1. Introduction
Scoliosis is a 3-dimensional deformity caused by lateral curvature and rotation of the spine [
1]. The aetiology of most scoliosis patients is unclear [
2]. The most commonly diagnosed type is adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), which usually occurs during adolescence [
3]. The worldwide prevalence of AIS varies between 0.93% and 12%, and the incidence and severity of spinal curvature is higher in girls than in boys [
4]. In our current knowledge, two different approaches are generally adopted for the treatment of scoliosis. According to the degree of Cobb angle, surgery is recommended for patients with a Cobb angle greater than 40°, while conservative treatment including orthosis or exercise therapy is recommended for patients with a Cobb angle less than 40° [
5].
Previous studies in individuals with scoliosis have reported an asymmetry in the activation of paraspinal muscles on the concave and convex sides of the curve [
6]. In individuals with AIS, higher electromyographic (EMG) muscle activity was found on the convex side of the curve compared to the concave side [
7,
8,
9]. Although it has not been fully confirmed whether the asymmetry in muscle activity is a cause or a consequence of spinal curvature, the current literature suggests that muscle asymmetry in the erector spinae plays an important role in the progression of scoliosis in individuals with AIS [
10,
11]. Therefore, posture training and scoliosis-specific exercises to improve symmetry in paraspinal muscle activity in AIS may reduce the risk of curve progression [
12].
Scoliosis-specific exercises are designed to bring patients asymmetrical posture into alignment and restore a correct upright position. It also includes sensorimotor and breathing exercises aimed at static/dynamic postural control, spinal stability and recalibration of breathing patterns [
13]. In a study examining the EMG activations of the paraspinal muscles during scoliosis exercise, it was observed that the EMG activity in the paraspinal muscle during exercise was higher than in the relaxed standing position. At the same time, EMG signals were found to be higher on the convex side of the curve during asymmetric exercise and on the concave side during symmetric exercise [
9,
14,
15,
16]. However, the effect of different forms of stimulation on these muscle activations during exercise is not available in the literature.
The aim of this study was to compare thoracic and lumbar erector spinae muscle activations during 3D elongation exercise given in three different ways in individuals with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. The hypotheses of this study were (1) the three different variations of the 3D elongation exercise will lead to significantly different activation levels in both thoracic and lumbar erector spinae muscles in individuals with AIS, (2) there will be a significant interaction effect between the type of 3D elongation exercise and the activation of thoracic and lumbar erector spinae muscles, and (3) there will be a significant difference in activation between thoracic and lumbar erector spinae muscles in all three exercise variations in individuals with AIS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
This study employed a prospective cohort design conducted at a single center. Twenty-four (15 females and 9 males) adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) with a mean age of 14.5±2.3 years were included in the study. The criteria for inclusion in this study were specifically defined as follows: Firstly, participants must conform to the diagnostic criteria for scoliosis as set by the International Society of Spine Surgery. Secondly, they should have a Cobb angle ranging between 10° and 20°. Thirdly, individuals included in the study should not have undergone surgical treatment for scoliosis, nor should they have plans to undergo brace treatment in the foreseeable future. Additionally, they must not have any motor organ diseases. Finally, participants must provide informed consent for this study, willingly participate, and sign the consent form. On the other hand, the exclusion criteria for this study were as follows: Individuals with nonidiopathic scoliosis were excluded. Participants with growth and developmental disorders, or a history of nerve, muscle, and bone infections, psychological issues, etc., were also not included. Furthermore, individuals with obvious deformities of the lower limbs and feet, or those who had undergone major surgery in the past, were not eligible for this study. The R package “pwr” was used to estimate the sample size (Franz Faul, University of Kiel, Germany) for two within-factors repeated measures design. The effect size for the side effect (η2partial=0.095) and the interaction effect (η2partial=0.032) was too small, so the sample size was calculated based on exercise type (η2partial=0.734, f=1.081). According to the pilot study based on five subjects’ values, the minimum sample size was obtained as 17 subjects with a power of 0.80, an alpha level of 0.05, and an effect size of f=0.6>0.40 as large. The study was completed with a total of 24 subjects. All the subjects gave informed consent; the study was approved by the XXXX University Ethics Committee for Human Investigation, and all procedures were conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. EMG Recording and Data Analysis
EMG data were collected using Noraxon Ultium EMG sensor system (Noraxon USA, Inc., Scottsdale, Arizona- sampling frequency of 4000 Hz. per channel; gain: 1000 (signal to noise ratio;1 μV RMS); common mode rejection rate (CMRR): -100 dB; input impedance >100 mΩ.). Any hair on the skin was first removed, and then the area was cleansed with an alcohol swab before electrodes were connected to detect EMG signals. The electrodes were positioned bilaterally on the iliocostalis lumborum pars lumborum (right ICL and left ICL) at the L3 level, midway between the lateral-most palpable border of the erector spinae and a vertical line through the posterosuperior iliac spine; on the longissimus thoracis (right LT and left LT) at the T9 level, midway between a line through the spinous process and a vertical line through the posterosuperior iliac spine, located approximately 5 cm laterally; and on the iliocostalis lumborum pars thoracis (right ICT and left ICT) at the T10 level, midway between the lateral-most palpable border of the erector spinae and a vertical line through the posterosuperior iliac spine[
17]. The sample rate was set to 2000 Hz. Two filters were applied, including a band-pass filtered from 10 to 500 Hz using a first-order high-passand fourth-order low-pass Butterworth filter to remove unacceptable artifacts and a notch filter (60 Hz) to eliminate noise. A moving 100-ms window was used to calculate root mean square (RMS) values. The Noraxon MyoResearch XP program was used to process the data (version 3.16; Noraxon Inc, Scottsdale, AZ, USA). The data for each trial were expressed as a percentage of the calculated mean RMS of the MVIC (%MVIC), and the mean %MVIC of 3 trials was used for analysis [
18].
