1. Introduction
Solid-state batteries (SSBs) represent a pivotal advancement in the realm of energy storage technologies, poised as the next evolutionary step beyond the conventional lithium-ion batteries that have underpinned the development of modern portable electronics and the electric vehicle (EV) industry [
1,
2,
3]. This innovative battery type, by substituting traditional liquid or gel electrolytes with solid alternatives, ushers in a radical redesign of battery architecture [
1]. This transformation harbors the potential to significantly enhance the efficiency, safety, and durability of energy storage systems, promising to redefine energy usage across a broad spectrum of applications, from consumer electronics to large-scale energy storage solutions [
4]. The allure of SSBs lies in their multifaceted advantages over their liquid-based predecessors [
4,
5]. Central to these is the higher energy density afforded by solid electrolytes, which translates into longer-lasting power sources without the need for increased size or weight [
5]. This is particularly critical for the electric vehicle sector, which constantly seeks to extend range without adding bulk. Moreover, the shift away from liquid electrolytes markedly reduces the risk of leakage and battery fires, thereby enhancing safety and potentially accelerating the adoption of EVs and portable devices alike [
6].
The transition from liquid to solid electrolytes is more than a mere material swap; it's a fundamental reimagining of the battery's internal architecture [
7]. Solid electrolytes—be they ceramic, glass, sulfide, or polymer—introduce a diverse palette of materials each with unique properties tailored to specific applications [
7,
8]. This versatility enables the design of batteries that are not only more efficient and safer but also customizable to the needs of different technologies and industries. Such a transition marks a crucial step toward overcoming the limitations that have long hampered the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries. The adoption of solid electrolytes significantly alters the landscape of ion transport within the battery, providing pathways for ions to move between electrodes without the volatility associated with liquid counterparts [
9]. This shift has profound implications for the battery's overall efficiency and operational temperature range, potentially enabling solid-state designs to operate more effectively across a wider spectrum of conditions than traditional batteries [
9,
10]. Additionally, the precision with which these materials can be engineered allows for improved control over ion flow, thereby reducing energy loss and enhancing charging speeds [
11].
However, the introduction of solid electrolytes highlights the challenge of interface dynamics—the interactions at the boundaries between the solid electrolyte and the battery's electrodes [
12,
13]. These interfaces are critical to the battery's performance, influencing the efficiency of ion transfer and, consequently, affecting the battery's capacity and lifespan. Addressing these dynamics necessitates innovative material science approaches to ensure these interfaces remain stable and conducive to ion movement. As development progresses, SSB technology stands as a beacon of potential for the future of energy storage, with superior energy density, safety profile, and longevity [
14]. SSBs could play a crucial role in advancing renewable energy adoption, powering next-generation electronics, and transforming the automotive industry, not merely refining the technology but also scaling up production processes to make SSBs a viable and sustainable option [
14,
15].
The environmental impact of material extraction for SSBs, however, presents significant concerns [
16]. Key components like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are often sourced from ecologically sensitive areas where mining activities can disrupt ecosystems, pollute water sources, and contribute to deforestation and carbon dioxide emissions [
16,
17,
18]. Addressing these concerns necessitates more sustainable mining practices, less invasive extraction technologies, and regulations to protect ecosystems and communities [
17]. Moreover, the production of SSBs is inherently energy-intensive, requiring high-temperature sintering processes for solid electrolytes and precise assembly conditions [
19,
20]. Optimizing these processes for energy efficiency is paramount, with innovations such as lower-temperature synthesis methods and the integration of renewable energy into manufacturing facilities potentially reducing the carbon footprint associated with battery production significantly [
19].
The use phase of SSBs also offers considerable environmental advantages due to their higher energy density and efficiency, leading to longer lifespans and less frequent replacements [
21,
22,
23]. This reduces the demand for raw materials and the energy associated with manufacturing new batteries while enhancing safety and stability, thereby mitigating the risk of environmental contamination. Yet, as these batteries reach the end of their useful life, their disposal poses unique challenges due to their novel materials and complex structures [
22]. Traditional recycling methods may not be directly applicable, necessitating new technologies capable of efficiently recovering valuable materials. These efforts are crucial for minimizing waste, reducing the demand for virgin materials, and lessening the environmental impact of battery production [
23]. Establishing a circular economy for battery materials, where components are reused and recycled, becomes an essential goal for sustainable battery technology [
21].
Addressing the environmental implications of SSBs is not merely about overcoming challenges; it represents an opportunity to lead in the transition to a more sustainable and responsible energy storage future. Through collaborative efforts among researchers, industry stakeholders, policymakers, and communities, it is possible to develop SSB technologies that not only advance the frontiers of energy storage but also do so in a manner that respects and preserves the environment for future generations. This comprehensive approach to sustainability, emphasizing the development of less harmful material extraction processes, energy-efficient manufacturing practices, and innovative recycling and disposal methods, can significantly mitigate the environmental impact of SSBs [
24,
25]. Regulatory frameworks and industry standards that emphasize sustainability can further drive improvements across the sector, encouraging the adoption of best practices and supporting research into more eco-friendly materials and processes, marking a significant shift towards more reliable, efficient, and safer energy storage solutions with far-reaching impacts across multiple sectors [
24].
This review evaluates the environmental impact of SSBs across their lifecycle, compared with conventional lithium-ion batteries, to illuminate both the progress and challenges in harmonizing technological advancement with environmental sustainability. It delves into the environmental implications of manufacturing SSBs, from raw material extraction to emissions and novel materials' potential hazards, offering a comprehensive comparison with traditional battery production methods. Additionally, it assesses operational impacts, end-of-life management, and recycling challenges, highlighting technological and economic barriers as well as innovative recycling techniques. By exploring strategies for sustainable lifecycle management and showcasing successful case studies, the review underscores the importance of interdisciplinary research in advancing SSB technologies. It aims to foster a balanced approach to technological innovation and environmental stewardship, advocating for continued research and policy development to support the sustainable evolution of energy storage solutions.
2. Environmental Impact of SSB Manufacture
2.1. Raw Material Extraction and Processing
In the realm of SSB manufacture, the environmental impact starts at the very beginning with the extraction and processing of raw materials. This phase is crucial as it directly affects natural resources and dictates the overall sustainability of battery technology. The extraction of key materials such as lithium, used for the battery's anode, and various metals and ceramics for solid electrolytes, poses significant environmental challenges [
26,
27]. Mining activities for these materials can lead to habitat destruction, water contamination, and a decrease in biodiversity. Furthermore, the extraction processes are energy-intensive, contributing to a substantial carbon footprint. A study by Raabe [
26] has highlighted that the metal production is responsible for 40% of industrial greenhouse gas emissions, consumes 10% of global energy, involves mining 3.2 billion tons of minerals, and generates billions of tons in by-products annually. Consequently, enhancing the sustainability of metals is imperative. The author explains that the circular economy model falls short due to the demand for metals surpassing the supply of available scrap by approximately two-thirds. Even in the best-case scenario, a significant portion of metal demand—around one-third—will continue to rely on primary production, which is associated with substantial emissions. Furthermore, Raabe argue that discussions on the impact of metals on global warming often focus on mitigation strategies and socio-economic considerations, overlooking the critical role of materials science in advancing the metallurgical sector's sustainability. This oversight may stem from the characterization of sustainable metals as a global issue rather than a cohesive field of study. Yet, the environmental impact of producing over 2 billion tons of metals annually underscores the urgency of addressing sustainability not just from a technological standpoint but also through foundational materials research.
The processing of these raw materials further escalates the environmental impact, with significant energy consumption and emissions being a primary concern [
28,
29]. The refinement of extracted minerals into usable forms for battery manufacture requires high energy inputs, often sourced from fossil fuels, thereby exacerbating the carbon emissions problem. According to Igogo
et al. [
28] the mining industry, a significant consumer of energy and a primary supplier of raw materials for various sectors including renewable energy technologies, faces increasing pressure to lower its emissions as global demand for minerals rises with the economic advancement of low-income economies.
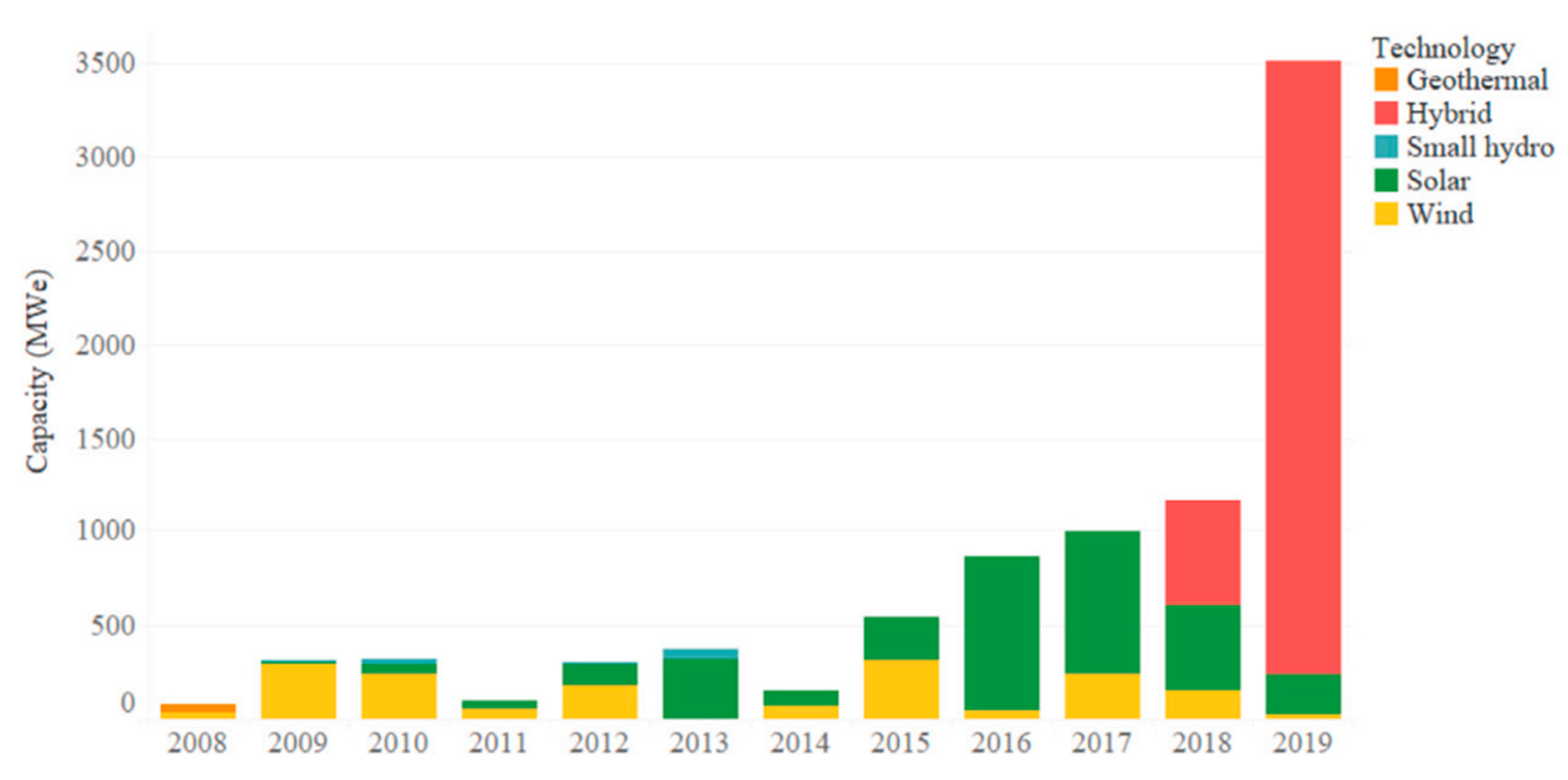
Figure 1 illustrates the trends in renewable energy projects from 2000 to 2019, highlighting a significant increase in the implementation of renewable energy by mining companies, particularly in recent years. Before the year 2000, renewable energy was almost non-existent in mining operations. However, there was a sharp increase in such projects by 2019, with the capacity of installed renewable systems growing from 42 MW per year in 2008 to 3,397 MW in 2019. Notably, the majority of the installations in 2018 and 2019 consisted of hybrid systems. These systems combine multiple technologies such as wind, solar, and energy storage, and are often supported by fossil fuels to mitigate the inconsistency of renewable energy production. The authors also explain that despite the financial appeal of reduced costs for wind and solar PV technologies, the adoption of renewable energy within mining remains limited, challenged by operational and technical complexities. Yet, integrating renewable energy—through increased energy efficiency, energy recovery, and direct use in electric, transportation, and thermal needs—presents a viable path to reduce carbon emissions and harness cost savings. The authors further explain that the feasibility of integrating renewables varies significantly with the mine's location, development stage, and whether it relies on external power or self-generation. Despite obstacles, strategic alliances between the mining and energy sectors, capacity building, information sharing, supportive government policies, and expanded research and development could facilitate a broader adoption of renewable energy, advancing the sector towards sustainability.
The impact on natural resources extends beyond the immediate environmental footprint of extraction and processing [
30,
31]. The demand for materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel is rapidly increasing, which raises concerns about the sustainability of these resources. The research by Ferrari
et al. [
30] emphasizes the increasing pressure on the supply of critical minerals essential for the production of SSBs, a cornerstone technology for the future of energy storage and electric vehicles. The group research underlines a critical junction at which the industry stands; without substantial progress in the recycling of these minerals and the innovation of alternative materials, the risk of supply shortages becomes increasingly likely. Such shortages pose a multifaceted threat, not only undermining environmental sustainability goals by hampering the shift away from fossil fuels but also jeopardizing the economic framework supporting the advancement of SSB technology. The potential scarcity of these vital components could lead to increased costs, slow down the adoption of green technologies, and ultimately impact the global push towards a more sustainable and electrified future. Furthermore, this situation highlights the need for a more circular economy in the materials sector, where recycling and reusing become as integral to the supply chain as mining and extraction currently are. It also calls for a concerted effort in research and development to identify and commercialize materials that can serve as viable substitutes for these critical minerals, ensuring the resilience and sustainability of the battery industry. Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining the pace of technological innovation and securing a sustainable future for energy storage systems.
