Introduction
Machine Learning (ML) has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing various academic disciplines and industries through its capacity to derive valuable insights from data. This powerful approach, which integrates statistical techniques, computational algorithms, and artificial intelligence, has gained widespread popularity due to its remarkable capacity to identify patterns, make predictions, and automate decision–making processes. The impact of machine learning has been profound across a diverse range of fields, including urban sciences, clinical research (Weissler et al., 2021; Miller, et al., 2023), biology (Noorbakhsh, et al., 2019; Greener et al., 2022; Chung, et al., 2021; Ahlquist, et al., 2023), engineering (Grande and Imbimbo, 2012; Barbhuiya and Sharif, 2023), computer simulations of physics–based models (Monteleoni, et al., 2011; Kashinath, et al., 2021; Willard et al., 2022; Jamous, et al., 2023) and many others. Its versatility and adaptability have made it an indispensable tool for researchers, scientists, and professionals seeking to unleash the full potential of their datasets.
Machine learning’s relationship with urban sciences is emblematic of its transformative power across academic and professional landscapes. As urban scholars grapple with the complexities of city life, machine learning offers a robust set of tools to illuminate the hidden patterns within urban data. The predictive prowess of machine learning algorithms can forecast urban growth, simulate the effects of policy changes, and provide a data–driven foundation for urban sustainability initiatives. In the context of urban sciences, machine learning aids in the analysis of social and spatial data, enabling researchers to uncover correlations between urban phenomena such as housing density, transportation networks, and public health outcomes. By harnessing the vast amounts of data generated within urban environments, from traffic sensors to housing market statistics, machine learning algorithms can help urban planners optimize land use, improve infrastructure, and enhance the quality of life for city dwellers. By employing statistical techniques, computational algorithms, and artificial intelligence, ML facilitates a nuanced exploration of the multifaceted challenges cities face, such as spatial analysis, urban gentrification (Reades, 2019), segregation, and sustainability (Li, et al., 2023; Tsagkis, et al., 2023).
Furthermore, machine learning’s ability to process and analyze large–scale geospatial data is invaluable for urban sciences. It can be used to monitor urban expansion, detect changes in land use (Yuh, et al., 2023), and to predict air quality (Zhu, et al., 2018). The integration of machine learning into urban sciences also facilitates the exploration of socio–economic disparities, providing a quantitative basis for addressing issues of inequality and social justice within urban settings. As machine learning continues to evolve, its applications in urban sciences are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering unprecedented opportunities for urban scholars to engage with complex urban challenges. The synergy between machine learning and urban sciences not only enhances our understanding of urban dynamics but also equips policymakers with the insights needed to foster more resilient and equitable urban futures.
Zheng, et al. (2023a) propose an AI model for spatial planning of urban communities. Key aspects cover representing urban areas as graphs to capture irregular topologies; formulating planning as a sequential decision–making problem on graphs; and using reinforcement learning with graph neural networks to explore vast solution space. The AI model outperforms human experts in objective metrics and can generate efficient plans tailored to different needs. A human–AI collaborative workflow is proposed to enhance productivity and plan quality. This demonstrates the potential of computational approaches in tackling complex urban planning challenges.
Zheng, et al. (2023b) propose a new approach to identify and analyze mixed–use urban functional areas in Jinan, China, using big spatiotemporal data. Key aspects include applying a revised information entropy method to quantify the degree of functional mixing; combining road network and kernel density methods for accurate identification of functional areas; and simulating urban layout in 2025 using the CA–Markov model. Their results show an increasing trend of mixed–use areas in Jinan’s central region from 2015 to 2025. The study suggests optimizing urban functions by expanding mixed–use areas, increasing infrastructure, and improving spatial efficiency.
Based on 140 publications, Wang and Biljecki (2022) highlights the growing importance of unsupervised learning (UL) techniques in urban sciences. Clustering and topic modeling emerge as the most widely used UL methods, applied across four main areas, namely urbanization, built environment, sustainability, and urban dynamics. While UL offers powerful pattern discovery capabilities from unlabeled data, limitations around data quality, interpretation, and validation need to be addressed. Nevertheless, the integration of multi–source urban data and the potential of UL to drive data–driven decision-making position it as a promising approach for understanding and managing complex urban systems.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the way we live and govern cities (Cugurullo, et al., 2024). This study looks at how AI is affecting the way cities develop and argues that it’s different from what's known as “smart urbanism”. In the future, AI could lead to the creation of “autonomous cities” that are different from traditional “smart cities”. It compares what we know about smart urbanism with new ideas and practices that are emerging due to AI; discusses the limitations and potential problems of AI in cities, and finally provide ways to understand and think about the impact of AI on cities now and in the future.
The transportation sector has experienced significant advancements through the incorporation of ML technologies, particularly in domains such as traffic management, route optimization, and predictive maintenance. The sustainable development of freight transport has become a major focus. To measure its impact, companies need to develop methods to assess their social and environmental performance. Castaneda, et al (2021) propose to use a supervised machine learning approach to determine the level of sustainability (high, medium, or low) based on specific indicators. The model is tested on an European company in the road freight sector, showing a high accuracy rate. The results enable the development of green strategies for sustainable development (see also Hamner, 2010; Ahmed and Abdel–Aty, 2013; Chung, 2013; Zhang and Haghani, 2015).
ML technology has also changed the real estate industry in recent years. It uses large datasets and complex algorithms to make property valuations, market analysis, and investment decisions more accurate and efficient. By leveraging these insights, stakeholders in the real estate sector can make more informed decisions and achieve better outcomes. According to recent studies (Ho, et al., 2021; Kalliola, et al., 2021; Hjort, et al., 2022; Calainho, et al., 2022; Lorenz, et al., 2023), ML–powered property valuation models are more accurate than traditional methods, and ML–based market analysis can help identify opportunities that may have been overlooked through traditional methods alone.
