1. Introduction
Oil exploration activities are crucial to the economy and society. However, the pollutants and toxic by-products resulting from these activities exert a direct impact on ecosystems, affecting rivers, soils, and oceans, as well as the fauna and flora in these environmental compartments [
1,
2].
The effects of this type of pollution can be acute or chronic. Acute impacts are those in which exposure to the contaminant in a short period of time is sufficient to have lethal effects on organisms. These effects generally result from accidents involving the spillage of petroleum products, as the water-soluble toxic fractions are quickly diluted. In contrast, activities conducted over a period of years have chronic effects, with the long-term exposure of organisms to the contaminating agent, leading to the persistence of toxic fractions in the environment and making it difficult or even impossible to recover the site [
3].
One of the technologies developed to remediate ecosystems contaminated with oil and its derivatives is the use dispersants containing chemical surfactants. However, these agents are highly toxic and have low biodegradability. Thus, there is increasing interest in replacing such products with green surfactants [
4].
Green surfactants are amphiphilic molecules derived from natural sources or synthesised from renewable raw materials. Triglycerides, carbohydrate sources, and organic acids obtained through fermentation are commonly used as raw materials for the synthesis of surfactants. Triglycerides and sterols provide the hydrophobic part, whereas sugars and amino acids contribute to the hydrophilic part. Natural surfactants can be produced through the chemical modification of renewable raw materials or by using the biosynthetic processes of living organisms, such as plants, microbes, and yeasts. When produced microbially, such products are denominated biosurfactants [
5].
Biosurfactants have several advantages over their synthetic counterparts, such as biodegradability and low toxicity as well as tolerance to extreme conditions of temperature, pH, and salinity. In addition to surfactant, emulsifying, and dispersant activities, these compounds also have antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties [
6,
7]. Biosurfactants comprise a wide variety of surface-active compounds, such as glycolipids, lipopeptides, polysaccharide-protein complexes, phospholipids, fatty acids, and neutral lipids [
8].
Contemporary society is characterised by increased spending, a growing emphasis on reusing materials, and environmental concerns, with a greater focus on recovery, recycling, and reuse. The need for environmental preservation has led to the use of various industrial by-products that would otherwise be discarded. This is particularly evident in the food industry. In recent decades, industrial waste products have attracted the interest of researchers as low-cost substrates for the production of biosurfactants [
9,
10]. However, the waste must provide the nutrients required for microbial growth and subsequent biosurfactant production. Industrial wastes with high carbohydrate or lipid contents are particularly suitable for use as substrates [
9]. When performed on an industrial scale, the benefits of using by-products from the agri-food industry as raw materials include the reduction in production costs and the generation of less waste [
10]. The use of agro-industrial waste and by-products as raw materials for the production of higher-value products has created new industrial opportunities in addition to contributing to the preservation of the environment, making the process more ecological and aligned with the principle of a circular bioeconomy. Agro-industrial by-products and food waste, such as corn steep liquor, sugarcane molasses, sugarcane bagasse, rice straw, potato, pineapple, orange, and beet peels, waste soybean frying oil, crude glycerol, and cassava wastewater, are commonly used for the synthesis of biosurfactants [
9].
Biosurfactants have been increasingly explored by the oil industry, where these natural compounds can participate in the oil extraction process or can be incorporated into lubricating oil formulations. Biosurfactants reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water, and are, therefore, used in the bioremediation of aquatic ecosystems and soil through the emulsification and dispersion of hydrocarbons, enhancing the degradation of these compounds in the environment. Other applications involve the dispersion of oil spills, the removal and mobilisation of oil residue in storage tanks, and microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) [
11,
12].
The detergent industry merits special attention, as raw materials used in the formulation of these products are often derived from petroleum. Biosurfactants can replace synthetic surfactants in the formulation of degreasers and natural detergents, which even exhibit greater efficiency in removing heavy oils [
13,
14]. The market for detergents that can clean surfaces contaminated with heavy oils is promising in Brazil due to the lack of companies specialized in the fabrication of such products. Efforts to develop biodetergent production technologies will enable access to innovative products in a field that remains underexplored in the country [
12,
15].
Recent studies have demonstrated the ability to incorporate microbial biosurfactants into the formulation of high-value-added bioproducts in the detergent industry [
16,
17,
18]. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the incorporation of a microbial biosurfactant produced by
Starmerella bombicola ATCC 22214 cultivated in a low-cost medium as a tensioactive agent in the formulation of a natural detergent.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The chemical reagents used in this work were all analytical grade. The growth media were purchased from Difco Laboratories, USA. Corn-steep liquor was obtained from Corn Products do Brazil in the city of Cabo de Santo Agostinho, Brazil, and contains 21–45% protein, 20–26% lactic acid, 8% ash (which contains Ca
2+, Mg
2+, and K
+), and 3% sugar, and has low fat content (0.9–1.2%) [
12].
2.2. Microorganism, Maintenance Medium, and Growth Medium
The yeast S. bombicola ATCC 22214 was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC®) and used for the production of biosurfactant. The yeast was kept at 5 °C in yeast mould agar (YMA) medium composed of yeast extract (0.3%), peptone (0.5%), D-glucose (1%), and agar (2%) dissolved in distilled water (100 mL), pH 7.0. Transfers were made to fresh agar slants each month to maintain viability. The yeast mould broth (YMB) growth medium had the same composition, excluding the agar.
2.3. Growth of Inoculum
The yeast inoculum was standardised by transferring the culture to a tube containing the YMA medium to obtain a young culture at 28°C. The sample was then transferred to a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of the YMB medium and incubated under aerobic conditions with orbital agitation at 150 rpm and 28°C for 48 hours. Dilutions were performed until obtaining a final concentration of 104 cells/mL, which was used at a concentration of 5% (v/v). Cell counts were performed in a Neubauer chamber.
2.4. Production Medium and Culture Conditions
The production medium comprised 10% sucrose (table sugar), 1.2% canola oil, 0.5% corn-steep liquor, 0.4% (NH4)2SO4, 0.1% K2HPO4, and 0.05% Mg2SO4.7H2O. Fermentation was carried out in 1000-mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 500 mL of the production medium with the pH adjusted to 6.0. The medium was sterilised in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 min, followed by incubation with 5% of the pre-inoculum and orbital shaking at 200 rpm and 28°C for 192 hours.
2.5. Surface Tension
The surface tension of the biosurfactant was measured in the cell-free broth centrifuged at 26000 x g for 20 min. The du Noüy ring method was employed using a Sigma 700 Tensiometer (KSV Instruments Ltd., Finland) at room temperature.
2.6. Isolation of Biosurfactant
A method developed in the laboratory was used to isolate the biosurfactant, which consisted primarily of liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate twice at a 1:4 (v/v) ratio with the non-centrifuged metabolic broth. The organic phase was centrifuged (2600 x g for 20 minutes), followed by filtration. The filtrate was transferred back to the separating funnel and a saturated sodium chloride (NaCl) solution was added to separate the remaining aqueous phase. The organic phase was transferred to an Erlenmeyer flask and anhydrous magnesium sulphate (MgSO4) was added until the formation of granules, following by filtration through qualitative filter paper and drying 50°C.
2.7. Formulation of Natural Detergent
The formulation of a natural detergent involves the union of three main elements: natural solvent, natural surfactant, and stabiliser. For the formulations in the present work, cottonseed oil was used as the natural solvent due to its compatibility with petroleum derivatives as well as its low cost and ease of acquisition, as previously described by Rocha e Silva et al. [
19]. The natural surfactant was the biosurfactant produced by
Starmerella bombicola ATCC 22214. The stabilisers tested to avoid the formation of phases were vegetable wax, sodium alginate, and hydroxyethyl cellulose. The concentrations of cottonseed oil and isolated biosurfactant were set at 1 and 40%, respectively. To obtain stable, homogeneous formulations, the stabilisers were tested at different concentrations (
Table 1). All formulations were prepared in aqueous solutions.
2.8. Emulsification Index (E24)
Emulsification activity was measured using the method described by Cooper and Goldenberg [
20]. Petroleum (2 mL) was added to 2 mL of the detergent solutions in a tube with a screw cap (100 mm x 13 mm) and the content was vortexed for 2 minutes at 50 Hz. After 24 hours, the emulsification index (E
24) was determined according to Equation 1:
in which
he is the height of the emulsion layer and
ht is the total height of the mixture in mm. All samples were stored at 27°C [
21].
2.9. Ecotoxicity Tests
2.9.1. Recruitment Test in Aquatic Environment
The method was based on studies developed by Fernandes et al. [
22], who conducted analyses of larval attachment and the establishment of the fouling community through the installation of metal plates at previously chosen points to monitor the larval recruitment process. In field activities, the experimental setup involved the use of metal plates measuring 20 cm in height, 10 cm in width, and 0.5 cm in thickness. Samples (50 mL) of the natural detergent were incorporated into a commercial water-based white paint (IQUINE Ltda., Brazil) at concentrations of 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, and 10.0% (w/v). A plate with only the commercial paint and another without the addition of any compound were used as controls. Each side of each plate constituted the same condition (duplicate experiments). The plates were attached to aluminium rails and the structure was placed in the Atlantic Ocean supported by buoys attached to the Pina Basin pier in the city of Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil, where the plates remained for 15 days.
Once removed from the water, the plates were placed in plastic bags in a polystyrene cooler and taken to the Environmental Studies Laboratory of the Advanced Institute of Technology and Innovation in the city of Recife, Brazil, for analysis. Coverage of the plates was estimated with the aid of an acrylic grid measuring 10 x 10 cm subdivided into 100 squares measuring 1 x 1 cm, with 81 intersections. Encrusting organisms at the intersections of the reading plate were analysed, with the calculation of the frequency of occurrence and relative abundance of the species and groups. Absolute frequency of organisms at the 81 intersections on each plate was determined. Relative frequency on each plate was calculated using the following equation:
in which Fr is relative frequency, Fa is absolute frequency, 100 is the number of quadrants on the acrylic grid, and 81 is the number of intersections on the acrylic grid.
