Submitted:
02 June 2024
Posted:
03 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
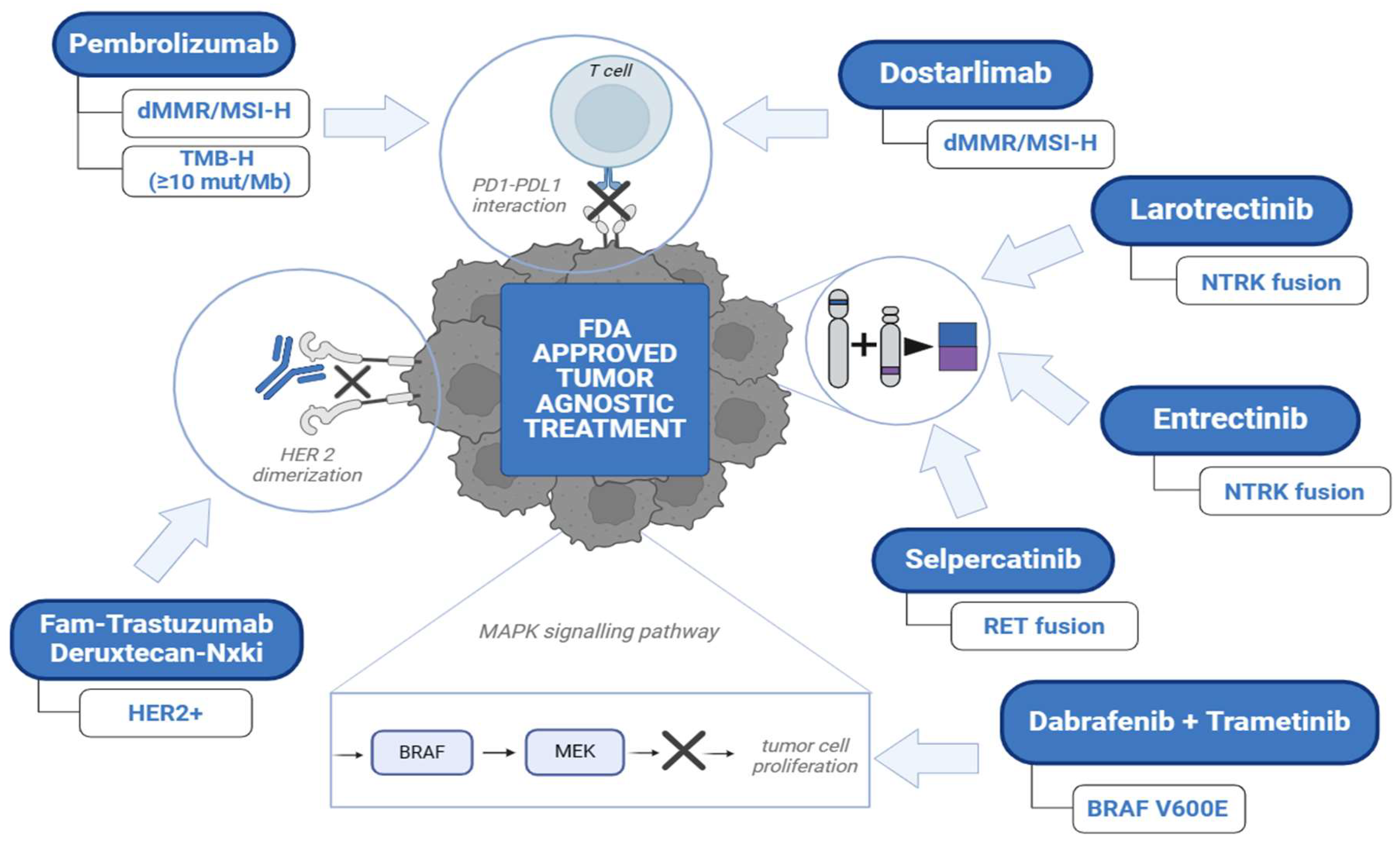
2. Approved Immunotherapy (Checkpoint Inhibitors) in the Field of Tissue Agnostic Drug Development
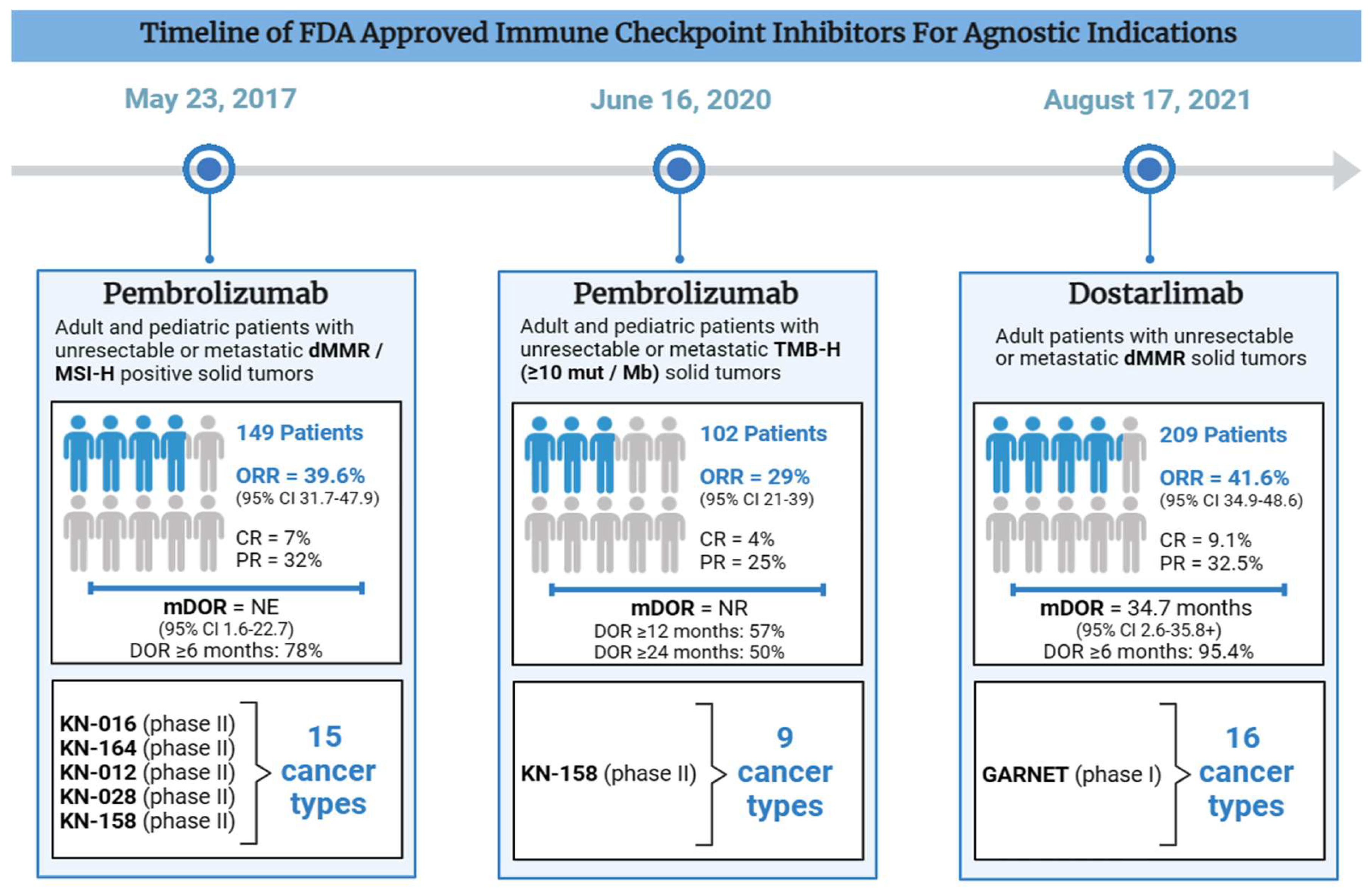
2.1. Pembrolizumab Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic dMMR/MSI-H Cancers (May 23, 2017)
| Drug Name | Pembrolizumab | Pembrolizumab | Dostarlimab-gxly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | PD-1 inhibition | PD-1 inhibition | PD-1 inhibition |
| Indications | Adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic dMMR / MSI-H positive solid tumors No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment OR Patients with dMMR/MSI-H CRC who have progressed with previous treatment (fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan) |
Adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H (≥10 mut / Mb) solid tumors No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment |
Adult patients with unresectable or metastatic dMMRsolid tumors No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment |
| Date of FDA Approval | May 23, 2017 | June 16, 2020 | August 17, 2021 |
| Clinical Trial (s) |
KN-016 (phase II) KN-164 (phase II) KN-012 (phase II) KN-028 (phase II) KN-158 (phase II) |
KN-158 (phase II) | GARNET (phase I) |
| Recommended Regimen |
Adults: IV 200 mg every 3 weeks Children: IV 2 mg/kg (maximum 200 mg) every 3 weeks |
Adults: IV 200 mg every 3 weeks OR IV 400 mg every 6 weeks Children: IV 2 mg/kg (maximum 200 mg) every 3 weeks |
IV 500 mg every 3 weeks (dose 1-4) IV 1000 mg every 6 weeks (3 weeks after 4; dose 5+) |
| Number of Patients (n) | 149 | 102 | 209 |
| Number of Unique Cancer Types | 15 | 9 | 16 |
| Most common cancer types | CRC, EC, gastric cancer, CCA | SCLC, CC, EC, anal cancer | EC, CRC, Gastric / GEJ cancer, small intestinal cancer |
| Major Efficacy Outcomes |
ORR = 39.6% (95% CI 31.7-47.9) CR = 11 (7%) PR = 48 (32%) mDOR = NE (95% CI 1.6-22.7) DOR ≥6 months: 78% |
ORR = 29% (95% CI 21-39) CR = 4% PR = 25% mDOR = NR DOR ≥12 months: 57% DOR ≥24 months: 50% |
ORR = 41.6% (95% CI 34.9-48.6) CR = 9.1% PR = 32.5% mDOR = 34.7 months (95% CI 2.6-35.8+) DOR ≥6 months: 95.4% |
| Most common TRAEs |
Systemic (fatigue, fever, pruritus) Gastrointestinal (constipation, diarrhea, nausea, reduced appetite) Respiratory (cough, dyspnea) Immune-mediated (colitis, endocrinopathies, hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis) Musculoskeletal (musculoskeletal pain) Dermatologic (rash) |
Systemic (fatigue, fever, pruritus, pain) Gastrointestinal (abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, reduced appetite, nausea) Respiratory (cough, dyspnea) Immune-mediated (colitis, endocrinopathies, hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis) Musculoskeletal (musculoskeletal pain) Dermatologic (rash) |
Most common all-grade TRAEs: Systemic (fatigue, asthenia) Gastrointestinal (diarrhea, nausea) Hematological (anemia) Immune-mediated (colitis, endocrinopathies, hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis) Dermatologic Most common high-grade TRAEs: General (fatigue, asthenia, sepsis) Hematologic (anemia) Hepatic (increased liver enzymes) Renal (acute kidney injury) |
| Reference (s) |
FDA, 2017 Marabelle et al, 2020 |
FDA, 2020 Marcus et al, 2021 |
FDA, 2021 Andre et al, 2023 |
2.2. Pembrolizumab Approved for Patients with Unresectable Or Metastatic TMB-H Cancers (June 16, 2020)
2.3. Dostarlimab Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic dMMR Cancers (August 17, 2021)
