1. Introduction
In 2022, the rural residential area in China exceeded 26 billion square meters[
1], and the per capita residential construction area was 4.8 times that of 1978 [
2]. Compared with the rapidly growing residential area, the comfort of rural housing has not been effectively improved. Rural housing causes a huge environmental burden throughout its entire lifecycle, but fails to provide comfortable living conditions [
3,
4]. Solving the problems of high energy consumption and low comfort has become a major challenge for the green development of residential buildings [
5,
6].
In this context, the low energy consumption and high comfort characteristics of green buildings are in line with the concept of sustainable development [
7,
8], and have become a necessary support for building green living environments in rural areas and a guiding paradigm for improving rural living conditions under carbon reduction and carbon neutrality goals [
9,
10,
11].
Researchers have conducted a series of evaluation studies on the two important characteristics of green buildings, energy efficiency and comfort. Among them, in research focused on energy efficiency, more attention is paid to the energy-saving renovation of existing buildings, and the performance improvement of building envelope structures such as roofs [
12] and exterior walls [
13] is explored in depth, but most of them ignore the differences in energy structure in rural areas; However, research focused on comfort focuses more on thermal comfort [
14,
15] and light environment [
3], and there is a lack of discussion on other indoor physical environments such as acoustic and air environments.
In the study of residential buildings in the southwest region, the energy efficiency of building envelope structure and indoor thermal environment comfort are still the main factors to be explored. Such as using renewable materials to improve the thermal performance of exterior walls [
16], determining the optimal thickness of insulation layer [
17], and proposing optimization strategies based on indoor thermal environment perception [
18].
Overall, in the research on rural green residential buildings in the southwest region, the exploration of local building components and indoor single physical environment has gradually become sufficient. However, most studies have not fully considered the openness, diversity of construction, and complexity of energy structure of rural housing environment, resulting in a certain research gap in the factor sorting and improvement path of rural green housing under the comprehensive framework.
Based on the above issues, this study integrates the boundary environment, structural characteristics, and energy structure of rural buildings, establishes a comprehensive evaluation system for rural green buildings, and selects the second circle of rural areas in Chengdu as a representative research object to reveal the differences in indicator scores and influencing mechanisms, explore the spatial differentiation characteristics of green degree in rural buildings, diagnose green degree obstacle factors, and finally propose targeted measures to improve the green degree of rural buildings, providing relevant basis for the development of green buildings in rural areas.
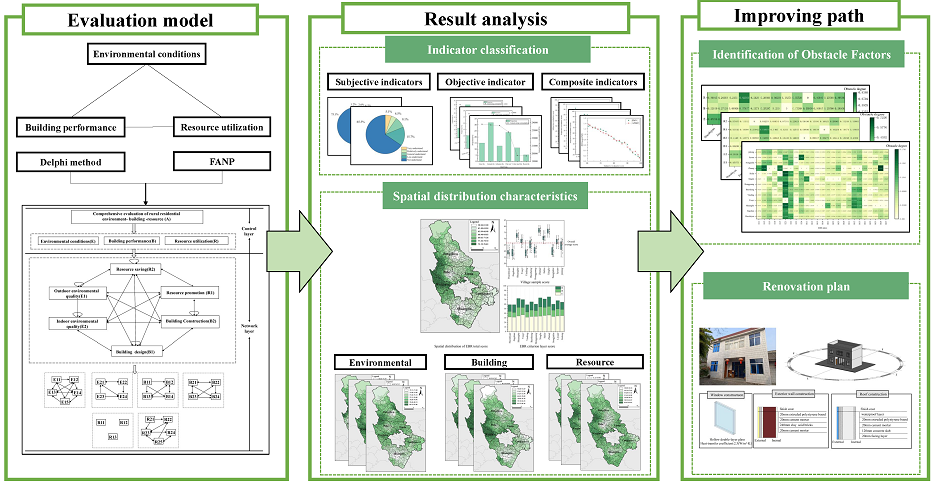
2. Research Technical Routes and Methods
The research framework mainly consists of the following three steps:
Constructed a comprehensive evaluation model. The influencing factors of rural green housing have been preliminarily extracted based on literature mining and brainstorming methods. Then determine the final evaluation indicators through the Delphi method, and calculate the weights of the indicators using fuzzy analytic network process(FANP). Determine the evaluation criteria for indicators through numerical simulation combined with fuzzy hierarchy theory.
Selected the research area for empirical analysis. Randomly sample the villages in the case selection area to obtain sample villages. Collect subjective and objective data from sample villages through on-site interviews and measurements to form preliminary evaluation results.
Result analysis. Explore the spatial distribution differences of greenness in rural buildings based on spatial interpolation method. Diagnose the greenness obstacle factors based on the obstacle degree model. Finally, based on the analysis of the results, targeted improvement strategies are proposed.As shown in
Figure 1.
2.2. Construction of Evaluation Models
2.2.1. Construction of Indicator System
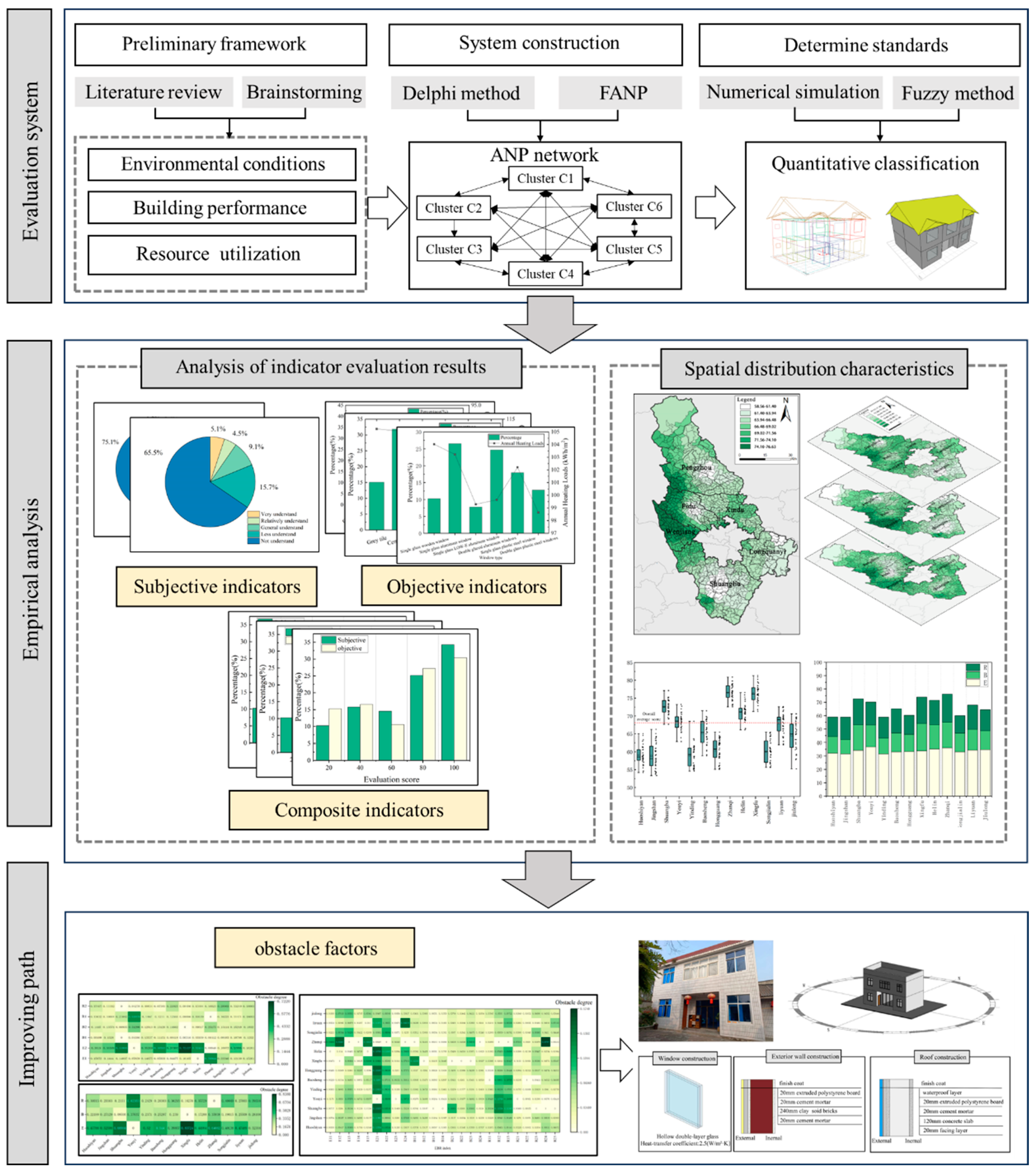
The indicator system focuses on the physical environment of buildings, boundary environment, and the unique energy structure of southwestern rural areas, and establishes the Environment-Building-Resources Model (EBR). The specific construction process of the evaluation system is as follows:
Preliminary selection of evaluation indicators. Referring to the relevant standards for green buildings and the initial indicators for literature collection, four members of the research group were organized to brainstorm and decompose and sort out the evaluation target layer, 26 indicators were initially selected based on the EBR model.
Selection of evaluation indicators. In the screening process of green comprehensive evaluation indicators for rural residential buildings, 12 experts were invited, including 8 from the field of green building, 2 from the field of resources and environment, and 2 from the field of human settlement environment. There is no conflict of interest between experts. Two rounds of questionnaire surveys were conducted according to the requirements of the Delphi method [
19]. The indicators such as “seismic design of buildings”, “room space layout”, and “type of shading measures” have been deleted, modified, or merged.
Determination of evaluation indicators. The final indicator system includes 3 criterion level indicators, 6 sub criterion level indicators, and 25 indicator level indicators (a total of 34 indicators). All 34 indicators meet the criteria of W (Kendall’s concordance coefficient)>0.2, coefficient of variation<0.25, and significance P<0.05, indicating a good degree of coordination among expert opinions and passing the consistency test. The final determined indicators are shown in
Table 1.
2.2.2. Method for Calculating Indicator Weights
Fuzzy analytic network process (FANP) is a weight calculation method that combines network analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. It can overcome the subjectivity of evaluators in the weight determination process when quantifying indicators, and also reflect the dependency relationships and feedback mechanisms between elements at different levels and within the same level, making the analysis results more accurate and effective. Suitable for evaluating problems that are difficult to quantify and have mutual influence of connotation factors. Considering the complexity of the indicator composition in the rural green residential buildings evaluation system, and the fact that the relationship between indicators tends to be more network structured, FANP adapts well to these characteristics. Choosing it to calculate indicator weights can ensure the scientificity and accuracy of the evaluation results [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
The calculation of weights using the FANP mainly includes the following steps:
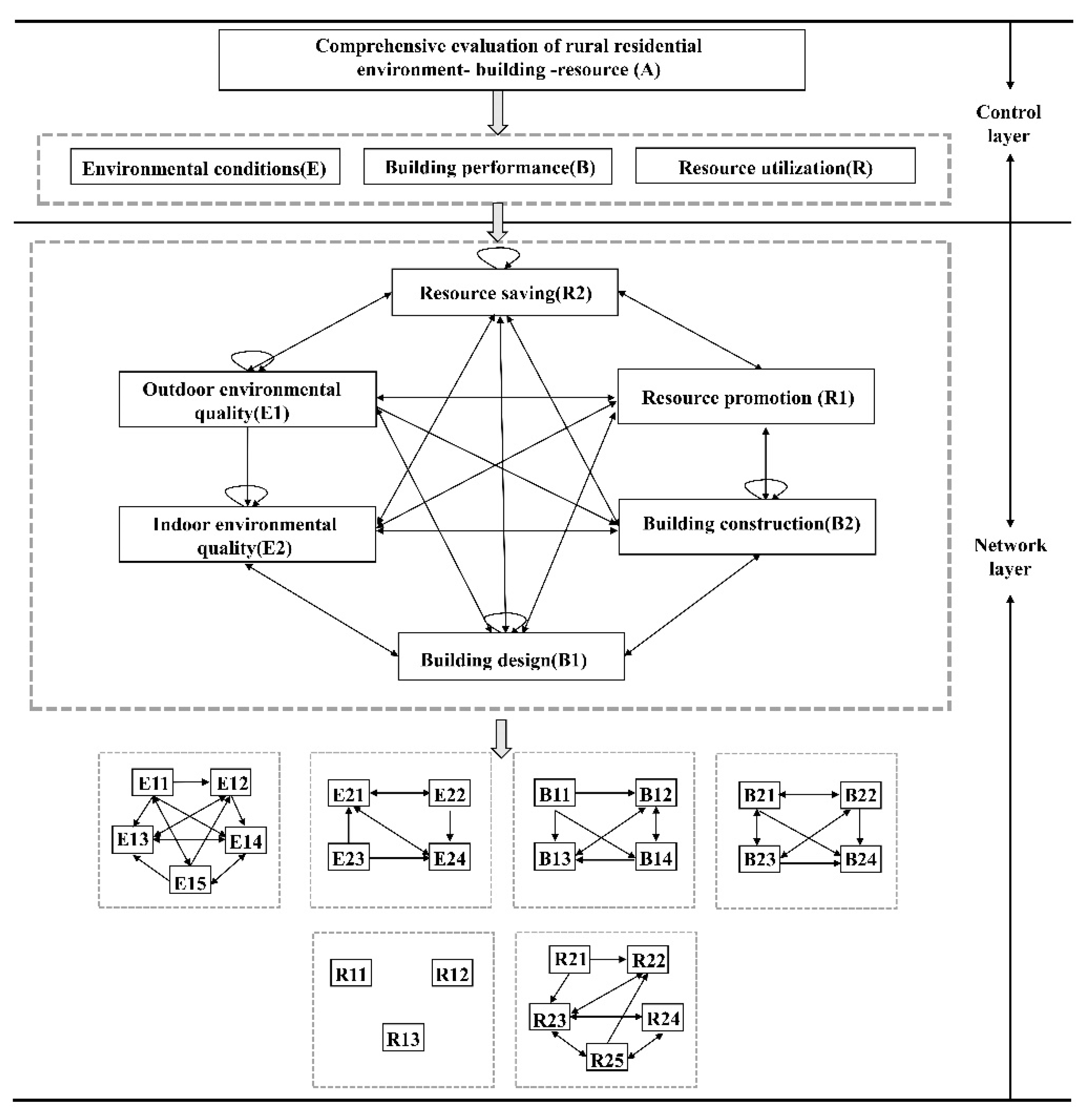
Modeled the network relationships of the indicator system. The indicator correlation questionnaire was filled out by 15 invited experts. In addition to the 12 experts involved in building the indicator system, 3 other relevant professional and technical personnel were also invited to conduct a questionnaire survey. Thus, the correlation between the indicators was determined, and the results obtained are shown in
Figure 2.
