1. Introduction
Coagulopathy and cardiovascular complications are amongst the most important outcomes of severe Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) (Xu, Shi et al. 2020, Yang, Yu et al. 2020). Studies have shown that endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction is central to this process (Charfeddine, Ibn Hadj Amor et al. 2021, Østergaard 2021). These data suggest that reduced vascular integrity in COVID-19-positive patients could expose prothrombotic subendothelial factors, resulting in platelet capture, activation of coagulation cascades, thrombin activation, and fibrin production (Wang, Hao et al. 2018). To support this, there is an EC-dependent inflammatory response that intensifies the hypercoagulability phenomenon and potentially results in disseminated intravascular coagulation (Kadl and Leitinger 2005).
Healthy blood vessels are lined by a monolayer of EC that plays a crucial role in preventing the formation of pathological thrombosis. This is due, at least in part, to the presence of several receptors expressed on EC that act to promote anticoagulant pathways (Loghmani and Conway 2018). The activated protein C (aPC) is a serine protease derived from its inactive zymogen, protein C (PC). PC activation is optimally performed on the EC surface when PC binds to its receptor, the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), through its γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain, and the activator thrombin is linked to EC-thrombomodulin (TM) (Esmon, Esmon et al. 1982). Endothelial cells play an important role in health hemostasis (van Hinsbergh 2012, Schupp, Adams et al. 2021). Whereas endothelial derangement can occur in several pathological conditions, such as infections and autoimmune diseases, contributing to the coagulopathy that frequently accompanies these conditions (Goncharova, Chan et al. 2020). The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mainly infects the respiratory tract and usually progresses rapidly to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), with subsequent systemic viral spread and cytokine storm to cause endothelitis of the vasculature of the intestine, kidney, heart, and brain (Calabretta, Moraleda et al. 2021).
Fogarty and collaborators (Fogarty, Townsend et al. 2020) described that coagulopathy was the main complication in a cohort of 67 patients with COVID-19, reflecting the crucial role of EC in this disease and suggesting that advances in understanding its pathophysiology could lead to identifying new potential therapeutic targets. However, despite tremendous advances in the field, the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers coagulopathy remain elusive. Histological analyses of COVID-19 patients and in vitro experiments demonstrated that EC does not support the productive replication of SARS-CoV-2. Still, direct exposure to SARS-CoV-2 induces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules (Schimmel, Chew et al. 2021, Won, Wood et al. 2022). This supports the hypothesis that virus components could mediate the endothelial dysfunction observed in COVID-19 patients.
Here, we hypothesized that PC could play a protective role against SARS-CoV2-induced EC coagulopathy and inflammatory response. To test this hypothesis, we used bioinformatics to access vascular EC through single-cell transcriptomes from healthy controls and COVID-19 patients (
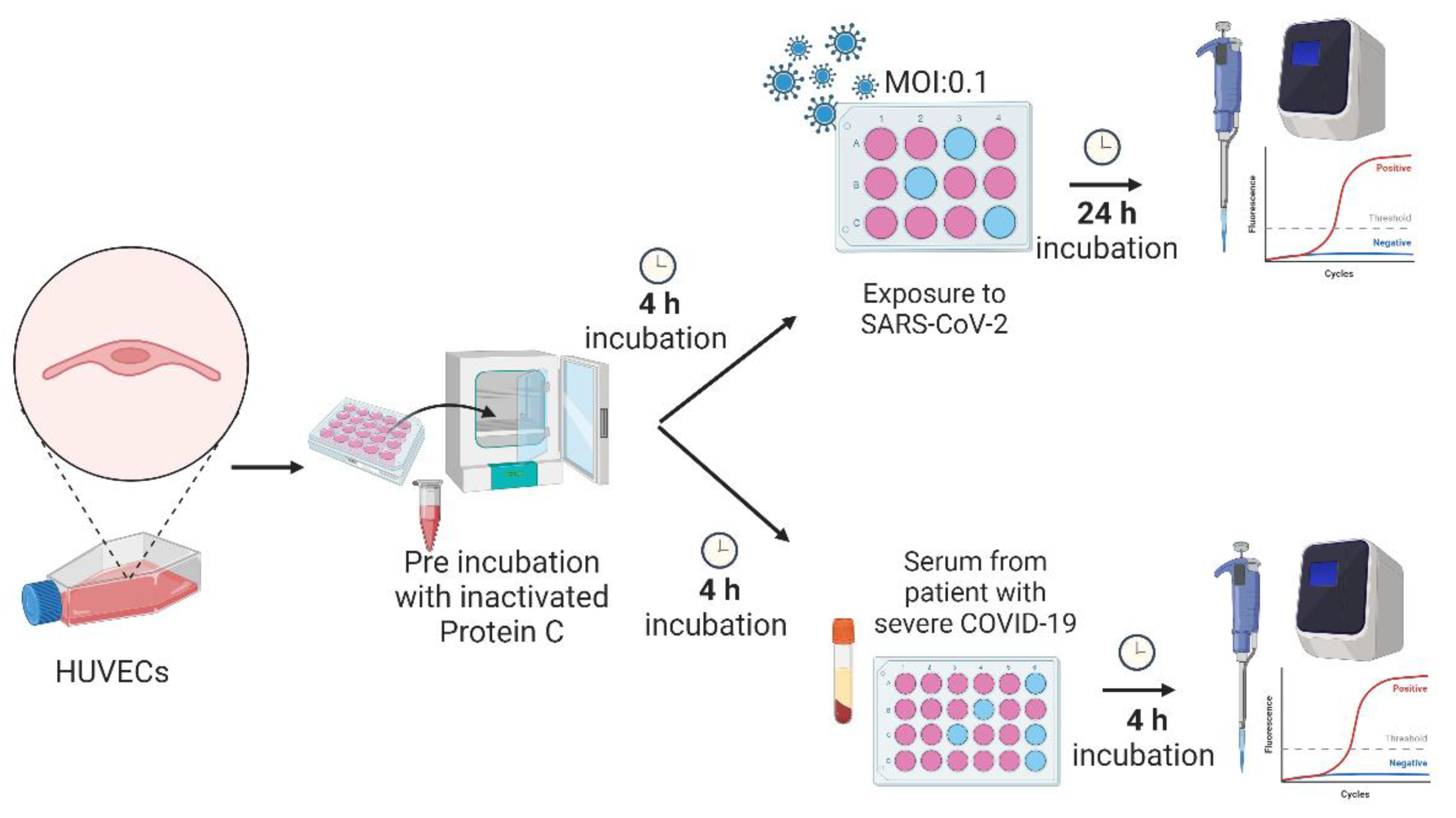
Figure 1A). Additionally, primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 particles or incubated with serum from patients with severe COVID-19 (
Figure 1B). Then, we explored PC signaling components and endothelial activation genes in the treated cells. We identified changes in the expression of pro-inflammatory, pro-coagulation, and cytoprotective genes in EC exposed to viral infection that were partly reversed by the PC treatment. This study suggests the PC system may contribute to restoring the local and systemic hemostatic derangement in COVID-19.
2. Materials and Methods
Cell culture. Primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were seeded in 12-well plates and incubated in 45% RPMI (Invitrogen), 45% 199 (Sigma-Aldrich) medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Experiments were performed when cells reached approximately 90% confluence per well.
