Submitted:
28 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
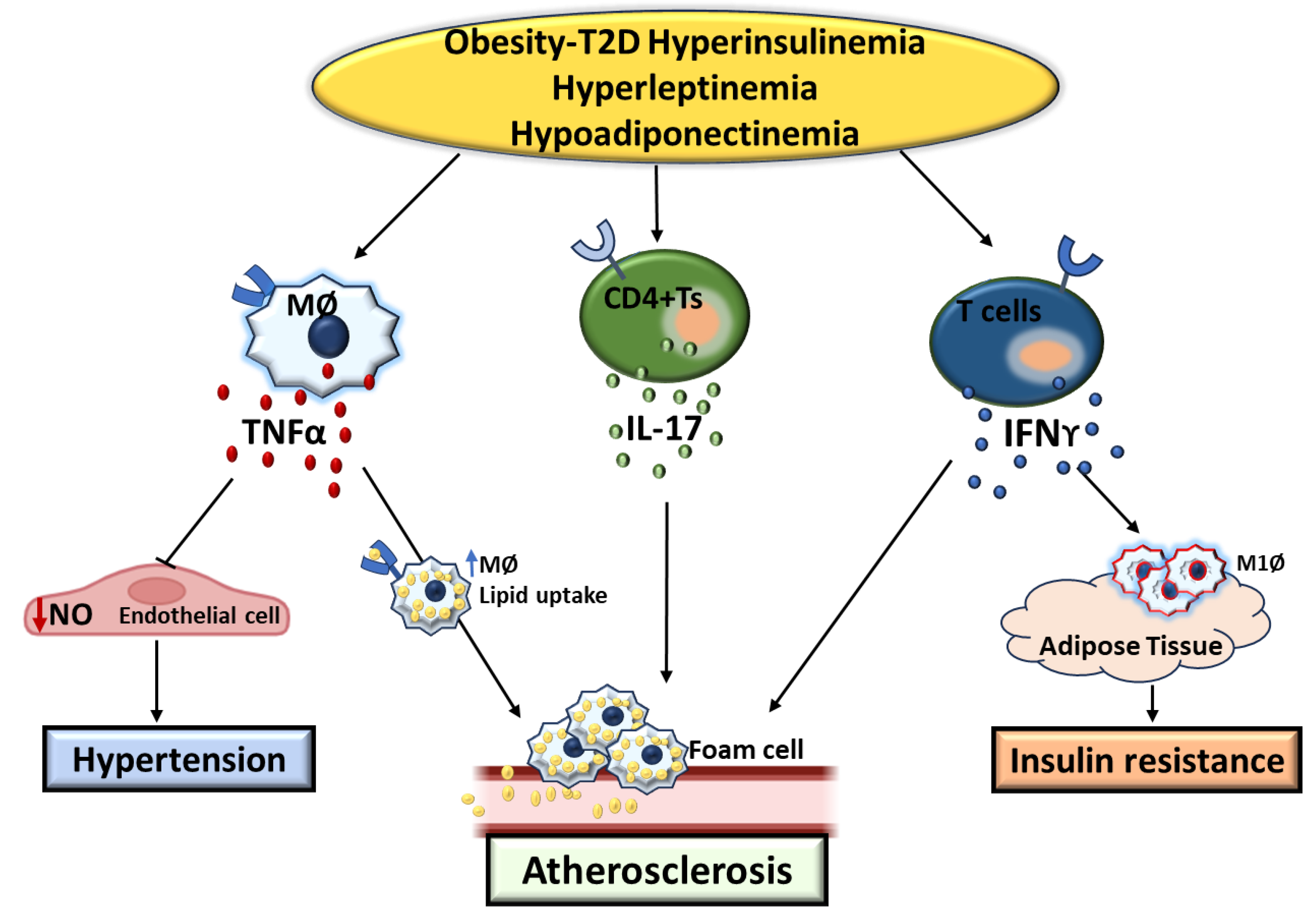
2. Effects of Cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα, IL17) on the Development of T2D and Its Related Cardiovascular Complications
3. Insulin and Altered Immune Response in the Development of T2D and CVDs
4. Association of Adipocyte Derived Hormone, the Immune System, and T2D-CVDs
5. Summary
6. Perspective
References
- DeFronzo, R.A., et al., Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2015. 1(1): p. 15019.
