1. Introduction
Obesity, a chronic and recurrent condition, is experiencing a significant rise in prevalence globally, resulting in substantial healthcare costs associated with its related comorbidities [
1,
2,
3]. Currently, body mass index (BMI) continues to serve as a categorical diagnostic measure for obesity. However, BMI has notable drawbacks as it does not offer insights into body composition (BC) or the metabolic status of individuals [
4,
5]. In this way, new methods, as muscle ultrasound (MUS), should be introduced into clinical practice to assess the BC of these patients, especially if they are candidates for bariatric surgery (BS), since weight loss caused by BS leads to changes in the BC. BS is one of the most effective options for weight loss in patients with obesity, as well as for controlling related comorbidities, especially metabolic diseases. Patients with obesity may be at high risk for developing sarcopenia, a condition known as sarcopenic obesity (SO), as well as an elevation in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Even with weight reduction, sarcopenia can continue in patients after BS [
6,
7,
8]. This loss of muscle mass has been associated with lower psychological health and quality of life (QoL) and higher prevalence of type 2 diabetes [
9,
10]. Thus, the maintenance of muscle mass during weight loss following BS holds clinical significance [
11]. However, BC assessment methods are often overlooked in daily clinical practice for managing obesity due to the absence of straightforward and reliable tests. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) has traditionally been regarded as a reference technique, quantifying the mass of various tissues in kilograms [
12]. Nonetheless, DEXA lacks the ability to provide information about specific muscle groups, thus failing to address regional sarcopenia. Additionally, accessibility to DEXA is limited in many clinics, and it is not routinely performed except for bone density assessment [
5,
13,
14]. Among the numerous methods available for assessing muscle mass, MUS is becoming increasingly recognized as a valuable tool in clinical settings, being a simple, real-time, noninvasive, radiation-free, low-cost, and easily transportable technique. Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the use of MUS for diagnosing sarcopenia [
15,
16], but there is insufficient research on its effectiveness in diagnosing SO and assessing changes in lean mass following BS [
17,
18]. In this scenario, MUS could be used as an alternative or complementary method in front of the parameters that could measure the traditional bioimpedance analysis (BIA) or DEXA [
19]. In addition, MUS could distinguish regional sarcopenia, such as rectus femoral thickness (RFT) of quadriceps muscle. This muscle group plays a crucial role in performing fundamental tasks necessary for an individual's autonomy, as it is indispensable for walking [
20] and subsequently for QoL [
17].
On this basis, the present study was designed with the following objectives: a) to assess the correlation and changes pre- and post-BS between RFT measured by MUS and other methods (BIA and DEXA), aiming to validate MUS as a valuable tool for evaluating BC and regional sarcopenia; b) to establish the correlation between body composition assessment methods, including MUS, and HOMA-IR, a well-established biomarker of diabetes and sarcopenia; c) to compare the efficacy of the different methods (MUS, BIA, DEXA, and dynamometer) in assessing QoL before and after BS.
2. Materials and Methods
We performed a prospective observational study carried out in our hospital. Subjects were recruited from the outpatient Obesity Unit between January 2020 and February 2022. Subjects were candidates for BS when their BMI was higher than 35 kg/m² with comorbidities or BMI > 40 kg/m². The study follows the STROBE guidelines for prospective studies [
21]. Exclusion criteria were age: ≥ 65 years, pregnancy, patients with clinical or personal characteristics that make monitoring difficult: drug or alcohol addiction, severe psychological or psychiatric disorders. Initially, we conducted an analysis of the HOMA-IR pre-surgery for all patients. Subsequently, handgrip strength was assessed using a dynamometer, while BIA was employed to determine the fat-free mass index (iFFM). The appendicular muscle index (AMI) was calculated by DEXA, and RFT was measured using ultrasound. These assessments were conducted one month prior to surgery and during the 12-month follow-up period to study changes in body composition. Additionally, QoL was evaluated using the Moorehead-Ardelt questionnaire both before and after BS. The Hospital’s Ethics Committee approved all the procedures carried out in the study and all subjects signed the informed consent before their inclusion in the study.