Literature Review
This section explores three machine learning algorithms used in urban problems. We start with Gradient Boosting Machine, a powerful ensemble learning algorithm that combines multiple weak models to create a strong and accurate predictor. It’s effective for complex datasets and can be used for regression, classification, and feature selection. Next, we examine Random Forest, a popular ensemble learning method that combines multiple decision trees to create a robust and accurate model. It’s known for handling large datasets and can be used for various tasks, including classification, regression, and clustering.
Finally, we discuss three hyperparameter tuning methods that can be used to optimize the performance of these algorithms. These methods are: Optuna, a state–of–the–art Bayesian optimization method that uses a tree–structured Parzen estimator to search for the optimal hyperparameters; Random Search, a simple and efficient method that randomly samples the hyperparameter space to find the optimal combination; and Grid Search, a brute–force method that exhaustively searches the hyperparameter space by evaluating each combination of hyperparameters.
Gradient Boosting Machine
GBMs have become as one of the most widely used machine learning techniques for both regression and classification tasks. They are a type of ensemble learning methods and combine multiple weak learners, typically decision trees, to transform into a strong predictive model. The idea behind gradient boosting is to iteratively improve the model by fitting new weak learners to the residuals of the previous iterations, thereby reducing the overall error (Friedman, 1999). GBMs excel in handling heterogeneous data types, feature interactions, and non–linear relationships, making them suitable for a wide range of real–world applications. They have been successfully applied in areas such as urban problems, real estate, finance, healthcare, and more.
Renaud et al. (2023) suggest using machine learning to detect and prevent Internet of Things (IoT) attacks. Their study focuses on detecting noise level anomalies in a city suburb using machine learning algorithms, including Gradient Boosting Machine and Deep Learning. Two types of attacks are tested: sudden and gradual changes in noise levels. Their results show that their approach can effectively detect these anomalies, even small changes in noise levels. This can help cities protect their infrastructure and ensure a safer and more sustainable environment for citizens.
Ho, et al. (2021) employs three machine learning algorithms, namely support vector machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM), to assess property prices. This study applies these methods to a dataset of 39,554 housing transactions in Hong Kong during the period between June 1996 and August 2014, and then compares their results. In terms of predictive power, GBM and RF outperform SVM, as demonstrated by their lower values of standard evaluation metrics.
Based on GBM, Long et al. (2022) introduce a non–parametric method to measure how connected financial institutions are, and how this affects their risk of failing. This paper studies the connections between banks in China, and finds that banks with similar characteristics tend to be more connected and riskier, especially those heavily involved in interbank activities like Industrial Bank. The banking system becomes more connected during times of financial stress, and state–owned banks are more likely to be the source of risk during instability.
Yin, et al. (2024) suggest that the GBM can effectively impute missing values related to monitoring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions in healthcare facilities. By using larger datasets and the GBM, researchers can improve the accuracy of filling missing values, providing a more precise depiction of GHG emissions from healthcare facilities. This could influence policy–making and regulatory practices for monitoring and reporting GHG emissions. In this paper, hyperparameters are optimized by tuning with Grid Search.
Despite their effectiveness, GBMs come with a myriad of hyperparameters that need to be carefully tuned to achieve optimal performance. Hyperparameters control various aspects of the model, such as tree depth, learning rate, regularization, and number of boosting iterations. Manual tuning of these hyperparameters can be time–consuming and inefficient, especially given the high–dimensional search space.
Random Forest
RF was introduced by Leo Breiman in 2001, as an ensemble method for classification and regression tasks (Breiman, 2001). This innovative approach combines bootstrap aggregation and decision trees to create a powerful predictive model, which has significantly influenced the field of machine learning and remains a cornerstone in the development of ensemble methods.
Random Forest operates by constructing a multitude of decision trees during the training phase, which are then combined to produce the final prediction. The strength of Random Forest lies in its ability to handle large datasets with high dimensionality, while also providing resistance to overfitting. Furthermore, due to the nature of the algorithm, it can naturally handle missing values and maintain predictive accuracy even with a large number of irrelevant features.
Urban planning is becoming increasingly complex due to the vast amount of data available. The integration and adoption of advanced information technologies within the domain of urban planning have progressed at a relatively gradual pace. This trend has been particularly evident in recent years, notably in the context of ‘smart city’ technologies and their implementation in urban environments. Despite the rapid advancements in information and communication technologies (ICTs) across various sectors, their application and assimilation into urban planning practices and methodologies have not kept pace with the potential offered by these innovations. This lag in technological adoption presents both challenges and opportunities for urban planners, policymakers, and researchers to bridge the gap between cutting–edge technological capabilities and their practical application in shaping more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban spaces. Advances in information technologies have moved very slowly in the field of urban planning, more recently concerning ‘smart city’ technologies (Sanchez, et al., 2022; Jun, et al., 2023).
Sideris, et al. (2019) propose a solution using machine learning techniques. They combined data from different sources and fed it into a Random Forest classifier and other machine learning models to compare their performance. The results showed that Random Forest performed best in terms of accuracy, precision, and other metrics.
Choy and Ho (2023) seek to demonstrate how machine learning can be used to deliver more accurate pricing predictions, using the real estate market as an example. Utilizing 24,936 housing transaction records, this paper employs Extra Trees (ET), k–Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and RF, followed by hyperparameter tuning by Optuna, to predict property prices and then compares their results with those of a hedonic price model. Their results suggest that these three algorithms markedly outperform the traditional statistical techniques in terms of explanatory power and error minimization.
A study by Aysan, et al. (2024) analyze survey data from 2016 to 2021 and find that Islamic banks' accuracy in survey responses improves with a country's level of development. The study also found a significant reduction in credit portfolio risk due to improved risk management practices, global economic growth, and stricter regulations. Additionally, concerns about terrorism financing and cybersecurity threats have decreased due to strengthened anti-money laundering regulations and investments in cybersecurity infrastructure and education.
