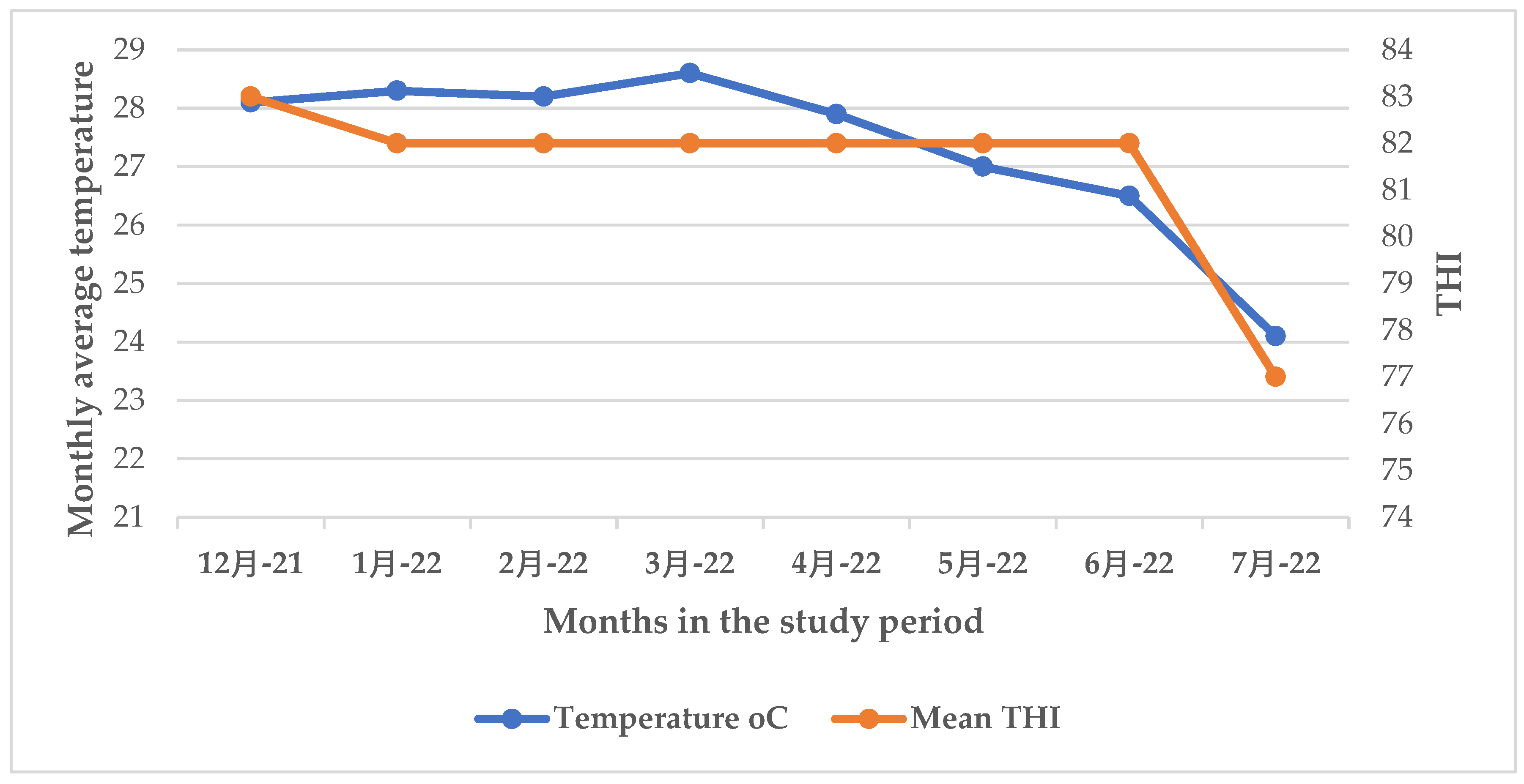
In this study, results show that the mean ambient temperature and THI values in the hot season (January – February) were higher than in the cool season (June – July). On the other hand, the mean relative humidity in the cool season was higher than in the hot season. Generally, the observed mean THI values were high in such a way that they can cause HS to the animals. Similar findings were reported by [
30] in their study about HS effects on milk production parameters of Holstein and Jersey dairy cattle in South Korea. Some studies reported that the dairy cattle thermoneutral zone ranges between 5
oC and 25
oC, but can fall to the range at 0.5
oC to 20
oC and 60% to 80%RH, although this varies depending on production status, feed type, acclimatization level and climatic conditions [
20,
30]. [
20] reported that when THI exceeds 72, dairy cattle begin to experience HS. In the present study, decline in milk yield and composition parameters were observed when THI values ranged from 77 to 84. In Rwanda, [
38] reported THI values ranging from 63.3 to 84.6 with an average of 75.8 THI as HS threshold for milk yield decline. This is in agreement with the THI thresholds obtained in this study. In Florida (USA), [
17] reported the THI values of above 68 as HS thresholds for dairy cattle. In India, [
59] reported THI value of 72 - 75 as the most favorable for dairy cows in the tropical region of Bengaluru because of the maximum milk production obtained. In the smallholder farms of Tanzania, [
16] reported a THI of 76 as HS threshold. The seasonal changes in THI thresholds and the associated variations in milk yield, milk composition, and physiological parameters observed in this study could be associated with variations in weather conditions over the months. These climatic variations lead to alterations in quality and quantity of diet provided to dairy cattle [
16].