3. Approved Targeted Cancer Therapeutics in the Subject of Histology Agnostic Drug Development
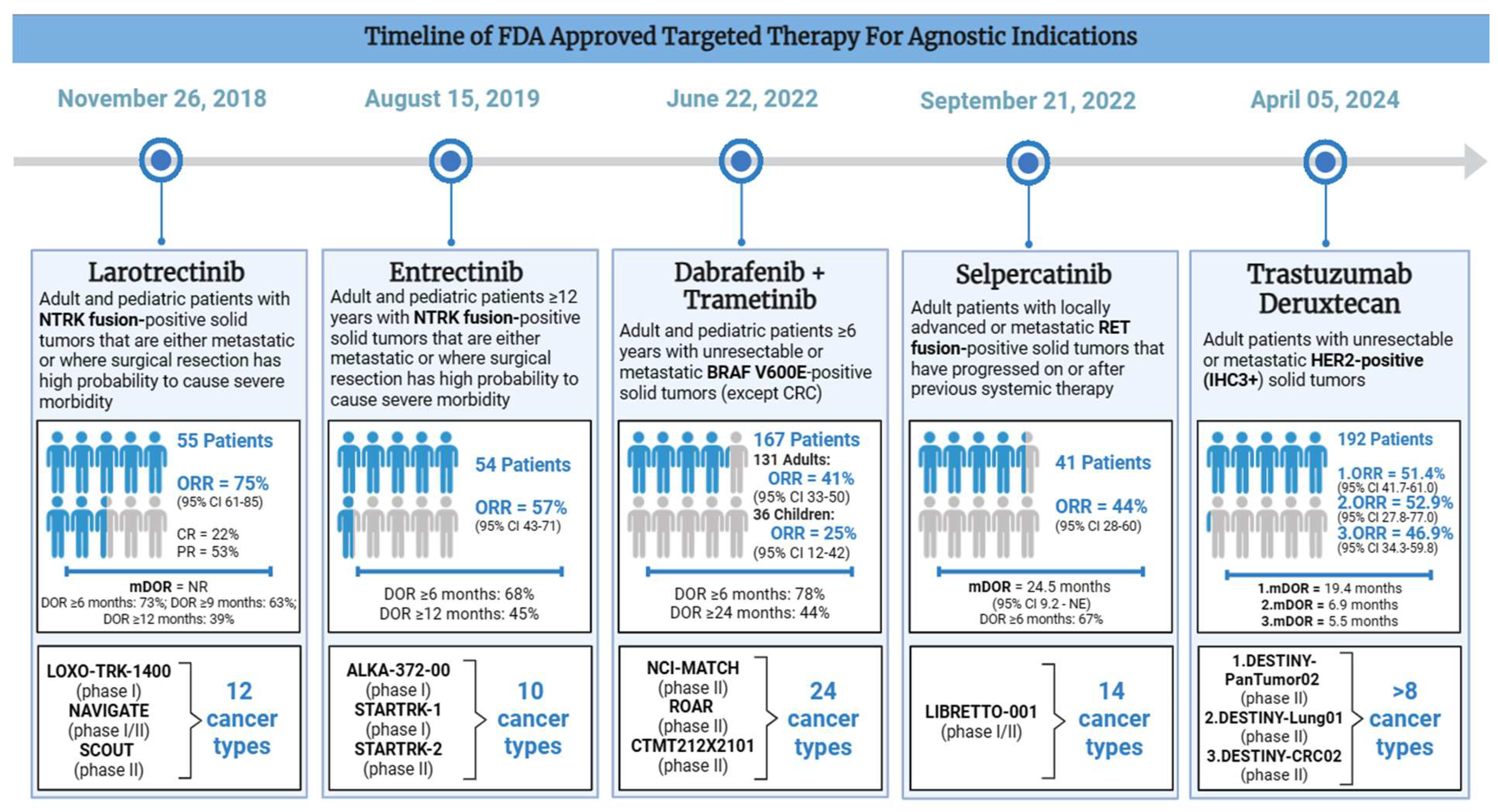
3.1. Larotrectinib Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Cancers (November 26, 2018)
| Drug Name (s) | Larotrectinib | Entrectinib | Dabrafenib + Trametinib | Selpercatinib | Trastuzumab Deruxtecan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | NTRK fusion inhibition | NTRK fusion inhibition | BRAF + MEK inhibition | RET fusion inhibition | HER2 inhibition |
| Indication | Adult and pediatric patients with NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors that are either metastatic or where surgical resection has high probability to cause severe morbidity No known acquired resistance and no satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression after treatment |
Adult and pediatric patients ≥12 years with NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors that are either metastatic or where surgical resection has high probability to cause severe morbidity No known acquired resistance and no satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression after treatment |
Adult and pediatric patients ≥6 years with unresectable or metastaticBRAFV600E-positive solid tumors (except CRC) No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment |
Adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive solid tumors that have progressed on or after previous systemic therapy No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment |
Adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive (IHC3+) solid tumors No satisfactory alternative treatments available or progression despite previous treatment |
| Date of FDA Approval | November 26, 2018 | August 15, 2019 | June 22, 2022 | September 21, 2022 | April 05, 2024 |
| Clinical Trial (s) |
LOXO-TRK-1400 (phase I) NAVIGATE (phase I/II) SCOUT (phase II) |
ALKA-372-00 (phase I) STARTRK-1 (phase I) STARTRK-2 (phase II) |
NCI-MATCH (phase II) ROAR (phase II) CTMT212X2101 (phase II) |
LIBRETTO-001 (phase I/II) |
DESTINY-PanTumor02 (phase II) DESTINY-Lung01(phase II) DESTINY-CRC02 (phase II) |
| Recommended Regimen |
Adult patients: PO 100 mg twice daily Pediatric patients: PO 100 mg/m2 (maximum of 100 mg) twice daily |
Route: Oral Dose: 600 mg (children ≥ 12 years: dose based on body surface area) Frequency: Once daily |
Adult patients: PO dabrafenib 150 mg (given as two 75 mg capsules) twice daily PLUS PO trametinib 2 mg once daily\ Pediatric patients: Weight-Based Doses* *no recommended dose established for patients <26 kg |
PO 120 mg twice daily (<50 kg) OR PO 160 mg twice daily (≥50 kg) | IV 5.4 mg/kg every 3 weeks |
| Number of Patients (n) | 55 | 54 | 167 (131 adults, 36 children) |
41 | 192 |
| Number of Unique Cancer Types | 12 | 10 | 24 (includes different LGG and HGG subtypes) |
14 | >8 |
| Most common cancer types | SGT, STS, IFS, TC | Sarcoma, NSCLC, MASC, BC, TC, CRC | BTC, HGG, LGG | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, CRC, SGT, unknown primary *NSCLC and TC excluded |
EC, CC, OC, URO, BTC, NSCLC, CRC |
| Major Efficacy Outcomes |
ORR = 75% (95% CI 61-85) CR = 22% PR = 53% mDOR = NR DOR ≥6 months: 73% DOR ≥9 months: 63% DOR ≥12 months: 39% |
ORR = 57% (95% CI 43-71) DOR ≥6 months: 68% DOR ≥12 months: 45% |
ORR (adult patients): 41% (95% CI 33-50) ORR (pediatric patients): 25% (95% CI 12-42) DOR ≥6 months: 78% DOR ≥24 months: 44% |
ORR = 44% (95% CI 28-60) mDOR = 24.5 months (95% CI 9.2 - NE) DOR ≥6 months: 67% |