2.9.2. Toxicity Test with Artemia salina as Indicator
The toxicity of the natural detergent was tested against larvae of the microcrustacean
Artemia salina as the bioindicator. Eggs were purchased from a local store. After 24 hours of incubation, tests were conducted in 10-mL flasks containing 10
Artemia larvae in 5.0 mL of seawater. The larvae were exposed to 5.0 mL of solutions containing the natural detergent at concentrations of 2.5%, 5%, 7.5%, and 10%. Mortality was determined after 24 h. Seawater without the natural detergent was used as the control [
23].
2.9.3. Toxicity Test with Desmodesmus armatus as Indicator
The procedures adopted in this toxicological test and the cultivation of the microalga under controlled conditions followed the technical standards established by ABNT NBR 12648 Aquatic ecotoxicology — Chronic toxicity — Test method with algae (Chlorophyceae) [
24].
A pre-culture was performed with the microalga Desmodesmus armatus three days prior to the test. For pre-cultivation, the alga was in an exponential growth phase, which was maintained under the same test conditions of temperature, light, and agitation. The microalgal inoculum added to the test containers had an initial concentration between 103 and 105 cells/mL. The test solutions comprised the cultivation medium, inoculum, defined volumes of stock solution (formulated detergent), and water for dilution.
For the test, the concentration range established in ABNT [
24] was used for tests with chemical/reference substances. Five concentrations were tested (56, 32, 18, 10, and 5.6 mg/L) plus the control. The control sample contained the cultivation medium, inoculum, and dilution water. The test containers were randomly distributed in the shaking system and their positions were changed daily to minimise possible spatial differences in light and temperature. The test was maintained at 23 to 27°C for 72 ± 2 h, with continuous light and stirring speed between 100 and 175 rpm. Algal biomass was determined at the beginning and end of the test in all test containers using the cell counting method under an optical microscope. The occurrence of abnormalities in the size or shape of the cells at the end of the test was also investigated under an optical microscope.
Table 2 summarises the requirements used for the test.
2.9.4. Toxicity Test with Danio rerio as Indicator
Cultivation of the zebrafish, Danio rerio, and exposure of embryos: adult matrices of D. rerio were fed nauplii of Artemia sp. four times per day. Three males and six females were separated in a 50-L aquarium. After fertilisation, viable fertilised eggs were selected by direct observation with an inverted microscope (magnification: 40 x). Eggs with coagulation or opacity were discarded. The fertilisation rate was higher than 90% and pH ranged from 7.2 to 7.8. Dissolved oxygen ranged from 5 to 6.5 mg/L and temperature was maintained at 27 ± 0.5°C.
Toxicity test using
D. rerio: exposure of fertilised eggs to the detergent was performed using a fish embryo test (FET) [
25]. Death was attributed to embryos in the occurrence of the coagulation of the egg, absence of somites after 24 hours, absence of heartbeat, or absence of movement. The mortality rate was determined as the number of deaths after 96 hours of exposure divided by the total of number of individuals (n = 20) exposed to each sample [
26].
Sublethal effects were investigated using the general morphology score (GMS), which is the sum of partial scores attributed to each embryo throughout the development of basic morphological structures in the first 96 hours of exposure, as described by Beekhuijzen [
27]. Twelve development markers were assessed every 24 hours and abnormalities were recorded as indicators of sublethal effects. Embryos exposed to different concentrations of the detergent were compared to the control. The maximum GMS is 18 for a perfectly developed larva at the end of 96 hours [
26,
27,
28].
Lethal effects (LC
50) at 96 h were calculated using a logistic curve in the R software 4.0.2 (R Development Core Team, 2020) [
29]. The mean GMS index at different concentrations was analysed separately using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test to detect significant differences compared to the control. Normality and homoscedasticity were determined using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Levene’s test, respectively. Statistical analysis was performed with the aid of the SigmaPlot software, version 12 (Jandel Scientific, Erkrath, Germany).
2.9.5. Phytotoxicity Test
Phytotoxicity of the detergent was determined in a static test involving the seed germination and root growth of cabbage (
Brassica oleracea), cherry tomato (
Solanum lycopersicum), and maroon cucumber (
Cucumis anguria) plants, as described by Tiquia et al. [
30]. Test solutions of the formulated detergent at different concentrations (2.5%, 5%, 7.5%, and 10%) were prepared in distilled water. The test was conducted in sterile Petri dishes (10 cm) containing Whatman No. 1 filter paper discs. Ten seeds previously treated with NaClO were symmetrically places in each dish, followed by inoculation with 5 mL of the test solution at 28°C. Distilled water was used as the control. Seed germination, root growth (≥ 5 mm), and the germination index (GI) were calculated after five days of incubation in the dark using the following equations:
2.10. Dispersion of Oil in Water by Detergent
The oil displacement test was used to determine the dispersing capacity of the formulated detergent by measuring the diameter of the clear area that emerged after dripping the detergent onto a thin layer of oil in water. Thirty mL of seawater were placed in a Petri dish (diameter: 15 cm), to which oil was added. The selected detergent solution was added at a detergent-to-contaminant ratio of 1:1 (v/v). The clear zone formed in the centre of the oil at room temperature was measured after 30 seconds. A larger clear zone diameter denotes greater surface activity of the detergent [
31,
32].
2.11. Cleaning Test on Rock Surface Impregnated with Petroleum
Rocks impregnated with petroleum were submitted to cleaning with the formulated detergent. For the purposes of comparison, commonly used commercial detergents were also tested. Oil removal was calculated with the following equation:
in which Mc is the mass of the contaminated rock, Mw is the mass of the rock after cleaning, and Mi is the initial mass of the rock.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The data were submitted to statistical analysis using the one-way procedure in Statistica® (version 7.0), followed by linear one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All triplicate results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Differences were determined using Tukey's post hoc test, with a 95% significance level.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield and Surface Tension of Biosurfactant
One of the most important properties for determining the effectiveness of a biosurfactant is the reduction in surface tension. According to Akbari et al. [
33], biosurfactants that reduce the surface tension of water from 72 to 35 mN/m are considered effective.
After fermentation, the biosurfactant produced by
Starmerella bombicola ATCC 22214 reduced surface tension to 31.846 mN/m and the yield of isolated biosurfactant was 22 g/L. This yield is considered very satisfactory, as the yield of most biosurfactants is low, which constitutes an obstacle for commercial applications of these biomolecules. Another important point is that the biosurfactant produced in this study was obtained from a low-cost medium containing renewable feedstocks, such as vegetable oil and sucrose as well as an agro-industrial by-product (corn steep liquor). The use of these cost-effective ingredients significantly contributes to reducing the overall production costs of the biosurfactant. Kumari et al. [
34] obtained a surface tension of 32.300 mN/m for a sophorolipid. Shah et al. [
35] found a similar result for a biosurfactant produced by
S. bombicola ATCC 22214 cultivated in a medium with 10% palm oil, which reduced the surface tension to 35.350 mN/m.
3.2. Selection of Natural Detergent Formulation
Table 3 displays the concentrations of the components of the natural detergent formulations tested and respective petroleum emulsification indexes, which was the criterion used in this work to assess the formulation, as this qualitative test is a quick method for determining the emulsifying properties of a detergent.
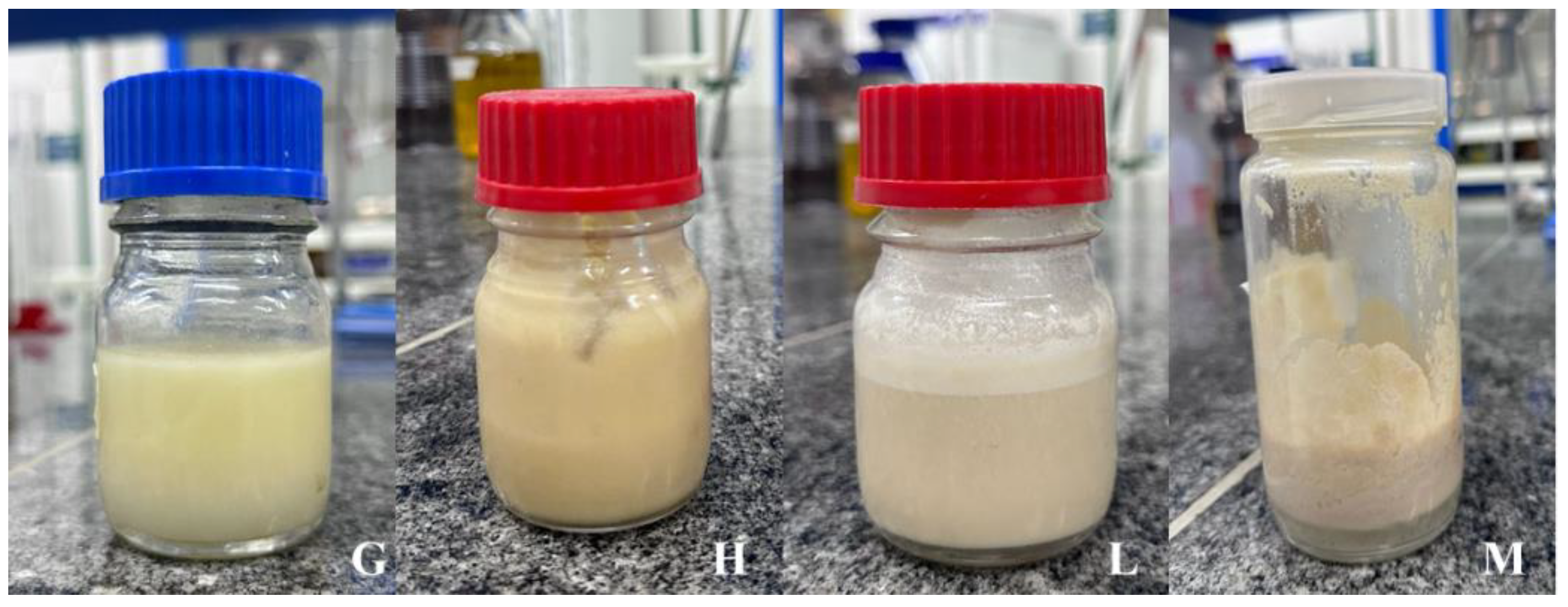
Formulations G, H, L, and M had petroleum emulsification indices above 90% and were, therefore, selected for the stability study over a 10-day period to determine a possible influence on petroleum emulsification. The stability of the formulations was also investigated to determine whether the samples would undergo any changes in physical characteristics (phase separation).