Calculated local weights. The local weights of each indicator were determined by using a pairwise comparison matrix (assuming no dependencies between indicators in this step).
Calculated dependency weights. The internal dependency matrix between indicators was determined using triangular fuzzy scaling, and the dependency weights were obtained by multiplying the dependency matrix with local weights.
Combined to obtain the global weights of the indicators. The global weight is obtained by multiplying the local weight in step 3 with the dependency weight in step 4. The organized results are shown in the weight column of
Table 1.
2.2.3. Indicator Scoring Rules
Divide indicator types into three categories: subjective indicators, objective indicators, and subjective objective composite indicators. The subjective indicator grading is mainly based on existing literature and normative standards, and the scoring method is based on the fuzzy hierarchy theory, as shown in
Table 2.
The classification of objective indicators is mainly based on reference standards [
25], numerical simulation results, and statistical yearbooks. The scoring method is linear interpolation, as shown in
Table 3.
The composite indicator combines the grading criteria [
26] and scoring methods of the above two indicators, and assigns a weight of 1/2 to each indicator before adding them up to obtain the rating of this type of indicator, as shown in
Table 4.
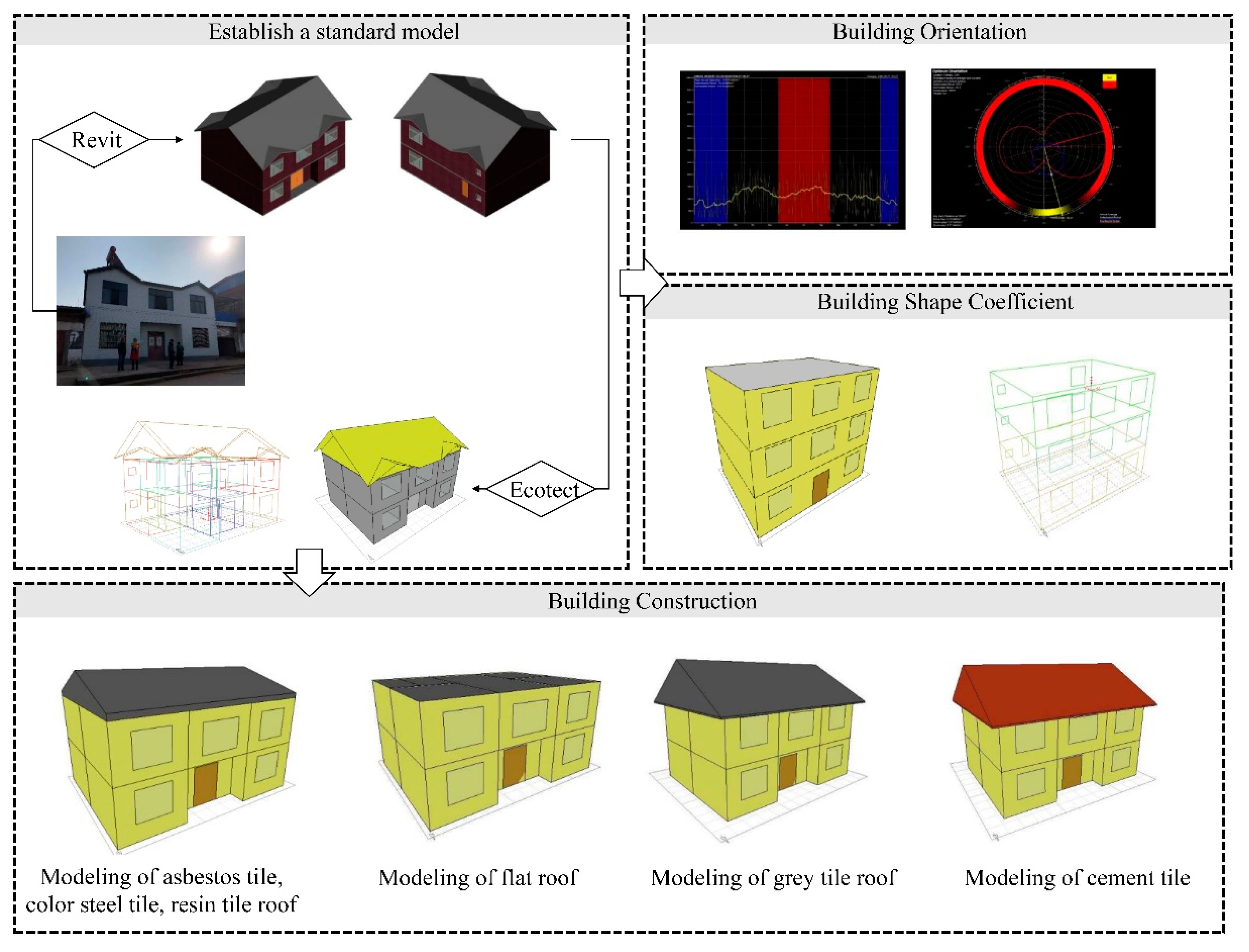
The quantification of building performance indicators used numerical simulation methods, and the specific steps are as follows:
During the preliminary research, information was collected on rural residences, and a typical rural building in Chengdu was identified based on the comprehensive construction area, building form, and materials used.
Establishing building standard models through Revit software,
Import the standard model into Ecotect software, input external environmental parameters (such as temperature, humidity, etc.), set various building component information (such as exterior walls, roofs, etc.), and visualize building energy consumption and indoor physical environment parameters. The specific process is shown in
Figure 3.
2.2.4. Calculation of EBR Comprehensive Score
The weighted sum method is used to obtain the comprehensive score (EBR) of rural building green degree, and the specific calculation formula is as follows:
where, Xij represents the specific score value of a sub indicator, and Wij represents the corresponding weight value.
2.2.5. Obstacle Degree Model
The obstacle model is a mathematical statistical method based on relevant comprehensive evaluation, which effectively identifies the main obstacles that hinder the development of things and goals. It has been widely used in key factor analysis and research in various disciplinary fields [
27,
28,
29]. The specific steps are as follows:
Firstly, standardize the indicators using formulas 2 and 3 respectively.
When Xij is a positive indicator:
When Xij is a negative indicator:
Where, Zij is the standardized value of a single indicator
Obstacle degree formula:
where, P
ij is the obstacle degree of a single indicator to the EBR of rural housing, Z
ij is the standardized value of a single indicator, W
ij is the global weight of a single indicator, and n is the total number of indicators.
2.3. Study Area and Data Sources
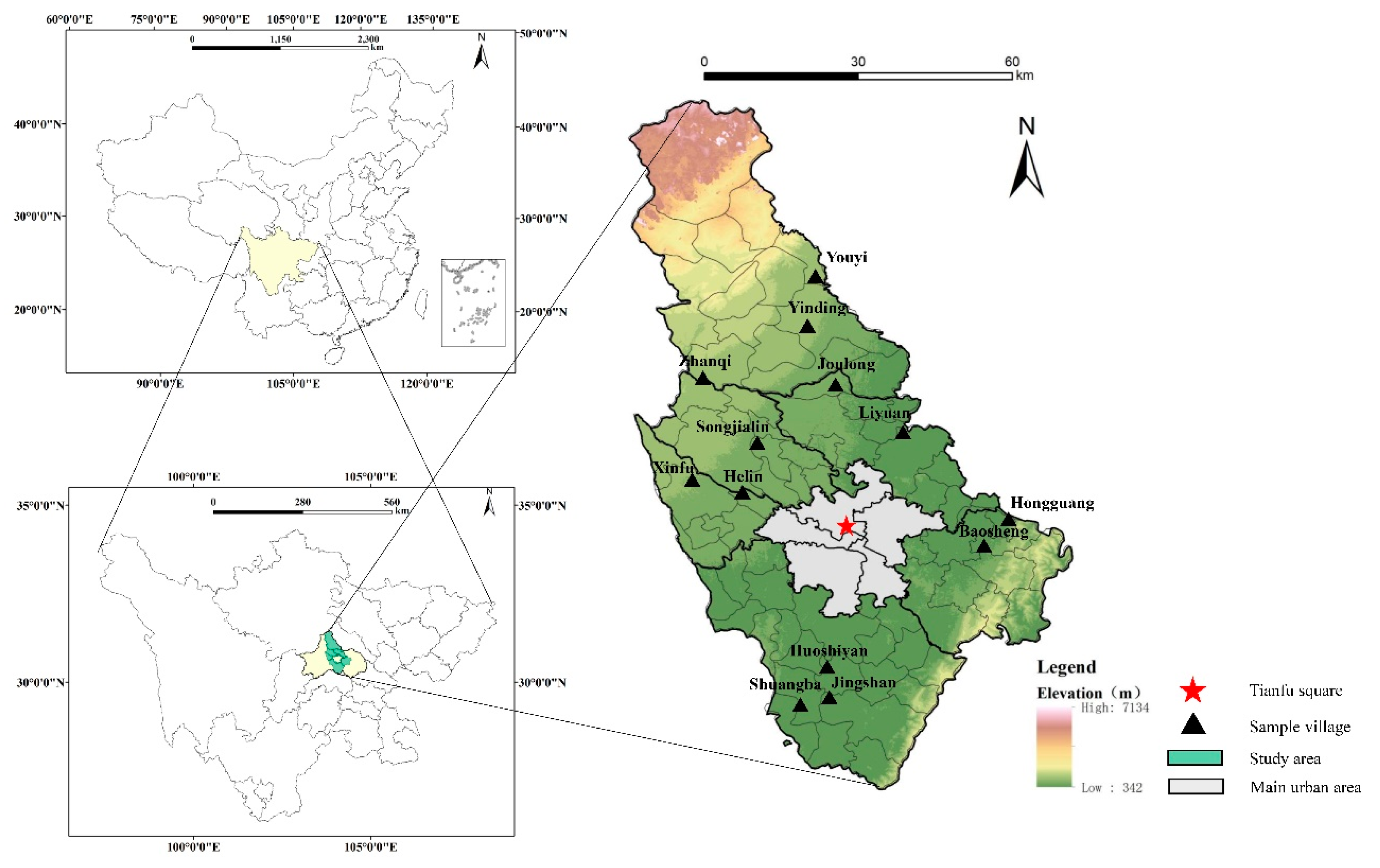
Chengdu is located on the western edge of the Sichuan Basin, as one of the economic centers in southwestern China, it has certain representativeness in natural climate, rural architectural form, and resource structure. Therefore, Chengdu is chosen as the research area.