2.3. Evaluation protocol
To standardize the electromyographic (EMG) data, each muscle underwent a maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC). We recorded the EMG signal amplitude during these contractions. While the test postures mirrored those found in standard physical therapy manuals for muscle testing, we applied additional manual resistance for the back muscles. This progressive manual pressure was gradually increased to a maximum and held for five seconds. With a 30-second rest period between each repetition, each muscle was tested three times. Additionally, we checked the accuracy of electrode placement by scrutinizing EMG amplitudes during these tests. Specifically, for assessing the erector spinae muscles, we stabilized the participant’s lower limbs while they performed maximal prone trunk extension, with resistance applied to the upper thoracic region [
8,
19].
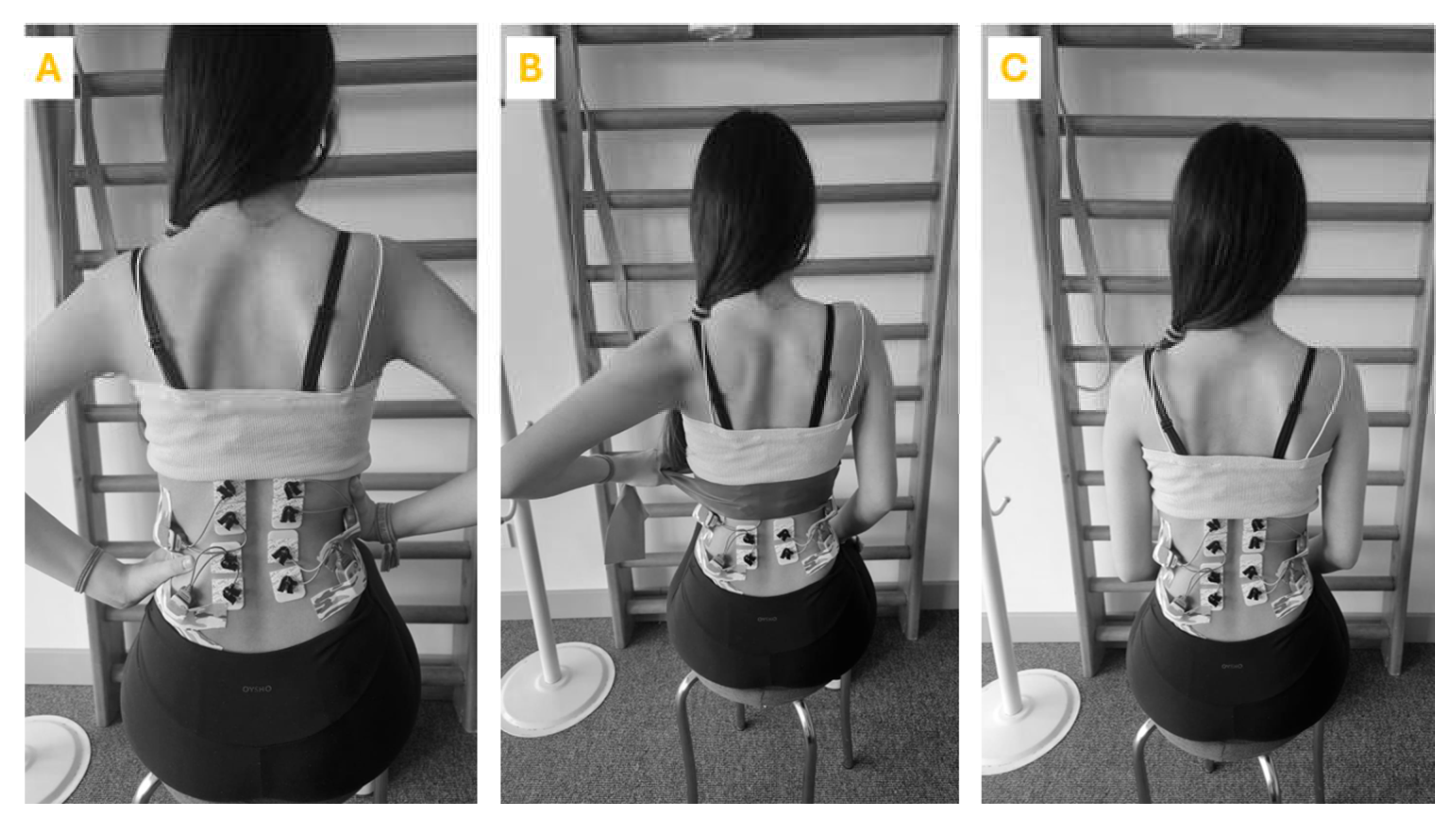
The exercises were performed in a controlled environment with adequate space and a non-slip surface. Each participant underwent an initial assessment to tailor the exercise to their specific scoliosis curve. The participant was seated with the spine in a neutral position. Participants then started the exercise by extending their spine. This involves lengthening the torso, focusing on creating space between the vertebrae. During the extension phase, correct breathing technique is emphasized with inhalation. Following the extension, the participant performs specific movements aimed at spinal de-rotation. This included lateral bending, rotational movements or shoulder and pelvic adjustments depending on the type of curvature. Throughout the exercise the participant practiced scoliosis-specific 3D exercise-specific breathing techniques. This includes breathing directed to the concave side of the body to facilitate de-rotation and increase rib cage mobility. The same exercise was then repeated with manual resistance and theraband (
Figure 1). To eliminate the learning effect and ensure randomization, each participant performed the exercises in random order. The exercises were carried out in a random order. In order to lessen the effects of tiredness, rest intervals of 30 seconds were permitted between each exercise repeat, and a minute-long break was provided between workouts.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
The data were summarized as frequency (percentage), mean±standard deviation, and median (quartile 1-quartile 3) based on the type of variable. The two-way repeated measures design and two-way mixed design were used to evaluate the main (exercise, side, Cobb angle) and interaction effects (exercise*side, exercise*cobb angle). The main effects were examined when the interaction effect was not statistically significant. The Bonferroni adjusted p-values were interpreted for all multiple comparisons. The effect size (f) was interpreted as follows: ≥0.40: large, 0.25-0.39: medium, 0.10-0.24: small effect size. The statistical analysis was conducted with R language (R Core Team, 2021) in R Studio 2022.02.3 and SPSS Version 21.0 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.). The following R packages were used: “ggplot2”, and “ggpubr”.
3. Results
Descriptive characteristics of the participants are shown in
Table 1.