DESTINY-PanTumor02: ORR = 51.4% (95% CI 41.7-61.0), mDOR = 19.4 (1.3 - 27.9+) months DESTINY-Lung0: ORR = 52.9% (95% CI 27.8-77.0), mDOR = 6.9 (4.0 - 11.7+) months DESTINY-CRC02: ORR = 46.9% (95% CI 34.3-59.8), mDOR = 5.5 (1.3+ - 9.7+) months |
| Most common TRAEs |
Systemic (fatigue) Gastrointestinal (constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) Hepatic (elevated liver enzymes) Neurological (dizziness) Respiratory (cough) |
Systemic (fatigue, edema, fever, increased weight) Gastrointestinal (constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) Respiratory (cough, dyspnea) Neurological (cognitive impairment, dizziness, dysgeusia, dysesthesia) Musculoskeletal (arthralgia, myalgia) Other (vision disorders) Most serious TRAEs: Cardiac (congestive heart failure, prolonged QT) Hepatic (liver toxicity) Neurological (central nervous system effects) Musculoskeletal (skeletal fractures) Other (high uric acid, vision disorders) |
Adult patients: Systemic (fever, fatigue, chills, edema) Gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea) Respiratory (cough) Hematologic (hemorrhage) Neurological (headache) Musculoskeletal (myalgia, arthralgia) Dermatologic (rash) Pediatric patients: Systemic (fever, fatigue) Gastrointestinal (vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, constipation) Respiratory (cough) Dermatologic (dry skin, rash, dermatitis acneiform) Neurologic (headache) Hematologic (hemorrhage) Other (paronychia) |
Systemic (edema, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension) Gastrointestinal (diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, nausea) Neurological (headache) Dermatologic (rash) |
Systemic (fatigue) Hematological (decreased lymphocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes) Gastrointestinal (vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, constipation, stomatitis) Hepatic (elevated liver enzymes) Respiratory (upper respiratory tract infection) Dermatologic (alopecia) Other (elevated alkaline phosphatase, decreased potassium and sodium) |
| Reference (s) | FDA, 2018 |
FDA, 2019 Doebele et al, 2020 |
FDA, 2022 | FDA, 2022 |
FDA, 2024 Meric-Bernstam et al, 2023 |
3.2. Entrectinib Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Cancers (August 15, 2019)
3.3. Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic BRAFV600E Positive Cancers (June 22, 2022)
3.4. Selpercatinib Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic RET-Positive Cancers in Patients ≥12 Years (September 21, 2022)
3.5. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan Approved for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic HER2-Positive Cancers (April 05, 2024)
4. Biostatistics—Trial Design and Conducting in Tissue-Agnostic Drug Approvals
5. Future Directions and Challenges
5.1. Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR)
5.2. Tackling Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Virus (KRASG12C)
6. Conclusions
Disclosures
References
- André, T.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2207-2218. [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409-413. [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Lemery, S.J.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Microsatellite Instability-High Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2019, 25, 3753-3758. [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cazzato, E.; Ladewig, E.; Frattini, V.; Rosenbloom, D.I.; Zairis, S.; Abate, F.; Liu, Z.; Elliott, O.; Shin, Y.J.; et al. Clonal evolution of glioblastoma under therapy. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 768-776. [CrossRef]
