1. Introduction
Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) are the major anionic surfactants widely used in cleaners and detergents, for both domestic and industrial applications. Large amounts of these anthropogenic compounds arrive at wastewater treatment plants or are discharged directly into bodies of water, either by accident or intentionally, and can generate environmental damage since they are toxic at certain concentrations and, with their hydrophobic characteristics, they persist in the first soil layers for long periods of time.
Although biodegradation is an important process in LAS elimination under aerobic conditions, it has been proven that in certain discharges in which these compounds access the saturated zone with low oxygen content, biodegradation is very slow or even stops [
1]. The fate of these compounds has recently been studied in lakes containing foam from undegraded domestic surfactants of which LAS is the most dominant type. These surfactants do not degrade under the prevailing conditions and time frame, and their presence was also observed in the sediment of organic sludge [
2].
Moreover, in recent years, the growing demand for water, especially in arid regions, has required the reuse of wastewater as a source of irrigation. Also, the use of wastewater sewage sludges for soil amendment has become a very common practice to improve the physical properties of soil in order to recover nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorous [
3], and to solve the disposal problem of the enormous amount of sewage sludge that is generated. Sludge application in croplands may lead to accumulation of harmful components in soil, such as heavy metals and organic compounds [
4], causing these components to enter the food chain, and producing reproductive and fetotoxic problems, as evidenced in some studies [
5].
Other uses of growing interest are the application of surfactants in remediation technologies for the treatment of soils and waters contaminated with organic compounds. Their use improves remediation and requires less time than the use of water alone [
6,
7].
Once LAS enters the terrestrial environment, sorption/desorption reactions play an important role in controlling its movement in soils and aquifers. But these processes depend on the characteristics of aquifer soil such as organic matter and clay content [
8] and the determination of the sorption equilibrium, which is very important when modelling and predicting the transport and reaction of LAS in the saturated zone. Kinetic studies are also of interest since they allow determining the rate to the adsorption of contaminant, as well as predicting its concentration in solution after a certain contact time with the adsorbent [
9].
Currently, hydrogeochemical studies play a significant role in characterising natural systems, understanding the migration of contaminants [
10,
11,
12], and carrying out remediation studies, among others. The modelling of the transport and reaction processes (
'reactive transport
') of contaminants can be carried out through the application of computer codes that allow hydrogeochemical modelling, based on compliance with the matter conservation equations and the principles that govern chemical balance.
Hydrogeochemical modelling must be supported by experimental data obtained either in the field or in the laboratory, where the influence of the variables involved can be carefully studied. Tests in laboratory columns for the study of the reactive transport of contaminants, such as LAS, are an essential tool to achieve the interpretation of processes that take place in the natural environment, as it has been demonstrated in previous works [
13,
14,
15]. Furthermore, obtaining data on the evolution of contaminant concentrations under certain conditions is essential to understanding the processes in which they are involved [
16].
Codes such as PHREEQC [
17] and ORCHESTRA [
18] have been developed to combine geochemical processes (acid-base reactions, adsorption, dissolution-precipitation, etc.) with transport calculations. In addition, there are computational codes that specialised in three-dimensional transport modelling in saturated media coupled to geochemical codes, such as MODFLOW 6 [
19].
In this work, PHREEQC has been used, which simulates transport processes and a large number of chemical reactions that occur in natural and contaminated waters, and is based on the chemical balance of aqueous solutions when they interact with minerals, gases, solid solutions, or exchange and sorption surfaces. It includes the ability to model kinetic reactions with rate equations specified by the user, through Basic-type statements. For all this, you need to introduce the value of certain parameters that approximate your response to the real behaviour of the process you want to simulate, obtained in the laboratory.
In the present study, the aim was to model the physical-chemical processes of transport and sorption of an organic contaminant (linear alkylbenzene sulfonate, LAS) that take place in a saturated aquifer medium on a laboratory scale, in which biodegradation has been eliminated. For this, both the experimental data obtained in column tests and the transport data will be available to calculate the parameters for the data input required by PHREEQC and to model with this program the reactive transport of LAS in the columns. This will allow the interpretation of the physical-chemical processes that take place between the LAS homologues and the solid material when sorption processes are predominant.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, experimental results obtained in tests carried out in laboratory columns will be used, whose characteristics and methodology are described in previous works [
8]. This section will include some important characteristics to describe the selected tests and the fundamental parameters to be able to model reactive transport with the PHREEQC software.
2.1. Description of the Experimental Column Tests Used in the Modelling with PHREEQC
A reactive transport study was carried out with pulse input from the data obtained in a laboratory column to simulate a one-dimensional study of a point discharge of a contaminant in agricultural soil.
Table 1 shows the main characteristics of the selected tests carried out in columns filled with different porous media and saturated with irrigation water. The pulse was carried out by introducing irrigation water prepared in a concentration of around 100 mg/L (100 ppm) of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) for 5 hours, simulating wastewater, and subsequently by introducing irrigation water as input.
A blank column filled with purified by acid and calcined for analysis sea sand (T0), from Merck was used, and another 2 columns with a mixture of the previous sand and clay-loam soil, containing a mixture of sand (23.6%), silt (38.0%) and clay (38.4%), extracted from a plot of land at the University of Alicante, where experimental studies are carried out. The T25 and T50 tests were carried out with different proportions of agricultural soil, which was previously sterilized in a J.P. Selecta Presoclave-II 75 Autoclave, to avoid biodegradation processes and study only adsorption processes.
The initial dissolution of LAS was obtained from Petroquimica Española S.A. (PETRESA), with different proportion of the four homologues of LAS. C
10-13LAS reflects the LAS alkyl chain length. The percentages of the composition of the LAS are 12.1% C
10LAS, 34.1% C
11LAS, 30.6% C
12LAS and 23.2% C
13LAS. The water used in the experiments comes from the drinking water supply of Alicante, used agricultural irrigation too. It was taken directly from the supply network, storing it for several days in a 25-litre tank. In this way, the residual chlorine it contains was eliminated, equilibrium with the atmosphere is reached at the temperature and partial pressure of CO
2 in the laboratory and, in addition, water of constant ion concentration is achieved during long-term tests [
20].
Table 2 shows the composition of the water used in the different tests. Before the tests, the water was sterilised by filtration through the Steripak GP-10 device by Millipore to prevent the proliferation of microorganisms and to minimize biodegradation processes. In LAS experiments, initially water saturating the soil columns and inflow water with LAS in solution had similar ion concentrations, in order to minimize the ionic exchange process, as a way to detect changes related to the LAS interactions, such as sorption and precipitation. The LAS precipitation with cations, and specifically with calcium is scarce, as was observed in the experimental results obtained for the cations of these tests [
8], therefore the adsorption of LAS in the porous medium is the predominant reactive process.
Thermostated stainless steel columns, made in University of Alicante, with an internal diameter of 2.5 cm were used, closed by two cylindrical heads, and containing an outer jacket for the circulation of water at 25°C. These columns were connected to HPLC pumps (Shimadzu LC-9A and LC-10AD), with nominal flow of 0.5 mL/min, controlled during experiments based on the weight of water fractions collected in a given period [
21,
22], and the column pressure was monitored continuously to perceive changes in system flow. The length and mean flow determined in each experiment are shown in
Table 3.
The hydrodynamic parameters are important to characterise the transport in the column (Boluda 2008). For this study, the hydrodynamic parameters were previously determined with a tracer (CaCl
2), calculated with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT [
23] which provided the best fit from breakthrough curves, with exact flow and column length which are shown in
Table 3. These parameters include mean residence time (t
m (L/ν), Péclet number (Pe), effective porosity (ε), interstitial velocity (ν(u/ε)), longitudinal dispersion coefficient D
L, and dispersivity (α(L/Pe)) and were transformed into PHREEQC language and used in modelling the LAS transport.