Table 4 presents the criteria investigated for Formulations G, H, L, and M after 10 days of storage at room temperature.
No phase formation was found after the storage of Formulations H and L, demonstrating that these formulations remained stable for 10 days. In contrast, instability was found for Formulations G and M (
Figure 1).
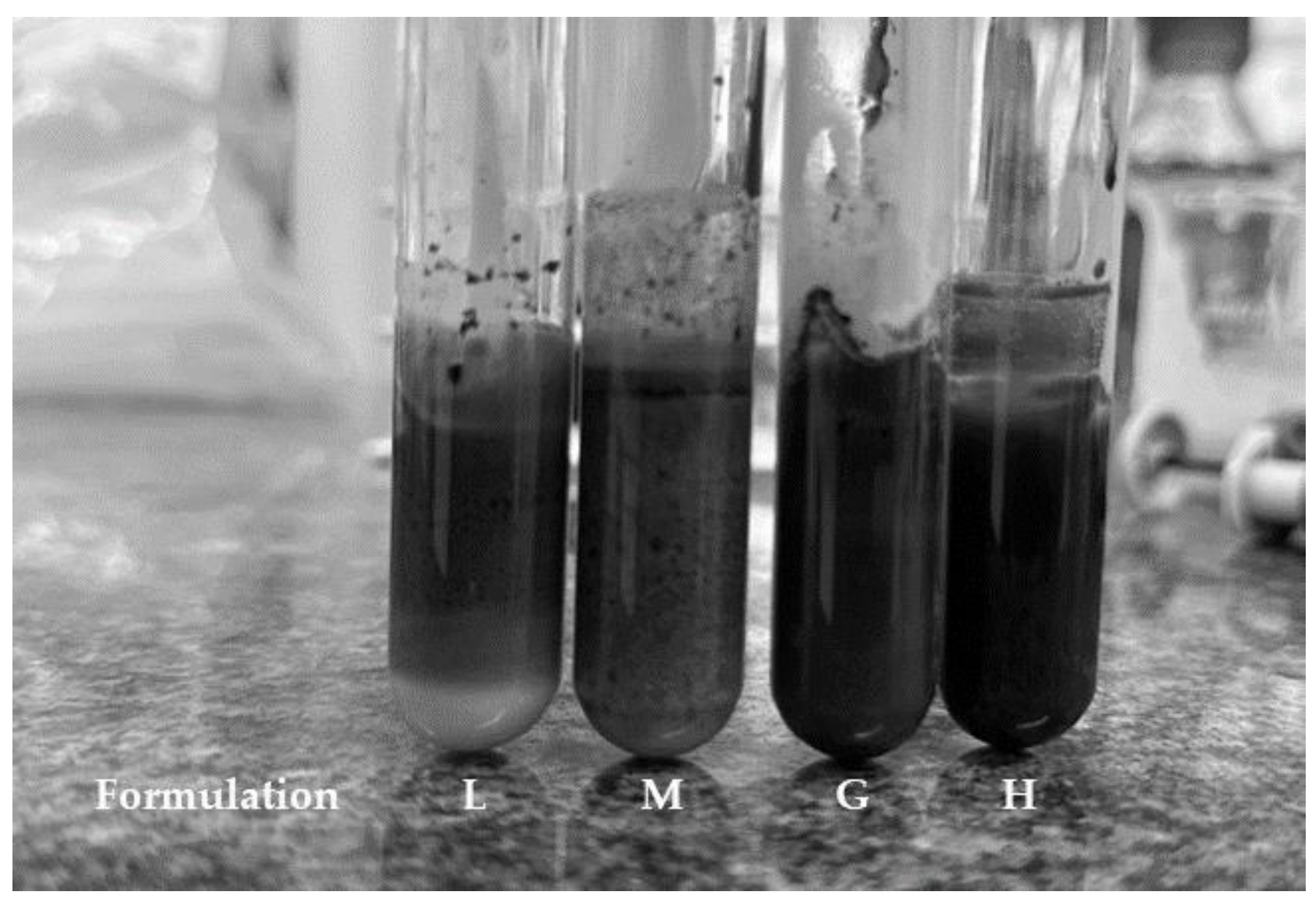
None of the formulations underwent significant changes in terms of oil emulsification efficiency, but only Formulation H was able to emulsify 100% of the oil after 10 days of storage (
Figure 2). Thus, neither the storage time nor the interaction of the components had any influence on the efficiency or stability of this formulation.
Formulation H achieved excellent petroleum emulsification results. This formulation comprised 40% cottonseed oil as the natural solvent, 1% biosurfactant produced by Starmerella bombicola ATCC 22214 as the surfactant, and 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose as the non-toxic stabilising agent. This formulation is also the most promising from an economic standpoint, considering the acquisition costs of the components. Thus, Formulation H was selected for further testing.
3.3. Ecotoxicity Tests
3.3.1. Recruitment Test in Aquatic Environment
Biofouling is the deposition of micro- and macro-organisms on natural and artificial surfaces that are either completely or partially submerged. For this phenomenon to occur, the surface must not have any inhibitor impeding the onset of the process and the formation of biofilm, which can evolve into more complex biological communities [
36,
37,
38]. Formulation H was tested to determine its effect on the fouling process of marine organisms. The absence of an effect would demonstrate that the formulation is non-toxic.
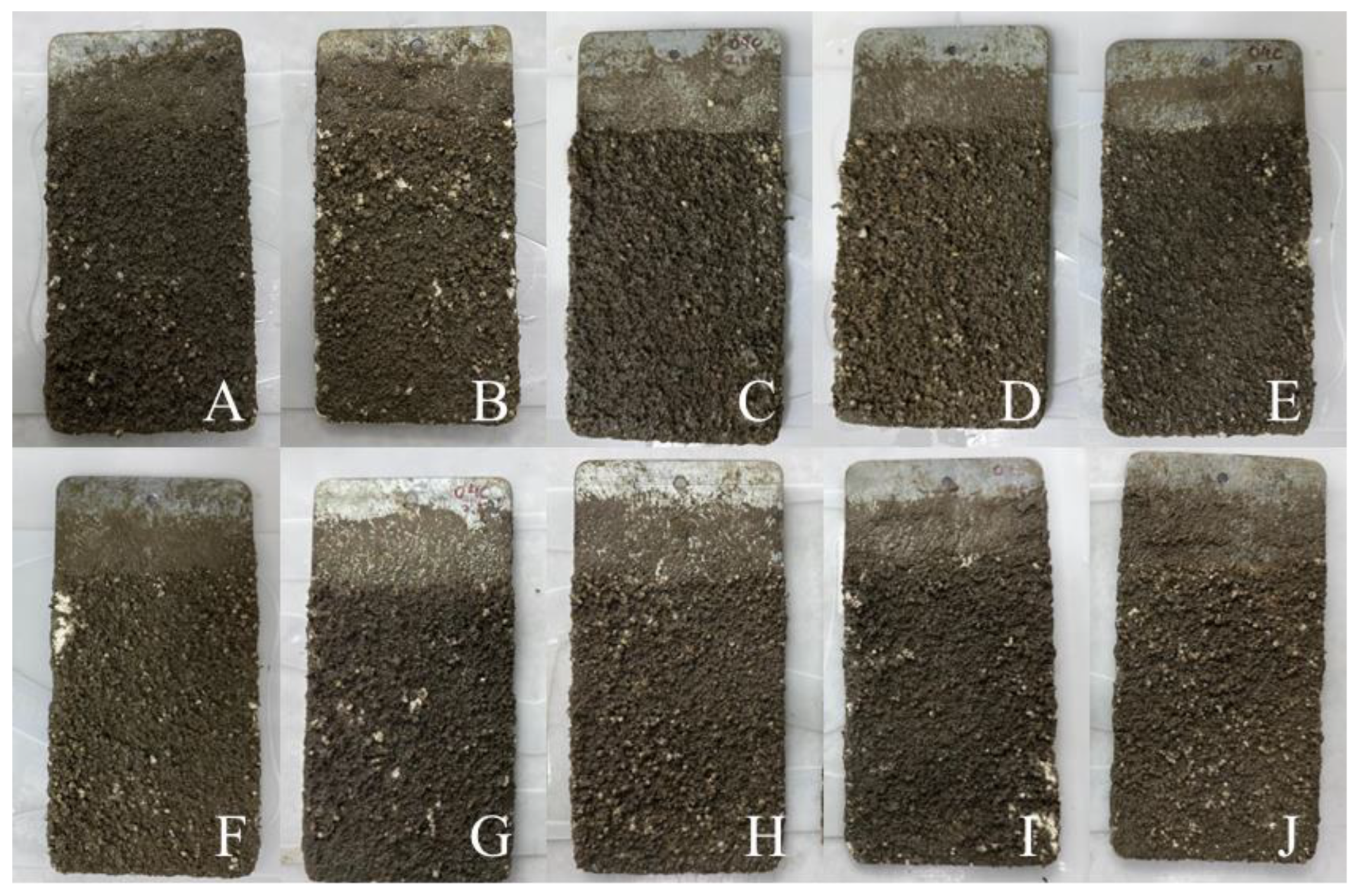
The recruitment test was performed using metal plates covered with a water-based paint into which different concentrations of Formulation H (2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10%) were incorporated. A plate without paint was used as a control and a plate with the paint alone (without the addition of the natural detergent) was also used for comparative purposes. The two sides of each plate (Side A and Side B) were duplicates of the same condition. The plates were submerged for 15 days in the Pina Basin of the Atlantic Ocean in the city of Recife, Brazil. After which, the encrustation of organisms on the plates was examined (
Figure 3).
