1. Introduction
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) has emerged as a significant innovation, particularly in critical care, where it has a transformative impact [
1]. EIT, grounded in the principle of impedance sensing, exploits the distinct electrical properties of tissues to create dynamic images of internal physiology without the use of ionizing radiation.
The aim of this review is to explore the convergence of EIT, variable ventilation and Artificial Intelligence (AI), analyzing their future applications in critical care and the patient-tailored approach they allow.
2. The Basics of EIT
2.1. Impedance Sensing in EIT
At the core of EIT lies the measurement of electrical impedance,
, a complex number comprising resistance
and reactance
, represented by the equation
. This impedance reflects the opposition that tissues offer to electrical current flow, varying distinctly among different tissue types due to their unique cellular structures and electrolyte contents. The lungs, with their air-filled alveoli interspersed with vascular structures, exhibit an impedance distinctly different from that of muscular or osseous tissues [
2]. EIT capitalizes on this disparity by administering minute, non-hazardous electrical currents through electrodes placed around the thorax and measuring the resulting voltage changes to deduce the impedance map within the target area.
The sensitivity of EIT to the conductivity
and permittivity
of tissues enhances its imaging capability. Conductivity, the tissue’s ability to carry electric current, is described by the relationship
, where
is the current density and
is the electric field at a given location (
Figure 1). Permittivity represents how an electric field interacts with a dielectric medium and varies with the applied electric field’s frequency (
Figure 2). The unique conductive and permittive properties of biological tissues at different frequencies enable EIT to distinguish between various tissue types, states, and changes such as the presence of air or fluid in the lungs [
3].
2.2. EIT Image Reconstruction
The process of reconstructing images in EIT is a sophisticated endeavor that transforms measured voltage fluctuations into coherent images depicting the body’s conductivity distribution. This task is accomplished via intricate algorithms designed to address the inverse problem—deducing the internal conductivity from surface voltage readings. These algorithms navigate the complexities posed by the limited data available, attributable to the finite count of electrodes and the intricate three-dimensional structure of human anatomy. A range of reconstruction methodologies exists, spanning from linear methods known for their computational efficiency—albeit with potential compromises in accuracy—to iterative algorithms that enhance the precision of reconstructions through progressive refinements. Notable techniques, including the Sheffield back-projection algorithm, Newton-Raphson iterative methods, the Graz Reconstruction Algorithm, along with contemporary enhancements in optimization through particle swarm and deep learning approaches, encapsulate the broad array of strategies utilized in EIT image reconstruction. (
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5) [
4,
5,
6].
These algorithms work in tandem with the hardware components of EIT systems, including current injectors, voltage sensors, multiplexers and data acquisition systems, to produce images that can be interpreted by clinicians. This process enables the visualization of dynamic physiological events such as pulmonary ventilation and perfusion, providing valuable real-time feedback for respiratory care management [
4,
7].
The Newton-Raphson method in EIT is used to update the conductivity estimate iteratively by minimizing the difference between the measured boundary voltages and the boundary voltages predicted by a forward model based on the current conductivity estimate [
8]. Graphical representation of this process involves:
Forward Model: compute the predicted boundary voltages from an initial guess of the conductivity distribution.
Jacobian Matrix: calculate the sensitivity of the boundary voltages to changes in conductivity, known as the Jacobian or sensitivity matrix.
Mismatch: determine the mismatch between the predicted and measured voltages.
Update: use the Newton-Raphson method to update the conductivity distribution based on the mismatch and the Jacobian matrix [
9].
The integration of contrast agents into EIT markedly enhances its ability to visualize and quantify pulmonary perfusion, thereby augmenting the modality’s diagnostic capabilities. Introducing a contrast agent, such as hypertonic saline, with electrical impedance properties distinct from blood, temporarily alters the electrical characteristics within the pulmonary vasculature. EIT’s sensitivity to these changes facilitates the mapping of lung blood flow patterns, offering a novel approach to assessing pulmonary perfusion.
This advancement is complemented by innovative dynamic filtering techniques, including principal component analysis and frequency domain filtering, which effectively segregate cardiac influences from pulmonary signals in EIT data. This real-time separation, achieved without the need for breath holding or ECG gating, is pivotal for the precise visualization of perfusion patterns, distinguishing blood flow signals from those related to ventilation. Employing a first-pass kinetics approach, where a bolus of hypertonic saline serves as the contrast medium during a brief respiratory pause, enhances EIT’s utility in lung perfusion assessment. The passage of this bolus through the pulmonary vasculature, given its higher conductivity relative to blood, generates a discernible signal within the EIT data. This facilitates a direct evaluation of perfusion anomalies and regional blood flow analysis, thereby improving the accuracy of perfusion imaging. These methodologies, whether utilizing ECG gating or principal component analysis-based algorithms, refine EIT data to mitigate the impact of heart-related impedance changes on the interpretation of perfusion metrics.
The adoption of EIT with contrast agents signifies a leap toward non-invasive, bedside monitoring of lung perfusion, offering insights into the ventilation-perfusion ratio. This ratio is crucial for diagnosing conditions like pulmonary embolism or edema and for assessing the efficacy of treatments, such as mechanical ventilation. Advancements in EIT technology and methods, as developed by Frerichs and colleagues, promise more detailed and ongoing analysis of lung function in clinical environments, underscoring the potential of EIT in revolutionizing pulmonary diagnostics and care [
10,
11].
3. EIT and ARDS: Unveiling Pulmonary Inhomogeneities
EIT represents a transformative advancement in the management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), a condition characterized by acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema [
12]. The complexity of ARDS, with its diverse lung injury patterns, necessitates precise, real-time imaging to guide therapeutic decisions and interventions [
13,
14].
Here’s a more detailed examination of how EIT is enhancing ARDS management across several crucial dimensions:
Detection of Regional Lung Function: EIT proves indispensable for identifying specific lung areas affected by over-distension and recruitment. By providing a clear image of these regions, EIT enables clinicians to tailor ventilatory support accurately, addressing the heterogeneity of lung damage that typifies ARDS. This capability is critical as it helps in avoiding the application of uniform ventilatory pressures across varied lung conditions, thus optimizing individual patient care [
10].
Monitoring Therapeutic Interventions: the effectiveness of ARDS treatments, such as Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) and prone positioning, significantly depends on the timely and accurate assessment of their impact on lung mechanics. EIT offers a direct view of how these interventions affect lung ventilation and perfusion in real-time. For instance, research by Songsangvorn et al. has demonstrated that EIT-guided PEEP titration not only enhances lung compliance, but also reduces the mechanical power and driving pressures required, thereby potentially decreasing the incidence of ventilator-induced lung injuries (VILI) and improving overall respiratory mechanics [
14,
15].