Empirical research will be conducted using on-site investigation of receipt data. Considering that the main urban area of Chengdu has been highly urbanized and there are relatively few traditional rural areas, in order to meet the needs of the research sample, five suburban areas in the second circle with a large number of villages, including Xindu, Pidu, Wenjiang, Shuangliu, and Longquanyi, as well as Pengzhou City in the third circle, were selected as the research area. This has formed a comprehensive coverage effect around Chengdu in terms of geographical location. Using Chengdu’s annual “Rural Revitalization” demonstration villages and “Sichuan’s Most Beautiful Villages” as the overall sample range, 13 villages were randomly selected as research villages at a 10% sampling ratio, including 6 new rural resettlement communities (A village where residential buildings have been uniformly planned and constructed) and 7 traditional villages. The sampling quantity meets the requirements, and the distribution of sample villages is shown in
Figure 4.
In order to obtain indoor environmental measurement values, subjective feelings of residents, and energy consumption under the most unfavorable conditions, the research group conducted four field investigations in the hottest and coldest months of Chengdu. The subjective indicators were collected through questionnaire interviews, as shown in
Figure 5a. The objective indicators were collected through on-site measurements, as shown in
Figure 5b,c,d.
The comprehensive indicators were collected through both interviews and on-site measurements. The measuring instrument used is shown in
Figure 5f. The specific information of instruments and measurements is shown in
Table 5. 391 questionnaires were ultimately collected, and after sorting and screening out invalid questionnaires, 386 valid questionnaires were obtained, with an effective questionnaire rate of 98.72%.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Subjective Indicators
Subjective indicators are distributed in all three dimensions of EBR, among which the three indicators in the resource utilization dimension, solar energy utilization (R11), Popularity of biogas facilities (R12), and green building material usage (R13), have relatively high weights of 0.03, 0.06, and 0.06, respectively. The score of solar energy utilization ranges from 20.11 to 40.25, the score of popularity of biogas facilities ranges from 21.54 to 51.64, and the score of green building material usage ranges from 20.48 to 59.64. The average score is relatively low.
The impact of biogas facilities and green building material usage on the total EBR score is more significant. For example, Jiulong Village in Xindu District has a score rate of over 75% in both environmental conditions and building performance dimensions, which is higher than the first ranked Zhanqi Village and the second ranked Xingfu Village. However, due to the scores of only 30.21 and 32.55 for the two indicators biogas facilities and green building material usage, the total EBR score is 64.46, which is lower than the average of 66.17.
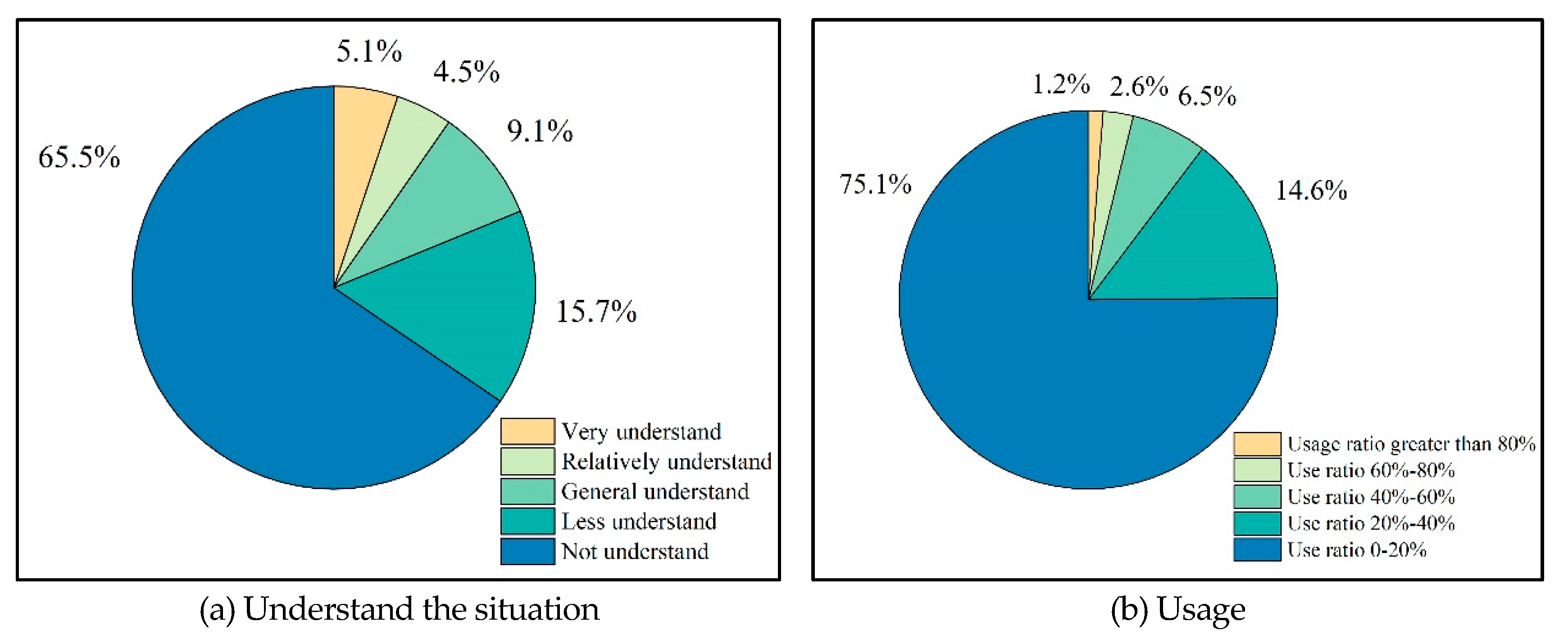
The main reason for the generally low levels of these three subjective indicators is the biased lifestyle habits of residents. Rural residents are more inclined to choose low-cost and easily accessible building materials, and lack attention to the green performance of building materials. The survey results show that 65.47% of residents have no understanding of the concept of green building materials, as shown in
Figure 6a. The proportion of using green building materials is only 24.9%, as shown in
Figure 6b.
In terms of energy utilization, residents place greater emphasis on comfort, convenience, and hygiene when choosing energy, and therefore tend to prefer the use of convenient commodity energy. 43.78% of rural households only use commodity energy, and only 4.93% of households have renewable energy facilities and use them normally.
3.2. Analysis of Objective Indicators
The objective indicators are mainly composed of indicators from the dimension of building performance, with the factors with significant differences mainly coming from the two indicators of the sub criterion level building structure, namely roof structure (B21), exterior wall structure (B22), and window structure (B23). The weights of the three indicators are 0.039, 0.04, and 0.04 respectively, with small differences. The evaluation results range from 40.63 to 87.19, 38.12 to 89.47, and 41.27 to 92.22, with a wide distribution range. Zhanqi Village in Pidu District has the highest roof structure score at 89.67, while Xingfu Village in Wenjiang District has the highest exterior wall structure and window structure scores at 90.25 and 92.22, respectively. The roof structure and exterior wall structure scores of Jingshan Village in Shuangliu District are both the lowest, with 47.75 and 49.76 respectively. The window structure score of Hongguang Village in Longquanyi District is the lowest, at 41.27.
Figure 7 shows the annual energy consumption of various types of roofs, exterior walls, and windows in the study area, as well as their proportion to the total sample. Energy consumption data is simulated by Ecotect software, and the proportion data comes from field research. The high energy consumption roof types are mainly small green tile roofs, cement tile roofs, and asbestos tile roofs, with heat transfer coefficients of 1.85 W/(m²·K), 1.71 W/(m²·K), 1.52 W/(m²·K). The main types of high-energy consumption walls are clay solid brick walls and sintered shale brick walls, with heat transfer coefficients of 1.89 W/(m²·K), 1.26 W/(m²·K). The main types of windows with high energy consumption are single glass aluminum windows and single glass plastic steel windows, with heat transfer coefficients of 5.75 W/(m²·K), 4.7 W/(m²·K).
Due to the fact that most of the heat loss in buildings is dissipated through the outer surface of the enclosure structure facing the surrounding environment, the thermal performance of these enclosure structures with high heat transfer coefficients is poor, resulting in high energy consumption that reduces the green performance of the building.
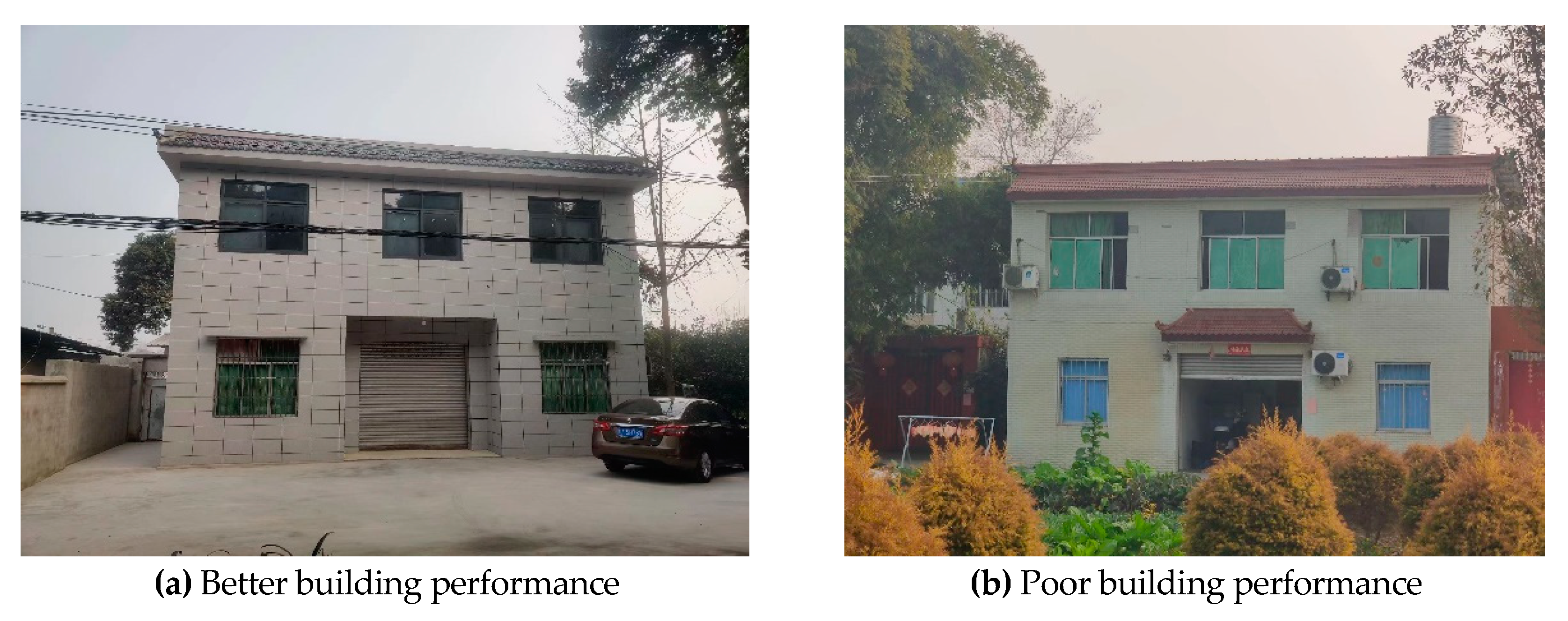
To further explore the impact of the difference in scores between roof construction and exterior wall construction indicators on the total EBR score, two residential properties in Liyuan Village, Xindu District were selected for comparison. The difference in scores for other indicators between the two residential areas in
Figure 8a and
Figure 8b is relatively small. The roof construction score for residential area a is 89.21, the B22 score is 92.14, and the total EBR score is 70.24; The B21 score for residential B is 40.21, the exterior wall construction score is 45.17, and the total EBR score is only 64.59.