- Olokoba, A.B., O.A. Obateru, and L.B. Olokoba, Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of current trends. Oman Med J, 2012. 27(4): p. 269-73. [CrossRef]
- Francisco, C.O., et al., Cytokine profile and lymphocyte subsets in type 2 diabetes. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2016. 49(4): p. e5062. [CrossRef]
- Stentz, F.B. and A.E. Kitabchi, Activated T lymphocytes in Type 2 diabetes: implications from in vitro studies. Curr Drug Targets, 2003. 4(6): p. 493-503. [CrossRef]
- Touch, S., K. Clément, and S. André, T Cell Populations and Functions Are Altered in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep, 2017. 17(9): p. 81. [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Espinosa, N., et al., CD39 expression on Treg and Th17 cells is associated with metabolic factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hum Immunol, 2015. 76(9): p. 622-30. [CrossRef]
- Martinez, N., et al., Chromatin decondensation and T cell hyperresponsiveness in diabetes-associated hyperglycemia. J Immunol, 2014. 193(9): p. 4457-68. [CrossRef]
- Menart-Houtermans, B., et al., Leukocyte Profiles Differ Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes and Are Associated With Metabolic Phenotypes: Results From the German Diabetes Study (GDS). Diabetes Care, 2014. 37(8): p. 2326-2333. [CrossRef]
- van Beek, L., et al., Increased systemic and adipose tissue inflammation differentiates obese women with T2DM from obese women with normal glucose tolerance. Metabolism, 2014. 63(4): p. 492-501.
- Regufe, V.M.G., C. Pinto, and P. Perez, Metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients: a review of current evidence. Porto Biomed J, 2020. 5(6): p. e101. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.L., K. Garrie, and M.D. Turner, Type 2 diabetes - An autoinflammatory disease driven by metabolic stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018. 1864(11): p. 3805-3823. [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P., et al., Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2019. 157: p. 107843. [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzam, N., et al., Hypertension prevalence and associated factors among patients with diabetes: A retrospective cross-sectional study from Jordan. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2021. 61: p. 126-131. [CrossRef]
- Almalki, Z.S., et al., Prevalence, risk factors, and management of uncontrolled hypertension among patients with diabetes: A hospital-based cross-sectional study. Prim Care Diabetes, 2020. 14(6): p. 610-615. [CrossRef]
- Alsaadon, H., et al., Hypertension and its related factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - a multi-hospital study in Bangladesh. BMC Public Health, 2022. 22(1): p. 198. [CrossRef]
- Sun, D., et al., Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension. Circ Res, 2019. 124(6): p. 930-937.
- Schernthaner, G., Cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in type-2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 1996. 31 Suppl: p. S3-13. [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H., Global health estimates: deaths by cause, age, sex and country, 2000-2012. Geneva, WHO, 2014. 9: p. c2014.
- Al-Goblan, A.S., M.A. Al-Alfi, and M.Z. Khan, Mechanism linking diabetes mellitus and obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2014. 7: p. 587-91.
- Ismail, L., H. Materwala, and J. Al Kaabi, Association of risk factors with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2021. 19: p. 1759-1785. [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U., et al., Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(17). [CrossRef]
- Singh, R., et al., Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia, 2001. 44(2): p. 129-46. [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.F., R. Ramasamy, and A.M. Schmidt, Mechanisms of Disease: advanced glycation end-products and their receptor in inflammation and diabetes complications. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2008. 4(5): p. 285-293. [CrossRef]
- Winer, D.A., et al., B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat Med, 2011. 17(5): p. 610-7. [CrossRef]
- Berbudi, A., et al., Type 2 Diabetes and its Impact on the Immune System. Curr Diabetes Rev, 2020. 16(5): p. 442-449.