To determine the evolution of LAS over time, the eluent was collected at the exit of the column in small fractions. The samples were analysed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), using an Agilent liquid chromatograph, with an Agilent 1100 ultraviolet light detector at 225 nm. A LiChroCART® 150-4.6 RP-8 column (5 μm) was used as the stationary phase, while the eluent or mobile phase consisted of a MeOH/H2O mixture solution (85/15) with 0.5 M NaClO4·H2O at a constant flow of 0.8 mL/min.
2.2. Description of the Experimental Batch Tests. Adsorption Models Used in PHREEQC
Column tests to characterise the distribution coefficients of a contaminant are carried out as batch adsorption tests, in which the adsorbent material makes contact with a solution with a known concentration of the species susceptible to being adsorbed. After a sufficient time, equilibrium is reached between the dissolved and adsorbed concentration of the species, providing the adsorption isotherm. The numerical value of the distribution coefficient is a function of the properties of the solid substrate and the solution composition and must be calculated experimentally for each system of interest since it cannot be easily transferred from one system to another [
24]. It is important to know the values obtained in batch studies in order to carry out the reactive transport modelling and compare with values from dynamic experiments, whose parameters will be lower since the adsorbent is compacted [
25].
Batch tests of sorption equilibrium, with different proportions of sand/soil, were performed by adding 50 mL of LAS (20 mg/L) to 5 g of sorbent (sand or a mixture of sand-soil). A mechanical rotatory shaker was used to agitate the samples at 15 rpm for 24 hours. Once equilibrium was established, the flask was centrifuged at 9000 rpm for 10 minutes, after which the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter unit. The determination of LAS was carried out using same procedure mentioned above. From these results, the distribution coefficient between the adsorbed and dissolved concentration was obtained for each of the homologues studied.
The relationship established in the linear adsorption equilibrium between the dissolved and adsorbed concentrations of the contaminating species is expressed through the distribution coefficient, k
d:
where C
ads is the adsorbed concentration of the solute in the solid phase (mg/kg adsorbent) and C
dis is the concentration of the solute in the solution (mg/L solution). The numerical value of the distribution coefficient k
d is a function of the properties of the solid substrate and the composition of the solution.
The Freundlich model is an empirical equation that does not assume homogeneity in the energy of the sites on the surface, has no limit on the maximum adsorption load, and shows a consistency of an exponential distribution of active centres characteristic of a heterogeneous surface, represented as equation 2:
where the Freundlich constant parameter k
F characterises the capacity, and n the adsorption intensity.
The kinetic study of adsorption allows us to determine the rate at which the contaminant is adsorbed, as well as to predict its concentration in solution after a certain contact time with the adsorbent has elapsed. In dynamic column tests, the retardation of contaminants due to the process of adsorption can be modelled with a linear reversible sorption expression [
26]. The rate expression for kinetic sorption involving species i are given by equation 3:
where r
i is the rate of species i in liquid phase (mol/L/h); k
m is the mass transfer coefficient in (h
-1); C
dis is the aqueous concentration of species i in (mol/L); C
ads is the adsorbed concentration of species i in (mol/g sediment); k
d is the distribution coefficient for linear equilibrium adsorption in (L/g). The expression within the parentheses represents the thermodynamic distance from equilibrium. The mass transfer coefficient represents the rate limitations due to the transport of the adsorbing species between the bulk solution and the mineral surface.
If the Freundlich isotherm is used, the equation is modified to include the n and k
F ((mg /g) (mg /L)
–1/n) (equation 4):
2.3. Modelling with PHREEQC
2.3.1. Tracer and LAS Transport
Using the PHREEQC program it was possible to model one-dimensional advective-dispersive transport in column tests. In order to simulate the tests, the program has a data input module called TRANSPORT, and the initial solution residing in the column and the one that is introduced was previously defined. Data output was carried out with the SELECT OUTPUT module, where the output file was indicated with data of interest that was processed using spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel.
For the tracer test, the data obtained with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT was used (
Table 3) and the specific transport parameters were introduced into PHREEQC, which was the best settings for the tracer breakthrough curves. In addition, the solution initial concentration and the tracer input solution were introduced.
Regarding LAS transport, species not found in the PHREEQC database, such as LAS homologues (C10LAS, C11LAS, C12LAS, C13LAS), was included in the data entry and their molecular weights indicated, so that they appear as species. Also, the irrigation water initially in the column and this water with LAS was included. To model the transport of the LAS pulse, it was necessary to introduce two transport modules: one that refers to the LAS adsorption process and another to model desorption, to finally obtain the column free of LAS.
2.3.2. LAS Reactive Transport
To model chemical processes related to kinetically controlled reactions, it is necessary to incorporate data blocks such as KINETICS or RATES that allow code in Basic language [
17] to be incorporated into the program to introduce variables and reaction rate equations defined by the user.
PHREEQC has a module in which an equation can be introduced to characterise the rate of the adsorption reaction (RATES module) which includes the expressions of this rate for each of the LAS homologues, first defining all the parameters that appear in it, so that the program can interpret this subroutine and incorporate it into the global calculations. The three parameters that must be indicated are: km (mass transfer coefficient), kd or kF (distribution coefficient), and n (adsorption intensity). Another factor, solids, is necessary to convert adsorbed moles/gram of sediment to adsorbed moles/L.
A statement has also been introduced, as a limiting factor, solely to indicate that the moles of reactant adsorbed are, at most, those established for equilibrium.
Next, another KINETICS module must be entered into the template, with the current and initial reactant moles and reaction parameters, with those used in the Runge-Kutta method. This method of solving differential velocity equations that are integrated over a time step uses time subintervals to maintain specified errors within tolerances.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Transport Modelling in PHREEQC
3.1.1. Tracer Transport
The TRANSPORT data block of PHREEQC requires the input of the parameters, which will be used to model the transport of LAS, by the user, previously obtained from the experimental breakthrough curve of the tracer (CaCl2). This adjustment requires numerous tests based on trial and error, so the ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT software was chosen since it provides the best fit to the breakthrough curve, and it also uses column length and diameter and flow rates.