- Daniel, P.; Sabri, S.; Chaddad, A.; Meehan, B.; Jean-Claude, B.; Rak, J.; Abdulkarim, B.S. Temozolomide Induced Hypermutation in Glioma: Evolutionary Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 41. [CrossRef]
- AlHarbi, M.; Ali Mobark, N.; AlMubarak, L.; Aljelaify, R.; AlSaeed, M.; Almutairi, A.; Alqubaishi, F.; Hussain, M.E.; Balbaid, A.A.O.; Said Marie, A.; et al. Durable Response to Nivolumab in a Pediatric Patient with Refractory Glioblastoma and Constitutional Biallelic Mismatch Repair Deficiency. The oncologist 2018, 23, 1401-1406. [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Larouche, V.; Campbell, B.B.; Merico, D.; de Borja, R.; Aronson, M.; Durno, C.; Krueger, J.; Cabric, V.; Ramaswamy, V.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for Hypermutant Glioblastoma Multiforme Resulting From Germline Biallelic Mismatch Repair Deficiency. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 2206-2211. [CrossRef]
- Suerink, M.; Wimmer, K.; Brugieres, L.; Colas, C.; Gallon, R.; Ripperger, T.; Benusiglio, P.R.; Bleiker, E.M.A.; Ghorbanoghli, Z.; Goldberg, Y.; et al. Report of the fifth meeting of the European Consortium 'Care for CMMRD' (C4CMMRD), Leiden, The Netherlands, July 6th 2019. Fam Cancer 2021, 20, 67-73. [CrossRef]
- Klempner, S.J.; Fabrizio, D.; Bane, S.; Reinhart, M.; Peoples, T.; Ali, S.M.; Sokol, E.S.; Frampton, G.; Schrock, A.B.; Anhorn, R.; et al. Tumor Mutational Burden as a Predictive Biomarker for Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review of Current Evidence. The oncologist 2020, 25, e147-e159. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.M.; Eng, K.; Beg, S.; Beltran, H.; Faltas, B.M.; Mosquera, J.M.; Nanus, D.M.; Pisapia, D.J.; Rao, R.A.; Robinson, B.D.; et al. Cancer-Specific Thresholds Adjust for Whole Exome Sequencing–Based Tumor Mutational Burden Distribution. JCO Precision Oncology 2019, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 1353-1365. [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.A.; Donoghue, M.; Yuan, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Gallagher, P.S.; Philip, R.; Ghosh, S.; Theoret, M.R.; Beaver, J.A.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of tumor mutational burden-high solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2021. [CrossRef]
- Oaknin, A.; Gilbert, L.; Tinker, A.V.; Brown, J.; Mathews, C.; Press, J.; Sabatier, R.; O'Malley, D.M.; Samouelian, V.; Boni, V.; et al. Safety and antitumor activity of dostarlimab in patients with advanced or recurrent DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability-high (dMMR/MSI-H) or proficient/stable (MMRp/MSS) endometrial cancer: interim results from GARNET-a phase I, single-arm study. J Immunother Cancer 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- André, T.; Berton, D.; Curigliano, G.; Sabatier, R.; Tinker, A.V.; Oaknin, A.; Ellard, S.; de Braud, F.; Arkenau, H.T.; Trigo, J.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Safety of Dostarlimab Monotherapy in Patients With Mismatch Repair Deficient Solid Tumors: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2341165. [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.; Roda, D.; Pikiel, J.; Trigo, J.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Drew, Y.; Kristeleit, R.; Hiret, S.; Bajor, D.L.; Cruz, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Dostarlimab in Patients With Recurrent/Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from Cohort E of the Phase I GARNET Trial. Clin Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e415-e427. [CrossRef]
