1. Introduction
Alopecia Areata (AA) is an autoimmune disorder influenced by a genetic predisposition along with other relevant factors [
1,
2,
3,
4]. The most common manifestation is the appearance of patches of hair loss on the scalp or body without signs of inflammation. The recommended treatments include topical or intralesional corticosteroids in mild cases, and systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors, among others, in moderate and severe cases [
5].
Multiple studies have highlighted a bidirectional communication between the gut microbiota and skin homeostasis, mainly through modulation of the immune system [
6,
7]. Indeed, there is clear evidence of an association between gut microbiota and inflammatory skin diseases such as acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis or psoriasis [
8,
9,
10]. Therefore, a connection between the development of a gut dysbiosis and an imbalance in skin homeostasis has been reported. In this sense, a limited number of previous investigations have analyzed both gut [
11,
12,
13,
14] and skin microbiota [
15,
16,
17] in AA patients, evidencing differences in its composition when compared with healthy subjects, and proposing not only its involvement in the origin [
11,
13], but also its usefulness as a prognostic biomarker of the disease [
12,
17].
AA patients present an increased risk of developing another autoimmune diseases and these pathologies could share common pathogenic mechanisms in which the gut microbiota could play a key role [
18]. In this context, beneficial effect of some oral probiotic mixtures has been proven in clinical trials in several inflammatory skin diseases [
19,
20]. Disruption of gut integrity, imbalance within microbial communities, systemic and local inflammation, are some of the mechanisms related to the pathogenesis of these diseases that oral probiotics can contribute to balance [
21].
Although the success of the Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) in AA has been documented in some case reports [
22,
23], to date and to our knowledge no clinical trials with a intervention with FMT nor oral probiotics have been published. Previous studies report beneficial effects of different Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum strains improving intestinal permeability [
24], gut dysbiosis [
25], appropriate balance between Th17 and Treg lymphocytes [
26], and decreased proinflammatory cytokines [
27].
The objectives of this pilot study were to evaluate the effect of an oral probiotic intake on severity variables of AA, on gut and skin microbiota, and the safety. The product evaluated in this clinical trial were obtained from the promoter collection of probiotic strains and selected by data previously communicated in the patent document PCT/EP2023/063439.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
This study was a 24-weeks randomized, double-blind, two-arms, placebo-controlled, pilot clinical trial of 24 weeks duration. The trial received approval from the Ethics Committee of University Hospital Vinalopó (Elche, Spain), and was carried out at Centro Dermatológico Estético (Alicante, Spain). Clinical trial was registered in the American Registry of Clinical Trials (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT05599607).
The study protocol stablished 6 face-to-face visits: baseline visit and at weeks 4, 8, 12, 16 and 24. Patients received the intralesional corticosteroid treatment along with probiotic or placebo, and researchers took photographs of affected scalp areas in every visit to assess severity and evolution of the lesions.
2.2. Study Population
For inclusion in the trial patients had to comply with the following defined criteria: male or female ≥18 years with a diagnosis of AA presenting at least two signs of AA activity visualized by trichoscopy assessed by a dermatologist. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and subjects who had required topical or systemic administration of antifungals and antibiotics in the previous two weeks or had consumed probiotics in the two months prior to the beginning of the study were excluded. Signed informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment in the study.
2.3. Randomization and Intervention
Participants were initially randomized to each of the two intervention groups (probiotic and placebo) in a 1:1 ratio (50% probability in both groups) following a list previously prepared by blinded staff.
Patients allocated to probiotic group received a daily capsule containing freeze-dried
Lactobacillus rhamnosus Bths-08 (CECT 30580) and
Bifidobacterium longum Bths-06 (CECT 30616) probiotic strains in 1:1 ratio at concentrations of 10
9 colony-forming units (cfu) per dose, with maltodextrin as a carrier. Participants of placebo group received a daily capsule containing only maltodextrin in an identical and indistinguishable format to probiotic product. Moreover, all patients received the habitual AA pharmacological treatment based on intralesional corticosteroids (triamcinolone acetonide 12 mg/mL) every 4 weeks during the intervention period [
5].
2.4. Outcomes
Primary variables were: (i) Percentage of patients with reduction of AA plaques, and (ii) Percentage of patients with reduction of the affected scalp surface area, assessed according to the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scale [
28]. This scale categorizes patients as S0 (0% scalp affected), S1 (1% to 24%), S2 (25 to 49%), S3 (50% to 74%), S4 (75% to 99%) and S5 (100%).
Secondary variables were: (i) Percentage of patients with activity signs improvement and mean number of signs of activity (such as black dots, exclamation mark hairs, broken hair, tapered hairs and pseudomoniletrhix), (ii) Percentage of patients with inactivity signs improvement and mean number of signs of inactivity (such as yellow dots, vellus hairs and empty follicular openings), and (iii) Percentage of patients with regrowth signs improvement and mean number of signs of regrowth (such as upright regrowing hairs, vellus hairs and pigtail hairs). These clinical secondary variables were assessed by trichoscopy [
29] at baseline and at weeks 24. Another secondary variable was (iv) Faecal and skin characterization of the microbiota composition (changes from baseline to the end of the study were analyzed). This characterization was performed by Next Generation Sequencieng (NGS) of 16S rRNA bacterial gene.
Finally, to assess security of the intervention, the total number of adverse events were registered during the follow-up period from baseline to week 24 in both groups of treatment.
The scoring interval for “activity” variable, based on the mean number of signs observed in the plaque set, was 0 to 5 for each plaque. To assess the difference of the “activity” variable between baseline and 24-weeks follow-up, the formula takes in account not only the total number of signs in all plaques, but also the resolved plaques at the end of the 24-weeks follow up. These resolved plaques were scored with the maximum value of 5, as appear in the used following formula: “Activity” = [(Activity Score24w × AA Plaques24w) - (Activity Score0w × AA Plaques0w)] - (5 × AA Resolved Plaques24w). It is important to note that the “activity” variable is inversely proportional to the “inactivity” and “regrowth” variables.