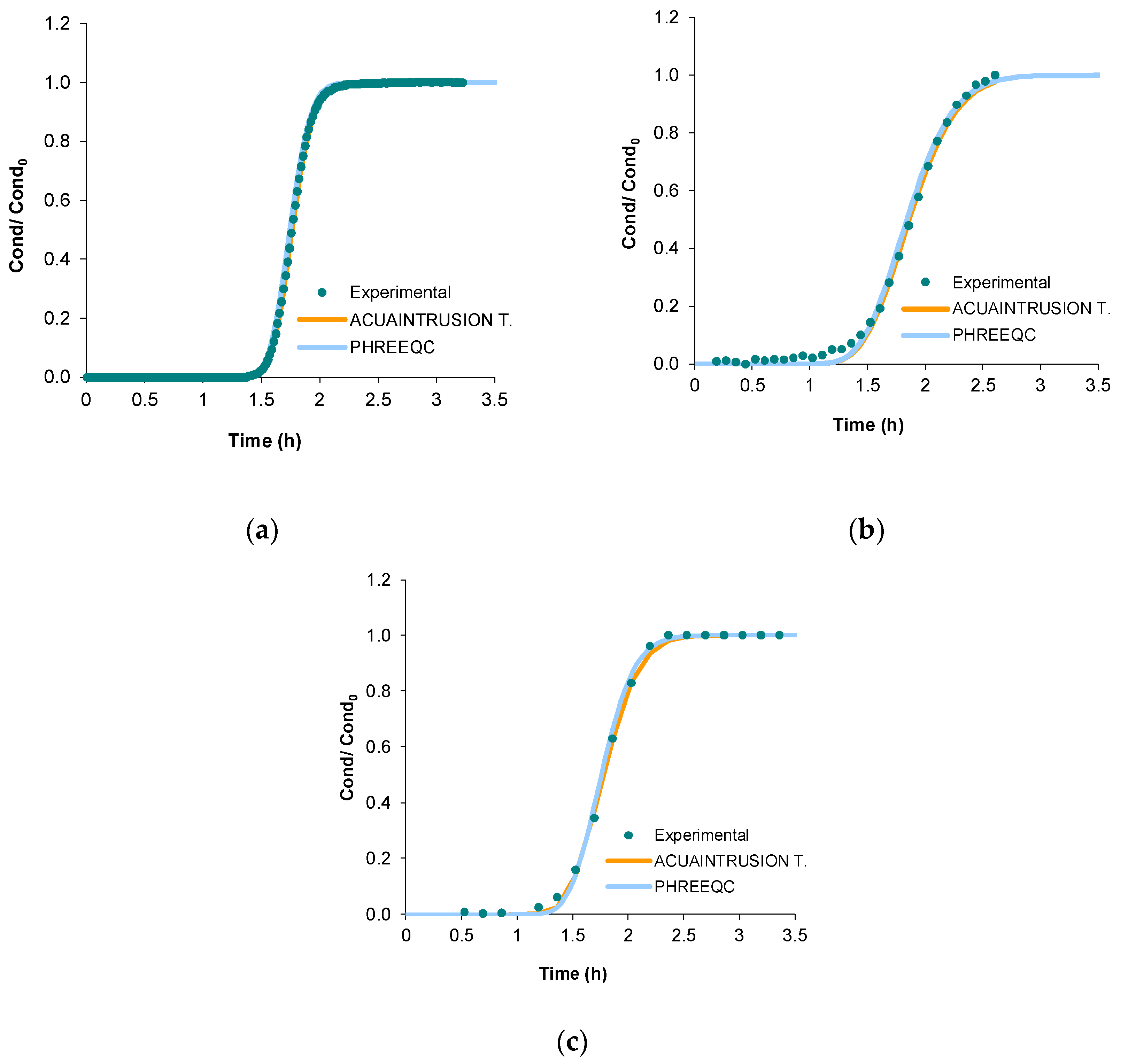
Figure 1 shows the fit of the experimental tracer breakthrough curves with those modelled with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT and PHREEQC. These indicate that the transport parameters obtained with the ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT software (
Table 3) were transformed and used in PHREEQC. As can be seen, PHREEQC shows a good fit, so it can be stated that ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT software facilitates the task of fitting the experimental tracer breakthrough curves.
The simulations carried out in PHREEQC use the block TRANSPORT with the following parameters: cells (number of cells into which the total length of the column is divided (50)); shifts (number of steps in which the simulation will be carried out; result of dividing the total test time by the time the solution needs to pass through each cell); time step (result of dividing the length of a cell by the interstitial velocity of the fluid); and the length and dispersivity of each cell. The program needs the diffusion coefficient, which has been considered zero, and it must also indicate the results should be printed (end of the column, cell = 50). In the test carried out with CaCl
2 as a tracer, the concentrations reported in
Figure 2 were used.
3.1.2. LAS Transport
Once the suitability of the application of PHREEQC has been demonstrated in case of tracer transport, these parameters were used to model the transport of LAS homologues. As mentioned in
Section 2.1., total pulse of LAS (100 ppm) is introduced for a brief period of time, with subsequent entry of irrigation water free of this family of compounds, until complete removal. The simulation with PHREEQC requires two TRANSPORT blocks whose parameters used in the case of the column filled with sand appear in
Table 4.
3.2. Reactive Transport of LAS Modelled in PHREEQC
3.2.1. Sand Column Tests Modelled
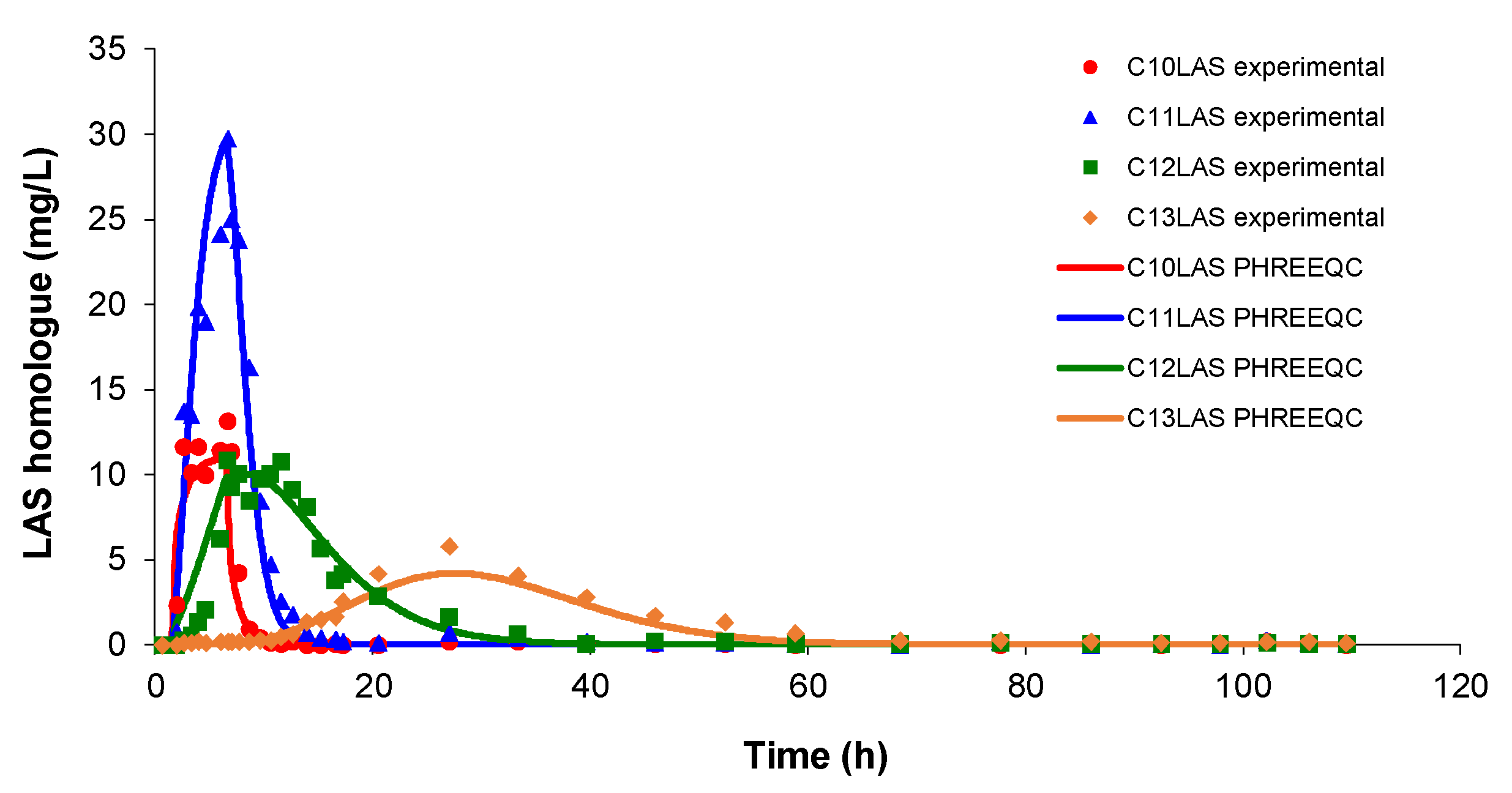
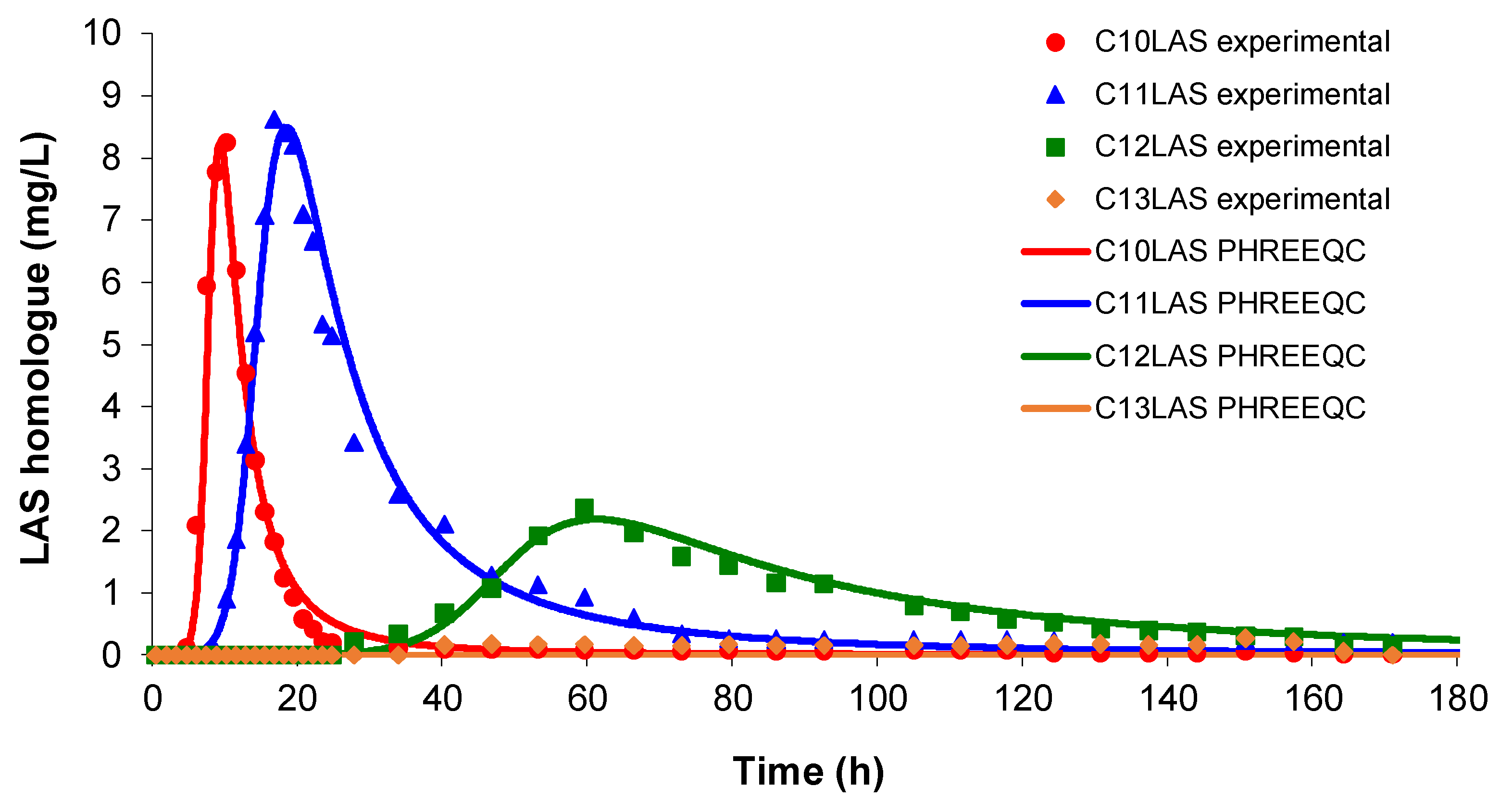
First, the pulse test has been studied in a column filled with sand and was compared with previous studies carried out both in batch and in column, with step adsorption and step desorption.