3.3. Analysis of Composite Indicators
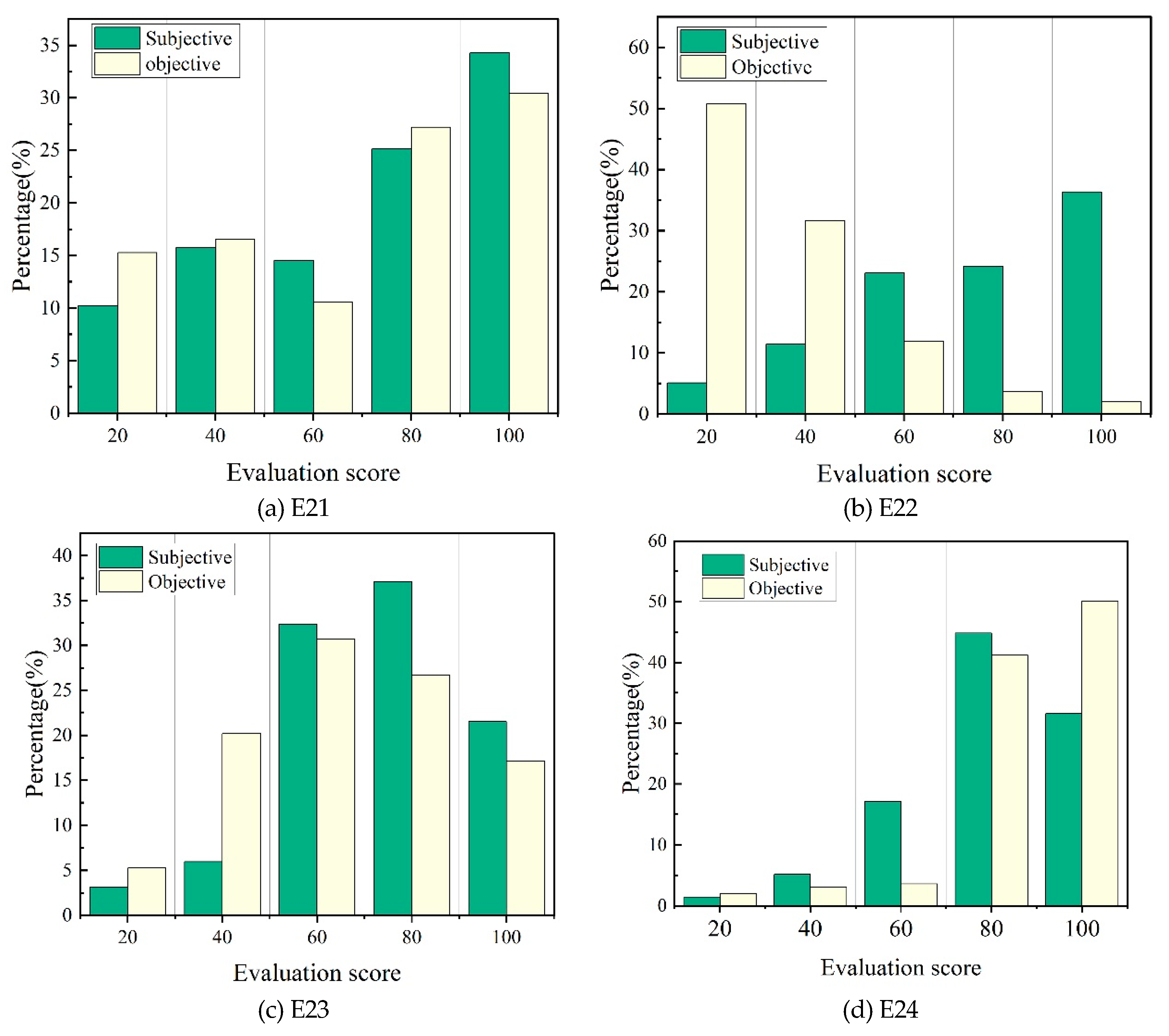
The Composite indicators (Indicators have both subjective and objective attributes) consist of four indicators: indoor thermal environment (E21), indoor light environment (E22), indoor sound environment (E23), and indoor air quality (E24). The trend of the subjective and objective evaluation results of the four indicators is shown in
Figure 9.
Among the four indicators, the scores of indoor sound environment and indoor air quality are between 57.66-81.01 and 65.33-81.07, with a small range of distribution and consistent subjective and objective evaluation results. As the most weighted indicator in the evaluation system, the indoor thermal environment has an overall score between 69.87 and 81.1, with an average score of 74.94, providing a significant contribution to the total EBR score. This is mainly reflected in the fact that the scores of indoor thermal environment in the top 5 villages in the total score are all greater than 74.
Compared with the evaluation results of the other three comprehensive factors, there is a significant difference between the subjective and objective results of indoor light environment. From
Figure 9b, it can be seen that subjective evaluations tend to be more biased towards “ Comfortable “ and “ Slight comfortable “, accounting for a total of 80% of the total. In objective evaluations, the daylighting coefficient is concentrated in the range of 1.2-2.4, corresponding to 20-40 points. This indicates that rural residents have a higher tolerance for light environments.
3.4. Overall Characteristics of EBR
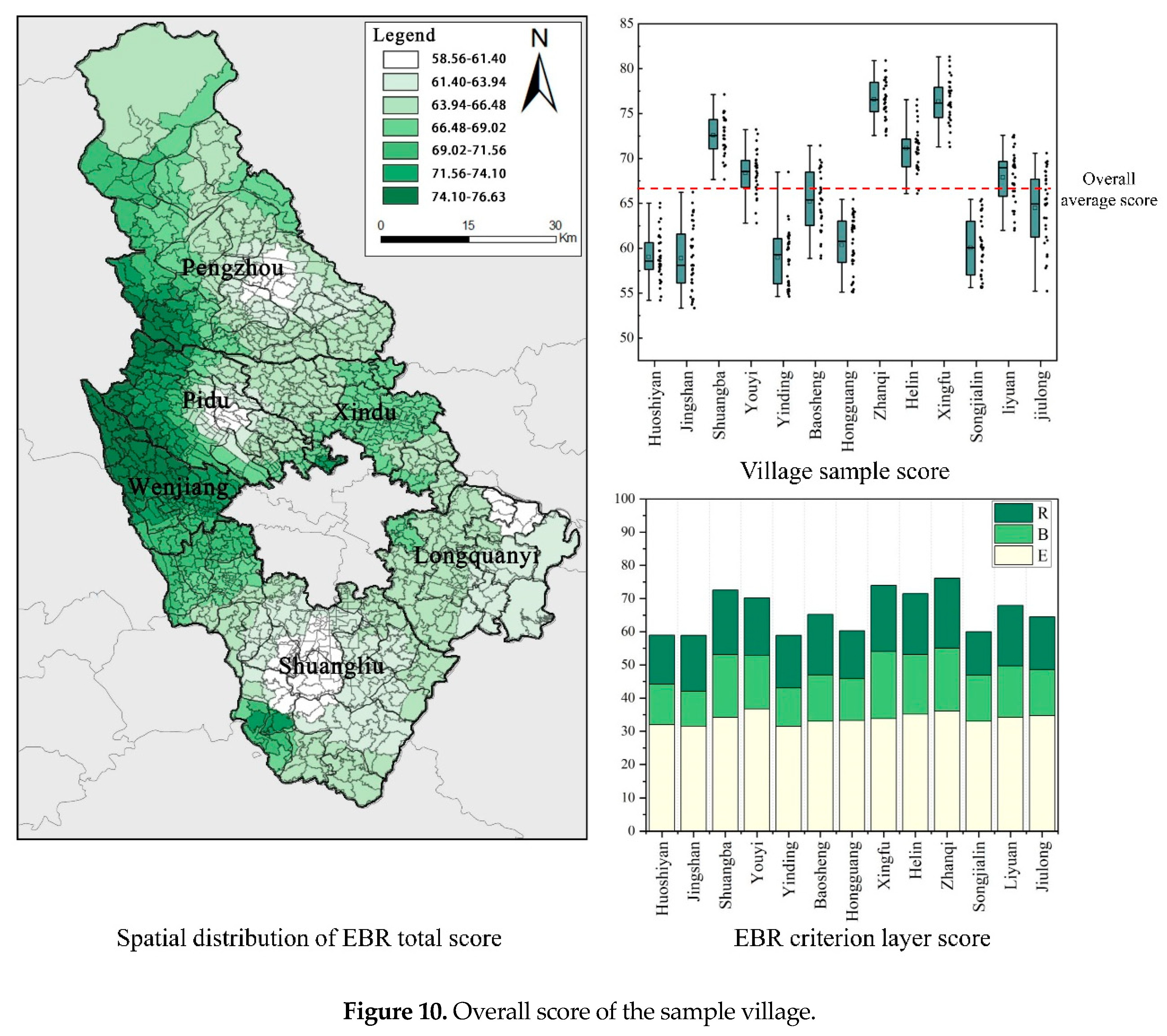
The overall and sub scores of EBR for rural residential buildings around Chengdu are shown in
Figure 10. Among them, the overall EBR score of rural buildings ranges from 76.65 to 58.86, with an average of 66.17, slightly higher than the median value of 65.21.
From the perspective of spatial distribution, the EBR spatial distribution of rural buildings around Chengdu shows a spatial gradient pattern with two high value centers, Pidu District and Wenjiang District, decreasing towards the edge. The green level of rural buildings in the surrounding areas of Chengdu varies greatly, with significant spatial differentiation.
3.5. local Spatial Features of EBR
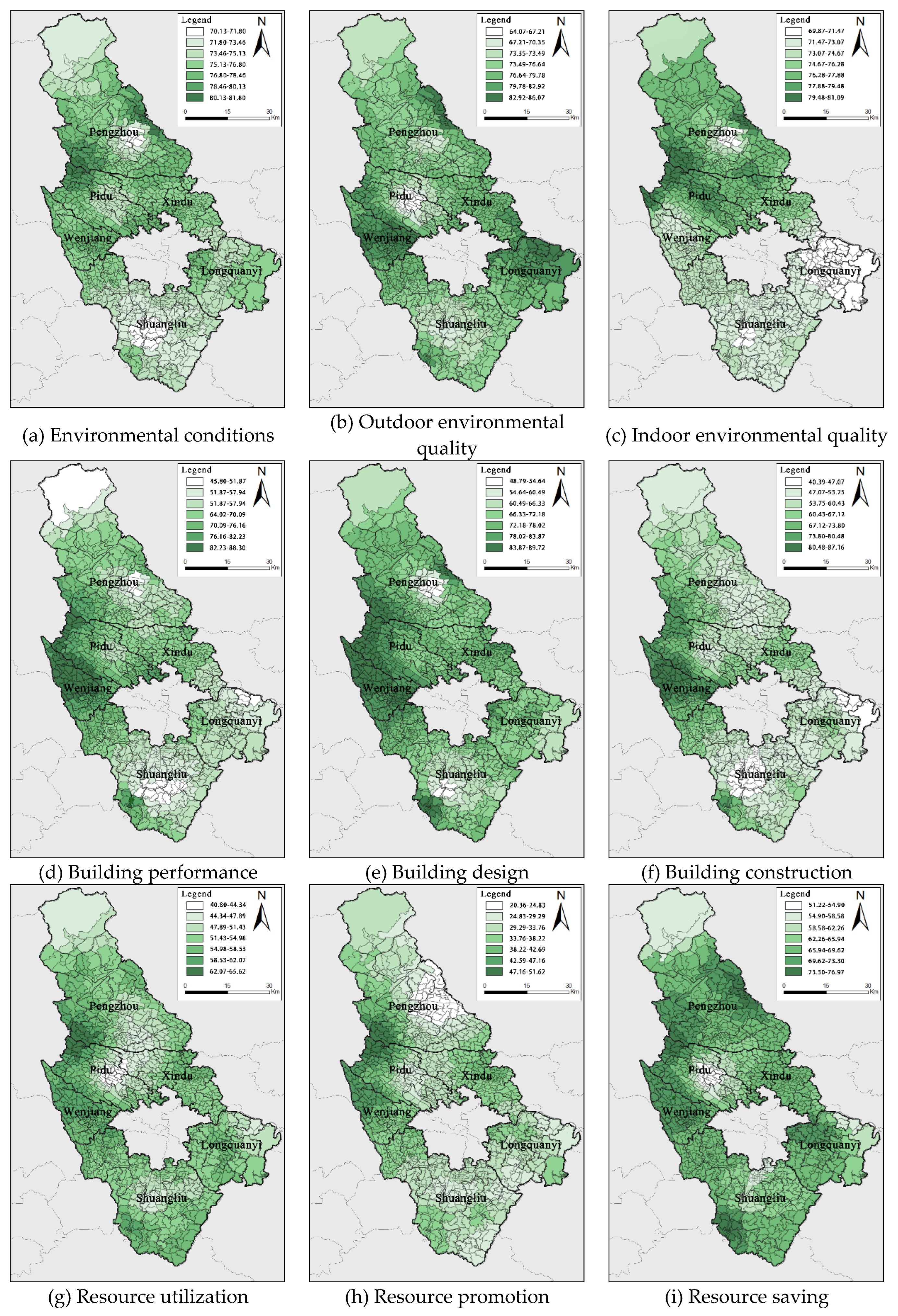
To further reveal the local spatial characteristics of the EBR of rural buildings in Chengdu, spatial interpolation analysis was conducted on the scores of the EBR criterion layer and sub criterion layer. Spatial interpolation analysis is completed in ArcGIS. Considering the similarity of rural residences in similar areas, the inverse distance weighting method is chosen for interpolation analysis. The results indicate that there are certain differences in the spatial distribution of scores in each dimension, as shown in
Figure 11.