- Donath, M.Y. and S.E. Shoelson, Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2011. 11(2): p. 98-107. [CrossRef]
- Nikolajczyk, B.S., et al., State of the union between metabolism and the immune system in type 2 diabetes. Genes & Immunity, 2011. 12(4): p. 239-250. [CrossRef]
- Girard, D. and C. Vandiedonck, How dysregulation of the immune system promotes diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk complications. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022. 9: p. 991716. [CrossRef]
- Rohm, T.V., et al., Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity, 2022. 55(1): p. 31-55.
- Strissel, K.J., G.V. Denis, and B.S. Nikolajczyk, Immune regulators of inflammation in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2014. 21(5): p. 330-8. [CrossRef]
- Altan-Bonnet, G. and R. Mukherjee, Cytokine-mediated communication: a quantitative appraisal of immune complexity. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2019. 19(4): p. 205-217. [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B., IFNγ: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2018. 18(9): p. 545-558. [CrossRef]
- Rocha, V.Z., et al., Interferon-gamma, a Th1 cytokine, regulates fat inflammation: a role for adaptive immunity in obesity. Circ Res, 2008. 103(5): p. 467-76.
- Zhang, H., et al., Interferon-gamma induced adipose tissue inflammation is linked to endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Basic Res Cardiol, 2011. 106(6): p. 1135-45. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S., et al., IFN-gamma potentiates atherosclerosis in ApoE knock-out mice. J Clin Invest, 1997. 99(11): p. 2752-61. [CrossRef]
- Whitman, S.C., et al., Exogenous interferon-gamma enhances atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-/- mice. Am J Pathol, 2000. 157(6): p. 1819-24.
- Lee, L.Y., et al., Interferon-γ Impairs Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Glucose Metabolism by Tryptophan Catabolism and Activates Fatty Acid Oxidation. Circulation, 2021. 144(20): p. 1612-1628.
- Benson, L., et al., The IFNγ-PDL1 Pathway Enhances the Interaction Between CD8+ T Cells and Distal Convoluted Tubules to Promote Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. The FASEB Journal, 2022. 36(S1).
- Abdel-Moneim, A., et al., Association of glycemic status and interferon-γ production with leukocytes and platelet indices alterations in type2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2019. 13(3): p. 1963-1969. [CrossRef]
- Kalliolias, G.D. and L.B. Ivashkiv, TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2016. 12(1): p. 49-62. [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B., et al., Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med, 1985. 161(5): p. 984-95. [CrossRef]
- Borsotti, C., et al., Absence of donor T-cell-derived soluble TNF decreases graft-versus-host disease without impairing graft-versus-tumor activity. Blood, 2007. 110(2): p. 783-6. [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S., N.S. Shargill, and B.M. Spiegelman, Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science, 1993. 259(5091): p. 87-91.
- Hotamisligil, G.S., et al., IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science, 1996. 271(5249): p. 665-8.
- Barath, P., et al., Tumor necrosis factor gene expression in human vascular intimal smooth muscle cells detected by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol, 1990. 137(3): p. 503-9.
- Ohta, H., et al., Disruption of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene diminishes the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis, 2005. 180(1): p. 11-7.
- Persson, J., J. Nilsson, and M.W. Lindholm, Interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha impede neutral lipid turnover in macrophage-derived foam cells. BMC Immunol, 2008. 9: p. 70. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., et al., Role of TNF-alpha in vascular dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond), 2009. 116(3): p. 219-30.
- Picchi, A., et al., Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in the prediabetic metabolic syndrome. Circ Res, 2006. 99(1): p. 69-77.
- Gao, X., et al., Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in Lepr(db) mice. Circulation, 2007. 115(2): p. 245-54.
- Hassan, N.F., A.H. Hassan, and M.R. El-Ansary, Cytokine modulation by etanercept ameliorates metabolic syndrome and its related complications induced in rats administered a high-fat high-fructose diet. Sci Rep, 2022. 12(1): p. 20227. [CrossRef]
- Yoshizumi, M., et al., Tumor necrosis factor downregulates an endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA by shortening its half-life. Circ Res, 1993. 73(1): p. 205-9.