As mentioned, it is important to know the batch values used as reference, and they will be maximum with respect to those obtained in the column simulations. The column step simulations for both adsorption and desorption of LAS provide parameters that can be used as a starting point for the pulse simulation.
In this assay, a total LAS was inputted (around 100 ppm) with the proportions of the homologues C
10LAS (12.1%), C
11LAS (34.1%), C
12LAS (30.6%) and C
13LAS (23.2%) over a brief period of time. The results obtained at the pulse input show that these proportions are not maintained at the output concentrations shown in
Figure 3. C
11 shows a value three times higher than C
12, even though the input the proportions were similar. For the two lighter homologues (C
10 and C
11), the response is closer to the proportions of the input concentrations and their elution is very rapid with a rapid increase simultaneously for both, while for the two heavier homologues (C
12 and C
13) their elution was slower with time, appearing much later. The signal obtained for C
13 presents much lower values than C
10, despite the fact that its proportion to the input is double, showing a much more delayed elution compared to C
12. The simulation carried out with PHREEQC agrees to the variations observed in the experimental data for all compounds whose complete elution takes 60 hours. The modelling presents a good fit with the experimental data, and the values of the parameters k
d and k
m were calculated by trial and error, after several simulations (
Table 5).
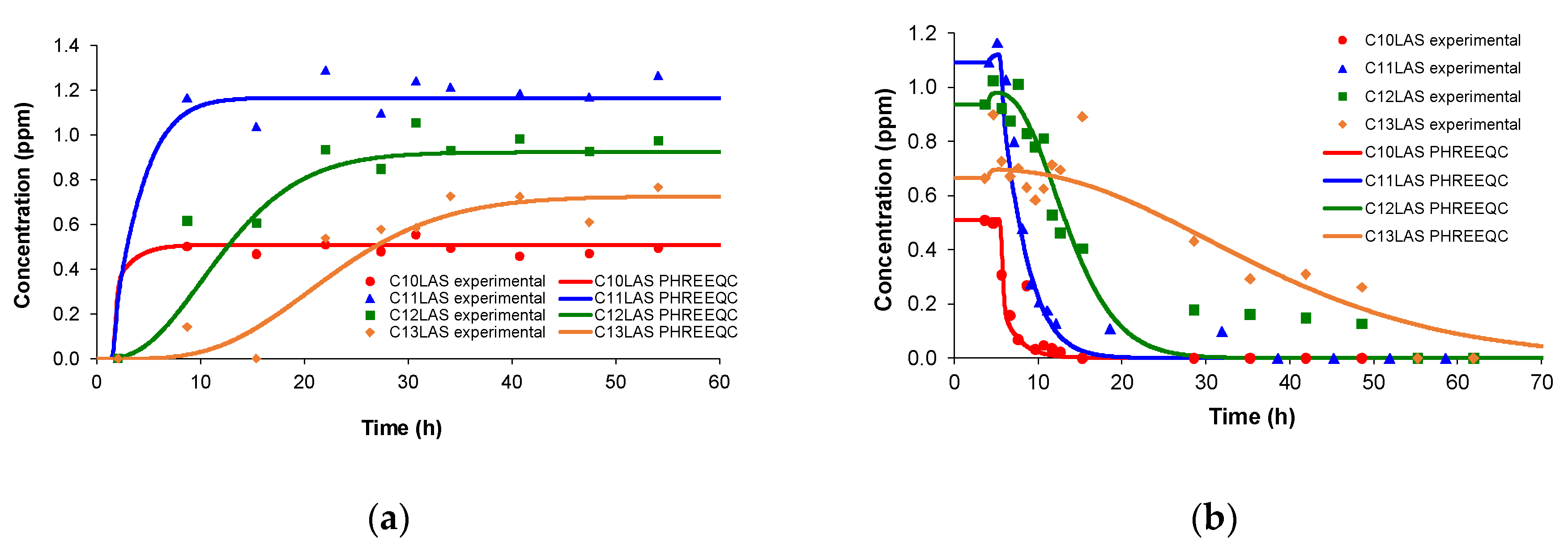
In previous studies (
Figure 4), experimental step adsorption and desorption tests were carried out [
27,
28], in which the constant input concentration of the different LAS homologues occurs in the proportions indicated above, until saturation. For desorption, the same columns were submitted to a constant input of irrigation water free of LAS until the concentration of each homologues drops to zero. In this work, the simulation of these step tests has been carried out and the parameters are very similar to those obtained for the LAS pulse tests (
Table 5). Furthermore,
Table 5 shows the distribution constants for linear adsorption obtained in batch (k
d), which are higher in all cases. These constants have been obtained from the experimental isotherms.