The scoring interval for “inactivity” variable, based on the mean number of signs observed in the plaque set, was 0 to 3 for each plaque. To assess the difference of the “inactivity” variable between baseline and 24-weeks follow-up, the formula takes in account not only the total number of signs in all plaques, but also the resolved plaques at the end of the 24-weeks follow up. These resolved plaques were scored with the maximum value of 3, as appear in the used formula: “Inactivity” = [(Inactivity Score24w ÷ AA Plaques24w) - (Inactivity Score0w ÷ AA Plaques0w)] + (3 × AA Resolved Plaques24w).
The scoring interval for “regrowth” variable, based on the mean number of signs observed in the plaque set, was 0 to 3 for each plaque. To assess the difference of the “regrowth” variable between baseline and 24-weeks follow-up, the formula takes in account not only the total number of signs in all plaques, but also the resolved plaques at the end of the 24-weeks follow up. These resolved plaques were scored with the maximum value of 3, as appears in the formula: “Regrowth” = [(Regrowth Score24w ÷ AA Plaques24w) - (Regrowth Score0w ÷ AA Plaques0w)] + (3 × AA Resolved Plaques24w).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics for quantitative variables were presented as mean and 95% confidence interval, while categorical variables as total and proportion of cases.
Data analysis was carried out on an intention-to-treat basis. Analysis of the continuous variables “activity”, “inactivity” and “regrowth” were performed as quantitative change in the score (see Outcomes) and by conversion to a respective qualitative variable (expressed in number and percentage) as “patients who improve”, at week 24 compared to baseline. Same strategy was used for the number of AA plaques. The effectiveness was considered as a reduction in the number of plaques (1 at least) at 24-weeks follow-up compared with baseline, and by conversion to a qualitative variable as “patients who improve”. Affected scalp surface area was assessed according to the SALT scale and percentage of “patients who improve” (defined as the change of at least 1 category of less extension) between baseline and 24-weeks follow-up were compared between both study groups.
For categorical and continuous variables, Pearson’s chi-squared test and Student’s t-test were respectively used for the analysis of statistically significant differences between the study groups. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05. Previously, condition of normality of continuous variables was evaluated using the Shapiro-Wilk test. However, “inactivity” and “regrowth” variables did not present normality by this test, but when examining their Q-Q plots, it was observed that their distributions resembled normality and were treated as such, but including a second analysis with a non-parametric test (data not shown), due that there is not a large sample size, to check the results and it was observed that these do not change substantially.
All statistical analysis was performed with SPSS Statistics for Windows v27.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
2.6. Gut and Skin Microbiota Study