- Chen, X., et al., Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Curr Hypertens Rev, 2008. 4(4): p. 245-255.
- Awad, A.S., et al., Macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-α mediates diabetic renal injury. Kidney Int, 2015. 88(4): p. 722-33.
- El-Edel, R., et al., Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Menoufia Medical Journal, 2020. 33(3): p. 920-925.
- Navarro, J.F. and C. Mora-Fernández, The role of TNF-alpha in diabetic nephropathy: pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2006. 17(6): p. 441-50.
- Kouri, V.-P., et al., IL-17A and TNF synergistically drive expression of proinflammatory mediators in synovial fibroblasts via IκBζ-dependent induction of ELF3. Rheumatology, 2022. 62(2): p. 872-885.
- Mills, K.H.G., IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2023. 23(1): p. 38-54.
- Huangfu, L., et al., The IL-17 family in diseases: from bench to bedside. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2023. 8(1): p. 402. [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C., S.-W. Hee, and L.-M. Chuang, T helper 17 cells: A new actor on the stage of type 2 diabetes and aging? Journal of Diabetes Investigation, 2021. 12(6): p. 909-913.
- Chang, Y.C., S.W. Hee, and L.M. Chuang, T helper 17 cells: A new actor on the stage of type 2 diabetes and aging? J Diabetes Investig, 2021. 12(6): p. 909-913.
- Wang, J., et al., Clinical significance of Interleukin 17 receptor E in diabetic nephropathy. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023. 120: p. 110324.
- Ohshima, K., et al., Roles of interleukin 17 in angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated insulin resistance. Hypertension, 2012. 59(2): p. 493-9.
- Ma, J., et al., Interleukin 17A promotes diabetic kidney injury. Sci Rep, 2019. 9(1): p. 2264.
- Smith, E., et al., Blockade of interleukin-17A results in reduced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation, 2010. 121(15): p. 1746-55.
- van Es, T., et al., Attenuated atherosclerosis upon IL-17R signaling disruption in LDLr deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009. 388(2): p. 261-5.
- Chen, S., et al., IL-17A is proatherogenic in high-fat diet-induced and Chlamydia pneumoniae infection-accelerated atherosclerosis in mice. J Immunol, 2010. 185(9): p. 5619-27.
- Eid, R.E., et al., Interleukin-17 and interferon-gamma are produced concomitantly by human coronary artery-infiltrating T cells and act synergistically on vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation, 2009. 119(10): p. 1424-32.
- Erbel, C., et al., Inhibition of IL-17A attenuates atherosclerotic lesion development in apoE-deficient mice. J Immunol, 2009. 183(12): p. 8167-75.
- Chang, S.L., et al., Interleukin-17 enhances cardiac ventricular remodeling via activating MAPK pathway in ischemic heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2018. 122: p. 69-79. [CrossRef]
- Kamat, N.V., et al., Renal transporter activation during angiotensin-II hypertension is blunted in interferon-γ-/- and interleukin-17A-/- mice. Hypertension, 2015. 65(3): p. 569-76.
- Norlander, A.E., et al., Interleukin-17A Regulates Renal Sodium Transporters and Renal Injury in Angiotensin II–Induced Hypertension. Hypertension, 2016. 68(1): p. 167-174.
- Amin, M.N., et al., Inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and cancer. SAGE Open Med, 2020. 8: p. 2050312120965752.
- Mehra, V.C., V.S. Ramgolam, and J.R. Bender, Cytokines and cardiovascular disease. J Leukoc Biol, 2005. 78(4): p. 805-18. [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.N. and D.J.P. Barker, The thrifty phenotype hypothesis: Type 2 diabetes. British Medical Bulletin, 2001. 60(1): p. 5-20.
- Campbell, J.E. and C.B. Newgard, Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021. 22(2): p. 142-158.
- Haeusler, R.A., T.E. McGraw, and D. Accili, Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018. 19(1): p. 31-44. [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.S., et al., Competing paradigms of obesity pathogenesis: energy balance versus carbohydrate-insulin models. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2022. 76(9): p. 1209-1221.