The BodyStat® 1500 MDD model was used for BIA, as previously described
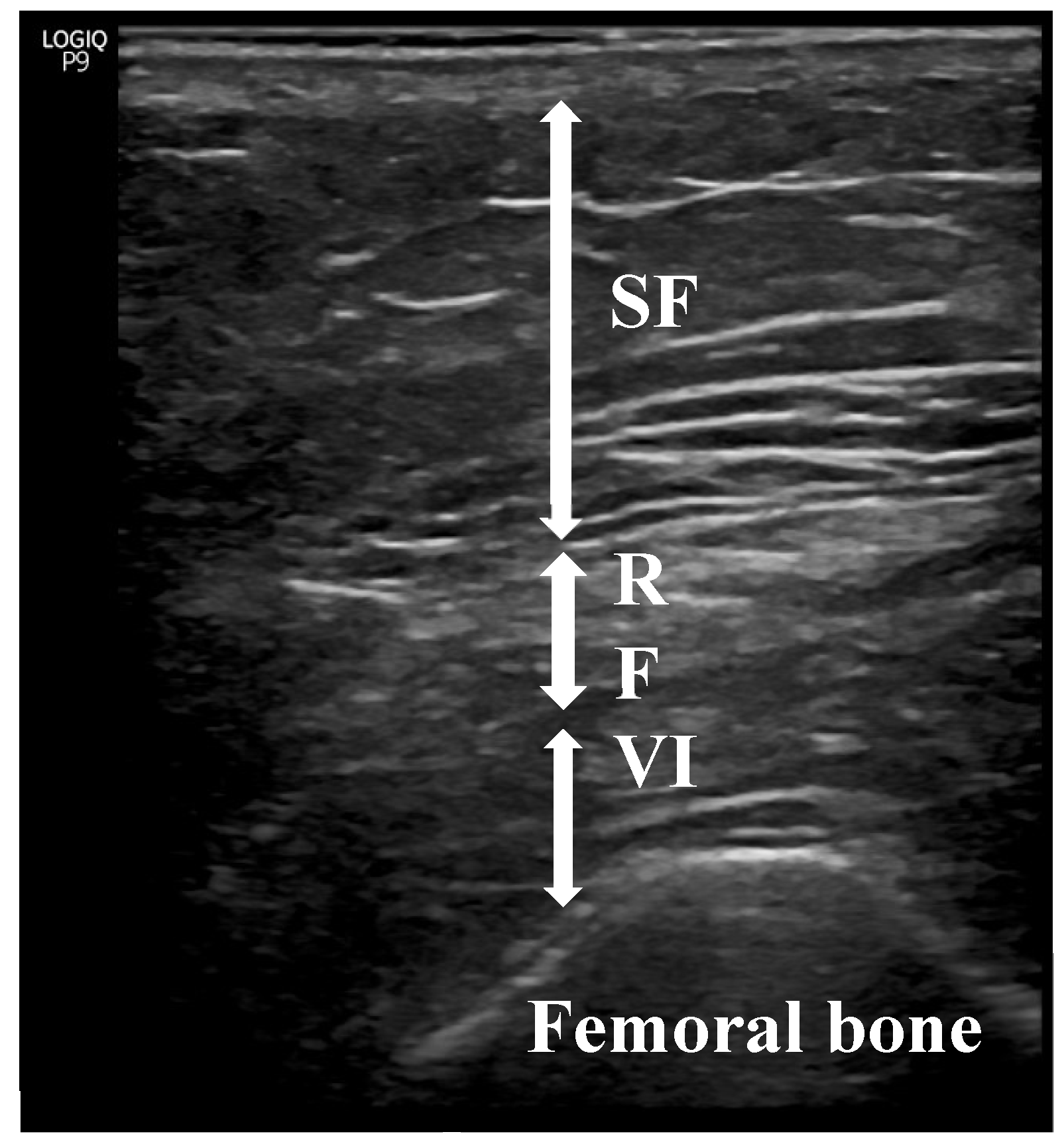
[17,22,23]. RFT measurements were made with a sonographic US Logiq P9 (GE Healthcare) equipment muscle-skeleton B-model using a linear multifrequency transducer (4–11 Hz) with adequate use of contact gel and minimal pressure to avoid excessive compression of the muscle. Patient positioning was done in accordance with what is reported in the literature (
Figure 1) [
17,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28].
Sarcopenia predominantly impacts the lower limbs; therefore, RFT was specifically selected [[
29]] for evaluation. Its assessment via ultrasound followed the guidelines set forth by the European Union Geriatric Medicine Society Sarcopenia Special Interest Group and aligned with previous literature [
19]. Three consecutive measurements were conducted, and the average value was recorded. The data were expressed in centimeters (cm) as means ± standard deviation. To minimize interindividual variability, all measurements were performed by the same physician (Endocrinologist A.S-S), who had 5 years of experience. Intra-observer reliability was assessed by evaluating intraclass correlation coefficients (CVs) using three images captured on three different days, yielding a CV of 0.94 for RFT.
Statistical Analysis
We utilized STATA statistical software version 14 (College Station, TX) for our analysis. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), unless otherwise stated, while categorical variables are presented as percentages. T-tests were employed to compare continuous variables between groups, Fisher's test for categorical variables, and Pearson's correlation test to examine relationships between variables. All analyses were two-tailed, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
The general information of the participants is presented in
Table 1. A total of 77 individuals were involved: 50 were females (64.9%), with an average age of 53.2 ± 8.67 years. The average initial BMI was 43.82 ± 5.08 kg/m2 and decreased by 12.95 ± 3.56 kg/m2 (p=0.001).