4.1. Heat Stress Effects on Milk Yield and Composition Parameters
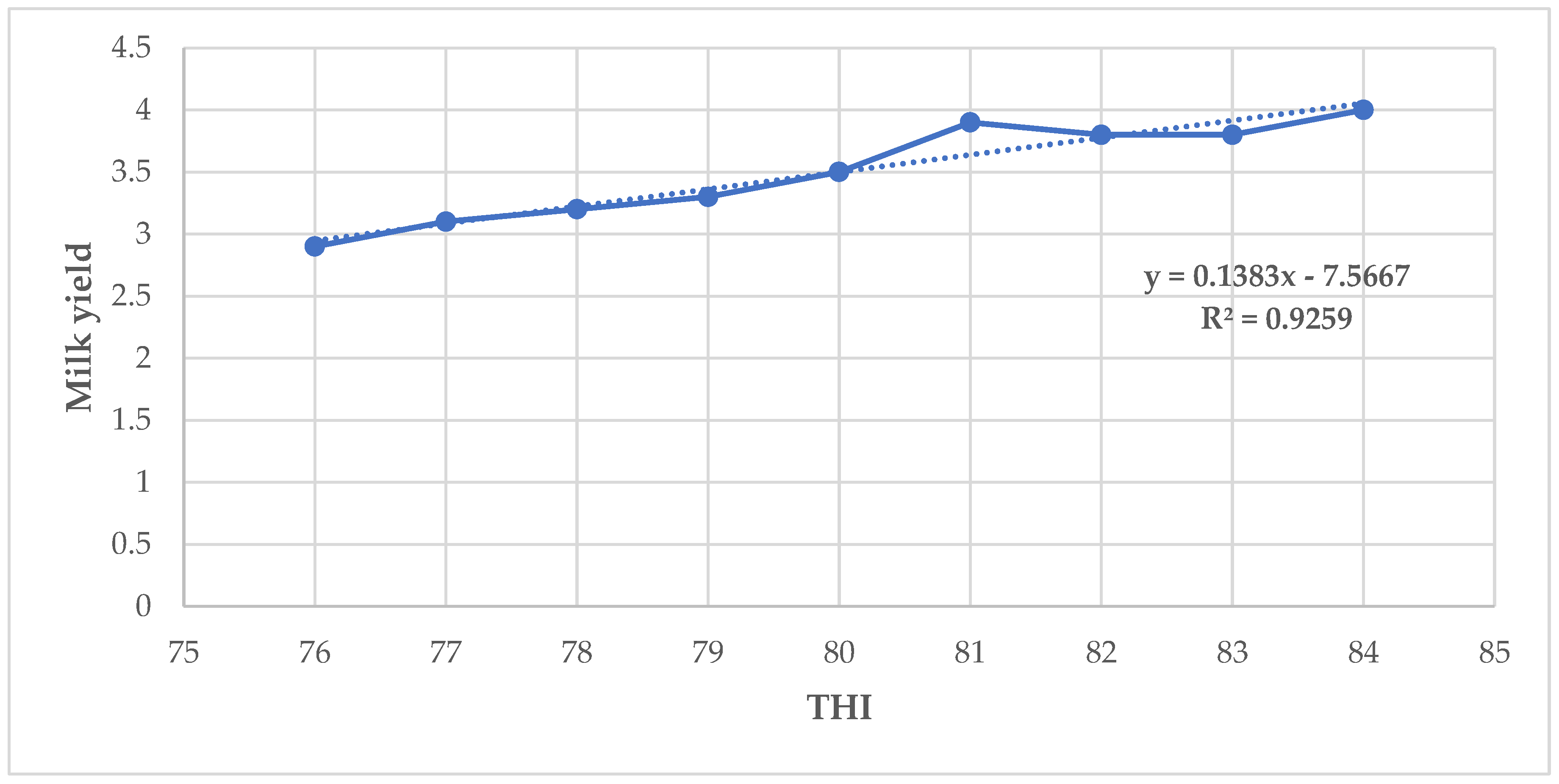
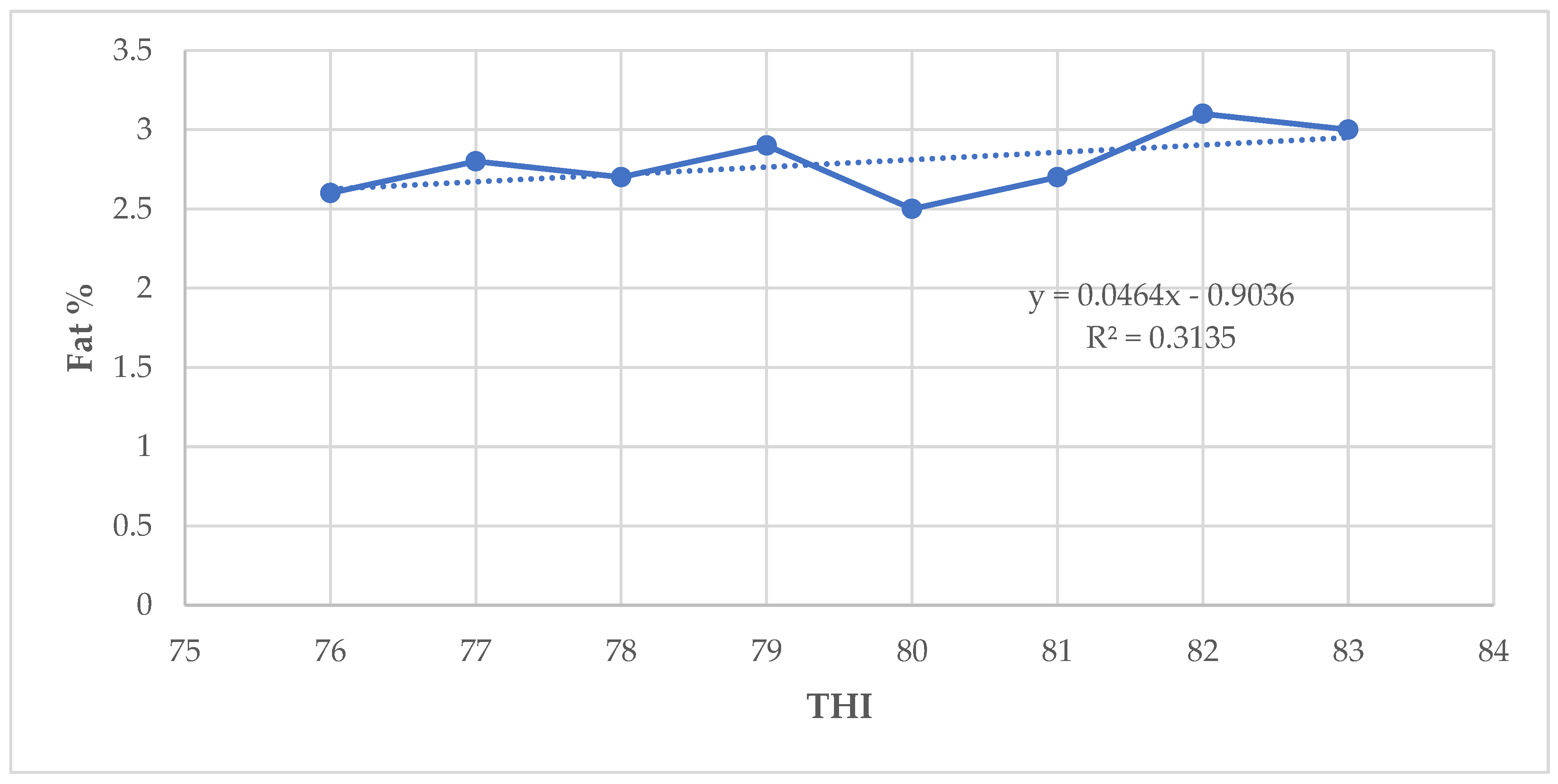
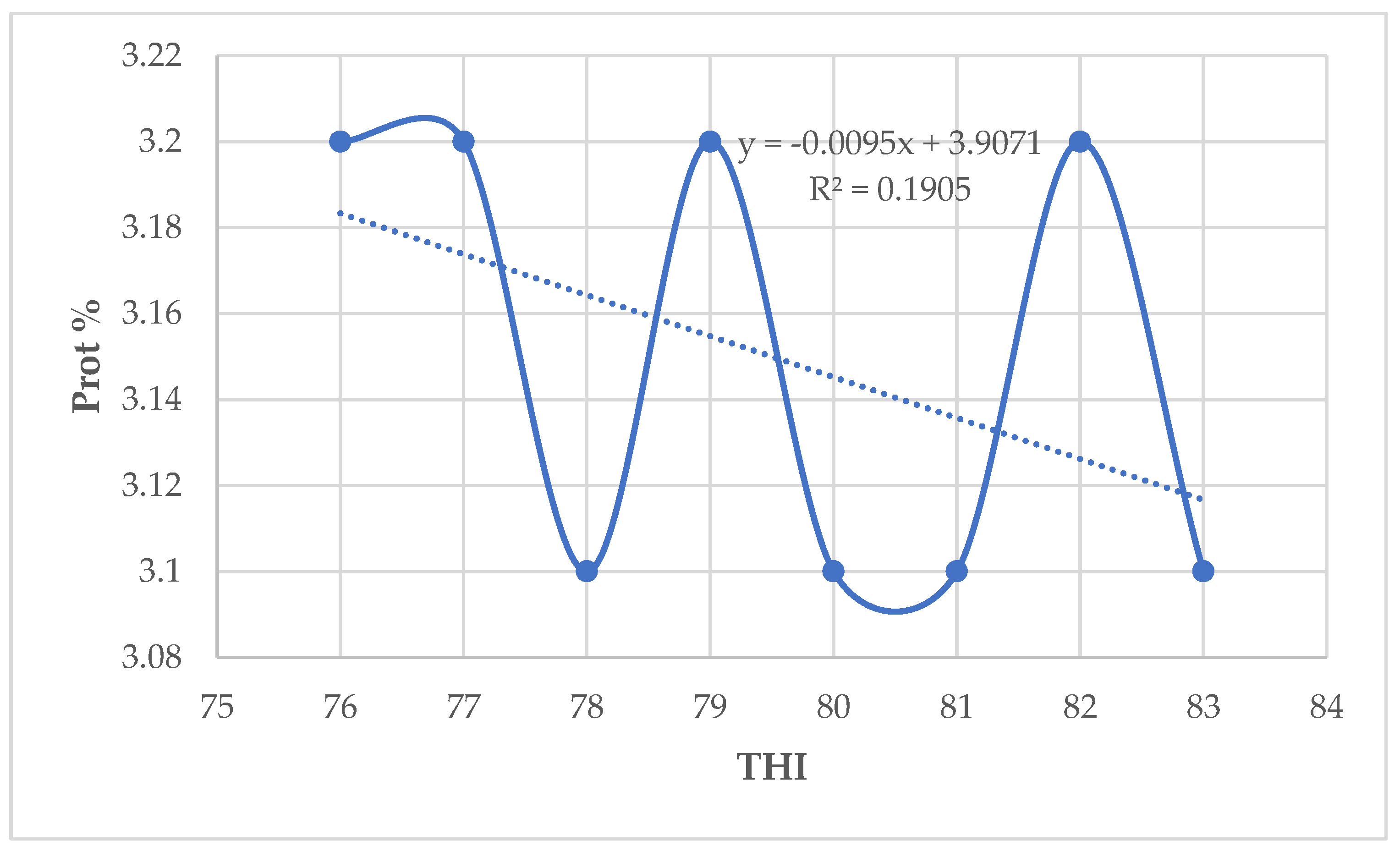
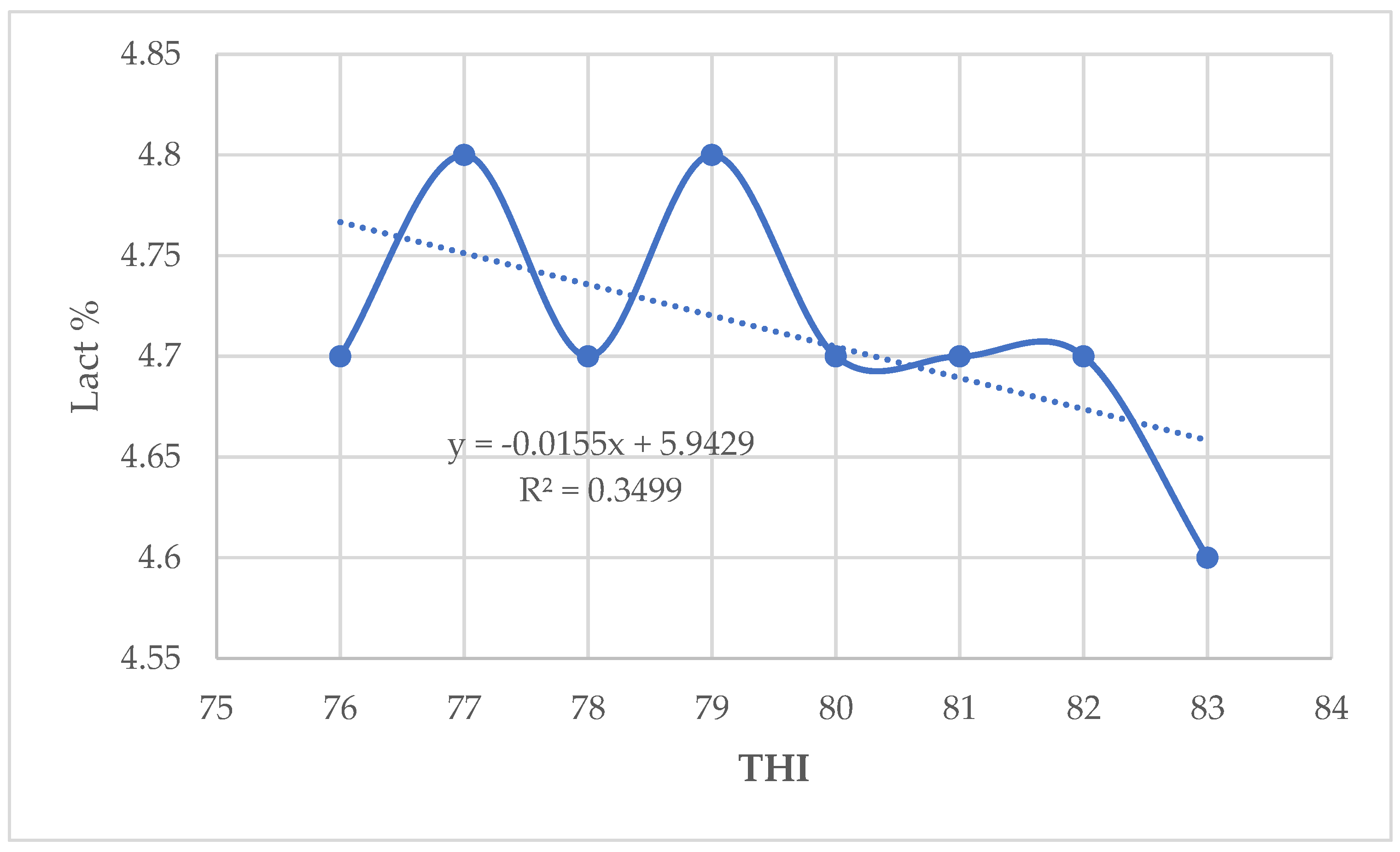
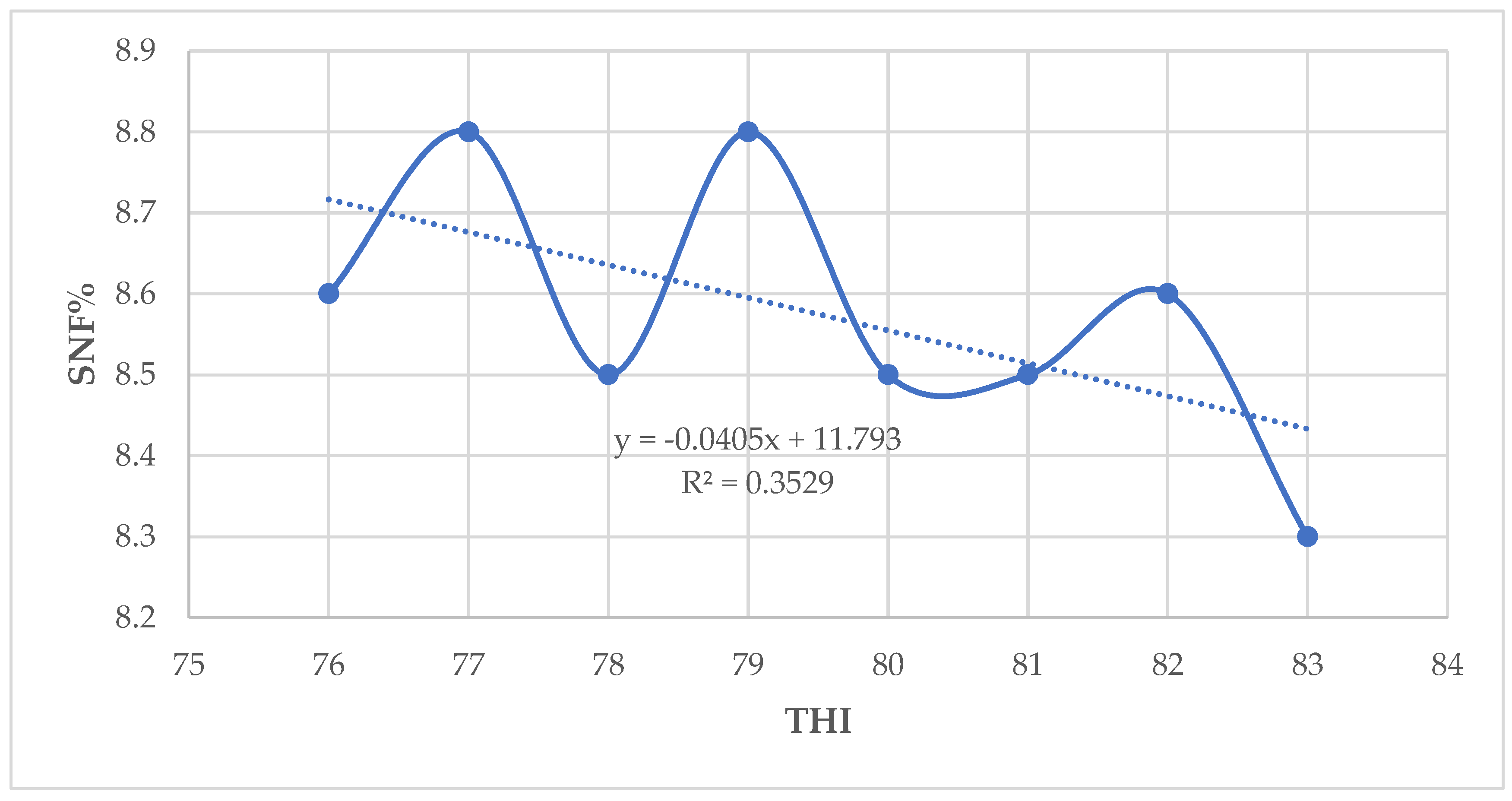
The results in the present study indicate that milk yield and fat percentage increased slightly whereas milk protein, lactose, and solids–not–fat percentages decreased when THI values increased from 76 to 84. A slightly increase in milk yield as THI increased implies that there was very little influence of THI above threshold on the milk production [
38]. These results are inconsistent with the findings by [
54] in Thailand, who reported that milk yield declines when THI reach 76. In Australia,[
55] reported that daily milk yield increased as THI was increasing up to a THI value of 65, and remained fairly constant until 85, and then decreased afterwards. This is in agreement with the findings of this study. In Brazil, [
53] indicated that an increase in THI thresholds generally causes a decline in milk production parameters which is in contrast with the findings of this study. Under the Mediterranean climatic conditions of Tunisia, [
10] reported a decline in milk fat percentage of 0.34% and 21% decline in milk yield when THI values increased from 68 to 78 for Holstein Friesian dairy cattle. In Rwanda, [