Optimizing Mechanical Ventilation: EIT’s ability to provide immediate feedback on lung mechanics is crucial for the fine-tuning of mechanical ventilation settings. This feedback helps clinicians balance the need for adequate oxygenation with the risk of exacerbating lung injury, thus significantly impacting patient prognosis. By adjusting ventilation parameters in response to real-time data, EIT helps mitigate the risk of VILI, a common complication in ARDS treatment [
16].
Guiding Recruitment Maneuvers: Recruitment maneuvers are useful for managing ARDS as they help open up collapsed alveoli, potentially improving oxygenation and reducing the overall risk of barotrauma. EIT’s instant feedback during these maneuvers guides clinicians in adjusting their techniques to achieve optimal results without overdistending the lungs, thereby refining the management strategy for ARDS [
17].
Integrating Concepts of Patient Self-Inflicted Lung Injury (P-SILI) and the Macklin Effect: EIT is instrumental in monitoring the risk factors associated with P-SILI, where patients’ spontaneous efforts can exacerbate lung injury, and the Macklin Effect, which involves air leakage along bronchovascular sheaths following alveolar rupture. This monitoring is critical for spontaneously breathing ARDS patients, where elevated intrathoracic pressures can lead to significant complications. EIT’s capability to detect early signs of these phenomena allows for prompt and effective interventions, preserving lung integrity and optimizing outcomes [
18].
The incorporation of EIT within the schema of ARDS management heralds a paradigmatic shift towards a more individualized, data-driven ethos of care. This integration not only fosters a more profound comprehension of the pathophysiology underpinning ARDS but also augments the avenue for personalized therapeutic stratagems. The confluence of EIT’s real-time visualization and the data-driven insights it engenders marks a new era in the quest for a more refined and effective management of ARDS. Through the lens of EIT, the veil shrouding pulmonary inhomogeneities in ARDS is gradually lifted, thus offering a clearer sight for tailored therapeutic interventions (
Figure 6).
4. Synergy with Variable Ventilation
4.1. Physiology of Respiratory Variability
Variable ventilation mimics the natural variability of human breathing, which is evident in the healthy lung’s response to different physiological states. This variability is characterized by changes in tidal volume and respiratory rate, enhancing respiratory system efficiency and adaptability. In pathophysiological states, such as ARDS or COPD, this inherent variability is significantly reduced, often leading to compromised lung function. The physiological rationale for introducing variability in mechanical ventilation is based on the premise that it can restore some of the natural dynamics of the respiratory system, potentially leading to improved lung recruitment and gas exchange [
15,
19,
20].
4.2. Technique of Mechanical Ventilation
Variable mechanical ventilation (VMV) employs alternating levels of tidal volumes and respiratory rates, unlike conventional mechanical ventilation which delivers set, uniform breaths. VMV aims to replicate the natural variability seen in spontaneous breathing, which may involve using patterns that distribute tidal volumes based on a Gaussian or power-law distribution. This approach is hypothesized to improve alveolar recruitment, reduce cyclic atelectasis, and minimize ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) by preventing the overdistension and repetitive opening and closing of alveolar units [
19,
20].
4.3. Potential Role of EIT in Guiding Variable Ventilation
EIT, a non-invasive monitoring technique, can significantly enhance the application of VMV by providing real-time images of regional lung ventilation. By visualizing how air distributes across the lung, EIT can help clinicians optimize ventilator settings to ensure more uniform lung aeration and reduce the risk of VILI. EIT’s ability to assess regional lung function dynamically makes it an invaluable tool in adjusting variable ventilation protocols to individual patient needs, thus enhancing the personalized approach in mechanical ventilation. In clinical practice, integrating EIT with variable ventilation could potentially transform patient outcomes in critical care by enabling a more precise management of ventilatory support, particularly in patients with heterogeneous lung diseases. The synergy between EIT and variable ventilation could lead to improved strategies in managing ARDS, where lung protection and optimization of gas exchange are crucial [
19,
21].
The integration of EIT into the management of variable ventilation represents a significant advancement in the personalized care of patients requiring mechanical ventilation. By leveraging the detailed, real-time data provided by EIT, clinicians can not only tailor ventilation more closely to the physiological needs of the patient but also potentially improve outcomes by minimizing lung injury and enhancing overall lung function [
22].
5. Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is continuously advancing, leading to an increasing number of applications in medical imaging and diagnostics. This chapter delves into the profound impact AI has on enhancing EIT, exploring the sophisticated techniques and innovative approaches that are shaping the future of this technology.
5.1. Advanced Neural Network Applications in EIT
Deep learning techniques have been pivotal in significantly improving the quality and resolution of EIT image reconstruction. Researchers have explored various methods to enhance EIT imaging. One such method is single network reconstruction, where individual neural networks are utilized to directly reconstruct images from EIT data. These networks are capable of learning complex relationships between electrical measurements and internal conductivity distributions, thereby producing high-resolution images that are crucial for accurate diagnostics [
23,
24,
25,
26].
Another approach involves the integration of these neural networks with traditional algorithmic EIT reconstruction techniques. By combining deep learning models with established EIT algorithms, researchers have developed synergistic methods that leverage the strengths of both approaches. This integration results in more robust and accurate image reconstructions, enhancing the clinical utility of EIT.
Furthermore, hybrid systems that combine multiple neural networks have been developed to tackle the challenges of EIT imaging. These systems enhance image quality by optimizing various aspects of the reconstruction process, such as measurement techniques and electrode placements. This holistic approach ensures that EIT can be effectively used for real-time monitoring and diagnostics, offering a significant improvement over traditional methods [
23,
24,
25,
26].
5.2. Challenges and Innovations
Despite these advances, the field faces several challenges. One of the primary issues is the need for large, high-quality datasets to effectively train AI models. Collecting and annotating such datasets is both resource-intensive and time-consuming. Additionally, integrating AI with existing medical technologies poses technical challenges related to data compatibility, processing speeds, and hardware limitations.
To address these challenges, researchers have turned to innovative solutions such as generative models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), for example, have been utilized to create synthetic data. This approach allows for the generation of extensive datasets that can be used to train AI models, thereby enhancing the predictive power of EIT without the constraints posed by small or inconsistent datasets [
26,
27,
28]. By generating realistic bioimpedance data, GANs facilitate the development of more accurate and reliable EIT models, ensuring that the technology can be effectively used in clinical settings.
Moreover, reinforcement learning algorithms have shown promise in clinical decision support systems. These algorithms can dynamically adjust EIT settings based on real-time patient data, optimizing the balance between image quality and patient safety. This adaptive capability is crucial for personalized medicine, where treatment protocols need to be tailored to the individual needs of each patient [
29].
5.3. Comparative Analysis and Mesh Optimization
Significant efforts have been made to optimize neural network training using refined and coarse mesh configurations. This optimization aims to reduce discretization errors, which are common in EIT image reconstruction. By training neural networks with inputs from a refined mesh and outputs defined by a coarser mesh, researchers have achieved a balance between computational efficiency and image fidelity.