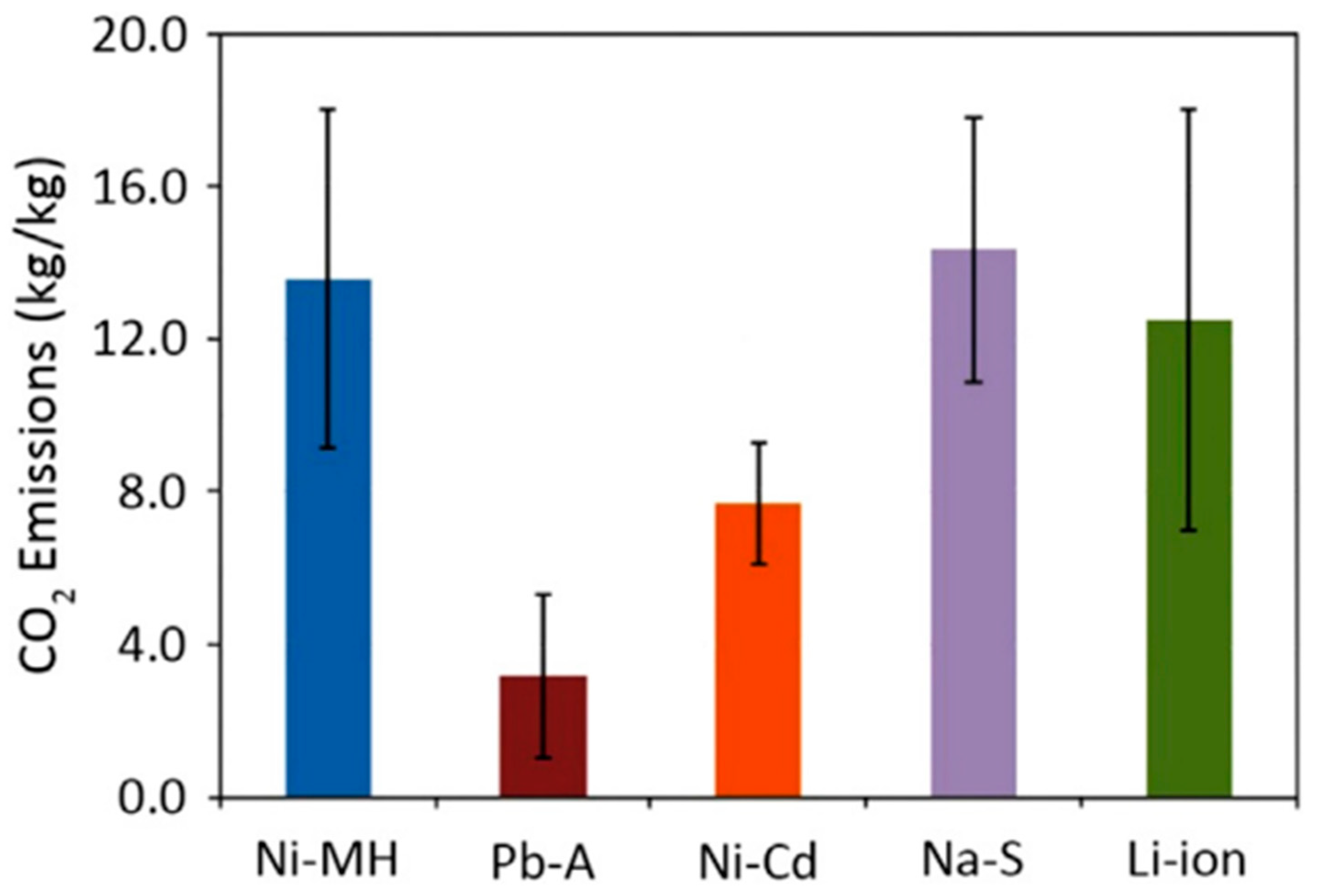
Given these challenges, there is a pressing need for the SSB industry to address environmental concerns from the outset. This includes investing in research and development efforts aimed at reducing energy consumption and emissions throughout the raw material extraction and processing stages, as well as exploring sustainable mining practices and alternative materials [
32]. The work by Dehghani-Sanij
et al. [
32] underscores the critical need for embracing a comprehensive perspective on environmental sustainability within the realm of battery production. The authors explain that the greenhouse gas emissions per kilogram of battery typically exceed direct CO
2 emissions, with Pb-A batteries having the smallest amount of CO
2 emissions (see
Figure 2). By advocating for the rigorous application of lifecycle assessments, their work illuminates the necessity to thoroughly evaluate and address the ecological ramifications of SSB manufacturing, from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal or recycling of end-of-life products. This approach is pivotal in identifying the direct and indirect environmental impacts associated with the production process, enabling the industry to devise strategies that minimize the depletion of natural resources and mitigate adverse effects on the ecosystem. Implementing such a holistic strategy not only facilitates the transition towards more eco-friendly manufacturing practices but also serves as a beacon for the integration of sustainability principles in the development of advanced battery technologies. Furthermore, by setting robust standards for environmental stewardship, the battery industry can contribute significantly to the global efforts aimed at reducing carbon footprints and combating climate change. This forward-thinking approach also fosters innovation in material efficiency and recycling technologies, ultimately paving the way for the realization of a circular economy in energy storage solutions.
2.2. Manufacturing Process of SSBs
The manufacturing process of SSBs signifies a pivotal departure from traditional methodologies employed in the production of conventional lithium-ion batteries. This shift is primarily due to the unique assembly requirements and material composition inherent to solid-state technologies. SSBs leverage a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid or gel electrolytes found in lithium-ion batteries, necessitating different synthesis and assembly techniques. These techniques, while promising higher energy densities and improved safety profiles, introduce distinct challenges and environmental implications, particularly in terms of energy consumption and the emissions generated during production [
33,
34,
35]. For instance, the sintering process required to create solid electrolytes is energy-intensive, potentially increasing the carbon footprint of the manufacturing phase compared to lithium-ion battery production [
33].
When comparing the manufacturing processes of SSBs to those of conventional lithium-ion batteries (see
Table 1), it becomes evident that each has its unique environmental footprint. Lithium-ion battery production is well-established, with optimization efforts focused on reducing energy use and emissions [
36]. However, it still relies heavily on the use of volatile organic compounds and presents risks related to the handling and disposal of toxic materials [
36]. In contrast, SSB manufacturing, while eliminating the need for these hazardous liquid electrolytes, requires high-temperature processes for the synthesis of solid electrolytes and the integration of components, leading to significant energy demands [
37].
The emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) and other pollutants during the manufacturing process of SSBs is a subject of growing concern [
37]. The high-temperature processes not only consume substantial amounts of energy, often derived from non-renewable sources, but also contribute to GHG emissions. Additionally, the extraction and refinement of raw materials necessary for SSB components, such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt, further contribute to the environmental burden [
37]. A study made by Keshavarzmohammadian
et al. [
37] examined the cradle-to-gate environmental repercussions of developing a sulfur-based solid-state lithium pyrite battery designed for use in electric vehicles. Employing a process-based attributional life cycle assessment approach, the authors integrated data from lab research, existing literature, U.S. patents, and the US-EI 2.2 life cycle inventory database to calculate the materials and energy consumption involved in the battery's projected production and assembly phases. The battery, weighing 440 kg with a specific energy capacity of 182 Whkg
−1, was engineered for an 80 kWh energy storage capacity and 100 kW output, enabling it to drive a full-size electric vehicle over a distance of 200 miles. Their findings reveal a cumulative energy demand (CED) of 3300 MJ kWh
−1 and a global warming potential (GWP100) of 199 kg CO
2 eq. kWh
−1 over a century-long perspective. The authors explain that major contributors to the overall CED (75%) and GWP100 (73%) include direct and upstream energy use in clean dry-room operations, with the cathode paste also being significant (10% for CED and 6% for GWP100). The group concluded that identifying areas for process improvements and cost reduction, particularly in clean dry-room operations and cathode paste production, is crucial. When compared to the well-to-wheel energy and emissions metrics of a similarly sized and ranged vehicle, the environmental impact of producing the pyrite battery is lower, offering a higher specific capacity than existing LIBs, with comparable CED and GWP100 figures.
Therefore, to fully realize the environmental advantages of SSBs, it is imperative to innovate and implement more energy-efficient manufacturing processes. This includes the exploration of low-temperature synthesis methods for solid electrolytes and the adoption of renewable energy sources in production facilities [
38,
39,
40]. Moreover, reducing the reliance on critical raw materials through material innovation and improving recycling methods will be key to minimizing the environmental impact. Liu and colleagues [
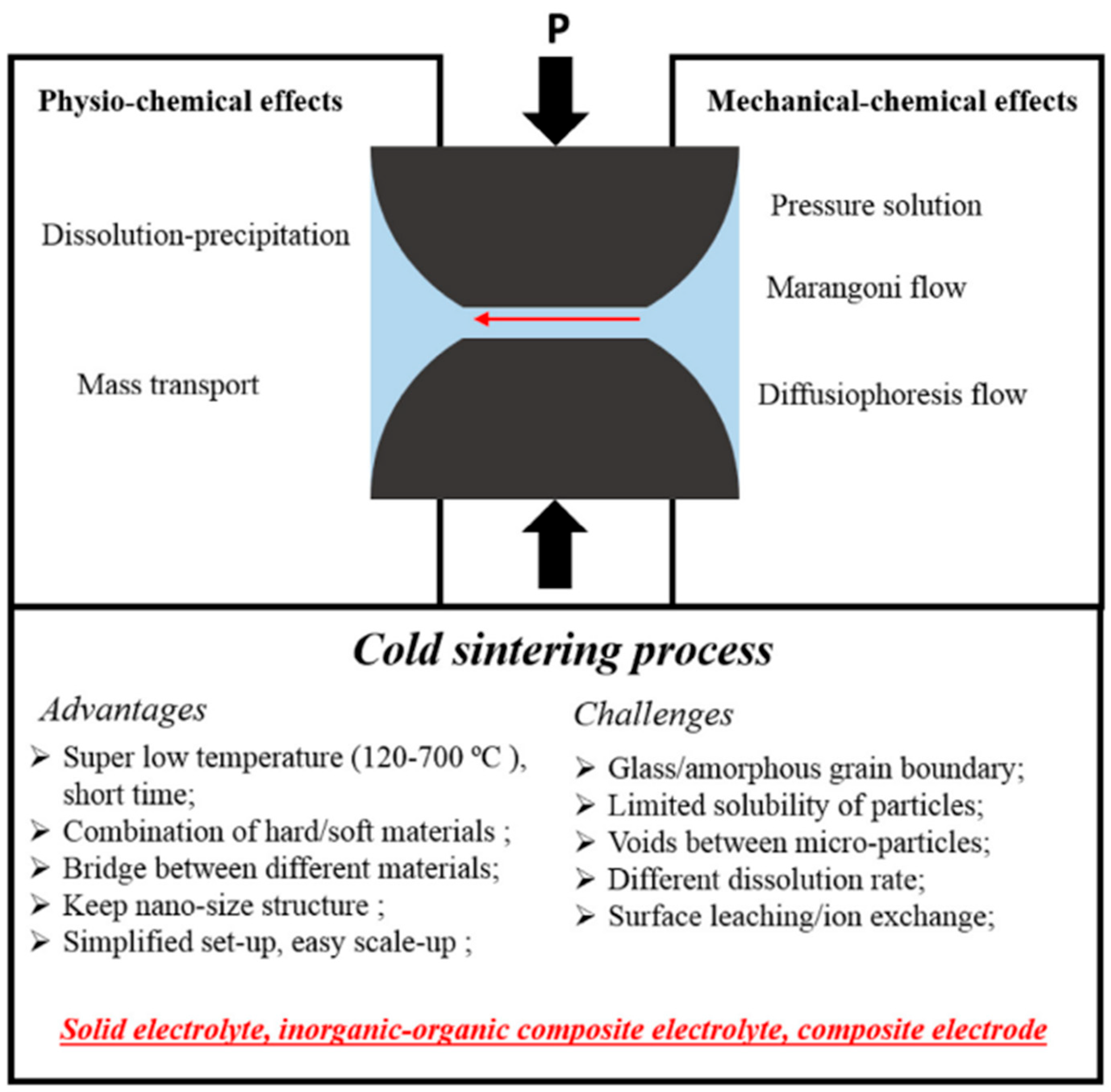
40] explain that the cold sintering process (CSP) has emerged as a promising low-temperature sintering technique that presents a viable alternative to traditional high-temperature thermal sintering processes used in the manufacturing of solid-state electrolytes and electrodes for batteries (see
Figure 3). Unlike conventional methods that often lead to the formation of blocking layers due to side reactions at high temperatures, CSP enables the densification of electrolyte and electrode materials at temperatures below 300°C, offering a significant reduction in thermal stress and potential damage. The authors argues that the process works through the dissolution of particle edges in a solvent, followed by the evaporation of the solvent and precipitation of the dissolved species, effectively filling voids between particles. This method not only maintains the structural integrity of the components but also allows for the creation of inorganic and inorganic-organic composites. The initial findings indicate reasonable performance of SSBs manufactured using CSP, pointing to its potential to revolutionize materials processing in battery production. The authors conclude that despite its promising start, the application of CSP in SSBs requires further refinement to meet practical application standards. Key issues that need addressing include the enhancement of ionic conductivity, which is dependent not only on the material density but also on the bonding at grain boundaries. Further research is needed to understand the chemical and physical properties of these boundaries to improve conductivity. Additionally, the solubility of some target materials remains a challenge, necessitating the use of additives to enhance bonding and conductivity. Moreover, the compatibility of composite cathodes with CSP needs careful consideration to prevent chemical instability or dissolution. Advanced protective coatings and the exploration of different additives could broaden the applicability of CSP. Looking ahead, scaling up CSP for larger-format SSBs will require integration with cost-effective manufacturing techniques like tape-casting, which could potentially allow for the large-scale production of advanced battery systems.
2.3. Potential Environmental Hazards Associated with Novel Materials Used in SSBs
The introduction of SSBs introduces a spectrum of potential environmental hazards, primarily due to the novel materials essential for their manufacture. The core components, such as lithium metal for anodes and various ceramics or sulfides for solid electrolytes, pose distinct challenges. Lithium extraction, critical for SSB efficiency, is notorious for its water-intensive nature, contributing to water scarcity and contamination issues in vulnerable ecosystems [
41,
42]. Moreover, the procurement of ceramics and rare earth elements for solid electrolytes involves processes that may lead to substantial habitat disruption and biodiversity loss, highlighting a crucial area for environmental concern [
41].
The environmental impact extends to the manufacturing phase, where the use of sulfide-based solid electrolytes introduces risks of toxic gas release. Improper handling or battery failure can result in the emission of hydrogen sulfide, a gas with significant health risks, necessitating stringent controls and safety protocols in manufacturing and recycling facilities [
43,
44]. Additionally, the synthesis processes for these electrolytes typically demand high temperatures and involve hazardous chemicals, leading to elevated greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to air and water pollution [
45].
Addressing these environmental challenges requires a multifaceted approach. Research into sustainable material alternatives that reduce reliance on water-intensive and ecologically damaging extraction processes is imperative. Moreover, the development of cleaner, energy-efficient manufacturing techniques and the implementation of comprehensive recycling programs are critical for mitigating the environmental impacts of SSBs. These strategies must be supported by robust regulatory frameworks and industry standards that prioritize environmental protection and resource conservation [
46,
47].
Future advancements in SSB technology must, therefore, balance performance gains with environmental sustainability. This includes leveraging life cycle assessments to understand and minimize the ecological footprint of battery production, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Innovations in material science and engineering, aimed at replacing hazardous substances with eco-friendly alternatives, and improvements in recycling technologies, are essential for ensuring that SSBs contribute positively to the global transition towards sustainable energy solutions [
48,
49,
50].
3. Usage and Operational Environmental Impact
3.1. Energy Efficiency of SSBs in Application
The transition to SSBs represents a paradigm shift in the landscape of energy storage technologies, promising not only improvements in safety and capacity but also significant advancements in energy efficiency. SSBs, by virtue of their construction, offer a more stable and efficient platform for energy storage and release, potentially reducing energy losses during charge and discharge cycles compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries [
51,
52]. This efficiency gain is pivotal, as it directly impacts the operational environmental footprint of devices and systems powered by these batteries, from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage solutions.
One of the hallmark advantages of SSBs is their ability to maintain higher levels of efficiency over a wider range of temperatures. This is due to the solid electrolyte's superior thermal stability, which minimizes efficiency losses in extreme conditions [
53]. Consequently, the operational energy efficiency of SSBs can contribute to a reduction in the overall energy consumption of electronic devices and electric vehicles, leading to a decrease in the environmental impact associated with their use [
53]. For instance, in electric vehicles, the enhanced efficiency of SSBs could result in longer ranges per charge, thereby reducing the frequency of charging sessions and the associated energy demand from the grid [
54].