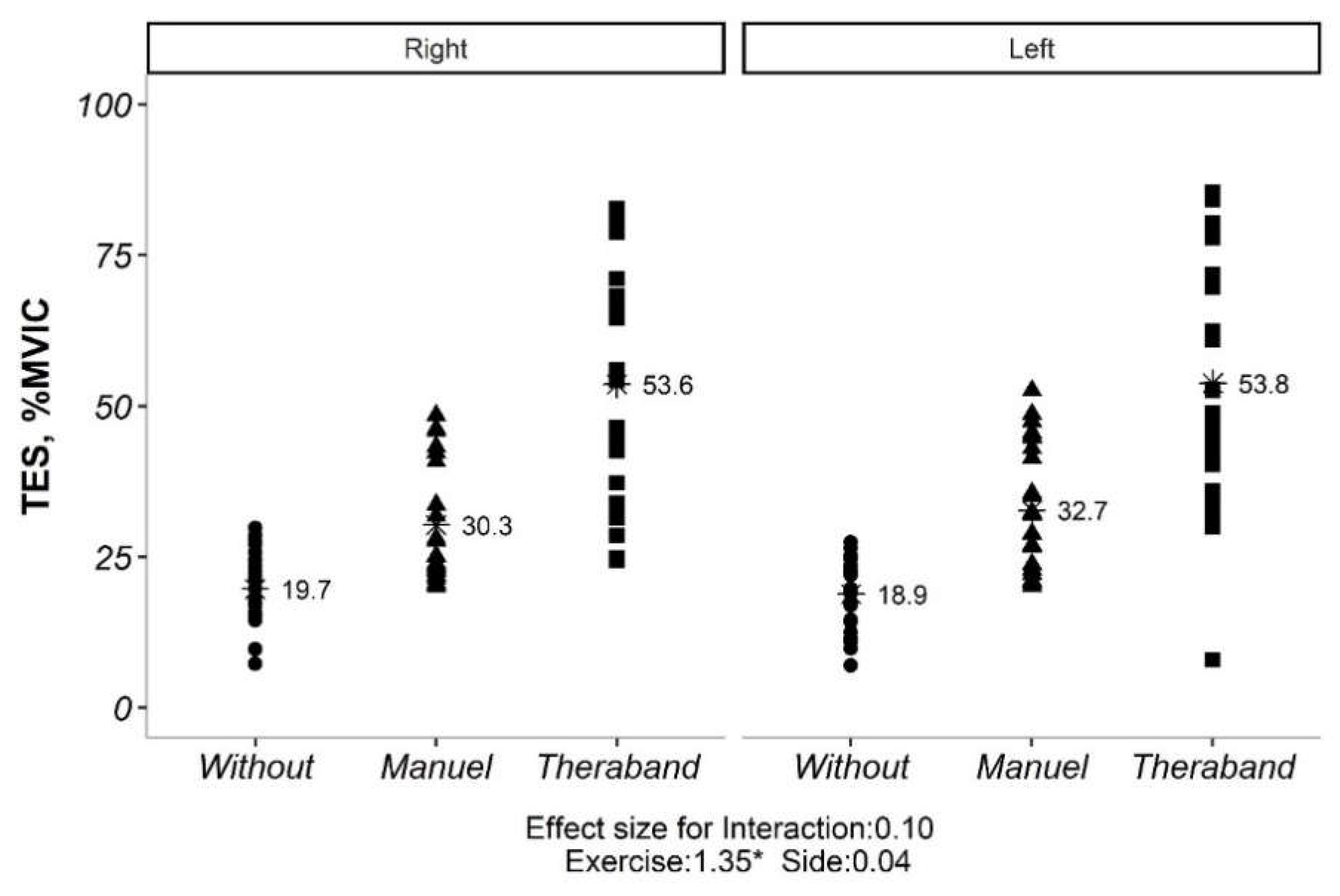
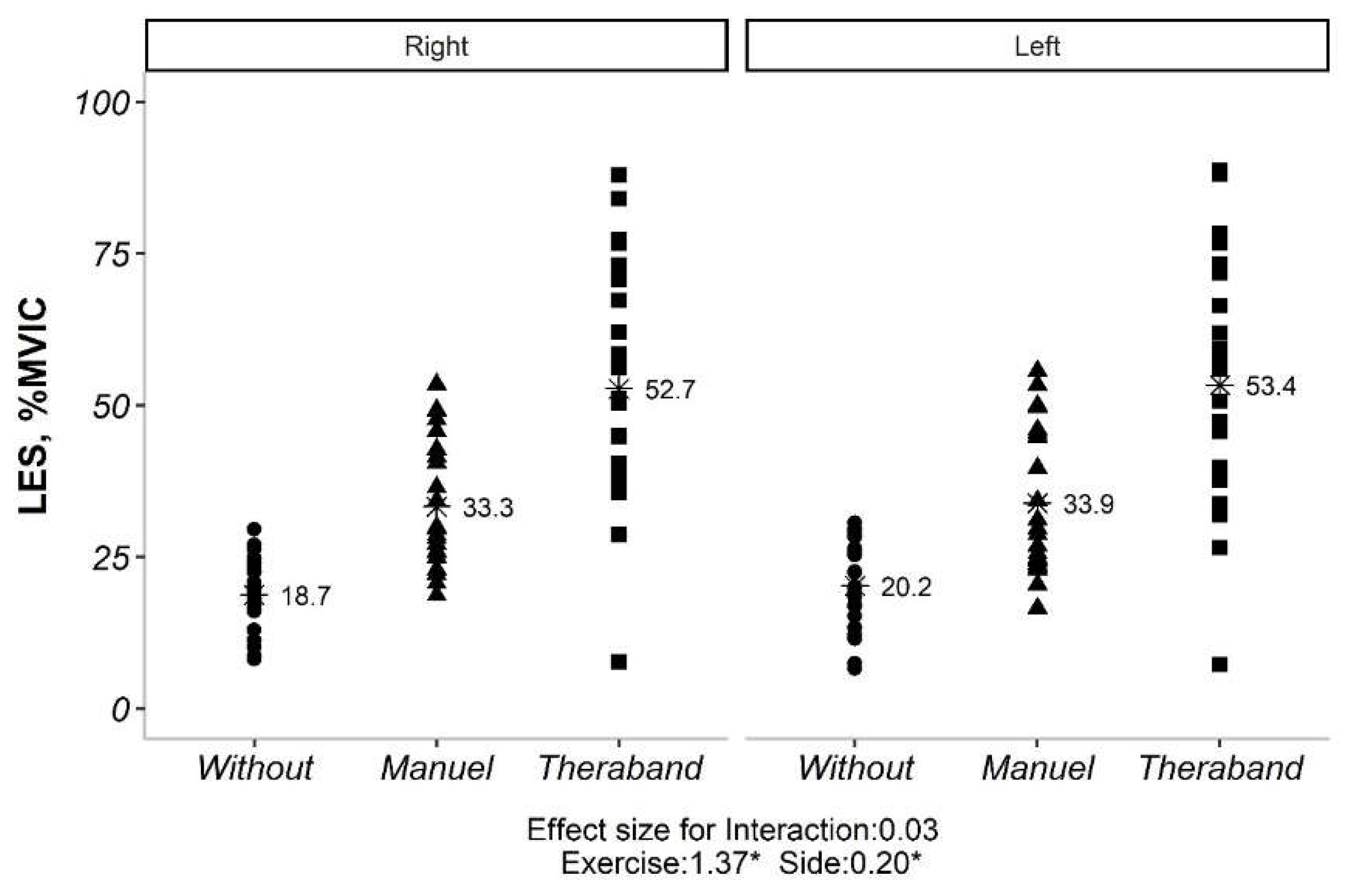
The interaction effect for both TES and LES were not significant (
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Table 2). Therefore, the main effects were analyzed. The main effects for exercise and side were also reported in
Table 2. For TES, all exercises were significantly different from each other. For LES, all exercises were significantly different from each other, and the sides were also significantly different.
The multiple comparisons from the main effects for the measurements were summarized in
Table 2.
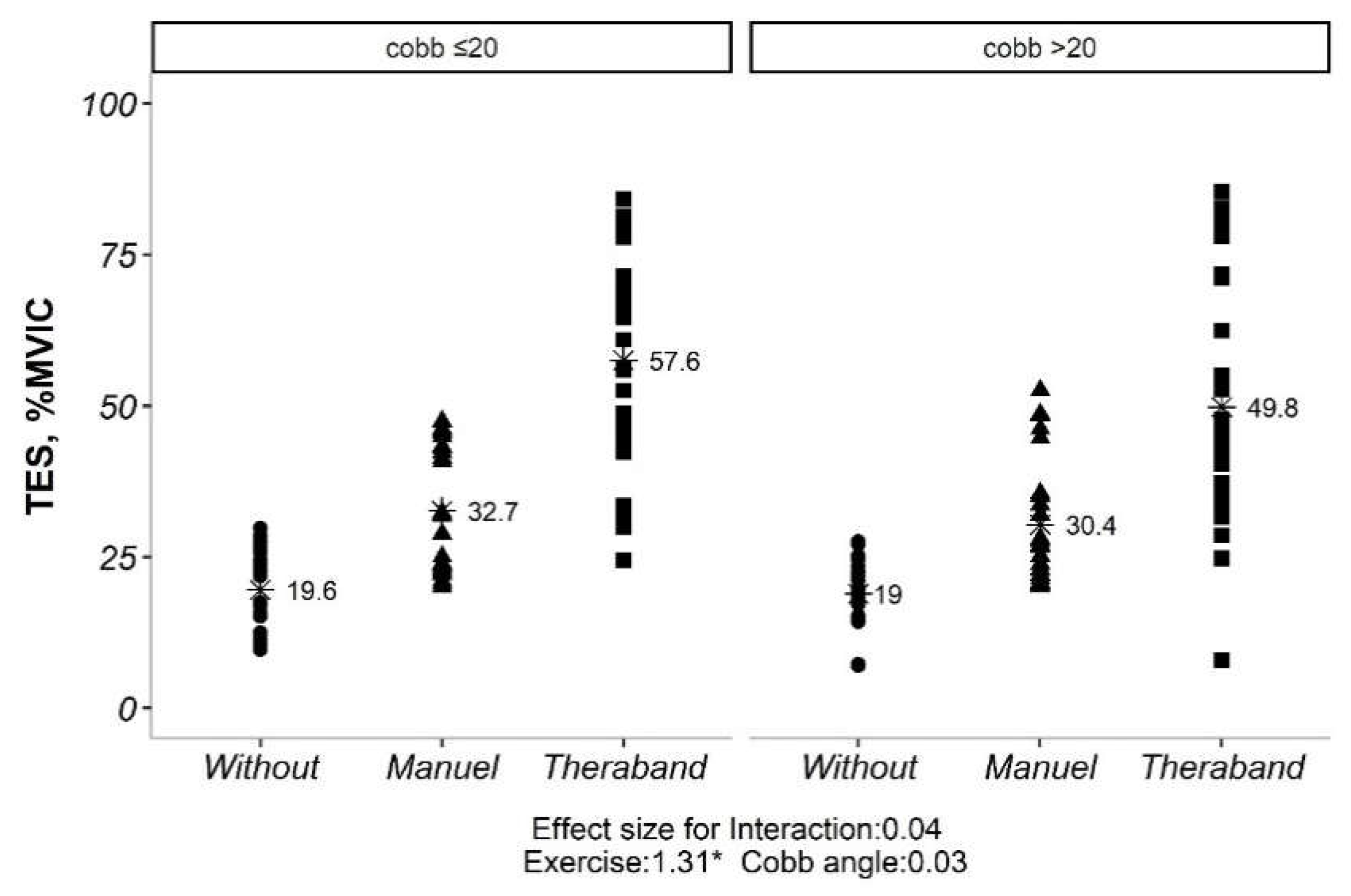
Our initial analysis revealed no significant interaction between exercise type and side (convex vs. concave) for both TES and LES (p> 0.05). This implies that the impact of exercise on muscle activation was not significantly influenced by the side of the curve. However, significant main effects were observed for both exercise type and side for TES (p <0.05). Similarly, for LES, all exercise types and sides showed significant differences in activation levels (p <0.05). Given the non-significant exercise*side interaction, subsequent analyses explored the influence of Cobb angle (under or over 20 degrees) on exercise-induced muscle activation. Interestingly, only the exercise effect remained significant