38] reported a decrease in milk yield for Holstein crossbreds’ dairy cattle when THI thresholds were above 76, which is not in agreement with the findings of this study. The decline in milk yield traits during HS could be the results of reduction in feed intake and decreased nutrient uptake by the portal drained viscera of dairy cattle [
10,
16,
40]. In this study, HS reduced milk yield and milk composition parameters when THI increased from moderate to high THI values for both HF50 and HF75 dairy cows. There was a higher decrease in milk composition parameters for HF75 than HF50 dairy cows when THI values increased from moderate to high THI thresholds, an indication that the later are relatively more heat tolerant than the HF75. In Brazil, [
1] reported that Girolando-Holstein Friesian with 75% blood level (GH75) were less tolerant to heat compared with GH50 which is in agreement with the findings of this study.
In Germany, [
28] reported milk fat and protein decline as THI increased from 60. [
18] indicated that under HS conditions, the higher fat content in dairy cattle milk is caused by an increase in free fatty acids during negative energy balance whilst a decline in milk protein is due to a lower synthesis of casein formation enzymes in the mammary gland. In the study by [
28] across Holstein Friesian dairy genotypes, milk protein, lactose, and solids-not-fat declined when THI changed from moderate to high THI. This is in agreement with the findings of this study. The findings of this study also partially agree with those reported by [
12] who observed an increase in fat and protein percentages, but without increase in lactose percentage. This shows that HS decreases protein content of milk without affecting the fat percentages. Also, the results in the present study concur with results reported by [
10] who found that HS reduced milk fat and protein percentages when season changed from spring to summer. Generally, HS effects on milk fat and protein percentages are largely non-consistent [
12]. [
46] reported a reduction in milk protein percentage of 0.13% during HS conditions. Moreover, individual animal differences and trait responses to HS are expected owing to animal-related factors like breed and physiological responses such as age, production status, feed intake, and animal behaviors [
33]. The decline in milk protein percentage detected in this study is in agreement with the results reported by [
10] and [
46]. Milk protein concentration is determined by the energy absorption or the energy content of the diet and its noneffective supply causes a decline in milk protein percentages [
28]. It is well recognized that HS decreases feed intake [
18,
60], but feed intake in animals grazing on pasture declines owing to feed shortage during hot weather conditions [
38]. Dairy cattle in this study were freely grazing on pasture and dry matter intake from the pasture was not recorded. Therefore, the lower milk yield observed in this study was a result of reduced feed intake from pasture combined with physiological and metabolic effects of HS [
28,
38].