Comparing
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, the pulse adsorption and desorption phenomena have very similar shapes to those obtained in step, which is reflected in the similarity to the parameters (
Table 5). The longer chain homologues are retained to a greater extent by the porous medium, presenting a higher value of the distribution coefficient k
d. The mass transfer coefficient k
m shows the same trend with the larger homologues showing greater delay. In conclusion, the simulations carried out in pulse and step for adsorption and desorption in columns filled with sand show similar values of distribution constants for these two stages, corresponding to the symmetric profiles of the experimental results, with sharp rises and falls. This behaviour is agreed with experimental results obtained in previous works carried out in sand columns for other polluting substances [
29].
3.2.2. Test modelling in agricultural soil columns
When replacing part of the sand with agricultural soil, the published pulse tests [
8] show very significant variations and it has been considered interesting to model the LAS in solution and obtain the adsorbed concentrations. In this way, the concentrations of surfactants that would be adsorbed in wastewater discharge in a specific place can be evaluated to know its effect in an environmental impact study. Surfactants that are not retained can migrate to deeper areas and cause contamination of aquifers [
30].
The simulation process with PHREEQC is identical to that discussed in the previous sections for the case of sand, but now the processes are more complex due to the interaction between the soil, with a varied composition that includes adsorbent substances that interact with LAS homologues.
New simulations have been carried out for columns with a mixture of soil and sand for the pulse tests, considering the transport parameters of the previous tests obtained with the tracer (
Figure 1b and c) and applying a linear adsorption and desorption model. To simulate the desorption of LAS, irrigation water is introduced, but it has been necessary to modify the dispersivity in these columns in order to obtain simulation data closer to the experimental data, which showed slow elution of the homologues. The dispersivity was increased ten times, in addition to being necessary to increase the calculation time (Shifts (input free LAS)), to try to achieve a better fit. The parameters used in the TRANSPORT module are shown in
Table 6.
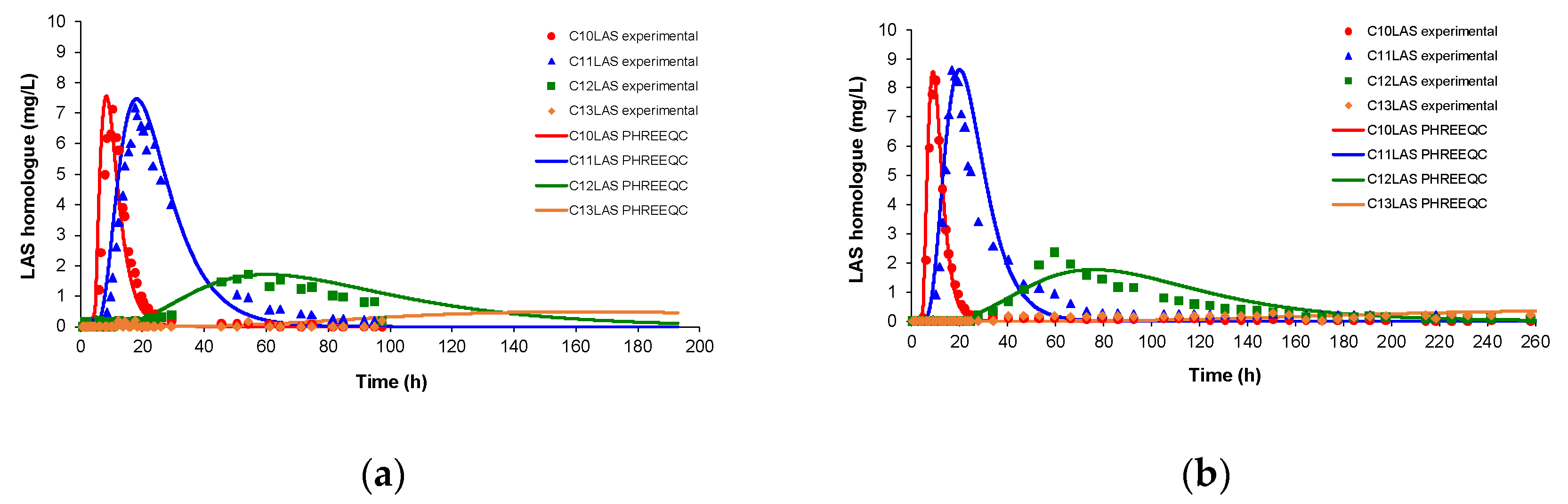
The experimental and modelled LAS homologue concentrations shows a good fit (
Figure 5). The input homologue proportions remained constant, as in the sand test (C
10LAS (12.1%), C
11LAS (34.1%), C
12LAS (30.6%) and C
13LAS (23.2%)). However, the results show that C
10 and C
11, with similar maximum concentrations for both T25 and T50, had a small difference in elution times, in contrast with T0 where both homologues increased their concentrations at the same time. Although C
11 and C
12 have the same proportion in the input LAS, the responses obtained are very different with a C
12 concentration four times lower and a substantial delay in elution time. In the case of C
13, although its concentration was double that of C
10, the elution occurred with a much greater delay over a long time, at very low concentrations near to the analysis detection limit.
The simulation carried out with PHREEQC responded to the variations observed in the experimental data, that is, after 60 hours there was complete elution for C
10 and C
11, while for C
12 it was reached at a time of 200 hours, but undeterminable for C
13 due to the long elution time. The modelled result presents a good fit with the experimental data for C
10. In the case of C
11, the desorption part presents slight differences also observed for C
12. The values of the parameters k
d and k
m for this pulse simulation are shown in
Table 7.
The behaviour of adsorption parameters follows the same trends mentioned in the sand column results: higher values in the columns with increasing amount of agricultural soil present. The batch adsorption values showed higher kd values in all case.