Loef et al. (2022) propose an approach to analyze large amounts of exposome data from long–term cohort studies. Their study uses machine learning to identify predictors of health and applied their method to the 30–year Doetinchem Cohort Study. Utilizing Random Forest (RF), their study finds that nine exposures, from different areas, are most important for predicting health, while 87 exposures have little impact. The approach shows an acceptable ability to distinguish between good and poor health, with an accuracy of 70.7%.
Hyperparameter Tuning
Hyperparameter tuning is the process of finding the best combination of hyperparameters for a machine learning model. It plays a crucial role in maximizing performance and generalization while avoiding overfitting. However, the operation of hyperparameter tuning can be computationally expensive, especially for complex models with plenty of hyperparameters. Several techniques have been proposed for hyperparameter tuning, including Grid Search, Random Search, Optuna, and more.
Traditional methods like Random Search and Grid Search often struggle to efficiently explore the high–dimensional hyperparameter space, leading to suboptimal results or excessive computational costs. Grid Search is a method that involves exhaustively evaluating a preset hyperparameter values to find out the optimal combination. Although Grid Search ensures the discovery of the global optimum within the search space, it can incur high computational costs, particularly when dealing with numerous hyperparameters or continuous parameters requiring precise resolutions.
In contrast, Random Search involves randomly sampling hyperparameters from specified distributions. Despite its simplicity, Random Search often surpasses Grid Search in terms of efficiency as it explores the search space more diversely (Bergstra and Bengio, 2012). However, there is no guarantee of finding the global optimum, and the quality of the solution heavily relies on the number of random samples taken.
Optuna represents a recent advancement in hyperparameter tuning techniques, introducing a more streamlined and automated approach centered around Bayesian optimization and tree–structured Parzen estimators (TPE). Diverging from the conventional Grid Search and Random Search methods, Optuna builds probabilistic models to capture the link between hyperparameters and the objective function, enabling informed decisions regarding which hyperparameters to investigate next.
Through the application of Bayesian optimization principles, Optuna intelligently navigates the hyperparameter space by emphasizing promising areas while disregarding less fruitful ones. This adaptive sampling methodology leads to notable reductions in computational expenses and faster convergence towards the optimal solution when compared to traditional approaches. A key strength of Optuna lies in its lightweight and versatile design, facilitating seamless integration with a variety of machine learning libraries and frameworks. Its Pythonic approach to defining search spaces and simple parallelization capabilities further support its user–friendliness and scalability (Optuna, 2018).
Methodology
To conduct a fair comparison, we first implement each hyperparameter tuning method on GBM with identical hyperparameter spaces. The experiments are performed on a dataset representative of real–world scenarios to ensure the relevance of the results. The performance of each method is evaluated based on two main criteria: computational efficiency and model performance metrics. In supplement, we also implement each hyperparameter tuning method on RF with identical hyperparameter spaces. The performance of each method is also evaluated based on the same criteria.
Gradient boosting is a powerful machine learning technique that constructs a predictive model by aggregating multiple weak prediction models, typically comprising decision trees. The fundamental principle underlying boosting is the transformation of a weak learner, a model that exhibits poor performance in predicting the outcome variable Y, into a strong learner. In each iteration, boosting assigns equal weights to each observation, aiming to reduce the differences between the predictions generated by the weak learner and the actual values.
The gradient boosting algorithm employs the error rate to compute the gradient of the loss function, utilizing this gradient to determine the optimal adjustments to the model parameters at each iteration. This iterative process is repeated
m times, where
m is a hyperparameter specified by the data scientist. Target variable
Y is assumed to be a continuous real–valued quantity. This approach endeavors to construct an approximation
to the weighted summation of functions derived from weak learners
.
We can then utilize Equation (2) to seek an approximation that minimizes the average value of the loss function over the training set, and commence with a model comprising a constant function, and subsequently transform it into Equation (3):
represents a base learner function where
h denotes the optimal function at each step. However, it is not feasible to precisely determine the optimal function
h that minimizes the loss function
L, as noted by Swathi and Shravani (2019). To address this minimization problem, data scientists can utilize a steepest descent approach. Under the assumption that
is the set of arbitrary differentiable functions on ℝ, the model can be updated according to the following equations:
where the derivatives are taken with respect to the functions
for
is the step length.
While this methodology may furnish an approximate solution to the minimization problem, it is essential to acknowledge that the estimation of a GBM will only yield an approximation. The performance of the model can be evaluated by calculating the coefficient of determination
for the test set, as well as assessing the mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and root mean squared error (RMSE) respectively.
where
and
represent the predicted value and actual value of the target variable
Y, respectively; and
m represents the number of observations in the test data.
Ultimately, the hyperparameters associated with the model can be optimized using various techniques, including Optuna, Random Search, and Grid Search, to further enhance the accuracy of the model. Hyperparameters are essential to determine the performance and ability to generalize of machine learning models. Properly tuned hyperparameters can significantly improve a model’s accuracy, efficiency, and robustness, enabling it to better capture the underlying patterns in the data and make more reliable predictions.
The Random Forest algorithm is a supervised learning technique that utilizes an ensemble learning approach for both classification and regression tasks. It operates by constructing a specified number of regression trees, subsequently combining these trees into a unified model to yield more accurate predictions than those generated by an individual tree. Random Forest undertakes the construction of numerous decision trees during the training phase, where predictions from all trees are aggregated to produce the final prediction.
By employing random sampling with replacement, a process known as “bagging” in machine learning terminology (Breiman, 1996; 1997), Random Forest aids data scientists in mitigating the variance associated with algorithms characterized by high variance, such as decision trees. When provided with a training set comprising features denoted as X and corresponding outputs designated as Y, bagging iteratively selects random samples from the training set times and fits the trees to these respective samples.
