1. Introduction
In late December 2019, a novel RNA beta-coronavirus was identified as the causative agent of pneumonia cases of unknown origin. This virus was subsequently named Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and the respiratory illness it causes was termed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [
1,
2]. The global spread of SARS-CoV-2 and the substantial death toll from COVID-19 led the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare a pandemic on March 11, 2020. To date, the pandemic has exacted a high toll in terms of human lives lost, economic repercussions, and increased poverty.
While most COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic or experience mild, self-limiting disease, 14% develop severe disease, and 5% progress to critical illness with complications such as interstitial pneumonia, respiratory failure with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) [
3]. It is well-established that SARS-CoV-2 primarily affects the respiratory system, although other organs are also involved [
4]. The virus enters host cells by binding its spike-like surface projections to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is mainly expressed on alveolar epithelial cells and in varying degrees across nearly all human organs. Thus, although the primary target of SARS-CoV-2 infection is the lung, the widespread distribution of ACE2 receptors in other organs can lead to cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, kidney, liver, central nervous system, and ocular damage, which must be closely monitored during the disease course [
5,
6].
The virus activates both the innate and adaptive immune systems, resulting in the release of numerous cytokines, known as a "cytokine storm," which is directly correlated with tissue injury and poor prognosis in severe lung disease [
7]. In particular, interleukin (IL)-6 seems to plays an important role in driving this cytokine release so that its increased levels have been recognized as a hallmark inflammatory signature in sera of COVID-19 patients [
8]. IL-6 is a polyfunctional cytokine with both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties which exerts its several functions through two main signal transduction pathways [
9]. In the classical signalling pathway, IL-6 binds to the membrane-bound IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) to form a complex that then binds to the membrane glycoprotein gp130, inducing its homo-dimerization and initiating intracellular signalling. This type of signalling is limited to cells that express IL-6R on their surface, such as hepatocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and T cells [
10].
Cells that do not express IL-6R, such as stromal and epithelial cells, can still respond to IL-6 through the soluble form of the receptor (sIL-6R). sIL-6R binds to IL-6 in the circulation and then anchors to the membrane-bound gp130 receptor, initiating the trans-signalling pathway. Therefore, sIL-6R increases IL-6 function and is considered the agonistic form of its receptor. When IL-6 levels increase, its effects are widely expressed because gp130 molecules are ubiquitous and present even in cells lacking membrane-bound IL-6R. Conversely, a soluble form of glycoprotein 130 (sgp130) can form a complex with sIL-6R, preventing it from binding to membrane-bound gp130. In this case, sgp130 decreases IL-6 function and acts as the antagonistic form of the IL-6 receptor system [
11].
Given the central role of IL-6 in the inflammatory pathology of COVID-19 and the consistent association between elevated IL-6 levels and severe disease outcomes observed early in the pandemic, we aim to analyse IL-6 and its soluble receptor complex behaviour across different waves of the COVID-19 pandemic. This analysis may reveal differences among the waves and help determine if these markers can be used as prognostic indicators of disease severity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
In this prospective observational study, patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of the University of Naples Federico II during different COVID-19 waves were enrolled. Specifically, patient recruitment spanned from March 10, 2020, to October 31, 2021, and included the following cohorts: (i) N=23, enrolled between March 10 and April 30, 2020 (WAVE I); (ii) N=104, enrolled between September 12 and December 31, 2020 (WAVE II); and (iii) N=30, enrolled between September 7 and October 31, 2021 (WAVE III).
Additionally, a group of patients (N=20) infected with the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 was included in the study.
According to WHO interim guidance, a confirmed case of COVID-19 was defined by a positive real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay result for SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab sample [
12]. Healthy volunteers matched by age and sex (N=32 in WAVE I, N=52 in WAVE II, and N=28 in WAVE III) were enrolled as controls.
The experimental protocol adhered to the current version of the Declaration of Helsinki, and each subject provided written informed consent before participating in the study.
2.2. Biological Samples
Fasting venous blood samples were collected from all patients and healthy subjects. Sera were obtained through standard centrifugation, divided into aliquots, and stored frozen until analysis. Samples were thawed only once and immediately assayed to ensure the integrity of the specimens.