Swabbing procedure of scalp surfaces of AA lesions was used to obtain skin samples. Stool and skin samples were introduced in sterile tubes with the nucleic acid stablishing solution RNAlater (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and conserved at -20 ºC until analysis. For characterization of the microbiota it was performed Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) of 16S rRNA bacterial gene.
In summary, the study this microbiota study was conducted as follows: In the first step, DNA extraction from the samples was performed. This DNA was also purified and tested for quality control. The second step was the preparation of the libraries. The genetic material obtained was amplified by a two-step PCR (polymerase chain reaction) using the Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit (Illumina) following the 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Illumina 15044223 B protocol, which allows the capture and amplification of the V3-V4 hypervariable region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. 16S based libraries were quantified by fluorimetry using Quant-iT™ PicoGreen™ dsDNA Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Prior to sequencing, 16S libraries were pooled and the size and quantity of the pool were assessed on the Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies) and with the KAPA Library Quantification Kit (Kapa Biosystems), respectively. These sequencing libraries were loaded onto the platform MiSeq (Illumina) following a 300bp x2 paired end design. The last step was the bioinformatic analysis which included the identification and elimination of low quality or chimeric sequences, the generation of the Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs) and the taxonomic assignment.
3. Results
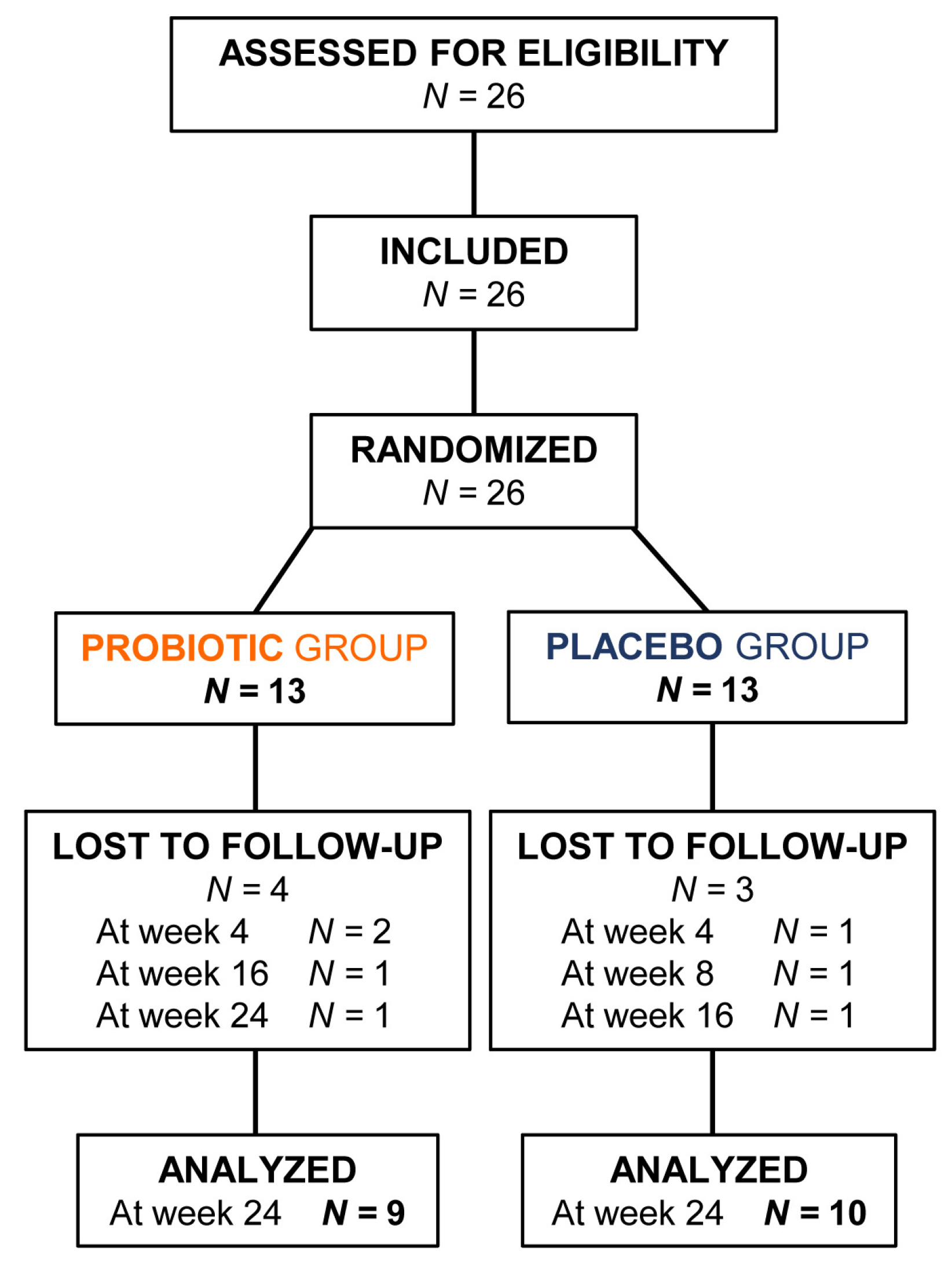
From March to October 2021, 26 AA patients who met all the inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria were enrolled in the study (13 were allocated to probiotic group and 13 to placebo group). In CONSORT diagram (
Figure 1) patients assessed for eligibility, included, randomized, lost to follow-up, and analyzed in both groups are reported.
3.1. Baseline Descriptive Data
Patients’ data included in the study at baseline appears in descriptive
Table 1. A homogeneity analysis of this baseline data in both study groups revealed that neither important variable was unbalanced after randomization.
3.2. Number of AA Plaques
A higher proportion of patients in the probiotic group reduced the AA plaques count after 24 weeks, being 5 of 9 (55%) compared to 3 of 10 (30%) in the placebo group (P = 0.10). Notably, 2 of the 8 patients improving the AA plaques count at the end of the study (therefore decreasing this count), resolved them completely (disappearing), belonging both to probiotic group.
3.3. Affected Scalp Surface Area (SALT Scale)
Regarding SALT scale, an improvement in 4 of 9 (45%) patients receiving the probiotic product was observed after 24 weeks compared 2 of 10 (20%) in the placebo group (P = 0.51).
3.4. Activity, Inactivity and Regrowth Scores
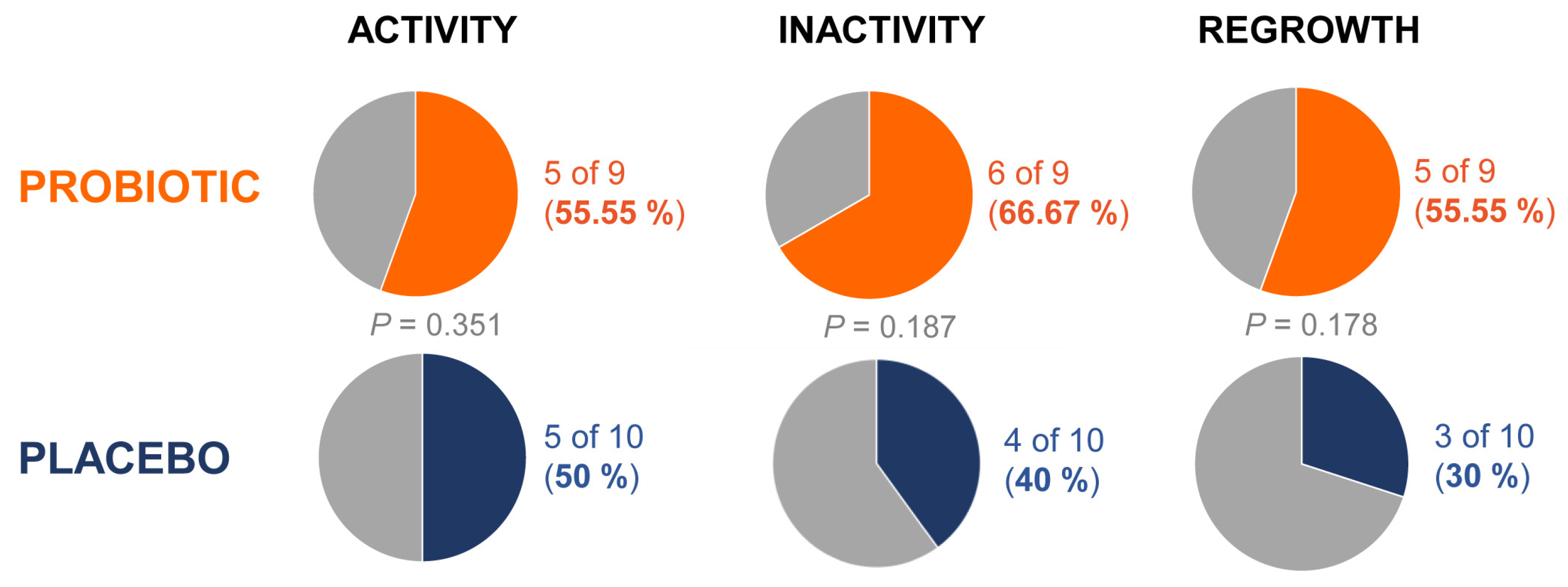
AA patients who receive the probiotic product exhibited an average difference in the scores “activity”, “inactivity” and “regrowth” of -5.8, 4.6 and 4.4 respectively, versus -3.0, 2.3 and 2.0 observed in the patients treated with placebo, after 24 weeks (
Table 2).