- Andre, T.; Berton, D.; Curigliano, G.; Jimenez-Rodriguez, B.; Ellard, S.; Gravina, A.; Miller, R.; Tinker, A.; Jewell, A.; Pikiel, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dostarlimab in patients (pts) with mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) solid tumors: Analysis of 2 cohorts in the GARNET study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2022, 40, 2587-2587. [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Vale, N. Dostarlimab: A Review. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Bencardino, K.; Pizzutilo, E.G.; Tosi, F.; Siena, S. Tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) biology and the role of NTRK gene fusions in cancer. Ann Oncol 2019, 30, viii5-viii15. [CrossRef]
- Manea, C.A.; Badiu, D.C.; Ploscaru, I.C.; Zgura, A.; Bacinschi, X.; Smarandache, C.G.; Serban, D.; Popescu, C.G.; Grigorean, V.T.; Botnarciuc, V. A review of NTRK fusions in cancer. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2022, 79, 103893. [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Hu, Z.I.; Lai, G.G.Y.; Tan, D.S.W. Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018, 15, 151-167. [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, T.W.; Hong, D.S. Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of TRK Fusion Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Drilon, A.E.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lin, J.J.; Kummar, S.; McDermott, R.S.; Berlin, J.; Italiano, A.; Lassen, U.N.; Leyvraz, S.; et al. Larotrectinib long-term efficacy and safety in adult patients (pts) with tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) fusion cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, 3141-3141. [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 731-739. [CrossRef]
- Mangum, R.; Parsons, D.W. TRK inhibition for pediatric and adult central nervous system tumors: Early promise and future questions. Neuro Oncol 2022, 24, 1008-1009. [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Donoghue, M.; Aungst, S.; Myers, C.E.; Helms, W.S.; Shen, G.; Zhao, H.; Stephens, O.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Entrectinib for the Treatment of NTRK gene Fusion Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 928-932. [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1-2 trials. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 271-282. [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; De Braud, F.; Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Patel, M.R.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, S.V.; Ahn, M.J.; Chiu, C.H.; Lin, J.J.; et al. Updated Integrated Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Entrectinib in Patients With NTRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2022, 28, 1302-1312. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Ullah, M.; de la Cruz, C.C.; Hunsaker, T.; Senn, C.; Wirz, T.; Wagner, B.; Draganov, D.; Vazvaei, F.; Donzelli, M.; et al. Entrectinib, a TRK/ROS1 inhibitor with anti-CNS tumor activity: differentiation from other inhibitors in its class due to weak interaction with P-glycoprotein. Neuro Oncol 2020, 22, 819-829. [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.A.; Subbiah, V. Expanding the Benefit: Dabrafenib/Trametinib as Tissue-Agnostic Therapy for BRAF V600E-Positive Adult and Pediatric Solid Tumors. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2023, 43, e404770. [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Gray, R.J.; Chen, A.P.; Li, S.; McShane, L.M.; Patton, D.; Hamilton, S.R.; Williams, P.M.; Iafrate, A.J.; Sklar, J.; et al. Molecular Landscape and Actionable Alterations in a Genomically Guided Cancer Clinical Trial: National Cancer Institute Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH). J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 3883-3894. [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Atreya, C.E.; Falchook, G.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Ryan, D.P.; Bendell, J.C.; Hamid, O.; Messersmith, W.A.; Daud, A.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition With Dabrafenib and Trametinib in BRAF V600-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2015, 33, 4023-4031. [CrossRef]