2.3. Quantitative Determination of IL-6, sIL-6R and sgp130
Quantitative determination of IL-6 serum levels was performed using Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) on the IMMULITE 2000 system (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Italy). Conversely, serum levels of sIL-6R and sgp130 were measured using an automated Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) on the Triturus System analyser (Grifols, Italy). R&D Quantikine ELISA Kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, distributed by DIACHEM S.r.l., Italy) were employed for all determinations. The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were less than 5% for IL-6 and sgp130 serum levels, and less than 10% for sIL-6R evaluation. Reference values were assessed in healthy control subjects with no family history of COVID-19, recruited from the employees of Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria “Federico II”, Naples, Italy.
2.3.1. Variables
Demographic, clinical, and analytical data were recorded for each patient to describe the clinical phenotype. The analytical data included leukocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, platelets, bilirubin, creatinine, glucose, troponin Ths, C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), ferritin, procalcitonin, and D-dimer levels.
2.3.2. cDNA Synthesis and Amplicon Libraries
RNA was extracted from nasopharyngeal swabs of patients using the QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The concentration and quality of all extracted RNA samples were measured and verified with the Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Viral genomes were amplified using a multiplex approach with version 1 of the CleanPlex SARS-CoV-2 Research and Surveillance Panel (Paragon Genomics, Hayward, CA, USA), starting with 50 ng of total RNA, followed by Illumina sequencing on a NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
The generated libraries were controlled with a High-Sensitivity Labchip and quantified using the Qubit Fluorometric Quantitation system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Raw data were trimmed and analysed using CLC Workbench 5 bioinformatics software and the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). Italian sequences imported into the GenBank database (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank) from March 2020 to November 2021, with released accession numbers, were used to construct phylogenetic trees.
3.2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
Sequences for the designated variants of concern and variants of interest were downloaded from GISAID (Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data). Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) was performed using MEGA X software, and phylogenetic trees were constructed using the 1000 replicate bootstrap method.
3.2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data that passed the normality test were analyzed using a two-tailed t-test. If the data did not pass the normality test, the Mann-Whitney test was employed to calculate statistical differences. Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 6.0 (GraphPad Software Inc, La Jolla, CA, USA) or SAS software v 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Discussion
The concept of "waves" in a pandemic refers to the cyclical patterns of infection rates over time, characterized by a rise to a peak followed by a decline. While there is no formal definition, waves are typically visualized on a graph as a wave-like pattern of increasing, peaking, and decreasing case numbers. This terminology has been widely adopted by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and other international health agencies.
The term "wave" was first used to describe the fluctuating patterns of infection during influenza outbreaks in the late 1800s and the devastating 1918-1929 "Spanish flu" pandemic [
16]. It has since become a common way to describe the recurring patterns of infections seen in pandemics.
In some cases, waves may also be referred to as surges or outbreaks [
15], particularly when describing sudden increases in case numbers within a specific timeframe. These terms all capture the idea of a temporary rise in infections followed by a decrease, reflecting the dynamic nature of infectious disease spread. Each wave has a different feature and can impact different populations, even within the same country.
The occurrence and intensity of pandemic waves can be influenced by various factors, including the seasonality of the disease and the population's immunity levels. Seasonal diseases, like influenza, may exhibit fluctuations in infection rates depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. For instance, during the summer when people spend more time outdoors and in well-ventilated spaces, transmission of respiratory viruses tends to decrease, leading to a decline in the number of cases [
18].
In contrast, distinct illnesses like H1N1 influenza may impact specific populations differently. For example, the H1N1 pandemic in 2009-2010 disproportionately affected older individuals with underlying health conditions [
17]. Understanding the demographic and epidemiological characteristics of the disease can help predict its spread and the occurrence of waves.
Furthermore, the development of immunity within human populations can play a significant role in mitigating pandemic waves. As more people become immune to the virus through natural infection or vaccination, the spread of the disease slows down, leading to a decline in case numbers. This concept, known as herd immunity, contributes to the eventual suppression of the virus and the reduction of pandemic waves. In Italy, like in many other countries, the COVID-19 pandemic has been characterized by multiple waves of infections. These waves, such as WAVE I, WAVE II, and WAVE III, represent distinct periods of increased transmission and varying impacts on public health and healthcare systems [
19]. Monitoring the occurrence and dynamics of these waves is essential for implementing effective control measures and managing the pandemic.