For each decision tree
, a random sample of instances is drawn with replacement from the training dataset. Each sequence of instances corresponds to a distinct random vector
, which in turn contributes to the formation of a specific tree. Due to the inherent variability in these sequences, the decision trees constructed from them also exhibit slight variance. De Aquino Afonso et al. (2020) propose that the prediction generated by the
K–th tree for a given input X can be expressed using Equation (10):
where
K is the number of trees. During the process of tree splitting, features are randomly selected at each node to prevent correlations among them. A node denoted as S can be divided into two subsets, S1 and S2, by choosing a threshold denoted as "c," which minimizes the disparity in the sum of squared errors.
By adhering to identical decision rules, any subtree’s output can be predicted as the mean or median output of the respective instances. Eventually, the final prediction can be derived as the average of the output from each tree, as articulated in Equation (12).
The performance of the model can be evaluated by calculating the coefficient of determination
for the test set, as well as assessing the mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and root mean squared error (RMSE) respectively. Ultimately, the hyperparameters associated with the model can be optimized using Optuna, Random Search and Grid Search to boost the performance of the model.
Table 1.
Hyperparameter Space for GBM and RF.
Table 1.
Hyperparameter Space for GBM and RF.
| |
GBM |
RF |
| bootstrap |
|
True |
| criterion |
friedman_mse |
friedman_mse |
| learning_rate |
0.1 |
|
| loss |
squared_error |
|
| max_depth |
2, 3, …, 10 |
10, 11, …, 20 |
| max_features |
sqrt |
sqrt |
| min_samples_leaf |
2, 3, …, 10 |
2, 3, …, 10 |
| min_samples_split |
2, 3, …, 10 |
2, 3, …, 10 |
| n_estimators |
500, 510, …, 600 |
50, 60, …, 150 |
| Subsample |
0.6 |
|
Data Definitions and Sources