Bianchessi et al. have conducted extensive comparative analyses of various neural network architectures, such as the LeNet model and fully connected feed-forward networks, to determine their efficacy in different EIT applications. Their findings indicate that certain configurations perform better under specific conditions, which is critical for tailoring AI strategies to meet the unique demands of EIT. These analyses are instrumental in identifying the most effective AI strategies for enhancing EIT applications, providing a roadmap for future research and development [
30].
5.4. Digital Twins in Medical Imaging
The concept of digital twins represents a groundbreaking advancement in the integration of AI with EIT. Digital twins (DTs) create virtual replicas of patients’ lungs, incorporating both biomechanical and electrical properties to simulate and predict physiological responses under various scenarios. As explored by Jiang et al., this technology, when combined with EIT, offers a dynamic and precise method for lung monitoring [
31]. Digital twins can provide real-time, patient-specific data that enhance the accuracy of diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, paving the way for truly personalized medicine. DTs further augment the capabilities of EIT by creating accurate virtual models of patients’ lungs. These models can simulate various physiological conditions, providing dynamic, real-time data that allows for personalized treatment plans [
32]. The integration of DTs with EIT facilitates a deeper understanding of lung pathophysiology, enabling clinicians to anticipate and react to changes in patients’ conditions more effectively.
In conclusion, the integration of AI with EIT, spearheaded by studies from Hou et al., Zhang et al., Chen et al., and Bianchessi et al., represents a significant advancement in medical imaging. This robust framework not only improves the resolution and accuracy of EIT imaging, but also extends its applications to predictive diagnostics and personalized medicine. The ongoing innovations in AI are set to offer more effective, tailored patient care, heralding a new era of medical technology integration [
33,
34,
35].
The collective efforts of these researchers are setting the stage for EIT to become a more powerful tool in medical imaging. By providing clinicians with faster, more accurate, and adaptively responsive imaging solutions, AI-enhanced EIT promises to revolutionize how respiratory conditions and other medical issues are diagnosed and monitored. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly lead to significant improvements in patient outcomes and the overall quality of healthcare [
23,
24,
25,
29,
30,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43]. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration will be crucial in advancing the integration of AI, EIT, and DTs technologies, fostering innovation that can transform critical care.
6. Conclusion - Revolutionizing the Art of Critical Care
EIT represents a pivotal innovation in critical care, offering a non-invasive, radiation-free modality for dynamic imaging of internal physiology. This review elucidates the foundational principles of EIT, emphasizing its reliance on impedance sensing to distinguish tissue types based on their electrical properties. The integration of EIT with variable ventilation and AI underscores a transformative shift towards predictive and personalized healthcare.
EIT’s utility in managing ARDS is profound, providing real-time insights into regional lung function, guiding therapeutic interventions, and optimizing mechanical ventilation. The technology’s capability to reveal pulmonary inhomogeneities in ARDS enhances individualized care strategies, facilitating precise adjustments to ventilation settings and improving patient outcomes.
Variable ventilation, mirroring natural respiratory variability, synergizes with EIT to refine ventilatory support, minimize VILI, and enhance gas exchange. EIT’s real-time imaging facilitates the dynamic adjustment of ventilation protocols, ensuring tailored treatment for heterogeneous lung conditions.
AI integration significantly advances EIT by enhancing image reconstruction quality through deep learning techniques, optimizing neural network configurations, and leveraging generative models for data augmentation. The development of DTs further augments EIT, offering virtual patient replicas that simulate physiological responses, thereby refining diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
In conclusion, the amalgamation of EIT, variable ventilation, and AI heralds a new era in critical care, characterized by predictive, personalized, and proactive patient management. These advancements not only enhance diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy but also pave the way for innovative research and interdisciplinary collaborations, setting the stage for a nuanced and compassionate healthcare future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C and I.C.; methodology, I.C.; software, I.C.; validation, G.C., I.C..; formal analysis, I.C.; investigation, I.C.; resources, G.C.; data curation, I.C.; writing—original draft preparation, I.C.; writing—review and editing, G.C. and L. C.; visualization, G.C.; supervision, G.C. project administration, G.C.; funding acquisition, I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable
Acknowledgments
not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maciejewski, D.; Putowski, Z.; Czok, M.; Krzych, Ł.J. Electrical Impedance Tomography as a Tool for Monitoring Mechanical Ventilation. An Introduction to the Technique. Adv. Med. Sci. 2021, 66, 388–395. [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.H.; Barber, D.C.; Seagar, A.D. Applied Potential Tomography: Possible Clinical Applications. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. Off. J. Hosp. Phys. Assoc. Dtsch. Ges. Med. Phys. Eur. Fed. Organ. Med. Phys. 1985, 6, 109–121. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M. Electrodynamics from Ampère to Einstein. Phys. Today 2002, 55, 53. [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. An Image Reconstruction Algorithm for Electrical Capacitance Tomography Based on Robust Principle Component Analysis. Sensors 2013, 13, 2076–2092. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, MarcosH.F.; Dos Santos, R.W.; Barra, L.PauloS.; Peters, FrancianeC. Simulation Study on the Determination of Cardiac Ejection Fraction by Electrical Impedance Tomography Using a Hybrid Heuristic Approach. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2014, 4, 113–121. [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K.; Nagaraju, J. Studies on Thin Film Based Flexible Gold Electrode Arrays for Resistivity Imaging in Electrical Impedance Tomography. Measurement 2014, 47, 264–286. [CrossRef]
- Lionheart, W.R.B. EIT Reconstruction Algorithms: Pitfalls, Challenges and Recent Developments. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 125–142. [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Huo, X. Modified Newton Raphson Algorithm for Electrical Impedance Image Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Advances in Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery; Xie, Q., Zhao, L., Li, K., Yadav, A., Wang, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 927–934.
- Tan, R.H.; Rossa, C. Electrical Impedance Tomography Using Differential Evolution Integrated with a Modified Newton Raphson Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC); October 2020; pp. 2528–2534.