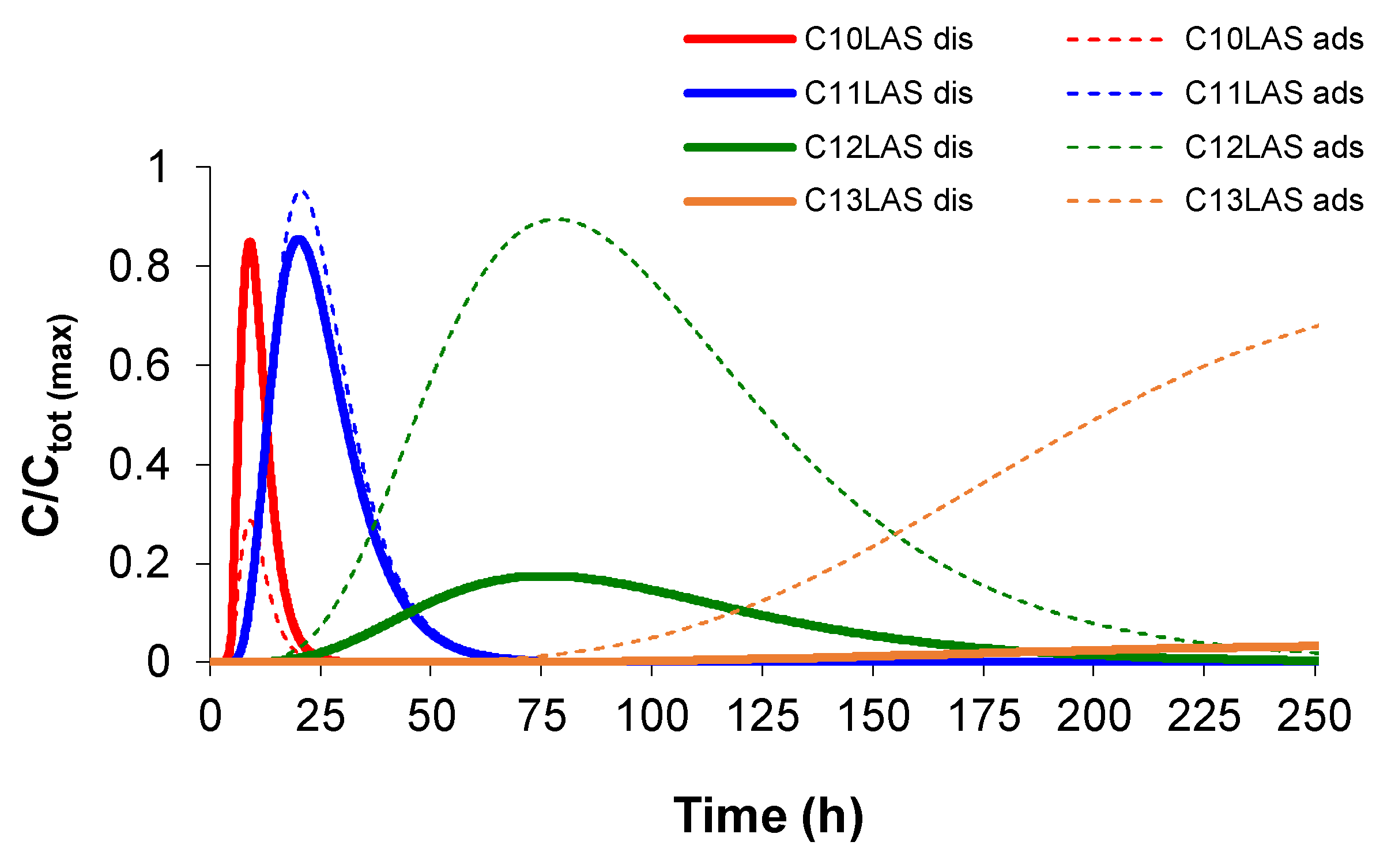
The modelled results obtained for the experimental data of the homologues in solution also allows PHREEQC to obtain the values of the adsorbed concentrations of such homologues, calculated at the end point of the column (
Figure 6). In this figure, the normalised concentrations have been calculated, considering the maximum value obtained from the sum of the concentrations of the different homologues, for both the dissolved and adsorbed species. At this point in the column, a perfect fit is obtained between the normalised maximum concentrations obtained for each homologue in solution with respect to the adsorbed, and these maintain their proportions according to the LAS entry (C
10LAS (12.1%), C
11LAS (34.1%), C
12LAS (30.6%) and C
13LAS (23.2%)). C
10 presents a higher proportion in solution with respect to the adsorbed material. Two homologues with a longer linear chain present the inverse behaviour, highlighting the high adsorbed concentrations of these homologues. In the case of C
11, high normalised concentrations are obtained both for dissolved and adsorbed, with a much faster elution than those with a longer chain.
3.2.3. Experimental Batch Isotherms and Proof to Confirm the Use of Linear Adsorption Model in PHREEQC
Batch tests provide data to calculate adsorption isotherms with different models giving the maximum values of these coefficients that could be obtained in a dynamic column test and can serve as a guideline value in the model.
Table 8 shows the values of the distribution coefficients (k
d and k
F) for the linear and Freundlich adsorption isotherms. Very similar increases can be seen when the alkylic chain is longer and when different proportions of agricultural soil increase in the sorption medium, because the agricultural soil contains organic matter and clays that have great adsorption capacity. Results are in accordance to previous references for C
14LAS [
31]. The fits obtained for each isotherm present a coefficient of determination (r
2) ≥ 0.97. For linear fits n is 1, and for Freundlich fits the n decreases as the length of the surfactant chain increases.
Freundlich isotherms are preferentially used in LAS adsorption. In this work, initially used in PHREEQC.
Figure 7 shows the results of the model for the T50 test with a good fit to the experimental results.
Table 9 includes the results of the mass transfer coefficient (k
m), the distribution coefficient (k
F) and the adsorption intensity (n) for the Freundlich model that have been used with PHREEQC for all tests carried out. Note that for each column, n increases with the percentage of soil, showing a greater intensity of adsorption in this medium. k
F increases with the length of the alkyl chain for each column.
However, k
F decreases when different proportions of agricultural soil increases in the sorption medium; this fact does not agree with batch results and is not coherent that adsorption decreases as the proportion of agricultural soil increases. For this reason, these fits have been discarded and the linear model has been considered. It should be noted that the Freundlich model has an additional parameter (n), which improves the simulation, but the mass transfer and distribution coefficients lose their physical meaning. In simulations carried out in other works [
25], it was preferred to use simpler models with a smaller number of parameters, even if the fit was not ideal.
4. Conclusions
The transport parameters obtained by ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT provide a good fit of the tracer breakthrough curves using PHREEQC and allow modelling the transport of LAS.
In pulse tests carried out in columns with 0, 25 and 50% agricultural soil mixed with sand, the solution concentrations of the different homologues measured at the end of the column did not maintain the proportions of the LAS concentration input. Modelling these LAS pulse tests with PHREEQC showed a good fit using the reactive transport modules.
The distribution and mass transfer coefficients obtained with the model in sand columns tests with step input for adsorption and desorption are similar to those obtained for pulse tests. In addition, the batch tests provided references values to model and establish the maximum value with respect to those obtained in dynamic column experiments.
Isotherms batches were fit by linear and Freundlich adsorption models with good regression coefficients. kd and kF obtained in both methods are very similar, increasing when the alkylic chain is longer and increasing with greater proportions of agricultural soil, being a consequence of content of organic matter and clays having great adsorption capacity. Using the Freundlich model, the fit improved because it introduced one more parameter (n), but minor values of kF were observed when increasing the soil-sand proportion, which was not reasonable. For this reason, these fits were not used and the linear model was been considered.
The elution times in the case of the heavier homologues, and in the columns with a higher percentage of soil, are very long, which translates into great persistence in the environment due to their adsorption, or in the case of contamination of the soil with wastewater, with surfactants. In the case of the lighter homologues, due to their rapid elution and lower adsorption, they could be transferred to aquifer formations with a higher proportion of sand, thus contaminating groundwater and contributing to environmental pollution.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used "Conceptualisation, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; methodology, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; software, N. Boluda, M.D. Saquete, V. Cases and E. Egea; validation, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; formal analysis, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; investigation, N. Boluda, M.D. Saquete, V. Cases and E. Egea; resources, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; data curation, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; writing—original draft preparation, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; writing—review and editing, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; visualisation, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; supervision, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; project administration, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete; funding acquisition, N. Boluda and M.D. Saquete All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript." Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
References
- Krueger, C.J.; Radakovich, K.M.; Sawyer, T.E.; Barber, L.B.; Smith, R.L.; Field, J.A. Biodegradation of the surfactant linear alkylbenznesulfonate in sewage-contaminated groundwater: A comparison of column experiments and field tracer tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3954–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Hoysall, C.; Rao, L. Unveiling the origin, fate, and remedial approaches for surfactants in sewage-fed foaming urban (Bellandur) Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 339, 122773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, P.-A.; Svensson, S.-E.; Hallefält, F.; Diedrichs, H. Nutrient and cost optimization of fertilizing strategies for Salix including use of organic waste products. Biomass Bioenerg. 1999, 17, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, D.A.; Healey, N. Contaminant risks from biosolids land application: Contemporary organic contaminant levels in digested sewage sludge from five treatment plants in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 126, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenkamp, H.; Part, P.; Erhardt, W.; Prüeß, A. EUR 20135 EN: Organic contaminants in sewage sludge for agricultural use, Institute for Environment and Sustainability (Joint Research Centre), Italy, 2002. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/73cc4273-3241-4e99-bda3-e0312355821a/language-en.