Moreover, the intrinsic characteristics of SSBs, such as their reduced risk of leakage and higher energy density, contribute to their longer lifespan [
55]. This longevity further diminishes the environmental impact over the operational life of the battery, as fewer replacements are needed, thereby conserving the resources and energy required for battery production, distribution, and disposal. Additionally, the extended battery life translates to less waste and a lower volume of batteries entering the recycling stream, easing the burden on recycling facilities and reducing the overall environmental footprint [
55].
Addressing the operational environmental impact of SSBs, particularly their energy efficiency, is crucial for evaluating their role in sustainable energy systems. As research into solid-state technology progresses, it is imperative to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments that consider not only the manufacturing and disposal phases but also the operational efficiency and its implications for environmental sustainability [
56,
57]. Such assessments will be instrumental in guiding the development of SSBs that not only meet the technical and safety requirements of modern energy storage applications but also align with the global goals for environmental protection and sustainability.
3.2. Comparison of the Operational Environmental Footprint with Traditional Battery Technologies
Understanding the operational environmental footprint of SSBs necessitates a detailed comparison with traditional battery technologies, particularly LIBs, which dominate current energy storage applications. This comparison revolves around several key factors, including energy efficiency, durability, and the overall lifecycle impact of these technologies [
58,
59]. SSBs, with their solid electrolytes, offer a significant leap in energy efficiency due to lower internal resistance, which reduces energy loss during charging and discharging cycles compared to their Li-ion counterparts [
59]. This inherent efficiency potentially leads to a reduced operational energy demand for devices and systems powered by SSBs, thereby contributing to a lower environmental footprint in terms of both direct energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions [
58].
Moreover, the operational durability of SSBs significantly surpasses that of traditional LIBs. This durability stems from the solid electrolytes' resistance to degradation mechanisms, such as electrolyte evaporation and dendrite formation, which plague LIBs [
60,
61]. Consequently, the extended lifespan of SSBs reduces the frequency of battery replacement, diminishing the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of batteries [
61]. This aspect is particularly relevant in applications with high energy demands and long operational life expectancies, such as electric vehicles and stationary energy storage systems, where the longevity of SSBs can lead to a notable decrease in the lifecycle carbon footprint [
60].
The operational environmental footprint of batteries is also influenced by the materials used in their construction. SSBs utilize novel materials that, while enhancing performance, may have different extraction and processing impacts compared to those used in LIBs [
62]. It is essential to consider these material impacts in a holistic assessment of operational environmental footprints. For instance, if the extraction of novel solid electrolyte materials requires more energy-intensive processes or involves more significant environmental degradation, these factors could offset the operational efficiency gains of SSBs. Thus, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis is required to fully understand and compare the environmental implications of these battery technologies [
63].
While SSBs exhibit promising operational advantages over traditional LIBs, including improved energy efficiency and durability, a thorough comparison of their environmental footprints requires consideration beyond immediate operational benefits. It necessitates an in-depth lifecycle analysis that encompasses material extraction, manufacturing, use, and end-of-life stages. Only through such a comprehensive approach can the true environmental benefits of SSB technology be accurately assessed and optimized. Future research should focus on not only advancing the technical performance of SSBs but also minimizing their environmental impact across the entire lifecycle, ensuring that these innovative energy storage solutions contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
3.3. Lifecycle Analysis and Overall Carbon Footprint during Operational Phase
The operational phase of SSBs represents a crucial period in their lifecycle, where the environmental impact, particularly the carbon footprint, comes into sharp focus. Lifecycle analysis (LCA) is a pivotal tool in quantifying this impact, offering insights into the emissions and energy consumption patterns unique to SSBs compared to traditional battery technologies [
64,
65]. Preliminary studies suggest that SSBs, with their enhanced energy density and efficiency, have the potential to significantly lower GHGs emissions during use, especially in high-demand applications like EVs and grid storage [
65]. This reduced carbon footprint is attributed to the decreased frequency of charging and longer operational life, leading to less energy drawn from potentially non-renewable sources [
64].
Comparatively, traditional LIBs, while having undergone significant improvements in efficiency and lifespan, still exhibit higher lifecycle GHGs emissions due to less optimal energy densities and the degradation of liquid electrolytes over time [
64]. The operational efficiency of SSBs, therefore, not only contributes to a reduction in direct operational emissions but also influences the broader lifecycle emissions profile of the battery. Enhanced durability and efficiency reduce the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, thereby diminishing the cumulative environmental impact associated with manufacturing, transportation, and disposal processes [
66].
However, the overall carbon footprint of SSBs during the operational phase cannot be fully understood without considering the source of electricity used for charging. The benefits of SSBs are maximized when paired with renewable energy sources; conversely, if the electricity is derived from fossil fuels, the potential environmental advantages may be negated [
67]. Therefore, the integration of SSBs into systems that prioritize or exclusively use renewable energy is crucial for realizing their potential in reducing lifecycle carbon emissions.
Future research and development in SSB technology must prioritize not only advancements in performance and safety but also the minimization of environmental impacts across all lifecycle stages, with a particular focus on the operational phase. This includes continuous improvement in material efficiency, the integration of low-impact manufacturing processes, and the development of effective recycling and end-of-life management strategies. Such comprehensive lifecycle assessments will be vital in guiding the sustainable deployment of SSBs, ensuring that their adoption contributes positively to the global effort to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change [
68,
69].
4. End of Life and Disposal of SSBs
In recent years, there has been a surge in the demand for energy storage solutions to support the growing reliance on renewable energy sources and the transition towards electric vehicles [
70]. As a result, SSBs have emerged as a promising technology for energy storage due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and improved safety [
71], compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These batteries employ a solid electrolyte instead of liquid electrolytes, offering higher energy densities and greater stability. SSBs have the potential to revolutionize the energy storage industry. However, like any technology, SSBs have a limited lifespan and eventually reach their end of life. This raises important questions regarding the disposal and recycling of SSBs to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource utilization [
72]. In this review, we will explore the challenges associated with the disposal of SSBs, the environmental risks associated with landfills and incineration, and the regulations and policies governing battery disposal.
4.1. Challenges in the Disposal of SSBs
SSBs are a promising technology for energy storage due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries [
73]. However, the disposal of SSBs presents several technical and logistical challenges [
74]. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, SSBs contain a solid electrolyte, which makes the recycling process more complex. One of the main challenges is the difficulty in material separation. SSBs consist of complex structures that involve multiple layers of solid electrolytes and electrodes [
22]. These layers are tightly integrated, making it difficult to separate and recover valuable materials without damaging their chemical structure. In addition to material separation challenges, the absence of a standardized battery design poses another obstacle in the recycling process [
75]. Due to the lack of a standardized design, each SSB may have unique configurations and construction methods. This variability in design makes it challenging to develop efficient and cost-effective recycling processes that can accommodate different battery architectures. Furthermore, the lack of established supply chains adds to the difficulties in recycling SSBs [
76]. Without established supply chains for collecting, transporting, and processing spent SSBs, it becomes challenging to recycle these batteries efficiently and effectively on a large scale while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, the disposal of SSBs raises concerns about the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment [
77]. The improper disposal of SSBs can lead to the leaching of toxic chemicals and heavy metals, posing significant environmental risks.
4.2. Environmental Risks Associated with Landfills and Incineration
In today's world, the increasing use of batteries in various industries has led to a growing concern about their end-of-life management and disposal. This concern stems from the potential environmental risks associated with improper disposal methods, such as landfilling and incineration [
74]. These risks are particularly relevant for SSBs, which are gaining prominence due to their high energy density and potential applications in electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage [
78]. SSBs offer advantages such as higher energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, their end-of-life management poses unique challenges due to their complex structure and materials composition [
22].
The disposal of SSBs through landfill or incineration can have detrimental environmental consequences [
79]. Landfilling SSBs can lead to the release of hazardous substances into the surrounding soil and groundwater. These substances can contaminate water sources and have long-term impacts on ecosystems. Incineration of SSBs can also release toxic emissions into the air, contributing to air pollution and potentially causing harm to human health [
80]. In addition to the direct environmental risks, landfilling and incineration of SSBs also lead to resource wastage [
81]. These batteries contain valuable and scarce materials, such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese [
78]. Disposing of SSBs in landfills or incinerating them means losing the opportunity to recover and reuse these valuable resources [
82]. Toxic pollutants from landfills and incineration may lead to soil and water quality degradation. Over time, this bioaccumulation can significantly disrupt ecological balances, leading to the potential collapse of local ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, and diminished ecosystem services upon which human societies often rely for food security and other needs [
83]. On the other hand, the health implications for humans resulting from improper battery disposal can be severe. Chronic exposure to heavy metals, for instance, can result in a range of health issues including neurological and developmental disorders, organ damage, and increased cancer risk. Moreover, the environmental degradation from battery pollutants impacts resources such as clean water and arable land, vital for human survival and health. Therefore, promoting sustainable disposal and treatment technologies for SSBs is crucial for minimizing these long-term health risks [
78].
4.3. Regulations and Policies Governing Battery Disposal
Due to the environmental risks associated with battery disposal, many countries have implemented regulations and policies to govern the proper handling [
81] and disposal of batteries, including SSBs. These regulations and policies aim to ensure the safe and responsible management of batteries throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. They often include guidelines for the collection, transportation, storage, and treatment of batteries, as well as requirements for recycling and resource recovery [
84]. SSBs have different characteristics and recycling requirements compared to lithium-ion batteries. Some regulations initially designed for traditional lithium-ion batteries may not fully cover every aspect of SSB recycling [
72]. These batteries contain hazardous materials, such as lithium and other toxic substances, which require careful handling during disposal to prevent contamination and hazardous waste accumulation.
Governments across the world have established regulations and policies to ensure proper battery disposal. For example, in Europe, the Batteries Directive (Directive 2006/66/EG) [
85] specifically does not differentiate SSBs from other battery types, but new regulations are proposed to be more inclusive regarding different battery chemistries and technologies. The European Union’s Batteries Directive has been criticized for being too general, and the lack of specific provisions for newer technologies like solid-state and lithium-ion batteries has been acknowledged. The European Green Deal and the Circular Economy Action Plan propose a new Batteries Regulation to better address these modern requirements [
82].
The European Union has recognized the need to strengthen the functioning of the internal market and promote a safe, circular, and sustainable value chain for all batteries, including those used in electric vehicles [
86]. In Brazil, automotive batteries have been recycled for several years, while the recycling of other types of batteries is just starting [
87]. To ensure efficient battery collection, it is essential to engage the population and inform them about the laws and regulations regarding battery disposal. This will help increase awareness about the importance of disposing of batteries with higher concentrations of heavy metals or toxic substances separately from domestic garbage [
88].
In the United States, it is essential to note that the mentioned regulations like the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) [
89] and the Universal Waste Rule [
90] are indeed applicable, but the specific requirements for battery recycling and disposal can greatly vary between states. Moreover, initiatives like the ReCell Center are working towards improving battery recyclability and are involved in developing new recycling technologies [
72,
91]. States like California have implemented stricter rules, requiring producers to establish take-back programs for used batteries and encouraging recycling through financial incentives. In China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has an emphasis on creating a closed-loop through recycling for electric vehicle batteries, including efforts to recycle and reuse battery materials. However, there might not be a specific mention of SSBs in the MIIT policy as of the current sources [
72]. These policies aim to develop a circular economy, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices in battery production and disposal.
5. Recycling and Reuse of SSBs
SSBs diverge significantly from traditional lithium-ion batteries in their construction and material use [
92,
93]. Unlike conventional batteries that utilize liquid electrolytes, SSBs employ solid electrolytes and electrodes that are integrated in a compact and dense matrix. This integration enhances battery performance and safety but complicates recycling processes [
93]. The extraction of valuable materials such as lithium, electrolyte salts, and other metals from SSBs is hindered by their solid-state nature. In traditional batteries, liquid electrolytes can be relatively easily drained and separated, but in SSBs, the solid electrolytes are intimately bonded with other materials, necessitating more complex and potentially damaging processes to separate and recover them [
93,
94]. Current technologies, which are primarily adapted from conventional battery recycling methods, are often inadequate for dealing with the tightly bound materials in SSBs, resulting in lower recovery efficiencies and potential damage to the integrity of the recyclable materials [
95]. SSBs are designed to withstand significant physical stresses, which makes them safer and more durable but also harder to disassemble [
93]. Mechanical disassembly processes, which are crucial for the initial stages of recycling, must be adapted to handle the robust nature of SSBs without causing thermal runaway—a risk that is mitigated in SSBs during operation but can become a concern during recycling if improper methods are applied [
96].
Establishing effective recycling processes for SSBs is not merely a technical challenge but also a financial one. The development of new recycling technologies that can efficiently process SSBs requires: i) Capital investment: Significant investment in research and development is necessary to innovate and deploy recycling methods that can effectively handle the unique properties of SSBs [
97]. This includes funding for the development of specialized machinery and facilities capable of processing solid electrolytes and tightly integrated battery structures; ii) Infrastructure development: Beyond the machinery, there is a need for building or modifying existing facilities to accommodate new processes [
97]. This includes the construction of secure environments that can safely handle the disassembly and material recovery stages, taking into account the specific safety requirements needed to manage the risks associated with SSB materials.
Additionally, the economic viability of recycling SSBs is heavily influenced by the market dynamics of the recovered materials. Factors influencing this include: i) Fluctuating demand and prices [
98,
99]: The demand for materials like lithium is projected to grow as the electric vehicle market expands, but this demand can be volatile and subject to economic cycles, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Prices for lithium and other critical materials recovered from SSBs can fluctuate significantly, impacting the profitability and sustainability of recycling operations; ii) Quality and purity of recovered materials [
100]: The economic return on recycled materials also depends on their purity and the cost of processing them to a usable quality. Materials recovered from SSBs often require additional purification steps to reach the quality standards demanded by battery manufacturers, adding to the complexity and cost of recycling [
94].
The recycling of SSBs presents a range of technological and economic challenges that must be addressed to make this process viable and sustainable. Overcoming these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach involving advancements in technology, substantial financial investments, and strategic market interventions. As the adoption of SSBs grows, driven by their advantages over traditional batteries, the development of effective recycling technologies will play a critical role in supporting the sustainable growth of the battery industry and the broader transition to renewable energy sources.