After 15 days of immersion in an aquatic environment, the plates were analysed separately using a laboratory magnifying glass.
Table 5 displays the data obtained from counting the organisms encrusted on the plates.
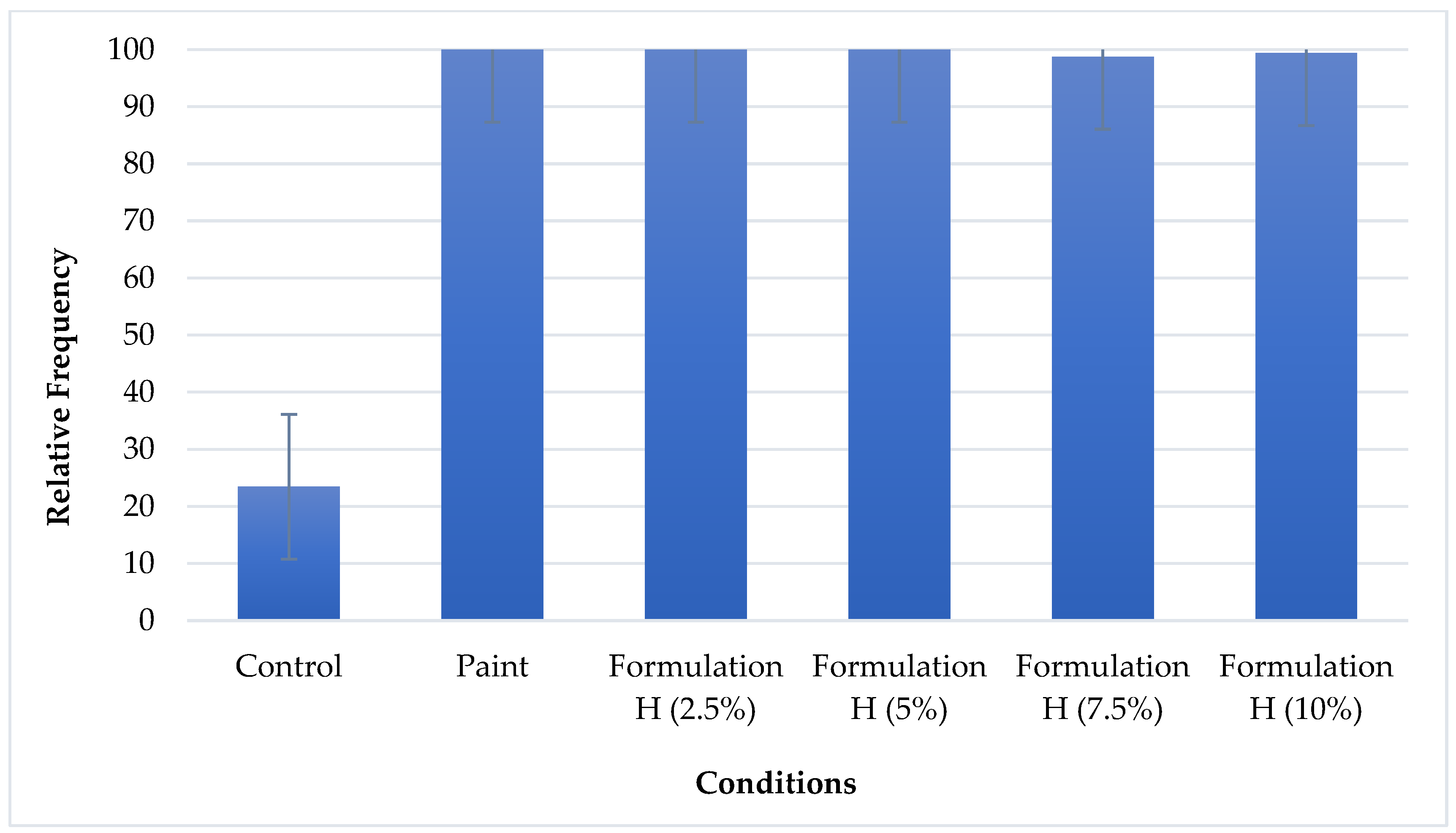
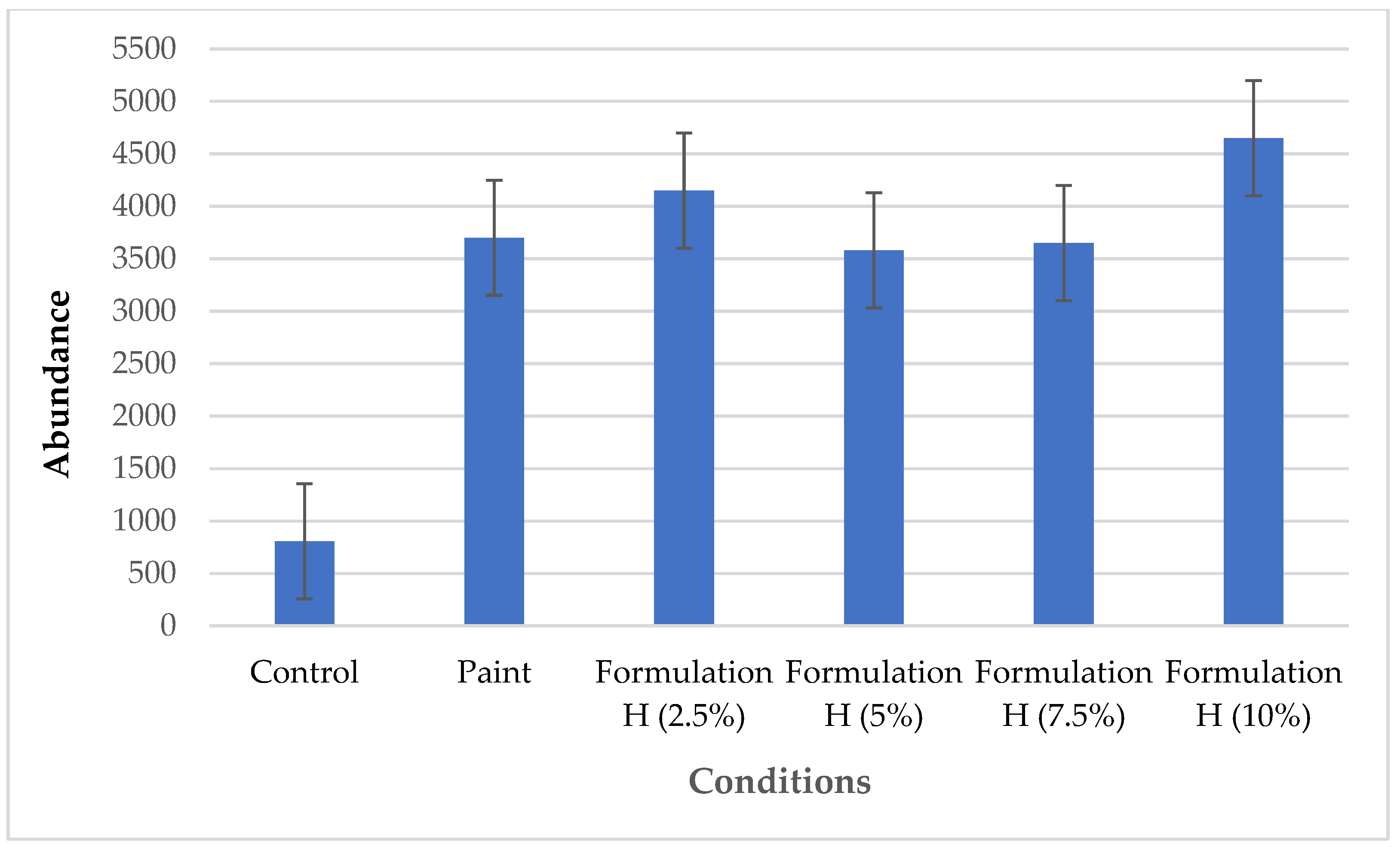
In the recruitment test, relative frequency and abundance data are important to understanding the fouling process. Two graphs were plotted for better visualisation and analysis of the data.
Figure 4 displays the relative frequency graph with the averages of both sides of each plate and
Figure 5 displays the abundance graph with the averages of both sides of each plate.
Figure 4 shows that the relative frequency was low on the control plate (23.44%), whereas the maximum frequency (100%) was reached on the plate with paint alone, demonstrating that the paint favoured the incrustation of the plate with organisms. The smoother surface due to the presence of the paint favoured the attachment of larvae. The plates with paint containing different concentrations of Formulation H had relative frequencies above 98%, which shows that the natural detergent incorporated into the paint did not have a significant inhibitory effect on the recruitment of organisms, demonstrating the non-toxic nature of Formulation H.
Figure 5 shows the abundance of organisms recruited onto the plates. As occurred in the relative frequency analysis, low recruitment was found on the control plate, whereas recruitment was nearly fivefold greater on the plate with paint alone. Excellent recruitment of organisms was also found on the plates with Formulation H, reaching 4650 individuals on the plate containing the formulation at a concentration of 10%. In addition to not having a significant inhibitory effect on the recruitment of organisms, Formulation H favoured their fixation. The data from the recruitment test reveal that Formulation H has low toxicity to marine organisms. No records were found in the literature on the process of marine organisms encrusting surfaces containing natural detergents.
3.3.2. Toxicity of Natural Detergent to Artemia salina
Due to its ease of maintenance in the laboratory, short lifecycle, and simple cultivation conditions, the microcrustacean Artemia salina is commonly used in ecotoxicity tests. Thus, the formulated detergent was assessed for toxicity to the larvae of this microcrustacean. The survival rate in these tests was 100% under all conditions tested: seawater (control) and solutions containing the detergent at concentrations of 2.5%, 5%, 7.5%, and 10%. The results demonstrated the absence of toxicity of the detergent.