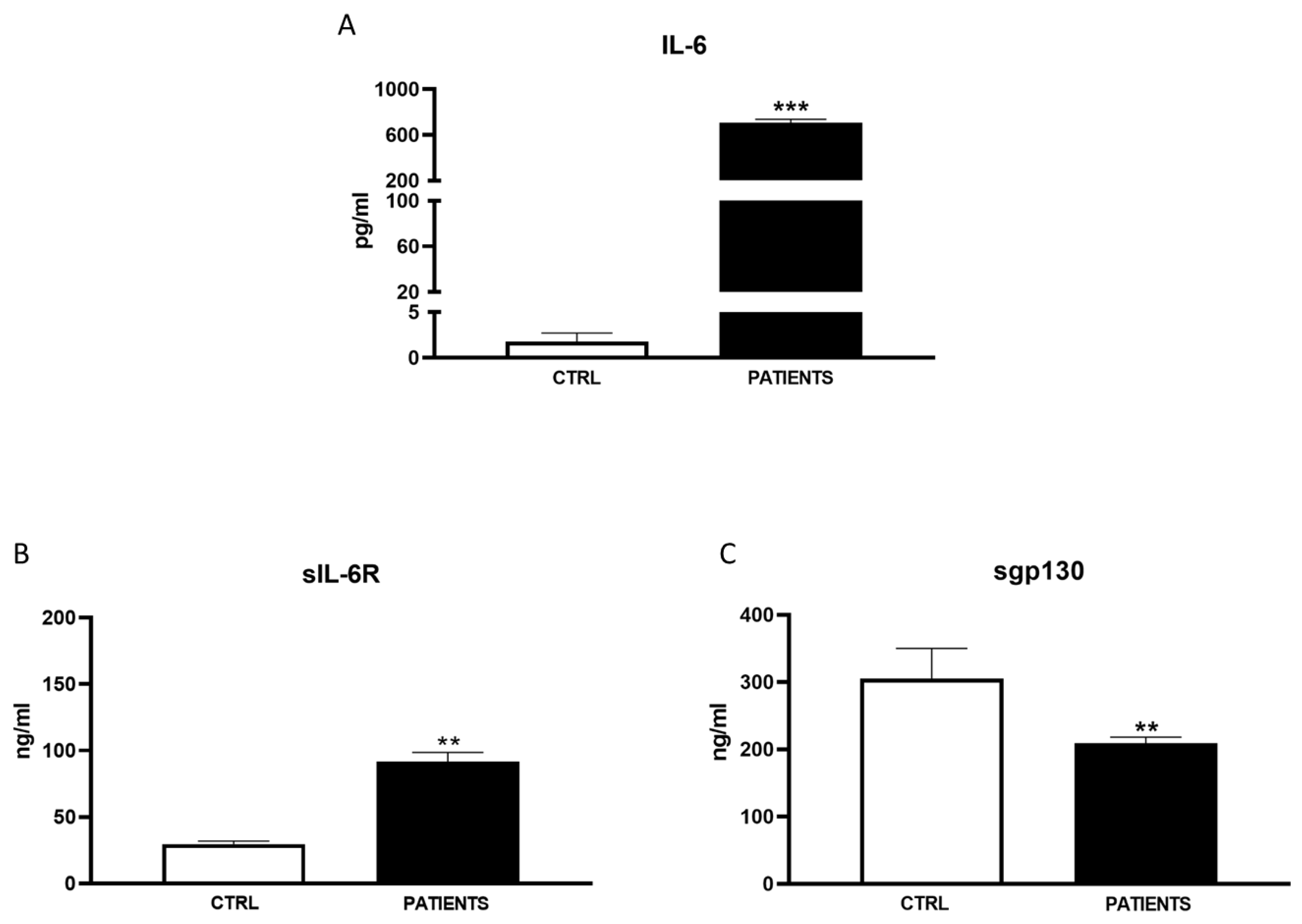
Our study aimed to investigate the variability in serum levels of IL-6 and its soluble receptor complex among COVID-19 patients across different waves of the pandemic. Consistent with previous findings and the established role of IL-6 as a hallmark inflammatory marker in COVID-19 patients, we observed a significant increase in IL-6 levels in patients compared to healthy controls during all pandemic waves [
20,
21]. However, the magnitude of cytokine increases was notably lower in the second and third waves compared to the initial wave. Additionally, we observed (Figure 9B) an increase in the IL-6 agonist sIL-6R in all patients compared to healthy controls, indicating a sustained inflammatory response across all waves. Conversely, levels of the antagonist sgp130 were drastically reduced in patients during WAVE I but gradually returned to control levels by WAVE III. These findings underscore the central role of IL-6 in driving the cytokine storm associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Moreover, the imbalance between IL-6 agonistic and antagonistic molecules suggests a dynamic modulation of IL-6 levels associated with the severity of infection [
22]. In particular, in WAVE I, we showed that great amounts of IL-6, about 400 times more in patients than healthy controls, were sustained by sIL-6R up-regulation, whereas sgp130 did not able to exert the antagonist modulation. It is known that enhancements in serum concentrations of IL-6 and sIL-6R during infection lead to an increased agonistic trans-signaling mechanism [
23]. At the same time, lower sgp130, that interacts with IL-6/sIL-6R-complex, leads a decreased block in IL-6 trans-signaling, thus confirming a reduced antagonistic role of sgp130 also during the viral infection [
24]. The contemporary changes in IL-6 and its receptors concentrations as well as the consequent increased in signaling transduction, are closely associated with increased mortality and unfavorable outcome in COVID-19 patients [
25].