- Frerichs, I.; Amato, M.B.P.; van Kaam, A.H.; Tingay, D.G.; Zhao, Z.; Grychtol, B.; Bodenstein, M.; Gagnon, H.; Böhm, S.H.; Teschner, E.; et al. Chest Electrical Impedance Tomography Examination, Data Analysis, Terminology, Clinical Use and Recommendations: Consensus Statement of the TRanslational EIT developmeNt stuDy Group. Thorax 2017, 72, 83–93. [CrossRef]
- Deibele, J.M.; Luepschen, H.; Leonhardt, S. Dynamic Separation of Pulmonary and Cardiac Changes in Electrical Impedance Tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, S1-14. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.T.; Chambers, R.C.; Liu, K.D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1904–1905. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Möller, K.; Steinmann, D.; Frerichs, I.; Guttmann, J. Evaluation of an Electrical Impedance Tomography-Based Global Inhomogeneity Index for Pulmonary Ventilation Distribution. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1900–1906. [CrossRef]
- Songsangvorn, N.; Xu, Y.; Lu, C.; Rotstein, O.; Brochard, L.; Slutsky, A.S.; Burns, K.E.A.; Zhang, H. Electrical Impedance Tomography-Guided Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Titration in ARDS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 617–631. [CrossRef]
- Blankman, P.; Hasan, D.; van Mourik, M.S.; Gommers, D. Ventilation Distribution Measured with EIT at Varying Levels of Pressure Support and Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist in Patients with ALI. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1057–1062. [CrossRef]
- Mauri, T.; Eronia, N.; Abbruzzese, C.; Marcolin, R.; Coppadoro, A.; Spadaro, S.; Patroniti, N.; Bellani, G.; Pesenti, A. Effects of Sigh on Regional Lung Strain and Ventilation Heterogeneity in Acute Respiratory Failure Patients Undergoing Assisted Mechanical Ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1823–1831. [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.L.V.; Borges, J.B.; Melo, A.; Suarez-Sipmann, F.; Toufen, C.; Bohm, S.H.; Amato, M.B.P. Bedside Estimation of Recruitable Alveolar Collapse and Hyperdistension by Electrical Impedance Tomography. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1132–1137. [CrossRef]
- Pulletz, S.; Krukewitt, L.; Gonzales-Rios, P.; Teschendorf, P.; Kremeier, P.; Waldmann, A.; Zitzmann, A.; Müller-Graf, F.; Acosta, C.; Tusman, G.; et al. Dynamic Relative Regional Strain Visualized by Electrical Impedance Tomography in Patients Suffering from COVID-19. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2022, 36, 975–985. [CrossRef]
- Huhle, R.; Pelosi, P.; de Abreu, M.G. Variable Ventilation from Bench to Bedside. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2016, 20, 62. [CrossRef]
- Spieth, P.M.; Carvalho, A.R.; Güldner, A.; Pelosi, P.; Kirichuk, O.; Koch, T.; de Abreu, M.G. Effects of Different Levels of Pressure Support Variability in Experimental Lung Injury. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 342–350. [CrossRef]
- Fontela, P.C.; Prestes, R.B.; Forgiarini, L.A.; Friedman, G. Variable mechanical ventilation. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiva 2017, 29, 77–86. [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.J.; Mador, M.J.; Guenther, S.M.; Lodato, R.F.; Sackner, M.A. Variability of Resting Respiratory Drive and Timing in Healthy Subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. Bethesda Md 1985 1988, 65, 309–317. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Zhu, C.; Pan, H.; Jia, J.; Wu, H.; Yao, J. Shape Reconstruction With Multiphase Conductivity for Electrical Impedance Tomography Using Improved Convolutional Neural Network Method. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 9277–9287. [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Guan, R.; Liang, G.; Dong, F. RCRC: A Deep Neural Network for Dynamic Image Reconstruction of Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Sun, K.; Tan, C.; Dong, F. A Two-Stage Deep Learning Method for Robust Shape Reconstruction With Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 4887–4897. [CrossRef]
- Guttulsrud, H. Generating Synthetic Medical Images with 3D GANs. Master thesis, Oslomet - storbyuniversitetet, 2023.
- Chen, X.; Roberts, R.; Liu, Z.; Tong, W. A Generative Adversarial Network Model Alternative to Animal Studies for Clinical Pathology Assessment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7141. [CrossRef]
- Mensing, D.; Hirsch, J.; Wenzel, M.; Günther, M. 3D (c)GAN for Whole Body MR Synthesis. In Proceedings of the Deep Generative Models; Mukhopadhyay, A., Oksuz, I., Engelhardt, S., Zhu, D., Yuan, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2022; pp. 97–105.
- Boyko, E.J. Ruling out or Ruling in Disease with the Most Sensitive or Specific Diagnostic Test: Short Cut or Wrong Turn? Med. Decis. Mak. Int. J. Soc. Med. Decis. Mak. 1994, 14, 175–179. [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R.S.; Filho, F.A.N.; Tsuzuki, M.; Martins, T.; Lima, R. Discretization Error and the EIT Forward Problem. IFAC Proc. Vol. IFAC-Pap. 2014, 19, 7535–7540.
- Zhu, L.; Lu, W.; Soleimani, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Electrical Impedance Tomography Guided by Digital Twins and Deep Learning for Lung Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, D.; Zhang, M.; Qiu Lin, J.; Chen, W.; Giorgio-Serchi, F.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. A Digital Twin of Electrical Tomography for Quantitative Multiphase Flow Imaging. Commun. Eng. 2022, 1, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tian, X.; Liu, X.; Ye, J.; Fu, F.; Shi, X.; Liu, R.; Xu, C. Advances of Deep Learning in Electrical Impedance Tomography Image Reconstruction. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1019531. [CrossRef]