Moreover, percentage of patients with improvement at 24 weeks of 55%, 67% and 55% was respectively observed among those with probiotic treatment, compared to 50%, 40% and 30% found in the placebo group (
Figure 2).
3.5. Microbiota Analysis
3.5.1. Gut Microbiota
A significant change of α-diversity according to Shannon index was not evidenced between study groups or after 24 weeks of intervention (
Figure S1 in Supplementary Material). There was no obvious clustering of stool samples by PCoA between study groups or between baseline and after follow-up period.
Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria were the phylum exhibiting the highest relative abundance in all stool samples (
Figure S2 in Supplementary Material). The families with the highest relative abundance in all stool samples were Lachnospiraceae, Bacteroidaceae, Oscillospiraceae, and Prevotellaceae (
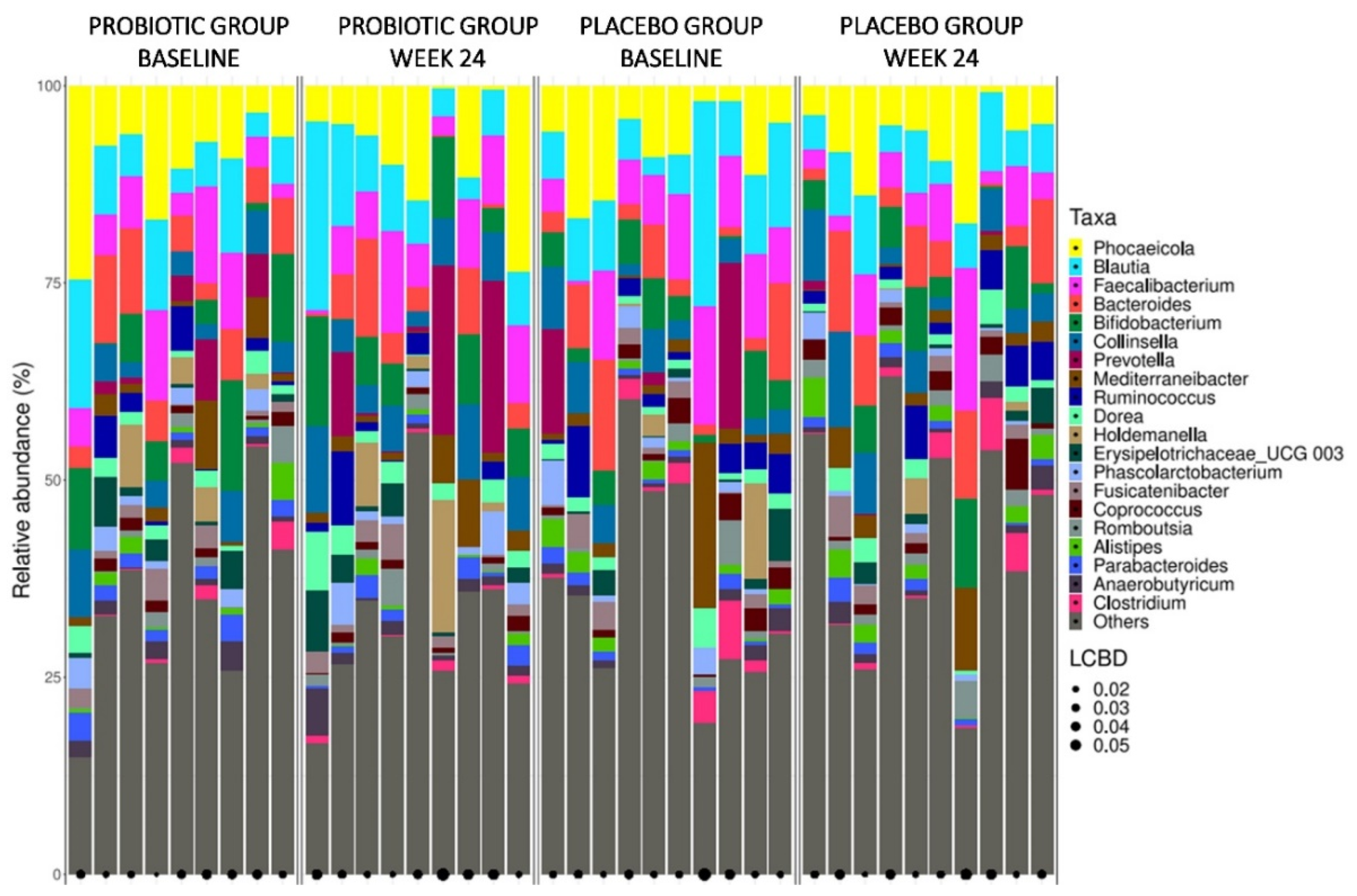
Figure S3 in Supplementary Material). Bacterial genera barplots of faecal samples from study groups at baseline and after 24 weeks of treatment are illustrated in
Figure 3. Genera with the highest relative abundance were
Phocaeicola,
Blautia and
Faecalibacterium.
After the intervention period with probiotic or placebo, no differentially abundant taxonomic markers from phylum to genus were detected between the groups compared to baseline data.