- Jensen, J. Fate and effects of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) in the terrestrial environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 226, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paria, S. Surfactant-enhanced remediation of organic contaminated soil and water. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 138, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boluda-Botella, N.; León, V.M.; Cases, V.; Gomis, V.; Prats, D. ; Fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate in agricultural soil columns during inflow of surfactant pulses. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, J. , Ayora, C., Acoplamiento de modelos de transporte de solutos y de modelos de reacciones químicas. Estud. Geol., 1993, 49, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Navarre-Sitchler, A.; Heil, E.; Peters, C. Addressing water and energy challenges with reactive transport modeling. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.; Trolard, F.; Gillon, M.; Cognard-Plancq, A.-L.; Chanzy, A.; Bourrié, G. Combination of a crop model and a geochemical model as a new approach to evaluate the sustainability of an intensive agriculture system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Guo, S.; Ma, J. Combinations of surfactant flushing and bioremediation for removing fuel hydrocarbons from contaminated soils. Clean-Soil Air Water 2015, 44, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, A.; Ayora, C.; Bernet, O.; Bolzicco, J.; Carrera, J.; Cortina, J.L.; Coscera, G.; de Pablo, J.; Domènech, C.; Galache, J.; Gibert. O.; Knudby, C.; Mantecón, R.; Manzano, M.; Saaltink, M.; Silgado, A. Barrera Geoquímica. Boletin Geológico y Minero. 2001, Especial Vol., 229 –256. Available online: https://www.hydrogeomodels.ch/publications/books/10-BARRERA%20GEOQ.pdf.
- Almendro Candel, M.B.; Navarro Pedreño, J.; Jordan Vidal, M.M.; García Sánchez, E.; Mataix Solera, J. Ensayos de movilidad de compuestos nitrogenados en zona no saturada. Investigación, gestión y recuperación de acuíferos contaminados. IGME Madrid, 2001, 15, pp. 23–24. Available online: https://www.igme.es/actividadesigme/lineas/HidroyCA/publica/libros4_CCA/lib15/pdflib15/003.pdf.
- Grolimund, D.; Borkovec, M. Colloid-facilitated transport of strongly sorbing contaminants in natural porous media: Mathematical modeling and laboratory column experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6378–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis-Yagües, V.; Boluda-Botella, N.; Ruiz-Beviá, F. Gypsum precipitation as an explanation of the decrease of sulphate concentration during seawater intrusion. J. Cont. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User's guide to PHREEQC (v2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259, 1999. pp. 312. [CrossRef]
- ORCHESTRA: Geochemical and Transport Modelling. Available online: https://orchestra.meeussen.nl/ (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- MODFLOW 6: USGS Modular Hydrologic Model. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/software/modflow-6-usgs-modular-hydrologic-model (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Cases López, V.P. Estudio de procesos de transporte del alquilbenceno sulfonato lineal en la zona saturada mediante columnas de laboratorio. Master's Degree. University of Alicante, Alicante (Spain), Julio 2009. http://hdl.handle.net/10045/143120.
- Gomis-Yagües, V.; Boluda-Botella, N.; Ruiz-Beviá, F. Column displacement experiment to validate hydro-geochemical models of seawater intrusions. J. Cont. Hydrol. 1997, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluda-Botella, N.; Gomis-Yagües, V.; Ruiz-Beviá, F. Influence of transport parameters and chemical properties of the sediment in experiments to measure reactive transport in seawater intrusion. J. Hydrol. 2008, 357, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boluda-Botella, N.; Gomis-Yagües, V.; Pedraza, R. ACUAINTRUSION – A graphical user interface for a hydrogeochemical seawater intrusion model. 1st SWIM-SWICA, Cagliary, Italy, 24–29 September 2006. https://rua.ua.es/dspace/bitstream/10045/2121/1/2006SWIMBoluda.pdf.
- Drever, J.I. The geochemistry of natural waters. Surface and groundwater environments. 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall, Hoboken, New Jersey, United States, 2002; pp. 436. ISBN 978-013-272-790-7.
- Boluda-Botella, N.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pedraza, R. Applying reactive models to column experiments to assess the hydrogeochemistry of seawater intrusion: Optimising ACUAINTRUSION and selecting cation exchange coefficients with PHREEQC. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebes-Stevens, C.; Valocchi, A.J.; VanBriesen, J.M.; Rittmann, B.E. Multicomponent transport with coupled geochemical and microbiological reactions: Model description and example simulations. J. Hydrol. 1998, 209, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea Llopis, E. Estudios de transporte reactivo de contaminantes en zona saturada: experimentos de inyección en columna y modelización con PHREEQC. Master's Degree. University of Alicante, Alicante (Spain), 2010. https://books.google.es/books/about/Estudios_de_transporte_reactivo_de_conta.html?id=rrSDMwEACAAJ&redir_esc=y.
- Boluda-Botella, N.; Cases López, V.; Gomis-Yagües, V.; León, V.M. ; Soriano, R. Experimental study and modelling of the desorption of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates in sand and soil. 11th Mediterranean Congress of Chemical Engineering. Barcelona. Spain, 21–24 October 2008. Available online: https://rua.ua.es/dspace/bitstream/10045/8706/6/Boluda_LAS_%20Expoquimia%202008.pdf.
- López-Ortiz, C.M.; Boluda-Botella, N.; Prats-Rico, D.; Sentana-Gadea, I. Fate of parabens and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in aquifer materials columns during step experiments with fresh and sea waters. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-Abellan, J.; Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Candela, L.; Jacques, D.; Kohfahl, C.; Tamoh, K. Reactive transport modelling to infer changes in soil hydraulic properties induced by non-conventional water irrigation. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, V.C.; Williams, G.K. Structure–activity relationships for sorption of linear alkyl-benzene sulfonates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Comparison of the breakthrough curves obtained with experimental tests, and modelled with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT and PHREEQC (a) T0; (b) T25; and (c) T50.
Figure 1.
Comparison of the breakthrough curves obtained with experimental tests, and modelled with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT and PHREEQC (a) T0; (b) T25; and (c) T50.
Figure 2.
Input file in PHREEQC to model the tracer transport (CaCl2) in the T0 experiment.
Figure 2.
Input file in PHREEQC to model the tracer transport (CaCl2) in the T0 experiment.
Figure 3.
Variation of LAS homologue concentrations obtained in a column test pulse. The lines showing the fits obtained with PHREEQC software in each case.
Figure 3.
Variation of LAS homologue concentrations obtained in a column test pulse. The lines showing the fits obtained with PHREEQC software in each case.
Figure 4.
Modelling of sand-filled column tests (a) adsorption; (b) desorption of LAS with input step.
Figure 4.
Modelling of sand-filled column tests (a) adsorption; (b) desorption of LAS with input step.
Figure 5.
Concentration of LAS homologues during the assay, obtained experimentally and with PHREEQC in (a)T25; (b)T50.
Figure 5.
Concentration of LAS homologues during the assay, obtained experimentally and with PHREEQC in (a)T25; (b)T50.
Figure 6.
Normalised concentration with respect to time at the end of the column for both dissolved (dis) and adsorbed (ads) species.
Figure 6.
Normalised concentration with respect to time at the end of the column for both dissolved (dis) and adsorbed (ads) species.
Figure 7.
Concentration of LAS homologues during the assay, obtained experimentally and with PHREEQC at T50 with Freundlich isotherms.
Figure 7.
Concentration of LAS homologues during the assay, obtained experimentally and with PHREEQC at T50 with Freundlich isotherms.
Table 1.
Main characteristics of the pulse experiments.
Table 1.
Main characteristics of the pulse experiments.
| Test |
Porous medium |
Sediment (g) |
LAS (mg/L) |
| T0 |
100% sea sand |
163.3 |
91 |
| T25 |
75% sea sand + 25% soil |
152.0 |
98 |
| T50 |
50% sea sand + 50% soil |
129.6 |
110 |
Table 2.