Similar results were found in the literature. Using the same ecotoxicity test to assess a natural detergent formulated with a microbial biosurfactant, Silva et al. [
39] also demonstrated the absence of toxicity of the bioproduct. Assessing a biodegradable biodetergent, Rocha e Silva et al. [
19] found
Artemia salina survival rates higher than 94%.
3.3.3. Ecotoxicity of Natural Detergent to Microalga Desmodesmus armatus
Formulation H was assessed with regards to two important parameters – chronic toxicity, which is the harmful effect on test organisms that may spend their entire lifecycle or part of it exposed to the substance, and the algistatic effect, which is the inhibition of the multiplication of algal cells without causing their death. When exposed to different concentrations of Formulation H (56, 32, 18, 10, and 5.6 mg/L), the microalga Desmodesmus armatus did not exhibit either effect, indicating the multiplication of algal cells and, consequently, the absence of toxicity to the bioindicator. Due to the absence of toxicity, it was not necessary to describe the lethal concentration (LC50) or other important parameters described in the methods.
3.3.4. Ecotoxicity of Biosurfactant to Danio rerio (Zebrafish)
The test followed sampling design standards suggested by the OECD [
25]. The test lasted 96 hours and investigated the lethal effects of Formulation H on the zebrafish (
Danio rerio), such as coagulation of fertilised eggs, absence of somites, absence of tail detachment, and absence of heartbeat, as well as sublethal effects from tail development to swim bladder inflation.
A total of 168 embryos were distributed among seven 24-well plates – a control plate (clean water) and others with the formulated detergent at concentrations of 150, 75, 37.5, 18.75, 9.37, and 4.69 mg/L. Embryo mortality is described in
Table 6. From these data, the lethal concentration for 50% of exposed individuals (LC
50) after 24, 48, and 96 hours of exposure was calculated (
Table 7).
A study using synthetic surfactants (sodium dodecyl sulphate, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride, and fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether) demonstrated 53% mortality in the first 10 hours of exposure at a concentration of 1 mg/L [
40]. Korbut et al. [
41] analysed a biosurfactant with properties to control aquatic pathogens (SPH6) and found a 10% mortality rate after 24 hours of exposure at a concentration of 20 mg/L. The data from the present study reveal a lack of toxicity for all concentrations ≤ 18.75 mg/L, which can be described as environmentally relevant concentrations, demonstrating lower toxicity of the natural detergent.
Regarding the lethal concentration for 50% of organisms (LC
50), the values were 120.87, 67.48, and 62.60 mg/L for 24, 48, and 96 hours of exposure, respectively, characterising the product as having low toxicity according to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service [
42]. Previous studies report lower LC
50 values. Al-Asmakh et al. [
43] found an LC
50 of 18.3 µ/L for the AEO-7 surfactant. Steartrimonium bromide, sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and nonylphenol exthoxylate (NPE) had LC
50 values of 5.77, 17.24, and 0.73 mg/L, respectively [
44]. The LC
50 of a biosurfactant produced by
Pseudomonas putida was 60 mg/L for zebrafish embryos exposed for 48 h [
45].
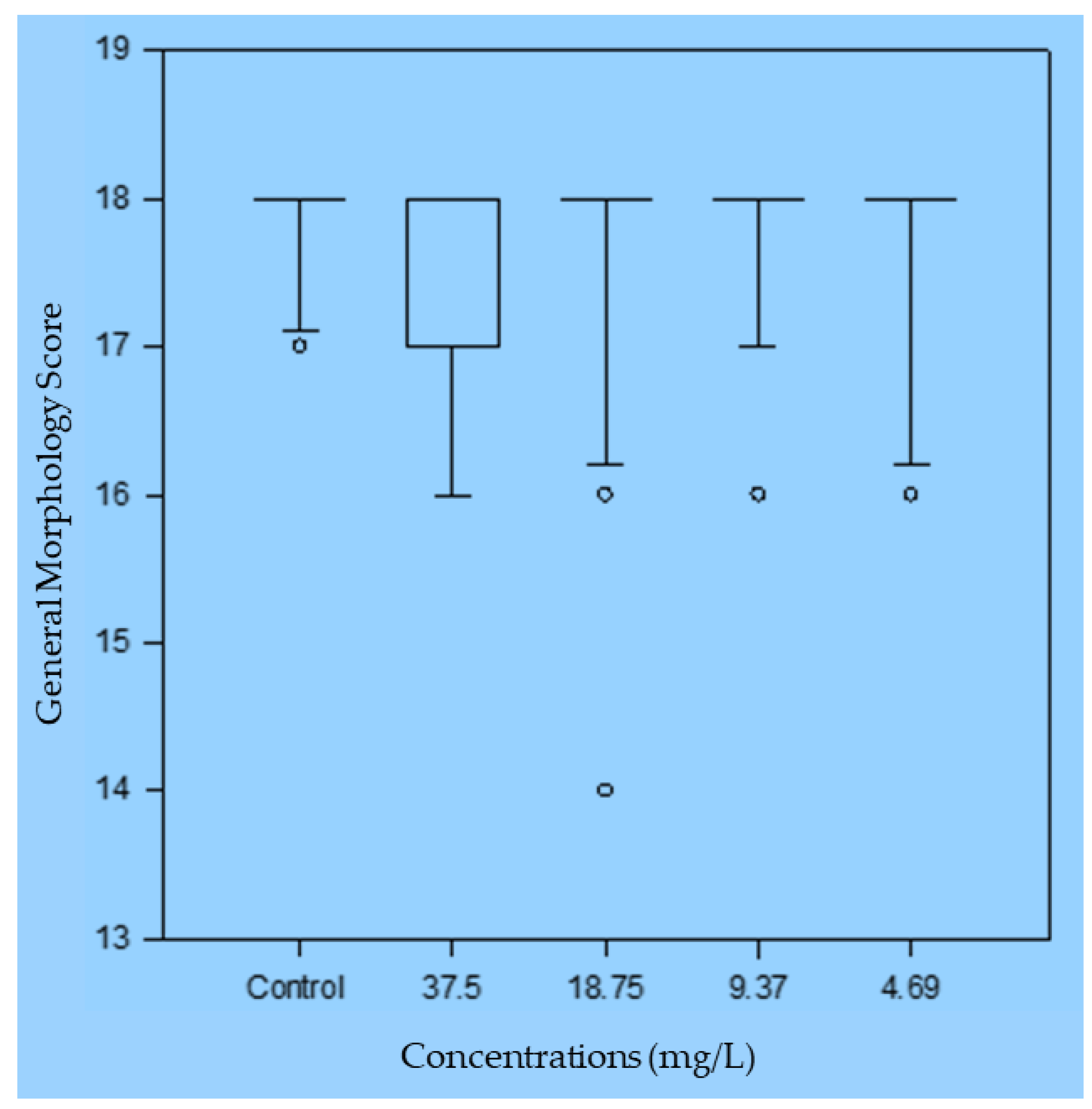
Sublethal effects for the four lowest concentrations were also investigated. The absence of a swim bladder, non-hatching, and non-protrusion of the mouth were found in some embryos. However, no significant differences were found compared to the control (
Figure 6). Regarding the frequency of pathologies, haemorrhage and pericardial oedema were found in only 15% of the embryos exposed to the concentration of 75 mg/L. No pathologies were found with the other concentrations of the formulated detergent.
Previous studies also reported pericardial oedema in zebrafish embryos and larvae exposed to different concentrations of surfactants: 10 mg/L of NPE, 0.5 mg/L of STAB [
44], and 12.8 µ/L of AEO-7 [
43], indicating the high potential of surfactants to induce sublethal effects in zebrafish embryos and larvae. These concentrations are lower than 75 mg/L, which was the concentration of Formulation H capable of causing pathologies in embryos.
Therefore, the tests performed in the present study demonstrated the lethal toxicity to zebrafish embryos at the two highest concentrations of the detergent formulation (75 and 37.50 mg/L), whereas no lethal or sublethal toxicity was found at the other concentrations tested (18.75, 9.37, and 4.69 mg/L).
3.3.5. Phytotoxicity Test
Toxicity is defined as the ability of a substance to exert a harmful effect on a living organism and depends on the concentration and properties of the chemical to which the organism is exposed as well as the exposure time [
12].
Table 8 displays the toxicity of the natural detergent to three plant species.
The toxicity of the formulated natural detergent was tested in a brief bioassay involving plants. This assay is important to predicting the effect of chemicals on an ecosystem. The germination index, which combines measurements of relative seed germination and relative root growth, was used to investigate the toxicity of the detergent formulation to the seeds of cabbage (Brassica oleracea), cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), and maroon cucumber (Cucumis anguria) plants. The test solutions had no inhibitory effect on seed germination or root growth, indicating low toxicity. In general, a reduction in the germination rate was found with the increase in the detergent concentration. No significant differences in the germination index were found for the four concentrations in the test involving cherry tomato seeds. The results demonstrate that this formulation has low toxicity and does not pose a risk to the environment.
3.4. Dispersion of Petroleum by Detergent
One of the parameters used to determine the quality of a detergent is its ability to disperse oily contaminants. The detergent (Formulation H) was able to disperse the initial diameter of the oil by up to three times at a detergent-to-petroleum ratio of 1:1 (v/v), as shown in
Figure 7. The results indicate that the natural detergent is an excellent hydrocarbon dispersant and can be used as a bioremediation agent in different environments.
Formulations with biosurfactants and organic solvents have been described as potential dispersants for remediating oil spills due to their non-toxic potential, as the toxicity of conventional surfactants poses a further threat to marine environments. Shah et al. [
46] assessed a binary mixture of an ionic liquid surfactant (choline laurate) and a sophorolipid as a dispersant and achieved dispersion efficiency of 83%. Hajibagheri et al. [
47] and Jian et al. [
48] reported the improvement of properties by combining different surfactants, testing binary mixtures of synthetic surfactants and biosurfactants (tea saponin).