for both TES and LES (p <0.05), regardless of Cobb angle category. Further pairwise comparisons of exercise types within each Cobb angle category revealed statistically significant differences for both TES and LES (p <0.01). However, comparisons between the two Cobb angle categories themselves (under vs. over 20 degrees) did not yield significant differences (p> 0.05) (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of three different exercise types on the electromyographic activity of the thoracic and lumbar erector spinae muscles in individuals with AIS. The results of the study showed that there was no significant interaction effect between exercise type and concave and convex sides for both the TES and LES muscles. This indicates that the effects of exercise on muscle activity were not significantly different between the concave and convex sides. Previous studies have highlighted that EMG activity tends to be higher on the convex side of scoliotic curves, suggesting a potential link between this overactivation of paraspinal muscles and Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS) [
9,
14,
15,
16]. On the contrary, de Oliveira et al., (2011) found no significant differences in the electromyographic amplitudes of the erector spinae muscles between the convex and concave sides [
20]. Similarly, Shiba et al. (2020) reported that there was no difference in multifidus and erector spinae muscle activation between the convex and concave sides of individuals with mild AIS and the control sides of healthy individuals [
19]. This discrepancy in findings may stem from methodological variances, such as differences in patient selection, a focus on specific types of scoliotic curves without adequate justification, or a failure to control for factors like improper posture [
21]. Considering these conflicting results, our study aimed to perform a more nuanced analysis. We specifically focused on dissecting the relationship between paraspinal muscle asymmetry and various types of scoliotic curves. This was done in response to previous studies not providing clear descriptions of curve classifications and recording levels, which could be crucial in understanding this relationship.
However, there was a significant main effect of exercise for both the TES and LES muscles. This means that the three different exercise types had different effects on muscle activity. The pairwise comparisons showed that all three exercise types were significantly different from each other for both the TES and LES muscles. The highest values were obtained for the TheraBand exercise, followed by the manual exercise, and finally the without exercise condition. Marchese et al. [
22] demonstrated that specific exercises tailored to individual curve patterns in scoliosis led to greater improvements in trunk muscle strength and endurance compared to generic exercises. This aligns with the present study’s finding that different exercise types elicit different responses. Bialek et al. [
23] found TheraBand exercises effective in increasing paraspinal muscle activity in individuals with scoliosis, supporting the present study’s observation of higher activation with TheraBand. They propose the elastic resistance of TheraBand provides progressive overload, potentially explaining its effectiveness. Fan et al. [
24] highlighted the importance of exercise specificity and dosage in scoliosis management. They emphasize the need for individualized programs considering curve type, severity, and muscle imbalances. The present study reinforces this, suggesting varying activation patterns across exercises. This paragraph showcases the study’s key finding- exercise type plays a crucial role in muscle activation for individuals with scoliosis. The specific exercise chosen can significantly impact the level of engagement, with the TheraBand option proving most effective in this study. This information can be valuable for healthcare professionals designing targeted exercise programs to address specific muscle activation needs in individuals with scoliosis.
