Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Databases: A Systematic Search Was Carried Out Using the Following Inclusion Criteria
- Articles published in journals indexed in JCR in the last 5 years (January 2019 to February 2024) using the MEDLINE database.
- Articles that included retrospective, prospective, case-control or cross-sectional studies.
- Searches were carried out by combining the following MESH and free terms: “Epileptogenesis” and “Neuroinflammation”
- High mobility group box 1/HMGB1”,
- Toll-Like-Receptor 4/ TLR-4”,
- Interleukin-1/IL-1”,
- Interleukin-6/IL-6”,
- Transforming growth factor beta/TGF-β” and
- Tumour necrosis factor-alpha/TNF-α”.
- 5.
- Articles published in English and/or Spanish.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Duplicate articles, editorials, letters to the editor, or reviews (both narrative and systematics).
- Articles that include basic research studies on tissues or animal models.
- Articles on studies not related to any type of epilepsy or focused on acute symptomatic seizures due to infectious, traumatic, vascular or oncological processes.
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
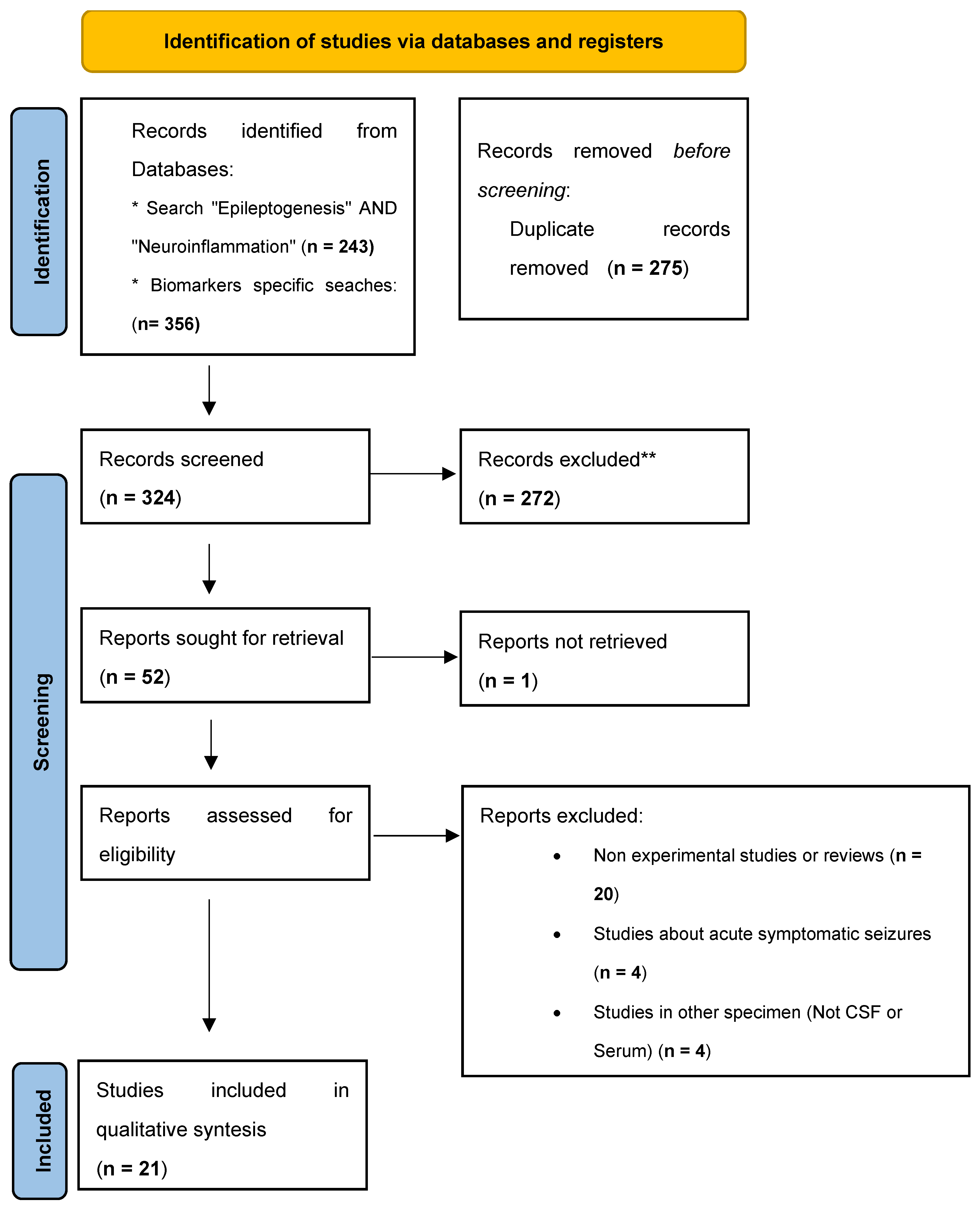
2.5. Flowchart 2020 PRISMA
3. Results and Discussion
- HMGB1: 31 results
- TLR-4: 38 results
- IL-1b: 69 results
- IL-6: 101 results
- TGF-β: 29 results
- TNF-a: 91 results
3.1. Interleukin 1β (IL-1β)
3.2. Interleukin 6 (IL-6)
3.3. Interleukin 17 (IL-17)
3.4. Other Interleukins
3.5. TNF-α
3.6. Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β)
3.7. Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR-4)
3.8. HMGB1
3.9. Chemokines
3.10. Soluble TNF-α Receptors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meizlish, M.L.; Franklin, R.A.; Zhou, X.; Medzhitov, R. Tissue Homeostasis and Inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2021, 39, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervellati, C.; Trentini, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Valacchi, G.; Valacchi, G.; Valacchi, G. Inflammation in Neurological Disorders: The Thin Boundary between Brain and Periphery. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.; De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Keane, R.W. Role of inflammasomes in multiple sclerosis and their potential as therapeutic targets. J Neuroinflammation. 2020, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Cannon, T.C.; Alto, L.T.; McAlpine, F.E.; Tansey, M.G. Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, A.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xue, G. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: current understanding and future therapeutic targets. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of chronic oxidative stress on neuroinflammatory response mediated by CD4+T cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Fewings, N.; Dervish, S.; Fois, A.F.; Duma, S.R.; Silsby, M.; et al. Novel Surrogate Markers of CNS Inflammation in CSF in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Front Neurol. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselingh, R.; Butzkueven, H.; Buzzard, K.; Tarlinton, D.; O’Brien, T.J.; Monif, M.; et al. Innate Immunity in the Central Nervous System: A Missing Piece of the Autoimmune Encephalitis Puzzle? Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guan, Y.; Li, T. The Potential Therapeutic Role of the HMGB1-TLR Pathway in Epilepsy. Curr Drug Targets. 2021, 22, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, N.; Tabatabaie, O.; Falsaperla, R.; Lubrano, R.; Pavone, P.; Mahmood, F.; et al. Epilepsy and innate immune system: A possible immunogenic predisposition and related therapeutic implications. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015, 11, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Castillo, M.J.; Cabezudo-García, P.; Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; García-Martin, G.; Marín-Gracia, M.; Estivill-Torrús, G.; et al. Immune Mechanism of Epileptogenesis and Related Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, N.; Granata, T.; Janigro, D. Inflammatory pathways of seizure disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Rüegg, S. Introduction. Immunity and Inflammation in Epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2011, 52 Suppl 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Rüegg, S. The pivotal role of immunity and inflammatory processes in epilepsy is increasingly recognized: introduction. Epilepsia. 2011, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Friedman, A.; Dingledine, R.J. The role of inflammation in epileptogenesis. Neuropharmacology. 2013, 69, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villasana-Salazar, B.; Vezzani, A. Neuroinflammation microenvironment sharpens seizure circuit. Neurobiol Dis. 2023, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A. Epilepsy and Inflammation in the Brain: Overview and Pathophysiology. Epilepsy Curr. 2014, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsini, A.; Foiadelli, T.; Costagliola, G.; Michev, A.; Consolini, R.; Vinci, F.; et al. The role of inflammatory mediators in epilepsy: Focus on developmental and epileptic encephalopathies and therapeutic implications. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.P.; Brennan, G.P.; Curran, M.; Kinney-Lang, E.; Dubé, C.; Rashid, F.; et al. Rapid, Coordinate Inflammatory Responses after Experimental Febrile Status Epilepticus: Implications for Epileptogenesis. eneuro. 2015, 2, ENEURO.0034–152015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Musto, A.E. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.; Rubio, T.; Garcia-Gimeno, M.A. Neuroinflammation and Epilepsy: From Pathophysiology to Therapies Based on Repurposing Drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamali, A.N.; Zian, Z.; Bautista, J.M.; Hamedifar, H.; Hossein-Khannazer, N.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; et al. The Potential Role of Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Epilepsy Pathogenesis. Endocrine, Metab Immune Disord - Drug Targets. 2021, 21, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani Khaboushan, A.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Neuroinflammation and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Epileptogenesis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkkonen, J.; Koskikallio, E.; Rainesalo, S.; Keränen, T.; Hurme, M.; Peltola, J. The balance of inhibitory and excitatory cytokines is differently regulated in vivo and in vitro among therapy resistant epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. 2004, 59(2–3):199–205.