Protein C pre-treatment. The dose and concentration of protein C (IHUPROCAI100UG, Innovative Research) used in the experiments were based on serum PC levels in human plasma (Gruber and Griffin 1992) and standardized according to the dose test and treatment time previously performed (data not shown). Cells at a confluence of 90% were washed with PBS before PC treatment and the medium (50% RPMI, 50% 199) without FBS was used for incubation. Approximately 400 μl of medium with purified human inactivated protein C (0.8 ng/μl) was added to the wells for 4 h. After incubation, the medium was removed, and exposure to SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant occurred, or patients’ sera was added.
Viral infection. HUVEC of different passages were seeded in 12-well plates and incubated in 45% RPMI, 45% 199 medium with 10% FBS at 37 °C under 5% CO2. This set of experiments was performed in four distinct groups. Control group (CLT): treated only with culture medium without FBS. SARS-CoV-2 group: cells were exposed to infection by the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. Protein C group (PTPC): cells were pre-treated for 4 h with purified human inactivated protein C (0.8 ng/μl). PTPC + SARS-CoV-2 group: cells were pre-treated for 4 h with purified human inactivated protein C (0.8 ng/μl) and then exposed to infection by the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. The SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant strain B.1.28 used in this study was kindly provided by the Emerging Viruses Laboratory of the University of Campinas, Brazil. Cells were infected with 4x105 FFU/ml of virus and an MOI of 0.1 for 1 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. The viral inoculum was then removed, and the medium was replaced with 50% RPMI and 50% 199 medium without FBS. After 24 h, medium and cell lysates were collected for ELISA test and quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR), respectively. All experiments with SARS-CoV-2 were performed under physical containment 3 (PC3) conditions.
Incubation of HUVEC with serum from healthy subjects or severe COVID-19 patients. A serum sample from a patient with severe COVID-19 collected upon admission to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and from a healthy subject (control group) collected before the COVID-19 outbreak were used at a concentration of 5% to incubate HUVECs for 4 h. The HUVECs were seeded as previously described and experiments were performed when cells reached a confluence of approximately 90% per well. This set of experiments was performed with six groups. Control group (CTL): treated only with culture medium (50% RPMI and 50% 199). PTPC group: cells were pre-treated for 4 h with purified human inactivated protein C (0.8 ng/μl). Severe serum group: cells were incubated for 4 h with culture medium at a concentration of 5% of serum from a patient with severe COVID-19. PTPC + Severe serum group: cells were pre-treated with purified human inactivated protein C at 0.8 ng/μl for 4 h; after incubation, protein C was removed, and then a culture medium with 5% serum from a severe COVID-19 patient was added for 4 h. Healthy serum group: cells were treated for 4 h with a culture medium at a concentration of 5% of serum from a healthy patient. PTPC + Healthy serum group: cells were pre-treated for 4 h with purified human inactivated protein C at 0.8 ng/μl; after incubation, the protein C was removed, and culture medium at a concentration of 5% of healthy serum was added for 4 h. After incubation, the cell lysate was collected for subsequent RNA extraction and analysis by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). All studies with human serum were previously approved by the Research Ethics Committee number 62864822.8.0000.5404.
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis. Total RNA was isolated from HUVECs using Trizol reagent according to the manufacturer's recommendations (Life Technologies, Frederick, MD). cDNA was synthesized using the high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
RT-qPCR Array. A total of 20 ng of reverse-transcribed cDNA from HUVEC viral infection and protein C treatment were used in each reaction of a real-time RT-qPCR array (RT² Profiler™ PCR Array Human Protease Activated Receptor Signaling - PAHS-159Z, Qiagen, Redwood City, United States) containing 84 related genes. Analyses were performed at
https://geneglobe.qiagen.com/us/analyze. Modulated genes were selected as candidate genes and validated by RT-qPCR (Supplementary Table S1).
Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). RT-qPCR was performed using LuminoCT PCR Master Mix (Sigma-Aldrich). The candidate genes obtained in the RT-qPCR Array and other genes of interest were evaluated. A total of 20 ng of reverse-transcribed cDNA were used in each reaction. The assay code of the primers is listed in Supplementary Table S2. Each PCR contained 20 ng of cDNA, 3 μl of LuminoCT PCR master mix (Sigma-Aldrich®), 0.25 μl of primers, and 0.25 μl of ultrapure water and was analyzed in the QuantStudio 6 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems). Each sample was tested in duplicate, and data was normalized to the average of two housekeeping genes (PPIA and GAPDH) and expressed as relative mRNA levels using the 2^-ΔCt method.
Viral quantification by RT-qPCR. The quantification of
SARS-CoV-2 was performed by one-step RT-qPCR using the set of primers: Forward: 5-ACA GGT ACG TTA ATA GTT AAT AGC GT-3; Reverse: 5-ATA TTG CAG CAG TAC GCA TAC GCA CAC A-3; Probe: 5–6FAM-ACA CTA GCC ATC CTT ACT GCG CTT CG-QSY-3. Each PCR contained 3 μl (20 ng) of total RNA, 4 μl of qPCRBIO Probe 1-Step Go (PCRBIOSYSTEMS, London, UK), 1.0 μl of each primer, 0.5 μl of the probe, and 0.5 μl of RTaseGo (PCRBIOSYSTEMS, London, UK). No infection was observed in HUVEC cell culture, as the final concentration of the virus in the cells was approximately 2x10
3 FFU/ml (
Supplementary Table S3).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay – ELISA. Activated Protein C levels were measured using the human activated protein C (Sandwich ELISA) ELISA Kit - LS-F54930 (LSBio, Shirley, MA, USA). The assay was performed following the manufacturer's protocol. Detection was performed on the microplate reader (MicroplateReader BioTek 800 Elx) and measurement was immediately conducted at 450 nm.
Single-cell transcriptomics analyses. Datasets were retrieved from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and the European Genome-phenome Archive (EGA) under accession numbers GSE171668 and EGAS00001004344, respectively. The raw data with the .h5 format were processed using the standard toolkit Scanpy 1.7.2 in Python igraph 0.9.6. processing and quality control flow previously described (Silva, Jara et al. 2022) and available at
https://scanpy-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pbmc3k.html. Data were then integrated using Harmony's algorithm, which designs cells in a shared embedding grouped by cell type (Korsunsky, Millard et al. 2019). Cell type identity was manually annotated, and differentially expressed genes (DEG) for each cluster and remaining cells were calculated using Wilcoxon's two-sided rank sum test (Zhu and Garmire 2019).
Statistical analysis. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between endothelial cells of patients with COVID-19 compared to healthy controls were determined with a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test Scanpy (Zhu and Garmire 2019). The p_val_cutoff = 0.05 and logfc_cutoff = 0.1 were established by the Scanpy utils function. GraphPad Prism version 8.0 was used for statistical analysis of real-time PCR gene expression and ELISA assays. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. with individual data points indicated. One- and two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison tests were used for statistical analyses. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and ****p<0.0001 compared to the indicated groups.
Generation of Diagrams and Illustrations. A licensed version of BioRender was employed to generate the diagrams present in most figures.