In this study, we focused on the analysis of one specific private housing estate, Ocean Shores, in the Tseung Kwan O district of Hong Kong. This housing estate is classified as one of the “selected popular residential developments” by the Rating and Valuation Department of the Hong Kong SAR Government. Ocean Shores consists of 15 residential blocks and 5,726 domestic units. Our dataset covers the period from January 2010 to December 2020, with a total of 7,652 cross–sectional observations. Detailed information on individual buildings, locations, transaction dates, occupation permits, sale prices, square footage, and other property characteristics (such as the inclusion of a parking space) is maintained by the government and compiled by a commercial entity known as "EPRC." Property prices in our analysis are adjusted for inflation using the popular housing estate price index published by the Rating and Valuation Department. Some records were excluded from our dataset due to inaccuracies.
where
represents the total transaction price of residential property i during time period t, measured in HK dollars.
represents the net floor area of residential property i.
represents the age of residential property i in years, which can be obtained by the difference between the date of issue of the occupation permit and the date of housing sales.
represents the floor level of residential property i resides.
represent eight orientations that residential property i is facing. They are assigned to be 1 if a property is facing a particular orientation, 0 otherwise. The omitted category is Northwest so that coefficients may be interpreted relative to this category.
Exploratory Data Analysis
Exploratory statistics is a field that focuses on exploring and summarizing datasets to gain insights into patterns, trends, and characteristics before modeling or hypothesis testing. By using graphical and numerical methods, researchers can conduct exploratory data analysis to examine key characteristics.
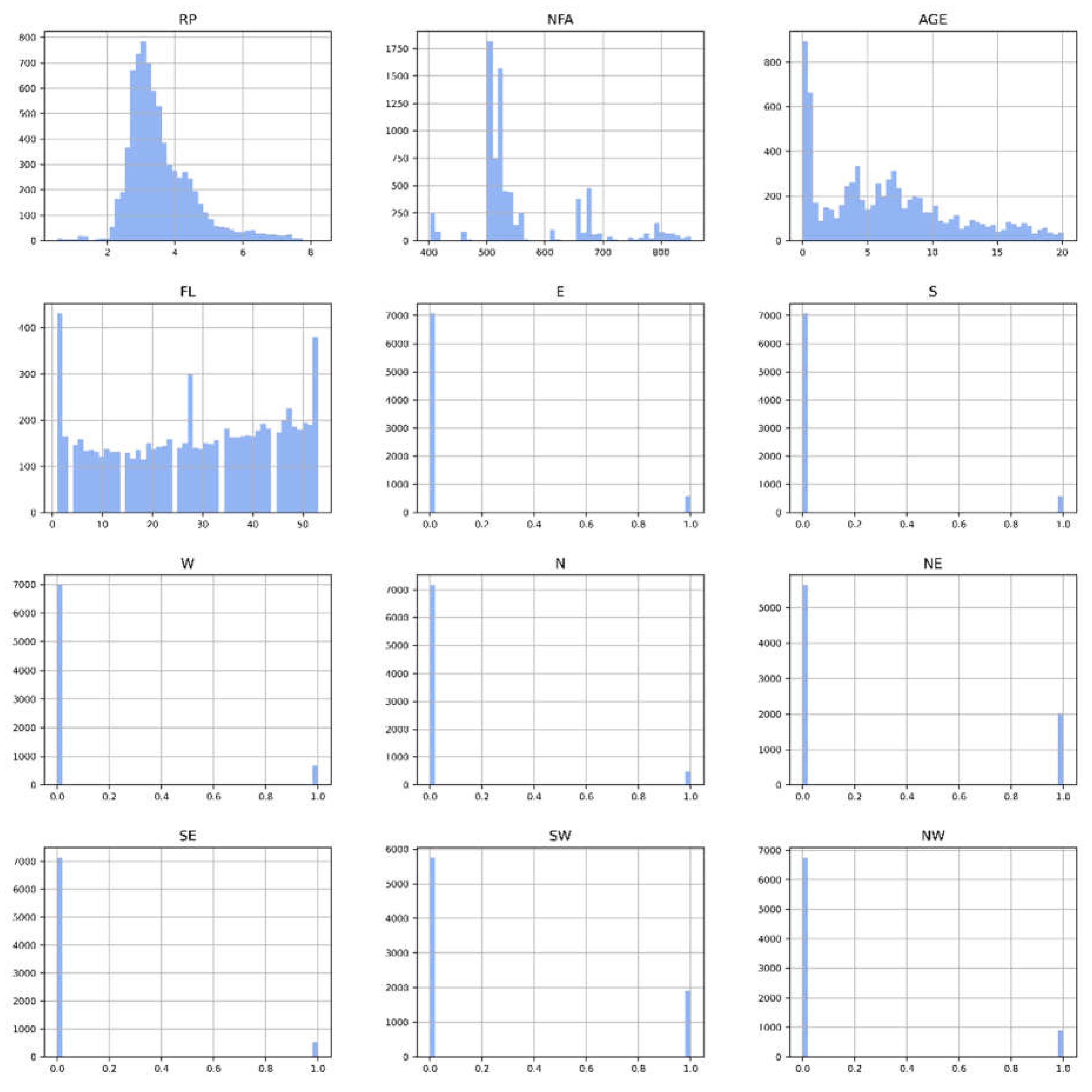
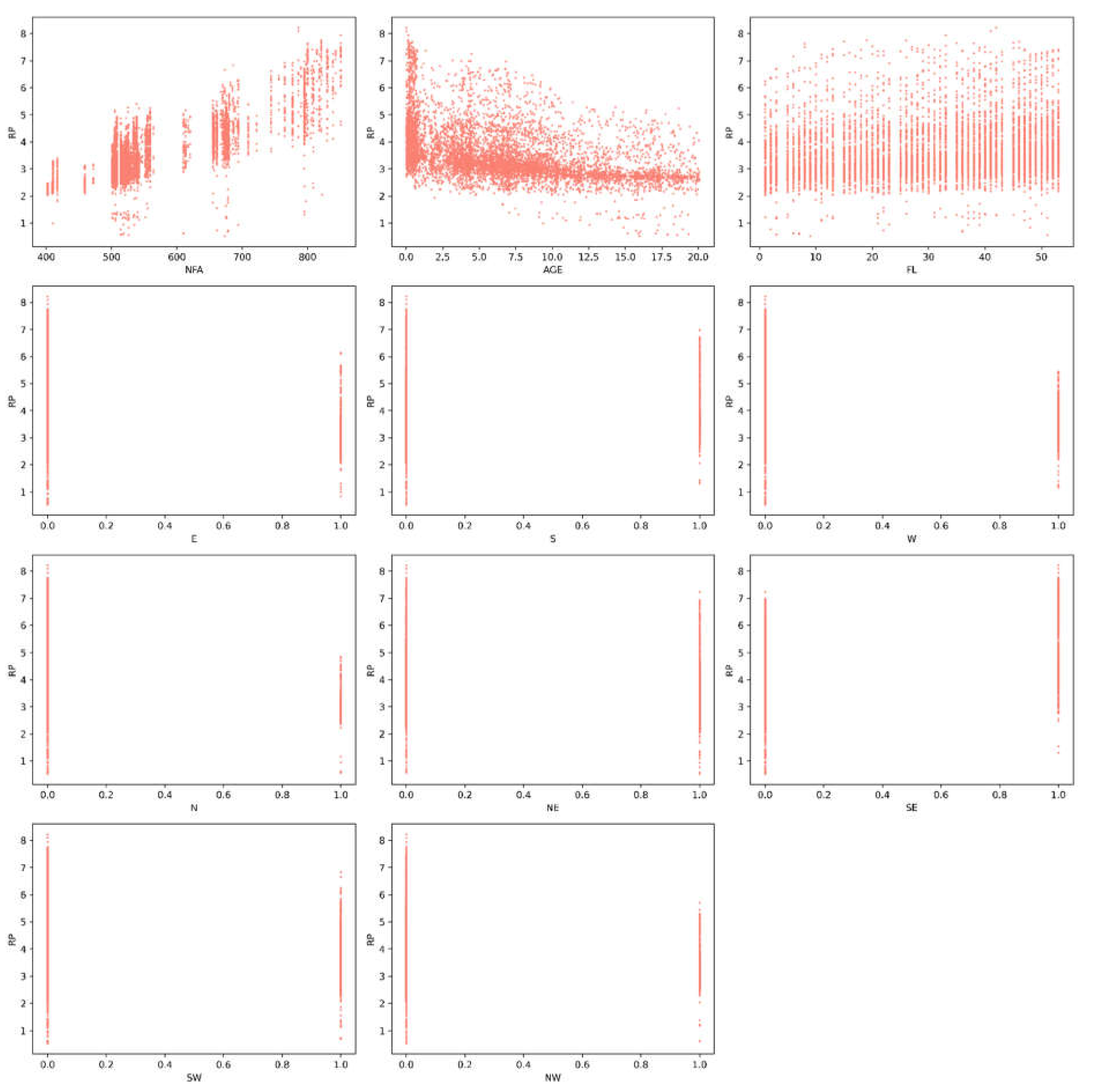
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show histograms, correlations, and a correlation matrix for property prices and features. The results reveal a high correlation between footage area and property prices at 0.8, as well as moderate correlations between southeast at 0.4 and property age at –0.4, and floor level and south at 0.2.
Table 2 provides a summary of descriptive statistics for the features analyzed in this study, offering a concise overview of the dataset.