- Bianchessi, A.; Akamine, R.H.; Duran, G.C.; Tanabi, N.; Sato, A.K.; Martins, T.C.; Tsuzuki, M.S.G. Electrical Impedance Tomography Image Reconstruction Based on Neural Networks. IFAC-Pap. 2020, 53, 15946–15951. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Abiri, P.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Yin, J.; Jabalera, A.M.; Arianpour, B.; Roustaei, M.; Zhu, E.; et al. Machine Learning-Directed Electrical Impedance Tomography to Predict Metabolically Vulnerable Plaques. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2024, 9, e10616. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Shan, Q.; Smyl, D.; Deng, J.; Du, J. DeepEIT: Deep Image Prior Enabled Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 9627–9638. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Han, Y. Electrical Resistance Tomography with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 055401. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ai, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Mask-Guided Spatial–Temporal Graph Neural Network for Multifrequency Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Moeyersons, J.; Morales, J.; Seeuws, N.; Van Hoof, C.; Hermeling, E.; Groenendaal, W.; Willems, R.; Van Huffel, S.; Varon, C. Artefact Detection in Impedance Pneumography Signals: A Machine Learning Approach. Sensors 2021, 21, 2613. [CrossRef]
- Smyl, D.; Liu, D. Optimizing Electrode Positions in 2-D Electrical Impedance Tomography Using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6030–6044. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Marple, K.; Salazar, E.; Gupta, G.; Tamil, L. A Physician Advisory System for Chronic Heart Failure Management Based on Knowledge Patterns. Theory Pract. Log. Program. 2016, 16, 604–618. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xiang, J.; Bagnaninchi, P.-O.; Yang, Y. MMV-Net: A Multiple Measurement Vector Network for Multifrequency Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 8938–8949. [CrossRef]
- Ball, L.; Vercesi, V.; Costantino, F.; Chandrapatham, K.; Pelosi, P. Lung Imaging: How to Get Better Look inside the Lung. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 294. [CrossRef]
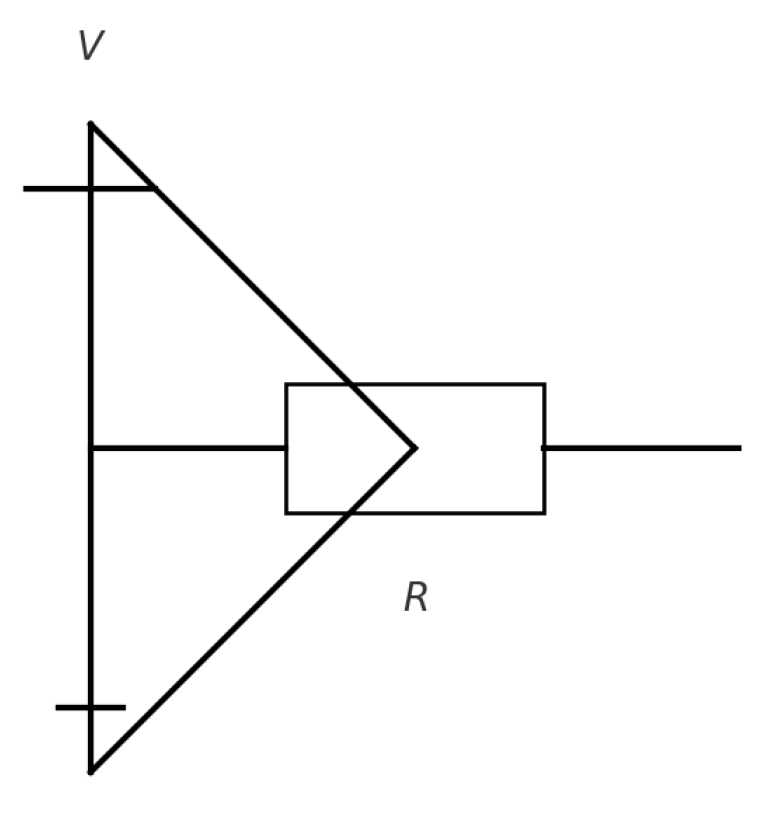
Figure 1.
A conductivity circuit comprising a voltage source, represented as , and a resistor, denoted as . Here, the resistor represents the material’s resistance to electrical current flow. Conductivity, symbolized as , measures the facility with which an electric current can navigate through a material. Analogous to circuitry, this concept is depicted through a simple resistor, encapsulating the principle that higher conductivity equates to lower resistance. The mathematical relation linking conductivity and resistivity, represented as , is given by . This relationship elucidates that materials characterized by high conductivity present low resistance, thereby facilitating the easier passage of electric current. Conversely, materials with low conductivity demonstrate higher resistance, thus hindering electrical flow.
Figure 1.
A conductivity circuit comprising a voltage source, represented as , and a resistor, denoted as . Here, the resistor represents the material’s resistance to electrical current flow. Conductivity, symbolized as , measures the facility with which an electric current can navigate through a material. Analogous to circuitry, this concept is depicted through a simple resistor, encapsulating the principle that higher conductivity equates to lower resistance. The mathematical relation linking conductivity and resistivity, represented as , is given by . This relationship elucidates that materials characterized by high conductivity present low resistance, thereby facilitating the easier passage of electric current. Conversely, materials with low conductivity demonstrate higher resistance, thus hindering electrical flow.
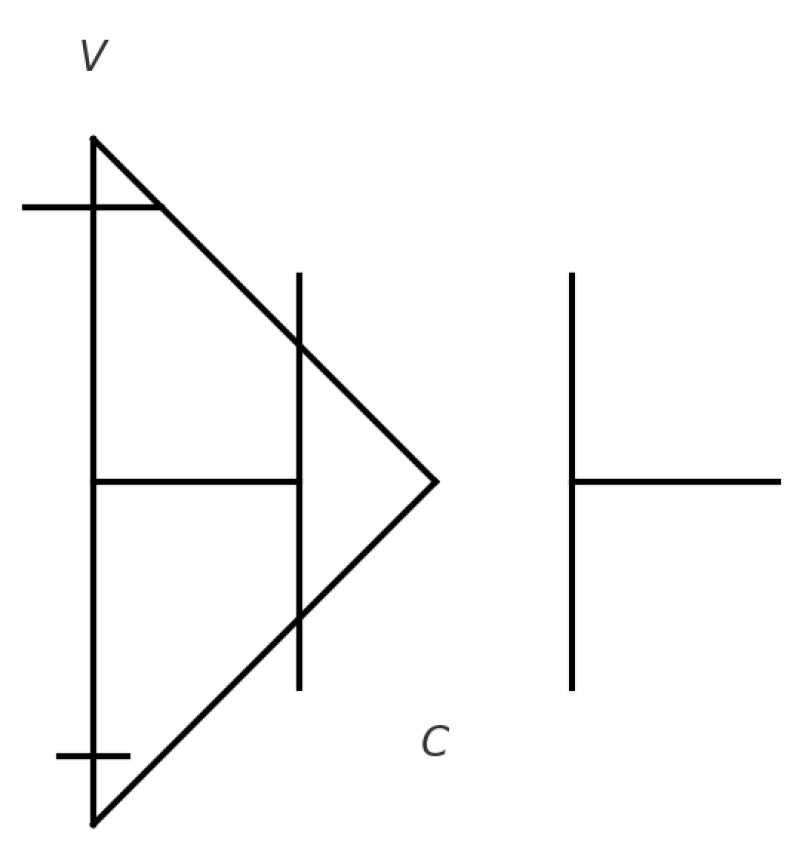
Figure 2.
A permittivity circuit with a voltage source and a capacitor . The capacitor represents a material’s ability to store electrical energy as an electric field, directly related to its permittivity, . Permittivity measures a material’s capacity to support an electric field. In circuits, capacitors illustrate this trait, with materials of higher permittivity able to store more electric charge, leading to greater capacitance. The relationship between permittivity and a parallel-plate capacitor’s capacitance is given by , where is the plate area and is the plate separation. This formula shows how capacitance increases with the capacitor’s size and its permittivity.
Figure 2.
A permittivity circuit with a voltage source and a capacitor . The capacitor represents a material’s ability to store electrical energy as an electric field, directly related to its permittivity, . Permittivity measures a material’s capacity to support an electric field. In circuits, capacitors illustrate this trait, with materials of higher permittivity able to store more electric charge, leading to greater capacitance. The relationship between permittivity and a parallel-plate capacitor’s capacitance is given by , where is the plate area and is the plate separation. This formula shows how capacitance increases with the capacitor’s size and its permittivity.
Figure 3.