3. Results
3.1. Expression of Genes Involved in Endothelial Damage and PC Pathway in Human Lung Endothelial Single Cells
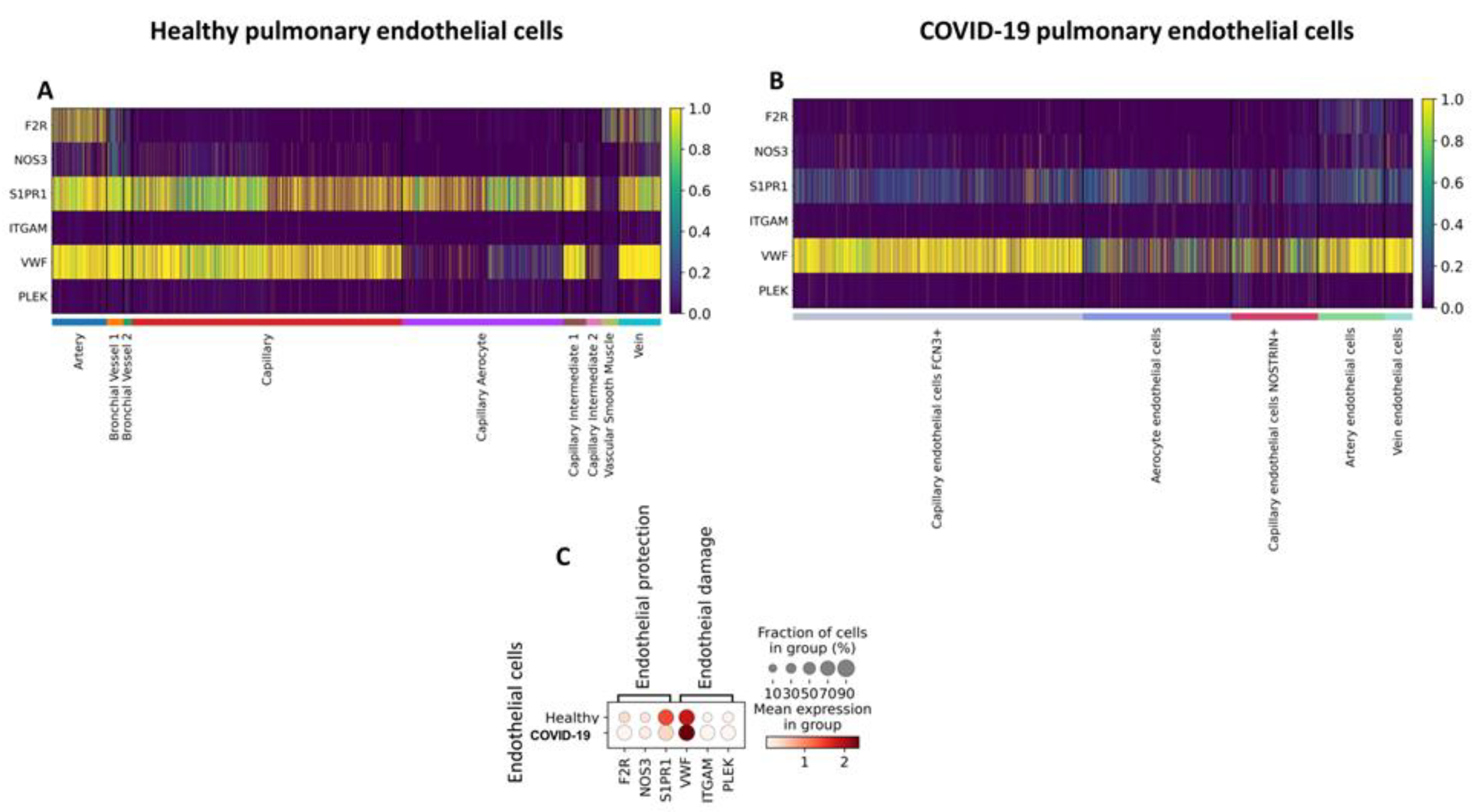
Although COVID-19 is primarily a respiratory disease, recent studies suggest that endothelial dysfunction may exacerbate deleterious events by inciting thrombotic, inflammatory, and microvascular processes, thus contributing to its extrapulmonary complications (Calabretta, Moraleda et al. 2021). To elucidate the mechanisms that drive endothelial damage in patients with COVID-19, we compared the expression of genes involved in endothelial activation and activated protein C (aPC) signaling in pulmonary EC from patients who died from COVID-19 to lung EC from healthy subjects in publicly available datasets. As a result, we identified genes encoding receptors involved in aPC signaling; F2R, S1PR1, and NOS3 were predominantly expressed by arterial and venous cells in the healthy lung. In addition, S1PR1 was expressed by most endothelial subtypes (
Figure 2A). The expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-coagulation-related genes ITGAM, PLEK, and vWF was detected by most cell subtypes (
Figure 2A). In ECs obtained from deceased patients who had COVID-19, the arterial subtype also predominantly expressed F2R, S1PR1, and NOS3. However, unlike in the healthy lung, S1PR1 was less expressed in the other subtypes (
Figure 2B,C). Additionally, we identified a decrease in the expression of F2R (p < 0.001), S1PR1 (p = 0), and NOS3 (p < 0.001) compared to healthy ECs (
Table 1; Figure 2C). However, in patients with COVID-19, the expression of ITGAM, vWF, and PLEK was higher when compared to ECs of healthy patients (
Table 1; Figure 2C).