On the other hand, genotype, parity, and months of lactation also influenced milk yield and composition parameters. [
12] reported that the higher percentage of protein and fat observed in the milk of heat-stressed dairy cattle could be the result of decline in milk production and subsequent increased concentration of protein and fat in addition to possibly greater non-protein nitrogen contents in the milk produced by dairy cattle under HS conditions. Furthermore, the results of the current study show that parity influenced milk yield and composition parameters, such that milk yield decreased from 2
nd parity to 3
rd parity, then slightly increased in the 4
th parity. On the other hand, milk composition parameters increased from 2
nd to 3
rd parity, then decreased in the 4
th parity. This could be due the differences in feeding rates as primiparous dairy cattle eat more slowly than multiparous ones during the peak lactation [
36]. Additionally, [
35] reported that high-producing dairy cattle such as multiparous dairy cattle show major heat sensitivity owing to increased intrinsic metabolic heat production compared to young lactating dairy cattle in the 2
nd parity. In the study by [
49], parity and lactation month had negative effect on milk yield, fat, protein, lactose, and solids – not – fat percentages which is in agreement with the findings of this study.
Regarding genotype and THI interaction, the findings showed different trends for milk yield and composition of HF50 and HF75 dairy cows when the THI values increased. There was a marked difference between HF50 and HF75 in milk yield at THI of 76 to 78. Milk yield declined and increased in HF75 and HF50 dairy cattle, respectively, when the THI values increased from moderate to high. Regarding milk composition parameters, HF50 showed high content of fat, protein, lactose, and solids – not – fat percentages than HF75. Nevertheless, fat % declined when THI changed from moderate to high THI values in both HF50 and HF75 whilst no reduction was observed for protein %. No large difference was observed for lactose percentage in both HF50 and HF75 when THI changed from low to high THI values. A large decline in solids – not – fat was observed in HF50 than in HF75 when THI changed from moderate to high THI values. These findings are in agreements with those reported by [
53] who observed a greater decrease in milk production for HF75 than HF50 when THI values increased from 79.2 to 80.32. The magnitude of milk yield decline and alteration of milk composition parameters including fat, protein, lactose, and solids - not - fat percentages as a result of HS are influenced by various mechanisms at different lactation stages and the mammary gland of lactating dairy cattle respond differently to HS [
40].
Parity and THI interaction influenced milk yield and composition such that milk yield decreased when THI increased both for the cows in the 2
nd and 3
rd parities. These findings concur with those reported by [
52]. Dairy cows in the 3
rd and 4
th parity showed higher milk yield and composition compared to those in the 2
nd parity, which indicates that multiparous dairy cattle are highly tolerant than primiparous dairy cows. In the study by [
41], dairy cattle in all parities were stressed by HS and responded by showing a significant decline in milk protein percentages, this is inconsistent with the results of this study. [
52] indicated that primiparous dairy cattle are lighter than multiparous ones, thus the ratio of surface area to volume is slightly higher, this predisposes them to heat loss. Moreover, limited studies have explored the relationship between lactation stages of dairy cattle and THI values [
62]. In this study, it was observed that dairy cattle in 3
rd month of lactation showed significant decline in milk yield compared to those in the 2
nd month of lactation. However, the reverse was observed for fat, protein, lactose, and solids – not – fat percentages, whereby significant effects of HS was observed in terms of reduced milk composition traits for the cows in the 2
nd month of lactation compared to those in the 3
rd month of lactation.
Dairy cows in the 3
rd month of lactation were highly affected by HS compared to those in the 2
nd month of lactation, as they showed higher decline in milk yield when THI increased from low to high THI values. On the other hand, cows in the 2
nd month of lactation showed higher decline in milk proteins, lactose, and solids-not fat percentages compared to those in the 3
rd month of lactation as THI increased from low to high THI values. This is in agreement with the findings of [
28] who reported that the major effects of HS on milk yield, fat, and protein percentages are identified in later lactation. Furthermore, the findings of the current study are supported by results from other studies, which reported that dairy cattle in early stages of lactation are highly affected by HS in terms of productivity [
7,
62]. In Australia, [
40] observed a significant effect of stage of lactation on daily milk yield, fat and protein percentages, which is in agreement with the findings of this study. In a pasture - based system, [
40] reported an increase in milk fat % and protein % by 3% and 2%, respectively, when THI changed from low to high THI. The reduction in milk fat, protein, lactose, and solids - not - fat percentages is mainly influenced by the adverse effects of hot weather conditions on the synthesis of these milk constituents in dairy cattle mammary gland [
7]. There are substantial milk yield losses induced by HS in any stage of lactation of dairy cattle. Thus, cooling of dairy cattle when the THI thresholds range between 77 and 86 is necessary through the use of trees in the farms, shading, provision of drinking water, supplementation of concentrate during milking, among others to minimize the decline in milk yield observed in the afternoon and hot season. However, the different cooling approaches should be done with consideration of the production cost of the cooling technologies applied [
61]. Under warm and humid conditions, dairy farmers could improve milk yield and avoid fluctuation in milk composition in different seasons through nutritional supplementation and manipulation of feeding practices. Furthermore, the provision of fans, sprinklers, shade, barns, and trees which enhance passive ventilation could improve body heat loss and increase the dry matter intake of cows and hence, improved dairy cattle milk composition [
20,
60,
63].