This figure illustrates the Sheffield back projection algorithm for EIT, a pioneering method developed at the University of Sheffield for EIT image reconstruction. It simplifies the process by representing the object’s cross-sectional boundary as a circle, with blue circles indicating electrodes around this boundary. A grey wedge shows the sensitivity map, highlighting regions most affected by voltage changes due to current injection. This algorithm, though less precise than contemporary iterative methods, offers a straightforward and quick solution for real-time imaging, making it invaluable for educational purposes and initial analysis. It operates by placing electrodes around the subject, applying alternating current, measuring voltage differences and then using these measurements to generate an image through back projection and filtering to counteract blurring. Despite its simplicity, modern techniques offering higher resolution and accuracy through advanced modeling have largely superseded it, yet its educational value and historical significance remain.
Figure 3.
This figure illustrates the Sheffield back projection algorithm for EIT, a pioneering method developed at the University of Sheffield for EIT image reconstruction. It simplifies the process by representing the object’s cross-sectional boundary as a circle, with blue circles indicating electrodes around this boundary. A grey wedge shows the sensitivity map, highlighting regions most affected by voltage changes due to current injection. This algorithm, though less precise than contemporary iterative methods, offers a straightforward and quick solution for real-time imaging, making it invaluable for educational purposes and initial analysis. It operates by placing electrodes around the subject, applying alternating current, measuring voltage differences and then using these measurements to generate an image through back projection and filtering to counteract blurring. Despite its simplicity, modern techniques offering higher resolution and accuracy through advanced modeling have largely superseded it, yet its educational value and historical significance remain.
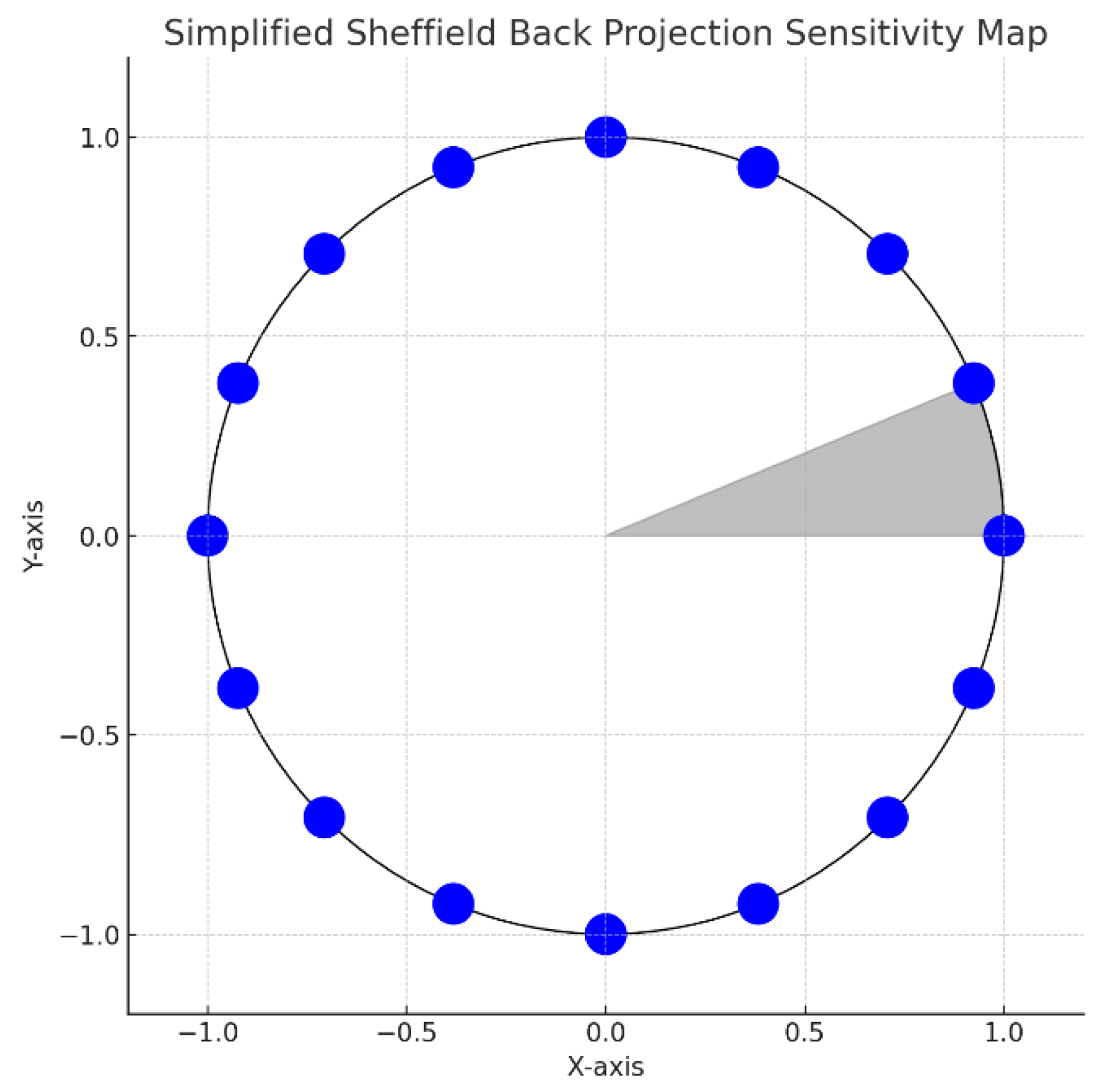
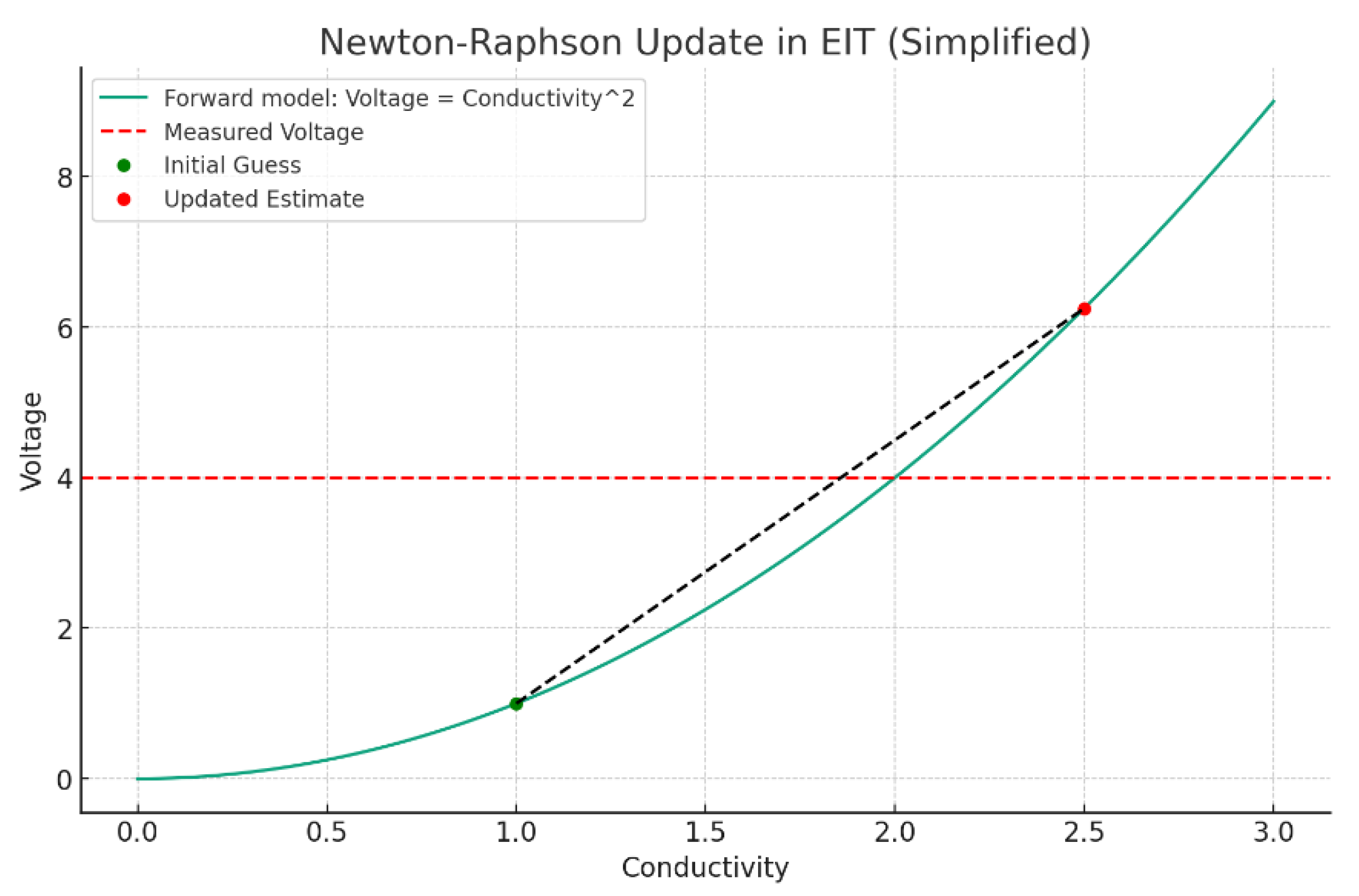
Figure 4.
This figure demonstrates the Newton-Raphson method in EIT through a simplified one-dimensional example. It illustrates the method’s iterative process of updating an initial conductivity estimate towards a more accurate value. Key elements include a forward model curve predicting voltage from conductivity, a measured voltage line indicating true conductivity, and markers for the initial and updated estimates. The black dashed line traces the update path from the initial guess to a closer approximation of true conductivity, highlighting the method’s effectiveness in reducing discrepancies between predicted and measured voltages for refining EIT conductivity images.
Figure 4.
This figure demonstrates the Newton-Raphson method in EIT through a simplified one-dimensional example. It illustrates the method’s iterative process of updating an initial conductivity estimate towards a more accurate value. Key elements include a forward model curve predicting voltage from conductivity, a measured voltage line indicating true conductivity, and markers for the initial and updated estimates. The black dashed line traces the update path from the initial guess to a closer approximation of true conductivity, highlighting the method’s effectiveness in reducing discrepancies between predicted and measured voltages for refining EIT conductivity images.