3.2. PC Pretreatment Reduces the Expression of CCL2, IL6, and SERPINE1 Genes in HUVECs Exposed to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
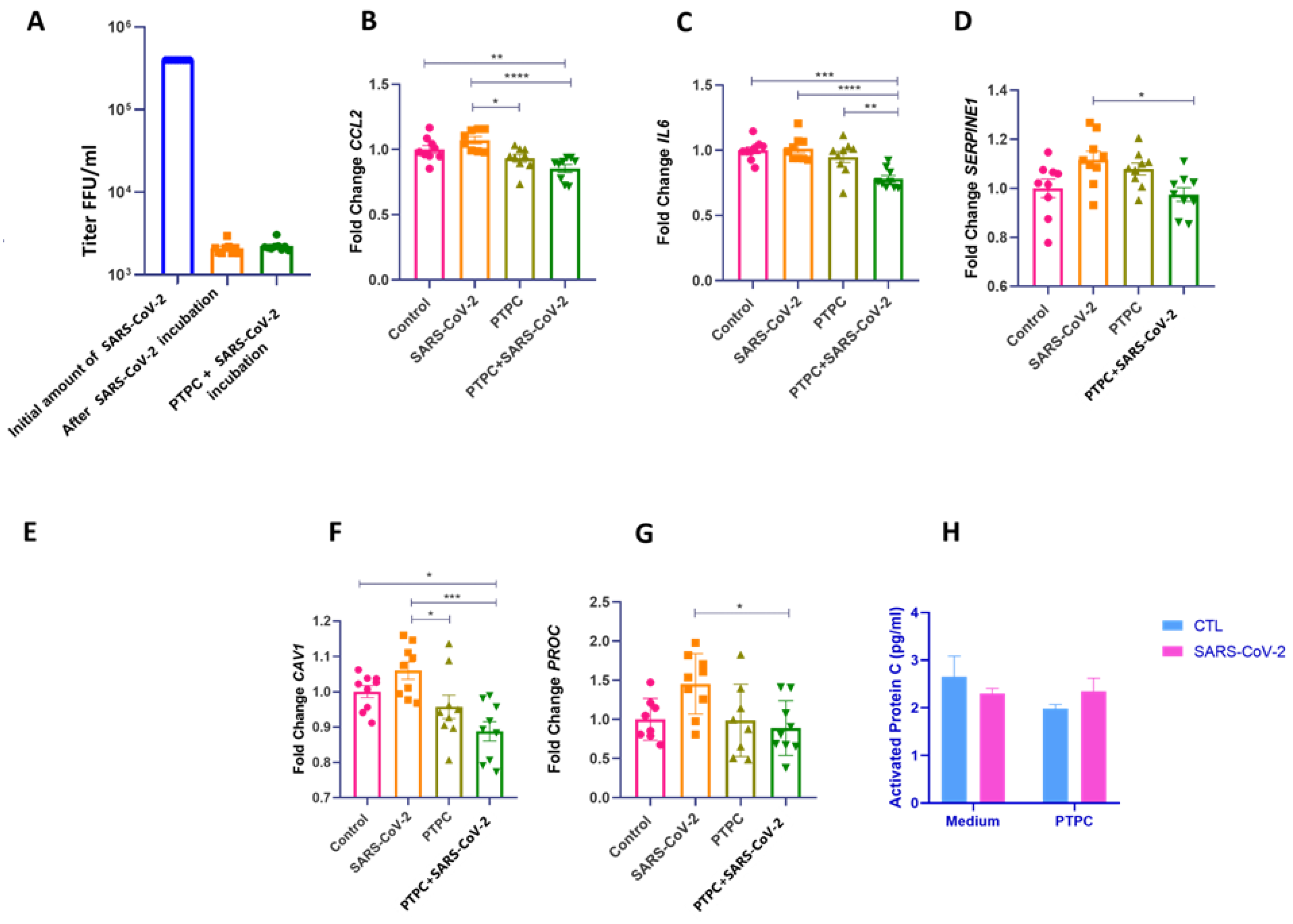
Previous studies suggest that the endothelial dysfunction seen in severe COVID-19 is possibly due to viral and pro-inflammatory proteins released by adjacent cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 rather than direct virus infection (Schimmel, Chew et al. 2021, Won, Wood et al. 2022). To explore EC dysfunction in the context of COVID-19, we exposed HUVECs to infection by the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. We did not find active viral replication in cell culture (
Figure 3A). Nevertheless, as our previous study suggested, protein C could play an important role in hypercoagulability in severe COVID-19 (Silva, Jara et al. 2022). We asked whether treatment of ECs with PC before exposure to SARS-CoV-2 infection could result in a protective endothelial effect. For this, HUVECs were pretreated for four hours with purified inactivated human protein C (IHUPROCAI100UG, Innovative Research) and subsequently exposed to infection by the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. In cells that received pre-treatment with PC and then were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection, the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-coagulant genes CCL2, IL6, and SERPINE1 significantly decreased compared to untreated cells (
Figure 3B–D). Furthermore, CAV1 and PROC expression were also decreased in cells pretreated with PC compared to cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 (
Figure 3E–G). There was no significant modulation in the gene expression of vWF, VCAM, F3, SELE, ITGAM, F2R, S1PR3, NOS3, PTGS2, PLEK, RHOH, TNF-a, and IL-3 between the groups
(Supplementary Figure S1).
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Does Not Promote Protein C Activation in HUVEC Cells
PC activation occurs through binding to the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex on the surface of endothelial cells; which is enhanced by the EPCR (Esmon, Esmon et al. 1982). Here, we used inactivated human protein C as pretreatment and hypothesized whether exposure to SARS-CoV-2 could promote its activation. Cells that received PC pretreatment with or without viral exposure showed no significant differences in the amounts of aPC (
Figure 3H).
3.4. Activated PC Present in Severe COVID-19 Serum May Protect ECs from Increased Expression of Inflammatory and Pro-Coagulation Genes
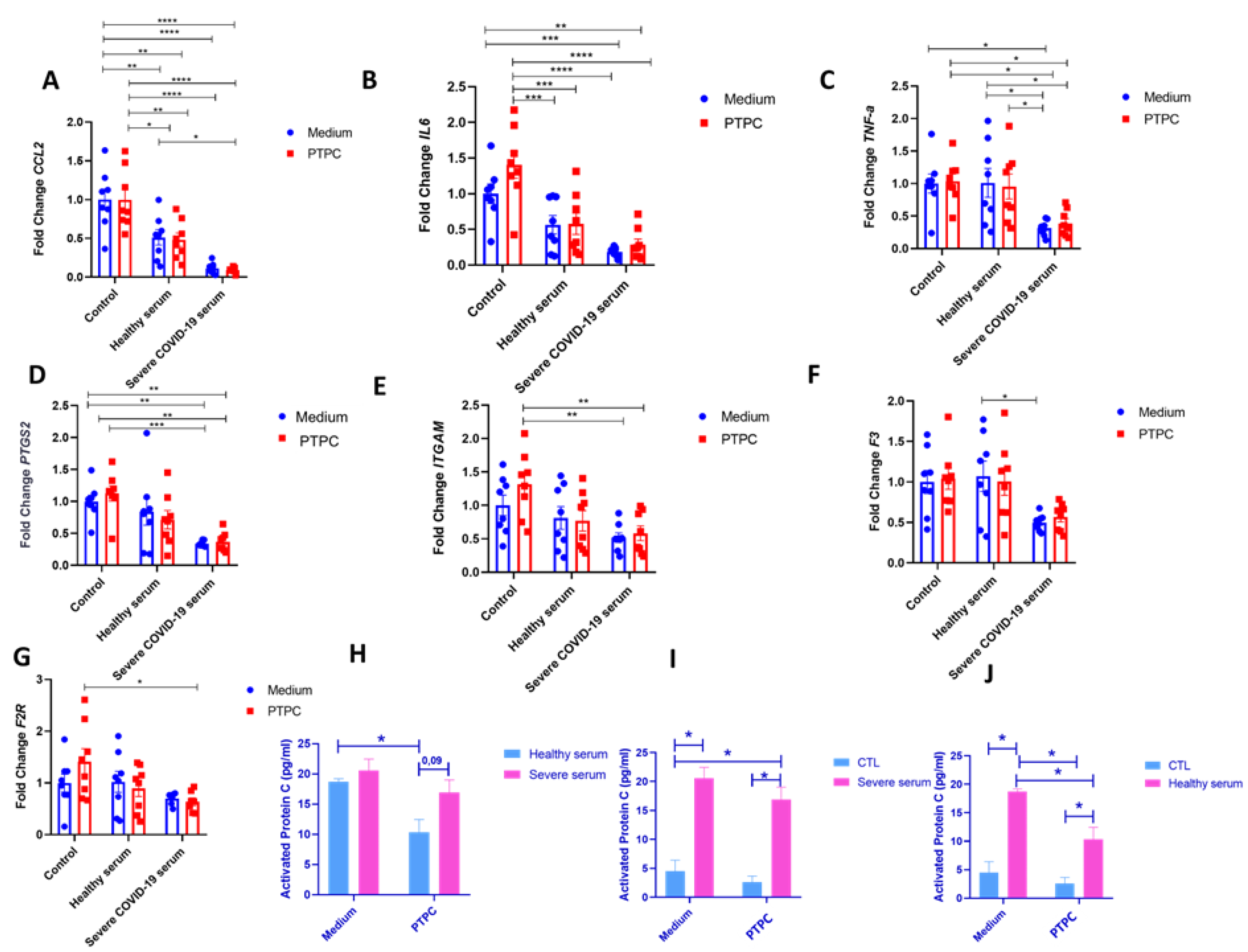
To mimic severe COVID-19, HUVECs were incubated for 4 hours in the serum of a patient with critical COVID-19; also, ECs were pretreated or not with PC before serum exposure. When incubating HUVECs with serum from a healthy individual, we observed a significant decrease in the expression of CCL2 and IL6 compared to the control pretreated with PC (
Figure 4A,B). Surprisingly, HUVECs incubated with severe COVID-19 serum also showed a decrease in the expression of CCL2, IL6, and the TNFa, PTGS2, and ITGAM expression compared to the control that received or did not receive pretreatment with PC (
Figure 4A–E). Compared with serum from a healthy individual, we observed a decrease in the expression of TNFa and F3 in cells incubated with severe COVID-19 serum (
Figure 4C,F). Pretreatment with PC before incubation with severe COVID-19 serum did not significantly alter the expression of inflammatory markers (
Figure 4A–G). No significant differences in the gene expression of SERPINE-1, SELE, PLEK, CAV-1, PROC, NOS-3, KDR, and S1PR-3 were observed between the groups
(Supplementary Figure S2). To understand the mechanism behind the effect of severe COVID-19 serum on HUVEC, aPC amounts were determined by ELISA (
Figure 4H–J). Severe serum showed a trend to increase aPC as compared to healthy serum. When PC was added before the incubation with healthy serum, the amount of aPC decreased significantly compared to healthy serum without PC pretreatment (probably due to the dilution of the aPC) (
Figure 4H). When a pretreatment with PC before incubation with severe serum occurred, the same effect was observed (without statistics), but the proportion of a higher amount of aPC in the severe COVID-19 serum remained (p = 0.09) (
Figure 4H). When adding inactive PC to severe and healthy serum, a small amount of aPC is detected, meaning that PC did not become aPC (
Figure 4I,J).
4. Discussion