- Banote, R.K.; Akel, S.; Zelano, J. Blood biomarkers in epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2022 Apr. [CrossRef]
- Janmohamed, M.; Brodie, M.J.; Kwan, P. Pharmacoresistance – Epidemiology, mechanisms, and impact on epilepsy treatment. Neuropharmacology. 2020 May;168. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Ji, T.; et al. Upregulation of HMGB1-TLR4 inflammatory pathway in focal cortical dysplasia type, I.I. J Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Bazhanova, E.D.; Kozlov, A.A.; Litovchenko A, V. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in the Pathogenesis of Epilepsy: Role of Neuroinflammation. A Literature Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11(5). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nagib, M.M.; Yasmen, N.; Sluter, M.N.; Littlejohn, T.L.; Yu, Y.; et al. Neuroinflammatory mediators in acquired epilepsy: an update. Inflamm Res. 2023, 72, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaşak, T.; Dilber, B.; Yaman, S.Ö.; Durgut, B.D.; Kurt, T.; Çoban, E.; et al. HMGB-1, TLR4, IL-1R1, TNF-α, and IL-1β: novel epilepsy markers? Epileptic Disord. 2020, 22, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, J.A.; Cole, A.J.; Faught, E.; Theodore, W.H.; Vezzani, A.; Liow, K.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Natalizumab as Adjunctive Therapy for People With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Neurology. 2021, 97, e1757–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Maroso, M.; Balosso, S.; Sanchez, M.A.; Bartfai, T. IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav Immun. 2011, 25, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.F.; Korevaar, D.A.; Altman, D.G.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Hooft, L.; et al. STARD 2015 guidelines for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies: explanation and elaboration. [CrossRef]
- Miller, J. The Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2002, 2, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; Lai, Q.; Li, X.; et al. TNF-α: A serological marker for evaluating the severity of hippocampal sclerosis in medial temporal lobe epilepsy? J Clin Neurosci. 2024, 123, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothur, K.; Bandodkar, S.; Wienholt, L.; Chu, S.; Pope, A.; Gill, D.; et al. Etiology is the key determinant of neuroinflammation in epilepsy: Elevation of cerebrospinal fluid cytokines and chemokines in febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome and febrile status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2019, 60, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gledhill, J.M.; Brand, E.J.; Pollard, J.R. ; St. Clair, R.D.; Wallach, T.M.; Crino, P.B. Association of Epileptic and Nonepileptic Seizures and Changes in Circulating Plasma Proteins Linked to Neuroinflammation. Neurology. 2021, 96, E1443–52. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lim, B.C.; Hwang, H.; Chae, J.H.; et al. Serum α-synuclein and IL-1β are increased and correlated with measures of disease severity in children with epilepsy: potential prognostic biomarkers? BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saengow, V.E.; Chiangjong, W.; Khongkhatithum, C.; Changtong, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Weeraphan, C.; et al. Proteomic analysis reveals plasma haptoglobin, interferon-γ, and interleukin-1β as potential biomarkers of pediatric refractory epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2021, 43, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvim, M.K.M.; Morita-Sherman, M.E.; Yasuda, C.L.; Rocha, N.P.; Vieira, É.L.; Pimentel-Silva, L.R.; et al. Inflammatory and neurotrophic factor plasma levels are related to epilepsy independently of etiology. Epilepsia. 2021, 62, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, C.; Montali, M.; Barachini, S.; Burzi, I.S.; Pratesi, F.; Petrozzi, L.; et al. Increased production of inflammatory cytokines by circulating monocytes in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: A possible role in drug resistance. J Neuroimmunol. 