- Ludwig, D.S., et al., The carbohydrate-insulin model: a physiological perspective on the obesity pandemic. Am J Clin Nutr, 2021. 114(6): p. 1873-1885.
- James, D.E., J. Stöckli, and M.J. Birnbaum, The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021. 22(11): p. 751-771.
- Cruz-Pineda, W.D., et al., The regulatory role of insulin in energy metabolism and leukocyte functions. J Leukoc Biol, 2022. 111(1): p. 197-208. [CrossRef]
- Helderman, J.H. and T.B. Strom, Emergence of insulin receptors upon alloimmune T cells in the rat. J Clin Invest, 1977. 59(2): p. 338-44.
- Kintscher, U., et al., T-lymphocyte infiltration in visceral adipose tissue: a primary event in adipose tissue inflammation and the development of obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2008. 28(7): p. 1304-10.
- Cham, C.M. and T.F. Gajewski, Glucose availability regulates IFN-gamma production and p70S6 kinase activation in CD8+ effector T cells. J Immunol, 2005. 174(8): p. 4670-7.
- Tsai, S., et al., Insulin Receptor-Mediated Stimulation Boosts T Cell Immunity during Inflammation and Infection. Cell Metab, 2018. 28(6): p. 922-934.e4.
- Bar, R.S., C.R. Kahn, and H.S. Koren, Insulin inhibition of antibody-dependent cytoxicity and insulin receptors in macrophages. Nature, 1977. 265(5595): p. 632-635. [CrossRef]
- Tessaro, Fernando H.G., et al., Insulin Influences LPS-Induced TNF-α and IL-6 Release Through Distinct Pathways in Mouse Macrophages from Different Compartments. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017. 42(5): p. 2093-2104.
- Tsiotra, P.C., et al., High insulin and leptin increase resistin and inflammatory cytokine production from human mononuclear cells. Biomed Res Int, 2013. 2013: p. 487081. [CrossRef]
- Ratter, J.M., et al., Insulin acutely activates metabolism of primary human monocytes and promotes a proinflammatory phenotype. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2021. 110(5): p. 885-891.
- Baumgartl, J., et al., Myeloid lineage cell-restricted insulin resistance protects apolipoproteinE-deficient mice against atherosclerosis. Cell Metab, 2006. 3(4): p. 247-56.
- Manhiani, M.M., M.T. Cormican, and M.W. Brands, Chronic sodium-retaining action of insulin in diabetic dogs. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2011. 300(4): p. F957-65.
- Brands, M.W., et al., Sustained hyperinsulinemia increases arterial pressure in conscious rats. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 1991. 260(4): p. R764-R768. [CrossRef]
- Bursztyn, M., et al., Chronic exogenous hyperinsulinaemia without sugar supplementation: acute salt-sensitive hypertension without changes in resting blood pressure. Journal of hypertension, 1993. 11(7): p. 703-707. [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A., et al., The effect of insulin on renal handling of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in man. J Clin Invest, 1975. 55(4): p. 845-55.
- Bie, P., Blood volume, blood pressure and total body sodium: internal signalling and output control. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2009. 195(1): p. 187-96.
- Gamble, J.-M., et al., Insulin use and increased risk of mortality in type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 2010. 12(1): p. 47-53.
- Yu, B., et al., Insulin Treatment Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab, 2021. 33(1): p. 65-77.e2. [CrossRef]
- Scheja, L. and J. Heeren, The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2019. 15(9): p. 507-524.
- Smith, U. and B.B. Kahn, Adipose tissue regulates insulin sensitivity: role of adipogenesis, de novo lipogenesis and novel lipids. J Intern Med, 2016. 280(5): p. 465-475.
- Grundy, S.M., Adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome: too much, too little or neither. Eur J Clin Invest, 2015. 45(11): p. 1209-17.
- Weisberg, S.P., et al., Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. The Journal of clinical investigation, 2003. 112(12): p. 1796-1808.