3.5. Cleaning Test of Rock Surface Impregnated with Petroleum
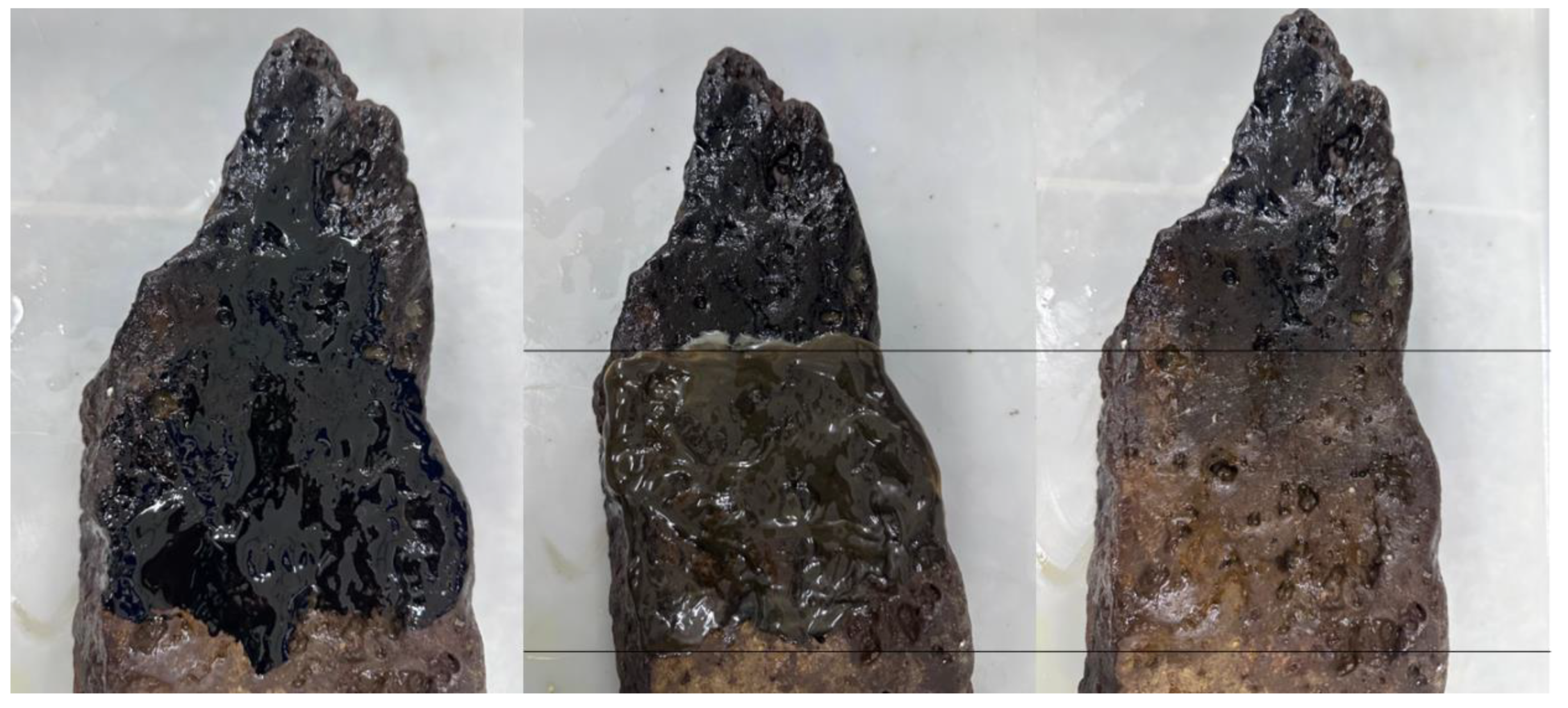
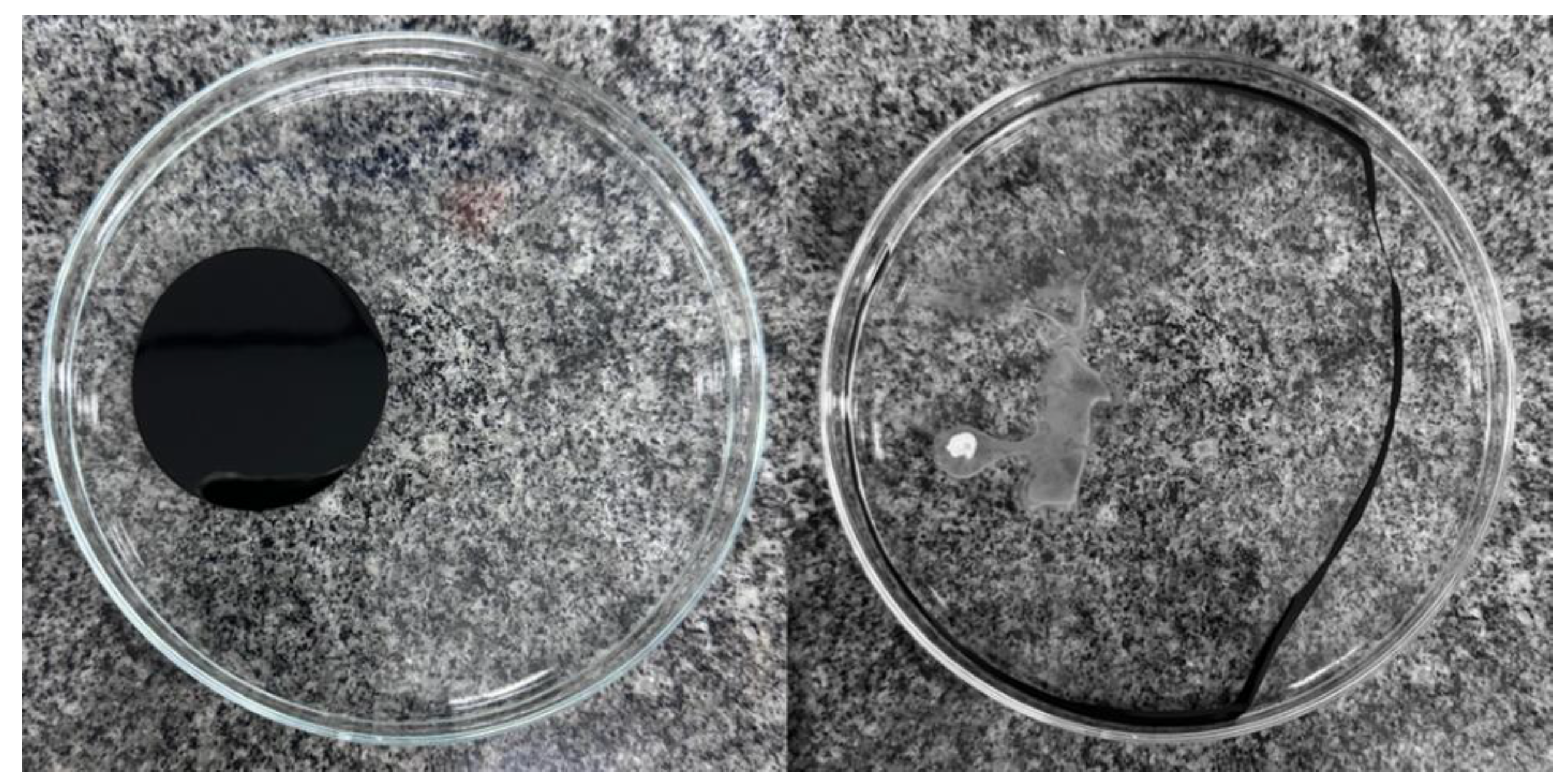
Considering the ability of detergents to solubilise hydrophobic pollutants, tests were performed to determine the cleaning capacity of formulated detergent on rock impregnated with petroleum. To better illustrate the efficiency of the formulated detergent, only a part of the contaminated surface was subjected to cleaning for comparative purposes with the uncleaned section, as shown in
Figure 8.
Formulation H removed oil from the rock surface, achieving a removal rate of 98% without considerable mechanical effort. This result demonstrates the viability of the natural detergent as a biotechnological additive for remediation processes in environments contaminated with petroleum and its derivatives.
Studies have reported the ability of natural detergents to remove heavy oils from different surfaces, highlighting the use of these bioproducts in the remediation of contaminated areas [
19]. The isolated use of biosurfactants in marine and industrial environments for the treatment of oils has also achieved good results. Ostendorf et al. [
23] showed that a biosurfactant produced by the bacterium
Bacillus cereus removed 91.0 ± 0.4% of motor oil adsorbed to marine rocks and dispersed 70.0 ± 0.4% of the oil in seawater. In the same study, the biosurfactant formulated with 0.2% potassium sorbate demonstrated potential for application in the oil industry when applied to mobilise oil in marine environments. Two biosurfactants were compared to two chemical surfactants (polysorbate 20 and polysorbate 80) in terms of dispersion and emulsification capacity and achieved similar results [
49]. Plant-derived surfactants also exhibited better surfactant properties than Tween 80 and synthetic sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) [
50].
4. Conclusions
The results obtained in the present study demonstrate the successful addition of the biosurfactant produced by Starmerella bombicola ATCC 22214 in the formulation of a natural detergent. Growing awareness and the need for environmental protection are driving researchers to develop environmentally friendly products and pave the way for using renewable resources for the development of green, safe surfactants. In Brazil, the lack of companies specialised in the formulation and production of natural detergents makes the biodetergent market very promising. Furthermore, few studies report the possibility of using microbial surfactants in the formulation of these detergents. The detergent formulated in the present study, in addition to being efficient and safe, has low-cost active ingredients, demonstrating that the use of renewable resources in the production of high-value-added products is promising from an industrial standpoint. Thus, the formulated natural detergent is a viable alternative to its synthetic counterparts and can help reduce the impacts on ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, L.A.S; methodology, LA.S., I.A.S., R.N.A., M.C.C.C., J.C.M.O., and F.C.G.A.; validation, L.A.S., I.A.S., and F.C.G.A.; formal analysis, L.A.S. and M.L.B.F.; investigation, I.A.S., J.C.M.O., R.N.A., J.C.M.O., and F.C.G.A.; resources, L.A.S.; data curation, L.A.S. and I.A.S; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.S., R.N.A., and F.C.G.A.; writing—review and editing, L.A.S. and M.L.B.F.; visualisation, L.A.S.; supervision, L.A.S.; project administration, L.A.S.; funding acquisition, L.A.S. All authors have read and approved the version of the manuscript for publication.