- Barbato, M.I.; Nashed, J.; Bradford, D.; Ren, Y.; Khasar, S.; Miller, C.P.; Zolnik, B.S.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Dabrafenib in Combination with Trametinib for BRAFV600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma. Clin Cancer Res 2024, 30, 263-268. [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; McCusker, M.G.; Russo, A.; Scilla, K.A.; Gittens, A.; Arensmeyer, K.; Mehra, R.; Adamo, V.; Rolfo, C. RET fusions in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 2019, 81, 101911. [CrossRef]
- Duke, E.S.; Bradford, D.; Marcovitz, M.; Amatya, A.K.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Nguyen, E.; Price, L.S.L.; Fourie Zirkelbach, J.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Selpercatinib for the Treatment of Advanced RET Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2023, 29, 3573-3578. [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Wolf, J.; Konda, B.; Kang, H.; Spira, A.; Weiss, J.; Takeda, M.; Ohe, Y.; Khan, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Tumour-agnostic efficacy and safety of selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumours other than lung or thyroid tumours (LIBRETTO-001): a phase 1/2, open-label, basket trial. Lancet Oncol 2022, 23, 1261-1273. [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Drilon, A.E.; Sukrithan, V.; Spira, A.I.; Robinson, B.; Deschler-Baier, B.; Barker, S.; Lin, Y.; Szymczak, S.; Ohe, Y. Durable efficacy of selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion+ solid tumors, with a focus on GI tumors: LIBRETTO-001. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2024, 42, 746-746. [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Drilon, A.; Solomon, B.; Tomasini, P.; Loong, H.H.F.; De Braud, F.G.M.; Goto, K.; Peterson, P.; Barker, S.; Liming, K.; et al. 35P Final data from phase I/II LIBRETTO-001 trial of selpercatinib in RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2024, 9. [CrossRef]
- Wirth, L.J.; Sherman, E.; Robinson, B.; Solomon, B.; Kang, H.; Lorch, J.; Worden, F.; Brose, M.; Patel, J.; Leboulleux, S.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET-Altered Thyroid Cancers. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 825-835. [CrossRef]
- Alrhmoun, S.; Sennikov, S. The Role of Tumor-Associated Antigen HER2/neu in Tumor Development and the Different Approaches for Using It in Treatment: Many Choices and Future Directions. Cancers 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Chari, R.V.; Miller, M.L.; Widdison, W.C. Antibody-drug conjugates: an emerging concept in cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2014, 53, 3796-3827. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.L.; Yang, H.T.; Huang, T.; Yu, Z.R.; Ren, N.; Su, J.Y.; Lin, X.L.; Zhou, H.R. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3 randomized controlled trials. Am J Cancer Res 2023, 13, 3266-3274.