Solid evidence shows that the vascular endothelium plays a key role in severe COVID-19 (Jin, Ji et al. 2020, Calabretta, Moraleda et al. 2021, Ionescu, Stoian et al. 2021). However, the mechanisms underlying this dysfunction remain mostly unclear. In this work, we used single-cell RNA sequencing transcriptomic data to access EC populations from patients who died as a result of severe COVID-19 and compare them with data from healthy subjects. Furthermore, we exposed HUVEC cells to SARS-CoV-2 infection and incubated these cells with serum from patients with severe COVID-19. We showed ECs were not infected with the virus; however, they underwent transcriptional alterations of inflammatory, coagulation, and cytoprotective genes. Part of the transcriptional changes observed in virus-exposed cells were reversed in cells pretreated with PC, demonstrating a modulating effect that extends beyond immunological changes to changes in coagulation and endothelial barrier stability, which are essential for hemostasis. Additionally, we observed that serum from a patient with severe COVID-19 contains more aPC than serum from healthy subjects, suggesting a protective effect of ECs from serum-induced activation. Thus, endothelial damage from COVID-19 could be, at least in part, mitigated by the aPC pathway.
The capacity or not of SARS-CoV-2 to directly infect ECs is a question with no consensus answer in the literature (Bernard, Limonta et al. 2020, Schimmel, Chew et al. 2021, Won, Wood et al. 2022) since angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) 2 expression is relatively low in these cell types (Schimmel, Chew et al. 2021). Other studies suggest that, even if SARS-CoV-2 could infect ECs, they are not capable of sustaining an active replication (Schimmel, Chew et al. 2021). Several studies have indicated that the significant endothelial dysfunction observed in COVID-19 is due to autoantibodies (Shi, Zuo et al. 2022), viral and pro-inflammatory proteins released by adjacent cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 (Bermejo-Martin, Almansa et al. 2020, Teuwen, Geldhof et al. 2020). In our study, we also did not observe infection or sustained viral replication in the HUVEC cultures studied. The susceptibility of ECs to the virus was evaluated by Urata and collaborators (Urata, Ikeda et al. 2022), who found that SARS-CoV-2 infects HUVECs; however, it does not replicate and disappears within 72 hours without causing serious cell damage. Furthermore, HUVECs with earlier passage are less susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection than senescent cells. Finally, more gene expression is affected in senescent ECs by SARS-CoV-2 infection than in early passage ECs. Here, although VWF, VCAM1, F3, ITGAM, S1PR3, PTGS2, PLEK, and RHOA markers have no statistical significance-sustained increase compared to control, it should be noted that exposure to the virus showed a trend increase in their expression (Figure 3 and Supplementary Figure S1). These changes could be more pronounced in senescent HUVECs, justifying the greater severity of COVID-19 in the elderly.
In addition to the increase in inflammatory and coagulation proteins, endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19 is related to the downregulation of cytoprotective proteins (Kobayashi 2021, Won, Wood et al. 2022). The aPC pathway is initiated by the formation of the complex of thrombin, thrombomodulin, and the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), allowing the conversion of vitamin K-dependent zymogenic circulating PC into its activated form (aPC) on the cell surface (Esmon 2003). Initial studies of gene expression profiling in HUVEC implicated broader biological activities of aPC. Administration of aPC to HUVECs after stimulation with TNF-α resulted in anti-apoptotic signals that promote cell survival (Joyce, Gelbert et al. 2001). aPC also reduces the endothelial expression of chemokine and adhesion molecules in the HUVECs (Brueckmann, Nahrup et al. 2006). Human coronary artery ECs exposed to a cocktail of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ) and recombinant aPC show no effect on the induction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, but drastically reduce intercellular adhesion molecule expression-1, as well as IL-6, IL-8 transcript and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) (Franscini, Bachli et al. 2004). Despite this, the benefits of the activated form of PC in pathological conditions remain unclear in the literature, where the path for more studies is open.
To control the immunological derangements observed in critically ill patients during the SARS-COV-2 pandemic, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved immunomodulatory drugs. One of them is tocilizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that acts by blocking interleukin 6 receptors, for use in certain adults hospitalized with COVID-19 (Group 2021). However, later REMDACTA and EMPACTA studies found that tocilizumab did not reduce all-cause mortality (Jeronimo, Farias et al. 2021, Rosas, Diaz et al. 2021). The lack of success of the therapeutic approach may be due to an isolated attempt to manage the immunological disorder or the virus itself rather than the coagulation system. We found that pretreatment of endothelial cells with PC decreased the expression of immunomodulators IL6 and CCL2, as well as the coagulation marker SERPINE1.