3.5.1. Skin Microbiota
As with gut microbiota, it was no observed a significant change of α-diversity according to Shannon index between study groups or after 24 weeks of intervention (
Figure S4 in Supplementary Material). In addition, no obvious clustering of skin samples by PCoA between study groups or after 24 weeks were observed.
Phylum with the highest relative abundance in all skin samples were Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria (
Figure S5 in Supplementary Material). Families with the highest relative abundance were Propionibacteriaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Bifidobacteriaceae, and Moraxellaceae (
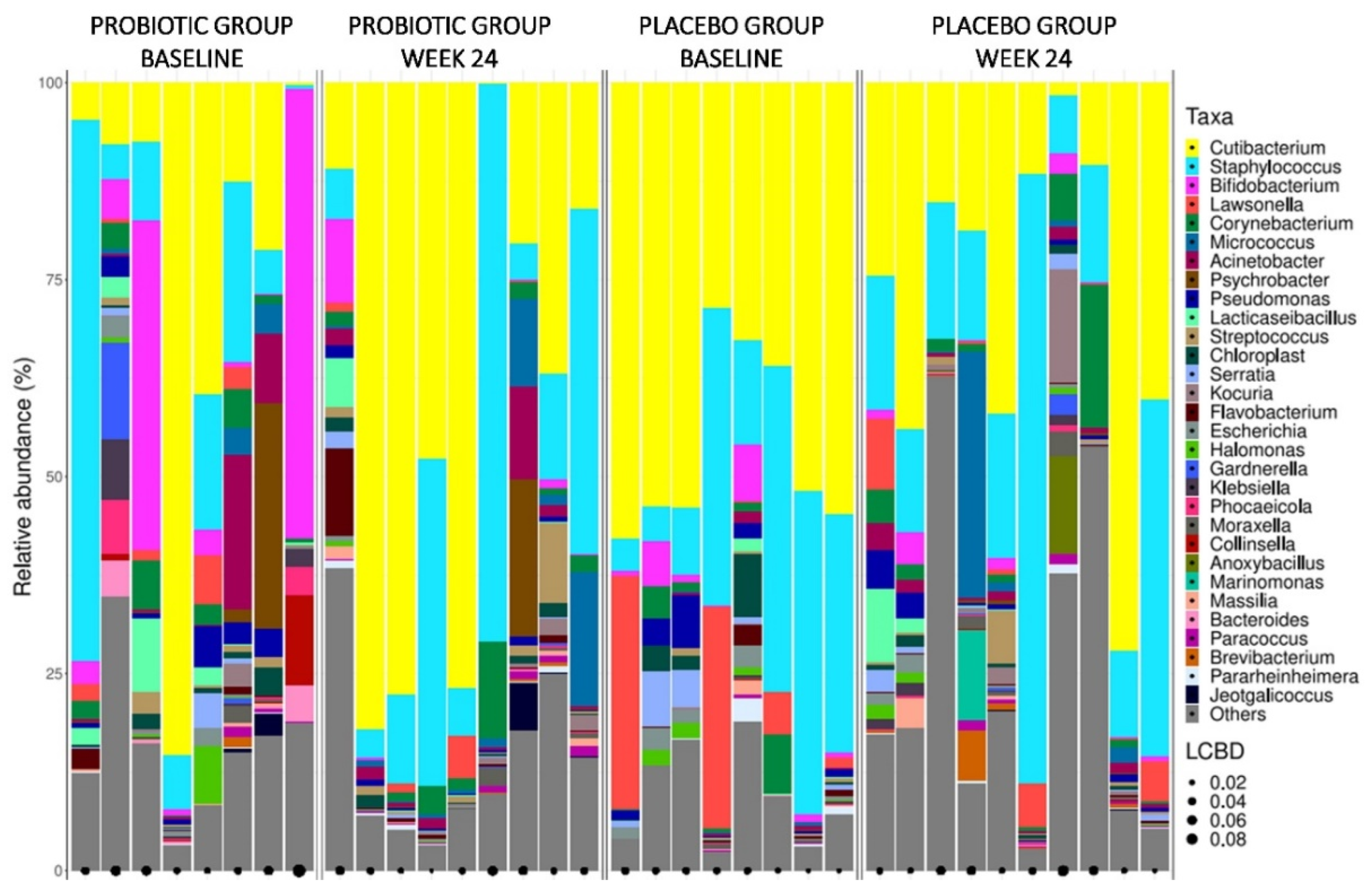
Figure S6 in Supplementary Material). In
Figure 4 are illustrated the bacterial genera barplots of skin samples from study groups at baseline and after 24 weeks of treatment. Genera with the highest relative abundance regarding all skin samples were
Cutibacterium,
Staphylococcus, and
Bifidobacterium.