3.5.1. Spatial Distribution of Environmental Conditions
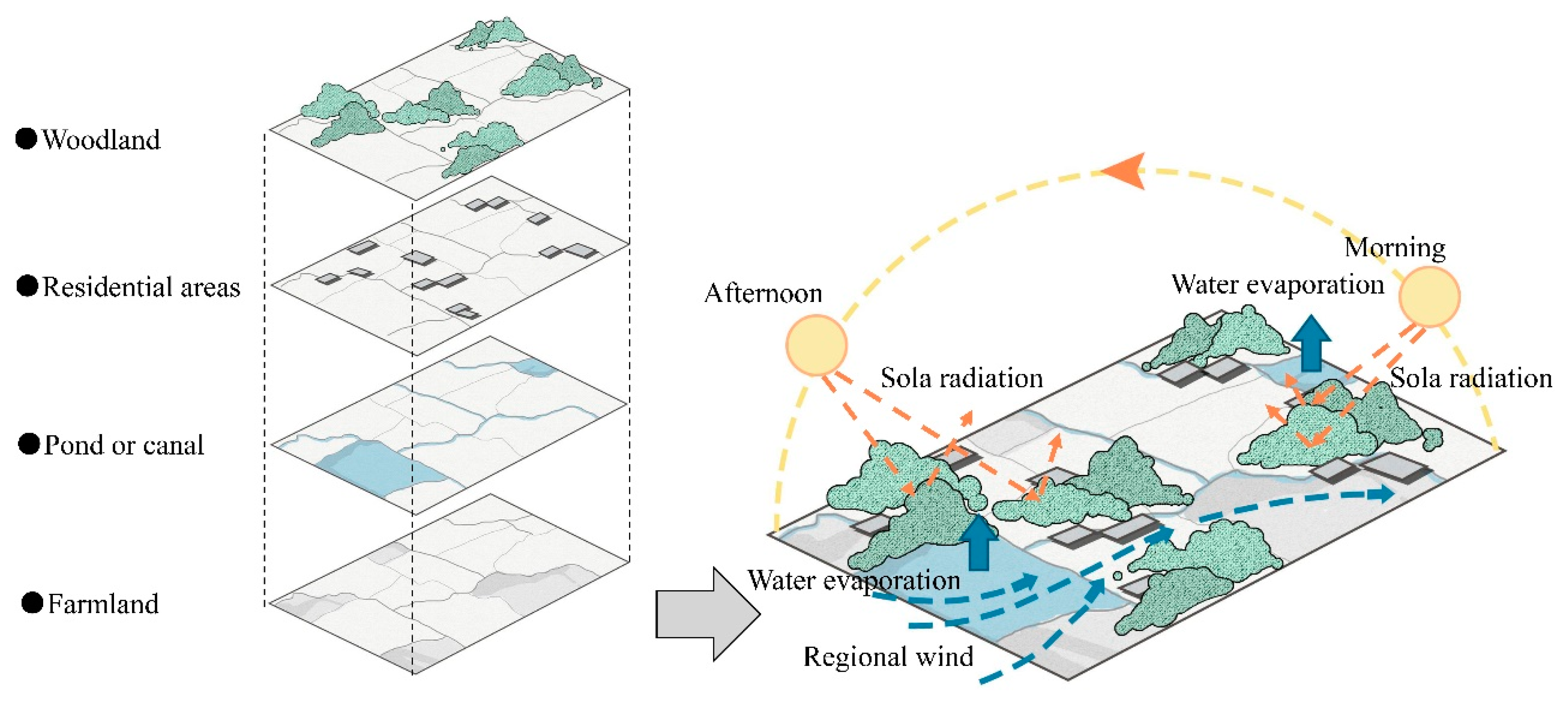
The spatial distribution pattern of the environmental dimension shows a pattern of high in the north and low in the south, especially in the indoor environment of the subcriteria layer. The analysis results of the previous indicators indicate that indoor thermal environment (E21) is a key influencing factor of indoor environment. Due to the openness of rural residential environments, indoor thermal environment is not only related to the structural performance of buildings, but also influenced by the outdoor environment of residential areas. The Chengdu region has a unique traditional settlement village form - the forest panel. The forest panel system consists of four units: forest, house, water, and field. Vegetation and water system elements help reduce solar radiation and greenhouse effect, thereby regulating indoor thermal environment. The specific path is shown in
Figure 12.
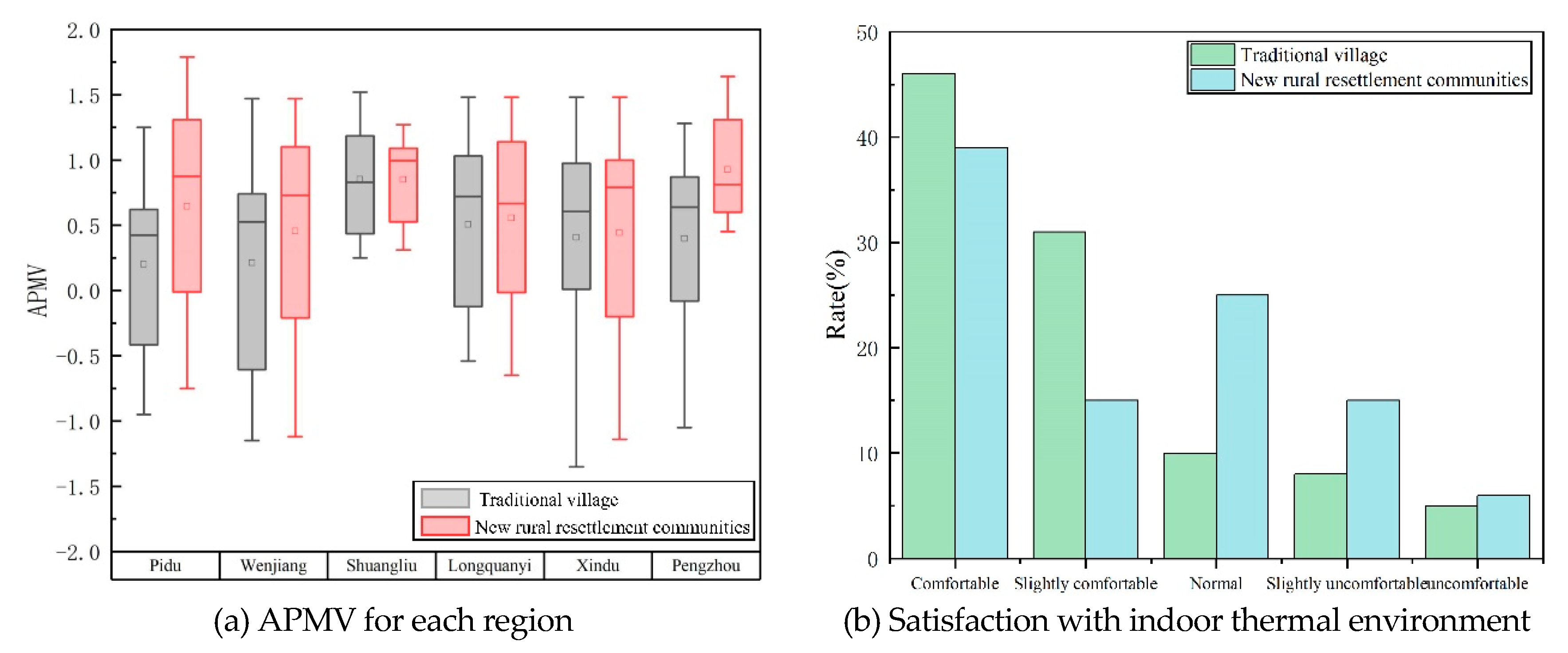
The data in
Figure 13a shows that traditional villages in the forest system have a better indoor thermal environment compared to new rural resettlement communities, mainly manifested by the fact that the absolute value range of APMV in traditional villages is more concentrated within the comfortable range of 0.5. The subjective statistical comparison results of indoor thermal comfort also assist in proving this phenomenon, as shown in
Figure 13b. In the subjective feelings of traditional village residents, the proportion of comfortable and more comfortable is larger, while the evaluation of new rural resettlement communities residents is more inclined towards general. From the perspective of forest distribution location, the forest distribution in the northern areas of Pengzhou, Pidu, and Xindu is more dense, while the villages in Shuangliu and Longquanyi districts in the south are concentrated in hills and mountains, with fewer forest clusters. The indoor thermal environment score is lower than that of Pidu and Xindu, resulting in a spatial differentiation of high temperature scores in the north and low in the south in the living environment.
3.5.2. Spatial Distribution of Building Performance
The score difference in the dimension of building performance is significant, and the spatial differentiation effect is significant. Among them, the highest score for building performance is 88.33 (Xingfu Village, Wenjiang District), and the lowest score is 45.78 (Jingshan Village, Shuangliu District). Due to systematic planning and design in terms of building structure and materials, the new rural resettlement communities residence has better building performance dimensions compared to traditional villages that mainly rely on self built houses. Therefore, each district presents a distribution pattern gradually decreasing from high-value centers in new villages to traditional villages in low value areas.
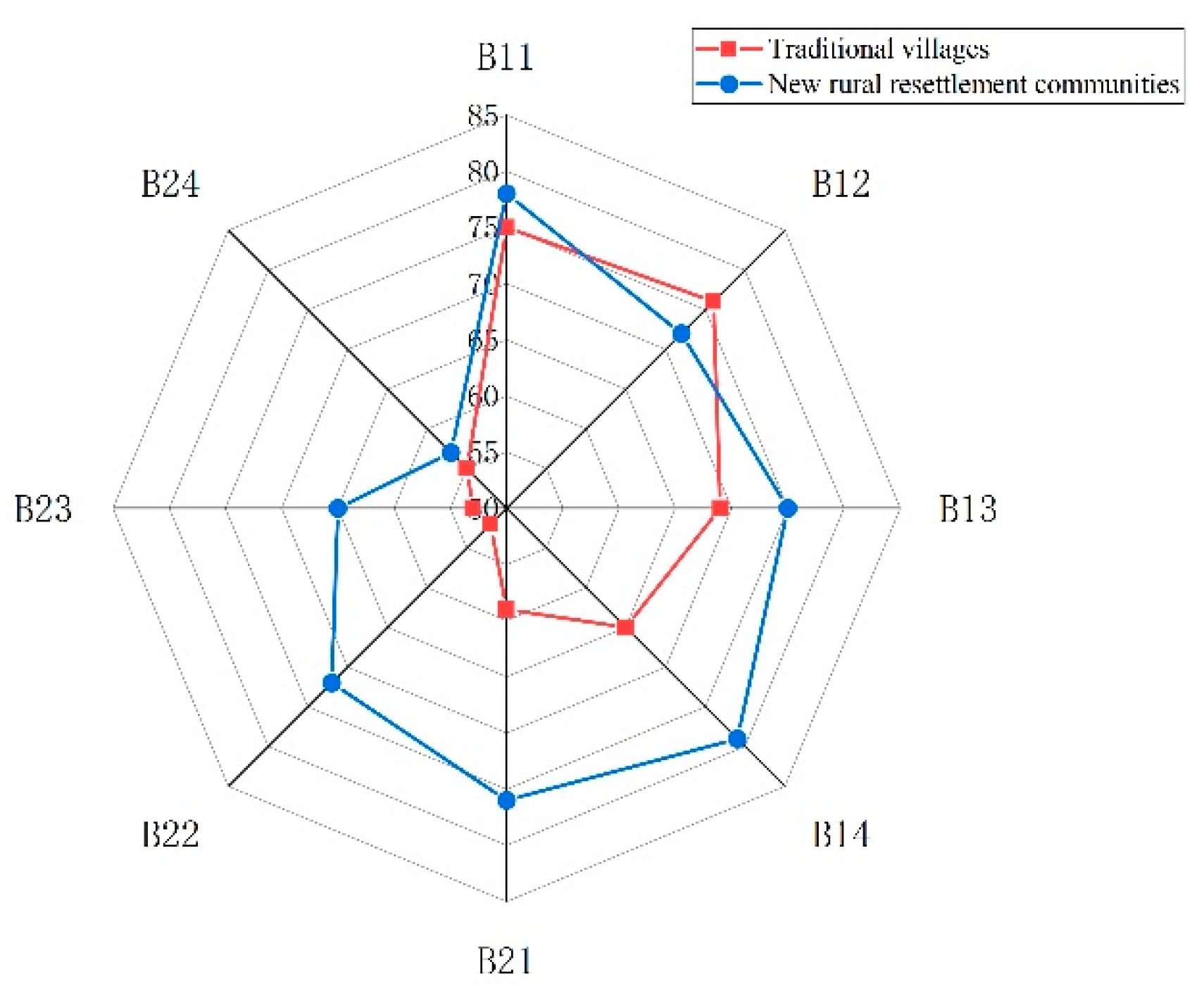
From the specific indicator scores in
Figure 14, among the 8 indicators in the dimension of building structure, traditional villages only score higher than new rural resettlement communities in the building shape coefficient (B12) indicator. This is because new rural resettlement communities have irregular building shapes and larger shape coefficients, which are less favorable for building energy efficiency. But the better structural materials in the new rural resettlement communities balance the disadvantage of the shape coefficient, and overall, the new rural resettlement communities is still superior to the traditional village in building performance.