Results and Discussions
In this study, we partition our dataset into 5 equal folds, using each fold as a test set in a specific iteration. We also apply k–fold cross–validation to evaluate the performance of machine learning models on a subset of the data, typically referred to as the training set (80% of the sample). The remaining 20% is used to generate predictions. This approach allows us to assess the model's performance on various subsamples, developing k distinct models in the process, and evaluating them on unseen data.
Table 3 compares the hyperparameter selections made by three tuning methods after estimating the GBM. The hyperparameters criterion, learning_rate, max_features, and subsample were fixed, while the tuning methods independently selected optimal values for max_depth, min_samples_leaf, min_samples_split, and n_estimators. The results indicate that the three methods do not converge on the same optimal hyperparameters. Specifically, Optuna selects a max_depth of 6, whereas Random Search and Grid Search agree on a value of 5. Similarly, Optuna chooses a min_samples_leaf of 9, while Random Search and Grid Search agree on a value of 10. Furthermore, Optuna selects n_estimators of 520, whereas Random Search and Grid Search agree on a value of 500 for this hyperparameter. Min_samples_split is another hyperparameter where the methods diverge, with Optuna selecting 9, while Random Search and Grid Search choose values of 3 and 2, respectively.
Table 4 presents the results of using GBM optimized by each method. Our findings indicate that Optuna outperforms Random Search and Grid Search in terms of computational efficiency and model performance. Optuna accomplishes the hyperparameter optimization process in a duration of approximately 4.84 minutes, thereby demonstrating a remarkable acceleration of 8.78 times compared to Random Search (42.52 minutes) and an impressive acceleration of 70.50 times compared to Grid Search (341.48 minutes). This substantial reduction in computation time is particularly valuable in situations where resources are limited or time–sensitive applications are involved.
Furthermore, GBM models optimized using Optuna exhibit superior performance metrics compared to those optimized using Random Search and Grid Search. Evaluation metrics such as mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), and root mean squared error (RMSE) consistently display lower values for models optimized by Optuna on the test set, suggesting that Optuna effectively traverses the hyperparameter space to identify optimal configurations that lead to models with enhanced predictive accuracy and generalization capabilities.
Table 3 also presents a comparison of the hyperparameter selections made by three different tuning methods after estimating a Random Forest (RF) model. In our experimental setup, the hyperparameters bootstrap, criterion, and max_features are fixed, while each tuning method independently determine optimal values for max_depth, min_samples_leaf, min_samples_split, and n_estimators. Interestingly, all three tuning methods select the same value for min_samples_leaf at 2. However, differences have emerged in the choice of max_depth, min_samples_split, and n_estimators. Optuna opts for a max_depth of 18, whereas Random Search and Grid Search select values of 19. With regard to min_samples_split, Optuna chooses a value of 3, whereas Random Search and Grid Search select values of 4 and 2, respectively. Furthermore, Optuna and Random Search agree on a value of 130 for n_estimators, while Grid Search selects a value of 110.
In
Table 4, our results based on RF indicate that Optuna surpasses both Random Search and Grid Search in terms of computational efficiency and model performance metrics. Notably, Optuna exhibits significantly faster computation speed, completing the hyperparameter optimization process in approximately 2.91 minutes, a reduction of 5.58 times compared to Random Search (16.23 minutes) and 53.61 times compared to Grid Search (156.02 minutes). RF optimized using Optuna also displays superior performance metrics compared to those optimized using Random Search and Grid Search. Evaluation metrics such as MAE, MSE, MAPE, and RMSE consistently show lower values for Optuna–optimized models based on test set, suggesting that Optuna effectively traverse the hyperparameter space to identify optimal configurations that lead to models with enhanced predictive accuracy and generalization capabilities.
In both algorithms, these lower error values indicate that Optuna–optimized models achieved higher predictive accuracy and better generalization capabilities on unseen test data. By effectively navigating the high–dimensional hyperparameter space, Optuna identifies optimal configurations that enables the trained models to capture the underlying patterns in the data more accurately, leading to improved performance across different error metrics. The exceptional performance of Optuna can be attributed to its innovative algorithmic design, specifically its utilization of Bayesian optimization and pruning techniques. Unlike Random Search, which explores the hyperparameter space randomly, and Grid Search, which follows a systematic search through predefined hyperparameter combinations, Optuna adopts a more intelligent approach by utilizing past trials to steer the search towards promising regions of the hyperparameter space.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the rapid development of machine learning algorithms has opened up new avenues for accelerating research and development in urban sciences research. By leveraging faster hyperparameter optimization methods like Optuna, researchers can optimize the performance of machine learning algorithms and identify new patterns and relationships in complex data sets. This, in turn, enables the development of targeted policies and interventions that can drive tangible real–world impact in urban sciences. The efficiency and accuracy in predictive modeling demonstrated by Optuna are crucial for urban scholarship, as they facilitate the effective analysis of complex urban dynamics and inform decision–making in this field. Therefore, the adoption of advanced hyperparameter tuning methods like Optuna is essential for accelerating the growth and development of urban sciences research.
The potential benefits of using Optuna in urban sciences are vast. By optimizing the performance of machine learning algorithms, researchers can unlock new insights into complex urban phenomena, such as traffic patterns and housing market trends. This, in turn, can inform more effective policy–making and decision–making at the local and national levels. Furthermore, the increased efficiency and accuracy of predictive modeling enabled by Optuna can also help to reduce costs and improve resource allocation in urban planning and development.
In addition, the adoption of advanced hyperparameter tuning methods like Optuna can also help to bridge the gap between academia and practice in urban sciences. By providing researchers with faster and more accurate methods for optimizing machine learning algorithms, Optuna can help to accelerate the translation of research findings into practical solutions for urban challenges. This, in turn, can help to drive innovation and progress in urban sciences research, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable solutions for urban challenges.
Funding
This research has been supported by a research grant from the Department Incentive Fund, Department of Building and Real Estate, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (Project ID P0049970).