The rationale for using the inactive form of PC in this study is primarily based on the short half-life of aPC, which has an average of 20 minutes compared to 10 hours for PC (Okajima, Koga et al. 1990). Moreover, we hypothesize that the aggressiveness of inflammatory proteins and viral exposure is faster and overcomes the endogenous activation capacity of the circulating PC zymogen that may be ineffective in protecting the vascular bed from SARS-CoV-2-induced dysfunction. The inactive PC may be stored in the EC (completing the PC reserve), and as soon as the cell is exposed to the virus, this protein quickly becomes activated and protects the vascular bed. Therefore, we observed here that PC pretreatment induced a significant decrease in inflammatory and procoagulant genes in cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to cells that did not receive pretreatment (Figure 3). Together, we propose a hypothesis that could explain the findings. First, the protective effect observed in HUVECs exposed to SARS-CoV-2 could be mediated by the inactive PC, since the ELISA carried out in the collected culture medium did not indicate activation of the protein (Figure 3H). It is already known that aPC generation requires thrombin (Ludeman, Kataoka et al. 2005), and hence the relative lack of it may contribute to the lack of PC activation. The second hypothesis is that experimental evidence demonstrates that the endothelial cell PC receptor (EPCR) can undergo translocation from the plasma membrane to the nucleus, where it redirects gene expression. During translocation, it can transport aPC to the nucleus, possibly being responsible for aPC's ability to modulate inflammatory mediator responses in the endothelium (Esmon 2008). It is possible that the inactive PC added was activated and translocated to the cell nucleus, which is why it was not captured in the ELISA test.
The demonstration that aPC is a normal plasma component (Bauer, Kass et al. 1984), whose enzymatic activity can be detected with specific and sensitive methods (Gruber and Griffin 1992, España, Zuazu et al. 1996), indicates that the PC anticoagulant pathway is continuously activated in vivo. In this sense, a long-standing effort has been made to clarify the serum levels of PC and aPC that could be related to thrombotic states, since congenital or acquired disorders characterized by the production or impaired function of aPC are associated with a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) (De Stefano, Finazzi et al. 1996). Clinical and experimental data on PC deficiency support the hypothesis that an aPC deficiency, whether due to impaired PC activation, PC zymogen deficiency, or increased aPC inhibition, can result in a prethrombotic state (De Stefano, Finazzi et al. 1996). However, establishing cut-off serum levels of PC and aPC is still a challenge, since several conditions influence their serum levels. Plasma levels of aPC are commonly increased under pathological conditions. Cattaneo and collaborators (Cattaneo, Franchi et al. 1998) described that mean plasma levels of aPC, and aPC/PC ratios were higher in patients with VTE than in healthy controls. Moreover, endogenous aPC formation was increased during endotoxemia (Derhaschnig, Reiter et al. 2003) and meningococcal sepsis in children (de Kleijn, de Groot et al. 2003). The normal average plasma concentration of PC is equal to 67 nmol/L (4.3 μg/ml), and of aPC is equal to 38 pmol/L (Gruber and Griffin 1992). Two related individuals with semi-normal levels of PC zymogen have semi-normal levels of circulating aPC and suggest that the level of aPC under basal conditions in the absence of hemostatic stress may be proportional to the circulating PC level (Gruber and Griffin 1992), where physiological aPC/PC ratio is close to 1. However, under pathological conditions, the APC/PC ratio may increase to protect the host.
Ilmakunnas and collaborators (Ilmakunnas, Petäjä et al. 2003), when evaluating preoperative serum levels of PC and aPC in patients who underwent liver transplantation, identified that despite PC deficiency, patients with liver failure managed to maintain normal aPC levels. Protein C levels were found to decrease during surgery, while aPC levels increased. As a result, the aPC/PC ratio showed a significant increase during surgery, reflecting increased aPC formation despite low PC levels. Our previous in silico data (Silva, Jara et al. 2022) revealed a decrease in hepatic expression of PROC in patients who died as a result of severe COVID-19. Additionally, previous studies have shown decreased plasma PC levels in patients with COVID-19 at hospital admission (Stanne, Pedersen et al. 2021); however, here we observed serum levels of aPC relatively higher in serum with severe COVID-19 than in healthy serum (Figure 4H). These data suggested that during PC deficiency in COVID-19, PC activation can increase to preserve blood coagulation homeostasis. Protection is evidenced in our results by the lower induction in the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-coagulation genes observed in HUVECs incubated with severe COVID-19 serum compared to healthy serum and control.
During sepsis, endogenous aPC production initially increases in apparent response to overcoming an intense procoagulant state. However, overwhelming inflammation ultimately results in deficiency of the PC system with reduced levels of precursor and activated form of PC (Neyrinck, Liu et al. 2009). A similar phenomenon may occur in severe COVID-19. Subcoagulant amounts of thrombin in the circulation can increase plasma levels of endogenous aPC, which can therefore be considered markers of a hypercoagulable state (Gruber and Griffin 1992). In the study by Kleijn and colleagues (de Kleijn, de Groot et al. 2003) in children with meningococcal sepsis, aPC levels paralleled thrombin markers and were positively related to severity, with the highest levels in non-survivors. Moreover, the serum evaluated in this study was obtained on the first day of admission to the ICU, and the outcome of this patient was death.
It is inevitable to note that severe COVID-19 serum has induced lower inflammatory and pro-coagulation gene expression in HUVECs compared to healthy serum and culture medium (Figure 4 A–D). These results oppose the endothelial activation induced by serum from COVID-19 patients described in the literature (Shi, Zuo et al. 2022). However, other studies observed that incubation with serum from COVID-19 patients altered the surface marker expression profile in HUVEC but did not induce an EC-activated phenotype. Instead, post-COVID-19 syndrome (PCS) serum and PCS with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) serum led to a significant reduction in surface expression of VCAM-1 and E-selectin, compared to healthy control serum samples (Flaskamp, Roubal et al. 2022). Vieceli and collaborators (Vieceli Dalla Sega, Fortini et al. 2023) also evaluated transcriptional changes, permeability, and thrombin generation in HUVECs incubated with serum from COVID-19 patients. They observed an increased expression of F3 (Tissue Factor [TF]) and decreased EPCR; however, other molecules involved in the endothelial regulation of coagulation, such as PLAT (tPA), SERPINE1 (PAI-1), TFPI (TF pathway inhibitor), THBD (thrombomodulin), and vWF (von Willebrand factor) were not significantly different in ECs treated with serum from patients with non-COVID-19 or COVID-19 pneumonia. Although other pro-inflammatory cytokines and marker genes for endothelial activation (ICAM and PSELECTIN) were not evaluated in our study, the lack of activation of EC after serum incubation, in this case, does not support the concept of endothelial damage caused by cytokines. Furthermore, it is possible that genes involved in endothelial PC signaling are not regulated on EC, at least not while serum aPC levels protect the endothelium. As discussed above, endogenous serum aPC levels may not be constant throughout COVID-19. Therefore, the apparent protection observed here may not be sustained and unable to avoid complications that compromise the patient's life throughout the progression of the disease.
There are some limitations in our study. First, it was not assessed whether SARS-COV-2 would be capable of infecting other endothelial cell lines and then comparing the effects of infection with the effects of exposure to the virus alone. Second, it is important to note that our study did not analyze patient cohorts. Therefore, it is difficult to draw broad conclusions; yet we found interesting actions about the PC and aPC's that deserve further investigation. Third, we used serum from patients infected with the initial strain of the virus. Therefore, we cannot rule out the possibility that currently prevalent or emergent variants could affect the endothelium in different ways.