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Makker, V.; Oaknin, A.; Oh, D.Y.; Banerjee, S.; González-Martín, A.; Jung, K.H.; Ługowska, I.; Manso, L.; Manzano, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Patients With HER2-Expressing Solid Tumors: Primary Results From the DESTINY-PanTumor02 Phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol 2024, 42, 47-58. [CrossRef]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Makker, V.; Oaknin, A.; Oh, D.-Y.; Banerjee, S.N.; Martin, A.G.; Jung, K.H.; Lugowska, I.A.; Manso, L.; Manzano, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) in patients (pts) with HER2-expressing solid tumors: DESTINY-PanTumor02 (DP-02) interim results. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, LBA3000-LBA3000. [CrossRef]
- Raghav, K.P.S.; Siena, S.; Takashima, A.; Kato, T.; Eynde, M.V.D.; Bartolomeo, M.D.; Komatsu, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Peeters, M.; Andre, T.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) in patients (pts) with HER2-overexpressing/amplified (HER2+) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): Primary results from the multicenter, randomized, phase 2 DESTINY-CRC02 study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, 3501-3501. [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.F.; Felip, E.; Uprety, D.; Nagasaka, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Paz-Ares Rodríguez, L.; Pacheco, J.M.; Li, B.T.; Planchard, D.; Baik, C.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (DESTINY-Lung01): primary results of the HER2-overexpressing cohorts from a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2024, 25, 439-454. [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Goto, Y.; Kubo, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Kim, S.W.; Planchard, D.; Ahn, M.J.; Smit, E.F.; de Langen, A.J.; Pérol, M.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Patients With HER2-Mutant Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Primary Results From the Randomized, Phase II DESTINY-Lung02 Trial. J Clin Oncol 2023, 41, 4852-4863. [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.A. The Brave New World of clinical cancer research: Adaptive biomarker-driven trials integrating clinical practice with clinical research. Mol Oncol 2015, 9, 951-959. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.H.; Siden, E.; Zoratti, M.J.; Dron, L.; Harari, O.; Singer, J.; Lester, R.T.; Thorlund, K.; Mills, E.J. Systematic review of basket trials, umbrella trials, and platform trials: a landscape analysis of master protocols. Trials 2019, 20, 572. [CrossRef]
- Redman, M.W.; Allegra, C.J. The Master Protocol Concept. Semin Oncol 2015, 42, 724-730. [CrossRef]
- Menis, J.; Hasan, B.; Besse, B. New clinical research strategies in thoracic oncology: clinical trial design, adaptive, basket and umbrella trials, new end-points and new evaluations of response. Eur Respir Rev 2014, 23, 367-378. [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.; Geyer, S.; Subramanian, J.; Roychowdhury, S. The Bayesian basket design for genomic variant-driven phase II trials. Semin Oncol 2016, 43, 13-18. [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, S.J.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Simon, R. Improving Clinical Trial Efficiency: Thinking outside the Box. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2015, e141-147. [CrossRef]
- Renfro, L.A.; Sargent, D.J. Statistical controversies in clinical research: basket trials, umbrella trials, and other master protocols: a review and examples. Ann Oncol 2017, 28, 34-43. [CrossRef]