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Ahlquis, K. D., Sugden, L. A. & Ramachandran, S. (2023). Enabling interpretable machine learning for biological data with reliability scores. PLOS Computational Biology, 19(5), e1011175. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. M. & Abdel–Aty, M. (2013). Application of stochastic gradient boosting technique to enhance reliability of real–time risk assessment. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2386, 26–34.
- Anjaneyulu. B., Goswami, S., Banik, P., Chauhan, V., Raghav, N. & Chinmay (2024). Revolution of Artificial Intelligence in Computational Chemistry breakthroughs. Chemistry Africa. [CrossRef]
- Aysan, A. F., Ciftler, B. S. & Unal, I. M. (2024). Predictive power of Random Forests in analyzing risk management in Islamic banking. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 17(3), 104. [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, S. & Sharif, S. (2023). Artificial Intelligence in concrete mix design: advances, applications and challenges. 3ICT 2023: International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing, and Technologies. University of Bahrain, Bahrain 20–21 Nov 2023 IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J. & Bengio, Y. (2012). Random Search for hyper-parameter optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 13, 281–305.
- Besson, P., Rogalski, E., Gill, N. P., Zhang, H., Martersteck, A. & Bandt, S. K. (2022). Geometric deep learning reveals a structuro–temporal understanding of healthy and pathologic brain aging. Frontier in Aging Neuroscience, 14, 895535. [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. (1996). Bagging predictors. Machine Learning, 24(2), 123–140.
- Breiman, L. (1997). Arcing the edge (Technical Report 486). Berkeley: Department of Statistics, University of California.
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
- Calainho, F. D., van de Minne, A. M., Francke, M. K. (2022). A machine learning approach to price indices: applications in commercial real estate. Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics. [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, J., Cardona, J. F., Martins, L. & Juan, A. A. (2021). Supervised machine learning algorithms for measuring and promoting sustainable transportation and green logistics. Transportation Research Procedia, 58, 455–462.
- Choy, L. H. T. & Ho, W. K. O. (2023). On the use of machine learning in real estate research. Land 12(4), 740. [CrossRef]
- Chung, C. W., Hsiao, T. H., Huang, C. J., Chen, Y. J., Chen, H. H., Lin, C. H., Chou, S. C., Chen, T. S., Chung, Y. F., Yang, H. I., Chen, Y. M. (2021). Machine learning approaches for the genomic prediction of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. BioData Mining, 14(52), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y. S. (2013). Factor complexity of crash occurrence: An empirical demonstration using boosted regression trees. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 61, 107–118.
- Cugurullo, F., Caprotti, F., Cook, M., Karvonen, A., MᶜGuirk, P. & Marvin, S. (2024). The rise of AI urbanism in post–smart cities: A critical commentary on urban artificial intelligence. Urban Studies, 61(6), 1168–1182.
- Friedman, J. (1999). Greedy function approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. IMS 1999 Reitz Lecture, February 24, 1999.
- Grande, E. & Imbimbo, M. (2012). A data–driven approach for damage detection: An application to the ASCE steel benchmark structure. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2, 73–85. [CrossRef]
- Greener, J. G., Kandathil, S. M., Moffat, L. & Jone, D. T. (2022). A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 23, 40–55. [CrossRef]
- Hamner, B. (2010). Predicting travel times with context–dependent random forests by modeling local and aggregate traffic flow. Paper presented at Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), 2010 IEEE International Conference on IEEE, 1357–1359.
- Hjort, A., Pensar, J., Scheel, I. & Sommervoll, D. E. (2022). House price prediction with gradient boosted trees under different loss functions. Journal of Property Research, 39(4), 338–364. [CrossRef]
- Ho, W. K. O., Tang, B. S. & Wong, S. W. (2021). Predict property prices with machine learning algorithms. Journal of Property Research, 38(1), 48–70. [CrossRef]
- Jamous, M., Marsooli, R. & Miller, J. K. (2023). Physics–based modeling of climate change impact on hurricane–induced coastal erosion hazards. npj Climate Atmospheric Science, 6, 86. [CrossRef]
- Jun, H. J., Jung, S., Kang, S., Kim, T., Cho, C. H., Jhoo, W. Y., & Heo, J. P. (2023). Factors associated with pedestrian-vehicle collision hotspots involving seniors and children: a deep learning analysis of street-level images. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 28(2), 359–377. [CrossRef]
- Kalliola, J., Kapočiūtė-Dzikienė, J., Damaševičius, R. (2021). Neural network hyperparameter optimization for prediction of real estate prices in Helsinki. PeerJ Computer Science, 7, e444. [CrossRef]
- Kashinath, K., Mustafa, M. A., Albert, A., Wu, J. L. & Jiang, C,. Esmaeilzadeh, S., Azizzadenesheli, K., Wang, R. A., Chattopadhyay, A., Singh, A., Manepalli, A., Chirila, D., Yu, R., Walters, R., White, B., Xiao, H., Tchelepi, H. A., Marcus, P., Anandkumar, A., Hassanzadeh, P. & Prabhat (2021) Physics–informed machine learning: case studies for weather and climate modelling. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 379(2194), 20200093. [CrossRef]
- de Jongh, S., Gielnik, F., Mueller, F., Schmit, L., Suriyah, M., Leibfried, T. (2022) Physics–informed geometric deep learning for inference tasks in power systems. Electric Power Systems Research, 211, 108362. [CrossRef]
- Leshem, G., Ritov, Y. A. (2007) Traffic flow prediction using Adaboost algorithm with Random Forests as a weak learner. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2(6), 404–409.
- Li, F., Yigitcanlar, T., Nepal, M., Nguyen, K. & Dur, F. (2023) Machine learning and remote sensing integration for leveraging urban sustainability: A review and framework. Sustainable Cities and Society, 96(13), 104653.