Funding
This study was funded by the Programa de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento da Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica (ANEEL) and by the Brazilian fostering agencies Fundação de Apoio à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco (FACEPE), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) (Finance Code 001).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Laboratories of Universidade Católica de Pernambuco (UNICAP) and to Instituto Avançado de Tecnologia e Inovação (IATI), Brazil.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wei, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Xu, Y.; Park, J-H.; Wang, J.J. Biochar-based materials as remediation strategy in petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil and water: Performances, mechanisms, and environmental impact. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 350-372. [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Almeida, F.G.C.; Silva, I.A.; Souza, T.C.; Meira, H.M.; Silva, R.C.F.S.; Luna, J.L.; Santos, V.A.; Converti, A.; Banat, I.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Production of green surfactants: Market prospects. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 51, 28-39. [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.A.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Souza, T.C.; Bezerra, K.G.O.; Durval, I.J.B.; Converti, A. Sarubbo, L.A. Oil spills: Impacts and perspectives of treatment technologies with focus on the use of green surfactants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 143. [CrossRef]
- Selva Filho, A.A.P.; Converti, A.; Silva, R.C.F.S.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants as multifunctional remediation agents of environmental pollutants generated by the petroleum industry. Energies. 2023, 16, 1209. [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.V.; Guimarães, C.R.; Marquita, R.L.S.; Santiago, V.M.J.; De Souza, M.P.; Nitschke, M.; Freire, D.M.G. Rhamnolipid and surfactin: Anti-adhesion/antibiofilm and antimicrobial effects. Food Control. 2016, 63, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- Gutnick, D.L.; Bach, H. Biosurfactants. In Reference Module in Life Sciences; Roitberg, B.D.; Elsevier, 2017.
- Jahan, R.; Bodratti, A.M.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Biosurfactants, natural alternatives to synthetic surfactants: Physicochemical properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102061. [CrossRef]
- Geetha, S. J.; Banat, Ibrahim, M.; Joshi, S. J. Biosurfactants: Production and potential applications in microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 23–32. [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, S.; Qamar, S.A. Cleaner production of biosurfactants via bio-waste valorization: A comprehensive review of characteristics, challenges, and opportunities in bio-sector applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111555. [CrossRef]
- Vuˇcurovi´c, D.; Baji´c, B.; Trivunovi´c, Z.; Dodi´c, J.; Zeljko, M.; Jevti´c-Muˇcibabi´c, R.; Dodi´c, S. Biotechnological Utilization of Agro-Industrial Residues and By-Products—Sustainable Production of Biosurfactants. Foods, 2024, 13, 711. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.G.; Soares Da Silva, R.C.F.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Santos, V.A.; Banat, I.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: Promising molecules for petroleum biotechnology advances. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1718. [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.K.F.; Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: Multifunctional biomolecules of the 21st century. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 401-430. [CrossRef]
- Durval, I.J.B.; Diniz, R.R.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactant as an environmental remediation agent: Toxicity, formulation, and application in the removal of petroderivate in sand and rock walls. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 34-48. [CrossRef]
- Farias, C. B. B.; Silva, R. C. F. S.; Meira, H. M.; Souza, T. C.; Almeida, F. C. G.; Silva, I. A.; Luna, J. M.; Sarubbo, L. A. Evaluation of the stability of a non-toxic biodetergent for the removal of petroderivates in industries. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 583-588. [CrossRef]
- Rocha E Silva, N.M.P.; Meira, H.M.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Silva, R.C.F.S.; Almeida, D.G.; Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Natural surfactants and their applications for heavy oil removal in industry. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2018, 47, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.F.S.; Souza, T.C.; Farias, C.B.B.; Almeida, F.C.G. Silva, I.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Evaluation of the stability of a biodetergent for industrial use. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 99, 481-486. [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.V.M.; Jara, A.M.A.T.; Bezerra, K.G.O.; Silva, I.A.; Costa, A.F.S.; Almeida, F.G.C.; Sarubbo, L.A. Production of the biosurfactent Candida guilliermondii and application in the formulation of a natural detergent. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 100, 85-90. [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Silva, R.C.F.S.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Converti, A.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Physicochemical upgrading of a biodetergent for application in the industrial energy sector. Energies, 2022, 15, 463. [CrossRef]
- Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Silva, F.M.P.R.; Luna, J.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Formulation of a biodegradable detergent for cleaning oily residues generated during industrial processes. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 23, 1111-1123. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.G.; Goldenberg, B.G. Surface active agents from two Bacillus species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 224-229. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, E.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Gui, M.; Wu, R.; Li, P. Rheological, emulsifying and thermostability properties of two exopolysaccharides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LPL061. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 230–237. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.L.B.; Silva, A.K.P. Ferreira, G.F.A.; Nery, P.P.C.F.; Chaves, A.C.; Magalhães, J.S.; Campos, J.D.S.; Oliveira, P.L.S. Estudo qualitativo de sucessão da fauna incrustante sobre recifes artificiais em área sob influência de usina termoelétrica em Pernambuco, Brasil. Rev. Nord. Zool. 2010, 4, 82-96.
- Ostendorf, T.A.; Silva, I.A.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Production and formulation of a new low-cost biosurfactant to remediate oil contaminated seawater. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 295, 71-79. [CrossRef]
- ABNT Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas, 2018. NBR 12648: Ecotoxicologia aquática - Toxicidade crônica - Método de ensaio com algas (Chlophyceae). Rio de Janeiro, Brasil.; 2018.
- OECD, 2013. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. French.; 2013.
- Alves, R.N.; Mariz, C.F.; Jr. Melo, A.M.K.; Cavalcanti, M.G.N.; Melo, T.J.B.; Arruda-Santos, R.H.; Zanardi-Lamardo, E.; Carvalho, P.S.M. Contamination and toxicity of surface Waters along rural and urban regions of the Capibaribe river in tropical Northeastern Brazil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3063-3077. [CrossRef]
- Beekhuijzen, M.; De Koning, C.; Flores-Guillén, M.E.; De Vries-Buitenweg, S.; Tobor-Kaplon, M.; Van De Waart, B.; Emmen, H. From cutting edge to guideline: A first step in harmonization of the zebrafish embryotoxicity test (ZET) by describing the most optimal test conditions and morphology scoring system. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 56, 64-76. [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.N.; Mariz, C.F.; Paulo, D.V.; Carvalho, P.S.M. Toxicity of effluents from gasoline stations oil-water separators to early life stages of zebrafish Danio rerio. Chemosphere. 2017, 178, 224-230. [CrossRef]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, 0146021. [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Hodgkiss, I.J. Effects of composting on phytotoxicity of spent pig-manure sawdust litter. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 93, 249–256. [CrossRef]
- Pornsunthorntawee, O.; Arttaweeporn, N.; Paisanjit, S.; Somboonthanat, P.; Abe, M.; Rujiravanit, R.; Chavadej, S. Isolation and comparison of biosurfactants produced by Bacillus subtilis PT2 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa SP4 for microbial surfactant-enhanced oil recovery. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008,42, 172–179. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Banat, I.M.; Teixeira, J.; Oliveira, R. Biosurfactants: Potential applications in medicine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 609–618. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Yunus, R.M.; Fayaz, F.; Alara, O.R. Biosurfactants - a new frontier for social and environmental safety: A mini review. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2018, 2, 81-90. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kumari, S.; Prasad, G.S.; Pinnaka, A.K. Production of sophorolipid biosurfactant by insect derived novel yeast Metschnikowia churdharensis f.a., sp. nov., and its antifungal activity against plant and human pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 678668. [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Sivapragasam, M.; Moniruzzaman, M; Talukder, M.M.R.; Yusup, S.B.; Goto, M. Production of sophorolipids by Starmerella bombicola yeast using new hydrophobic substrates. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 127, 60-67. [CrossRef]
- Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 244. [CrossRef]
- Yebra, D.M. Kill, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology—Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75-104. [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M. Marine epibiosis. I. Fouling and antifouling: Some basic aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175-189. [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.G.S.; Pappalardo, J.R.; Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Converti, A.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Sarubbo, L.A. Treatment of motor oil-contaminated soil with green surfactant using a mobile remediation system. Processes. 2023, 11, 1081. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Sun, M., Wei, Z., Wang, Y., Gao, A., Chen, D., Zhao, X., Feng, X. Exploring the effects of different types of surfactants on zebrafish embryos and larvae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10107. [CrossRef]
- Korbut, R.; Skjolding, L. M.; Mathiessen, H.; Jaafar, R.; Li, X.; Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Kania, P.W.; Wu, B.; Buchmann, K. Toxicity of the antiparasitic lipopeptide biosurfactant SPH6 to green algae, cyanobacteria, crustaceans and zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 243, 106072. [CrossRef]
- El-Harbawi, M. Toxicity measurement of imidazolium ionic liquids using acute toxicity test. Procedia Chem. 2014, 9, 40-52. [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmakh, M.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Abdullah, A.M.; Younes, N.; Da’as, S.I.; Radwan, A.B.; Sliem, M.H.; Ech-Cherif, H.; Pintus, G.; Nasrallah, G.K. AEO-7 surfactant is “super toxic” and induces severe cardiac, liver, and locomotion damage in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 149. [CrossRef]
- Yi, X., Wei, Y., Zhai, W., Wang, P., Liu, D., Zhou, Z. Effects of three surfactants on the degradation and environmental risk of metolachlor in aquatic environment. Chemosphere. 2022, 300, 134-295. [CrossRef]
- Johann, S.; Seiler, T.-B.; Tiso, T.; Bluhm, K.; Blank, L.M.; Hollert, H. Mechanism-specific and whole-organism ecotoxicity of mono-rhamnolipids. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548-549, 155-163. [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sivapragasam, M.; Talukder, M.M.R.; Yusup, S.B.; Goto, M. A binary mixture of a biosurfactant and an ionic liquid surfactant as a green dispersant for oil spill remediation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 111–119. [CrossRef]
- Hajibagheri, F.; Hashemi, A.; Lashkarbolooki, M.; Ayatollahi, S. Investigating the synergic effects of chemical surfactant (SDBS) and biosurfactant produced by bacterium (Enterobacter cloacae) on IFT reduction and wettability alteration during MEOR process. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 277–285. [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.-L.; Liao, X.-X.; Zhu, L.-W.; Zhang, W.-M.; Jiang, J.-X. Synergism and foaming properties in binary mixtures of a biosurfactant derived from Camellia oleifera Abel and synthetic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 359, 487– 492. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, L.; Rincón-Fontán, M.; Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Biological surfactants vs. Polysorbates: Comparison of their emulsifier. Tenside Surfact. Det. 2018, 55, 273–280. [CrossRef]
- Tmáková, L; Sekretár, S.; Schmidt, S. Plant-derived surfactants as an alternative to synthetic surfactants: Surface and antioxidant activities. Chem. Pap. 2015, 70, 188–196. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Natural detergents after 10 days of storage at room temperature (Formulation G: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% hydroxyethyl cellulose; Formulation H: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose; Formulation L: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% sodium alginate; Formulation M: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% sodium alginate).
