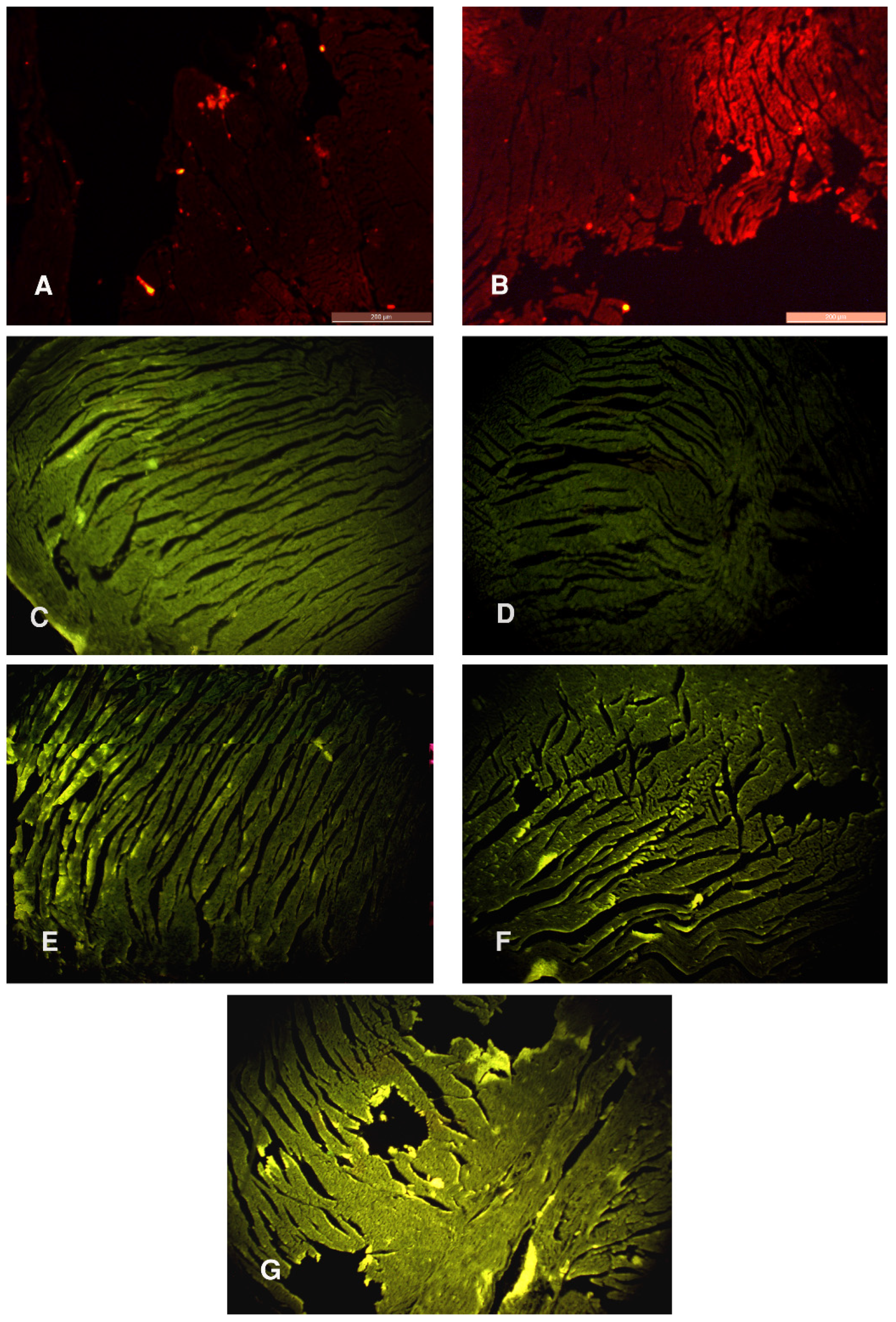
3.4. PKH26 Fluorescence Stain and Immunofluorescent Study for Ki-67
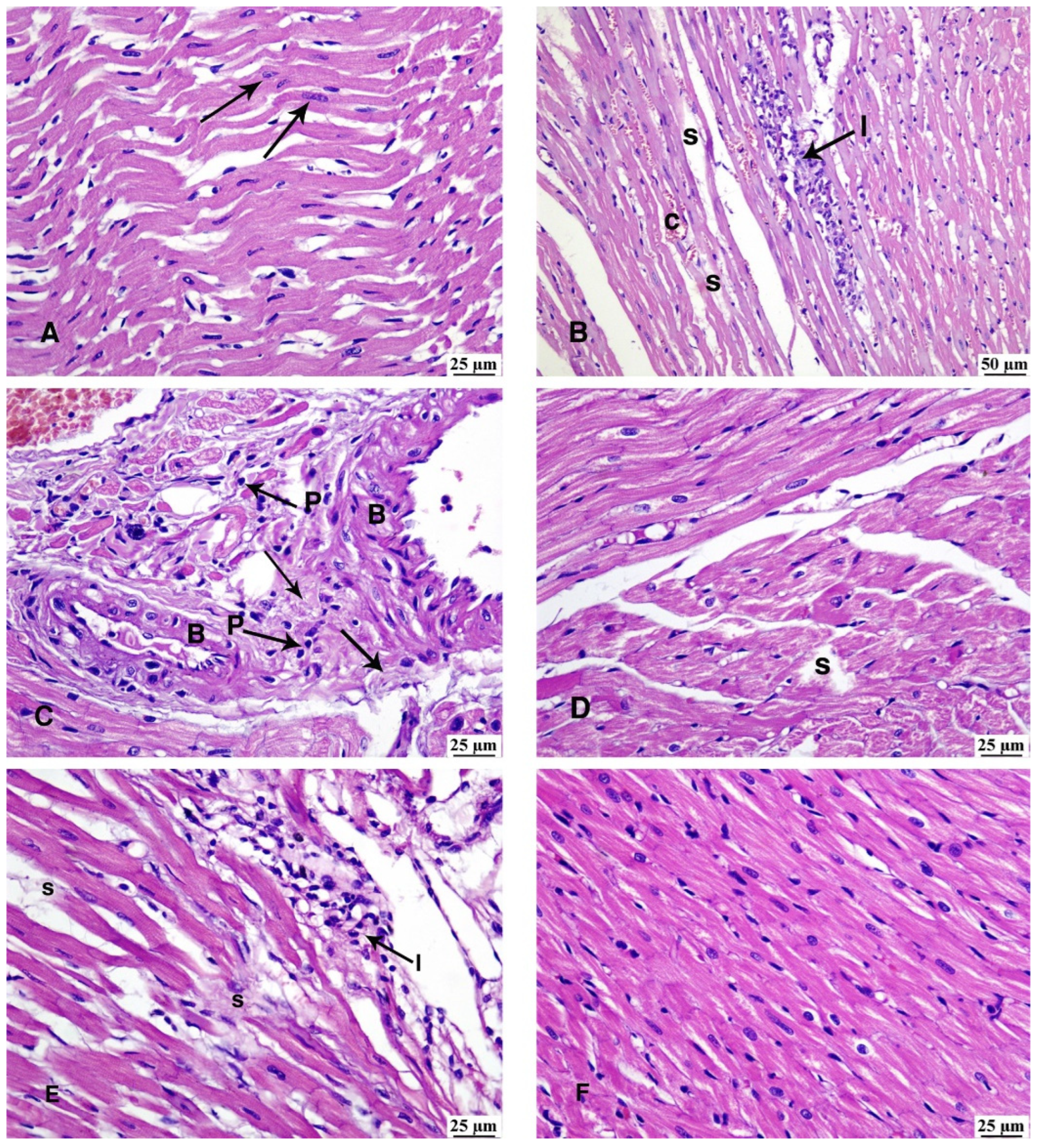
3.5. Haematoxylin and Eosin Stain
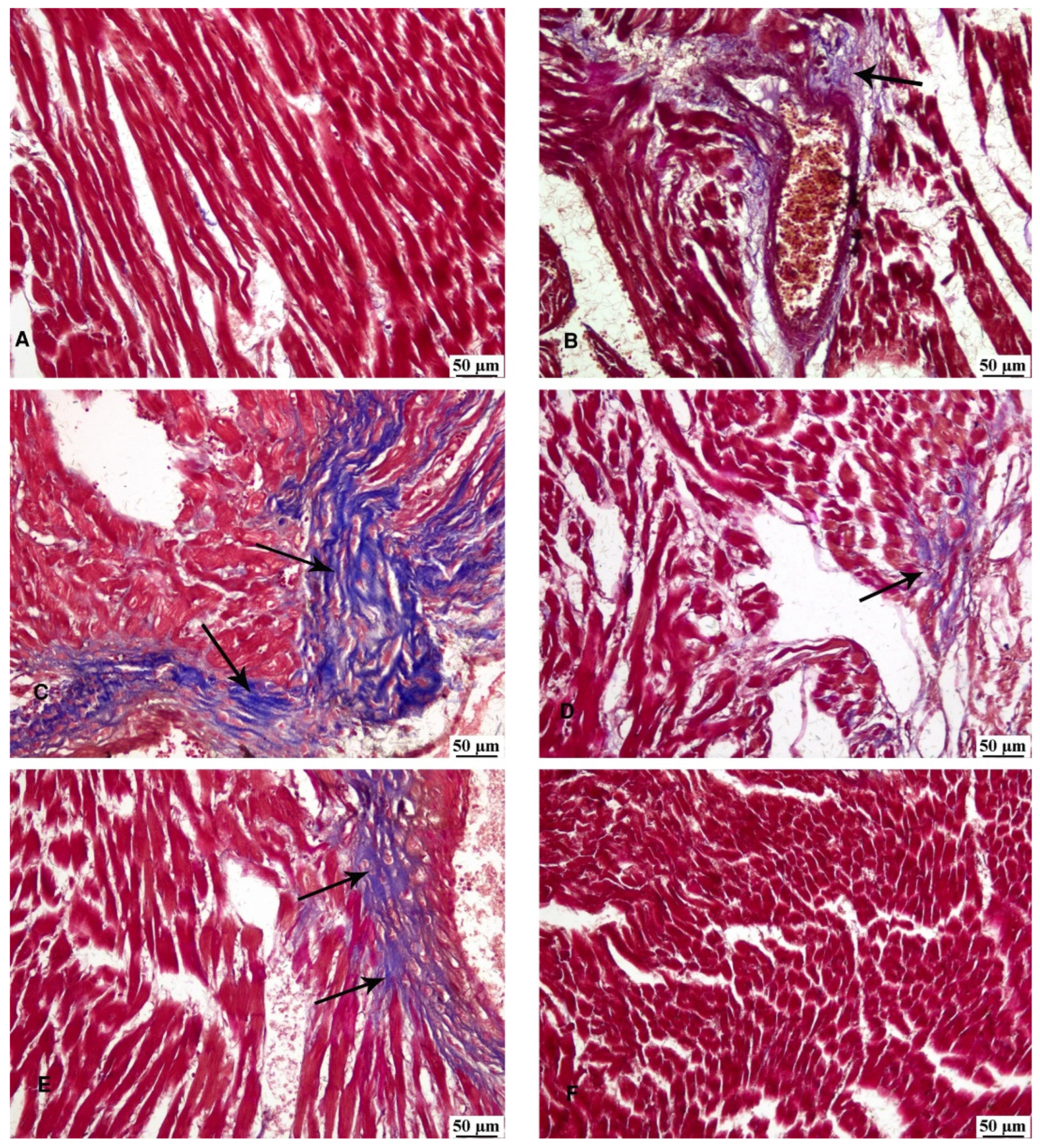
3.6. Masson’s Trichrome Stain
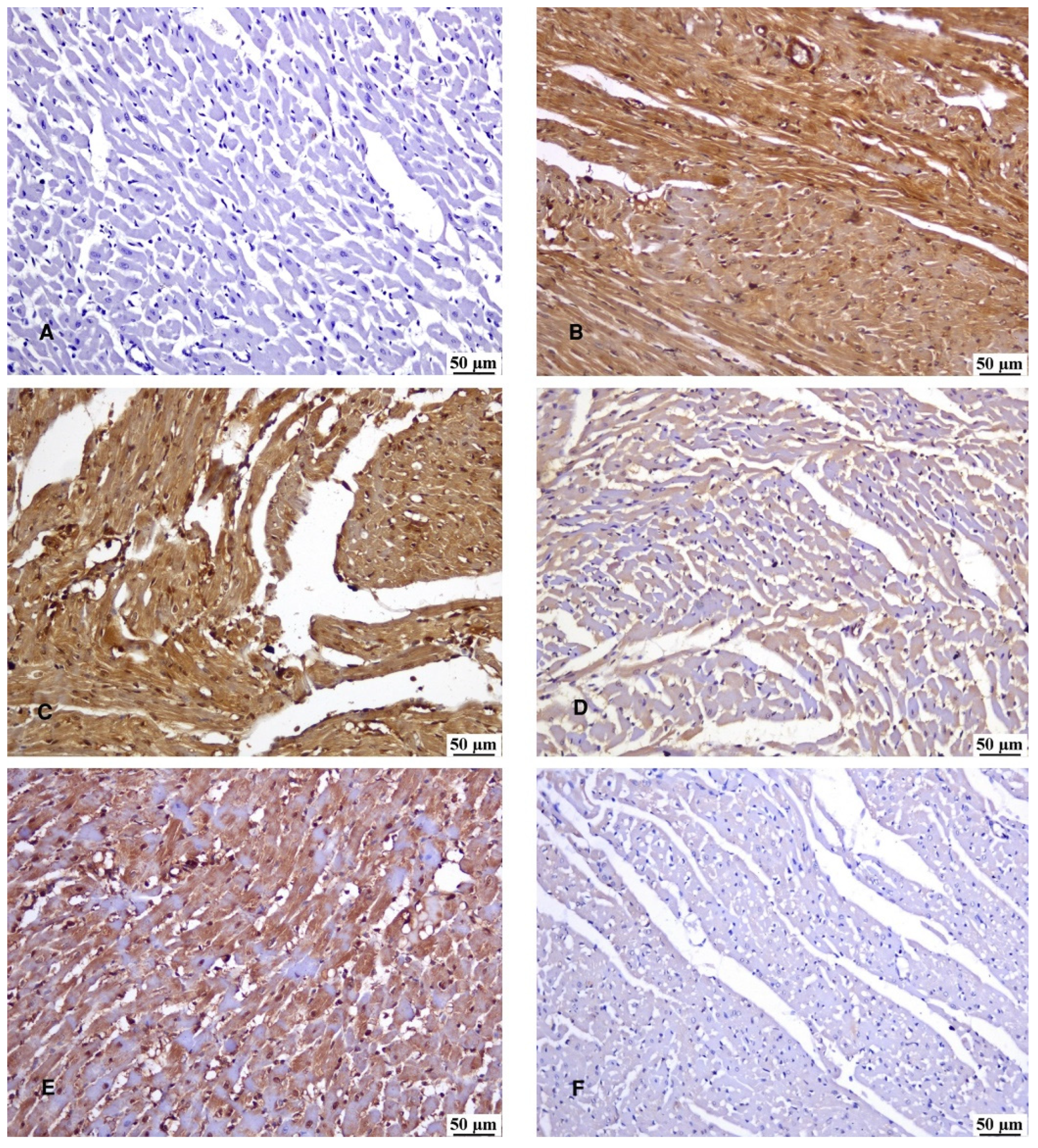
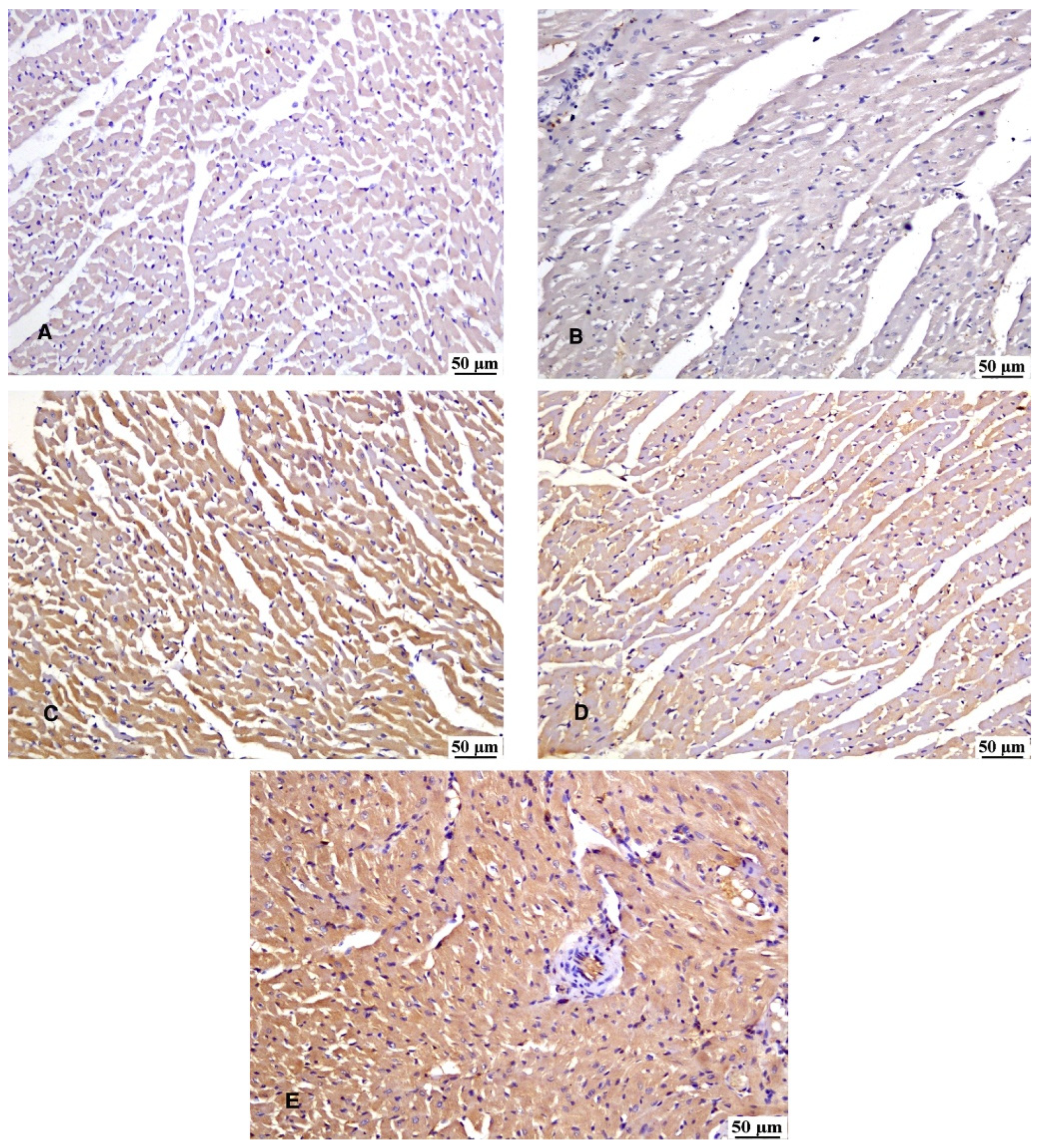
3.7. Immunohistochemical Reaction
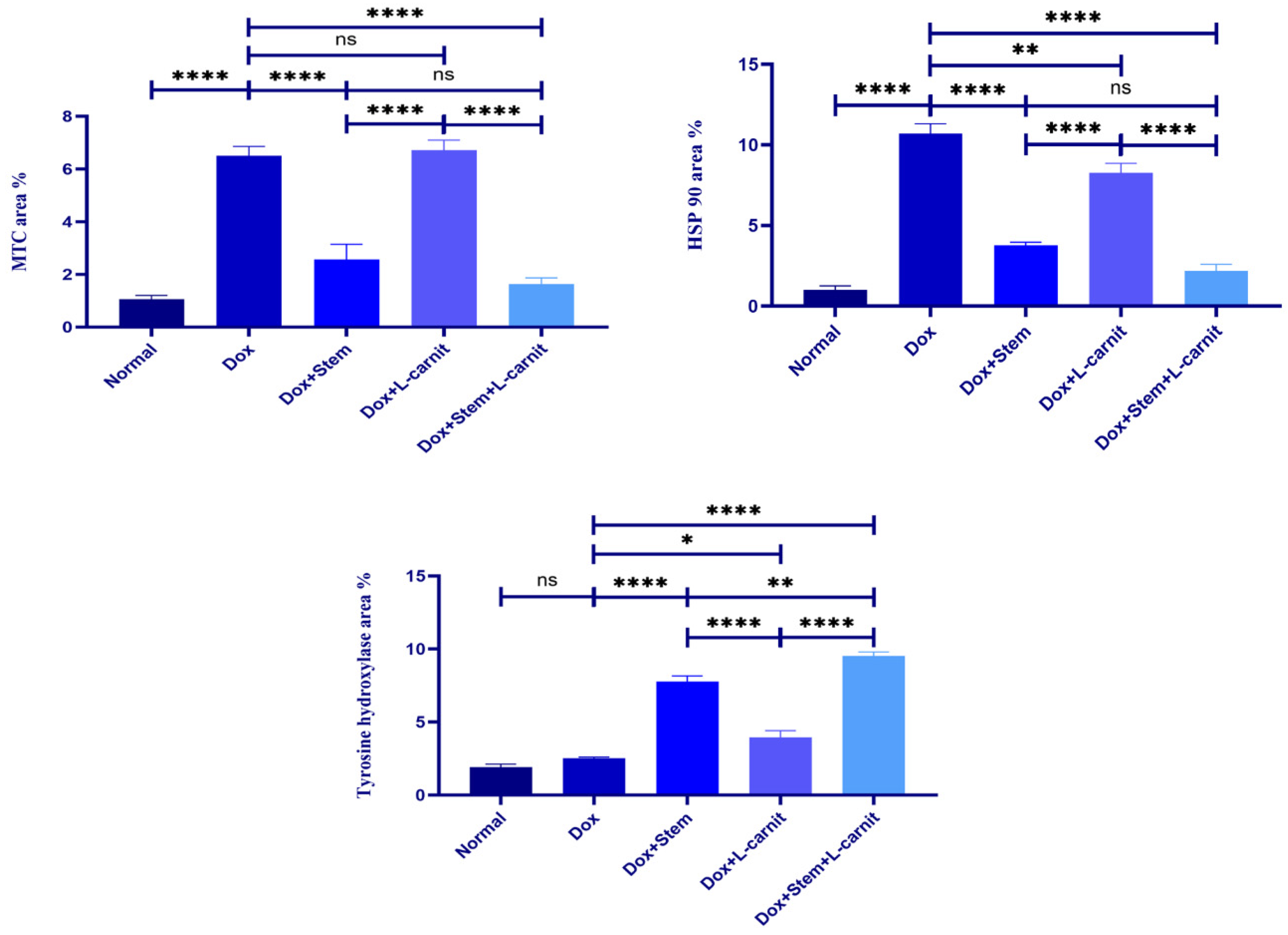
3.8. Histomorphometric Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, S.S.; Islam, S.; Rosengren, A. Risk factors for myocardial infarction in women and men: insights from the INTERHEART study. Eur Hear J 2008, 29, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emran, T.; Chowdhury, N.I.; Sarker, M. L-carnitine protects cardiac damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory response via inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 143, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zou, Y.G.; Xue, Y.Z. Long non-coding RNA H19 protects acute myocardial infarction through activating autophagy in mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018, 22, 5647–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.F.; Sun, J.; Zou, Z.Y. MiRNA-488-3p suppresses acute myocardial infarction-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via targeting ZNF791. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019, 23, 4932–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, A.; Sethi, A.; Rathor, P. Acute complications of myocardial infarction in the current era: Diagnosis and management. J Investig Med 2015, 63, 844–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Penna, C.; Musso, T. Platelets, diabetes and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2017, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.C.D. L-Carnitine Reduces Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating Nuclear Transcription-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2)/Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) Signaling Pathway. Med Sci Monit 2020, 26, e92325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetz, J.; Moslehi, J.; Sarosiek, K. Radiation-induced cardiovascular toxicity: mechanisms, prevention, and treatment. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 2018, 20, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, A. R.; López-Fernándezl, T.; Couch, L.S. 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International CardioOncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Heart J 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linders, A. N.; Dias, I. B.; López Fernández, T.; Tocchetti, C. G.; Bomer, N. A review of the pathophysiological mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and aging. Npj Aging 2024, 10(1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C. R. Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol 2013, 65(2), 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends-An Update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2016, 25, 25,16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.Y.; Guo, Z.; Song, P. Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death. Int J Biol Sci, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.S.; Goldenberg, R.C. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: From Mechanisms to Development of Efficient Therapy. Cardiotoxicity, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelburne, N.; Simonds, N.I.; Adhikari, B. Changing Hearts and Minds: Improving Outcomes in Cancer Treatment-Related Cardiotoxicity. Curr Oncol Rep 2019, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu, K.; Abilash, V.; Tirupathi Pichiah, P. B.; Arunachalam, S. Molecular mechanism of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy—an update. Eur J Pharmacol 2018, 818, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chung, J.; Byun, Y.; Kim, K.H.; An, S.H.; Kwon, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Protect Cardiomyocytes from Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Upregulating Survivin Expression via the miR-199a-3p-Akt-Sp1/p53 Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenningmann, N.; Knapp, M.; Ande, A.; Vaidya, T.R.; Ait-Oudhia, S. Insights into Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity: Molecular Mechanisms, Preventive Strategies, and Early Monitoring. Molecular Pharmacology. [CrossRef]
- van der Zanden, S. Y.; Qiao, X.; Neefjes, J. New insights into the activities and toxicities of the old anticancer drug doxorubicin. FEBS J 2021, 288, 6095–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.C.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: causative factors and possible interventions. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2022, 74(12), 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Peng, X.; Luo, Y. Quercetin protects cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced toxicity by suppressing oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function via 14-3-3γ. Toxicol Mech Methods 2019, 29, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Y. Doxorubicin Induces Endotheliotoxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via ROS/eNOS/NO Pathway. Front Pharmacol, 2020; 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M. M.; Khalifa, H. A.; Ahmed, A. A. Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2017, 80(4), 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, R.; Macciocca, M.; Vicenti, R. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits doxorubicin-induced inflammation on human ovarian tissue. Biosci Rep, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kotamraju, S.; Konorev, E.; Kalivendi, S.; Joseph, J.; Kalyanaraman, B. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB during doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells and myocytes is pro-apoptotic: the role of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 2002, 367(3), 729–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakjoo, M.; Ahmadi, S.E.; Zahedi, M. Interplay between proteasome inhibitors and NF-κB pathway in leukemia and lymphoma: a comprehensive review on challenges ahead of proteasome inhibitors. Cell Commun Signal 2024, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cova, L.; Armentero, M.T.; Zennaro, E. Multiple neurogenic and neurorescue effects of human mesenchymal stem cell after transplantation in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain research 2010, 1311, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaoz, E.; Okcu, A.; Ünal, Z.S.; Subasi, C.; Saglam, O.; Duruksu, G. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells efficiently differentiate into insulin-producing cells in pancreatic islet microenvironment both in vitro and in vivo. Cytotherapy 2013, 15(5), 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports 2023, 19(5), 1214–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Winkle, A.P.; Gates, I.D.; Kallos, M.S. Mass transfer limitations in embryoid bodies during human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cells Tissues Organs 2012, 196, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.; Vaupel, P. Hypoxia, Lactate Accumulation, and Acidosis: Siblings or Accomplices Driving Tumor Progression and Resistance to Therapy? Oxygen Transport to Tissue, Van Huffel, S.; Naulaers, G.; Caicedo, A.; Bruley, D.F.; Harrison, D.K. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. [CrossRef]