There was also no significant interaction effect between exercise type and Cobb angle for either the TES or LES muscles. This indicates that the effects of exercise on muscle activity were not significantly different between individuals with Cobb angles less than 20 degrees and those with Cobb angles greater than 20 degrees. The pathological underpinnings of scoliosis extend far beyond the simple quantification of Cobb angle. Recent research exemplified highlights the multifactorial nature of the condition, encompassing not just curvature severity but also neuromuscular control deficits and biomechanical imbalances [
25]. This inherent complexity might explain the observed consistency in exercise-induced muscle activation across varying Cobb angles. Importantly, this study prioritizes assessing muscle activation itself, distinct from directly targeting Cobb angle correction. While Cebellos-Laita et al., [
26] suggest specific exercises can influence Cobb angle, others, Mohamed et al., [
27] emphasize the disassociation between muscle activation and curvature correction. This underscores the crucial need for research that delves into both aspects separately. Furthermore, the present study focuses on the short-term dynamics of muscle activation, excluding the long-term trajectory of Cobb angle progression. Long-term studies hint at the potential of exercise to prevent curve progression, but further exploration is necessary to elucidate the nuanced effects of specific exercise types on different Cobb angle presentations [
28].
However, there was a significant main effect of exercise for both the TES and LES muscles. This means that the three different exercise types had different effects on muscle activity, regardless of Cobb angle. The pairwise comparisons showed that all three exercise types were significantly different from each other for both the TES and LES muscles. The highest values were obtained for the TheraBand exercise, followed by the manual exercise, and finally the without exercise condition.
These results suggest that all three exercise types can be effective in increasing muscle activity in individuals with scoliosis. However, the TheraBand exercise appears to be the most effective, followed by the manual exercise, and finally the without exercise condition. These findings may have implications for the design of exercise programs for individuals with scoliosis. This study had several limitations. First, the sample size was relatively small. Future studies with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm these findings. Second, the study only included individuals with mild to moderate scoliosis. Future studies should investigate the effects of exercise in individuals with more severe scoliosis. Third, the study only investigated the short-term effects of exercise. Future studies should investigate the long-term effects of exercise on muscle activity and Cobb angle in individuals with scoliosis.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that all three exercise types can be effective in increasing muscle activity in individuals with scoliosis. However, the TheraBand exercise appears to be the most effective, followed by the manual exercise, and finally the without exercise condition. These findings may have implications for the design of exercise programs for individuals with scoliosis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H.; methodology, N.U.Y.; software, B.H. and C.S.; validation, N.U.Y.; formal analysis, B.H., C.S and P.D.; investigation, B.H., C.S and P.D.; resources, B.H. and C.S.; data curation, C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.H. and C.S.; writing—review and editing, B.H., C.S. and P.D.; visualization, C.S.; super-vision, B.H. and C.S.; project administration, B.H., C.S., N.U.Y. and P.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of XXX (approval number: XXX; date of approval: XXX).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants in this study
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang H, Guo C, Tang M, Liu S, Li J, Guo Q, et al. Prevalence of scoliosis among primary and middle school students in Mainland China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine. 2015;40(1):41-9. [CrossRef]
- Misterska, E.; Głowacki, J.; Głowacki, M.; Okręt, A. Long-term effects of conservative treatment of Milwaukee brace on body image and mental health of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0193447. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Reinhardt, J.; He, C.; Wong, M. Epidemiological study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Eastern China. J. Rehabilitation Med. 2017, 49, 512–519. [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [CrossRef]
- Falk B, Rigby WA, Akseer N. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: the possible harm of bracing and the likely benefit of exercise. The Spine Journal. 2015;15(6):1169-71. [CrossRef]
- Wilczyński, J.; Karolak, P. Relationship Between Electromyographic Frequency of the Erector Spinae and Location, Direction, and Number of Spinal Curvatures in Children with Scoliotic Changes. Risk Manag. Heal. Policy 2021, ume 14, 1881–1896. [CrossRef]