5.1. Overview of Existing Recycling Methods for Batteries
Recycling batteries is a complex process that involves several stages, each critical for efficient material recovery and environmental sustainability. The primary methods include mechanical, pyrometallurgical, and hydrometallurgical processes, each suited to different components and types of batteries: i) Mechanical Recycling [
93] is the initial step in the battery recycling chain. This process starts with the shredding of batteries to reduce their size and make the materials easier to handle. Shredders break down batteries into smaller fragments, which are then sorted using advanced techniques. Air classification uses air streams to separate light from heavy materials, allowing for the efficient isolation of valuable metallic components [
101]. Magnetic separation takes advantage of the magnetic properties of metals like iron and nickel, pulling them from the mixed debris [
102]. Screening further refines the process by sorting the shredded battery fragments based on size, ensuring that subsequent recycling stages are more targeted and effective; ii) Pyrometallurgical Recycling involves the treatment of battery materials at high temperatures [
72,
103]. This process is primarily used to recover valuable metals such as nickel, cobalt, and copper, which have significant industrial and economic value. During smelting, battery components are exposed to temperatures that melt the metals, allowing them to be separated from the slag. However, this method is less effective for recovering lithium, as it tends to evaporate at high temperatures due to its high reactivity and low boiling point. This limitation necessitates alternative methods for lithium recovery to optimize resource utilization; and iii) Hydrometallurgical Recycling [
104] contrasts with pyrometallurgy by using chemical solutions to dissolve metals from processed battery materials. The process starts with leaching, where acids or bases break down the solid waste to release metals into a solution. Factors like the choice of chemical, temperature, and concentration are critical to maximize efficiency [
104]. After leaching, the solution undergoes solvent extraction and precipitation to refine and recover the metals. Solvent extraction uses selective chemicals that bond with specific metals, facilitating their separation. Precipitation then isolates these metals by altering the chemical conditions of the solution, such as its pH, to convert dissolved metals into a solid form that can be easily collected and reused [
104].
The interplay between these methods highlights a multi-faceted approach to battery recycling. Mechanical processes prepare the batteries for more detailed chemical separation, while pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical methods handle the complex chemistry of battery components [
105]. Each method has its strengths and limitations, requiring ongoing innovation and adaptation, especially as new battery technologies like SSBs enter the market. These newer technologies present unique challenges due to their dense, integrated construction and lack of liquid electrolytes, which necessitates modifications in traditional recycling approaches [
106].
Advancements in battery recycling are critical for managing the lifecycle of battery materials sustainably [
93]. They help minimize environmental impacts, conserve natural resources, and support the recycling industry's adaptation to changing technologies. As the demand for batteries grows, particularly for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, improving recycling technologies becomes increasingly important to ensure that battery materials are not only recovered efficiently but also returned to the supply chain in a form that meets industry standards for reuse [
93].
5.2. Innovations in Recycling: Emerging Technologies and Methodologies
The recycling landscape of SSBs is undergoing significant transformations, driven by breakthrough technologies and innovative methodologies that aim to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and boost sustainability throughout the recycling lifecycle [
97]. These advancements are crafted not only to tackle the unique challenges posed by SSBs but also to improve the environmental footprint of the entire recycling process.
Direct Recycling Technologies [
107] represent a significant shift in the approach to recycling SSBs. Unlike conventional recycling methods that break down battery components into their constituent metals, direct recycling targets the preservation and reuse of electrode materials in their intact form. This method is particularly advantageous as it retains the unique properties of electrode materials, minimizing the need for extensive reprocessing and thus conserving energy and resources. By reducing the number of processing steps required, direct recycling also decreases operational costs and lessens the environmental impact associated with these processes [
107].
Electrohydraulic Fragmentation [
108] is an innovative approach that uses shock waves to disassemble battery components. This method allows for precise material separation within the complex structures of SSBs, promoting more efficient disassembly. The precision of electrohydraulic fragmentation ensures that valuable materials are not lost or degraded during the separation process, addressing a common issue with more invasive mechanical methods [
108]. This technique leads to a cleaner and more efficient separation, improving the purity of recovered materials and enhancing the sustainability of the recycling process.
Enhanced Leaching Techniques [
109] mark a pivotal evolution in battery recycling technologies. Traditional leaching processes typically involve harsh chemicals that may harm the environment. Innovations such as ultrasonic-assisted leaching are revolutionizing this landscape. Ultrasonic leaching enhances the penetration of solvents into solid materials through high-frequency sound waves, thereby increasing the efficiency of the metal recovery process [
95]. The integration of eco-friendly solvents into the leaching process also diminishes the environmental impact, aligning with global initiatives to foster green technologies in industrial applications.
Closed-loop Recycling Systems [
110] represent the apex of sustainable recycling methodologies. These systems are meticulously designed to recover every possible material from a spent battery and reintroduce them into the manufacturing cycle. By enabling the complete recycling of all battery components, closed-loop systems significantly minimize waste and the need for new, virgin materials. This approach not only conserves natural resources but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with the production of new batteries. Implementing closed-loop recycling for SSBs poses significant challenges due to the integrated nature of these batteries, yet it remains a vital objective for attaining genuine sustainability in battery production and recycling.
As the field of SSB recycling continues to develop, these pioneering technologies and methodologies are set to play a decisive role in sculpting a more sustainable future. The introduction of direct recycling, electrohydraulic fragmentation, enhanced leaching techniques, and closed-loop recycling systems not only meets the immediate needs of the recycling industry but also establishes a new benchmark for environmental stewardship across the entire lifecycle of battery technologies. With ongoing research and development pushing the limits of current capabilities, the potential for substantial reductions in environmental impact and enhancements in resource efficiency is both promising and imminent.
6. Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are produced on a large scale to address the escalating demand for sustainable energy solutions across consumer electronics, renewable energy systems, and electric vehicles. However, the growing accumulation of spent LIBs at the end of their lifecycle poses significant environmental challenges and raises concerns regarding the sustainability of these manufacturing processes.
The interest in SSBs, which utilize solid electrolytes instead of traditional liquid electrolytes, is increasing due to their superior safety, enhanced thermal and electrochemical stability, and greater energy density. As SSBs approach commercial viability, the imperative to recycle lithium and other battery components becomes critical to prevent the environmental burden of non-recoverable waste at the end of their lifecycle. To this end, insights from the recycling of conventional LIBs are invaluable in preempting the potential challenges associated with SSB recycling. Battery recycling represents a viable solution to these issues, promoting environmental protection and advancing sustainable manufacturing practices. Research and development efforts are underway to devise efficient and eco-friendly methods to reclaim lithium from SSBs, thus supporting the development of a circular economy for critical materials such as lithium [
111,
112,
113].
Although the SSB market is still under development and not yet at mass production, it is crucial to begin establishing an economical and energy-efficient recycling infrastructure. Experiences gleaned from the recycling of conventional materials suggest that adjustments in separation processes, such as modifications to temperature, concentration, and other parameters, are necessary for SSBs. Compared to conventional LIBs, recent studies have highlighted the potential of organic acids like citric acid, which serve as complexing agents and provide necessary acidification, to effectively separate electrode materials in lithium SSBs, offering improvements over traditional methods that use HCl [
114]. This strategy also avoids the issues of lithium residues from liquid electrolytes, thereby preserving the stoichiometry of the cathode materials and enhancing their potential for re-synthesis. These challenges present an opportunity for a profound transformation in current industrial practices, emphasizing the development and exploitation of emerging battery technologies with an inherent focus on recyclability.
6.1. Analysis of Successful Implementations of Recycling and Sustainable Practices in SSB Lifecycle Management
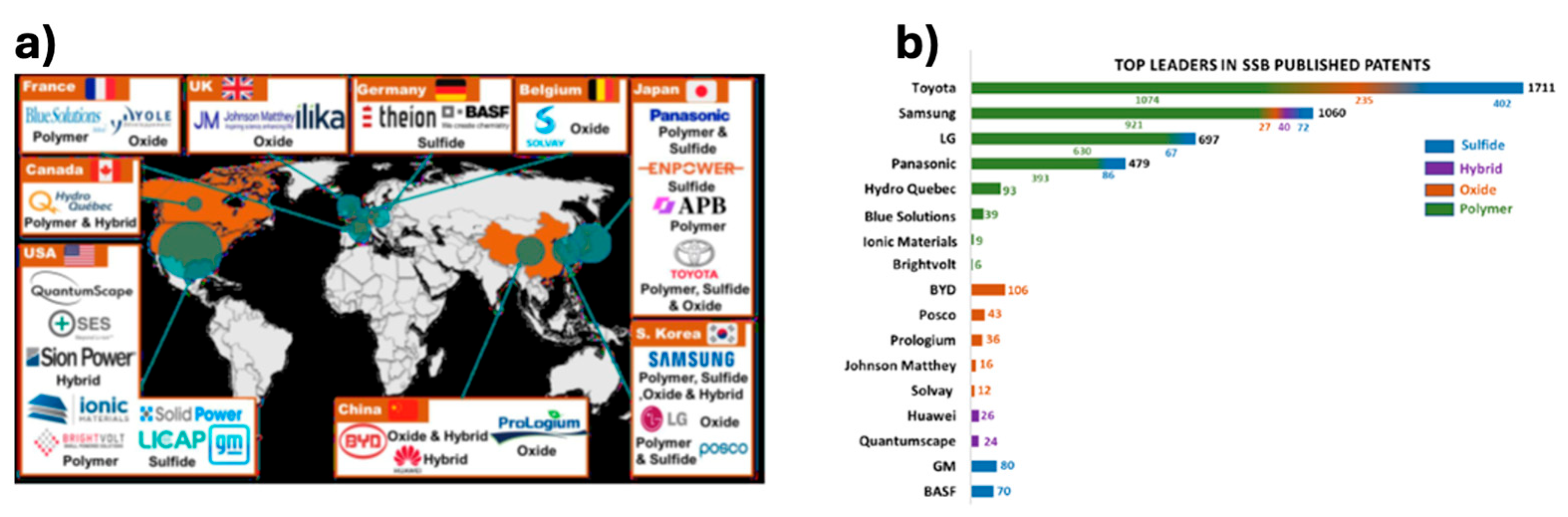
Figure 4a depicts the foremost corporations excelling in SSB technology, with a distinct concentration in Asia (notably Japan, the Republic of Korea, and China) due to the regional aggregation of the battery sector [
115]. This concentration fosters enhanced collaborative efforts in research and development (R&D) as well as infrastructure.
Figure 4b presents data on the issuance of patents pertaining to a crucial component of SSBs, the solid electrolyte (SE). These patents provide insights into the companies employing these electrolytes and primarily address the challenges and applications associated with the development of SE. An analysis of these patents, in collaboration with the involved companies, will be conducted to assess their recycling protocols and sustainability measures.
In Japan, Toyota holds the majority of patents for SSBs, totaling over 1700. Among these, notable innovations include Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. Patent [
117], which was the pioneer in using a halide solid electrolyte (Li
3YCl
6) in the positive electrode layer. This composition reduces the likelihood of oxidative decomposition reactions, thereby enhancing the voltage endurance of the battery. The application of Li
3YCl
6 both in the positive electrode and as a component of the solid electrolyte significantly boosts the voltage withstand capacity. The integration of a halide solid electrolyte, known for its high ionic conductivity and stability, into the positive electrode layer is particularly significant, as these are crucial attributes for SSB performance.
The technology was further advanced in a subsequent patent by Panasonic Corp. and Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. [
118], which utilizes both halide (Li
3YCl
6) and sulfide (Li
2S・P
2S
5) in the solid electrolyte. This combination ensures excellent mechanical properties and high thermal stability within the battery.
Another intriguing development by Toyota Motor Corp. [
119] explores the anode-free battery concept, where lithium metal is not initially present during cell assembly but forms during the battery's charge-discharge cycles. This patent focuses on addressing dendrite formation through precise formulations and concentrations of the solid electrolyte. The anode-free approach reduces lithium usage, which is vital given lithium’s scarcity and the importance of sustainable resource management.
Moreover, Toyota Motor Corp. has developed a solid electrolyte that prevents the formation of hydrogen sulfide, a common issue when solid electrolytes react with moisture [
120]. By substituting lithium with sodium to produce Li
5.1Na
0.3PS
4.4Cl
1.6, this innovation prevents water reactions and inhibits Na substitution for protons.
Additionally, Toyota has patented technologies to enhance the durability of SSBs, including solid electrolytes that prevent crack propagation in electrodes, potentially leading to short circuits [
121]. They have also developed a method [
122] to use impedance measurements for assessing the impact of electrode cracks on battery degradation.
In addition to the development of patents aimed at enhancing the durability and longevity of battery components to minimize waste, Toyota is actively engaged in initiatives designed to foster a circular ecosystem for batteries, such as the "Battery 3R" initiative [
123]. Representing "Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle," Battery 3R is a comprehensive environmental strategy that spans multiple global markets, including Japan, the USA, Europe, China, and other Asian countries. Notable examples of successful implementations from this initiative include a collaboration between JERA Co., Inc. and Toyota, which led to the development of a large-capacity energy storage system using repurposed EV batteries for non-automotive applications [
124]. Additionally, Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) and Toyota have jointly developed a stationary storage battery system now being tested at Eurus Tashirohira Wind Farm, furthering efforts towards a recycling-oriented society [
125]. On the recycling front, Toyota’s expanding partnership with Redwood Materials underscores their commitment to scaling up battery collection and recycling globally.
In Canada, Hydro-Québec, based in Montreal, is a leader in the energy sector, focusing on the advancement of lithium-ion batteries and their recycling. This company holds patents for a new type of electrolyte for solid-state lithium batteries [
126] and anode-free battery concepts [
127,
128], aiming to commercialize these innovations. Recently, Hydro-Québec entered into a licensing agreement with Dongshi Kingpower Science and Technology Ltd. (China) to manufacture solid-state lithium batteries for the Chinese automotive market [
129]. In the realm of battery recycling, Hydro-Québec is developing sustainable methods for managing and reusing battery materials, aligning with global initiatives aimed at reducing waste and the environmental impact of used batteries. They collaborate with entities such as Lithion Recycling [
130], which specializes in recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel for reuse in battery production. These efforts reflect Hydro-Québec’s dedication to sustainable practices and the promotion of a circular economy in the battery industry.
In China, as of January 2024, leading electric vehicle (EV) and battery manufacturers CATL and BYD have united under the China All-Solid-State Battery Innovation Collaboration Platform (CASIP) [
131]. This initiative aims to establish a SSB supply chain by 2030 through a consortium that integrates government, academic, and industrial sectors. The primary goals of CASIP include developing and manufacturing globally competitive SSBs with a focus on empowering Chinese companies. The consortium is dedicated to fundamental research, pivotal technologies, and the collaborative development and manufacturing of electric vehicles equipped with SSBs, as well as forging a robust SSB supply chain. Furthermore, CATL’s active recycling efforts [
132], including their agreement with Volvo [
133], highlight their commitment to sustainability. They aim to reclaim retired batteries for the extraction of metals such as nickel, cobalt, and lithium, utilizing these recycled materials to fabricate new batteries for Volvo Cars. This initiative supports a circular economy, reducing the average carbon emissions of vehicles, enhancing the business model for the recycling and reuse of EV batteries, and serving as a significant example of sustainable development.
In Europe, BASF is prominently featured for its substantial contributions to SSB technology, particularly in developing sulfide electrolytes. BASF has a dedicated recycling and battery materials center in Europe [
134]. Their recently opened recycling plant in Schwarzheide is notable for being Germany’s first high-performance active cathode materials production plant and Europe’s first fully automated large-scale active cathode materials production facility. BASF’s strategy includes recycling end-of-life lithium-ion batteries to produce new cathode active materials. Currently, BASF offers battery recycling services through strategic partnerships and is planning further expansions and investments to enhance its capabilities as the market grows. A significant part of this expansion is the strategic partnership with SVOLT [
135], which focuses on the development of cathode active materials, the supply of raw materials, and the recycling of SVOLT batteries globally. This collaboration not only boosts the research and development capabilities of both companies in sustainable battery materials but also strengthens their competitive edge in the global market, particularly in China.
6.2. Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Specific companies exclusively dedicated to recycling SSBs may not yet be widespread due to the nascent stage of SSB technology commercialization. However, numerous well-established battery recycling companies and research institutions are preparing to tackle the recycling challenges presented by emerging battery technologies, including SSBs.