3.5.3. Spatial Distribution of Resource Utilization
The score of resource utilization dimension is generally low, and the spatial differentiation shows a distribution pattern of low center and high edge. In the sub criterion layer, the resource saving (R2) weight for resource conservation is relatively high, but the score range of the R2 indicator layer is small, so the R2 score is relatively uniform in spatial distribution. The previous analysis results indicate that the acceptance rate of biogas facilities in resource promotion resource promotion (R1) is popularity of biogas facilities (R12), and the usage rate of green building materials is R13, which are key indicators affecting the sub criterion layer R1 and the total EBR score.
From a spatial perspective, villages near the centers of each district are affected by urbanization, with more complete energy infrastructure construction and a predominantly commodity energy structure. High power electrical appliances are used more frequently, resulting in a greater demand for energy. Among them, the most obvious is Songjialin Village in Pidu District. Songjialin Village is located in the center of Pidu District and belongs to the urban-rural integration type village. The residents mainly use electricity and natural gas for energy, and the utilization of renewable energy is relatively weak. The R12 score is 24.07, and the R13 score is 25.88, both of which are in a relatively low value.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Obstacle Factors
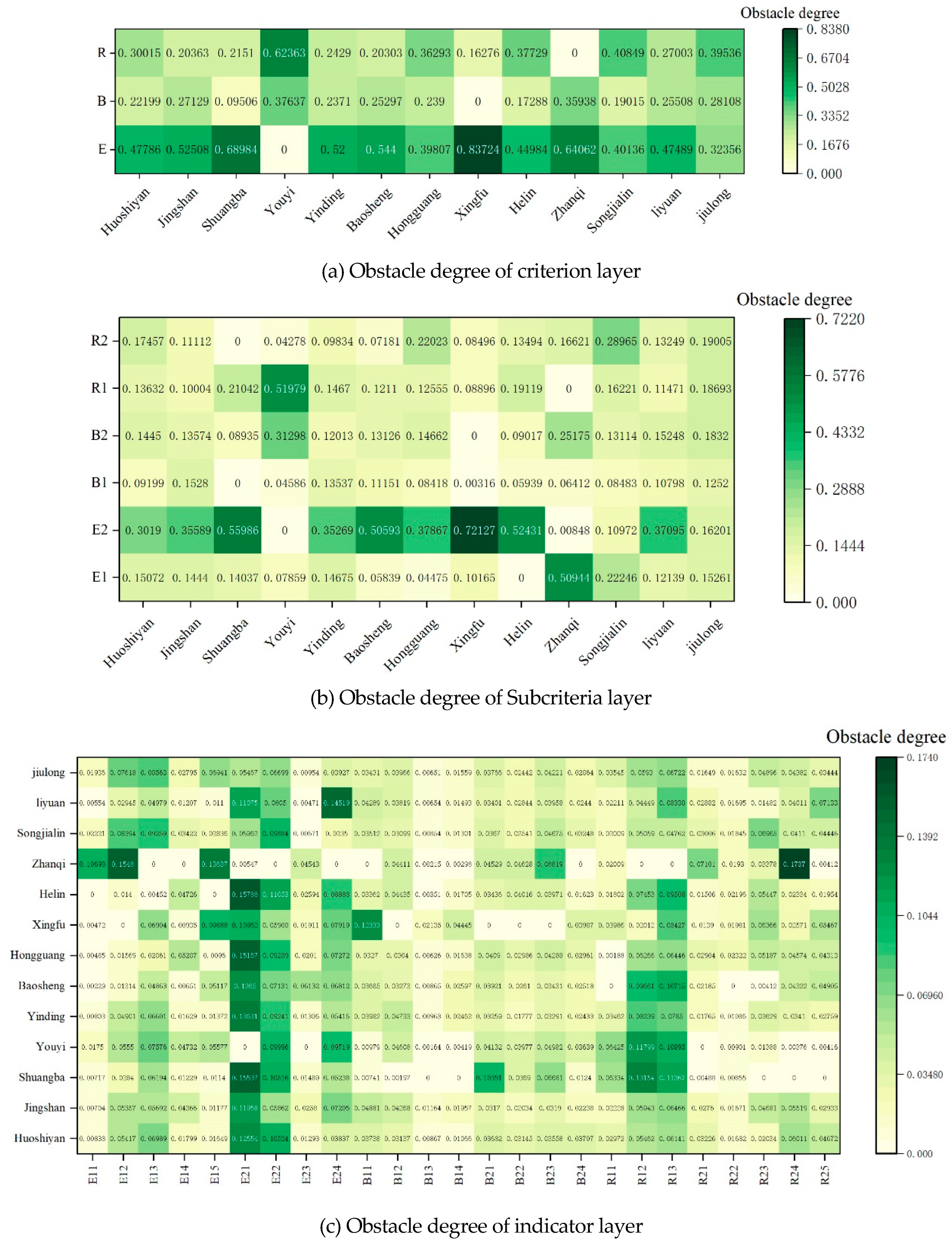
In order to further identify the key obstacle factors that affect the overall EBR, an obstacle degree model was used to comprehensively diagnose and analyze EBR, and targeted improvement strategies were proposed based on the analysis results.
4.1.1. Spatial Distribution of Environmental Conditions
The diagnostic results in
Figure 15a show significant differences in the degree of obstacles in the three dimensions of the criterion layer. When there is only one criterion layer with an obstacle degree greater than 30%, it is designated as a single dominant obstacle type, and when there are two criterion layers with an obstacle degree greater than 30%, it is designated as a double dominant obstacle type. The villages in the sample that belong to the single dominant obstacle type include Jingshan Village, Shuangba Village, Yinding Village, Baosheng Village, Xingfu Village, and Liyuan Village. Among them, the obstacle degree of environmental conditions exceeds 40% in single dominant obstacle type villages. Villages belonging to the dual dominant obstacle type include Huoshiyan Village, Youyi Village, Hongguang Village, Helin Village, Zhanqi Village, Songjialin Village, and Jiulong Village. Among them, 71.4% of villages are dominated by environmental conditions and resource utilization as obstacles, indicating that. The environmental situation is a crucial obstacle dimension.
The obstacle diagnosis results of the subcriteria layer are shown in
Figure 15b. In the sub criterion layer, the obstacle level of indoor environment (E2) is the most significant, with 69.23% of villages having an obstacle level exceeding 30%, indicating that the obstacle level of environmental situation E is mainly contributed by E2.
4.1.2. Obstacle Analysis of Indicator Layer
The diagnostic results of obstacle degree in
Figure 15c indicate that the top four indicators of overall obstacle degree are E21, E22, R13, and R12, which are basically consistent with the analysis results of the previous indicators.
The score range of indoor thermal environment (E21) is relatively small, and its obstacle degree mainly comes from the high weight of the indicator itself. The obstacle level of indoor light environment (E22) is due to the significant difference between subjective and objective evaluations, resulting in a low overall score and a more significant obstacle level.
Overall, the obstacles in the dimension of building performance are relatively average, and there is no obvious clustering. The weight distribution of indicators in this dimension is relatively uniform. The difference in scores between the two indicators of roof construction (B21) and exterior wall construction (B21) is significant, but it has not become a significant obstacle factor. The main reason is that B21 and B21 have relatively small weights and are weaker in obstacle priority compared to high weight indicators such as E21 and R12.
In the dimension of resource utilization, there are significant obstacles in the popularity of biogas facilities (R12) and green building material usage (R13). The weight and score range of R12 and R13 is significant, with 69.23% of villages having low scores in R12 and R13, showing significant clustering on the obstacle heatmap.
4.2. Strategies for Enhancing Rural Green Residential Buildings
The diagnostic results of EBR obstacle factors in rural buildings around Chengdu indicate that indoor thermal environment (E21), indoor light environment (E22), popularity of biogas facilities (R12), and green building material usage (R13) are key obstacle factors. Based on the characteristics of the above four factors, balancing the relationship between energy efficiency, comfort, and economy, targeted improvement strategies are summarized as follows:
(1) Improve indoor thermal environment
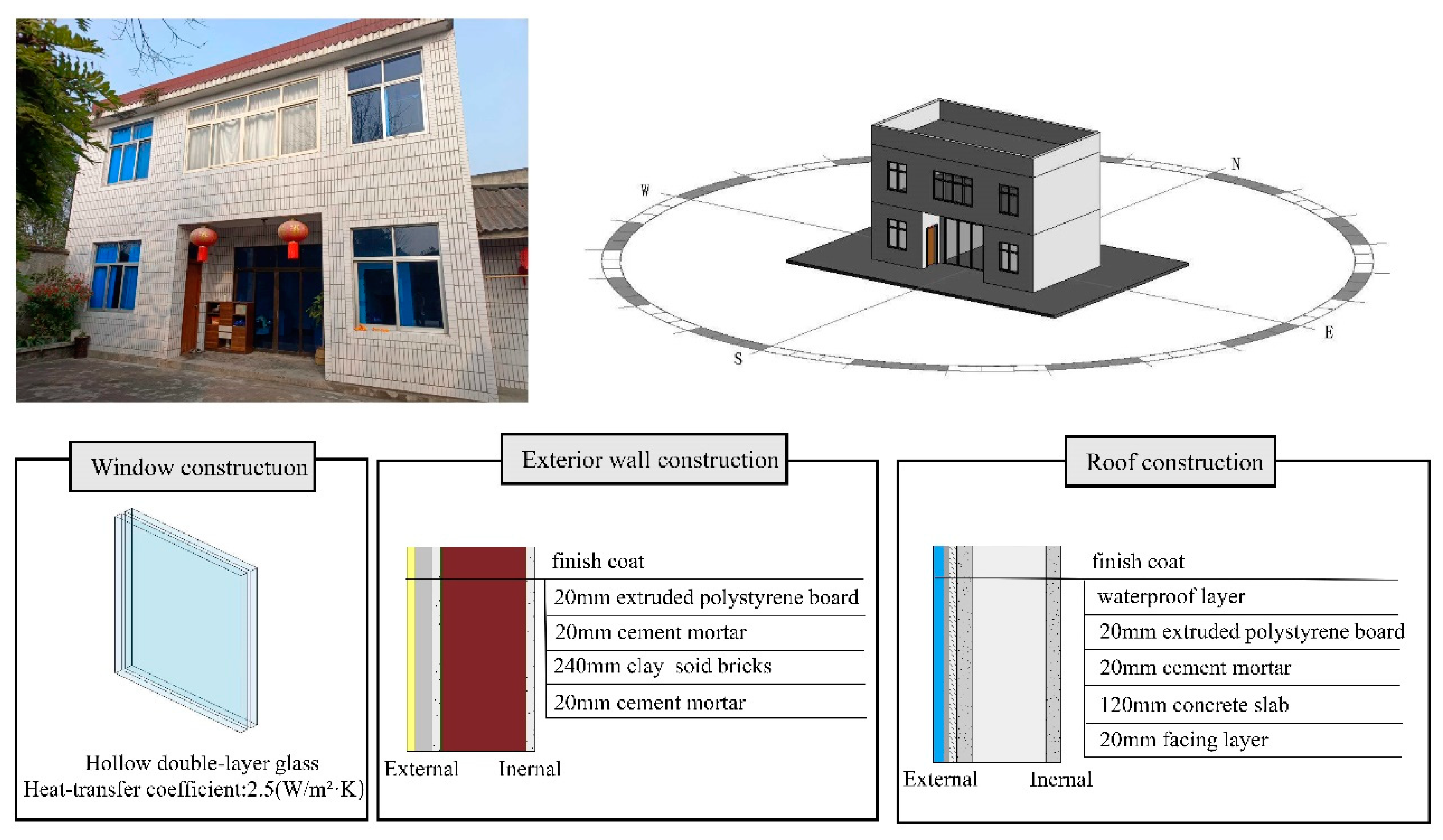
The indoor thermal environment, as the most significant obstacle factor, needs to be given priority consideration when improving the EBR of residential buildings. Taking Wenjiang District and Lin Village as an example, the indoor thermal environment of the village reached 15.19%. Field research has found that the thermal performance of residential buildings in Helin Village is poor and cannot meet the thermal comfort requirements of residents. Passive energy-saving technology can be used to transform the enclosure structure of existing residential buildings.