Figure 5.
The images illustrate a simplified approach to EIT reconstruction using the Graz Reconstruction Algorithm. Initially, a finite element method (FEM) mesh, assuming uniform conductivity, models the area under study, such as a thorax cross-section. This model assigns voltages based on proximity to simulate a forward problem. Subsequently, an ‘inverse problem’ step recalibrates the mesh’s conductivity to reflect new measured voltages, incorporating simulated noise to mirror real conditions. This results in an updated conductivity map, visualizing the internal distribution inferred from external measurements. The Graz Algorithm tackles the reconstruction through iterative solutions, addressing the inverse problem’s complexity and the ill-posed nature of estimating internal conductivity from surface measurements. It involves advanced mathematical techniques and regularization strategies to stabilize the solution against inaccuracies. The process begins with voltage predictions at electrode boundaries, based on an assumed internal conductivity distribution, and iteratively refines this estimate to minimize discrepancies between predicted and measured voltages. This iterative reconstruction culminates in a visual representation of spatial conductivity variations, offering insights into physiological aspects like lung ventilation or perfusion. The Graz Algorithm’s incorporation of electrode behavior models and mathematical optimizations enhances reconstruction accuracy, proving essential for real-time, clinical monitoring of physiological parameters. Developing and applying such sophisticated algorithms requires deep knowledge in numerical methods, inverse problem-solving, and physiology, often facilitated by specialized software integrated with EIT hardware.
Figure 5.
The images illustrate a simplified approach to EIT reconstruction using the Graz Reconstruction Algorithm. Initially, a finite element method (FEM) mesh, assuming uniform conductivity, models the area under study, such as a thorax cross-section. This model assigns voltages based on proximity to simulate a forward problem. Subsequently, an ‘inverse problem’ step recalibrates the mesh’s conductivity to reflect new measured voltages, incorporating simulated noise to mirror real conditions. This results in an updated conductivity map, visualizing the internal distribution inferred from external measurements. The Graz Algorithm tackles the reconstruction through iterative solutions, addressing the inverse problem’s complexity and the ill-posed nature of estimating internal conductivity from surface measurements. It involves advanced mathematical techniques and regularization strategies to stabilize the solution against inaccuracies. The process begins with voltage predictions at electrode boundaries, based on an assumed internal conductivity distribution, and iteratively refines this estimate to minimize discrepancies between predicted and measured voltages. This iterative reconstruction culminates in a visual representation of spatial conductivity variations, offering insights into physiological aspects like lung ventilation or perfusion. The Graz Algorithm’s incorporation of electrode behavior models and mathematical optimizations enhances reconstruction accuracy, proving essential for real-time, clinical monitoring of physiological parameters. Developing and applying such sophisticated algorithms requires deep knowledge in numerical methods, inverse problem-solving, and physiology, often facilitated by specialized software integrated with EIT hardware.