- Avikainen, V.J.; Rezasoltani, A.; Kauhanen, H.A. Asymmetry of Paraspinal EMG-Time Characteristics in Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clinical Spine Surgery. 1999;12(1):61-7. [CrossRef]
- Kwok, G.; Yip, J.; Cheung, M.-C.; Yick, K.-L. Evaluation of Myoelectric Activity of Paraspinal Muscles in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis during Habitual Standing and Sitting. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Halbertsma, J.P.K.; Veldhuizen, A.G.; Sluiter, W.J.; Maurits, N.M.; Cool, J.C.; van Horn, J.R. A preliminary study on electromyographic analysis of the paraspinal musculature in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 130–137. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, A.; Hai, Y.; Li, W.; Yin, L.; Guo, R. Asymmetric biomechanical characteristics of the paravertebral muscle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 65, 81–86. [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Li, Q. Effect of Core Stability Training on Correction and Surface Electronic Signals of Paravertebral in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Elattar, E.A.; Saber, N.Z.; Farrag, D.A. Predictive factors for progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a 1-year study. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabilitation 2015, 42, 111–119. [CrossRef]
- He C, Yang J-T, Zheng Q, Mei Z, Ma CZ-H. How do Paraspinal Muscles Contract during the Schroth Exercise Treatment in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)? Bioengineering. 2022;9(6):234. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Veldhuizen, A.G.; Halbertsma, J.P.K.; Maurits, N.M.; Sluiter, W.J.; Cool, J.C.; Van Horn, J.R. The Relation Between Electromyography and Growth Velocity of the Spine in the Evaluation of Curve Progression in Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2004, 29, 1011–1016. [CrossRef]
- Farahpour, N.; Ghasemi, S.; Allard, P.; Saba, M.S. Electromyographic responses of erector spinae and lower limb’s muscles to dynamic postural perturbations in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 645–651. [CrossRef]
- Stetkarova, I.; Zamecnik, J.; Bocek, V.; Vasko, P.; Brabec, K.; Krbec, M. Electrophysiological and histological changes of paraspinal muscles in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3146–3153. [CrossRef]
- Park K-h, Oh J-s, An D-h, Yoo W-g, Kim J-m, Kim T-h, et al. Difference in selective muscle activity of thoracic erector spinae during prone trunk extension exercise in subjects with slouched thoracic posture. PM&R. 2015;7(5):479-84. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-S.; Cynn, H.-S.; Won, J.-H.; Kwon, O.-Y.; Yi, C.-H. Effects of Performing an Abdominal Drawing-in Maneuver During Prone Hip Extension Exercises on Hip and Back Extensor Muscle Activity and Amount of Anterior Pelvic Tilt. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 320–324. [CrossRef]
- Shiba, editor Evaluation of Paraspinal Muscle Properties in Adolescents with Mild Idiopatic Scoliosis Using Surface EMG Power Spectral Analysis 2020.
- de Oliveira AS, Gianini PES, Camarini PMF, Bevilaqua-Grossi D. Electromyographic analysis of paravertebral muscles in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2011;36(5):E334-E9. [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Beom, J.; Ryu, J.S. Asymmetrical activation and asymmetrical weakness as two different mechanisms of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Marchese R, Du Plessis J, Pooke T, McAviney J. The Improvement of Trunk Muscle Endurance in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis Treated with ScoliBrace® and the ScoliBalance® Exercise Approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024;13(3):653. [CrossRef]
- Białek, M. Conservative treatment of idiopathic scoliosis according to FITS concept: presentation of the method and preliminary, short term radiological and clinical results based on SOSORT and SRS criteria. Scoliosis 2011, 6, 25–25. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ren, Q.; To, M.K.T.; Cheung, J.P.Y. Effectiveness of scoliosis-specific exercises for alleviating adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Marya, S.; Tambe, A.D.; Millner, P.A.; Tsirikos, A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: : a review of aetiological theories of a multifactorial disease. The Bone and Joint Journal 2022, 104B, 915–921. [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Laita, L.; Carrasco-Uribarren, A.; Cabanillas-Barea, S.; Pérez-Guillén, S.; Pardos-Aguilella, P.; DEL Barrio, S.J. The effectiveness of Schroth method in Cobb angle, quality of life and trunk rotation angle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabilitation Med. 2023, 59, 228–236. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.A.; Yousef, A.M. Impact of Schroth three-dimensional vs. proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation techniques in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized controlled study. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2021, 25, 7717–7725. [CrossRef]
- Kikanloo SR, Tarpada SP, Cho W. Etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a literature review. Asian spine journal. 2019;13(3):519. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).