Irrigation water used in different column experiments.
Table 2.
Irrigation water used in different column experiments.
| Ion concentration (mg/L) |
|---|
| Test |
Ca2+
|
Na+
|
K+
|
Mg2+
|
Cl-
|
SO42-
|
HCO3-
|
| T0 |
35 |
70 |
2.0 |
35 |
115 |
55 |
180 |
| T25 |
138 |
116 |
2.9 |
45 |
240 |
100 |
320 |
| T50 |
70 |
70 |
2.8 |
38 |
150 |
80 |
220 |
Table 3.
Hydrodynamic parameters of the experiments carried out in columns obtained with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT.
Table 3.
Hydrodynamic parameters of the experiments carried out in columns obtained with ACUAINTRUSION TRANSPORT.
| Test |
Flow (mL/min) |
Length (cm) |
tm
(h) |
Pe (νL/DL) |
Effective ε
|
ν
(cm/h) |
DL (cm2/h) |
α
(cm) |
| T0 |
0.479 |
22.4 |
1.77 |
315 |
0.46 |
12.66 |
0.90 |
0.071 |
| T25 |
0.458 |
22.4 |
1.89 |
67 |
0.47 |
11.86 |
3.94 |
0.332 |
| T50 |
0.473 |
20.2 |
1.79 |
103 |
0.51 |
11.26 |
2.20 |
0.196 |
Table 4.
Input parameters in PHREEQC to model the transport of pulse tests with LAS injection in the sand-filled column.
Table 4.
Input parameters in PHREEQC to model the transport of pulse tests with LAS injection in the sand-filled column.
| PHREEQC parameters |
T0 |
| Time step (s) |
124 |
| Cells lengths (m) |
4.48 × 10-3
|
| Shifts (input LAS) |
145 |
| Shifts (input free LAS) |
3036 |
| Cells dispersivities (m) (input LAS) |
0.71 × 10-3
|
| Cells dispersivities (m) (input free LAS) |
0.71 × 10-3
|
Table 5.
Distribution coefficient, kd, for batch (Ads. batch) and column test (pulse, adsorption (Ads. step) and desorption (Des. step)) and the mass transfer coefficient, km, for the sand column tests introduced in PHREEQC model.
Table 5.
Distribution coefficient, kd, for batch (Ads. batch) and column test (pulse, adsorption (Ads. step) and desorption (Des. step)) and the mass transfer coefficient, km, for the sand column tests introduced in PHREEQC model.
| |
kd 103(L/g) |
km (hr-1) |
| Homologues |
Ads.
batch |
Pulse |
Ads.
step |
Des.
step |
Pulse |
Ads.
step |
Des.
step |
| C10LAS |
1.00 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.40 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
| C11LAS |
1.93 |
0.35 |
0.36 |
0.36 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
| C12LAS |
3.76 |
1.50 |
1.80 |
1.30 |
2 |
4 |
4 |
| C13LAS |
9.80 |
4.90 |
3.50 |
4.90 |
8 |
8 |
4 |
Table 6.
Input parameters in PHREEQC to model the transport of pulse tests with LAS injection in the tests in agricultural soil columns.
Table 6.
Input parameters in PHREEQC to model the transport of pulse tests with LAS injection in the tests in agricultural soil columns.
| PHREEQC parameters |
T25 |
T50 |
| Time step (s) |
135 |
130 |
| Cells lengths (m) |
4.48 × 10-3
|
4.04 × 10-3
|
| Shifts (input LAS) |
133 |
138 |
| Shifts (input free LAS) |
5000 |
8000 |
| Cells dispersivities (m) (input LAS) |
3.32 × 10-3
|
1.96 × 10-3
|
| Cells dispersivities (m) (input free LAS) |
33.2 × 10-3
|
19.6 × 10-3
|
Table 7.
Mass transfer coefficient, km, and distribution coefficient, kd, together with kd ads. batch (batch values) obtained for the tests in sand column (T0) and columns with agricultural soil mixtures (T25 and T50), introduced in PHREEQC model.
Table 7.
Mass transfer coefficient, km, and distribution coefficient, kd, together with kd ads. batch (batch values) obtained for the tests in sand column (T0) and columns with agricultural soil mixtures (T25 and T50), introduced in PHREEQC model.
| |
T0 |
T25 |
T50 |
| Homologues |
km
(hr-1) |
kd 103 (L/g) |
kd ads.
batch 103 (L/g) |
km
(hr-1) |
kd 103 (L/g) |
kd ads.
batch 103 (L/g) |
km
(hr-1) |
kd 103 (L/g) |
kd ads.
batch 103 (L/g) |
| C10LAS |
0.4 |
0.10 |
0.995 |
20 |
1.00 |
1.86 |
20 |
1.12 |
4.27 |
| C11LAS |
2 |
0.35 |
1.93 |
20 |
3.4 |
5.64 |
20 |
3.70 |
10.9 |
| C12LAS |
2 |
1.50 |
3.76 |
20 |
14 |
16.1 |
20 |
17.0 |
29.2 |
| C13LAS |
8 |
4.90 |
9.80 |
40 |
40 |
47.4 |
40 |
70.0 |
81.8 |
Table 8.
Parameters determined from adsorption in batch experiments for linear and Freundlich isotherms.
Table 8.
Parameters determined from adsorption in batch experiments for linear and Freundlich isotherms.
| Sorption medium |
|
C10LAS |
C11LAS |
C12LAS |
C13LAS |
| |
103
|
|
r2
|
n |
|
r2
|
n |
|
r2
|
n |
|
r2
|
n |
T0
|
kd
|
0.995 |
0.982 |
1.0 |
3.76 |
0.989 |
1.0 |
3.76 |
0.994 |
1.0 |
9.80 |
0.996 |
1.0 |
| kF
|
1.23 |
0.999 |
1.4 |
4.75 |
0.999 |
1.3 |
4.75 |
0.982 |
1.2 |
9.99 |
0.980 |
1.1 |
T25
|
kd
|
1.86 |
0.982 |
1.0 |
16.1 |
0.993 |
1.0 |
16.1 |
0.997 |
1.0 |
47.4 |
0.991 |
1.0 |
| kF
|
1.74 |
0.996 |
1.5 |
15.4 |
0.996 |
1.2 |
15.4 |
0.989 |
1.2 |
66.5 |
0.979 |
0.7 |
| T50 |
kd
|
4.27 |
0.970 |
1.0 |
29.2 |
0.971 |
1.0 |
29.2 |
0.986 |
1.0 |
81.8 |
0.990 |
1.0 |
| kF
|
3.95 |
0.981 |
1.3 |
30.4 |
0.993 |
1.3 |
30.4 |
0.996 |
1.2 |
140 |
0.993 |
0.6 |
Table 9.
Mass transfer coefficient, km, and the distribution coefficient, kF, and n for the Freundlich model that have been used in PHREEQC for all the tests.
Table 9.
Mass transfer coefficient, km, and the distribution coefficient, kF, and n for the Freundlich model that have been used in PHREEQC for all the tests.
| |
T0 |
T25 |
T50 |
| Homologues |
km (hr-1) |
kF 103 |
n |
km (hr-1) |
kF 103 |
n |
km (hr-1) |
kF 103 |
n |
| C10LAS |
0.4 |
0.10 |
1.0 |
8.0 |
0.043 |
1.5 |
6.2 |
0.019 |
1.7 |
| C11LAS |
2.0 |
0.35 |
1.0 |
6.0 |
0.12 |
1.5 |
7.0 |
0.059 |
1.7 |
| C12LAS |
2.0 |
1.50 |
1.0 |
6.0 |
0.28 |
1.5 |
10.5 |
0.13 |
1.7 |
| C13LAS |
8.0 |
4.90 |
1.0 |
8.0 |
31.3 |
1.5 |
8.0 |
31.3 |
1.7 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).