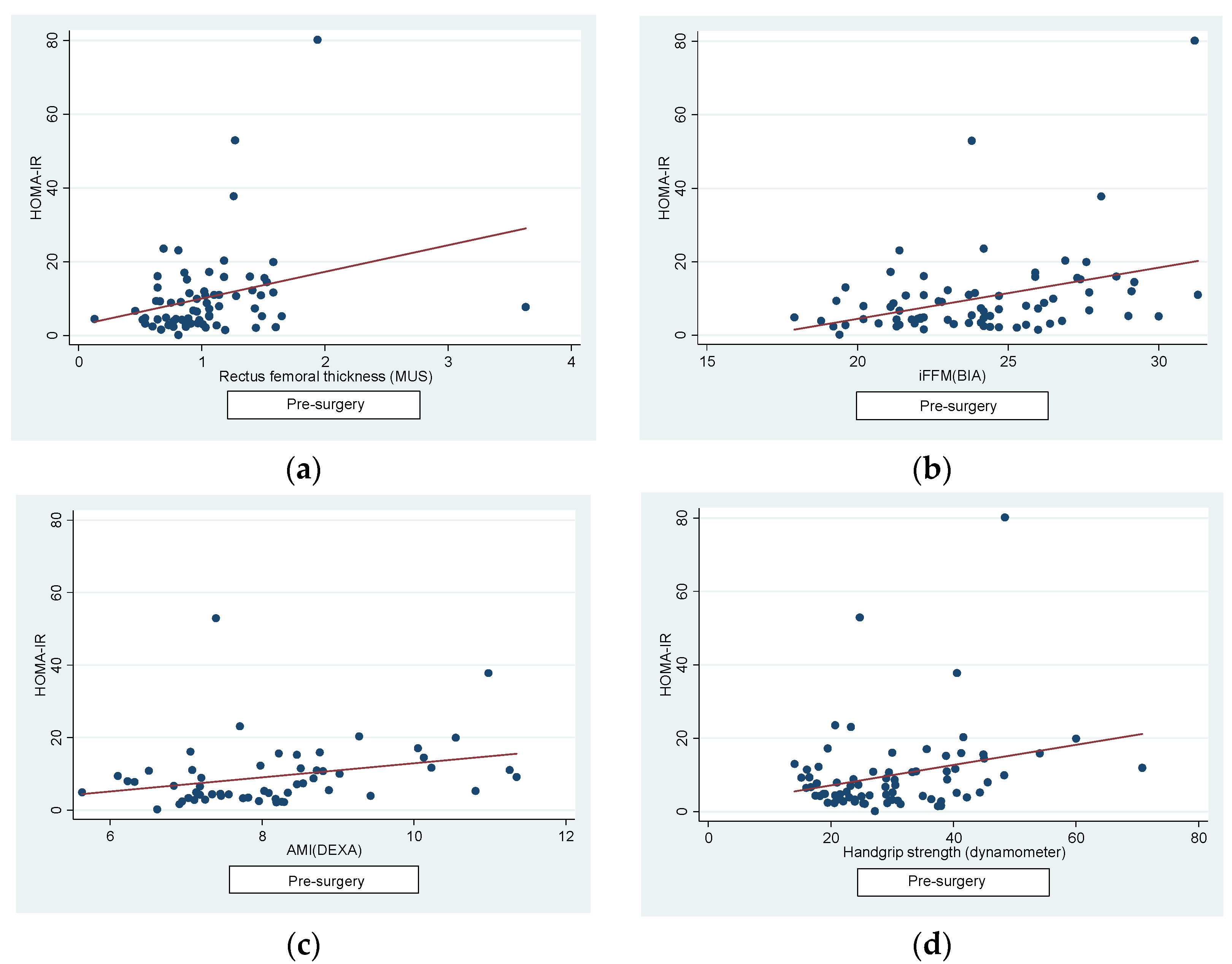
Regarding the correlations, firstly, we found a positive correlation pre-surgery between HOMA-IR and: RFT (r=0.27, p=0.02), iFFM (r=0.36, p=0.001), AMI (r=0.31, p=0.01) and dynamometer (r=0.26, p=0.02) (
Figure 2).