In a retrospective study, Gorham et al. assessed IL-6 concentrations in patients admitted to the ICU during the first wave of the pandemic, distinguishing between survivors and non-survivors. They observed a significant discrepancy in IL-6 levels, with non-survivors exhibiting considerably higher levels (720 pg/ml) compared to survivors (336 pg/ml). This led them to suggest repeated evaluation of IL-6 as a prognostic marker in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2-induced disease [
26].
Subsequently, there was a proposal to employ IL-6 pathway blockade to manage cytokine release syndrome stemming from virus infection [
27]. While initial data on anti-IL-6 agents, particularly tocilizumab, showed promise, early randomized trials yielded mixed results in terms of clinical benefit [
28,
29]. Larger trials such as RECOVERY and REMAP-CAP later established anti-IL-6 therapy, in combination with steroids, as a potential option for hypoxic patients exhibiting evidence of hyperinflammation [
30]. Notably, results from critically ill patients, where the cytokine storm had already commenced, suggested that steroids may be more effective than tocilizumab in controlling the inflammatory reaction [
31]. Furthermore, it's conceivable that dysregulation in immunological mediators implicated in COVID-19, including IL-6, sIL-6R, and sgp130, may contribute to varied prognoses and responses to pharmacological interventions such as tocilizumab and steroids.