- Moeinabadi-Bidgoli, K.; Babajani, A.; Yazdanpanah, G. Translational insights into stem cell preconditioning: From molecular mechanisms to preclinical applications. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 142, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Kim, A.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Go, H.; Kim, D. Enhancement of angiogenic effects by hypoxia-preconditioned human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. Cell Biol Int 2016, 40, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, N.; Mizukami, A.; Caliári-Oliveira, C. Priming approaches to improve the efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahrizi, M.S.; Mousavi, E.; Khosravi, A. Recent advances in pre-conditioned mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSCs) therapy in organ failure; a comprehensive review of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther 2023, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 36. Longo, N; Frigeni, M.; Pasquali, M. Carnitine transport and fatty acid oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2422. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, Y.; Bharti, R.; Sharma, R. Myths and reality of L-carnitine (3-Hydroxy 4-N trimethylammonium butyrate) supplementation and its chemistry: A systematic review, Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 48(5), 1277-1282. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Reda, A.; Elnegris, H. Role of L-carnitine Treated Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Histological Changes in Spleen of Experimentally Induced Diabetic Rats and the Active Role of Nrf2 Signaling. Egyptian Journal of Histology 2021, 44(3), 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R.; Charoudeh, H.N. L-carnitine contributes to enhancement of neurogenesis from mesenchymal stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin and PKA pathway. Exp Biol Med 2017, 242(5), 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarak, H.; Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R.; Zarghami, N.; Javanmardi, S. L-carnitine significantly decreased aging of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Vet Res Commun 2017, 41, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, A.; Elfadadny, A.; Mandour, A.S. Potential protective effects of L-carnitine against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2024, 31, 18813–18825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z. L-Carnitine Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction by Ischemic Insults Through Akt Signaling Pathway. Toxicological Sciences 2017, 160(2), 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sadik, A.; El Ghamrawy, T.A.; Abd El-Galil, T.I. The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Chitosan Gel on Full Thickness Skin Wound Healing in Albino Rats: Histological, Immunohistochemical and Fluorescent Study. PLoS ONE, 0137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, D.; Aboelkomsan, E.; El Sadik, A. O. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Ascorbic Acid and N-Acetylcysteine on TNF-α, IL 1β, and NF-κβ Expressions in Acute Pancreatitis in Albino Rats. Journal of Diabetes Research. [CrossRef]