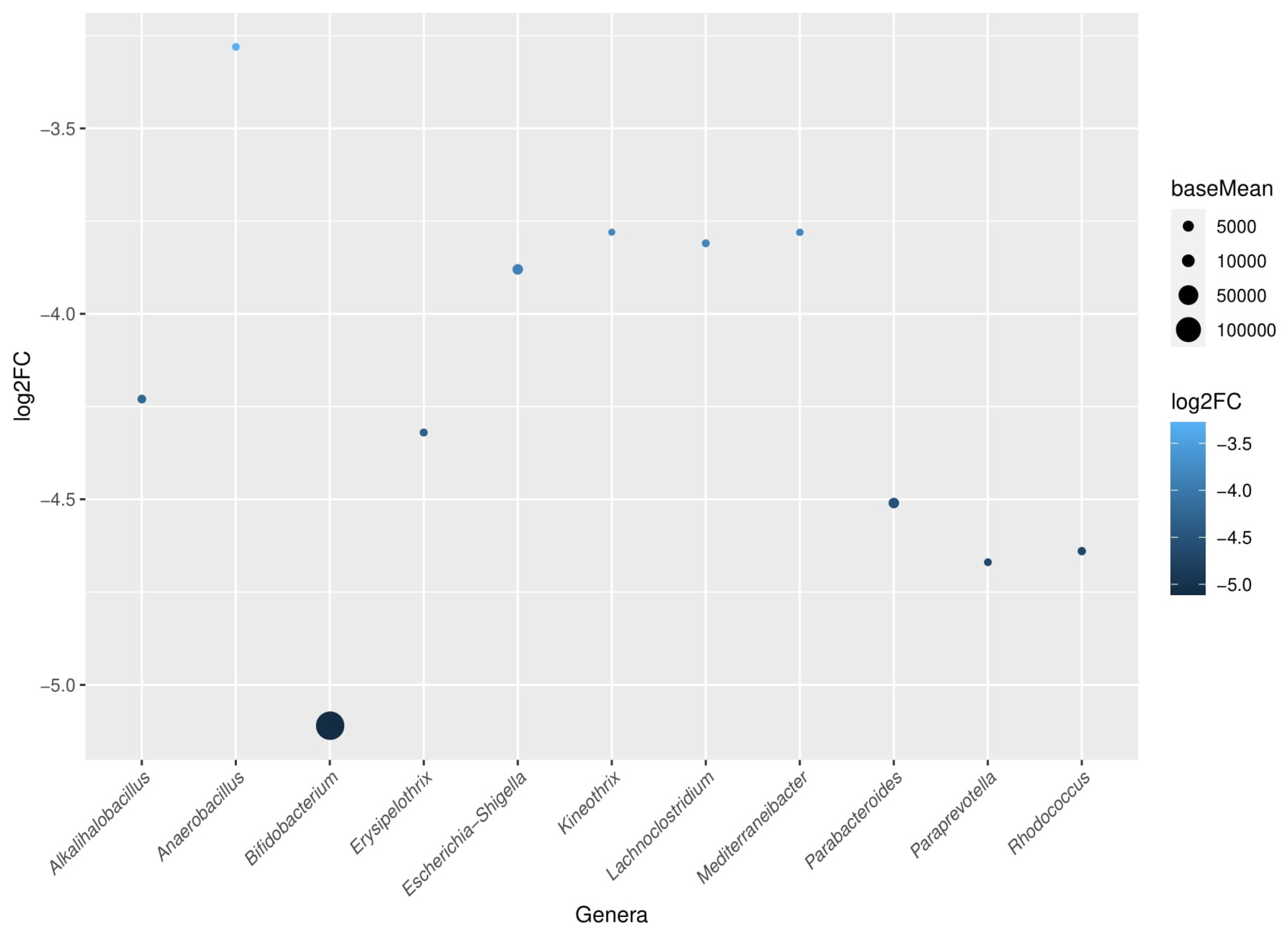
Notably, when comparing baseline versus week 24, it was detected a significant reduction of Bifidobacteriaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, and Nocardiaceae families in the probiotic group at the end of the follow-up period. Among these families, a reduction of
Bifidobacterium,
Erysipelothrix, and
Rhodococcus genera was also respectively significant. All bacteria that were characteristically reduced in the probiotic group at the end of the study are shown in
Figure 5.
3.6. Safety
Overall, 5 adverse events were reported: 1 in the probiotic group and 4 in the placebo group. Of the 5 adverse events reported, 3 of them were potentially attributable to the treatment received by the patients, all of them in the placebo group (abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhoea).
4. Discussion
To date, no clinical studies with oral probiotics targeting microbiome modulation have been published. Notably, this is the first clinical trial assessing the efficacy and safety of a probiotic product in patients with AA in a conventional clinical practice setting.
Results obtained from this proof-of-concept study indicate a beneficial effect of the probiotic preparation on signs of activity, inactivity, and hair regrowth, with a decrease in the number of AA plaques and a reduced affected skin surface area. Due to the type of study proposed, with a limited sample size, the changes between groups throughout the study did not reach statistical significance. However, analyzing the overall data, we consider the effects obtained with the probiotic as clinically relevant, since they are consistent with a same trend of beneficial effects on the evolution of AA. To confirm these results, a clinical trial with a larger sample size should be conducted.
Any significant change of gut microbiota was not observed between AA patients belonging either of the two study groups and after 24 weeks of treatment. This implies that administration of the probiotic formula does not appear to modify the composition and diversity of gut microbiota in AA patients. It is also unknown whether the probiotic strains have colonized the gut microbiota or whether its effect have been transient. To verify this issue, it should be necessary to perform a quantitative PCR (qPCR) specific to the probiotic strains used in the present study. On the other hand, only two studies have compared the gut microbiota of AA patients with that of healthy controls (an adult population as in the present study) and although no changes in α- and β-diversity are evident, there are characteristic differences in relation to the composition. In the study of Moreno-Arrones
et al., an increased relative abundance of
Holdemania filiformis,
Parabacteroides johnsonii,
Clostridiales vadin BB60 group,
Bacteroides eggerthii and
Parabacteroides distasonis, and Eggerthellaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Lachnospiraceae, was reported in AA patients [
12]. Lu et al. found out increased levels in
Blautia,
Phyllobacterium,
Dorea,
Anaerostipes,
Megasphaera,
Collinsella,
Sphingomonas, and
Pseudomonas [
13]. In the study of Rangu S et al. there was not evidenced significant difference regarding α- and β-diversity between siblings with and without AA, but a linear mixed model revealed that
Ruminicoccus bicirculans exhibited lower relative abundance in children with AA [
14]. These results, although discordant, could indicate the presence of a dysbiosis in patients with AA. It is necessary to emphasize that in the present study no comparison with healthy controls was performed and only microbiome analysis between groups and after the follow-up period have been assessed. Therefore, it cannot be concluded that these patients with AA exhibited a gut dysbiotic state.