Figure 1.
Natural detergents after 10 days of storage at room temperature (Formulation G: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% hydroxyethyl cellulose; Formulation H: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose; Formulation L: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% sodium alginate; Formulation M: 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% sodium alginate).
Figure 2.
Emulsifications capacity of Formulations L (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% sodium alginate), M (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% sodium alginate), G (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% hydroxyethyl cellulose), and H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) after ten days of storage at room temperature.
Figure 2.
Emulsifications capacity of Formulations L (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% sodium alginate), M (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% sodium alginate), G (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 1.5% hydroxyethyl cellulose), and H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) after ten days of storage at room temperature.
Figure 3.
Metal plates after fouling process for 15 days in marine environment. (A) Side A of plate with paint alone; (B) Side B of plate with paint alone; (C) Side A of plate with paint containing 2.5% Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) at concentration of 2.5%; (D) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 2.5%; (E) Side A of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 5%; (F) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 5%; (G) Side A of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 7.5%; (H) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 7.5%; (I) Side A of plate with paint containing formulation H at concentration of 10% (J) Side B with paint containing formulation H at concentration of 10%.
Figure 3.
Metal plates after fouling process for 15 days in marine environment. (A) Side A of plate with paint alone; (B) Side B of plate with paint alone; (C) Side A of plate with paint containing 2.5% Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) at concentration of 2.5%; (D) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 2.5%; (E) Side A of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 5%; (F) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 5%; (G) Side A of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 7.5%; (H) Side B of plate with paint containing Formulation H at concentration of 7.5%; (I) Side A of plate with paint containing formulation H at concentration of 10% (J) Side B with paint containing formulation H at concentration of 10%.
Figure 4.
Relative frequency of fouling on control plate, plate with paint alone, and plates with paint containing different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 4.
Relative frequency of fouling on control plate, plate with paint alone, and plates with paint containing different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 5.
Abundance of organisms on control plate, plate with paint alone, and paint with different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 5.
Abundance of organisms on control plate, plate with paint alone, and paint with different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 6.
General morphology score for Danio rerio embryos and larvae exposed to different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 6.
General morphology score for Danio rerio embryos and larvae exposed to different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 7.
Drop of oil dispersed by Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 7.
Drop of oil dispersed by Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 8.
Illustration of steps of cleaning process of stone impregnated with petroleum using Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Figure 8.
Illustration of steps of cleaning process of stone impregnated with petroleum using Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Table 1.
Concentrations of stabilisers of natural detergent formulations containing 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil.
Table 1.
Concentrations of stabilisers of natural detergent formulations containing 1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil.
| Formulations |
Stabiliser concentration (%) |
| |
Vegetable wax |
| A |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
| B |
| C |
| D |
| |
Hydroxyethyl cellulose |
| E |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
| F |
| G |
| H |
| |
Sodium alginate |
| I |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
| J |
| L |
| M |
Table 2.
Requirements for chronic toxicity test with microalga Desmodesmus armatus.
Table 2.
Requirements for chronic toxicity test with microalga Desmodesmus armatus.
| Requirements |
Conditions |
| Test |
Static |
| Elution water |
Cultivation medium |
| Inoculum |
Cultivation in exponential growth phase |
| Minimum number of dilutions |
Five plus control |
| Minimum number of replicates per dilution |
Three |
| Temperature |
23 to 27°C |
| Illumination |
Continuous, approximately 4500 lux |
| Rotation speed |
100 rpm at 175 rpm |
| Observed effect |
Inhibition of algal cell multiplication |
| Expression of results |
Concentration of No Observed Effect, Concentration of Observed Effect, Chronic Value, Effect Concentration, Toxicity Factor, Toxic and Non-toxic |
Table 3.
Concentrations of stabilisers in natural detergent formulations and petroleum emulsification indices.
Table 3.
Concentrations of stabilisers in natural detergent formulations and petroleum emulsification indices.
| Formulations |
Stabiliser concentration (%) |
Petroleum emulsification index (%) |
| |
Vegetable wax |
|
| A |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
81.27 ± 0.25 |
| B |
81.48 ± 0.84 |
| C |
83.25 ± 1.18 |
| D |
81.67 ± 0.07 |
| |
Hydroxyethyl cellulose |
|
| E |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
87.57 ± 0.52 |
| F |
87.12 ± 0.26 |
| G |
99.12 ± 0.23 |
| H |
100 ± 0.01 |
| |
Sodium alginate |
|
| I |
0.5
1
1.5
2 |
85.14 ± 0.98 |
| J |
88.27 ± 0.52 |
| L |
90.14 ± 0.65 |
| M |
92.48 ± 0.39 |
Table 4.
Natural detergent formulations and criteria investigated after 10 days of storage.
Table 4.
Natural detergent formulations and criteria investigated after 10 days of storage.
| Formulations |
Stabiliser concentration (%) |
|
Criteria |
| |
Petroleum emulsification index (%) |
Stability |
| |
Hydroxyethyl cellulose |
|
|
|
| G |
1.5
2 |
|
98.25 ± 0.87 |
No |
| H |
|
100 ± 0.01 |
Yes |
| |
Sodium Alginate |
|
|
|
| L |
1.5
2 |
|
87.14 ± 0.04 |
Yes |
| M |
|
89.75 ± 0.76 |
No |
Table 5.
Absolute frequency (Fa), relative frequency (Fr), abundance (Abund), and respective averages on both sides of test plates containing formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
Table 5.
Absolute frequency (Fa), relative frequency (Fr), abundance (Abund), and respective averages on both sides of test plates containing formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose).
| Plates |
Side A |
Side B |
Average |
| Fa |
Fr |
Abund |
Fa |
Fr |
Abund |
Fa |
Fr |
Abund |
| Control |
21 |
32.81 |
1053 |
9 |
14.06 |
559 |
15 |
23.44 |
806.00 |
| Paint |
81 |
100.00 |
3500 |
81 |
100.00 |
3900 |
81 |
100.00 |
3700.00 |
| Formulation H (2.5%) |
81 |
100.00 |
4600 |
81 |
100.00 |
3700 |
81 |
100.00 |
4150.00 |
| Formulation H (5.0%) |
81 |
100.00 |
3900 |
81 |
100.00 |
3800 |
81 |
100,00 |
3850.00 |
| Formulation H (7.5%) |
79 |
97.53 |
3400 |
81 |
100.00 |
3900 |
80 |
98.77 |
3650.00 |
| Formulation H (10.0%) |
80 |
98.77 |
4700 |
81 |
100.00 |
4600 |
80.5 |
99.38 |
4650.00 |
Table 6.
Number of individuals killed when exposed to different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) and mortality rate at the end of 96 hours of exposure (total of 20 individuals in each treatment).
Table 6.
Number of individuals killed when exposed to different concentrations of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) and mortality rate at the end of 96 hours of exposure (total of 20 individuals in each treatment).
| Concentration (mg/L) |
Deaths in 24 h |
Deaths in 48 h |
Deaths in 96 h |
Mortality rate at end of test (96 h) |
| 75.00 |
11 |
6 |
3 |
100% |
| 37.50 |
8 |
5 |
7 |
100% |
| 18.75 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0% |
9.37
4.69
|
0
0 |
0
0 |
0
0 |
0%
0% |
Table 7.
Lethal concentration for 50% of individuals exposed (LC50) to Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) according to exposure time.
Table 7.
Lethal concentration for 50% of individuals exposed (LC50) to Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) according to exposure time.
| Exposure time (hours) |
LC50 (mg/L) |
| 24 |
120.87 |
| 48 |
67.48 |
| 96 |
62.60 |
Table 8.
Phytotoxicity of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) to vegetable seeds.
Table 8.
Phytotoxicity of Formulation H (1% biosurfactant + 40% cottonseed oil + 2% hydroxyethyl cellulose) to vegetable seeds.
| Detergent concentration (%) |
Germination index (%) |
| Cabbage (Brassica oleracea) |
| 2.5 |
85.99 ± 0.15 |
| 5 |
67.02 ± 0.05 |
| 7.5 |
64.76 ± 0.28 |
| 10 |
59.45 ± 0.35 |
| Cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) |
| 2.5 |
76.14 ± 0.04 |
| 5 |
75.18 ± 0.12 |
| 7.5 |
74.79 ± 0.09 |
| 10 |
75.15 ± 0.02 |
| Maroon cucumber (Cucumis anguria) |
| 2.5 |
93.58 ± 0.36 |
| 5 |
9315 ± 0.27 |
| 7.5 |
90.48 ± 0.12 |
| 10 |
88.26 ± 0.14 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).