2024, 386, 578272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Česká, K. ; Papež J, Ošlejšková, H. ; Slabý, O.; Radová, L.; Loja, T.; et al. CCL2/MCP-1, interleukin-8, and fractalkine/CXC3CL1: Potential biomarkers of epileptogenesis and pharmacoresistance in childhood epilepsy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023, 46, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ethemoglu, O.; Calık, M.; Koyuncu, I.; Ethemoglu, K.B.; Göcmen, A.; Güzelcicek, A.; et al. Interleukin-33 and oxidative stress in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 176, 106738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova T, V. , Zabrodskaya, Y. M.; Litovchenko A V., Paramonova, N.M.; Kasumov, V.R.; Kravtsova S V., et al. Relationship between Neuroglial Apoptosis and Neuroinflammation in the Epileptic Focus of the Brain and in the Blood of Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 12561. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Zou, Y.; Du, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; et al. Altered cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of TGFβ1 in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Neurochem Res. 2014, 39, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Tang, J.; Peng, S.; Cai, X.; Rong, X.; Yang, L. Serum concentration of high-mobility group box 1, Toll-like receptor 4 as biomarker in epileptic patients. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 192, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, M.; Song, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, P. Circulating high mobility group box-1 and toll-like receptor 4 expressions increase the risk and severity of epilepsy. Brazilian J Med Biol Res. 2019, 52(7). [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.E.; Sills, G.J.; Jorgensen, A.; Alapirtti, T.; Peltola, J.; Brodie, M.J.; et al. High-mobility group box 1 as a predictive biomarker for drug-resistant epilepsy: A proof-of-concept study. Epilepsia. 2022, 63(1). [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Ma, B.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. CSF high-mobility group box 1 is associated with drug-resistance and symptomatic etiology in adult patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 177, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.D.; Wagner, M.; Surges, R.; Holdenrieder, S. Time courses of HMGB1 and other inflammatory markers after generalized convulsive seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panina, Y.S.; Timechko, E.E.; Usoltseva, A.A.; Yakovleva, K.D.; Kantimirova, E.A.; Dmitrenko D, V. Biomarkers of Drug Resistance in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Adults. Metabolites. 2023, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gakharia, T.; Bakhtadze, S.; Lim, M.; Khachapuridze, N.; Kapanadze, N. Alterations of Plasma Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Children with Refractory Epilepsies. Children. 2022, 9, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronisz, E.; Cudna, A.; Wierzbicka, A.; Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I. Serum Proteins Associated with Blood–Brain Barrier as Potential Biomarkers for Seizure Prediction. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selenica M-LB, Alvarez, J. A.; Nash, K.R.; Lee, D.C.; Cao, C.; Lin, X.; et al. Diverse activation of microglia by chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 overexpression in brain. J Neuroinflammation. 2013, 10, 856.
- Oby, E.; Janigro, D. The blood-brain barrier and epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2006, 47, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, K.M.; Sun, M.; Crack, P.; O’Brien, T.J.; Shultz, S.R.; Semple, B.D. Inflammation in epileptogenesis after traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2017, 14(1). [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, T.G.; Rehni, A.K. An Insight into Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Epileptogenesis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2020, 19, 750–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrone, G.; Balosso, S.; Pauletti, A.; Ravizza, T.; Vezzani, A. Inflammation and reactive oxygen species as disease modifiers in epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2020, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroso, M.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T.; Liu, J.; Bianchi, M.E.; Vezzani, A. Interleukin-1 type 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signalling in epilepsy: The importance of IL-1beta and high-mobility group box 1. Journal of Internal Medicine. J Intern Med; 2011, 319–326.