- Loef, B., Wong, A., Janssen, N. A. H., Strak, M., Hoekstra, J., Picavet, H. S. J., Boshuizen, H. C. H., Verschuren, W. M. M. & Herber, Gerrie–Corr M. (2022) Using Random Forest to identify longitudinal predictors of health in a 30–year cohort study. Scientific Reports, 12, 10372. [CrossRef]
- Long, Y. S., Zeng, L. Q., Wang, J., Long, X. C. & Wu, L. (2022) A gradient boosting approach to estimating tail risk interconnectedness. Applied Economics, 54(8), 862–879. [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, F., Willwersch, J., Cajias, M. &, Fuerst, F. (2023) Interpretable machine learning for real estate market analysis. Real Estate Economics, 51(5), 1178–1208. [CrossRef]
- Miller, M. I., Shih, L. C. & Kolachalama, V. B. (2023) Machine learning in clinical trials: A primer with applications to neurology. Neurotherapeutics, 20, 1066–1080. [CrossRef]
- Monteleoni, C., Schmidt, G. A., Saroha, S. & Asplund, E. (2011) Tracking climate model. Statistical Analysis and Data Mining, 4, 372–392. [CrossRef]
- Noorbakhsh, J., Chandok, H., Karuturi, K. M. (2019) Machine learning in biology and medicine. Advances in Molecular Pathology, 2(1), 143–152. [CrossRef]
- Optuna (2018). Optuna: A hyperparameter optimization framework. https://optuna.readthedocs.io/en/stable/.
- Reades, J., De Souza, J. & Hubbard, P. (2019). Understanding urban gentrification through machine learning: Predicting neighbourhood change in London. Urban Studies, 56(5), 922–942. [CrossRef]
- Renaud, J., Karam, R., Salomon, M. & Couturier, R. (2023) Deep learning and gradient boosting for urban environmental noise monitoring in smart cities. Expert Systems with Applications, 218, 119568. [CrossRef]
- Sideris, N., Bardis, G., Voulodimos, A., Miaoulis, G. & Ghazanfarpour, D. (2019). Using Random Forests on Real–World City Data for Urban Planning in a Visual Semantic Decision Support System. Sensors (Basel), 19(10), 2266. /. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, M., Bekir, Z., Demiray, B. Z., Xiang, Z. R., Ewing, G. J., Sermet, Y. & Demir, I. (2020). A comprehensive review of deep learning applications in hydrology and water resources. Water Science and Technology, 82(12), 2635–2670. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, T. W., Shumway, H., Gordner, T., & Lim, T. (2022). The prospects of artificial intelligence in urban planning. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 27(2), 179–194. [CrossRef]
- Thackway, W., Ng, M., Lee,C. L. & Pettit, C. (2023). Building a predictive machine learning model of gentrification in Sydney. Cities, 134, 104192.
- Tsagkis, P., Bakogiannis E. & Nikitas, A. (2023). Analysing urban growth using machine learning and open data: An artificial neural network modelled case study of five Greek cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 89, 104337.
- Wang, Y. (2011). Prediction of weather impacted airport capacity using ensemble learning. 2011 IEEE/AIAA 30th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 2011, pp. 2D6–1–2D6–11. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. & Biljecki, F. (2022). Unsupervised machine learning in urban studies: A systematic review of applications. Cities, 129(12), 103925.
- Weissler, E. H., Naumann, T., Andersson, T., Ranganath, R., Elemento, O., Luo, Y., Freitag, D. F., Benoit, J., Hughes, M. C., Khan, F., Slater, P., Shameer, K., Roe, M., Hutchison, E., Kollins, S. H., Broedl, U., Meng, Z. L., Wong, J. L., Curtis, L., Huang, E. & Ghassemi, M. (2021). The role of machine learning in clinical research: transforming the future of evidence generation, Trials, 22, 537. [CrossRef]
- Whitehall, B. L. & Lu, S. C. Y. (1991). Machine learning in engineering automation–The present and the future. Computers in Industry, 17, 91–100.
- Willard, J., Jia, X. W. & Xu, S. M., Steinbach, M. & Kumar, V. (2022). Integrating scientific knowledge with machine learning for engineering and environmental systems, ACM Computing Survey, 55(4), 1–37. [CrossRef]
- Worden, K. & Manson, G. (2006). The application of machine learning to structural health monitoring. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 365(1851), 515–537. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C., Wang, J., Wang, M. & Kraak, M. J. (2024). Machine learning–based characterisation of urban morphology with the street pattern. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 109, 102078.
- Yang, J., Fricker, P. & Jung, A. (2024) From intangible to tangible: The role of big data and machine learning in walkability studies. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 109, 102087.
- Yin, H., Sharma, B., Hu, H., Liu, F., Kaur, M., Cohen, G., McConnell, R. & Eckel, S. (2024). Predicting the climate impact of healthcare facilities using Gradient Boosting Machines. Cleaner Environmental System, 12, 100155. [CrossRef]
- Yuh, Y. G., Tracz, W., Matthews, H. D. & Turner, S. E. (2023). Application of machine learning approaches for land cover monitoring in northern Cameroon. Ecological Informatics, 74, 101955. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. R. & Haghani, A. (2015) A gradient boosting method to improve travel time prediction. Transportation Research Part C, 58, 308–324.
- Zheng, M. R., Wang, H. Y., Shang, Y. Q. & Zheng, X. Q. (2023a). Identification and prediction of mixed–use functional areas supported by POI data in Jinan City of China. Scientific Reports, 13, 2913. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y., Lin, Y., Zhao, L., Wu, T. H., Jin, D. P. & Li, Y. (2023b) Spatial planning of urban communities via deep reinforcement learning. Nature Computer Science, 3, 748–762. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D. X., Cai, C. J., Yang, T. B. & Zhou, X. (2018) A machine learning approach for air quality prediction: Model regularization and optimization. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 2(1), 5. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).