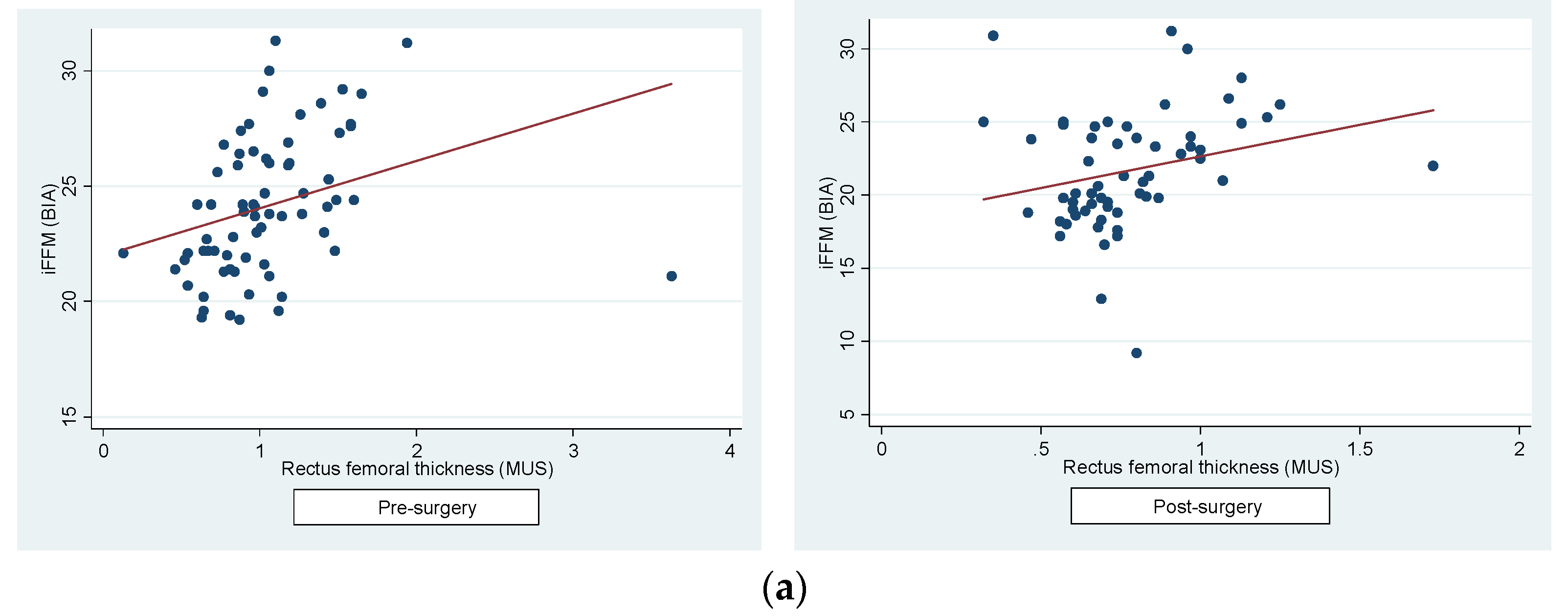
Secondly, we determined a positive correlation between the RFT and iFFM (pre-surgery: r=0.31, p=0.01; post-surgery: r=0.25, p=0.05) (
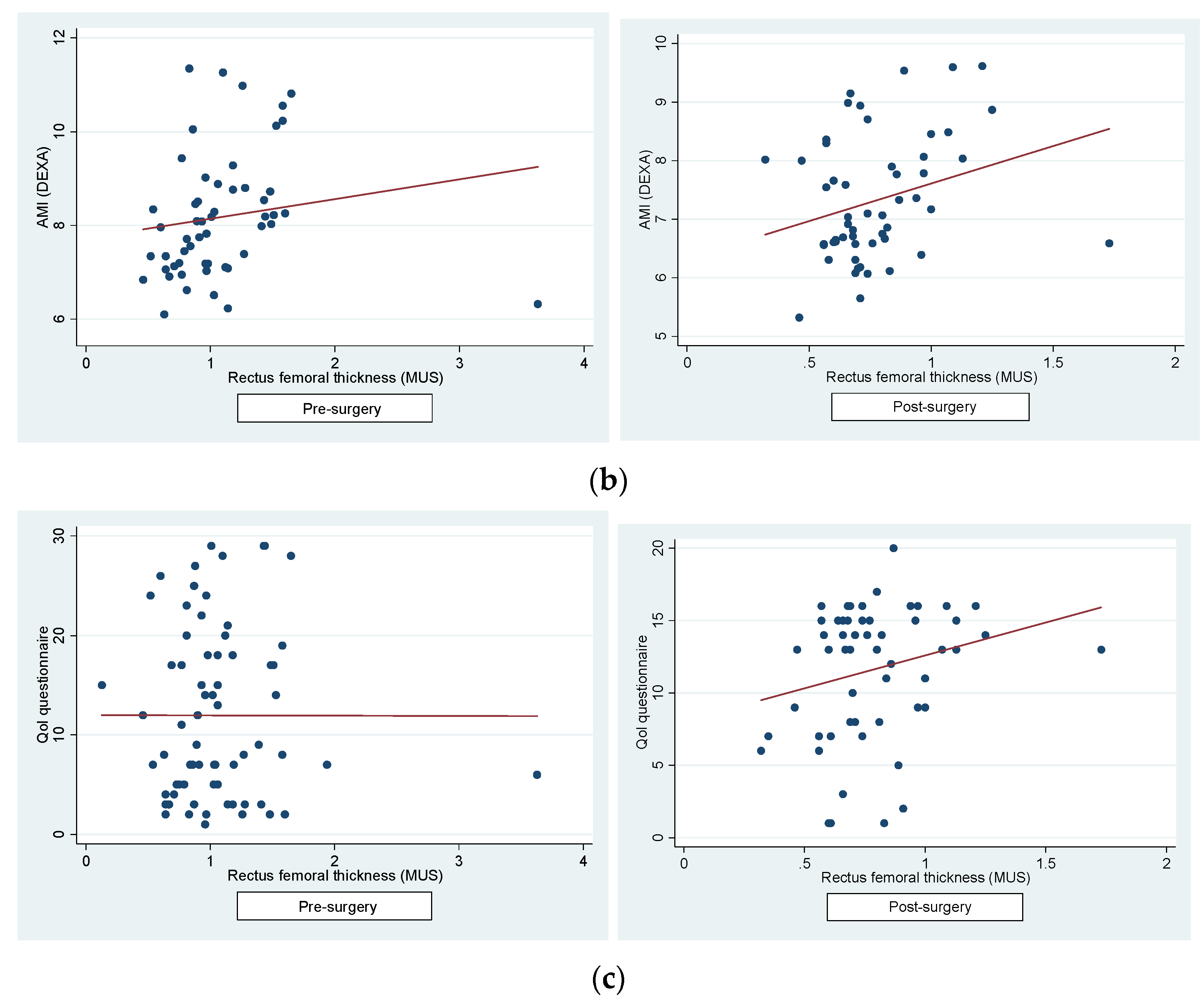
Figure 3a) and between RFT and lower extremities AMI post-surgery (pre-surgery: r=0.15, p=0.26; post-surgery: r=0.27, p=0.04) (
Figure 3b). A significant shift in the correlation pattern between the QoL questionnaire and RFT was observed pre- and post-surgery. Prior to surgery, a negligible negative correlation was noted (r=-0.0018, p=0.98), while post-surgery, the correlation turned positive (r=0.23, p=0.079), albeit not reaching statistical significance (
Figure 3c). Conversely, correlations between the QoL questionnaire and iFFM (pre-surgical: r=0.09, p=0.4; post-surgical: r=0.0024, p=0.1) and AMI (pre-surgical: r=0.11, p=0.4; post-surgical: r=0.09, p=0.5) remained weak and consistently positive, albeit yet not statistically significant. Furthermore, no significant correlation was found between the QoL questionnaire and handgrip strength, both pre- and post-surgery (pre-surgical: r=0.14, p=0.22; post-surgical: r=0.12, p=0.3). These results underscore the unique influence of BS on the relationship between QoL and RFT, diverging from the patterns observed with other BC measures.
The anthropometric parameters assessed by BIA (iFFM), DEXA (AMI) and MUS (RFT) are displayed in
Table 2. We found significant reductions in: RTF (1.05 ± 0.067 vs 0.77 ± 0.03, p=0.0002), iFFM (23.79 ± 0.38 vs 21.07 ± 0.59, p=0.001), AMI (7.99 ± 0.18 vs 7.16 ± 0.14, p=0.001) and lower extremities AMI (6.02 ± 0.12 vs 5.39 ± 0.11, p=0.001). However, there were no statistically significant differences regarding grip strength measured by dynamometry (29.33 ± 1.26 vs 29.38 ± 1.29, p=0.94). On the other hand, significant statistical differences were found when comparing the QoL test before and after surgery (w0: 2.92, p = 0.001).
Delving deeper into the obtained results, it was found that 6 patients within the total sample experienced an increase in RFT despite the statistically significant overall reduction. It is noteworthy that in these 6 subjects, the score of the Qol test increased considerably in all of them (Table 3).
4. Discussion
In the present study, changes in BC were evaluated in patients undergoing BS at baseline and after 12-month follow-up. The results showed a statistically significant loss of RFT, iFFM and AMI but not of handgrip strength, confirming what is described previously in the literature [
30,
31], and positioning MUS as another valid tool for the study of BC. Furthermore, we demonstrate a good correlation pre-BS between HOMA-IR and RFT, iFMM and AMI which shows us that imaging methods, including MUS of RFT, can predict SO in these patients, since insulin resistance is a predictive factor for muscle deterioration and diabetes. Moreover, to validate MUS as a useful tool we establish a good correlation between pre- and post-BS using US and BIA for assessing BC. These good correlations have been observed between RFT and lower extremities AMI only post-surgery, thus supporting the value of US to assess the follow-up of these patients after BS. The lack of a pre-BS correlation between MUS and DEXA may be attributed to the sample size and the diminished precision in patients with obesity, characterized by a significant adipose tissue layer overlying muscle tissue and hyperhydration.