- Ravizza, T.; Terrone, G.; Salamone, A.; Frigerio, F.; Balosso, S.; Antoine, D.J.; et al. High Mobility Group Box 1 is a novel pathogenic factor and a mechanistic biomarker for epilepsy. Brain Behav Immun. 2018, 72, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, Y.N.; Semple, B.D.; Jones, N.C.; Othman, I.; Shaikh, M.F. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) as a novel frontier in epileptogenesis: from pathogenesis to therapeutic approaches. J Neurochem. 2019, 151, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Pang, Z.; Lin, Y. Hmgb1/cxcl12-mediated immunity and TH17 cells might underlie highly suspected autoimmune epilepsy in elderly individuals. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020, 16, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivannan, S.; Wales, E.; Zaben, M. The Role of HMGB1 in Traumatic Brain Injury—Bridging the Gap Between the Laboratory and Clinical Studies. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2021, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhai, F.; Liang, S. Role of HMGB1/TLR4 and IL-1β/IL-1R1 Signaling Pathways in Epilepsy. Front Neurol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvim MMKM, Morita-Sherman, M. E.M.; Yasuda, C.L.; Rocha, N.N.P.; Vieira, É.É.L.; Pimentel-Silva, L.R.; et al. Inflammatory and neurotrophic factor plasma levels are related to epilepsy independently of etiology. Epilepsia. 2021, 62, epi17023.
- Yung, S.C.; Farber, J.M. Chemokines. Second Edi. Elsevier Inc.; 2013. [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.J.; Nakamura, T.; Miyazaki, D.; Ohbayashi, M.; Dawson, M.; Toda, M. Chemokines: Roles in leukocyte development, trafficking, and effector function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003, 111, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisi, G.M.; Foresti, M.L.; Katki, K.; Shapiro, L.A. Increased CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, and IL-1β cytokine concentration in piriform cortex, hippocampus, and neocortex after pilocarpine-induced seizures. J Neuroinflammation. 2015, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Viviani, B. Neuromodulatory properties of inflammatory cytokines and their impact on neuronal excitability. Neuropharmacology. 2015, 96, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viviani, B.; Bartesaghi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Vezzani, A.; Behrens, M.M.; Bartfai, T.; et al. Interleukin-1β Enhances NMDA Receptor-Mediated Intracellular Calcium Increase through Activation of the Src Family of Kinases. J Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8692–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, C.; Gong, J. Cerebrospinal fluid neuron specific enolase, interleukin-1β and erythropoietin concentrations in children after seizures. Child’s Nerv Syst. 2017, 33, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bauer, S.; Nowak, M.; Norwood, B.; Tackenberg, B.; Rosenow, F.; et al. Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure. 2011, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, S.M.; Wilkinson, T.S.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Jones, S.; Horiuchi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. IL-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Orchestrate a Temporal Switch in the Pattern of Leukocyte Recruitment Seen during Acute Inflammation. Immunity. 2001, 14, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltola, J.; Palmio, J.; Korhonen, L.; Suhonen, J.; Miettinen, A.; Hurme, M.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with recent tonic–clonic seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 41, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltola, J.; Hurme, M.; Miettinen, A.; Keränen, T. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 may occur in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with recent epileptic seizures. Epilepsy Res. 1998, 31, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alapirtti, T.; Rinta, S.; Hulkkonen, J.; Mäkinen, R.; Keränen, T.; Peltola, J. Interleukin-6, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1beta production in patients with focal epilepsy: A video–EEG study. J Neurol Sci. 2009, 280(1–2):94–7.