- Mansinho, A.; Fernandes, R.M.; Carneiro, A.V. Histology-Agnostic Drugs: A Paradigm Shift-A Narrative Review. Adv Ther 2023, 40, 1379-1392. [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, B.P.; Pestana, R.C.; Zabor, E.C.; Kaizer, A.M.; Hong, D.S. Basket Trials: Review of Current Practice and Innovations for Future Trials. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 3520-3528. [CrossRef]
- Tissue Agnostic Drug Development in Oncology. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/tissue-agnostic-drug-development-oncology (accessed on May 17).
- Kaizer, A.M.; Koopmeiners, J.S.; Kane, M.J.; Roychoudhury, S.; Hong, D.S.; Hobbs, B.P. Basket Designs: Statistical Considerations for Oncology Trials. JCO Precis Oncol 2019, 3, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Renfro, L.A.; An, M.W.; Mandrekar, S.J. Precision oncology: A new era of cancer clinical trials. Cancer Lett 2017, 387, 121-126. [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, B.P.; Berry, D.A.; Coombes, K.R. 17 - Biostatistics and Bioinformatics in Clinical Trials. In Abeloff's Clinical Oncology (Sixth Edition), Niederhuber, J.E., Armitage, J.O., Kastan, M.B., Doroshow, J.H., Tepper, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, 2020; pp. 284-295.e282.
- Burock, S.; Meunier, F.; Lacombe, D. How can innovative forms of clinical research contribute to deliver affordable cancer care in an evolving health care environment? Eur J Cancer 2013, 49, 2777-2783. [CrossRef]
- Sleijfer, S.; Bogaerts, J.; Siu, L.L. Designing transformative clinical trials in the cancer genome era. J Clin Oncol 2013, 31, 1834-1841. [CrossRef]
- Singer, J.; Irmisch, A.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Singer, F.; Toussaint, N.C.; Levesque, M.P.; Stekhoven, D.J.; Beerenwinkel, N. Bioinformatics for precision oncology. Brief Bioinform 2019, 20, 778-788. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Fang, W. FGFR families: biological functions and therapeutic interventions in tumors. MedComm (2020) 2023, 4, e367. [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Schuler, M.H.; Iyer, G.; Witt, O.; Doi, T.; Qin, S.; Tabernero, J.; Reardon, D.A.; Massard, C.; Welsh, L.; et al. Tumor agnostic efficacy and safety of erdafitinib (erda) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors with prespecified FGFR alterations (FGFRalt): RAGNAR primary analysis. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, 3121-3121. [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Schuler, M.; Iyer, G.; Witt, O.; Doi, T.; Qin, S.; Tabernero, J.; Reardon, D.A.; Massard, C.; Minchom, A.; et al. Erdafitinib in patients with advanced solid tumours with FGFR alterations (RAGNAR): an international, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 2023, 24, 925-935. [CrossRef]
- Vega, L.L.D.L.; Comeau, H.; Sallan, S.; Al-Ibraheemi, A.; Gupta, H.; Li, Y.Y.; Tsai, H.K.; Kang, W.; Ward, A.; Church, A.J.; et al. Rare FGFR Oncogenic Alterations in Sequenced Pediatric Solid and Brain Tumors Suggest FGFR Is a Relevant Molecular Target in Childhood Cancer. JCO Precision Oncology 2022, e2200390. [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.H.; Gerlach, D.; Misale, S.; Petronczki, M.; Kraut, N. Expanding the Reach of Precision Oncology by Drugging All KRAS Mutants. Cancer Discov 2022, 12, 924-937. [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.; LoRusso, P.; Patel, M.R.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Garralda, E.; Forster, M.D.; Santoro, A.; Falcon, A.; Kim, T.W.; Paz-Ares, L.; et al. Single-Agent Divarasib (GDC-6036) in Solid Tumors with a KRAS G12C Mutation. N Engl J Med 2023, 389, 710-721. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