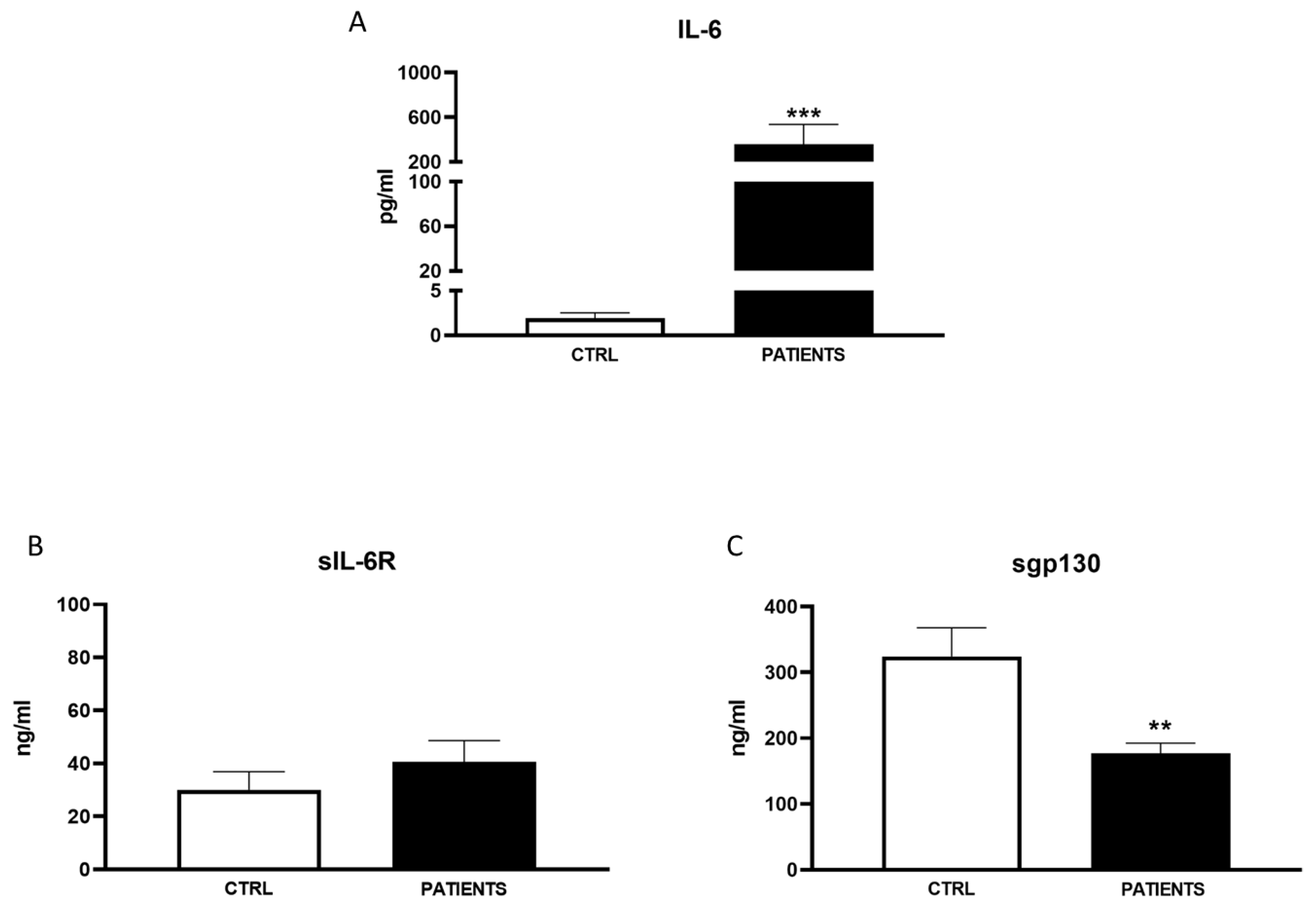
Several clinical investigations noted a less pronounced cytokine storm during the second wave of the pandemic compared to the first [
29]. This could be attributed to better and faster treatments available to patients admitted to the ICU during the second wave. Our findings reflected a lower increase in IL-6 and sIL-6R levels among WAVE II patients compared to controls, while sgp130 levels exhibited a higher decrease relative to the control group. This suggests that patients during the second wave experienced less severe disease, leading to hospitalization in a smaller percentage of cases. Consequently, the mortality rate was notably lower, possibly due to early COVID-19 diagnosis, improved management of infected patients, and better-prepared health systems, alongside preferential protection measures for older and higher-risk vulnerable individuals.
However, despite the advancements, the second wave still resulted in excess mortality among patients over 70 years old, especially those with comorbidities. Additionally, the health consequences of COVID-19 persisted beyond acute infection, emphasizing the need for ongoing surveillance of patients who have survived the acute phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection [
31]. Towards the end of the second wave, despite high vaccination rates among the adult Italian population, a new surge in COVID-19 infections emerged, underscoring the ongoing challenges in managing the pandemic.