Taking a residential building in Helin Village as an example, the original enclosure structure of the building was wooden doors, single glass plastic steel windows, and the roof and exterior walls were not insulated, resulting in significant heat loss. Considering economic and regional feasibility, a numerical simulation was conducted to determine the renovation plan, as shown in
Figure 16. The renovation results show that by replacing the windows with double-layer hollow plastic steel windows and changing the method of roof exterior walls, the indoor thermal environment score has been increased from 64.39 to 72.45, and the unit energy consumption has been reduced by 25.34% compared to the original. At the same time, it meets the requirements of comfort and energy efficiency.
(2) Optimize indoor lighting paths
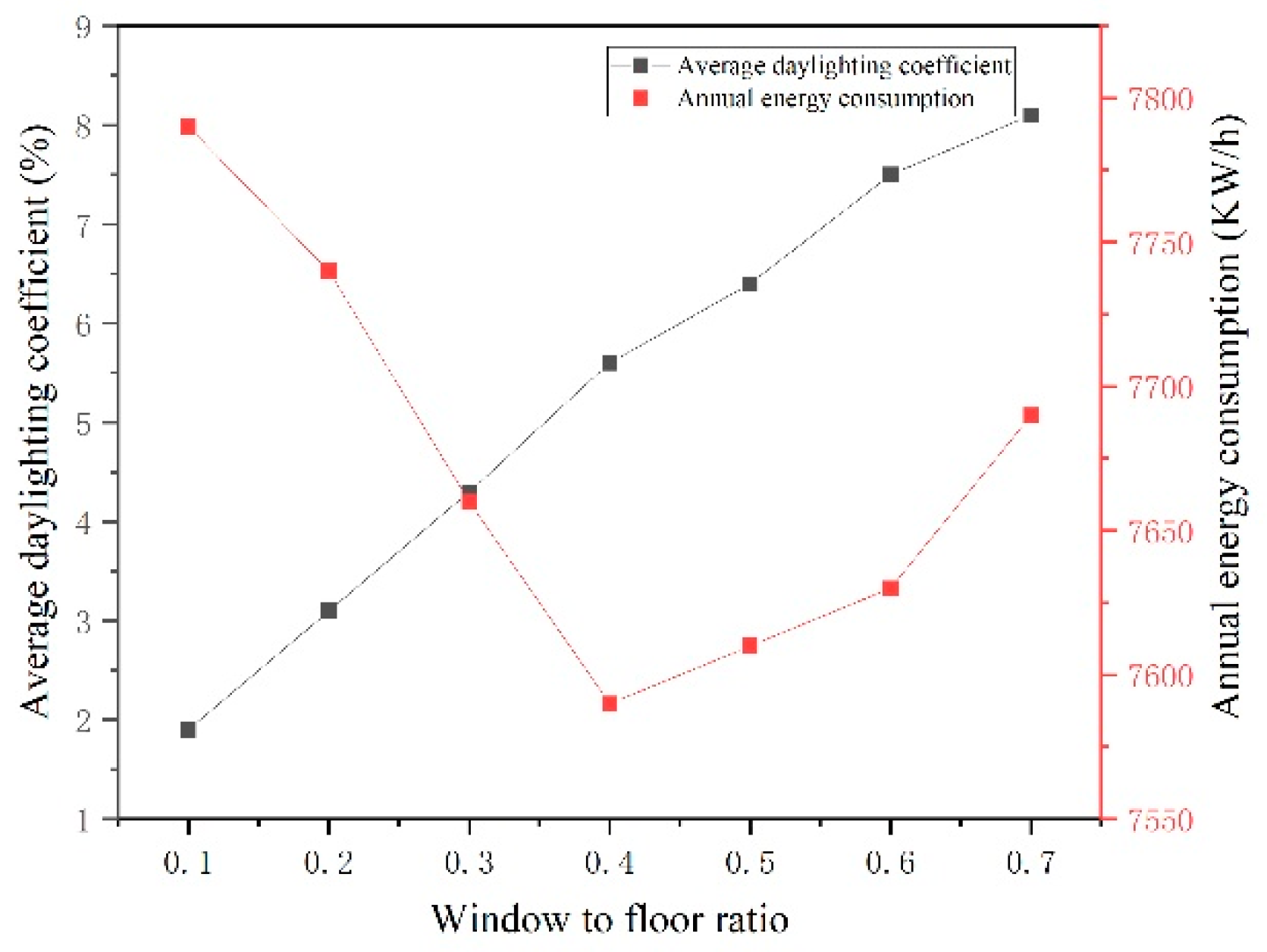
The obstacle level of indoor lighting environment is second only to indoor thermal environment. Taking Huoshiyan Village in Shuangliu District as an example, the obstacle level of indoor lighting environment in the village is 10.52%, with an average daylight factor of 1.8%. From the numerical simulation results in
Figure 17, it can be seen that when the window to ground ratio is 0.4, the annual energy consumption is the lowest and good lighting effects can be achieved. The indoor lighting environment evaluation score can be increased from 52.37 to 65.25. In addition to increasing the window area, setting up lighting wells and roofs can increase the average daylight factor to 2.9% and 2.6% respectively, and the indoor lighting environment evaluation score can be increased from 52.37 to 64.15.
(3) Strengthen the utilization of green resource
The biogas facility penetration rate and Green building material usage scores of Zhanqi Village in Pidu District are the highest, and Songjialin Village in the same area can learn from Zhanqi Village’s green ecological development model in terms of resource utilization. In terms of energy utilization structure, promote renewable energy facilities according to local conditions, comprehensively prohibit straw incineration in resource utilization, and promote the energy utilization of crop straw through methods such as biogas gasification, vaporization, and solidification [
30]; In the use of building materials, reducing the use of traditional clay building materials can replace traditional solid clay bricks with sintered porous bricks. By following the above path to optimize the energy structure and building material selection, the resource utilization dimension score of Songjialin Village can be increased from 40.79 to 68.14, and the total score of EBR can be increased from 60.07 to 68.88.
5. Conclusions
A greenness evaluation system for rural residential buildings was constructed based on three dimensions of environment, building, and energy consumption. The main indicators affecting EBR were analyzed, and spatial interpolation analysis was used to explore the spatial distribution pattern of rural building EBR. Based on the obstacle degree model, obstacle factors were identified and diagnosed, filling the gap in rural green building evaluation research in Southwest China and providing a foundation for the development of green buildings in similar regions. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) An innovative comprehensive evaluation system was constructed based on the composite perspective of EBR, and the weight ofthe impact factors were calculated by FANP. The results show that the system has a certain universality in rural settlements in southwest China, which will lay a foundation for the study of similar areas, and form a basic research framework and preliminary data support.
(2) The EBR greenness comprehensive scoring standards of each influence factor were established by means of questionnaire, field measurement and numerical simulation. In particular, the numerical simulation work based on BIM technology has been successfully adopted in the greenness scoring standard and case analysis, which provides new means to try and path exploration for the development of work in this direction.
(3) By innovative combination of obstacle degree model and spatial interpolation analysis, the key factors affecting the greening of rural buildings were diagnosed. It provides the basis for the leap from qualitative recognition to quantitative accurate evaluation, and realizes the further analysis of scientific problems, which has great social value.
Author Contributions
All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
Date Availability
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the project team members for their help. This study was funded by the Philosophy and Social Science Research Fund Project of Chengdu University of Technology (YJ2021-ZD002), Project of Western Ecological Civilization Research Center (XBST2021-YB002), Development Funding Program for Young and Middle-aged Key Teachers of Chengdu University of Technology(10912-JXGG2021-01003). These supports are greatly appreciated.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. 2022 Statistical Yearbook of Urban and Rural Construction(2022).
- Tongze H ,Ping L ,Changlin N , et al.Evaluation of energy-saving retrofit projects of existing rural residential envelope structures from the perspective of rural residents: the Chinese case. Environment, development and sustainability, 2022, 25(8): 21-28.
- Molake A ,Zhang R ,Zhou Y .Multi-Objective Optimization of Daylight Performance and Thermal Comfort of Enclosed-Courtyard Rural Residence in a Cold Climate Zone, China. Sustainability, 2023, 15(10): . [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong G ,Lanchi L ,Tao W , et al.Modelling interrelationships between barriers to adopting green building technologies in China’s rural housing via grey-DEMATEL. Technology in Society, 2022, 70.
- Li B ,You L ,Zheng M , et al.Energy consumption pattern and indoor thermal environment of residential building in rural China. Energy and Built Environment,2020,1(3):327-336.
- Jiebing W ,Kairui Y ,Lingling Q , et al.Gravity center change of carbon emissions in Chinese residential building sector: Differences between urban and rural area. Energy Reports, 2022, 810644-10656.
- Cao Z ,Meng Q ,Gao B .The consumption patterns and determining factors of rural household energy: A case study of Henan Province in China. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 146.
- Senhong C ,Zhonghua G .Are Green Spaces More Available and Accessible to Green Building Users? A Comparative Study in Texas. Land, 2023, 12(1): 226-226. [CrossRef]
- Ding Z ,Fan Z ,Tam W V , et al.Green building evaluation system implementation. Building and Environment, 2018, 13332-40.
- Wenxi Z ,Jing Z ,Da W , et al.Study on the Critical Factors Influencing High-Quality Development of Green Buildings for Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality Goals of China. Sustainability,2023,15(6): 5035-5035.
- Xiaolong G ,Kangkang Y ,Tao W .Using fuzzy cognitive maps to develop policy strategies for the development of green rural housing: A case study in China. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 2023, 192. [CrossRef]
- Xinyi H ,Yiming X ,Hong Z , et al.Active–passive combined energy-efficient retrofit of rural residence with non-benchmarked construction: A case study in Shandong province, China. Energy Reports, 2021, 71360-1373.
- Deng Q , Zhang S ,Shan M , et al.Research on Envelope Thermal Performance of Ultra-Low Energy Rural Residential Buildings in China. Sustainability,2023, 15(8):.
- Lyu Y , Chen Z .Seasonal thermal comfort and adaptive behaviours for the occupants of residential buildings: Shaoxing as a case study. Energy & Buildings, 2023, 292.
- Jinhao Z , Jun L ,Wu D , et al.Thermal comfort investigation of rural houses in China: A review. Building and Environment, 2023, 235.
- Bai X ,Guan J ,Jiang L , et al.Thermal performance study of straw concrete external walls for rural residences in hot-summer and cold-winter zone of China. Energy & Buildings, 2024, 311114140-.
- Jiawen H ,Tao Z ,Zu’an L , et al.A study on influencing factors of optimum insulation thickness of exterior walls for rural traditional dwellings in northeast of Sichuan hills, China.Case Studies in Construction Materials,2022,16.
- Yanru L ,Tai Z ,Ziming W , et al.Environment improvement and energy saving in Chinese rural housing based on the field study of thermal adaptability. Energy for Sustainable Development,2022,71315-329.
- Boban D ,Oskar F , Evelin K .Determinants of autonomous train operation adoption in rail freight: knowledge-based assessment with Delphi-ANP approach. Soft Computing, 2023,27(11): 7051-7069.
- Naijie C ,Wenliang Z ,Ziyu C , et al. Multi-attribute fire safety evaluation of subway stations based on FANP - FGRA - Cloud model. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2024, 144105526-.
- S. A A ,Osman T ,Bulent G , et al. A fuzzy ANP-based criticality analyses approach of reliability-centered maintenance for CNC lathe machine components. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 2024, 17(1):.
- Tirkolaee B E ,Mardani A ,Dashtian Z , et al. A novel hybrid method using fuzzy decision making and multi-objective programming for sustainable-reliable supplier selection in two-echelon supply chain design. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 250(C):119517-119517. [CrossRef]
- A.F.C. P ,J.M.M. S . Assisted site-dependent selection of the most suitable Airborne Wind Energy system via Fuzzy Analytic Network Process. Energy Reports, 2023, 92881-2899.
- Feyzi S , Khanmohammadi M , Abedinzadeh N , et al.Multi- criteria decision analysis FANP based on GIS for siting municipal solid waste incineration power plant in the north of Iran. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2019, 47101513-101513. [CrossRef]
- Environmental quality standards for surface water . State Environmental Protection Administration . Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese).
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55-2020: Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy. Atlanta: American Society of Heating Refrigerating and Air-conditioni ng Engineers,inc, 2020.
- Xiaorong H , Chaoyue C , Jianxiong T , et al. Analysis of coupling coordination and obstacle factors between tourism development and ecosystem services value: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 157. [CrossRef]
- Yi C ,Yuliang Z , Juliang J , et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics and obstacle factors identification of agricultural drought disaster risk: A case study across Anhui Province, China. Agricultural Water Management, 2023, 289.