In relation to the skin microbiota, some studies have reported differences in scalp microbiota of AA lesions compared to healthy controls. The study of Pinto et al. describes an increase of
Propionibacterium and a decrease of
Staphylococcus in AA subjects [
15]. Juhasz et al. also communicated a significant decrease in class Clostridia in AA patients [
16]. In other study an increased α-diversity in AA patients was described, with decreased levels in Staphylococcaceae and Burkholceriaceae families. This study also describes how
Cutibacterium/
Staphylococcus caprae ratio was increased compared to healthy controls [
17]. In our study skin microbiota was similar in both groups at baseline. After 24 weeks of treatment several changes were detected in patients of the probiotic group, with reductions in characteristic families and genera, but not observed in patients that received the placebo. These finding imply that the skin microbiota in this group has been modified by the administration of the probiotic strains. In relation to the pathophysiology, it suggests a reduced penetration of immunogenic material of bacterial origin into the hair follicle and, therefore, a reduction of peribulbar inflammation, that is a key mechanism in the pathogenesis of AA [
1,
30]. In addition, results reported in patients receiving the probiotic product evidence a potential usefulness of measuring levels of some of these genera (for example
Bifidobacterium that showed the greatest reduction), as a potential diagnostic and prognostic skin biomarker in patients with AA.
Importantly, throughout the clinical trial the probiotic formula was used as an adjuvant treatment to intralesional corticosteroids. Intralesional corticosteroids are a first line treatment mainly in mild to moderate cases such as those included in this study [
31]. Because the dose of corticosteroid is important for its efficacy in these AA cases, one hypothesis we propose is that probiotic treatment could reduce the dose and treatment time required and, therefore, could lead to a lower frequency of adverse effects, such as skin atrophy [
32]. Future studies would be necessary to verify this promising hypothesis.
As conclusions, this investigated probiotic formulation as an adjuvant treatment in a routine clinical practice setting appears to improve the clinical course of patients with AA. As this is a preliminary study, this trend needs to be confirmed in larger clinical trials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Boxplot of α-diversity in stool samples at the ASV level ac-cording to the Shannon index; Figure S2: Bacterial profiles of faecal samples from study groups at phylum level; Figure S3: Bacterial profiles of faecal samples from study groups at family level; Figure S4: Boxplot of α-diversity in skin samples at the ASV level according to the Shannon index; Figure S5: Bacterial profiles of skin samples from study groups at phylum level; Figure S6: Bacterial profiles of skin samples from study groups at family level.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.N.-L. and M.R.N.-B.; Methodology, V.N.-L and M.R.N.-B.; Software, P.S.-P., E.N.-D., L.N.-M., and V.N.-L.; Validation, M.R.N.-B., A.A.-G., P.S.-P., E.N.-D., L.N.-M., M.M.-V., A.G.-N. and V.N.-L.; Formal analysis, A.A.-G., P.S.-P., E.N.-D., L.N.-M., and V.N.-L.; Investigation, M.R.N.-B. and A.G.-N.; Resources, M.R.N.-B. and V.N.-L.; Data curation, P.S.-P., E.N.-D., L.N.-M., and V.N.-L.; Writing—Original draft preparation, P.S.-P., E.N.-D. and V.N.-L.; Writing—Review and editing, P.S.-P., A.A.-G., E.N.-D., M.M.-V., and V.N.-L.; Visualization, M.R.N.-B., A.A.-G., P.S.-P., E.N.-D., L.N.-M., M.M.-V., A.G.-N., and V.N.-L.; Supervision, V.N.-L.; Project administration, V.N.-L.; Funding acquisition, V.N.-L.
Funding
This clinical trial was sponsored by Bionou Research S.L. The study received the grant IMIDTA/2020/92 from the Valencian Institute of Business Competitiveness (Instituto Valenciano de Competitividad Empresarial, IVACE).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved on 24 February 2021 by Research Ethic Committee of University Hospital Vinalopó (Elche, Spain), protocol code ALO.PRO.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
P.S-P., E.N-D. and L.N-M. belong scientific staff of Bioithas. V.N-L is shareholder of Bionou Research and Bioithas. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rajabi, F.; Drake, L.A.; Senna, M.M.; Rezaei, N. Alopecia Areata: A Review of Disease Pathogenesis. Br J Dermatol 2018, 179, 1033–1048. [CrossRef]
- Suchonwanit, P.; Kositkuljorn, C.; Pomsoong, C. Alopecia Areata: An Autoimmune Disease of Multiple Players. Immunotargets Ther 2021, 10, 299–312. [CrossRef]
- Simakou, T.; Butcher, J.P.; Reid, S.; Henriquez, F.L. Alopecia Areata: A Multifactorial Autoimmune Condition. J Autoimmun 2019, 98, 74–85. [CrossRef]
- Minokawa, Y.; Sawada, Y.; Nakamura, M. Lifestyle Factors Involved in the Pathogenesis of Alopecia Areata. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 1038. [CrossRef]
- Meah, N.; Wall, D.; York, K.; Bhoyrul, B.; Bokhari, L.; Sigall, D.A.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Betz, R.C.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Callender, V.; et al. The Alopecia Areata Consensus of Experts (ACE) Study: Results of an International Expert Opinion on Treatments for Alopecia Areata. J Am Acad Dermatol 2020, 83, 123–130. [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.R.; Akter, S.; Tamanna, S.K.; Mazumder, L.; Esti, I.Z.; Banerjee, S.; Akter, S.; Hasan, M.R.; Acharjee, M.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Impact of Gut Microbiome on Skin Health: Gut-Skin Axis Observed through the Lenses of Therapeutics and Skin Diseases. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2096995. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.A.; Monteleone, G.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Paus, R. The Gut-Skin Axis in Health and Disease: A Paradigm with Therapeutic Implications. Bioessays 2016, 38, 1167–1176. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Sánchez-Pellicer, P.; Agüera-Santos, J.; Navarro-Moratalla, L. Probiotics in the Therapeutic Arsenal of Dermatologists. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1513. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pellicer, P.; Navarro-Moratalla, L.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Agüera-Santos, J.; Navarro-López, V. Acne, Microbiome, and Probiotics: The Gut-Skin Axis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1303. [CrossRef]