4.2. Heat Stress Effects on Physiological Parameters
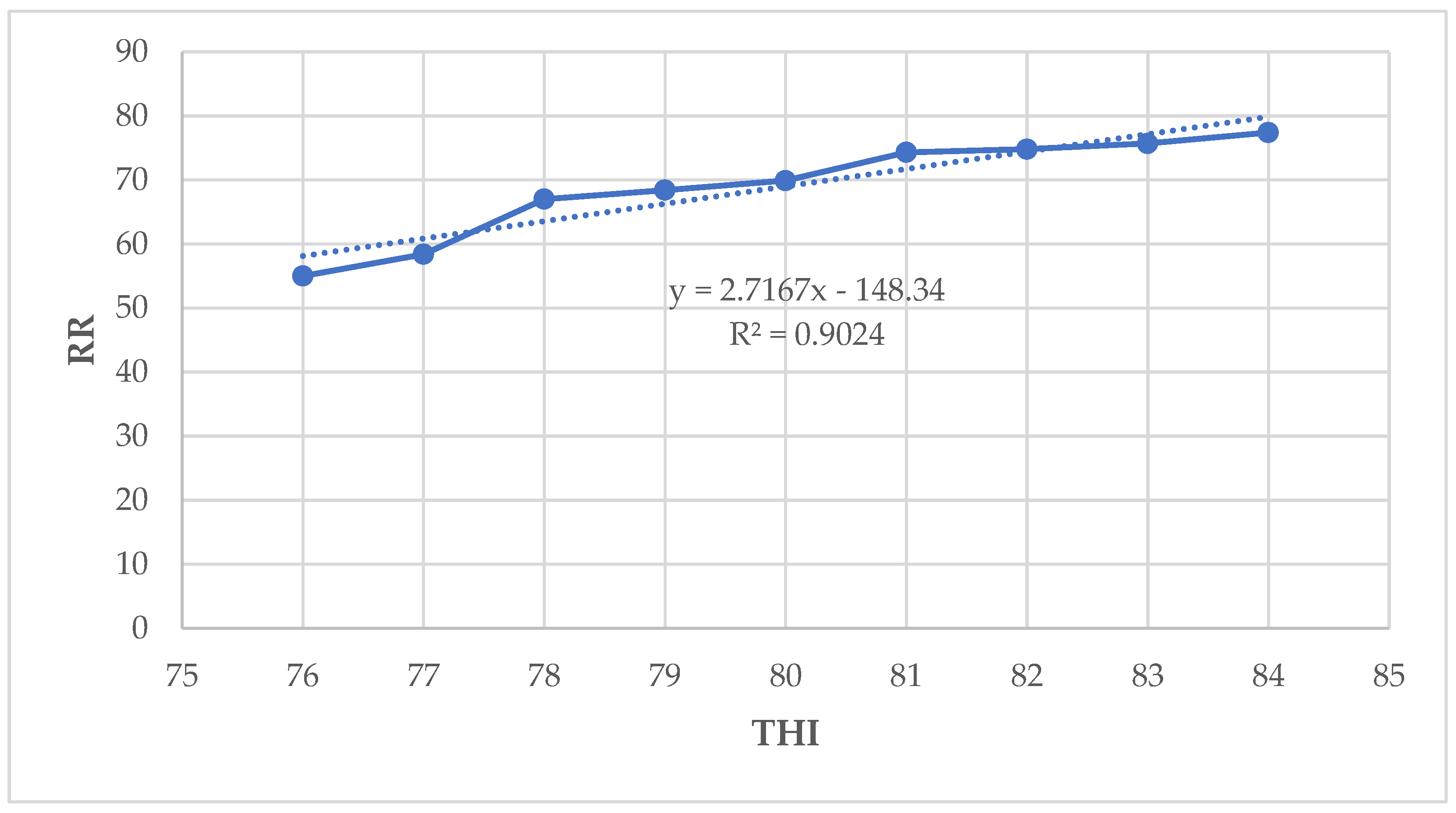
Studies have shown that the RR greater than 60 breaths/min indicates HS when dairy cattle use evapotranspiration as the key mechanism for losing body temperature [
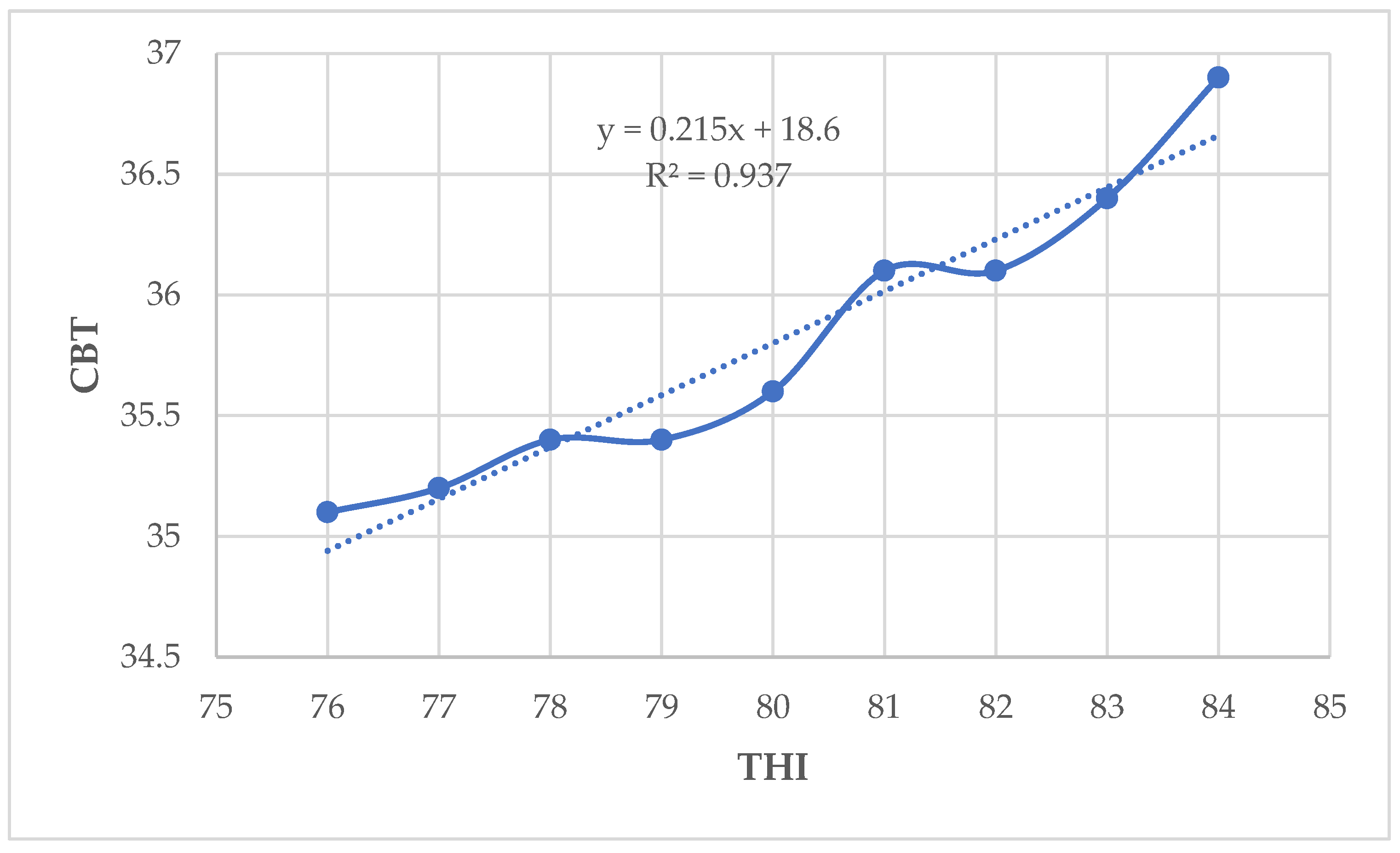
18]. In the present study, when THI values increased from 76 to 84, the cows responded by increasing the RR. Also, when THI values increased from 76 to 84, there was an increase of 0.4
oC for CBT and RT, and 11 breaths per min. Similar patterns of responses to HS were observed in the study conducted in Tunisia by [
14]. In their study, HS altered RT, RR, and HR such that a daily increase of 1.2
oC was observed when THI values increased from 55 to 78, while HR and RR increased by 3 beats per min and 35 breaths per min, respectively. The physiological responses to HS observed in this study are an adaptive mechanism initiated by dairy cattle in an attempt to restore their thermal balance [
14]. The CBT of dairy cattle varies many times as it is a crucial tool for regulating body temperature and relies on the peripheral blood flow [
29]. When dairy cattle want to reduce its body temperature, body heat is transported from the core of the body to the skin by blood, thus blood flow to the skin will rise, thereby increasing skin temperature [
29].