- Elzainy, A.; El Sadik, A.; Altowayan, W.M. Comparison between the Regenerative and Therapeutic Impacts of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pre-Treated with Melatonin on Liver Fibrosis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Melo, M.B.; Carvalho, J.L. Doxorubicin Cardiotoxicity and Cardiac Function Improvement After Stem Cell Therapy Diagnosed by Strain Echocardiography. J Cancer Sci Ther 2013, 5(2), 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmanová, E.; Bartošová, L.; Khazneh, E.; Parák, T.; Suchý, P. Comparison of the specificity of cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase MB in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity model in rats. Acta Vet Brno. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Lin, N.; Pang, S. Correlation of cardiomyocyte apoptosis with duration of hypertension, severity of hypertension and caspase-3 expression in hypertensive rats. Exp Ther Med 2019, 17(4), 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chiu, S.; Liang, X. Rap1-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) activity regulates the paracrine capacity of mesenchymal stem cells in heart repair following infarction. Cell Death Discovery 2015, 1, 15007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harouki, N.; Nicol, L.; Remy-Jouet, I. The IL-1β Antibody Gevokizumab Limits Cardiac Remodeling and Coronary Dysfunction in Rats With Heart Failure. J Am Coll Cardiol Basic Trans Science 2017, 2(4), 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yeo, H.C.; Doniger, S.J.; Ames, B.N. Assay of aldehydes from lipid peroxidation: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry compared to thiobarbituric acid. Anal. Biochem 1997, 245, 245,161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymol 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sadik, A.; Mohamed, E.; Elzainy, A. Postnatal changes in the development of rat submandibular glands in offspring of diabetic mothers: Biochemical, histological and ultrastructuralstudy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13(10), e0205372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Aasar, H.; Rashed, L.; El Sadik, A.; Amer, R.; Emam, H. (2021). The role of the adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells enriched with melatonin on pancreatic cellular regeneration. Folia Morphologica, 8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.; Berry, G. Statistical methods in medical research, 3rd ed., 1994, Blackwell Scientific Publications, London.