Table 2 outlines companies involved in lithium-ion battery (LIB) recycling, detailing their locations, methods employed, volumes processed, and current status [
136]. These entities are actively engaged in battery recycling efforts and are likely to extend their services to encompass SSBs as the technology further develops and becomes more prevalent.
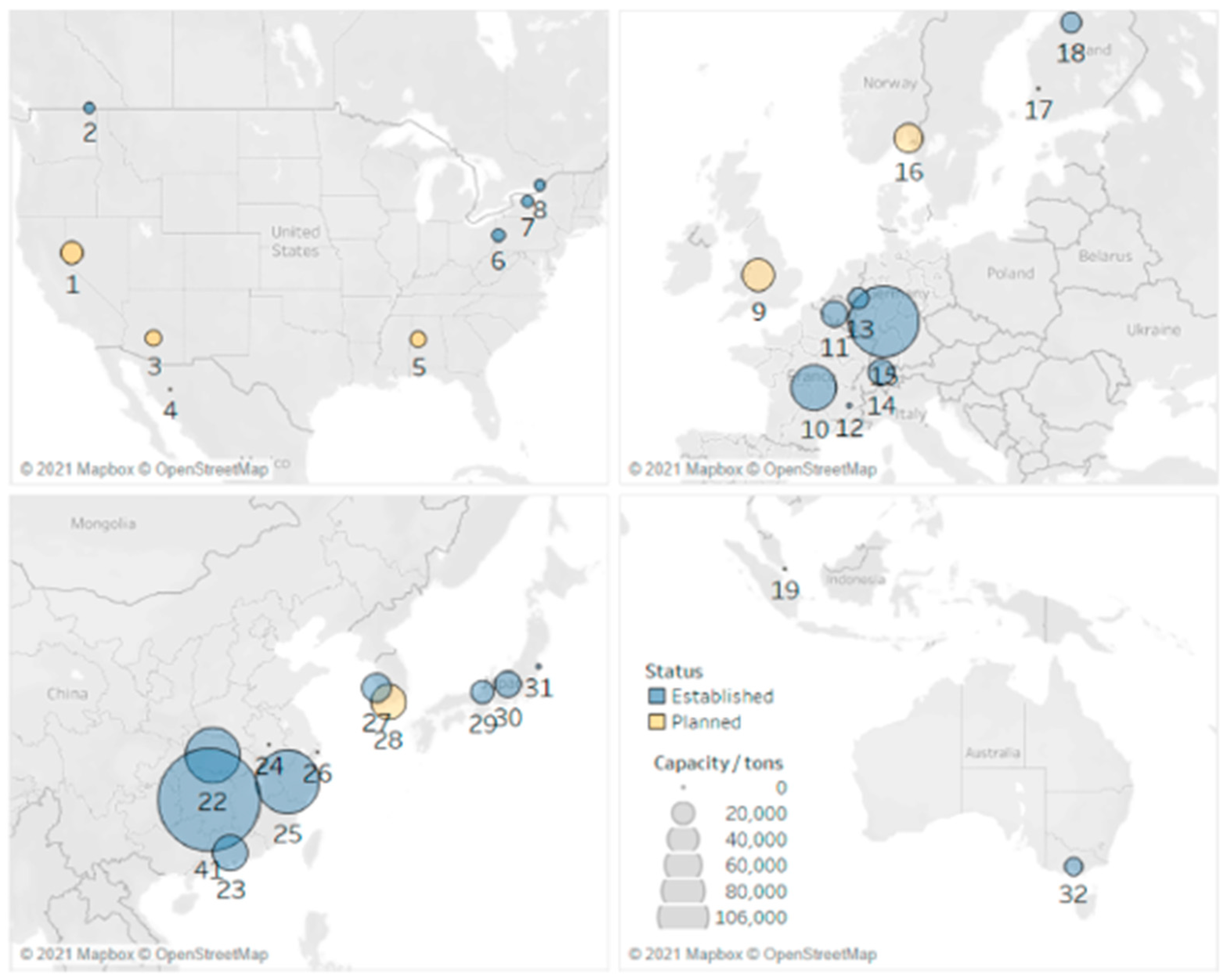
Figure 5 maps the geographic distribution of lithium-ion battery recycling facilities, both existing and planned, illustrating the global spread and strategic placement of these initiatives.
To learn about the best practices in battery recycling and to apply these in the future SSB market, we summarize here the various recycling methods currently used for LIB active materials. Lithium-ion batteries, due to their complex structure and diverse material composition, must undergo several processes before they can be reused or recycled.
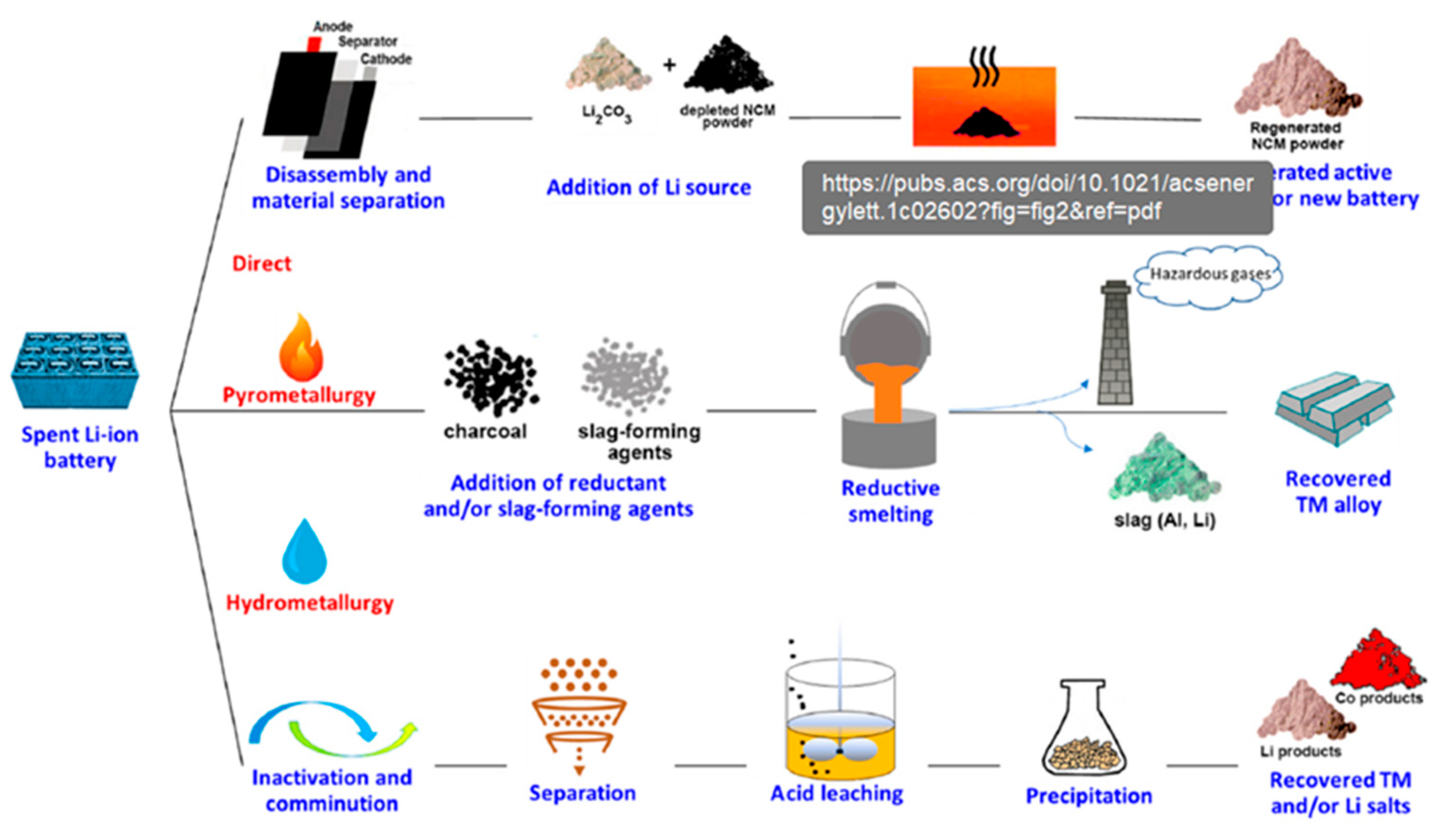
Figure 6 illustrates the common recycling methods for the active materials in LIBs, such as direct recycling, pyrometallurgy, and hydrometallurgical methods, each involving distinct steps. These techniques are employed by companies like OnTo [
137], Umicore [
138,
139], and Recupy [
140] in their recycling processes.
Pyrometallurgical methods are often chosen due to their adaptability with various battery feedstock and the significant investments already made in existing facilities. This method involves high-temperature processes that can efficiently recover valuable metals from batteries, making it highly effective for recycling materials such as cobalt, nickel, and copper. However, the high energy requirements and potential environmental pollution due to emissions of toxic gases during smelting are significant downsides. Consequently, while pyrometallurgy is economically viable and technically straightforward, it raises concerns regarding its sustainability and ecological footprint.
In contrast, hydrometallurgical methods, although still developing, are becoming increasingly popular due to their lower initial setup costs for facilities. Institutions like Lithorec and Aalto University have pioneered these methods, which involve using chemical solutions to dissolve battery components and selectively recover valuable materials through precipitation or electrochemical methods. While more environmentally friendly than pyrometallurgy, requiring less energy and producing fewer emissions, hydrometallurgy is not without its challenges. The method demands a significant amount of chemical reagents and extensive water treatment to manage the effluents produced, which can complicate its operation and increase costs.
Direct recycling represents an innovative approach, aiming to recover and reuse battery materials without breaking them down into their base components [
141]. This method focuses on conserving the electrochemical properties of the cathode materials by directly refurbishing them for reuse. The direct method offers several advantages, including lower energy consumption and reduced chemical use compared to the other methods, as well as diminished facility-related expenditures. However, it requires that the batteries be in relatively good condition to ensure the integrity of the materials being recovered, which necessitates meticulous sorting and can lead to higher labor costs [
142]. Despite these challenges, direct recycling is particularly promising for reducing the overall environmental impact of battery disposal.
The complexities associated with the diverse chemistries, designs, and sizes of LIBs further complicate the recycling process, often necessitating manual sorting and disassembly. To overcome these challenges, there is a growing emphasis on the need for standardization in battery design and labeling. This would facilitate more efficient, automated recycling processes and help minimize environmental impacts.
Research institutions such as the ReCell Center at Argonne National Laboratory [
91] and ReLiB [
143] at the Faraday Institution are at the forefront of exploring these recycling technologies. Their work not only advances understanding but also fosters the development of more specialized methods tailored to different types of batteries, including emerging SSBs. Furthermore, national laboratories and research institutes like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory [
144] and Germany's Fraunhofer Institute [
145] play pivotal roles in this field. Their ongoing research helps to shape industry practices and could potentially lead to breakthroughs in recycling technologies that are specifically designed for the next generation of SSBs. By continuing to innovate and improve recycling methods, these organizations contribute significantly to the sustainability of battery technologies and the circular economy.
7. Future Directions and Research Needs
7.1. Identification of Gaps in Current Research and Technology
Solid-state lithium batteries exhibit potential to substantially enhance energy efficiency, sustainability, and safety at reduced costs relative to advanced lithium-ion batteries [
146]. However, widespread adoption faces significant challenges, with current research efforts and collaborations directed toward overcoming these barriers [
147].
The increasing utilization of lithium-ion batteries, spurred by the demand from portable electronics and electric vehicles, has escalated concerns regarding their disposal and recycling [
148,
149]. The imperative for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is growing globally due to the considerable amounts of hazardous and valuable materials they contain. Various international firms have initiated production lines dedicated to the recycling of metals from spent LIBs, utilizing pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical, or hybrid approaches. The electrolyte, accounting for 10−15 wt% of a spent LIB, presents significant recycling challenges due to its hazardous nature, yet it contains economically valuable lithium-based salts [
149]. Nonetheless, scaling these recycling technologies to an industrial level remains economically challenging.
According to Niu
et al. [
148], an integrated approach to LIB design, manufacturing, and recycling is essential to reduce complexity and energy consumption, advocating for global standardization in manufacturing, classification, collection, and recycling processes to enhance both economic and environmental sustainability [
148]. Yao
et al. [
149] assess various recycling methods, highlighting that hydrometallurgical processes are preferable for mitigating environmental pollution and resource wastage. However, pretreatment phases pose difficulties, as mechanical methods often fail to efficiently separate LIB components [
149]. Among pretreatment methods, sulfuric acid leaching is prominent for extracting cathode active materials, though challenges arise with the dissolution of aluminum foil and the costs and energy demands of the leaching process, which depend on acid concentration and operational temperatures. Bioleaching, despite its eco-friendly attributes, is yet impractical for industrial application. Selective leaching facilitates metal separation but is limited to less complex cathode materials. Solvent extraction and chemical precipitation are routinely utilized for metal recovery from leachates, yet they require enhancements to handle complex material compositions. The resynthesis of cathode materials from leaching solutions represents a simplified recovery approach. Moreover, the diversifying landscape of LIBs, characterized by varied cathode materials, calls for adaptable recycling methodologies. Yao
et al. [
149] also recommend comprehensive studies of all components, including anodes and electrolytes, to address potential environmental risks.
Wang
et al. [
150] identify that global recycling rates for lithium-ion batteries are critically low, primarily due to the reliance on antiquated metallurgy-based methods that require complex decomposition processes and extensive use of chemical reagents. To overcome these limitations, there is a pressing need for innovative and economically viable recycling approaches, with direct recycling/regeneration emerging as a particularly promising solution. Wang
et al. [
150] also highlight the crucial role of integrating information technology into battery recycling, specifically the enhanced traceability enabled by assigning unique QR codes to individual batteries, to improve recycling rates in the digital era. However, significant challenges persist, especially in the labor-intensive pretreatment phase of direct cathode material recycling. Potential solutions could include the adoption of more sophisticated sorting techniques. Addressing these challenges is vital due to the complex interdependencies between battery recycling methods and the evolution of battery technologies. The authors emphasize the need for advancements in the performance of existing cathode materials, such as LCO, LFP, and NCM. Moreover, Wang
et al. point out that the rise of all-solid-state lithium metal batteries introduces additional recycling challenges due to the higher value and complexities of their materials. The urgent development of sustainable direct recycling methods is essential, particularly as the volume of spent power batteries from electric vehicles (EVs) is projected to reach its peak within the next three to five years.
Due to the high demand for batteries, the lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery emerges as a promising next-generation technology due to its potential for high energy densities without rare metal inclusion, offering environmental and resource advantages over lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) [
151]. While LIBs are currently mass-produced, Li-S batteries are not, prompting a prospective life cycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate their environmental and resource impacts under various scenarios. According to Wickerts
et al. [
151] the Li-S batteries has a lower carbon footprint associate with their production and use, lower environmental impact across life-cycle, and high potential benefits for used as a stationary energy due its high energy density and efficiency but challenges such as durability and long-term stability of Li-S batteries, as well as to improve manufacturing and recycling processes to further reduce their environmental impact [
151]. Freitas
et al. [
152] relationship between academics, stakeholders, and policymakers is essential to success, not only on technological advancements and economic regulations but also on user acceptance, which remains an underexplored aspect. Additionally, emerging technologies like microgrids, vehicle-to-grid systems, and blockchain are poised to reshape PV-EV-battery synergy, while outdated economic regulations and automotive sector strategies could hinder potential benefits [
152].