The RT is considered to be a good indicator of deep CBT, although there are significant changes among various parts of core body at different scales of the day [
29]. In this study, significantly higher CBT and RT were recorded when THI values were above 82 - 84. These results are in agreement with those reported by [
18] in Brazil who found significant effect of THI on RT and RR. Also, the findings in this study are in agreement with [
65] who reported that RT start to rise when ambient temperature reach above 20
oC. In this study, the average RT increased by 0.4
oC when THI thresholds ranged from 76 - 84. The RT was higher at 38.4
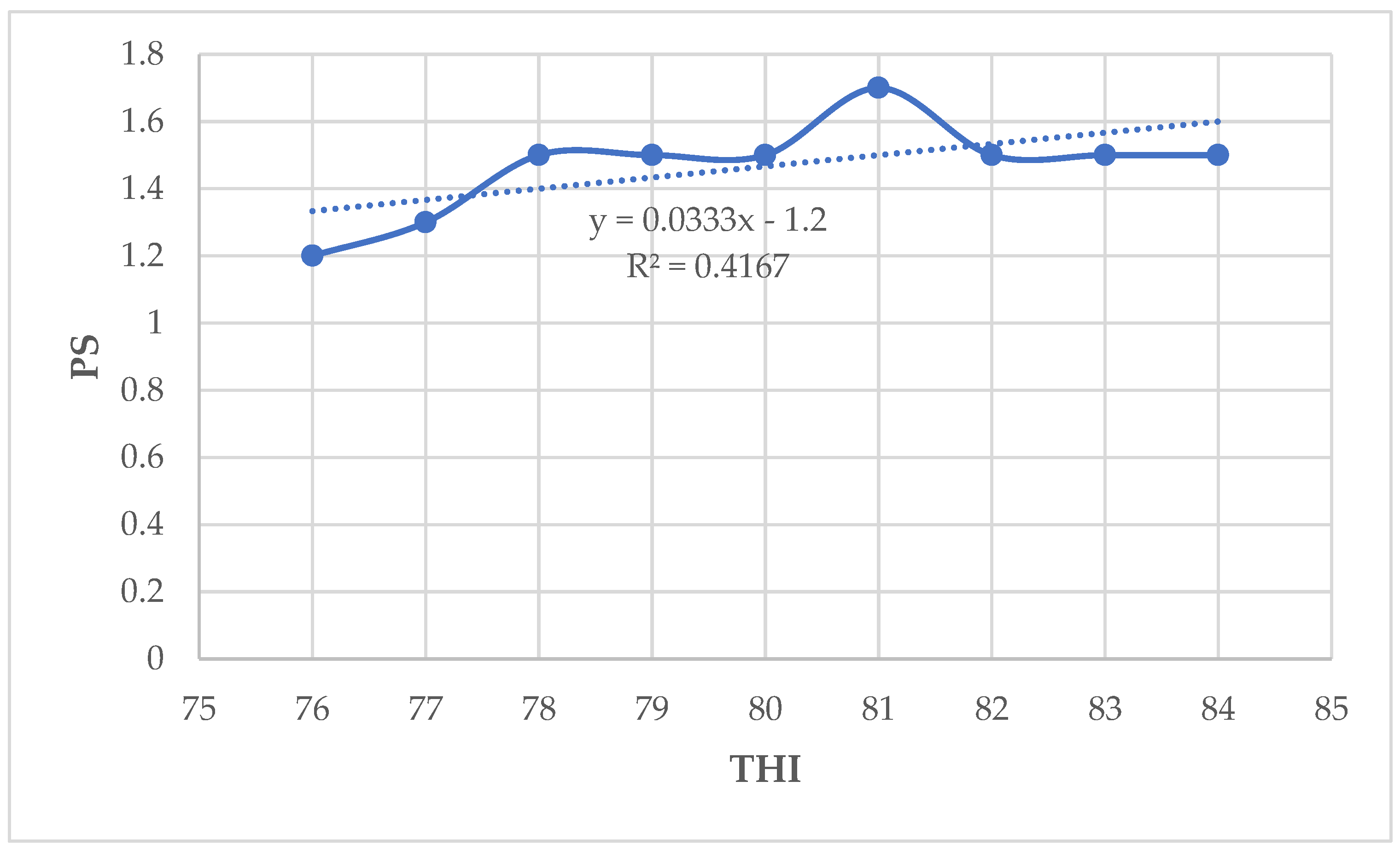
oC for HF50 compared to HF75 at extreme THI values of 82 - 84, suggesting that HF50 were slightly less heat tolerant than HF75. However, other physiological parameters indicated that they were better tolerant to heat stress compared to HF75. All animals showed mild to moderate HS for all physiological parameters when THI ranged from 76 - 78 and 79 - 81. For instance, the high PS value observed at higher THI values and afternoon hours were comparable with first-phase panting and the point at which HS mitigation should be considered [
31]. During HS, dairy cattle increase RR and PS, which increases in body fluid loss and affects dehydration and blood homeostasis [
29].