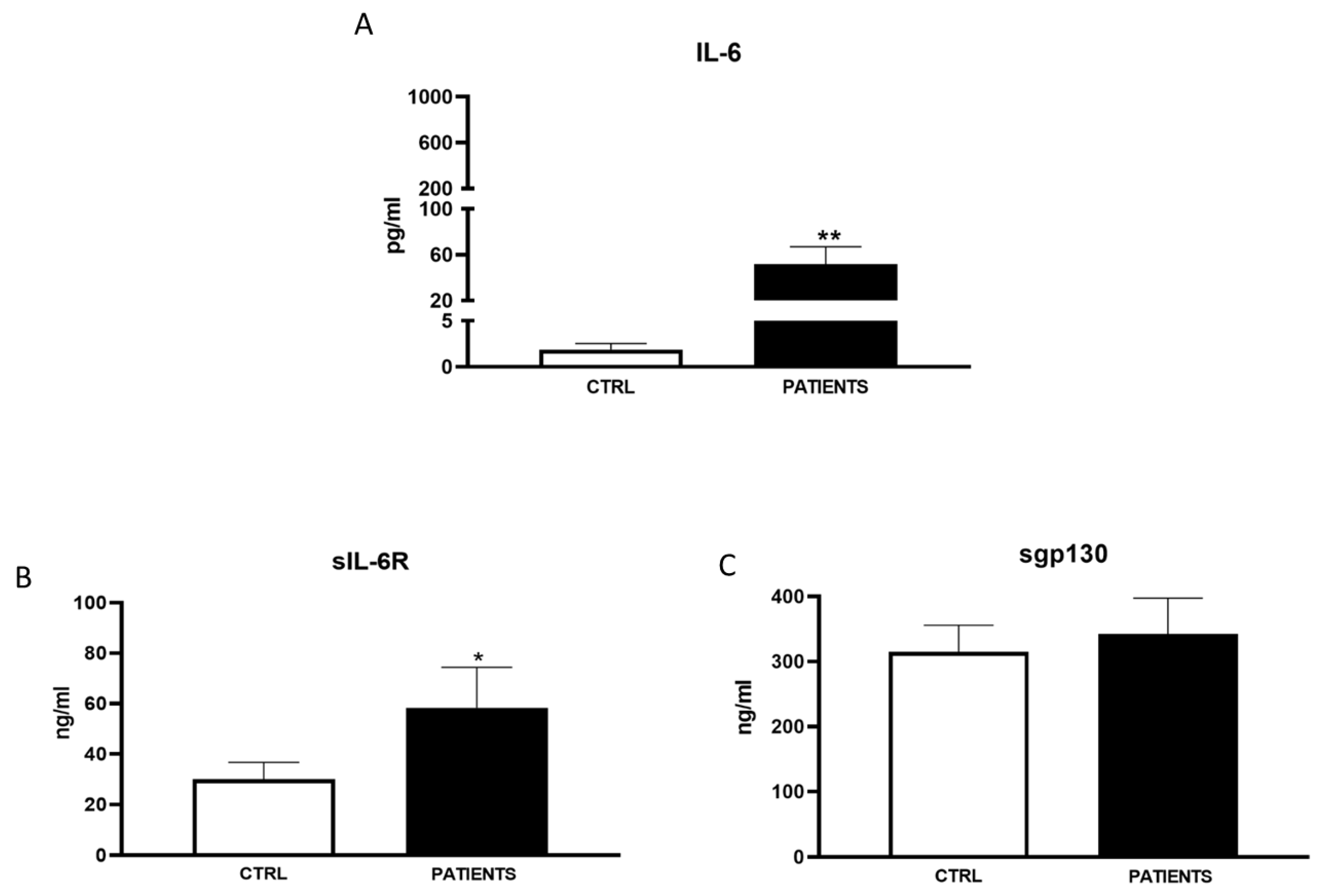
We found that levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R continued to be significantly increased in COVID-19 patients compared to healthy controls (63,15±18,5 pg/ml vs 1,91±0,89 pg/ml and 75,21±14,29 ng/ml vs 26,51±8,16 ng/ml, respectively). However, there was a substantial decrease in IL-6 values respect to the previous waves. Interestingly, levels of antagonist sgp130 increased in COVID-19 patients returning to those of the controls ones (312,12±53,14 ng/ml vs 308,24±24,91 ng/ml). Several clinical trials have demonstrated that, in comparison with the first and second, patients in the third wave had with less comorbidities and presented with moderate COVID-19 infection [
32]. Indeed, influence of age, gender and comorbidities on the occurrence of severe COVID-19 was less marked in the third wave compared with the first two, and the interactions between age and comorbidities less important. The changes in these clinical risk factors can be explained by a change in the exposed population as the virus spread in the population between first waves and by the vaccination campaign [
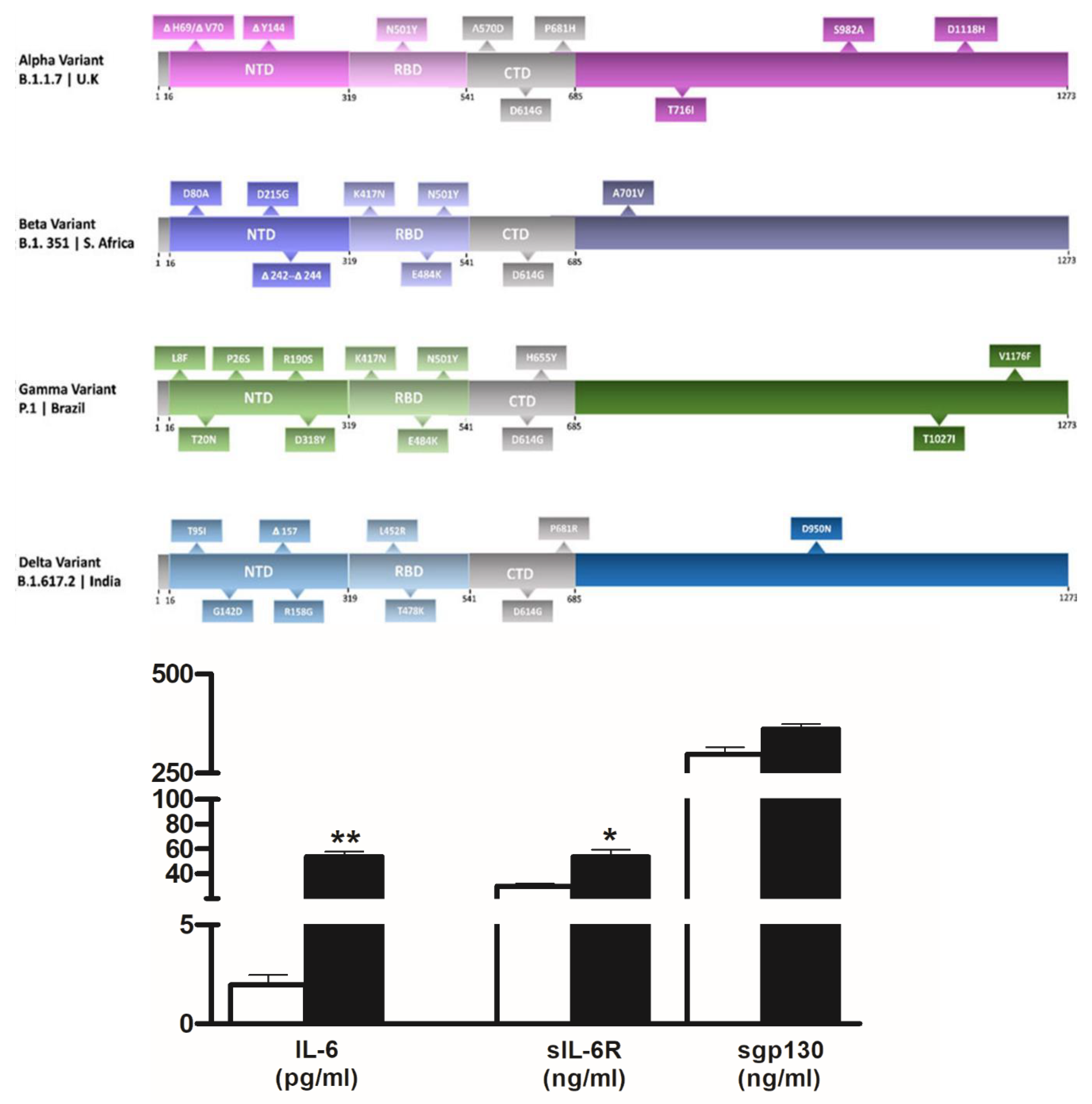
33]. Thus, it was expected that the generalization of vaccination in a context where the virus and its recent variant forms continued to be very present in the general population could modify the profile of people severely affected by the disease. In particular, SARS-COV-2 infected patients in WAVE III resulted less symptomatic intensive respiratory support being required in a limited number of cases, and an elevation of blood inflammatory markers (C-Reactive Protein and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio) was found in a lower proportion of cases (data not shown). The third wave of the pandemic was largely driven by the delta variant of SARS-COV-2 [
34,
35]. Our results showed that serum levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R continued to significantly increase in patients whereas those of antagonist sgp130 returned to the controls ones. It is known that VOC may impact virus properties or behavior with consequences on virus transmissibility, disease severity or neutralization mechanisms of antibodies generated during previous infection and vaccination. As such, our study provides additional support for the growing body of literature confirming the central role of IL-6 in COVID-19, also in delta positive patients whereas further researches are needed to understand the functions of its agonist and antagonist molecules on the disease changes due to the virus variants.