7.2. Potential Avenues for Future Innovations in Recycling and Reducing Environmental Impact
The escalating use of portable electronics and electric vehicles has highlighted the impending challenge of lithium-ion battery (LIB) disposal. Inadequate disposal methods, such as landfilling or incineration, pose significant environmental and safety risks due to the batteries' flammable nature and high metal content. Consequently, there's an urgent need for battery recycling to sustain economic and environmental health. Key considerations in battery production include standardized labeling and design features for easy disassembly and modular structure, alongside advanced battery management systems for monitoring and control. Material recycling methods vary in efficiency and environmental impact, requiring a comprehensive approach considering factors like recovery rate and economic viability [
76,
97]. Different new investigations are developed to optimize recycling processes, minimizing the environmental problems that these processes may cause. The use of solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) are promising for SSBs due to their flexibility and low cost, but face challenges like low Li
+ conductivity and a narrow electrochemical window [
153]. Xie
et al. [
153] studied 23 fluorinated linear polyesters with varied coordination units and flexible linkage segments. They found a molecular asymmetry crucial for Li
+ conductivity enhancement, with tailored polyesters exhibiting a 10-fold increase in conductivity. Notably, solvent-free poly(pentanediol adipate) achieves the highest room-temperature Li
+ conductivity of 0.59 × 10
−4 S cm
−1, attributed to chelating coordination enhancing antioxidation capability. Additionally, 90% LiTFSI recycling and 86% polyester regeneration offer cost-effective solutions, elucidating structure-property relationships and guiding sustainable SSB development [
153]. Another study by Barbosa
et al. [
154], the SPEs are pivotal for SSB advancement, particularly in meeting the demands of electric vehicle proliferation and portable electronics. To address environmental concerns, a shift towards eliminating liquid electrolytes and adopting sustainable materials and processes is imperative. Despite ongoing efforts to enhance sustainability by substituting synthetic polymers with natural counterparts in SPEs, but further research is needed to optimize battery performance, particularly regarding conductivity and compatibility between polymers and fillers [
154]. Poizot
et al. [
155] study the use of organic materials (conducting polymers, organic molecules, and carbon-based material) as electrodes in batteries. Organic materials such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, graphene, carbon nanotubes, amorphous carbon, quinone derivatives, and redox-active organic compounds offer opportunities for lightweight, flexible, and environmentally friendly energy storage solutions. An example is the use of organic polymers electrodes such polyaniline and polypyrrole in electrochemical as energy storage, due to their abundance, low cost, and tunable properties. Also, demonstrate high-density potential and diversity. But challenges related to stability, cyclability, electrochemical performance, solubility, degradation mechanisms, and poor conductivity need to be addressed to achieve practical application [
155]. Transition metal sulfide (eg. CuS, TiS
2) were studied by Whang and Zeier to have the potential to be used in SSBs [
156]. The utilization of transition metal sulfides in SSBs represents a promising approach to advancing energy storage technology. These materials offer several advantages, including high theoretical capacities, good electrical conductivity, and abundance of raw materials, making them attractive candidates for battery electrodes. Also, transition metal sulfides demonstrate enhanced electrochemical performance, with high reversible capacities and improved cycling stability, essential for long-lasting energy storage solutions. Despite these advantages, challenges such as volume expansion during cycling and poor electrical contact with solid electrolytes need to be addressed through further research and development [
156]. Another research uses an organic solvent, N-methylformamide (NMF) to dissolution and recrystallization of Li
3PS
4 to prepare a solid electrolyte [
157]. The investigation underscores NMF's promise as a solvent for Li
3PS
4 dissolution and recrystallization, augmenting solubility and processing capacities for solid-state electrolyte materials. Nonetheless, comprehensive evaluation of its drawbacks, inclusive of toxicity and compatibility concerns, is imperative for its pragmatic integration into lithium-ion battery technologies [
157]. Chen
et al. [
158] utilized waste acrylic yarn to produce recycled fibers for constructing a 3D acrylic-based ceramic composite nanofiber solid electrolyte, enhancing ion conduction pathways and improving thermal and electrochemical stability. The resulting flexible LLZTO/acrylic electrolyte demonstrated enhanced ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, leading to stable lithium symmetric and all-SSBs with high reversible capacity and long-term stability [
158].
A new direction to reduce the possibility of environmental contamination, hazardous waste and increase the use of eco-friendly compounds, green chemistry was used in future clean-energy technologies. Zhang
et al. [
159] develop a waste-free method for synthesizing lithium sulfide (Li
2S), crucial for advanced batteries. This novel approach involves precipitating crystalline Li
2S directly from an organic solution via metathetic reaction, offering advantages such as ambient operation, zero hazardous waste generation, and enhanced economic viability compared to conventional methods. Employing a "solventing-out crystallization" technique with a low boiling point antisolvent allows for efficient separation of valuable byproducts, enabling direct reuse of unreacted lithium salt. This closed-loop process, devoid of waste discharge, holds promise for industrial-scale production while demonstrating impressive battery performance, underscoring its practical application potential [
159]. The demand for LIBs necessitates efficient postconsumer recycling to recover valuable metals like cobalt and nickel. Piątek
et al. [
160] study a bioinspired microporous metal−organic framework (MOF) SU-101 demonstrates selective sorption of Ni
2+ ions from mixed cobalt−nickel aqueous solutions under mild conditions. The adsorption capacity for Ni
2+ reached 100.9 mg/g, while Co
2+ ions showed near-zero adsorption, enabling a high yield Ni
2+ removal of up to 96% at pH 5 and 22 °C. Molecular dynamics calculations suggest Ni
2+ ions' preference for entering MOF canals, offering a green pathway for the selective recycling of valuable metals from cobalt-containing LIBs [
160].
7.3. The Role of Interdisciplinary Research in Advancing Sustainable SSBs Technologies
Over the past decade, the proliferation of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to portable electronics and electric vehicles has raised concerns regarding future development and environmental impact. Repurposing degraded electrode materials for alternative applications adds further value. Establishing a cascade utilization system prioritizes battery repair for units with high-capacity retention and proper recycling for others. With the evolving landscape of LIB chemistry, recycling facilities must adapt to handle diverse chemistries. Clear responsibilities for LIB collection, sorting, and disposal are essential, with manufacturers bearing the cost of recycling [
97]. Rajaeifar
et al. [
161] delves into the intricate landscape of electric vehicle (EV) battery supply and value chains, scrutinizing their sustainability implications. The researchers identified a plethora of challenges spanning the entire battery life cycle, encompassing raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation logistics [
161,
162], and end-of-life management. Despite these hurdles, recent innovations offer promising avenues for sustainability improvements, including advancements in raw material extraction methods, eco-friendly manufacturing processes, energy-efficient transportation modalities, and innovative recycling technologies. Authors present the necessity for collaborative efforts between academia, manufacturers, OEMs, and the battery recycling industry to implement circular economy strategies for environmentally friendly and cost-efficient battery supply, use, and recycling. These developments herald potential benefits such as reduced environmental impact, enhanced resource efficiency, improved social responsibility, and increased economic viability [
161].
Albertsen
et al. [
163] propose a circular business model (CBMs) and Circular Economy (CE) strategies [
164] as potential solutions to address resource scarcity and environmental degradation associated with LIBs. The research demonstrates the prevalence of CE strategies focused on repair, refurbishment, and repurposing, with variations in implementation linked to manufacturer involvement and internal dynamics. The research emphasized the collaboration among stakeholders is essential for successful CBMs, along with the need for design considerations and expertise to extend the lifespan of LIBs. While the proposed EU legislation aims to incentivize CE strategies, further policy development is advocated to ensure compliance with waste management principles [
163]. Closed-loop recycling systems offer a promising avenue to mitigate environmental impacts and reclaim valuable materials for new battery manufacturing [
165]. Bai
et al. [
109] introduce the concept of the Battery Identity Global Passport (BIGP) as an strategy for increase a sustainable recycling process. According to Mayyas
et al. [
165] although current environmental regulations for end-of-life batteries are lacking, proactive measures coupled with advancements in recycling technologies could significantly enhance the sustainability and resource efficiency of the LIB supply chain, emphasizing the importance of recycling from both environmental and value chain perspectives [
165]. Rey
et al. [
166] evaluates the environmental footprint of graphite recycling methods, scaling up from laboratory to pilot-scale processes, and quantify their impacts on various indicators such as global warming and ecotoxicity under the circular economy principles, attention is shifting towards battery recycling to reintroduce materials into the economic cycle sustainably. The results of the research indicate that combined processes involving hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy offer environmentally preferable outcomes, highlighting the potential for sustainable LIB recycling practices [
166]. Bird
et al. [
84], emphasize the importance of learning from the experience of lead-acid battery recycling to inform LIB recycling policies and address associated environmental and health challenges [
84]. Through detailed material flow analysis, Zhang
et al. [
97] elucidates the route of battery components such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite through the recycling process, pinpointing critical stages where material losses occur. The study evaluates the energy flow associated with LIB recycling, quantifying energy inputs required at various stages and assessing overall energy efficiency. The technological limitations and cost were challenges found in the research. By optimizing material and energy flows and addressing existing challenges, economical and ecofriendly LIB recycling can pave the way for a circular economy, ensuring the long-term sustainability of battery manufacturing while minimizing resource depletion and environmental degradation [
97].
Regulatory agencies are setting recycling targets in response to this trend [
167]. Various recycling processes for batteries have different effects on greenhouse gas emissions and economic viability, which may vary depending on the specific battery compositions. Through comprehensive analysis and cost modeling, Ciez and Whitacre [
168] assessed the environmental and economic impacts of producing and recycling lithium-ion cells with different cathode chemistries. The findings suggest that direct cathode recycling could reduce emissions and be economically feasible, underscoring the importance of recycling policies that prioritize efficient methods to collect batteries and reduce emissions [
168]. Slattery
et al. [
169] determine that to have a successful recycling system there are three pillars of sustainability to take into consideration: social, environmental, and economic [
169]. In the EU, the Battery Regulation aims to promote domestic industries, protect the environment, and foster a circular economy. However, the lack of coordination with other global regions may lead to unpredictable consequences. According to Melin
et al. [
170], disruptions in the European battery value chain could hinder the production of electric vehicles, especially with impending bans on internal combustion engine vehicles by 2030. Establishing clear global standards for battery supply chains could provide EU firms with a competitive advantage and promote environmental sustainability [
170]. During the 20th century, the United States transitioned from being a major producer of lithium to heavily relying on imports, particularly for lithium-ion batteries. To forecast potential futures for U.S. lithium use, four scenarios, including COVID-19 implications, were modeled for key applications such as electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and electronics. The "Sustainable Future" scenario shows the highest lithium demand, peaking at 53 Gg in 2040, while "Fossil Fuel Everything" requires only 500 Gg, peaking at 26 Gg in 2050. COVID-19 impacts are deemed negligible in the long term. According with the research, the future electrification of the U.S. vehicle fleet and energy storage systems hinges on a robust international supply chain for lithium chemicals and batteries, along with robust recycling efforts [
171].
8. Conclusions
This review has provided a comprehensive examination of the environmental aspects and recycling challenges of SSBs, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices throughout their lifecycle. From the extraction of raw materials to end-of-life disposal and recycling, SSBs exhibit both opportunities and complexities that are critical to the future of energy storage technologies.
The manufacturing phase of SSBs has shown that while these batteries offer significant improvements in safety and energy density compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, they also pose distinct environmental challenges. These include high energy consumption and emissions during production, as well as concerns regarding the extraction of novel materials required for their construction. However, the operational phase offers a brighter outlook, with SSBs demonstrating superior energy efficiency and a potentially lower overall carbon footprint, suggesting an advantageous environmental impact during their usage compared to conventional battery technologies.
The end-of-life management of SSBs presents significant hurdles, particularly in the realms of disposal and recycling. Current recycling processes, including mechanical, pyrometallurgical, and hydrometallurgical methods, face technological and economic challenges specific to the nature of SSBs. Innovations in recycling methodologies, such as direct recycling and electrohydraulic fragmentation, are emerging to address these barriers, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Case studies and real-world examples have illustrated successful implementations of sustainable practices in the lifecycle management of SSBs. These instances not only highlight the feasibility of innovative recycling and sustainability strategies but also provide valuable lessons and best practices that can be scaled and adapted across the industry.