- Lu, Y.; Xue, T.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xi, Z.; et al. Increased expression of TGFβ type I receptor in brain tissues of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin Sci. 2009, 117, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivens, S.; Kaufer, D.; Flores, L.P.; Bechmann, I.; Zumsteg, D.; Tomkins, O.; et al. TGF-β receptor-mediated albumin uptake into astrocytes is involved in neocortical epileptogenesis. Brain. 2007, 130, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costagliola, G.; Depietri, G.; Michev, A.; Riva, A.; Foiadelli, T.; Savasta, S.; et al. Targeting Inflammatory Mediators in Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Its Molecular Basis and Clinical Applications. Front Neurol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, S.; Villeneuve, N.; Trébuchon, A.; Kaphan, E.; Lepine, A.; McGonigal, A.; et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy (adalimumab) in Rasmussen’s encephalitis: An open pilot study. Epilepsia. 2016, 57, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, S.; Boucraut, J.; Bartolomei, F. Medical treatment of Rasmussen’s Encephalitis: A systematic review. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022. [CrossRef]
- Paudel, Y.N.; Khan, S.U.; Othman, I.; Shaikh, M.F. Naturally Occurring HMGB1 Inhibitor, Glycyrrhizin, Modulates Chronic Seizures-Induced Memory Dysfunction in Zebrafish Model. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020, 12(18). [CrossRef]
- Li Y jun, Wang, L. ; Zhang, B.; Gao, F.; Yang, C.M. Glycyrrhizin, an HMGB1 inhibitor, exhibits neuroprotective effects in rats after lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 390–399.
- Walker, L.E.; Sills, G.J.; Jorgensen, A.; Alapirtti, T.; Peltola, J.; Brodie, M.J.; et al. High-mobility group box 1 as a predictive biomarker for drug-resistant epilepsy: A proof-of-concept study. Epilepsia. 2022, 63, e1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaşak, T.; Dilber, B.; Yaman, S.Ö.; Durgut, B.D.; Kurt, T.; Çoban, E.; et al. HMGB-1, TLR4, IL-1R1, TNF-α, and IL-1β: novel epilepsy markers? Epileptic Disord. 2020, 22, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegler, A.; Pascotini, E.T.; Caprara, A.L.F.; Arend, J.; Gabbi, P.; Duarte, M.M.; et al. Relationship between seizure type, metabolic profile, and inflammatory markers in blood samples of patients with epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2021, 23, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochol, M.; Taubøll, E.; Aukrust, P.; Ueland, T.; Andreassen, O.A.; Svalheim, S. Interleukin 18 (IL-18) and its binding protein (IL-18BP) are increased in patients with epilepsy suggesting low-grade systemic inflammation. Seizure. 2020, 80, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Biomarkers studied | Sample Type | Type of study | Results | N | Level of evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kothur et al. [36] | IL-1ra, GM-CSF, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-2,IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17A, IFN-γ, CCL2/MCP-1, CCL5/RANTES, CXCL1/GRO, CXCL10/IP-10,CCL3/MIP-1a, CCL4/MIP-1b, IL-12 (p40), IL-12 (p70), IFN-α, G-CSF, CCL11/eotaxin. IL-21, IL-23, CXCL13/BCA-1, CCL17/TARC, CCL21/6Ckine, CXCL12/SDF-1. CXCL9/MIG, CXCL11/I-TAC, and CCL19/MIP-3b | CSF | Case-control | TNF-α and CCL19 were mildly elevated in chronic epilepsy. | Patients with FIRES/FIRES-related disorders (FRD; n = 6), FSE (n = 8), afebrile status epilepticus (ASE; n = 8), and chronic epilepsy (n = 21) | 2- |
| Yue et al. [46] | HMGB1 y TLR4 | Serum | Case-control | HMGB1 y TLR4 were elevated in chronic epilepsy | 72 epilepsy patients diagnosed with epilepsy vs 43 healthy controls | 2 |
| Jieun et al. [38] | α-synuclein, IFN-β, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α | Serum | Case-control | α-synuclein levels were significantly increased in children with epilepsy. Serum IL-1β levels showed significant correlation only with drug resistance in children with epilepsy. |