- De Pessemier, B.; Grine, L.; Debaere, M.; Maes, A.; Paetzold, B.; Callewaert, C. Gut-Skin Axis: Current Knowledge of the Interrelationship between Microbial Dysbiosis and Skin Conditions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 353. [CrossRef]
- Borde, A.; Åstrand, A. Alopecia Areata and the Gut-the Link Opens up for Novel Therapeutic Interventions. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2018, 22, 503–511. [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Arrones, O.M.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Perez-Brocal, V.; Saceda-Corralo, D.; Morales-Raya, C.; Rodrigues-Barata, R.; Moya, A.; Jaen-Olasolo, P.; Vano-Galvan, S. Analysis of the Gut Microbiota in Alopecia Areata: Identification of Bacterial Biomarkers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020, 34, 400–405. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, P.; Hu, R.; Qi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Q. Gut Microbiota Characterization in Chinese Patients with Alopecia Areata. J Dermatol Sci 2021, 102, 109–115. [CrossRef]
- Rangu, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Hu, W.; Bittinger, K.; Castelo-Soccio, L. Understanding the Gut Microbiota in Pediatric Patients with Alopecia Areata and Their Siblings: A Pilot Study. JID Innov 2021, 1, 100051. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Sorbellini, E.; Marzani, B.; Rucco, M.; Giuliani, G.; Rinaldi, F. Scalp Bacterial Shift in Alopecia Areata. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0215206. [CrossRef]
- Juhász, M.L.W.; Chen, S.; Khosrovi-Eghbal, A.; Ekelem, C.; Landaverde, Y.; Baldi, P.; Mesinkovska, N.A. Characterizing the Skin and Gut Microbiome of Alopecia Areata Patients. SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine 2020, 4, 23–30. [CrossRef]
- Won, E.J.; Jang, H.H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.J. A Potential Predictive Role of the Scalp Microbiome Profiling in Patients with Alopecia Areata: Staphylococcus Caprae, Corynebacterium, and Cutibacterium Species. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 864. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, W.-S. Comorbidities in Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019, 80, 466-477.e16. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Ramírez-Boscá, A.; Ramón-Vidal, D.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Genovés-Martínez, S.; Chenoll-Cuadros, E.; Carrión-Gutiérrez, M.; Horga de la Parte, J.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Codoñer-Cortés, F.M. Effect of Oral Administration of a Mixture of Probiotic Strains on SCORAD Index and Use of Topical Steroids in Young Patients With Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol 2018, 154, 37–43. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Martínez-Andrés, A.; Ramírez-Boscá, A.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; Carrión-Gutiérrez, M.A.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Codoñer-Cortés, F.; Ramón-Vidal, D.; Genovés-Martínez, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Administration of a Mixture of Probiotic Strains in Patients with Psoriasis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Acta Derm Venereol 2019, 99, 1078–1084. [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 1459. [CrossRef]
- Rebello, D.; Wang, E.; Yen, E.; Lio, P.A.; Kelly, C.R. Hair Growth in Two Alopecia Patients after Fecal Microbiota Transplant. ACG Case Rep J 2017, 4, e107. [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.-R.; Yang, X.-Y.; Xia, H.H.-X.; Wu, L.-H.; He, X.-X. Hair Regrowth Following Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in an Elderly Patient with Alopecia Areata: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. World J Clin Cases 2019, 7, 3074–3081. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment improves intestinal permeability and modulates microbiota dysbiosis in an experimental model of sepsis. Int J Mol Med 2019, 43, 1139–1148. [CrossRef]
- Panpetch, W.; Hiengrach, P.; Nilgate, S.; Tumwasorn, S.; Somboonna, N.; Wilantho, A.; Chatthanathon, P.; Prueksapanich, P.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Additional Candida albicans administration enhances the severity of dextran sulfate solution induced colitis mouse model through leaky gut-enhanced systemic inflammation and gut-dysbiosis but attenuated by Lactobacillus rhamnosus L34. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 465–480. [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wu, R.; Han, N.; Fu, J.; Luo, Z.; Guo, L.; Su, Y.; Du, J.; Liu Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG regulate the Th17/Treg balance in colitis via TLR4 and TLR2. Clin Transl Immunology 2020, 9, e1213. [CrossRef]
- Potrykus, M.; Czaja-Stolc, S.; Stankiewicz, M.; Kaska, Ł.; Małgorzewicz, S. Intestinal Microbiota as a Contributor to Chronic Inflammation and Its Potential Modifications. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3839. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.; Hordinsky, M.; McDonald-Hull, S.; Price, V.; Roberts, J.; Shapiro, J.; Stenn, K. Alopecia Areata Investigational Assessment Guidelines. National Alopecia Areata Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999, 40, 242–246. [CrossRef]
- Waśkiel, A.; Rakowska, A.; Sikora, M.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Trichoscopy of Alopecia Areata: An Update. J Dermatol 2018, 45, 692–700. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pellicer, P.; Navarro-Moratalla, L.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; Agüera-Santos, J.; Navarro-López, V. How Our Microbiome Influences the Pathogenesis of Alopecia Areata. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13, 1860. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Carviel, J.L.; Foley, K.A.; Shear, N.H.; Piraccini, B.M.; Piguet, V.; Tosti, A. Monotherapy for Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Skin Appendage Disord 2019, 5, 331–337. [CrossRef]
- Yee, B.E.; Tong, Y.; Goldenberg, A.; Hata, T. Efficacy of Different Concentrations of Intralesional Triamcinolone Acetonide for Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2020, 82, 1018–1021. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).