On the other hand, our study supports the already known concept that sarcopenia is first affected in the lower extremities rather than the upper ones, as no differences were detected in grip strength measured by dynamometry [
32,
33]. Our study population is under 65 years old, and their functional limitations of upper limbs should not be affected, and consequently handgrip strength. In our sample, obesity leads them to reduced mobility and less walking, which could explain a greater tendency towards sarcopenia in the lower limbs.
When analyzing the relationship between the methods employed and QoL, we observed a slight negative correlation between RFT and pre-surgery QoL. This suggests that higher muscle mass is associated with lower QoL, likely due to its correlation with higher obesity levels in patients. However, following BS, this relationship is reversed, indicating a positive correlation between RFT and QoL post-BS. This shift implies that increased muscle mass corresponds to improved QoL, as patients no longer maintain obese status post-BS. Interestingly, this reversal of correlation was not evident with the parameters analyzed, nor with BIA or DEXA. This underscores the complex interplay between BC changes and QoL outcomes following BS, suggesting a need for further investigation into the underlying mechanisms driving these associations. These results lead us to consider that the MUS of RFT may be more useful and complementary for monitoring patients undergoing BS, as the quadriceps alone is a strong indicator of possible regional sarcopenia and autonomy [
34,
35]. Therefore, patients could improve the QoL even if the total lean mass does not show improvement by BIA, since the improvement of the quadriceps can allow patient autonomy. In fact, we detected 6 patients out of the total sample who exhibited an increase in RFT despite the overall statistically significant decrease. Specifically, in these 6 patients, the score of QoL questionnaire increased substantially in all of them.
This prospective study demonstrates that the BC changes resulting from BS are significant and can be accurately assessed using MUS. So, incorporating MUS into BC assessments for individuals being considered for BS offers a more comprehensive understanding of post-intervention BC. Currently, BC evaluations are not systematically conducted in many centres, likely due to resource constraints. Methods such as DEXA, CT and MRI are not only costly and difficult to access but also involve radiation exposure. In contrast, MUS is becoming more readily available in clinics and could serve as a valuable tool for assessing BC or even screening for SO. Since MUS can provide localized information about muscle groups, it can complement the other accessible methods as BIA and dynamometry, which assess functional aspects. In summary, our findings suggest the need for further investigation into the utility of MUS in this context and the establishment of specific criteria, as cut-off points, for diagnosing regional sarcopenia.
The primary constraint in our study is the absence of a control group comprising individuals with a normal weight. However, our study was designed to assess post-BS progression, with patients serving as their own reference points [
36]. Moreover, changes in BC may be exaggerated or underestimated by inadequate control of confounders, as physical activity, or other life habits [
37]. The drawbacks associated with MUS primarily stem from the absence of standardized procedures and its heavy reliance on the proficiency and capabilities of the operator [
38]. The ability to interpret muscle-fat interfaces is constrained by the similarity in acoustic impedance between muscle and fat tissues. Additionally, an operator using ultrasound may inadvertently introduce measurement errors by applying excessive pressure with the transducer onto the skin, potentially compressing the muscle tissue [
39]. Furthermore, we lacked data regarding quadriceps muscle function. Nonetheless, considering the significance of the quadriceps in mobility assessments, measurements of the RFT offer a valuable proxy for strength [
40,
41,
42]. All measurements were conducted by the same physician, which limited the reproducibility of the test.
To sum up, the measurements acquired from the MUS of RFT represent novel and readily accessible parameters that we can incorporate into clinical practice to enhance the assessment of BC. Specifically, morphological features derived from MUS measurements of the quadriceps muscle could serve as a tool for screening and initial assessment of SO in individuals considering BS, and particularly in their postoperative monitoring. This strategy will provide us with fresh perspectives on the potential benefits of MUS [
23].
5. Conclusions
Our results suggest that MUS of RFT can be complementary to BIA and DEXA for the evaluation and the follow-up of BC in patients operated on for BS, as they are statistically significant correlated and all of them reduce statistically significative post-BS. Moreover, RFT, as the other methods for the study of BC, correlates with HOMA pre-BS which demonstrated the relation with sarcopenia or diabetes in the population of our study. Moreover, MUS of RFT might be more closely associated with QoL than other methods. Therefore, it represents an accessible, noninvasive, and cost-effective tool that could offer valuable insights into quadriceps sarcopenia for the monitoring of this population.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Simó-Servat A. and Barahona MJ.; methodology Simó-Servat A. and Ibarra M and Libra M.; validation, Barahona MJ, Perea V.; formal analysis, Simó-Servat A, Perea V, Barahona MJ; investigation, Simó-Servat A and Barahona MJ.; writing—original draft preparation, Simó-Servat A and Barahona MJ; writing—review and editing, Simó-Servat A and Barahona MJ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript..
