Submitted:
27 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Summary Effects
2.2. Heterogeneity and Moderation Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stress
2.3. Detailed Moderation Effect Analysis
2.4. Heterogeneity and Moderation Analysis under Non Stress Conditions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection
- a)
- Only transgenic plants of any plant species, including insertional mutants;
- b)
- Only drought or salinity stress;
- c)
- Only proline metabolic genes (both anabolic and catabolic);
- d)
- No exogenous proline treatments;
- e)
- No mutants or allelic variant;
- f)
- All the measures are expressed as fresh weight.

4.2. Effect Size and Moderation Analysis
4.3. Meta-Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| P5C | -pyrroline-5-carboxylate |
| P5CS | 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase |
| OAT | Ornithine aminotransferase |
| GSA | Glutamate-5-semialdehyde |
| P5CR | -pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase |
| ProDH | Proline dehydrogenase |
| P5CDH | -pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase |
| CaMV35S | Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S promoter |
| ACT | ACT constitutive promoter |
| AIPC | ABA inducible promoter complex |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| APX | Ascorbate peroxidase |
| RWC | Relative water content |
| Rec | Relative electric conductivity |
References
- Trovato, M.; Mattioli, R.; Costantino, P. Multiple roles of proline in plant stress tolerance and development. Rendiconti Lincei 2008, 19, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C. Proline accumulation in plants: a review. Amino acids 2008, 35, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlani, G.; Trovato, M.; Funck, D.; Signorelli, S. Regulation of proline accumulation and its molecular and physiological functions in stress defence. Osmoprotectant-mediated abiotic stress tolerance in plants: recent advances and future perspectives 2019, pp. 73–97.
- Trovato, M.; Forlani, G.; Signorelli, S.; Funck, D. Proline metabolism and its functions in development and stress tolerance. Osmoprotectant-mediated abiotic stress tolerance in plants: recent advances and future perspectives 2019, pp. 41–72.
- Signorelli, S. The fermentation analogy: a point of view for understanding the intriguing role of proline accumulation in stressed plants. Frontiers in Plant Science 2016, 7, 213126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskara, G.B.; Yang, T.H.; Verslues, P.E. Dynamic proline metabolism: importance and regulation in water limited environments. Frontiers in Plant Science 2015, 6, 147002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KAVI KISHOR, P.B.; Sreenivasulu, N. Is proline accumulation per se correlated with stress tolerance or is proline homeostasis a more critical issue? Plant, cell & environment 2014, 37, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Bauduin, S.; Latini, M.; Belleggia, I.; Migliore, M.; Biancucci, M.; Mattioli, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L.; Funck, D.; Trovato, M. Interplay between proline metabolism and ROS in the fine tuning of root-meristem size in arabidopsis. Plants 2022, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Palombi, N.; Funck, D.; Trovato, M. Proline accumulation in pollen grains as potential target for improved yield stability under salt stress. Frontiers in plant science 2020, 11, 582877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.E.; Schmidt, F.L. Methods of meta-analysis: Correcting error and bias in research findings; Sage, 2004.
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta-regression. Statistics in medicine 2004, 23, 1663–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Brini, F.; Mseddi, K.; Rhizopoulou, S.; Jones, M.A. A holistic and sustainable approach linked to drought tolerance of Mediterranean crops. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14, 1167376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, K.B.; Abdelly, C.; Savouré, A. How reactive oxygen species and proline face stress together. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2014, 80, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia.; Mohanty, P.; Matysik, J. Effect of proline on the production of singlet oxygen. Amino acids 2001, 21, 195–200. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnoff, N.; Cumbes, Q.J. Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of compatible solutes. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabro, G.; Kovács, I.; Pavet, V.; Szabados, L.; Alvarez, M.E. Proline accumulation and AtP5CS2 gene activation are induced by plant-pathogen incompatible interactions in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2004, 17, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Villamor, J.G.; Verslues, P.E. Essential role of tissue-specific proline synthesis and catabolism in growth and redox balance at low water potential. Plant physiology 2011, 157, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klümper, W.; Qaim, M. A meta-analysis of the impacts of genetically modified crops. PloS one 2014, 9, e111629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, A.; Veresoglou, S.D.; Leifheit, E.F.; Rillig, M.C. Arbuscular mycorrhizal influence on zinc nutrition in crop plants–a meta-analysis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2014, 69, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Understanding mechanisms of soil biota involvement in soil aggregation: A way forward with saprobic fungi? Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2015, 88, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wujeska, A.; Bossinger, G.; Tausz, M. Responses of foliar antioxidative and photoprotective defence systems of trees to drought: a meta-analysis. Tree physiology 2013, 33, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, H. A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity. Econometrica: journal of the Econometric Society 1980, pp. 817–838.