- Keuper, M., On the role of macrophages in the control of adipocyte energy metabolism. Endocr Connect, 2019. 8(6): p. R105-r121.
- Chavakis, T., V.I. Alexaki, and A.W. Ferrante, Macrophage function in adipose tissue homeostasis and metabolic inflammation. Nature Immunology, 2023. 24(5): p. 757-766.
- Boutens, L. and R. Stienstra, Adipose tissue macrophages: going off track during obesity. Diabetologia, 2016. 59(5): p. 879-94.
- Li, H., et al., Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Cells, 2022. 11(19).
- Khan, M. and F. Joseph, Adipose tissue and adipokines: the association with and application of adipokines in obesity. Scientifica (Cairo), 2014. 2014: p. 328592.
- Yamauchi, T., et al., The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med, 2001. 7(8): p. 941-6. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.V. and P.E. Scherer, Adiponectin, the past two decades. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 2016. 8(2): p. 93-100.
- Almer, G., et al., Globular domain of adiponectin: promising target molecule for detection of atherosclerotic lesions. Biologics, 2011. 5: p. 95-105.
- Liu, X., et al., Globular adiponectin ameliorates insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by enhancing the LKB1-mediated AMPK activation via SESN2. Sports Med Health Sci, 2023. 5(1): p. 34-41. [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T., et al., Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature, 2003. 423(6941): p. 762-9.
- Denzel, M.S., et al., T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2010. 120(12): p. 4342-4352.
- Berg, A.H., et al., The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med, 2001. 7(8): p. 947-53.
- Combs, T.P., et al., Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J Clin Invest, 2001. 108(12): p. 1875-81.
- Maeda, N., et al., Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat Med, 2002. 8(7): p. 731-7.
- Hong, X., et al., Association between adiponectin and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in population with the clustering of obesity, dyslipidaemia and hypertension: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open, 2023. 13(2): p. e060377.
- Luo, N., et al., AdR1-TG/TALLYHO mice have improved lipid accumulation and insulin sensitivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013. 433(4): p. 567-72.
- Yamauchi, T., et al., Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem, 2003. 278(4): p. 2461-8.
- Salvator, H., et al., Adiponectin Inhibits the Production of TNF-α, IL-6 and Chemokines by Human Lung Macrophages. Front Pharmacol, 2021. 12: p. 718929.
- Tian, L., et al., Adiponectin reduces lipid accumulation in macrophage foam cells. Atherosclerosis, 2009. 202(1): p. 152-61.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Adiponectin's globular domain inhibits T cell activation by interacting with LAIR-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021. 573: p. 117-124.
- Surendar, J., et al., Adiponectin Limits IFN-γ and IL-17 Producing CD4 T Cells in Obesity by Restraining Cell Intrinsic Glycolysis. Front Immunol, 2019. 10: p. 2555. [CrossRef]
- Picó, C., et al., Leptin as a key regulator of the adipose organ. Rev Endocr Metab Disord, 2022. 23(1): p. 13-30.
- Halaas, J.L., et al., Weight-Reducing Effects of the Plasma Protein Encoded by the <i>obese</i> Gene. Science, 1995. 269(5223): p. 543-546.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature, 1994. 372(6505): p. 425-32.
- Ingalls, A.M., M.M. Dickie, and G.D. Snell, Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered, 1950. 41(12): p. 317-8.
- Kelesidis, T., et al., Narrative review: the role of leptin in human physiology: emerging clinical applications. Ann Intern Med, 2010. 152(2): p. 93-100.
- Flak, J.N. and M.G. Myers, Jr., Minireview: CNS Mechanisms of Leptin Action. Molecular Endocrinology, 2016. 30(1): p. 3-12. [CrossRef]
- Brydon, L., et al., Circulating leptin and stress-induced cardiovascular activity in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2008. 16(12): p. 2642-7.
- Obradovic, M., et al., Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021. 12: p. 585887.