- Lv Y , Li Y , Zhang Z , et al.Spatio-temporal evolution pattern and obstacle factors of water-energy-food nexus coupling coordination in the Yangtze river economic belt. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 444141229-.
- Liu X ,Liu J ,Liu Z .Developing a model of propagating the straw burning prohibition policy in Chinese rural communities and exploring its countermeasures. Energy Reports ,2024, 112556-2564.
Figure 1.
Research framework.
Figure 1.
Research framework.
Figure 2.
Network model for comprehensive evaluation of rural residential buildings.
Figure 2.
Network model for comprehensive evaluation of rural residential buildings.
Figure 3.
Numerical simulation process.
Figure 3.
Numerical simulation process.
Figure 4.
Location of the case selection area and survey sites.
Figure 4.
Location of the case selection area and survey sites.
Figure 5.
On site research and data measurement.
Figure 5.
On site research and data measurement.
Figure 6.
Understanding and using green building materials.
Figure 6.
Understanding and using green building materials.
Figure 7.
Annual energy consumption and proportion of roof, exterior wall and window.
Figure 7.
Annual energy consumption and proportion of roof, exterior wall and window.
Figure 8.
Photos of two rural residential buildings in Pidu district.
Figure 8.
Photos of two rural residential buildings in Pidu district.
Figure 9.
Comparison between subjective evaluation and objective evaluation.
Figure 9.
Comparison between subjective evaluation and objective evaluation.
Figure 10.
Overall score of the sample village.
Figure 10.
Overall score of the sample village.
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of criterion layer and Subcriteria layer.
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of criterion layer and Subcriteria layer.
Figure 12.
The elements of Linpan and the path of microclimate regulation.
Figure 12.
The elements of Linpan and the path of microclimate regulation.
Figure 13.
Statistical situation of two types of villages.
Figure 13.
Statistical situation of two types of villages.
Figure 14.
Comparison of Building Performance Index Layer Scores.
Figure 14.
Comparison of Building Performance Index Layer Scores.
Figure 15.
Obstacle analysis.
Figure 15.
Obstacle analysis.
Figure 16.
Residential structural renovation plan.
Figure 16.
Residential structural renovation plan.
Figure 17.
The relationship between indoor lighting environment parameters and energy consumption.
Figure 17.
The relationship between indoor lighting environment parameters and energy consumption.
Table 1.
Comprehensive evaluation index system of rural green residential buildings.
Table 1.
Comprehensive evaluation index system of rural green residential buildings.
| Criterion layer |
Subcriteria layer |
Indicator layer |
Indicator Description |
Global Weight |
| Environmental conditions (E) |
Outdoor environmental (E1) |
Village terrain (E11) |
The terrain where the village is located is plain, hilly, or mountainous |
0.007 |
| Village water environment level(E12) |
Water quality level of villages, ponds, rivers, and lakes |
0.039 |
| Village green coverage rate(E13) |
Forest and grass coverage by the water, houses, roads, and villages |
0.042 |
| Degree of rural farmland construction(E14) |
The degree of improvement in the construction of high standard farmland in villages |
0.015 |
| Convenience of village roads(E15) |
Village road hardening rate, road density and flatness |
0.011 |
Indoor environmental (E2)
|
Indoor thermal environment (E21) |
PMV (Predicted Mean Vote), APMV (adaptive predicted mean vote) [18], and thermal comfort |
0.093 |
| Indoor light environment (E22) |
Daylight factor and satisfaction with lighting environment |
0.063 |
| Indoor acoustic environment (E23) |
Noise level and satisfaction with acoustic environment |
0.082 |
| Indoor air quality (E24) |
Formaldehyde content and air quality satisfaction |
0.052 |
Building performance
(B) |
Building design (B1) |
Building orientation (B11) |
Influence of building orientation on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.052 |
| Building shape coefficient (B12) |
The influence of building shape coefficient on building energy consumption |
0.046 |
| Building Graphic Design (B13) |
Rationality of room space layout and its impact on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.012 |
| Building Style Design (B14) |
Satisfaction with the exterior and cultural heritage design of buildings |
0.024 |
| Building Construction (B2) |
Roof construction (B21) |
Influence of roof material, thickness and color on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.039 |
| Exterior wall construction (B22) |
Influence of material, thickness and color of exterior wall on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.030 |
| Window construction (B23) |
Influence of window frame material and window floor area ratio on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.040 |
| Affiliated parts (B24) |
Mainly consider the impact of building shading on indoor environment and building energy consumption |
0.035 |
| Resource utilization (R) |
Resource promotion (R1) |
Solar energy utilization (R11) |
The ownership and usage level of solar facilities (solar water heaters, photovoltaic panels, passive solar houses, etc.) |
0.033 |
| Popularity of biogas facilities (R12) |
The construction and usage level of biogas facilities (traditional biogas digesters, modern biogas treatment facilities, etc.) |
0.060 |
| Green building material usage (R13) |
Degree of use of green building materials in rural residential buildings |
0.060 |
Resource saving
(R2) |
Land resource utilization (R21) |
Per capita residential land level of rural households |
0.033 |
| water resources utilization (R22) |
Types of domestic water use and per capita water consumption level in rural households |
0.021 |
| Power consumption (R23) |
Per capita living electricity consumption level of rural households in the hottest or coldest month |
0.075 |
| Gas electricity consumption (R24) |
Per capita gas consumption level of rural households |
0.052 |
| Fuel wood usage frequency (R25) |
The frequency of using firewood for cooking per household in rural households |
0.048 |
Table 2.
Scoring rules for subjective indicators.
Table 2.
Scoring rules for subjective indicators.
| Indicator layer |
Evaluation criteria and score allocation |
| 100 |
80 |
60 |
40 |
20 |
| Degree of rural farmland construction(E14) |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Poor |
very poor |
| Convenience of village roads(E15) |
Very convenient |
Convenient |
Average |
Less convenient |
Inconvenient |
| Building Graphic Design (B13) |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Poor |
very poor |
| Building Style Design (B14) |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Poor |
very poor |
| Solar energy utilization (R11) |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Poor |
very poor |
| Popularity of biogas facilities (R12) |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Poor |
very poor |
| Green building material usage (R13) |
90% or more |
70% - 90% |
50% - 70% |
30% - 50% |
Less than 30% |
| Fuel wood usage frequency (R25) |
Not using firewood |
Low frequency of using firewood |
The frequency of using firewood is average |
Frequent use of firewood |
The frequency of using firewood is very high |
Table 3.
Scoring rules for objective indicators.
Table 3.
Scoring rules for objective indicators.
| Indicator layer (D) |
Evaluation criteria and score allocation |
| 100 |
80 |
60 |
40 |
20 |
| Village terrain (E11) |
Plain/Basin |
Small undulating mountains |
hills |
mountainous region |
plateau |
| Village water Environment level(E12) |
Class Ⅰ |
Class Ⅱ |
Class Ⅲ |
Class Ⅳ |
Class Ⅴ |
| Village green coverage rate(E13) |
X13=285.71Rg-11.43 Rg is the green coverage rate |
| Building orientation (B11) |
[85 °, 115 °),
[265 °, 285 °) |
[55 °, 85 °), [115 °, 135 °), [165 °, 175 °), [245 °, 265 °), [285 °,295 °) |
[135 °,165 °), [175 °,195 °), [225 °,245 °), [295 °,315 °), [355 °,25 °) |
[25 °,65 °), [195 °,225 °), [315 °,325 °), [345 °,355 °) |
[205 °,215 °), [325 °,345 °) |
| Building shape coefficient (B12) |
X12=-63.4S+98.34 S is the building shape coefficient |
| Roof construction (B21) |
Resin tile |
Color steel tile |
Asbestos tile /Flat roof |
Cement tile |
Grey tile |
| Exterior wall construction (B22) |
Sintered porous bricks |
Adobe wall |
Clay solid bricks and sintered porous bricks |
Sintered shale brick |
Clay solid bricks |
| Window construction (B23) |
X23=400Ac/Ad-24 Ac/Ad is the window to ground ratio |
| Affiliated parts (B24) |
(1.5,2] |
(1.2,1.5] |
(0.9.1.2] |
(0.6,0.9] |
(0,0.6] |
| Land resource utilization (R21) |
(20,30] |
(30,50] |
(50.70] |
(70,90] |
(90,∞] |
| water resources utilization (R22) |
Monthly per capita water consumption L < 2t
|
Monthly per capita water consumption 2t ≤ L < 5t
|
Monthly per capita water consumption 5 t ≤ L < 10 t
|
Monthly per capita water consumption L ≥ 10t
|
Mainly using well water, or only using well water without tap water |
| Power consumption (R23) |
Monthly per capita electricity consumption Q < 30KWh |
Monthly per capita electricity consumption 30KWh ≤ Q < 55KWh |
Monthly per capita electricity consumption 55 KWh ≤ Q < 75KWh |
Monthly per capita electricity consumption 75KWh ≤ Q < 95KWh |
Monthly per capita electricity consumption Q ≥ 95 KWh |
| Gas electricity consumption (R24) |
Monthly per capita gas consumption N < 2Nm3
|
Monthly per capita gas consumption 2 Nm3 ≤ N < 5.5Nm3
|
Monthly per capita gas consumption 5.5 Nm3 ≤ N < 9Nm3
|
Monthly per capita gas consumption 9 Nm3 ≤ N < 12.5Nm3
|
Monthly per capita gas consumption N ≥ 12.5Nm3
|
Table 4.
Scoring rules for Composite indicators.
Table 4.
Scoring rules for Composite indicators.
| Indicator layer (D) |
Evaluation criteria and score allocation (subjective/objective) |
| 100 |
80 |
60 |
40 |
20 |
| indoor thermal environment (E21) |
Comfortable /|PMV|≤0.5, |APMV|≤0.5 |
Slight comfortable /0.5<|PMV|≤1, 0.5<|APMV|≤1 |
Normal /1<|PMV|≤1.5, 1<|APMV|≤1.5 |
Slight uncomfortable / 1.5<|PMV|≤2, 1.5<|APMV|≤2 |
Uncomfortable |PMV|>2, |APMV|>2 |
| Indoor light environment (E22) |
Comfortable /Daylight Factor(C)>6% |
Slight comfortable / 4.8%<Daylight Factor(C) ≤6% |
Normal / 3.6%<Daylight Factor(C) |≤4.8% |
Slight uncomfortable / 2.4%<Daylight Factor(C) |≤3.6% |
Uncomfortable / 0<Daylight Factor(C) ≤2.4% |
| Indoor acoustic environment (E23) |
Satisfied/ LAeq (0,40dB] |
Slight satisfied /(40 dB,45 dB] |
Normal /(45 dB,55 dB] |
Slight unsatisfied /(55 dB,70 dB] |
Unsatisfied /(70 dB,∞] |
| Indoor air quality (E24) |
Satisfied / Formaldehyde concentration (0,0.02] |
Slight satisfied / Formaldehyde concentration (0.02,0.035] |
Normal / Formaldehyde concentration (0.035,0.05] |
Slight unsatisfied / Formaldehyde concentration (0.05,0.065] |
Unsatisfied / Formaldehyde concentration (0.065,0.08] |
Table 5.
Measuring instruments and measured parameters.
Table 5.
Measuring instruments and measured parameters.
| Indicator |
Instrument/ Model |
Parameters |
Accuracy |
Measurement method |
| Indoor thermal environment |
Comprehensive temperature thermal index meter/ AZ87783
|
Black globe temperature |
±0.6 ℃ |
The height of the measuring point is 0.6m (sitting posture) and 1.1m (standing posture) |
| Air temperature |
| Relative humidity |
±5 % |
| Air velocity meter/ ZTW1801B |
Air velocity |
±5 % |
The measuring point is located at the entrance of the room, with a testing height of 1.5 meters and the measuring instrument facing the incoming flow direction |
| Indoor light environment |
Illuminance meter/ UT383 |
Illumination |
±4 % |
The test height is 0.75 meters, and the measuring instrument is aligned with the direction of natural light incidence |
| Indoor acoustic environment |
Noise meter/ JD-105 |
Noise level |
0.1 dB |
The measuring point should be at least 1 meter away from the wall and windows, and 1.2-1.5 meters high from the ground (ear position), with doors and windows closed during measurement |
| Indoor air quality |
Air quality detector/ JD-3002 |
Formaldehyde concentration |
±5 % |
The measuring point is at the same height as the human breathing zone, with a relative height between 0.5 -1.5 meters |
| Building shape coefficient, Window construction, Affiliated parts |
Tape measure |
Length and width |
±1 mm |
/ |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).