Furthermore, we used HUVEC, a robust in vitro model, to investigate the biology of the human endothelium. However, ECs in districts such as the venous or arterial endothelium may behave differently. Finally, pharmacological treatments administered to patients with COVID-19, which may still be present in serum, could act as confounding factors, masking some effects on ECs. We performed in silico and cell culture experiments, and future in vivo experiments should test the effect of aPC.
5. Conclusions
The main finding of this study was that severe COVID-19 serum decreased the expression of inflammatory and pro-coagulation genes in HUVECs compared to healthy serum and culture medium. Interestingly, this decrease is associated with a higher serum level of aPC in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to healthy patients. It is known that under stress conditions, serum aPC levels naturally rise in response to tissue damage; however, these levels may subsequently fall, allowing the already-known correlation of initially high serum aPC levels being associated with a worse prognosis in COVID-19. Given the considerable number of patients with severe COVID-19 who die as a result of thrombo-inflammatory complications, even though initial serum levels of aPC can protect the EC from potential dysfunction, it is unlikely this proportion will be maintained to avoid significant endothelial damage. On the other hand, the inactive form of PC added before viral exposure showed significant modulation of CCL2, IL6, and SERPINE1, which can act as an alternative to protect the endothelial bed. However, the exact mechanisms by which PC or aPC carry out transcriptional modulation in HUVECs are unclear and should be investigated further.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1, Figure S2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Araujo EP, Velander WH, Silva BRS and Morari J; methodology, Morari J, Silva BRS, Bombassaro B, Proença-Modena LP and Parise PL; software, Jara CP and Silva BRS; validation, Velloso LA, Araujo EP; formal analysis; Araujo EP, Morari J, Jara CP, Sidarta-Oliveira D; in-vestigation, Silva BRS; resources, Velloso LA and Araujo EP—review and editing, Araujo EP, Velander WH; visualization, Proença-Modena LP, supervision, Araujo EP; project administration, Silva BRS; funding acquisition, Araujo EP. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was carried out with the support of the Sao Paulo Research Foundation and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel – Brazil (CAPES) – Financing Code 001 and by CEPID – FAPESP – OCRC – Obesity and Comorbidities Research Center, Brazil – Process nº 2013 / 07607-8.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of State University of Campinas (protocol code 62864822.8.0000.5404 - November 30, 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bauer, K. A., B. L. Kass, D. L. Beeler and R. D. Rosenberg (1984). "Detection of protein C activation in humans." The Journal of clinical investigation 74(6): 2033-2041. [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Martin, J. F., R. Almansa, A. Torres, M. González-Rivera and D. J. Kelvin (2020). "COVID-19 as a cardiovascular disease: the potential role of chronic endothelial dysfunction." Cardiovascular research 116(10): e132-e133. [CrossRef]
- Bernard, I., D. Limonta, L. K. Mahal and T. C. Hobman (2020). "Endothelium infection and dysregulation by SARS-CoV-2: evidence and caveats in COVID-19." Viruses 13(1): 29. [CrossRef]
- Brueckmann, M., A. S. Nahrup, S. Lang, T. Bertsch, K. Fukudome, V. Liebe, J. J. Kaden, U. Hoffmann, M. Borggrefe and G. Huhle (2006). "Recombinant human activated protein C upregulates the release of soluble fractalkine from human endothelial cells." British journal of haematology 133(5): 550-557. [CrossRef]
- M. Moraleda, M. Iacobelli, R. Jara, I. VlodaCalabretta, E., J. M. Moraleda, M. Iacobelli, R. Jara, I. Vlodavsky, P. O’Gorman, A. Pagliuca, C. Mo, R. M. Baron and A. Aghemo (2021). "COVID-19-induced endotheliitis: emerging evidence and possible therapeutic strategies." British Journal of Haematology 193(1): 43-51vsky, P. O’Gorman, A. Pagliuca, C. Mo, R. M. Baron and A. Aghemo (2021). "COVID-19-induced endotheliitis: emerging evidence and possible therapeutic strategies." British Journal of Haematology 193(1): 43-51. [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, M., F. Franchi, M. L. Zighetti, I. Martinelli, D. Asti and P. M. Mannucci (1998). "Plasma levels of activated protein C in healthy subjects and patients with previous venous thromboembolism: relationships with plasma homocysteine levels." Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 18(9): 1371-1375. [CrossRef]
- Charfeddine, S., H. Ibn Hadj Amor, J. Jdidi, S. Torjmen, S. Kraiem, R. Hammami, A. Bahloul, N. Kallel, N. Moussa and I. Touil (2021). "Long COVID 19 syndrome: is it related to microcirculation and endothelial dysfunction? Insights from TUN-EndCOV study." Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine: 1702.
- de Kleijn, E. D., R. de Groot, C. E. Hack, P. G. Mulder, W. Engl, B. Moritz, K. F. Joosten and J. A. Hazelzet (2003). "Activation of protein C following infusion of protein C concentrate in children with severe meningococcal sepsis and purpura fulminans: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study." Critical care medicine 31(6): 1839-1847. [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, V., G. Finazzi and P. M. Mannucci (1996). "Inherited thrombophilia: pathogenesis, clinical syndromes, and management." BLOOD-NEW YORK- 87: 3531-3544.
- Derhaschnig, U., R. Reiter, P. Knöbl, M. Baumgartner, P. Keen and B. Jilma (2003). "Recombinant human activated protein C (rhAPC; drotrecogin alfa [activated]) has minimal effect on markers of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and inflammation in acute human endotoxemia." Blood 102(6): 2093-2098. [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C. T. (2003). "The protein C pathway." Chest 124(3): 26S-32S.
- Esmon, C. T. (2008). "Reprint of Crosstalk between inflammation and thrombosis." Maturitas 61(1-2): 122-131. [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C. T., N. Esmon and K. Harris (1982). "Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation." Journal of Biological Chemistry 257(14): 7944-7947. [CrossRef]
- España, F., I. Zuazu, V. Vicente, A. Estellés, P. Marco and J. Aznar (1996). "Quantification of circulating activated protein C in human plasma by immunoassays-enzyme levels are proportional to total protein C levels." Thrombosis and haemostasis 75(01): 056-061. [CrossRef]
- Flaskamp, L., C. Roubal, S. Uddin, F. Sotzny, C. Kedor, S. Bauer, C. Scheibenbogen and M. Seifert (2022). "Serum of post-COVID-19 syndrome patients with or without ME/CFS differentially affects endothelial cell function in vitro." Cells 11(15): 2376. [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, H., L. Townsend, C. Ni Cheallaigh, C. Bergin, I. Martin-Loeches, P. Browne, C. L. Bacon, R. Gaule, A. Gillett and M. Byrne (2020). "COVID19 coagulopathy in Caucasian patients." British journal of haematology 189(6): 1044-1049. [CrossRef]
- Franscini, N., E. B. Bachli, N. Blau, M.-S. Leikauf, A. Schaffner and G. Schoedon (2004). "Gene expression profiling of inflamed human endothelial cells and influence of activated protein C." Circulation 110(18): 2903-2909. [CrossRef]
- Goncharova, E. A., S. Y. Chan, C. E. Ventetuolo, N. Weissmann, R. T. Schermuly, C. J. Mullin and M. T. Gladwin (2020). "Update in pulmonary vascular diseases and right ventricular dysfunction 2019." American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 202(1): 22-28. [CrossRef]
- Group, R. C. (2021). "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial." Lancet (London, England) 397(10285): 1637. [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A. and J. H. Griffin (1992). "Direct detection of activated protein C in blood from human subjects.".