- Sims, E.D., et al., Circulating leptin levels are associated with adiposity in survivors of childhood brain tumors. Scientific Reports, 2020. 10(1): p. 4711. [CrossRef]
- Ma, D., et al., Leptin Is Associated With Blood Pressure and Hypertension in Women From the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart Study. Hypertension, 2009. 53(3): p. 473-479. [CrossRef]
- Simonds, S.E., et al., Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell, 2014. 159(6): p. 1404-16.
- Chiba, T., et al., Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis, 2008. 196(1): p. 68-75.
- Bodary, P.F., et al., Recombinant Leptin Promotes Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2005. 25(8): p. e119-e122.
- Taleb, S., et al., Defective leptin/leptin receptor signaling improves regulatory T cell immune response and protects mice from atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2007. 27(12): p. 2691-8.
- Beltowski, J., Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, 2006. 189(1): p. 47-60. [CrossRef]
- Lord, G.M., et al., Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature, 1998. 394(6696): p. 897-901.
- De Rosa, V., et al., A key role of leptin in the control of regulatory T cell proliferation. Immunity, 2007. 26(2): p. 241-55.
- De Rosa, V., et al., Leptin neutralization interferes with pathogenic T cell autoreactivity in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest, 2006. 116(2): p. 447-55.
- Gerriets, V.A., et al., Leptin directly promotes T-cell glycolytic metabolism to drive effector T-cell differentiation in a mouse model of autoimmunity. Eur J Immunol, 2016. 46(8): p. 1970-83. [CrossRef]
- La Cava, A. and G. Matarese, The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol, 2004. 4(5): p. 371-9.
- Saucillo, D.C., et al., Leptin Metabolically Licenses T Cells for Activation To Link Nutrition and Immunity. The Journal of Immunology, 2014. 192(1): p. 136-144.
- Tedgui, A. and Z. Mallat, Cytokines in atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev, 2006. 86(2): p. 515-81.
- Koga, M., et al., Postnatal blocking of interferon-gamma function prevented atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Hypertens Res, 2007. 30(3): p. 259-67.
- Rahman, M.S., et al., Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int J Mol Sci, 2021. 22(12).
- Luo, L. and M. Liu, Adiponectin: friend or foe in obesity and inflammation. Medical Review, 2022. 2(4): p. 349-362.
- Fernández-Riejos, P., et al., Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediators Inflamm, 2010. 2010: p. 568343.
- Makhijani, P., et al., Regulation of the immune system by the insulin receptor in health and disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023. 14: p. 1128622.
- Gao, M., D. Cui, and J. Xie, The role of adiponectin for immune cell function in metabolic diseases. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 2023. 25(9): p. 2427-2438.
- Yanai, H. and H. Yoshida, Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci, 2019. 20(5).
- Chen, L., et al., Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Insulin Resistance. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2015. 2015: p. 508409.
- Kawai, T., M.V. Autieri, and R. Scalia, Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2021. 320(3): p. C375-c391. [CrossRef]
- Rocha, V.Z., et al., Interferon-γ, a Th1 Cytokine, Regulates Fat Inflammation. Circulation Research, 2008. 103(5): p. 467-476.
- Shirai, T., et al., Macrophages in vascular inflammation--From atherosclerosis to vasculitis. Autoimmunity, 2015. 48(3): p. 139-51.
- Tomic, D., J.E. Shaw, and D.J. Magliano, The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2022. 18(9): p. 525-539.
- Lamharzi, N., et al., Hyperlipidemia in Concert With Hyperglycemia Stimulates the Proliferation of Macrophages in Atherosclerotic Lesions: Potential Role of Glucose-Oxidized LDL. Diabetes, 2004. 53(12): p. 3217-3225.
- Cervantes, J. and J.E. Kanter, Monocyte and macrophage foam cells in diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023. 10: p. 1213177. [CrossRef]
- Schett, G. and M.F. Neurath, Resolution of chronic inflammatory disease: universal and tissue-specific concepts. Nature Communications, 2018. 9(1): p. 3261.
- Deckers, J., et al., Engineering cytokine therapeutics. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 2023. 1(4): p. 286-303.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