- Williams, R.L. A note on robust variance estimation for cluster-correlated data. Biometrics 2000, 56, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. Journal of statistical software 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nature methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Shang, X.; Shao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W.; Ma, Y. Meta-analysis of the effect of expression of MYB transcription factor genes on abiotic stress. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ping, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, Y. Meta-analysis of the effects of overexpression of WRKY transcription factors on plant responses to drought stress. BMC genetics 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, D.; Wisniewski, M.; Cheng, Z.M. Meta-analysis of the effect of overexpression of dehydration-responsive element binding family genes on temperature stress tolerance and related responses. Frontiers in Plant Science 2018, 9, 365405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Viechtbauer, W. Bias and efficiency of meta-analytic variance estimators in the random-effects model. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics 2005, 30, 261–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in medicine 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W.; Cheung, M.W.L. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Research synthesis methods 2010, 1, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
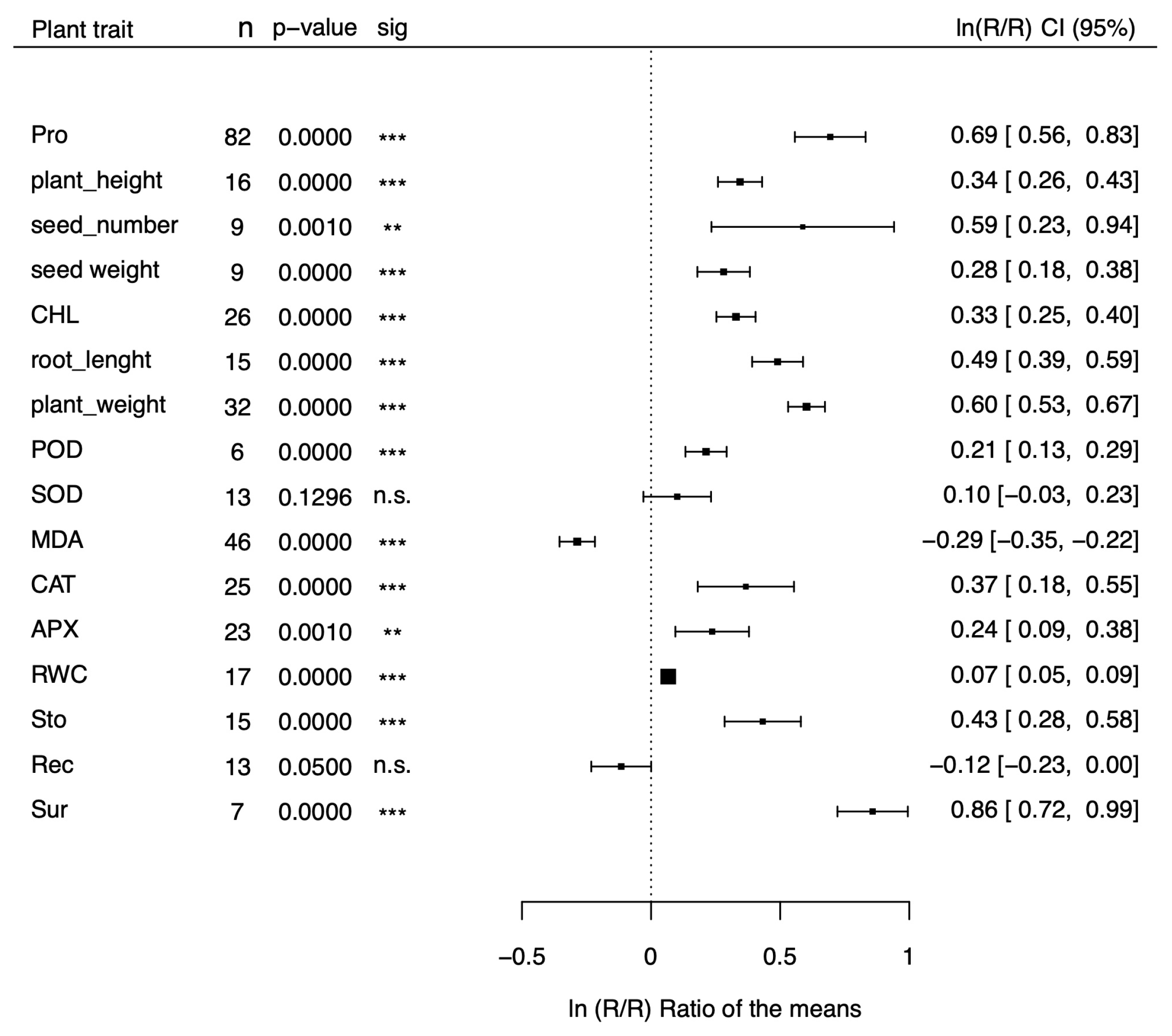
| Parameter | Q test | PI | Exp | % change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proline | 0.3906 | 0.0000 | 99.53% | 0.53 / 1.92 | 0.6939 | 2.00 | 100% |
| Plant height | 0.0234 | 0.0000 | 97.63% | 0.03 / 0.65 | 0.3445 | 1.44 | 44% |
| Seed number | 0.2817 | 0.0000 | 99.33% | 0.60 / 5.40 | 0.5874 | 1.80 | 80% |
| Seed weight | 0.0155 | 0.0000 | 81.21% | 1.02 / 1.73 | 0.2810 | 1.32 | 32% |
| Chlorophyll | 0.0250 | 0.0000 | 83.54% | 1.01 / 1.91 | 0.3289 | 1.39 | 39% |
| Root length | 0.0279 | 0.0000 | 98.74% | 0.15 / 0.83 | 0.4400 | 1.63 | 63% |
| Plant weight | 0.0264 | 0.0000 | 96.37% | 1.32 / 2.53 | 0.6021 | 1.83 | 83% |
| POD activity | 0.0074 | 0.0000 | 92.00% | 1.03 / 1.49 | 0.2129 | 1.24 | 24% |
| SOD activity | 0.0550 | 0.0000 | 98.43% | 0.69 / 1.78 | 0.1013 | 1.11 | 11% |
| MDA activity | 0.0434 | 0.0000 | 92.84% | -0.50 / -1.14 | -0.2860 | 0.75 | -25% |
| CAT activity | 0.2044 | 0.0000 | 96.39% | 0.58 / 3.57 | 0.3671 | 1.44 | 44% |
| APX activity | 0.0909 | 0.0000 | 92.36% | -0.37 / 0.84 | 0.2366 | 1.26 | 26% |
| RWC | 0.0012 | 0.0000 | 83.68% | 1.00 / 1.15 | 0.0665 | 1.07 | 7% |
| Stomatal conductance | 0.0461 | 0.0000 | 81.12% | 0.01 / 0.87 | 0.4325 | 1.54 | 54% |
| Electric conductivity | 0.0365 | 0.0000 | 97.28% | 0.94 / 1.00 | -0.1156 | 0.89 | -11% |
| Survival | 0.0177 | 0.0000 | 74.90% | 1.76 / 3.17 | 0.8582 | 2.36 | 136% |