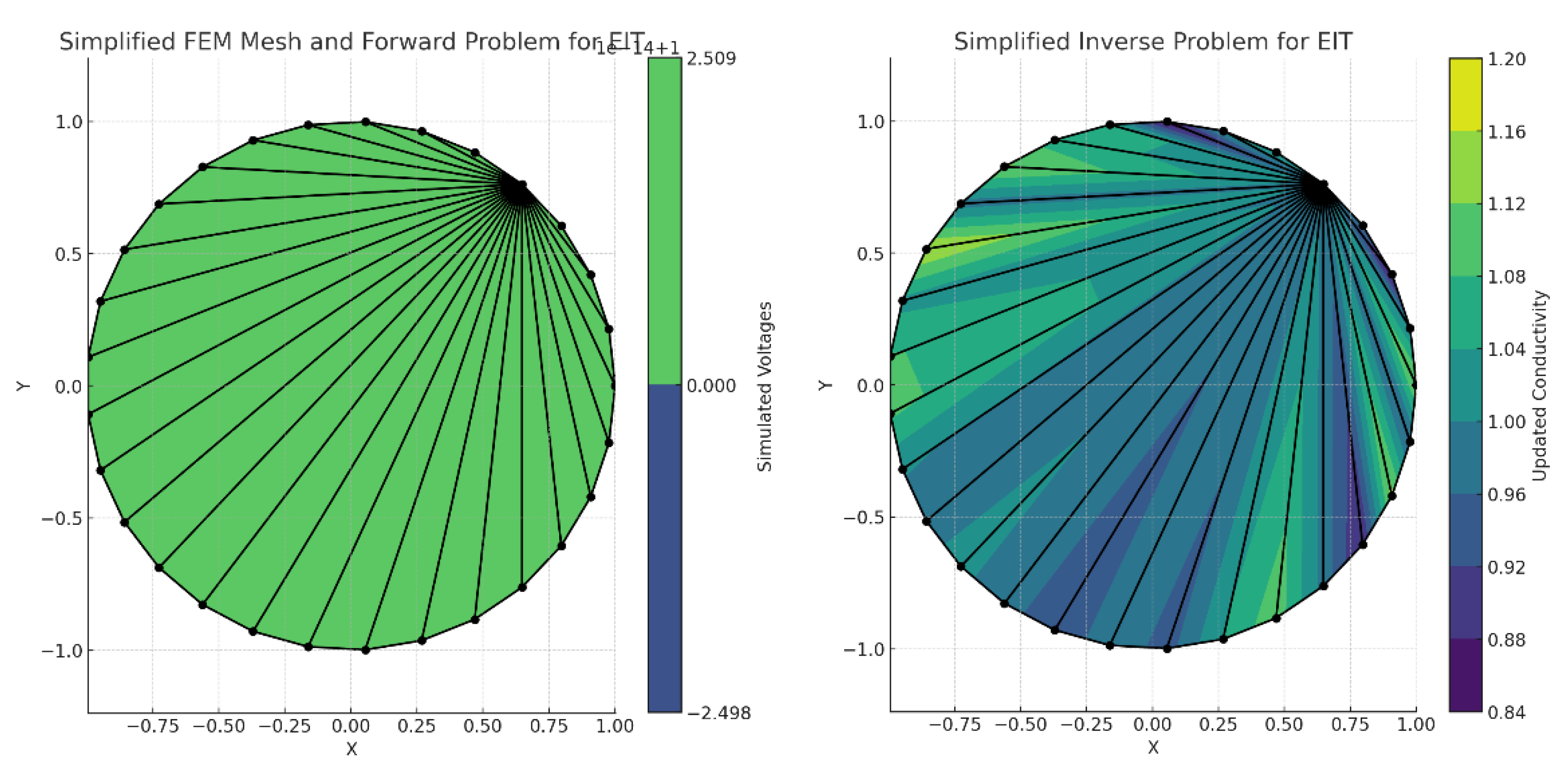
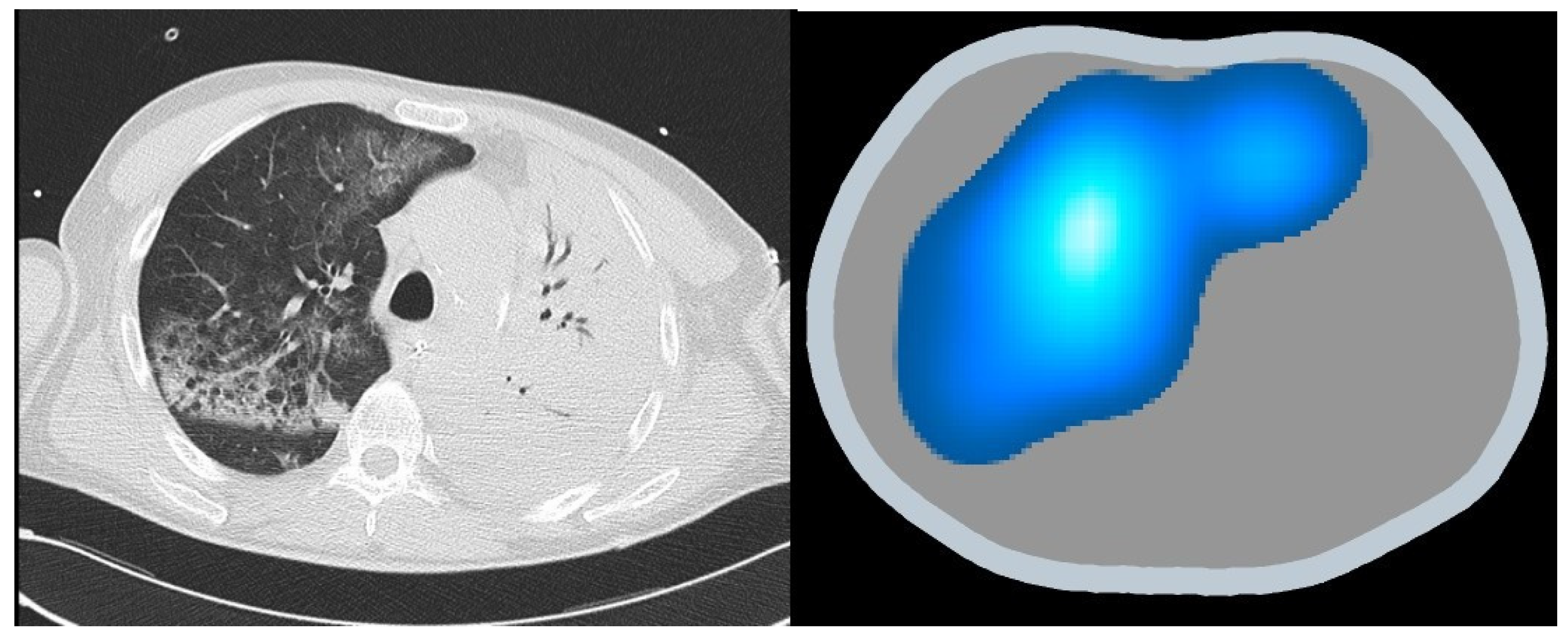
Figure 6.
Revealing lung inhomogeneities in ARDS: comparing CT scan with EIT.
Figure 6.
Revealing lung inhomogeneities in ARDS: comparing CT scan with EIT.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).