Funding
This research was funded by from “Fundació Docència i Recerca MútuaTerrassa” (Exp.P12/2018)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Ethics Committee of University Hospital MutuaTerrassa (Spain) (EO1938).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. .
References
- Jayedi A, Soltani S, Motlagh SZT, Emadi A, Shahinfar H, Moosavi H, et al. Anthropometric and adiposity indicators and risk of type 2 diabetes: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ 2022, 376. [CrossRef]
- Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, de Gonzalez AB, et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data metaanalysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. <italic>Lancet</italic> <bold>2016</bold>, <italic>388</italic>, 776–786. [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Ambrosi J, Silva C, Galofré JC, Escalada J, Santos S, Millán D, et al. Body mass index classification misses subjects with increased cardiometabolic risk factors related to elevated adiposity. Int J Obes. 2012, 36, 286–294. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 5. Palmas F, Ciudin A, Guerra R, Eiroa D, Espinet C, Roson N, Burgos R and Simo R. Comparison of computed tomography and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in the evaluation of body composition in patients with obesity. Front. Endocrinol. [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Tan, C.S.; Tan, K.W.; Lim, S.P.Y.; So, J.B.Y.; Shabbir, A. Sleeve gastrectomy and roux-en-Y gastric bypass lead to comparable changes in body composition in a multiethnic Asian population. J Gastrointest Surg. 2019, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, O.; Ruthes, E.M.P.; Malinowski, A.K.C.; Lima, A.L.; Veiga, M.S.; Krause, M.P.; et al. Changes in bone mass and body composition after bariatric surgery. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baad VMA, Bezerra LR, de Holanda NCP, et al. Body Composition, Sarcopenia and Physical Performance After Bariatric Surgery: Differences Between Sleeve Gastrectomy and Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass. Obes Surg. 2022, 32, 3830–3838. [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Shin, M.J. Sarcopenic obesity is associated with lower indicators of psychological health and quality of life in Koreans. Nutr Res. 2015, 35, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, Y. Association of sarcopenic obesity with the risk of all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizoo, D.; de Heide, L.J.; Emous, M.; van Zutphen, T.; Navis, G.; van Beek, A.P. Measuring Muscle Mass and Strength in Obesity: a Review of Various Methods. Obes Surg. 2021, 31, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [CrossRef]
- Gupta N, Balasekaran G, Victor Govindaswamy V, Yong Hwa C, Meng Shun L. Comparison of body composition with bioelectric impedance (BIA) and dual energy Xray absorptiometry (DEXA) among Singapore Chinese. J Sci Med Sport 2011, 14, 33–35. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toombs RJ, Ducher G, Shepherd JA, De Souza MJ. The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obesity 2012, 20, 30–39. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineau, J.C.; Guihard-Costa, A.M.; Bocquet, M. Validation of ultrasound techniques applied to body fat measurement. A comparison between ultrasound techniques, air displacement plethysmography and bioelectrical impedance vs. dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Ann Nutr Metab. 2007, 51, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Narici, M.V.; Lauretani, F.; Nouvenne, A.; Colizzi, E.; Mantovani, M.; Corsonello, A.; Landi, F.; Meschi, T.; Maggio, M. Assessing sarcopenia with vastus lateralis muscle ultrasound: an operative protocol. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018, 30, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó-Servat A, Ibarra M, Libran M, et al. Usefulness of Ultrasound in Assessing the Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Body Composition: a Pilot Study. Obes Surg. 2023, 33, 1211–1217. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, O.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Sengul Aycicek, G.; Unsal, P.; Esme, M.; Ucar, Y.; Burkuk, S.; Sendur, A.; Yavuz, B.B.; Cankurtaran, M.; Halil, M. Role of Ultrasonography in Estimating Muscle Mass in Sarcopenic Obesity. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2020, 44, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ido, A.; Nakayama, Y.; Ishii, K.; Iemitsu, M.; Sato, K.; Fujimoto, M.; et al. Ultrasound-Derived Abdominal Muscle Thickness Better Detects Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Obese Patients tan Skeletal Muscle Index Measured by Dual-Energy XRay Absorptiometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkisas, S.; Bastijns, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beaudart, C.; Beckwée, D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Gasowski, J.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Kasiukiewicz, A.; Landi, F.; Małek, M.; Marco, E.; Martone, A.M.; de Miguel, A.M.; Piotrowicz, K.; Sanchez, E.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, D.; Scafoglieri, A.; Vandewoude, M.; Verhoeven, V.; Wojszel, Z.B.; De Cock, A.M. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: 2020 SARCUS update. Eur Geriatr Med. 2021, 12, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó-Servat, A.; Ibarra, M.; Libran, M.; Rodríguez, S.; Perea, V.; Quirós, C.; Orois, A.; Pérez, N.; Simó, R.; Barahona, M.J. Usefulness of Muscle Ultrasound to Study Sarcopenic Obesity: A Pilot Case-Control Study. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó-Servat, A.; Ibarra, M.; Libran, M.; Rodríguez, S.; Perea, V.; Quirós, C.; Orois, A.; Pérez, N.; Simó, R.; Barahona, M.J. Usefulness of Muscle Ultrasound to Study Sarcopenic Obesity: A Pilot Case-Control Study. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ito, K.; Tsushima, M.; Kobayakawa, T.; Morozumi, M.; Tanaka, S.; Machino, M.; Ota, K.; Kanbara, S.; Ito, S.; Ishiguro, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Imagama, S. Ultrasound measurement of thigh muscle thickness for assessment of sarcopenia. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2018, 80, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Kera, T.; Hirayama, R.; Hirano, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ihara, K.; Kojima, M.; Obuchi, S. Morphological and qualitative characteristics of the quadriceps muscle of community-dwelling older adults based on ultrasound imaging: classification using latent class analysis. Aging clinical and experimental research 2018, 30, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.V.; Moorey, H.; Stringer, H.; Sahbudin, I.; Filer, A.; Lord, J.M.; Sapey, E. Bilateral Anterior Thigh Thickness: A New Diagnostic Tool for the Identification of Low Muscle Mass? J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019, 20, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.A.; Oliveira, D.; Cupolilo, E.N.; Miranda, C.S.; Colugnati, F.A.B.; Mansur, H.N.; Fernandes, N.M.D.S.; Bastos, M.G. Rectus femoris muscle mass evaluation by ultrasound: Facilitating sarcopenia diagnosis in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease stages. Clinics 2018, 73, e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, D.; Ndanyo, L.S.; Brown, S.; Agyapong-Badu, S.; Warner, M.; Stokes, M.; Samuel, D. Thigh muscle and subcutaneous tissue thickness measured using ultrasound imaging in older females living in extended care: A preliminary study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minetto, M.A.; Caresio, C.; Menapace, T.; Hajdareviv, A.; Marchini, A.; Molinari, F.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Ultrasound-based detection of low muscle mass for diagnosis of sarcopenia in older adults. PM&R 2016, 8, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Benaiges, D.; Goday, A.; Pedro-Botet, J.; et al. Bariatric surgery: to whom and when? Minerva Endocrinol. 2015, 40, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald, H.; Avidor, Y.; Braunwald, E.; et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004, 292, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis Román, D.; Garrachón Vallo, F.; Carretero Gómez, J.; et al. La masa muscular disminuida en la diabetes de tipo 2. Una comorbilidad oculta que debemos tener en cuenta [Decreased muscle mass in type-2 diabetes. A hidden comorbidity to consider]. Nutr Hosp. 2023, 40, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani RR, Corriere M, Ferrucci L. Age-related and disease-related muscle loss: the effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 819–829. [CrossRef]
- Bozan A, Erhan B. The relationship between quadriceps femoris thickness measured by US and femoral cartilage thickness in knee osteoarthritis, its effect on radiographic stage and clinical parameters: comparison with healthy young population. J Frailty Sarcopenia Falls 2023, 8, 155–162. [CrossRef]
- Jung SY, Kim HJ, Oh KT. Comparative Analysis of Preoperative and Postoperative Muscle Mass around Hip Joint by Computed Tomography in Patients with Hip Fracture. Hip Pelvis. 2022, 34, 10–17. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.C.; Meli, E.F.; Candia, F.P.; Filippi, F.; Vilallonga, R.; Cordero, E.; Hernández, I.; Eguinoa, A.Z.; Burgos, R.; Vila, A.; Simó, R.; Ciudin, A. The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on the Muscle Mass in Patients with Obesity: 2-Year Follow-up. Obes Surg. 2021, 32, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat N, Kazemi A, Asbaghi O, et al. Long-term effect of bariatric surgery on body composition in patients with morbid obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2021, 40, 1755–1766. [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, C.; Cavaliere, A.; Lupi, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Quaia, E. Established paths and new avenues: a review of the main radiological techniques for investigating sarcopenia. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 2020, 10, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, M.; Marzetti, E.; Cesari, M.; et al. Measurement of muscle mass in sarcopenia: from imaging to biochemical markers. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research 2017, 29, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikai, M.; Fukunaga, T. The size and strength per unit cross-sectional area of human muscle by means of ultrasonic measurement. Int Z Angew Physiol. 1968, 26, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Young, A.; Stokes, M.; Crowe, M. The size and strength of the quadriceps muscles of old and young woman. Eur J Clin Invest. 1984, 14, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Tabara, Y.; Kido, T.; Uetani, E.; Ochi, N.; Igase, M.; Miki, T.; Kohara, K. Quadriceps sarcopenia and visceral obesity are risk factors for postural instability in the middle-aged to elderly population. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2010, 10, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).