- Ilmakunnas, M., J. Petäjä, K. Höckerstedt, H. Mäkisalo, J. A. Fernandez, J. H. Griffin, S.-E. Jansson, H. Repo and E. J. Pesonen (2003). "Activation of protein C during reperfusion in clinical liver transplantation." Transplantation 75(4): 467-472. [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M., A. P. Stoian, M. Rizzo, D. Serban, D. Nuzzo, L. Mazilu, A. I. Suceveanu, A. M. Dascalu and I. R. Parepa (2021). "The role of endothelium in COVID-19." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22(21): 11920. [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, C. M. P., M. E. L. Farias, F. F. A. Val, V. S. Sampaio, M. A. A. Alexandre, G. C. Melo, I. P. Safe, M. G. S. Borba, R. L. A. Netto and A. B. S. Maciel (2021). "Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a randomized, double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial." Clinical Infectious Diseases 72(9): e373-e381. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y., W. Ji, H. Yang, S. Chen, W. Zhang and G. Duan (2020). "Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: from basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 5(1): 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D. E., L. Gelbert, A. Ciaccia, B. DeHoff and B. W. Grinnell (2001). "Gene expression profile of antithrombotic protein C defines new mechanisms modulating inflammation and apoptosis." Journal of Biological Chemistry 276(14): 11199-11203. [CrossRef]
- Kadl, A. and N. Leitinger (2005). "The role of endothelial cells in the resolution of acute inflammation." Antioxidants & redox signaling 7(11-12): 1744-1754. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J. (2021). "Lifestyle-mediated nitric oxide boost to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection: A perspective." Nitric Oxide 115: 55-61. [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I., N. Millard, J. Fan, K. Slowikowski, F. Zhang, K. Wei, Y. Baglaenko, M. Brenner, P.-r. Loh and S. Raychaudhuri (2019). "Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony." Nature Methods 16(12): 1289-1296. [CrossRef]
- Loghmani, H. and E. M. Conway (2018). "Exploring traditional and nontraditional roles for thrombomodulin." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 132(2): 148-158y (2018). "Exploring traditional and nontraditional roles for thrombomodulin." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 132(2): 148-158. [CrossRef]
- Ludeman, M. J., H. Kataoka, Y. Srinivasan, N. L. Esmon, C. T. Esmon and S. R. Coughlin (2005). "PAR1 cleavage and signaling in response to activated protein C and thrombin." Journal of Biological Chemistry 280(13): 13122-13128. [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A. P., K. D. Liu, J. P. Howard and M. A. Matthay (2009). "Protective mechanisms of activated protein C in severe inflammatory disorders." British journal of pharmacology 158(4): 1034-1047. [CrossRef]
- Okajima, K., S. Koga, M. Kaji, M. Inoue, T. Nakagaki, A. Funatsu, H. Okabe, K. Takatsuki and N. Aoki (1990). "Effect of protein C and activated protein C on coagulation and fibrinolysis in normal human subjects." Thrombosis and haemostasis 63(01): 048-053. [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L. (2021). "SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation." Physiological reports 9(3): e14726. [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I. O., G. Diaz, R. L. Gottlieb, S. M. Lobo, P. Robinson, B. D. Hunter, A. W. Cavalcante, J. S. Overcash, N. A. Hanania and A. Skarbnik (2021). "Tocilizumab and remdesivir in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial." Intensive care medicine 47: 1258-1270. [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, L., K. Y. Chew, C. J. Stocks, T. E. Yordanov, P. Essebier, A. Kulasinghe, J. Monkman, A. F. R. dos Santos Miggiolaro, C. Cooper and L. de Noronha (2021). "Endothelial cells are not productively infected by SARS-CoV-2." Clinical & translational immunology 10(10): e1350. [CrossRef]
- Schupp, J. C., T. S. Adams, C. Cosme Jr, M. S. B. Raredon, Y. Yuan, N. Omote, S. Poli, M. Chioccioli, K.-A. Rose and E. P. Manning (2021). "Integrated single-cell atlas of endothelial cells of the human lung." Circulation 144(4): 286-302. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H., Y. Zuo, S. Navaz, A. Harbaugh, C. K. Hoy, A. A. Gandhi, G. Sule, S. Yalavarthi, K. Gockman and J. A. Madison (2022). "Endothelial cell–activating antibodies in COVID-19." Arthritis & Rheumatology 74(7): 1132-1138. [CrossRef]
- Silva, B. R. S., C. P. Jara, D. Sidarta-Oliveira, L. A. Velloso, W. H. Velander and E. P. Araújo (2022). "Downregulation of the Protein C Signaling System Is Associated with COVID-19 Hypercoagulability—A Single-Cell Transcriptomics Analysis." Viruses 14(12): 2753. [CrossRef]
- Stanne, T. M., A. Pedersen, M. Gisslén and C. Jern (2021). "Low admission protein C levels are a risk factor for disease worsening and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19." Thrombosis Research 204: 13-15. [CrossRef]
- Teuwen, L.-A., V. Geldhof, A. Pasut and P. Carmeliet (2020). "COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed." Nature Reviews Immunology 20(7): 389-391 389-391. [CrossRef]
- Urata, R., K. Ikeda, E. Yamazaki, D. Ueno, A. Katayama, M. Shin-Ya, E. Ohgitani, O. Mazda and S. Matoba (2022). "Senescent endothelial cells are predisposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent endothelial dysfunction." Scientific Reports 12(1): 11855. [CrossRef]
- van Hinsbergh, V. W. (2012). Endothelium—role in regulation of coagulation and inflammation. Seminars in immunopathology, Springer.
- Vieceli Dalla Sega, F., F. Fortini, D. Licastro, S. D. Monego, M. Degasperi, A. Ascierto, L. Marracino, P. Severi, M. D’Accolti and I. Soffritti (2023). "Serum from COVID-19 patients promotes endothelial cell dysfunction through protease-activated receptor 2." Inflammation Research: 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., H. Hao, N. J. Leeper and L. Zhu (2018). "Thrombotic regulation from the endothelial cell perspectives." Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 38(6): e90-e95. [CrossRef]
- Won, T., M. K. Wood, D. M. Hughes, M. V. Talor, Z. Ma, J. Schneider, J. T. Skinner, B. Asady, E. Goerlich and M. K. Halushka (2022). "Endothelial thrombomodulin downregulation caused by hypoxia contributes to severe infiltration and coagulopathy in COVID-19 patient lungs." EBioMedicine 75: 103812. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z., L. Shi, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, L. Huang, C. Zhang, S. Liu, P. Zhao, H. Liu and L. Zhu (2020). "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome." The Lancet respiratory medicine 8(4): 420-422. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Y. Yu, J. Xu, H. Shu, H. Liu, Y. Wu, L. Zhang, Z. Yu, M. Fang and T. Yu (2020). "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study." The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 8(5): 475-481. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. and L. X. Garmire (2019). Data Analysis in Single-Cell RNA-Seq. Single-Cell Omics. V. A. Debmalya Barh, Elsevier: 419-432.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).