115 epilepsy patients having afebrile seizure attacks within the last 48 h vs vs 146 healthy controls. | 2+ |
| Saengow et al. [39] | gamma (IFN-c), IL-1β, and TNF-a | Serum | Case-control | IL-1β level was significantly decreased in patients with DRE. IFN-c level was significantly increased in patients with DRE. TNF-a showed no statistical change between groups. |
65 patients with drug-resistant epilepsy vs 6 healthy controls | 2- |
| Walker et al. [84] | HMGB1 | Serum | Case-control | Patients with drug-resistant epilepsy had higher levels of HMGB1 than both healthy controls and patients with drug-responsive epilepsy | 65 patients with drug-resistant epilepsy vs 74 healthy controls |
2+ |
| Kamaşak et al. [85] | HMGB-1, TLR-4, IL-1R1, TNF-a, IL-1β | Serum | Case-control | Significantly higher levels of HMGB-1, TLR-4, TNF-a and IL-1β in the severe epilepsy group than in the other two groups | 28 children with DRE vs 29 children with controlled epilepsy vs 27 healthy controls | 2 |
| Aline et al. [86] | TNF-a, Caspase and Lipid factors | Serum | Case-control | No significant differences. But patients with generalized epilepsy demonstrated a significant correlation between TNF-α and caspase 8, caspase 3, and Picogreen. | 43 epileptic patients vs 41 healthy controls | 2 |
| Alvim et al. [40] | IL-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IFNγ, TNF-α, soluble TNF receptor 1 (sTNFr1), sTNFr2, BDNF, neurotrophic factor 3 (NT3), NT4/5, ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). | Serum | Case-control | The plasma levels of BDNF, NT3, NGF, and sTNFr2 were higher, whereas IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IFNγ, TNFα, CNTF, and sTNFr1 were lower in patients than controls. The molecule sTNFr2 was the best marker to discriminate patients from controls also differing between patients with frequent and infrequent seizures. |
446 patients with epilepsy vs 166 healthy controls. | 2+ |
| Minchen et al. [47] | HMGB1 and TLR4 | Serum | Case-control | HMGB1 and TLR4 levels were higher in epilepsy patients compared with controls HMGB1 and TLR4 expressions were correlated with higher possibility of drugs resistance. | 105 epilepsy patients vs 100 healthy controls | 2 |
| Ethemoglu et al. [43] . | IL-33 | Serum | Case-control | IL-33 level was found higher in all the patients with epilepsy compared to the control group. | 60 patients with epilepsy (21 patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy and 39 patients with well-controlled epilepsy) vs 35 control subjects | 2 |
| Panina et al. [51] | BDNF, TNF-a, HMGB1 and NTRK2 | Serum | Case-control | A decrease in the concentration of BDNF, TNF-a, and HMGB1 was registered in the group of patients with TLE compared with the control group. |
166 patients with epilepsy (49 with treatment-resistant epilepsy and 117 patients with well-controlled epilepsy) vs 203 controls. | 2 |
| Wang et al. [35] | IL-1β, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, IFN-γ and TNF-α | Serum | Prospective, population-based study | The level of TNF-α in the mTLE-HS-P group was significantly higher than that of the patients in the mTLE-HS-N and healthy control groups, and the level of TNF-α in the patients in the mTLE-HS-N group was significantly higher than that of the patients in the healthy control group. | 71 patients with medial TLE vs 20 controls | 2++ |
| Milano et al. [41] | IL-6, TNF-α, IL-33, IL-8, CCL2, IL-13, IL-1β, IFN-γ, IL-1Ra, CCL3, IL-4, CCL4, IL-5, IL-1α, IL-17 A, IL-18, IL-33r, IL-1RII, IL-1RI | Serum | Case-control | Levels of CCL2, CCL3 and IL-8 were elevated in the serum of patients with epilepsy compared to healthy controls, without differences between drugs-resistant and drug-sensitive patients. | 47 patients diagnosed with MTLE vs 25 healthy controls | 2 |
| Sokolova et al. [44] | IL-1RA, interferon IFN-, IL-10 IL-2, IL-8, IL-7, TNF-α, IL-4, sCD40L | Serum | Case-control. | The level of the immunoregulatory cytokine IL-2 and the chemoattractant proinflammatory IL-8 was decreased in DRE patients. Proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-4, sCD40L) was increased. |