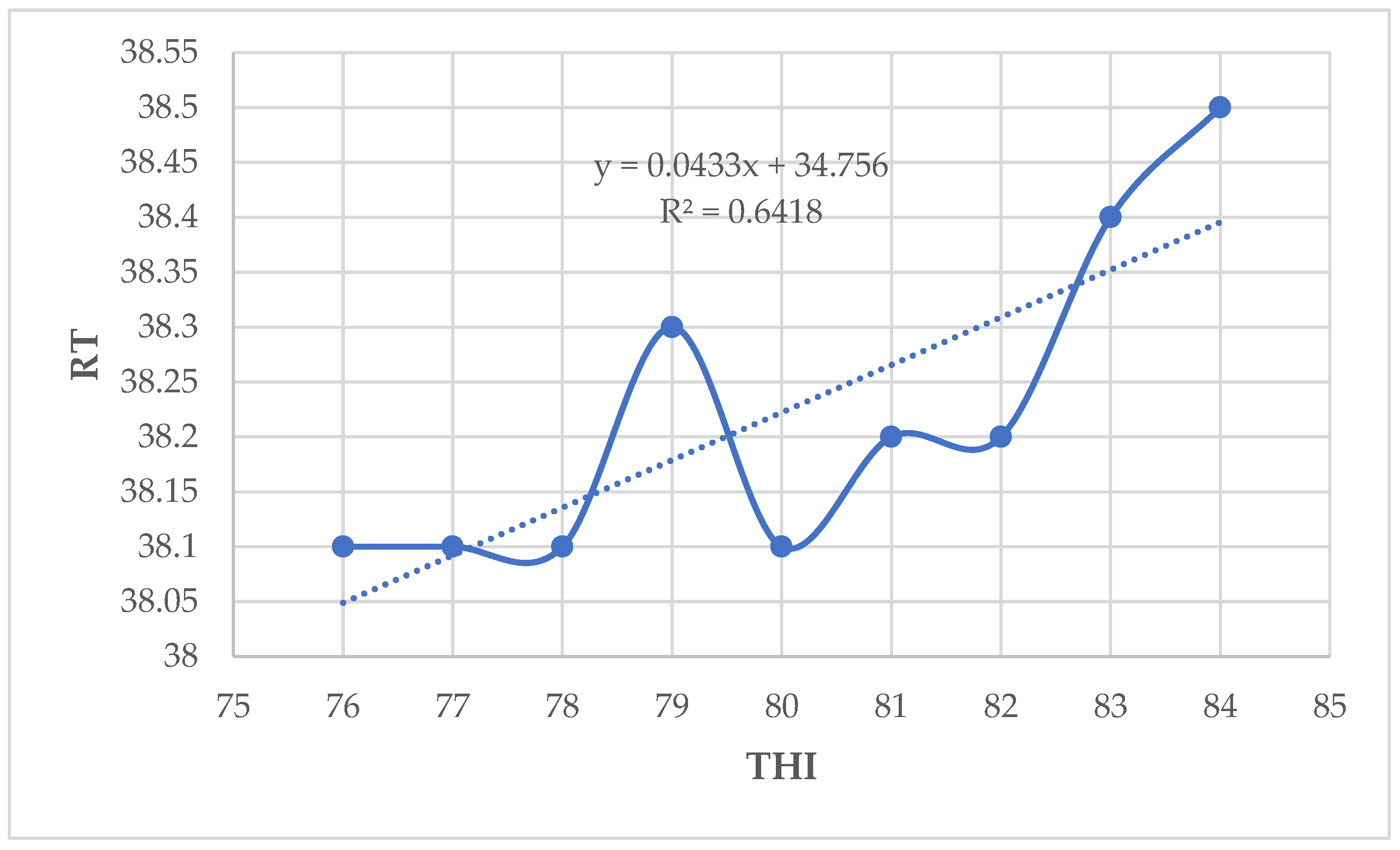
In this study, the cows respired significantly faster and panted relatively more frequently at higher THI values. These results differ with those obtained by [
14] who reported 63 breaths/min at THI of 80 for Holstein Friesian dairy cattle reared in the Mediterranean climate of Tunisia. The increased rate of RR and PS is an indication that these animals are losing heat as an attempt to maintain homeothermy [
40]. Respiration rates increase when the ambient temperature surpasses dairy cattle thermoneutral zone, which typically ranges from -5
oC to 25
oC, and declines again below this thermoneutral zone [
30]. The increase of RR in dairy cattle is used to disperse around 30% of body heat by respiratory vaporization. This respiratory vaporization and convection dissipate of body heat help dairy cattle to maintain its thermal balance [
29]. The RR has been shown to be the first physiological response to increased ambient temperature for Holstein Friesian dairy cows in late stages of lactation reared in the Netherland [
61,
65].
In the present study, cows in the 3
rd month of lactation indicated slightly increase in CBT, RT, RR, and PS compared to those in the 2
nd month of lactation, an indication that this group of animals experience higher HS effects than their counterparts. These findings partially concur with those reported by [
62], who found that stage of lactation significantly influences the thresholds for surface temperature maximum, but with less significant effect on surface temperature average. [
62] also reported that dairy cattle in the 3
rd month of lactation are more susceptible to increase in HS conditions than those in the 2
nd month and 1
st month of lactation and this is in agreement with the findings of the current study. The findings of this study are in partial agreement with those reported by [
40] for lactating Holstein dairy cattle grazing during Australian summer in Melbourne. In their study, lactation stage had no significant effect on RR, PS, and ST, but affected (
P≤0.05) average daily milk yield and milk solids. [
61] indicated that some dairy cattle may transition from the previous stage of lactation to the next stage during the research period. This results into failure to detect the potential effect of the stage of lactation. Moreover, parity influences the physiological responses of dairy cattle to HS [
61]. In this study, cows in the 3
rd parity showed higher patterns of responses to HS with significant increase in CBT, RT, RR, and PS compared to those in the 2
nd and 4
th parity. These findings concur with those reported by [
61]. In their study, they analyzed the effects of parity on RT and RR and found that dairy cattle in the 3
rd parity had higher RR compared to dairy cattle in the 1
st and 2
nd parity. Our findings also concur with those reported by [
14] that parity affects RT and RR.
4.3. Relationship between THI and Milk Yield and Composition Parameters
During HS conditions, dairy cattle exhibit several behavioral and physiological conditions that have negative effects on milk yield and composition parameters [
41]. In this study, the THI showed low positive correlation with milk yield and fat percentage but was negatively correlated with protein, lactose, and solids – not – fat percentages. [
9] reported a significant negative relationship between THI and milk yield, fat, protein, lactose, and solids – not - fat percentage which is in partial agreement with the findings of this study. The findings in this study are also in contrast with those reported by [
10] who observed a negative relationship between milk yield and THI. These findings partially concur with those reported by [
6] who fitted a linear model on large dataset of Italian Holstein dairy cattle milk yield records, and observed a significant negative relationship between extreme THI thresholds and milk production parameters. These findings also partially concur with those reported by [
30] with a negative relationship between milk yield and THI for Holstein dairy cattle and a positive association between the later and milk yield for Jersey dairy cattle. A low positive correlation between THI and milk yield and fat percentage observed in this study implies that milk yield and fat tend to increase slightly with the rise of THI [
9].
These results suggest that milk composition parameters are more sensitive than milk yield to the effects of HS [
41]. At the Mediterranean climate of Italy, [
7] reported a strong positive correlation between THI and fat % (r = 0.98) and protein % (r = 0.99) for a retrospective study on Holstein dairy cattle for data collected between 2003 and 2009. However, these findings are partially consistent with the results of this study. Furthermore, the findings of this study partially concur with those reported in China by [
61], who observed a positive correlation between milk yield and THI values. In their study, they observed a positive correlation between milk yield and THI and a positive association between THI and milk fat %, milk protein %, and milk lactose.