Looking forward, there is a clear need for ongoing research to address the gaps identified in this review, particularly in the development of more sustainable material extraction techniques, enhanced recycling technologies, and comprehensive lifecycle analyses. The future of SSB recycling will likely depend on interdisciplinary research and collaboration across various sectors, including industry, academia, and government. In conclusion, while SSBs represent a promising advance in battery technology with the potential to significantly reduce environmental impacts, realizing this potential requires concerted efforts in research, policy development, and industry practices. The transition towards sustainable SSB technologies will be pivotal in ensuring that the benefits of these advancements are fully realized, supporting a shift towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M., M.C. and A.M.; methodology, F.M.; investigation, A.M., M.C., F.D., J.D., C.M., and F.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M., M.C., F.D., J.D., C.M., and F.M.; writing—review and editing, A.M., C.M. and F.M.; supervision, F.M.; funding acquisition, A.M., M.C., F.D., J.D., C.M., and F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support from NSF Center for the Advancement of Wearable Technologies-CAWT (Grant 1849243), and from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, under NanoCat-Com Project (PID2021-124667OB-I00), are gratefully acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data is contained in the article and is available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
List of Acronyms
SSB: Solid-state battery
EV: Electric vehicle
Pb-A: Lead-acid
LIB: Lithium-ion battery
GHG: Greenhouse gas
CED: Cumulative energy demand
GWP100: Global warning potential for 100-year time horizon
CSP: Cold sintering process
LCA: Lifecycle analysis
RCRA: Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
MIIT: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology
TEPCO: Tokyo Electric Power Company
CASIP: China All-Solid-State Battery Innovation Collaboration Platform
LCO: Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2)
LFP: Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4/C)
NCM: Lithium Nickel Cobalt Manganese Oxide (LiNiCoMnO2)
PV-EV: Photovoltaic-electric vehicle
SPE: Solid polymer electrolyte
LiTFSI: Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide
NMF: N-methylformamide
LLZTO: Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 garnet electrolyte
MOF: Metal−organic framework
OEM: Original equipment manufacturer
CE: Circular economy
CBM: Circular business model
EU: European Union
BIGP: Battery identity global passport
References
- Zeng, D.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Yan, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, L. Promoting Favorable Interfacial Properties in Lithium-Based Batteries Using Chlorine-Rich Sulfide Inorganic Solid-State Electrolytes. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lei, Y.; Tang, S.; Xu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Liu, J.; et al. Quasi-Solid-State Zn-Air Batteries with an Atomically Dispersed Cobalt Electrocatalyst and Organohydrogel Electrolyte. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ji, S.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. In Situ Construction a Stable Protective Layer in Polymer Electrolyte for Ultralong Lifespan Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Advanced Science 2022, 9, 2104277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Rong, X.; Gao, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, M.; Qi, X.; Chai, G.; Zhang, Q.; Suo, L.; et al. Rational Design of a Topological Polymeric Solid Electrolyte for High-Performance All-Solid-State Alkali Metal Batteries. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnmann, P.; Strauss, F.; Bielefeld, A.; Ruess, R.; Adelhelm, P.; Burkhardt, S.; Dreyer, S.L.; Trevisanello, E.; Ehrenberg, H.; Brezesinski, T.; et al. Designing Cathodes and Cathode Active Materials for Solid-State Batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2022, 12, 2201425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, F.; Shen, L.; Deng, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Yao, X. 20 μ m-Thick Li 6.4 La 3 Zr 1.4 Ta 0.6 O 12 -Based Flexible Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Energy Mater Adv 2022, 2022, 2022/9753506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albero Blanquer, L.; Marchini, F.; Seitz, J.R.; Daher, N.; Bétermier, F.; Huang, J.; Gervillié, C.; Tarascon, J.-M. Optical Sensors for Operando Stress Monitoring in Lithium-Based Batteries Containing Solid-State or Liquid Electrolytes. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Qiao, L.; Santiago, A.; Judez, X.; De Buruaga, A.S.; Jimenez, G.; Armand, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Perspective of Polymer-Based Solid-State Li-S Batteries. EM 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.H.S.; Meng, Y.S.; Jang, J. Scaling up High-Energy-Density Sulfidic Solid-State Batteries: A Lab-to-Pilot Perspective. Joule 2022, 6, 1755–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, F.; Kmiec, S.; Dong, H.; Xu, R.; Zhao, K.; Ai, Q.; Terlier, T.; Wang, L.; et al. An Electrochemically Stable Homogeneous Glassy Electrolyte Formed at Room Temperature for All-Solid-State Sodium Batteries. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Yoon, K.; Han, S.; Lee, M.H.; Ko, Y.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, W.; Kang, K. Design of a Lithiophilic and Electron-Blocking Interlayer for Dendrite-Free Lithium-Metal Solid-State Batteries. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq0153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Teo, J.H.; Walther, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, R.; Mazilkin, A.; Tang, Y.; Goonetilleke, D.; Janek, J.; Bianchini, M.; et al. Advanced Nanoparticle Coatings for Stabilizing Layered Ni-Rich Oxide Cathodes in Solid-State Batteries. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lai, C.; Chen, K.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, C. Dual Fluorination of Polymer Electrolyte and Conversion-Type Cathode for High-Capacity All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, W.-Q. From Liquid to Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries: Fundamental Issues and Recent Developments. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalnaus, S.; Dudney, N.J.; Westover, A.S.; Herbert, E.; Hackney, S. Solid-State Batteries: The Critical Role of Mechanics. Science 2023, 381, eabg5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janek, J.; Zeier, W.G. Challenges in Speeding up Solid-State Battery Development. Nat Energy 2023, 8, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Gong, Y.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in All-Solid-State Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lou, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Kakar, A.; Emley, B.; Ai, Q.; Guo, H.; Liang, Y.; Lou, J.; et al. Current Status and Future Directions of All-Solid-State Batteries with Lithium Metal Anodes, Sulfide Electrolytes, and Layered Transition Metal Oxide Cathodes. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shaqsi, A.Z.; Sopian, K.; Al-Hinai, A. Review of Energy Storage Services, Applications, Limitations, and Benefits. Energy Reports 2020, 6, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitali, J.; Dhinakaran, S.; Mohamad, A.A. Energy Storage Systems: A Review. Energy Storage and Saving 2022, 1, 166–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, G.G.; Zhang, H.; Judez, X.; Adenusi, H.; Armand, M.; Passerini, S.; Figgemeier, E. Production of High-Energy Li-Ion Batteries Comprising Silicon-Containing Anodes and Insertion-Type Cathodes. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Mao, J.; Dai, K.; Yan, C.; Zheng, J. An Advance Review of Solid-State Battery: Challenges, Progress and Prospects. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2021, 29, e00297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Shuai, H.; Luo, Z.; Wang, B.; Fang, S.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Peng, H.; Ji, X. Recent Advances of Composite Electrolytes for Solid-State Li Batteries. Journal of Energy Chemistry 2022, 67, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Liao, Y.; Qu, R.; Zhang, Z. Liquid Electrolytes for Low-Temperature Lithium Batteries: Main Limitations, Current Advances, and Future Perspectives. Energy Storage Materials 2023, 56, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachmann, N.; Petranikova, M.; Ebin, B. Electrolyte Recovery from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using a Low Temperature Thermal Treatment Process. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2023, 118, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D. The Materials Science behind Sustainable Metals and Alloys. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 2436–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaretto, N.; Garbayo, I.; Valiyaveettil-SobhanRaj, S.; Quintela, A.; Li, C.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Aguesse, F. Lithium Solid-State Batteries: State-of-the-Art and Challenges for Materials, Interfaces and Processing. Journal of Power Sources 2021, 502, 229919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igogo, T.; Awuah-Offei, K.; Newman, A.; Lowder, T.; Engel-Cox, J. Integrating Renewable Energy into Mining Operations: Opportunities, Challenges, and Enabling Approaches. Applied Energy 2021, 300, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampatori, D.; Raimondi, P.P.; Noussan, M. Li-Ion Batteries: A Review of a Key Technology for Transport Decarbonization. Energies 2020, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Falco, M.; Muñoz-García, A.B.; Bonomo, M.; Brutti, S.; Pavone, M.; Gerbaldi, C. Solid-State Post Li Metal Ion Batteries: A Sustainable Forthcoming Reality? Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, B.E.; Toghill, K.E.; Tapia-Ruiz, N. A Perspective on the Sustainability of Cathode Materials Used in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani-Sanij, A.R.; Tharumalingam, E.; Dusseault, M.B.; Fraser, R. Study of Energy Storage Systems and Environmental Challenges of Batteries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2019, 104, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzio, J.; Scown, C.D. Life-Cycle Assessment Considerations for Batteries and Battery Materials. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, J.; Tietz, F.; Singer, C.; Hofer, A.; Billot, N.; Reinhart, G. Prospects of Production Technologies and Manufacturing Costs of Oxide-Based All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1818–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, F.; Schütte, M. Life Cycle Assessment of the Energy Consumption and GHG Emissions of State-of-the-Art Automotive Battery Cell Production. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 330, 129798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Gu, H.; Chen, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, F.; Han, X.; Guo, Y.; Bhagat, R.; Zheng, Y. Investigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Environmental Impacts from the Production of Lithium-Ion Batteries in China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 372, 133756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzmohammadian, A.; Cook, S.M.; Milford, J.B. Cradle-to-Gate Environmental Impacts of Sulfur-Based Solid-State Lithium Batteries for Electric Vehicle Applications. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 202, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, A.; Yang, Z. Research Progress and Application Prospect of Solid-State Electrolytes in Commercial Lithium-Ion Power Batteries. Energy Storage Materials 2021, 35, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaish, M.; Gonzalez-Rosillo, J.C.; Kim, K.J.; Zhu, Y.; Hood, Z.D.; Rupp, J.L.M. Processing Thin but Robust Electrolytes for Solid-State Batteries. Nat Energy 2021, 6, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, D.; Adair, K.; Liang, J.; Sun, X. Development of the Cold Sintering Process and Its Application in Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Journal of Power Sources 2018, 393, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, W.; Hatzell, K.B. Processing and Manufacturing of next Generation Lithium-Based All Solid-State Batteries. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2022, 26, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Aetukuri, N.P.B.; Nanda, J. Solid State Lithium Metal Batteries – Issues and Challenges at the Lithium-Solid Electrolyte Interface. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2022, 26, 100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanavendan, S.; Selvaraj, S.K.; Dev, S.J.; Mahato, K.K.; Swathish, R.S.; Sundaramali, G.; Accouche, O.; Azab, M. Challenges, Solutions and Future Trends in EV-Technology: A Review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 17242–17260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, S. Implementation of Green Manufacturing Practices in Automobile Fields: A Review. In Sustainable Machining and Green Manufacturing; Thirumalai Kumaran, S., Ko, T.J., Eds.; Wiley, 2024; pp. 221–248 ISBN 978-1-394-19783-5.
- Karpagaraj, A.; Gopikrishnan, T.; Singh, S.K. Reuse and Recycling of Electronic Waste from a Global Solution Perspective. In Electronic Waste Management; Kumar, S., Kumar, V., Eds.; Wiley, 2023; pp. 104–123 ISBN 978-1-119-89151-2.
- Berrueta, A.; Ursua, A.; Martin, I.S.; Eftekhari, A.; Sanchis, P. Supercapacitors: Electrical Characteristics, Modeling, Applications, and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 50869–50896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunde, G.B.; Sehgal, B. Industrial Innovation Through Sustainable Materials. In Handbook of Smart Materials, Technologies, and Devices; Hussain, C.M., Di Sia, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 1–42. ISBN 978-3-030-58675-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Adair, K.R.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. Recent Advances and Perspectives on Thin Electrolytes for High-Energy-Density Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 643–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yuan, X. The Advances and Opportunities of Developing Solid-State Battery Technology: Based on the Patent Information Relation Matrix. Energy 2024, 296, 131178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, H.; Malyi, O.I.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, G.; Tang, Y. New Emerging Fast Charging Microscale Electrode Materials. Small 2024, 20, 2307027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Nie, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ju, Z.; Zhuang, Q. Inorganic Cathode Materials for Potassium Ion Batteries. Materials Today Energy 2022, 25, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaravel, V.; Bartlett, J.; Pillai, S.C. Solid Electrolytes for High-Temperature Stable Batteries and Supercapacitors. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2002869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress in Solid Electrolytes for Energy Storage Devices. Adv Funct Materials 2020, 30, 2000077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger; Julien; Paolella; Armand; Zaghib Building Better Batteries in the Solid State: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 3892. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; Ibn-Mohammed, T.; Koh, L.; Reaney, I.M. Life Cycle Assessment of Functional Materials and Devices: Opportunities, Challenges, and Current and Future Trends. J Am Ceram Soc 2019, 102, 7037–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonemann, N.; Schulte, A.; Maga, D. How to Conduct Prospective Life Cycle Assessment for Emerging Technologies? A Systematic Review and Methodological Guidance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgett, E.; Papageorgopoulos, D. System-level Constraints on Fuel Cell Materials and Electrocatalysts. In Electrocatalysis for Membrane Fuel Cells; Alonso-Vante, N., Di Noto, V., Eds.; Wiley, 2023; pp. 1–22 ISBN 978-3-527-34837-4.
- Fonseca, N.; Thummalapalli, S.V.; Jambhulkar, S.; Ravichandran, D.; Zhu, Y.; Patil, D.; Thippanna, V.; Ramanathan, A.; Xu, W.; Guo, S.; et al. 3D Printing-Enabled Design and Manufacturing Strategies for Batteries: A Review. Small 2023, 19, 2302718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.S.; Wagh, N.K.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Li, Na, K, Mg, Zn, Al, and Ca Anode Interface Chemistries Developed by Solid-State Electrolytes. Advanced Science 2023, 10, 2304235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zor, C.; Turrell, S.J.; Uyanik, M.S.; Afyon, S. Lithium Plating and Stripping: Toward Anode-Free Solid-State Batteries. Adv Energy and Sustain Res 2023, 2300001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalkhani, M.; Habibi, S. Review of the Li-Ion Battery, Thermal Management, and AI-Based Battery Management System for EV Application. Energies 2022, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.G.; Elfeky, K.E.; Wang, Q. Recent Advancement and Enhanced Battery Performance Using Phase Change Materials Based Hybrid Battery Thermal Management for Electric Vehicles. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2022, 154, 111759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasapu, U.; Hehenberger, P. A Design Process Model for Battery Systems Based on Existing Life Cycle Assessment Results. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 407, 137149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, K.W.; Synnevåg, T.A.; Lamb, J.J.; Lien, K.M. The Carbon Footprint of Electrified City Buses: A Case Study in Trondheim, Norway. Energies 2021, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S. Challenges and Strategies for Fast Charge of Li-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soini, M.C.; Parra, D.; Patel, M.K. Impact of Prosumer Battery Operation on the Cost of Power Supply. Journal of Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, M.; Abd El-Hady, D.; Alshitari, W.; Al-Bogami, A.S.; Lu, J.; Amine, K. Commercialization of Lithium Battery Technologies for Electric Vehicles. Advanced Energy Materials 2019, 9, 1900161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dühnen, S.; Betz, J.; Kolek, M.; Schmuch, R.; Winter, M.; Placke, T. Toward Green Battery Cells: Perspective on Materials and Technologies. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pohl, O.; Bhatt, A.I.; Collis, G.E.; Mahon, P.J.; Rüther, T.; Hollenkamp, A.F. A Review on Battery Market Trends, Second-Life Reuse, and Recycling. Sustainable Chemistry 2021, 2, 167–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Structural Model, Size Effect and Nano-Energy System Design for More Sustainable Energy of Solid State Automotive Battery. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 65, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.H.S.; Xu, P.; Yang, H.; Kim, M.; Nguyen, H.; Wu, E.A.; Doux, J.-M.; Banerjee, A.; Meng, Y.S.; Chen, Z. Sustainable Design of Fully Recyclable All Solid-State Batteries. MRS Energy & Sustainability 2020, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemchainan, J.; Bruce, P.G. All-Solid-State Batteries and Their Remaining Challenges: A Potential Route towards Safer, Higher Performing Batteries. Johnson Matthey Technology Review 2018, 62, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, K.M.; Laux, S.J.; Townsend, T.G. A Review on the Growing Concern and Potential Management Strategies of Waste Lithium-Ion Batteries. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2018, 129, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghi, M.; Braghin, F.; Roveda, L. Enhancing Disassembly Practices for Electric Vehicle Battery Packs: A Narrative Comprehensive Review. Designs 2023, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudet, A.; Larouche, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Key Challenges and Opportunities for Recycling Electric Vehicle Battery Materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.F.; Baumann, M.; Zimmermann, B.; Braun, J.; Weil, M. The Environmental Impact of Li-Ion Batteries and the Role of Key Parameters – A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 67, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noudeng, V.; Quan, N.V.; Xuan, T.D. A Future Perspective on Waste Management of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles in Lao PDR: Current Status and Challenges. IJERPH 2022, 19, 16169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.H.P.; Chen, M.; Ogunseitan, O.A. Potential Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Rechargeable Lithium Batteries in Electronic Waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5495–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozik, W.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Heidrich, O.; Christensen, P. Environmental Impacts, Pollution Sources and Pathways of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 6099–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rarotra, S.; Sahu, S.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, P.; Srinivasan, M.; Veksha, A.; Lisak, G. Progress and Challenges on Battery Waste Management :A Critical Review. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 6182–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.D.J.; Kendrick, E.; Anderson, P.A.; Mrozik, W.; Christensen, P.; Lambert, S.; Greenwood, D.; Das, P.K.; Ahmeid, M.; Milojevic, Z.; et al. Roadmap for a Sustainable Circular Economy in Lithium-Ion and Future Battery Technologies. J. Phys. Energy 2023, 5, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Fu, H.-Z.; Ho, Y.-S. A Global Perspective of Bioaccumulation Research Using Bibliometric Analysis. COLLNET Journal of Scientometrics and Information Management 2018, 12, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.; Baum, Z.J.; Yu, X.; Ma, J. The Regulatory Environment for Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RICHTLINIE 2006/66/EG DES EUROPÄISCHEN PARLAMENTS UND DES RATES 2006.