- Guijarro, D.; Lebrin, M.; Lairez, O. Intramyocardial transplantation of mesenchymal stromal cells for chronic myocardial ischemia and impaired left ventricular function: Results of the MESAMI 1 pilot trial. Int J Cardiol 2016, 209, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Hamo, C.E.; Udelson, J.E. Reassessing Phase II Heart Failure Clinical Trials: Consensus Recommendations. Circ Heart Fail 2017, 10, e003800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghian-Jahromi, I.; Matta, A.G.; Canitrot, R. Surfing the clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Stem Cell Res, 2021; 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraitis, D.; Giordano, C.; Ruel, M.; Musaro, A.; Suuronen, E.J. Exploiting extracellular matrix-stem cell interactions: A review of natural materials for therapeutic muscle regeneration. Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khubutiya, M.S.; Vagabov, A.V.; Temmov, A.A.; Sklifas, A.N. Paracrine mechanisms of proliferative, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells in models of acute organ injury. Cryotherapy 2014, 16, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodarac, A.; Šarić, T.; Oberwallner, B.; Mahmoodzadeh, S.; Neef, K.; Albrecht, J. Susceptibility of murine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. Stem Cell Res 2015, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R. Application of L-carnitine as nutritional supplement in veterinary medicine. Rom J Biochem 2014, 51(1), 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, N.; Yousif, N.G.; Al-amran, F.G. Vitamin E and telmisartan attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiac injury in rat through down regulation of inflammatory response. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2012, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.A.T.; Kabil, S.L. Liraglutide ameliorates cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in rats through the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 2017, 390, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, P.L.; Mocan, M.; Coadă, C.A. Doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity is associated with increased oxidative stress, autophagy, and inflammation in a murine model. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.C.; Silva, A.M.; Diogo, C.V.; Carvalho, F.S.; Monteiro, P.; Oliveira, P.J. Drug-induced cardiac mitochondrial toxicity and protection: from doxorubicin to carvedilol. Curr Pharm Des 2011, 17, 17,2113–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, X.W. Chemokine receptor 7 overexpression promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration and proliferation via secreting Chemokine ligand 12. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacante, F.; Senesi, P.; Montesano, A.; Frigerio, A.; Luzi, L.; Terruzzi, I. L-Carnitine: An Antioxidant Remedy for the Survival of Cardiomyocytes under Hyperglycemic Condition. J Diabetes Res 2018, 9, 2018–4028297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Ishida, M.; Nakatani, T. Bone marrow is a source of regenerated cardiomyocytes in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances migration of bone marrow cells and attenuates cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin under electron microscopy. J Heart Lung Transplant 2004, 23, 577–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Abdo, S.A.M.; Anas, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Potential Mechanisms, Governing Factors, and Implications of the Heart Stem Cell Debate. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro, M.; Del Pizzo, M.; Marzocco, S. Inflammatory mediators in a short-time mouse model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2016, 293, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Catalpol ameliorates doxorubicin-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in H9C2 cells through PPAR-γ activation. Exp Ther Med 2020, 20, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakjoo, M.; Ahmadi, S.E.; Zahedi, M. Interplay between proteasome inhibitors and NF-κB pathway in leukemia and lymphoma: a comprehensive review on challenges ahead of proteasome inhibitors. Cell Commun Signal, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.; Wong, W.; Lee, M.L. Exosomes in Inflammation and Inflammatory Disease. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y. Stem cell-derived exosomes: Emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther 2023, 14, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Lu, W.; Liang, L. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha alleviate liver injury by modulating anti-inflammatory functions in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Barrera, M.; Flórez-Zapata, N.; Lemus-Diaz, N. Integrated Analysis of Transcriptome and Secretome from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Reveal New Mechanisms for the Modulation of Inflammation and Immune Activation. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 575488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, T.; Mayer, M.P.; Rudiger, S.G.D. The Hsp70-Hsp90 Chaperone Cascade in protein folding. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 29,164–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabaud-Gibouin, V.; Durand, M.; Quere, R.; Girodon, F.; Garrido, C.; Jego, G. Heat shock proteins in leukemia and lymphoma: multitargets for innovative therapeutic approaches. Cancers 2023, 15, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, Z. Hsp90 inhibitor STA9090 sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Hyperthermia-Induced DNA damage by suppressing DNA-PKcs protein Stability and mRNA transcription. Mol Cancer Ther 2021, 20, 1880–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Yi, G.; Yu, K.; Feng, C.; Deng, S. The Role of HSP90 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells 2022, 11(21), 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisimura, L.M.; Bousquet, P.; Muccillo, F.; Tibirica, E.; Garzoni, L.R. Tyrosine hydroxylase and β2-adrenergic receptor expression in leukocytes of spontaneously hypertensive rats: putative peripheral markers of central sympathetic activity. Braz J Med Biol Res 2020, 53(12), e9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, C.; Bártulos, O.; Martínez-Campos, E. Tyrosine hydroxylase is expressed during early heart development and is required for cardiac chamber formation. Cardiovascular Research 2010, 88(1), 88(1),111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
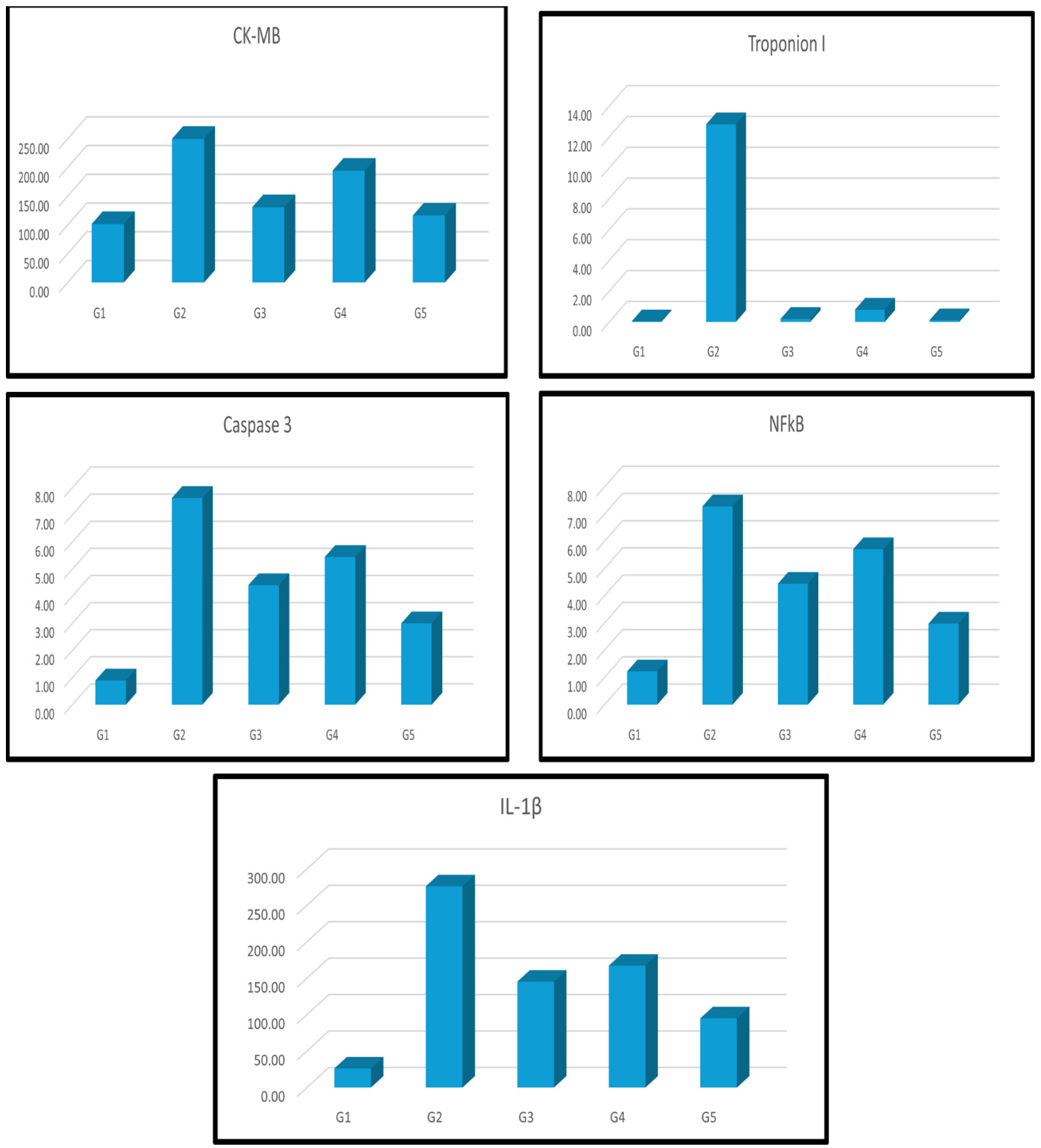
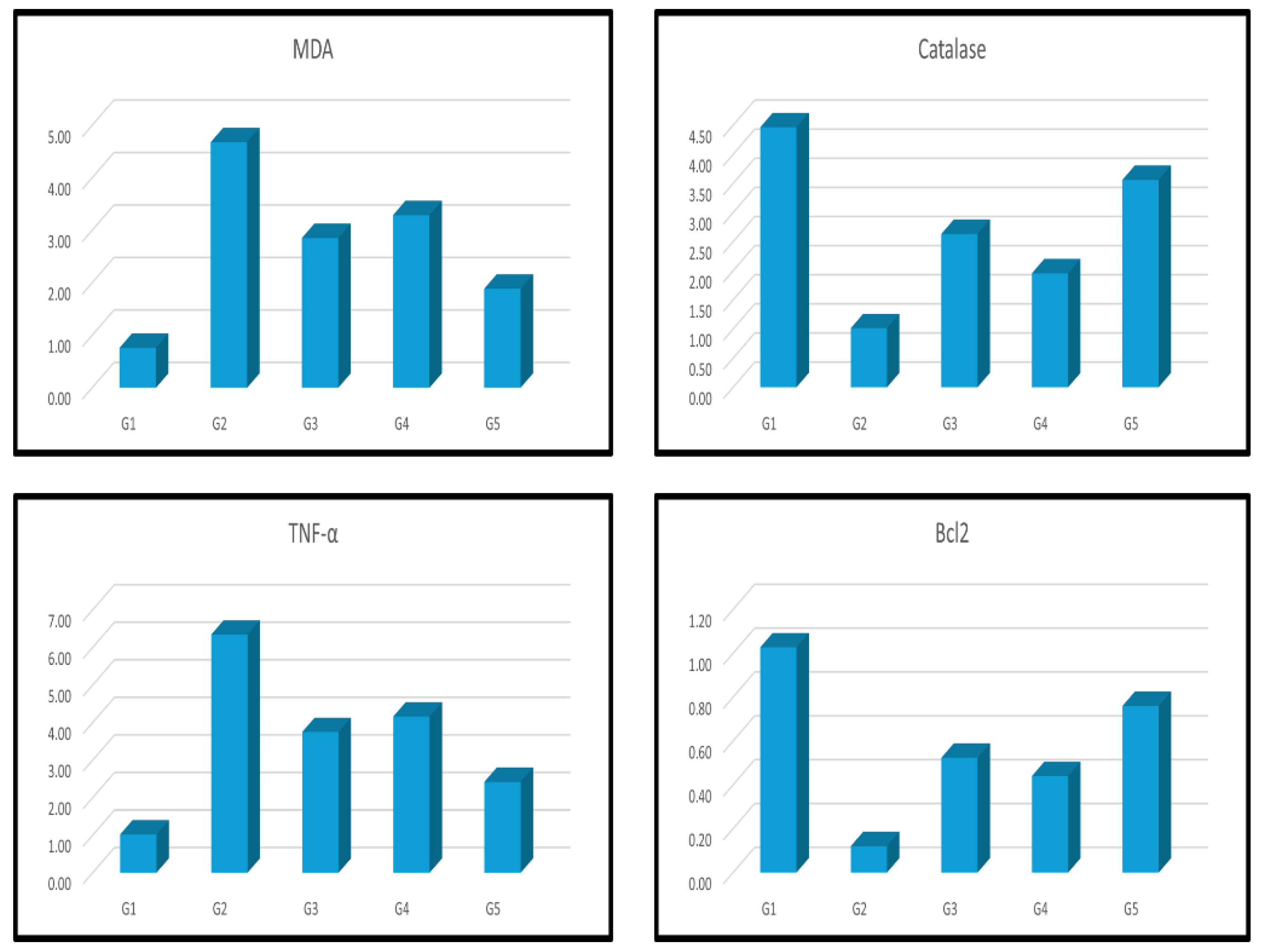
| Groups | CK-MB | Troponin I | Caspase 3 | NF-ҡβ | IL-1β |
| Group I刘(Control) | 1.02±1.78b | 0.04±0.01b | 0.89±0.05b | 1.22±0.07b | 26.27±1.68b |
| Group II刘(Dox) | 2.50±9.79a | 12.81±0.90a | 7.62±0.37a | 7.28±0.36a | 276.24±8.02a |
| Group III刘(Dox+MSCs) | 1.31±5.11a b | 0.19±0.06b | 4.40±0.23 a b | 4.44±0.10 a b | 145.37±6.83a b |
| Group IV刘(Dox+Lcarnitine) | 1.95±5.24a b | 0.79±0.03 a b | 5.44±0.12 a b | 5.71±0.13 a b | 167.28±7.15a b |
| Group V刘(Dox+MSCs+Lcarnitine) | 1.17±2.44a b | 0.10±0.01b | 2.99±0.06 a b | 2.97±0.09 a b | 95.00±3.47a b |
| Groups | MDA | Catalase | TNF-α | Bcl2 |
| Group I刘(Control) | 0.76±0.02b | 4.47±0.17b | 1.02±0.33b | 1.03±0.40b |
| Group II刘(Dox) | 4.68±0.14a | 1.02±0.07a | 6.34±0.46a | 0.12±0.03a |
| Group III刘(Dox+MSCs) | 2.85±0.25a b | 2.63±0.32a b | 3.75±0.17a b | 0.52±0.02a b |
| Group IV刘(Dox+Lcarnitine) | 3.29±0.16a b | 1.96±0.34a b | 4.16±0.24a b | 0.44±0.01a b |
| Group V刘(Dox+MSCs+Lcarnitine) | 1.89±0.05a b | 3.56±0.22a b | 2.42±0.19a b | 0.76±0.11b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