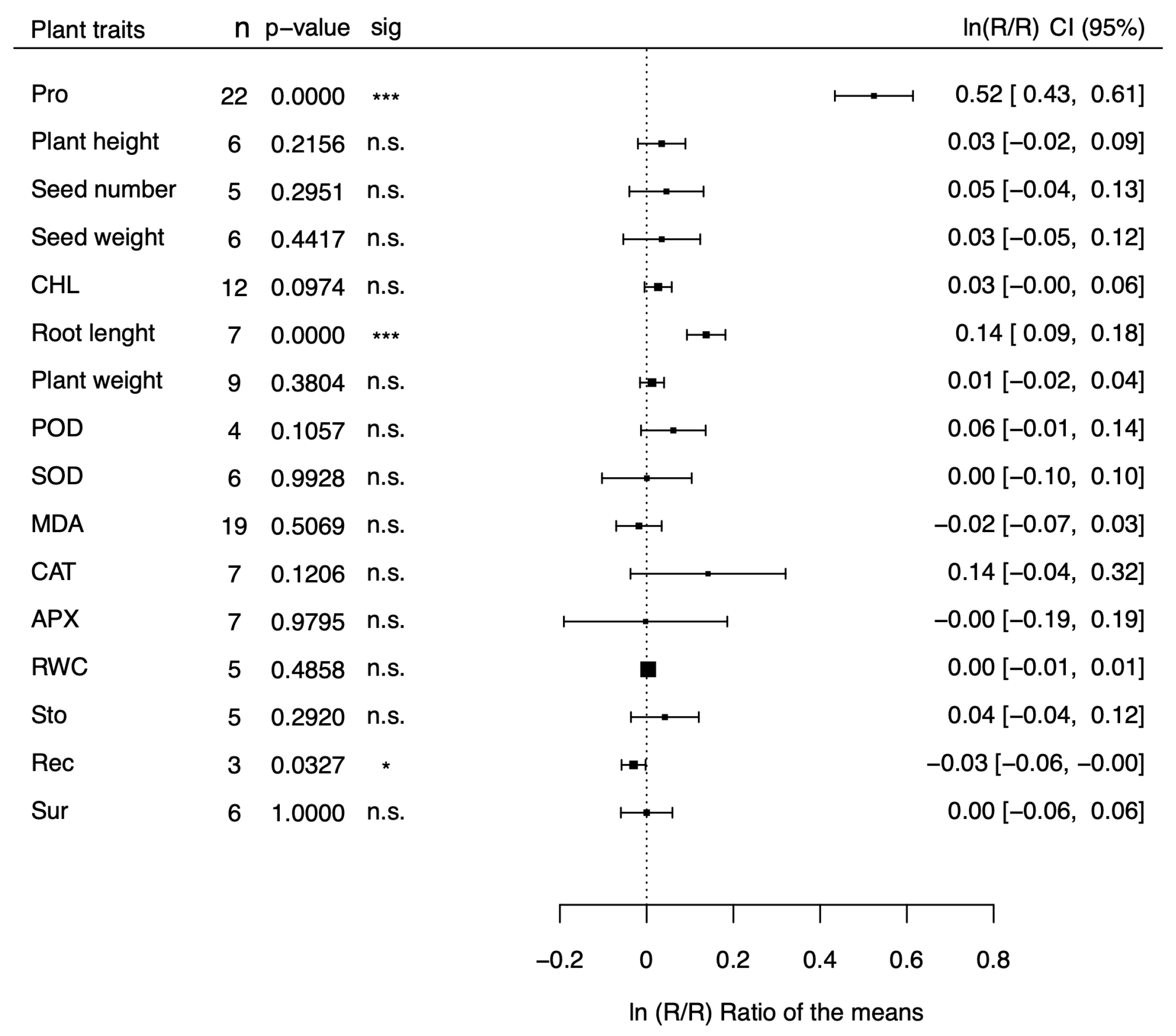
| Parameter | Q test | PI | Exp | % change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proline | 0.0218 | 0.0000 | 71.60% | 1.25 / 2.29 | 0.5241 | 1.64 | 64% |
| Plant height | 0.0027 | 0.0000 | 68.79% | 0.92 / 1.16 | 0.0346 | 1.04 | 4% |
| Seed number | 0.0063 | 0.0000 | 73.94% | 0.88 / 1.25 | 0.0457 | 1.05 | 5% |
| Seed weight | 0.0038 | 0.0343 | 32.26% | 0.89 / 1.20 | 0.0348 | 1.04 | 4% |
| Chlorophyll | 0.0012 | 0.0025 | 54.37% | 0.95 / 1.11 | 0.0265 | 1.03 | 3% |
| Root length | 0.0019 | 0.0000 | 0.68% | 1.09 / 1.12 | 0.1032 | 1.11 | 11% |
| Plant weight | 0.0005 | 0.0000 | 62.94% | 0.96 / 1.07 | 0.0124 | 1.01 | 1% |
| POD activity | 0.0000 | 0.6647 | 0.00% | 0.99 / 1.15 | 0.0615 | 1.06 | 6% |
| SOD activity | 0.0127 | 0.0000 | 83.16% | -0.24 / 0.24 | 0.0005 | 1.00 | 0% |
| MDA activity | 0.0055 | 0.0000 | 80.07% | 0.84 / 1.09 | -0.0468 | 0.95 | -5% |
| CAT activity | 0.0396 | 0.0000 | 74.29% | -0.29 / 0.67 | 0.1416 | 1.15 | 15% |
| APX activity | 0.0434 | 0.0000 | 84.32% | 0.91 / 1.34 | 0.0980 | 1.10 | 10% |
| RWC | 0.0000 | 0.9893 | 0.00% | 0.97 / 1.01 | -0.0060 | 0.99 | -1% |
| Stomatal conductance | 0.0032 | 0.0204 | 48.52% | 0.91 / 1.20 | 0.0421 | 1.04 | 4% |
| Electric conductivity | 0.0000 | 0.9583 | 0.00% | 0.94 / 1.00 | -0.0302 | 0.97 | -3% |
| Survival | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.00% | 0.94 / 1.06 | 0.0000 | 1.00 | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