- Zanoletti, A.; Carena, E.; Ferrara, C.; Bontempi, E. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues. Batteries 2024, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocce Romano Espinosa, D.; Moura Bernardes, A.; Alberto Soares Tenório, J. Brazilian Policy on Battery Disposal and Its Practical Effects on Battery Recycling. Journal of Power Sources 2004, 137, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2020/1055 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 July 2020 Amending Regulations (EC) No 1071/2009, (EC) No 1072/2009 and (EU) No 1024/2012 with a View to Adapting Them to Developments in the Road Transport Sector 2020.
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Laws and Regulations 2024. https://www.epa.gov/rcra (accessed february 14, 2024).
- Universal Waste. https://www.epa.gov/hw/universal-waste (accessed may 6, 2024).
- ReCell Center. https://www.recellcenter.org (accessed may 6, 2024).
- Pacios, R.; Villaverde, A.; Martínez-Ibañez, M.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Aguesse, F.; Kvasha, A. Roadmap for Competitive Production of Solid-State Batteries: How to Convert a Promise into Reality. Advanced Energy Materials 2023, 13, 2301018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuis, M.; Doose, S.; Vogt, D.; Michalowski, P.; Zellmer, S.; Kwade, A. Recycling of Solid-State Batteries. Nat Energy 2024, 9, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, L.; Bong, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Recycling for All Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Matter 2020, 3, 1845–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ji, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Liang, Z. Toward Sustainable All Solid-State Li–Metal Batteries: Perspectives on Battery Technology and Recycling Processes. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2301540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, K.; Selvin, P.C.; Abhilash, K.P.; Palaniyandy, N.; Helen, P.A.; Somasundharam, G. Recycling of All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. In Solid State Batteries; Palaniyandy, N., Abhilash, K.P., Nalini, B., Eds.; Advances in Material Research and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 245–274. ISBN 978-3-031-12469-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, X.-W.; Liu, X.; Gu, Q.; Mu, J.; Luo, W.-B. Economical and Ecofriendly Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Material Flow and Energy Flow. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 2511–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessia, A.; Alessandro, B.; Maria, V.-G.; Carlos, V.-A.; Francesca, B. Challenges for Sustainable Lithium Supply: A Critical Review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 300, 126954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastanaki, E.; Giannis, A. Dynamic Estimation of End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Batteries in the EU-27 Considering Reuse, Remanufacturing and Recycling Options. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 393, 136349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Wissel, K.; Clemens, O. Recycling of Solid-State Batteries—Challenge and Opportunity for a Circular Economy? Mater. Futures 2024, 3, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, H.A.; Pecht, M. Preprocessing of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Recycling: Need, Methods, and Trends. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2022, 168, 112809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M. State-of-the-Art Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Technologies. Circular Economy 2022, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, Z.A.; Marshall, A.; Kennedy, J. A Review on Sustainable Recycling Technologies for Lithium-Ion Batteries. emergent mater. 2021, 4, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Sui, P.-C.; Zhang, J. Hydrometallurgical Recycling of Lithium-Ion Battery Materials; 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2022; ISBN 978-1-00-326920-5. [Google Scholar]
- Larouche, F.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Recycling of Li-Ion and Li-Solid State Batteries: The Role of Hydrometallurgy. In Extraction 2018; Davis, B.R., Moats, M.S., Wang, S., Gregurek, D., Kapusta, J., Battle, T.P., Schlesinger, M.E., Alvear Flores, G.R., Jak, E., Goodall, G., Free, M.L., Asselin, E., Chagnes, A., Dreisinger, D., Jeffrey, M., Lee, J., Miller, G., Petersen, J., Ciminelli, V.S.T., Xu, Q., Molnar, R., Adams, J., Liu, W., Verbaan, N., Goode, J., London, I.M., Azimi, G., Forstner, A., Kappes, R., Bhambhani, T., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 2541–2553. ISBN 978-3-319-95021-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tanhaei, M.; Beiramzadeh, Z.; Kholghi Eshkalak, S.; Katal, R. Recycling and Management of Lithium Battery as Electronic Waste. In Handbook of Solid Waste Management; Baskar, C., Ramakrishna, S., Baskar, S., Sharma, R., Chinnappan, A., Sehrawat, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1605–1634. ISBN 9789811642296. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.-M.; Zhou, G. Fundamentals, Status and Challenges of Direct Recycling Technologies for Lithium Ion Batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8194–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piątek, J.; Afyon, S.; Budnyak, T.M.; Budnyk, S.; Sipponen, M.H.; Slabon, A. Sustainable Li-Ion Batteries: Chemistry and Recycling. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2003456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Muralidharan, N.; Sun, Y.-K.; Passerini, S.; Stanley Whittingham, M.; Belharouak, I. Energy and Environmental Aspects in Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries: Concept of Battery Identity Global Passport. Materials Today 2020, 41, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Dong, E.; Bingguo, L.; Yuwen, C.; Niu, Y.; Ji, G.; Chen, W.; Hou, K.; Zhang, L.; Guo, S. Eco-Friendly Closed-Loop Recycling of Nickel, Cobalt, Manganese, and Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes 2024.
- Wang, T.-W.; Liu, T.; Sun, H. Direct Recycling for Advancing Sustainable Battery Solutions. Materials Today Energy 2023, 38, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.P.; Ranawat, N.S.; Chakraborty, A.; Mishra, R.P.; Khandelwal, M. The Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Process from a Circular Economy Perspective—A Review and Future Directions. Energies 2023, 16, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidha, A.I.; Salihovic, A.; Jacob, M.; Vanita, V.; Aktekin, B.; Brix, K.; Wissel, K.; Kautenburger, R.; Janek, J.; Ensinger, W.; et al. Recycling of All-Solid-State Li-ion Batteries: A Case Study of the Separation of Individual Components Within a System Composed of LTO, LLZTO and NMC. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202202361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Nowroozi, M.; Iqbal Waidha, A.; Jacob, M.; Van Aken, P.A.; Predel, F.; Ensinger, W.; Clemens, O. Towards Recycling of LLZO Solid Electrolyte Exemplarily Performed on LFP/LLZO/LTO Cells. ChemistryOpen 2022, 11, e202100274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacenet: European Pattent Office. https://worldwide.espacenet.com (accessed may 5, 2024).
- Karkar, Z.; Houache, M.S.E.; Yim, C.-H.; Abu-Lebdeh, Y. An Industrial Perspective and Intellectual Property Landscape on Solid-State Battery Technology with a Focus on Solid-State Electrolyte Chemistries. Batteries 2024, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K.; Miyazaki, A. Solid State Battery. Patent WO2021177212A1 (september 10, 2021).
- Sasaki, I.; Fujinoki, N.; Miyazaki, A.; Shiotani, S.; Sugiyama, T. Positive Electrode Material and Battery. Patent WO2021157361A1 (august 12, 2021).
- Morita, K.; Yada, C.; Suzuki, Y. Method for Producing All Solid State State Battery 2022. Patent JP2022052690A (april 4, 2022).
- Takeuchi, K.; Shiotani, S.; Otomo, T. Solid Electrolyte. Patent JP2020061326A (april 16, 2020).
- Li, X. All Solid-State Battery and Manufacturing Method for All Solid-State Battery 2022. Patent EP4117058A1 (july 5, 2022).
- Nagano, A. Method of Evaluating All-Solid-State Battery. Patent JP2022076604A (may 10, 2022).
- Emerging Technology News. https://etn.news/buzz/toyota-ev-battery-reduce-reuse-recycling-initiatives-global-markets (accessed may 5, 2024).
- Jera´s Action. https://www.jera.co.jp/en/action/discover/009 (accessed may 4, 2024).
- Tepco. https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/hd/newsroom/press/archives/2023/20230529_01.html (accessed may 3 2024).
- Fleutot, B.; Zhang, X.; Garitte, E. Solid Electrolytes Comprising an Ionic Bifunctional Molecule and Use Thereof in Electrochemistry. Patent WO2023/133642 (july 1, 2023).
- Delaporte, N.; Morizur, V.; Lajoie, G. Anodeless Coating Layer for All-Solid-State Battery and All-Solid-State Battery Incuding Anodeless Coating Layer. Patent WO2023/141720 (august 2, 2023).
- Amouzegar, K.; Leblanc, D.; Paolella, A.; Guerfi, A.; Kaboli, S. Process for Producing an Anode for Lithium Batteries 2023. Patent WO2023/133627 (july 1, 2023).
- Hydro-Québec. https://news.hydroquebec.com/en/press-releases/1317/hydro-quebec-licenses-dongshi-kingpower-science-and-technology-to-use-its-solid-state-lithium-battery-technology/ (accessed may 3, 2024).
- Lithion. https://www.lithiontechnologies.com/en/solutions/recycle-your-batteries/ (accessed may 3, 2024).
- Electrive. https://www.electrive.com/2024/02/13/chinas-car-and-battery-industry-launches-solid-state-battery-offensive/ (accessed may 5, 2024).
- Catl. https://www.catl.com/en/solution/recycling/ (accessed may 2, 2024).
- CATL and Volvo Cars Join Hands for Sustainable Development. https://www.catl.com/en/news/6234.html (accessed may 5, 2024).
- Basf. https://catalysts.basf.com/industries/recycling/lithium-ion-battery-recycling (accessed may 12, 2024).
- Svolt. https://www.svolt-eu.com/en/our-heartbeat/ (accessed may 11, 2024).
- Baum, Z.J.; Bird, R.E.; Yu, X.; Ma, J. Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling─Overview of Techniques and Trends. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloop, S.; Crandon, L.; Allen, M.; Koetje, K.; Reed, L.; Gaines, L.; Sirisaksoontorn, W.; Lerner, M. A Direct Recycling Case Study from a Lithium-Ion Battery Recall. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2020, 25, e00152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoof, G.; Robertz, B.; Verrecht, B. Towards Sustainable Battery Recycling: A Carbon Footprint Comparison between Pyrometallurgical and Hydrometallurgical Battery Recycling Flowsheets. Metals 2023, 13, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umicore. https://brs.umicore.com/en/recycling/ (accessed may 9, 2024).
- Tedjar, F. F. J.C. Method for the Mixed Recycling of Lithium Based Anode Batteries and Cells. Patent US7820317B2 (october 26, 2010).
- Lan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Yao, W.; Cheng, H.; Tang, Y. Direct Regenerating Cathode Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Advanced Science 2024, 11, 2304425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, K.; Chen, W.H.; Dietrich, F.; Dröder, K.; Kara, S. Robot Assisted Disassembly for the Recycling of Electric Vehicle Batteries. Procedia CIRP 2015, 29, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ReLib. https://www.faraday.ac.uk/research/lithium-ion/recycle-reuse/ (accessed may 3, 2024).
- Argonne National Lab. https://www.anl.gov/topic/battery-recycling (accessed may 5, 2024).
- Fraunhofer Institute. https://www.iwks.fraunhofer.de/en/competencies/Energy-Materials/Batteries-and-PV-modules.html (accessed may 2, 2024).
- Aizat Razali, A.; Norazli, S.N.; Sum, W.S.; Yeo, S.Y.; Dolfi, A.; Srinivasan, G. State-of-the-Art of Solid-State Electrolytes on the Road Map of Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries for E-Mobility. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7927–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertus, P.; Anandan, V.; Ban, C.; Balsara, N.; Belharouak, I.; Buettner-Garrett, J.; Chen, Z.; Daniel, C.; Doeff, M.; Dudney, N.J.; et al. Challenges for and Pathways toward Li-Metal-Based All-Solid-State Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Qin, Y. Recycling Hazardous and Valuable Electrolyte in Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Urgency, Progress, Challenge, and Viable Approach. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 8718–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, B.; Fan, Y.; Hua, Z. Hydrometallurgical Processes for Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Critical Review. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13611–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Jia, K.; Ji, G.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, H.-M. Toward Direct Regeneration of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Next-Generation Recycling Method. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 2839–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickerts, S.; Arvidsson, R.; Nordelöf, A.; Svanström, M.; Johansson, P. Prospective Life Cycle Assessment of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries for Stationary Energy Storage. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 9553–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas Gomes, I.S.; Perez, Y.; Suomalainen, E. Coupling Small Batteries and PV Generation: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 126, 109835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Qin, X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W. Rational Design of F-Modified Polyester Electrolytes for Sustainable All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5940–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, J.C.; Gonçalves, R.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Toward Sustainable Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14457–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poizot, P.; Gaubicher, J.; Renault, S.; Dubois, L.; Liang, Y.; Yao, Y. Opportunities and Challenges for Organic Electrodes in Electrochemical Energy Storage. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 6490–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whang, G.; Zeier, W.G. Transition Metal Sulfide Conversion: A Promising Approach to Solid-State Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 5264–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, K.; Riegger, L.M.; Schneider, C.; Waidha, A.I.; Famprikis, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Grabowski, B.; Dinnebier, R.E.; Lotsch, B.V.; Janek, J.; et al. Dissolution and Recrystallization Behavior of Li 3 PS 4 in Different Organic Solvents with a Focus on N -Methylformamide. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 7790–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Pan, P.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Fu, K. A Three-Dimensional Fiber-Network-Reinforced Composite Solid-State Electrolyte from Waste Acrylic Fibers for Flexible All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 38507–38521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, A.; Zhang, X.; Tian, R.; Yang, S.; Xu, S.; Song, D.; Yang, Y. Green Synthesis for Battery Materials: A Case Study of Making Lithium Sulfide via Metathetic Precipitation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piątek, J.; Budnyak, T.M.; Monti, S.; Barcaro, G.; Gueret, R.; Grape, E.S.; Jaworski, A.; Inge, A.K.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Slabon, A. Toward Sustainable Li-Ion Battery Recycling: Green Metal–Organic Framework as a Molecular Sieve for the Selective Separation of Cobalt and Nickel. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 9770–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaeifar, M.A.; Ghadimi, P.; Raugei, M.; Wu, Y.; Heidrich, O. Challenges and Recent Developments in Supply and Value Chains of Electric Vehicle Batteries: A Sustainability Perspective. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2022, 180, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Petranikova, M.; Meeus, M.; Gamarra, J.D.; Younesi, R.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—Current State of the Art, Circular Economy, and Next Generation Recycling. Advanced Energy Materials 2022, 12, 2102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsen, L.; Richter, J.L.; Peck, P.; Dalhammar, C.; Plepys, A. Circular Business Models for Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries: An Analysis of Current Practices of Vehicle Manufacturers and Policies in the EU. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2021, 172, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Iyer-Raniga, U. Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling in the Circular Economy: A Review. Recycling 2022, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayyas, A.; Steward, D.; Mann, M. The Case for Recycling: Overview and Challenges in the Material Supply Chain for Automotive Li-Ion Batteries. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2019, 19, e00087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, I.; Vallejo, C.; Santiago, G.; Iturrondobeitia, M.; Lizundia, E. Environmental Impacts of Graphite Recycling from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Life Cycle Assessment. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14488–14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Macias-Garbett, R.; Malacara-Becerra, A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Environmental Impact of Emerging Contaminants from Battery Waste: A Mini Review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering 2021, 3, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciez, R.E.; Whitacre, J.F. Examining Different Recycling Processes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nat Sustain 2019, 2, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.; Dunn, J.; Kendall, A. Transportation of Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries at End-of-Life: A Literature Review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2021, 174, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, H.E.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Ku, A.Y.; Kendall, A.; Harper, G.; Heidrich, O. Global Implications of the EU Battery Regulation. Science 2021, 373, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miatto, A.; Wolfram, P.; Reck, B.K.; Graedel, T.E. Uncertain Future of American Lithium: A Perspective until 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16184–16194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).