6 DRE patients vs 5 healthy controls. | 2- |
| Wang et al. [49] | HMGB1 | CSF and Serum | Case-control | The CSF HMGB1 concentrations were significantly higher in the DRE vs the other groups. Patients with symptomatic etiology showed significantly high levels of CSF HMGB1. Patients without remission expressed elevated levels of CSF HMGB1 at one-year follow-up. CSF HMGB1 levels were positively associated with seizure frequency. |
27 DRE patients, 56 Newly diagnosed epileptic patients and 22 other non-inflammatory neurological disorders | 2- |
| Mochol et al. [87] | IL-18; Interleukine 18 binding protenin (IL-18BP) | Serum | Case-control | Increased serum levels of IL-18 and IL-18BP in epilepsy patients. | 119 patients with epilepsy and 80 healthy controls | 2 |
| Nass et al. [50] | c-reactive protein (CRP), HMGB1, S100, RAGE, ICAM1 and MMP9 | Serum | Case Series | Rapid postictal increase of HMGB1 and S100. |
28 patients with Epilepsy with Generalized Seizures. | 3 |
| Gakharia et al. [52] | CCL2, CCL4 and CCL11 and PGE2 | Serum | Case-control | High CCL11 and PGE2 levels correlated with their seizure frequency and epilepsy severity. | 40 epileptic patients (20 DRE and 20 Controlled epilepsy) vs 16 healthy controls. | 2 |
| Bronisz et al. [53] | MMP-9, MMP-2, CCL-2, S100B, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, ICAM-1, TSP-2, P-selectin) |
Serum | Case series | Levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, and CCL-2 were found to influence seizure count in 1, 3, 6, and 12 months of observation. | 49 patients with epilepsy. | 3 |
| Gledhill et al. [37] | CRP, calbindin, cytokeratin-8, eotaxin, eotaxin-2, eotaxin-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, ICAM-1, IFN–γ, IL-1β, IL-1α, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12/IL-23 p40, IL-12 p70, IL-13, IL-15, IL-16, IL-17, IFN-γ-inducible protein 10, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)–1, MCP-2, MCP-4, macrophage-derived chemokine, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)–1β, MIP-1α, MIP-5, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1, MMP-3, MMP-9, Nectin-4, Osteoactivin, osteonectin, P-cadherin, serum amyloid protein A, stem cell factor (SCF), thymus and activation regulated chemokine, TNF–α, TNF-β, TNF–r1, TNF–r2 (R2), TNF–related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and vascular endothelial growth factor A |
Serum | Case-control | TRAIL, ICAM-1, MCP-2, and TNF-r1 were elevated in epilepsy within 24 hours after seizure | 137 patients with epilepsy vs 29 controls. | 2+ |
| Česká et al. [42] | IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, CXCL10/IP-10, CCL2/MCP-1, BLC, TNF-α, C-X3-X and fractalquine (CXC3CL1) | CSF and Serum | Case-control | Significant elevation of CCL2/MCP-1 in CSF and serum. Higher levels of fractalkine/CXC3CL1 in serum of pharmacoresistant patients than in controls |
26 patients with epilepsy (22 DRE, 4 non-DRE) vs 9 healthy controls. | 2- |
| Biomarkers | Number of studies with positive results | Sample | Quality of the evidence | Conclusions of the studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1 | 6 Case-control studies | Serum & CSF | 2+ | Possible biomarker of DRE. Possible biomarker of seizure frequency. Temporal Relationship with Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures. |
| TNF-a | 2 Case-control studies & 1 Prospective population-based study | Serum & CSF | 2+ | Possible biomarker of DRE. |
| TLR-4 | 3 Case-control studies | Serum | 2 | Possible biomarker of DRE. Possible biomarker of seizure frequency. |
| rTNFr2 | 1 Case-control study | Serum | 2- | Possible biomarker of seizure frequency. |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | 1 Case-control study | Serum & CSF | 2- | Possible biomarker of DRE |
| IL-33 | 1 Case-control study | Serum | 2- | Possible biomarker of epilepsy. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





