Submitted:
07 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Research Methods
Discussion
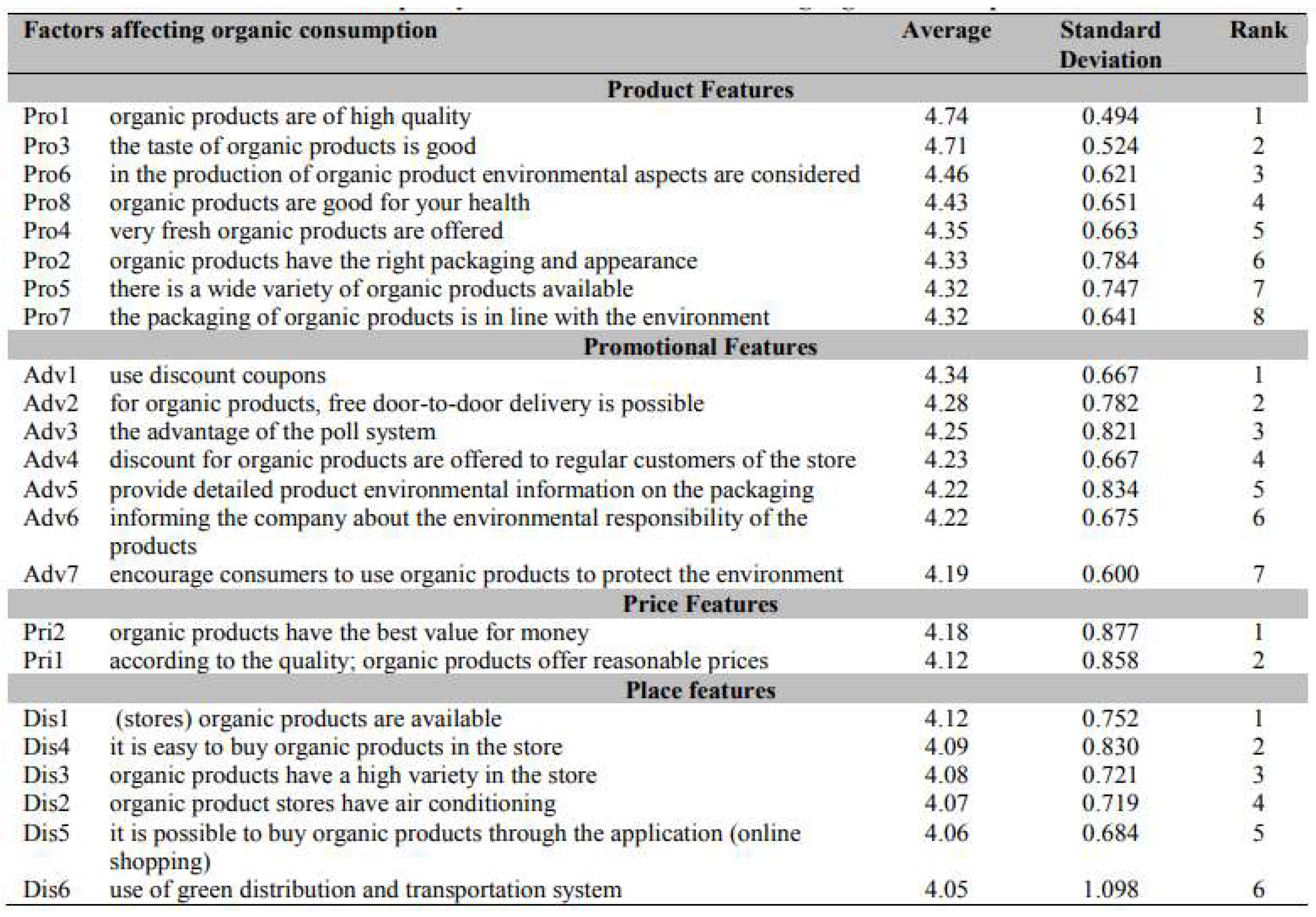
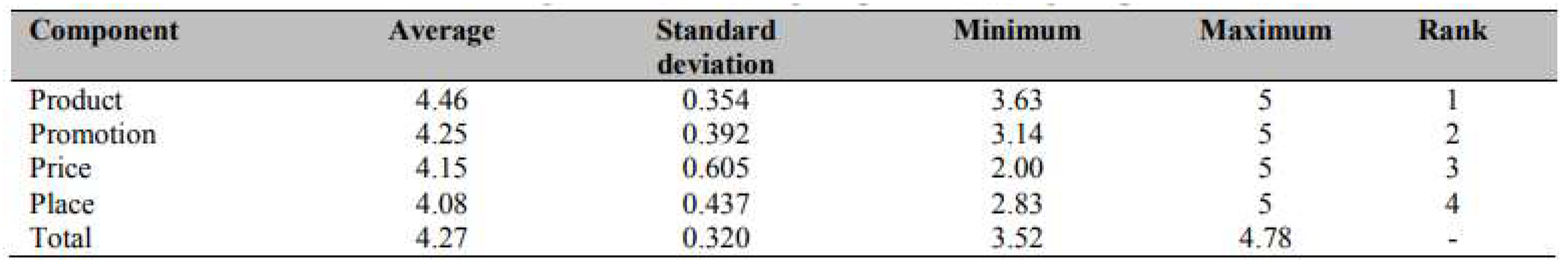
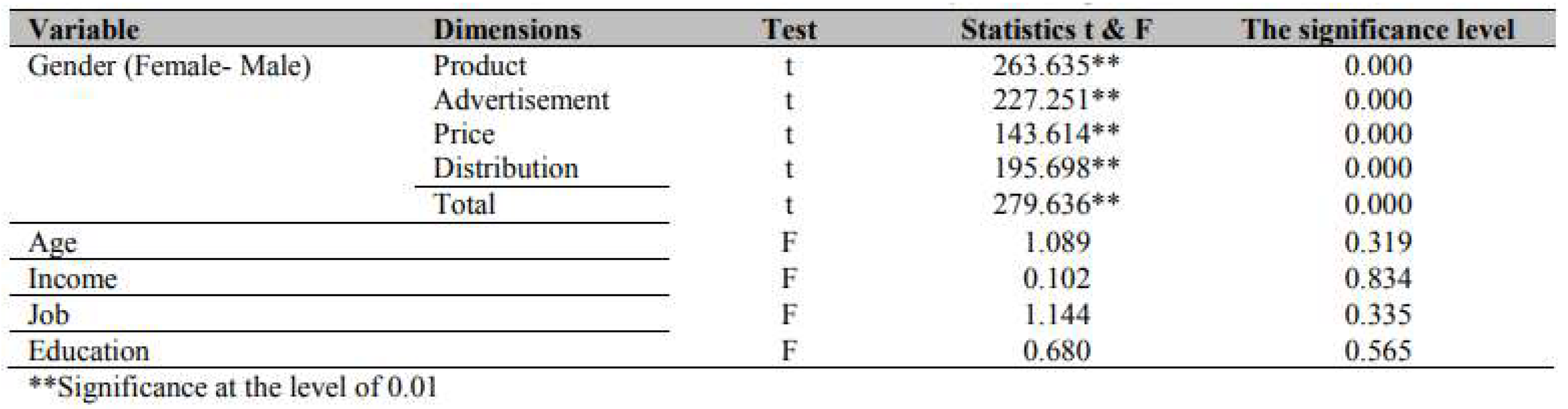
Results
References
- Abolgasemi, K. & Barghi Moghaddam, J. (2016). The Position of Green marketing on Sport Goods Consumer's Behavior by TOPSIS. 2nd International Conference on Behavioral Sciences & Social Studies, Istanbul, Turkey, 18 March.
- Azizi, Jafar, (2024). The Prospect of Food Security with Artificial Intelligence. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, Jafar, Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In-Farm (, 2024). 19 May. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, J. (2024). A Review of Food Supply Chain and Food Security's Indicators. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn. 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, Jafar and Rahmani, Seyed Mehdi Klateh, Analysis of the Data Flow Diagram in the Market of Agricultural Products (, 2024). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn. 12 May 4825. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, J. (2023). Investigating the role and effectiveness of local water use association (WUAs) in managing water resource. International Journal of Water Resources and Arid environments, 12(1): 56-66. https://www.psipw.org/attachments/article/3023/IJWRAE_APR_2023_vol12_1_56-66.
- Azizi. J. (2018). Analysis of food consumption model and food insecurity border of rural households of Guilan province. Journal of Rural Economic Research. NO.8. VOL.4. Pages: 35-50. http://ruraleconomics.kiau.ac.ir/article_536261_en.
- Azizi, J. (2007). Economic evaluation of rice marketing strategies in guilan province. Journal of agricultural sciences, 12(4), 715-728. (In Persian).
- Azizi, J. (2001). Sustainability of agricultural water. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Development, 9(36), 137-113 (In Persian).
- Azizi, J. , and Aref Eshghi, T. (2011). The Role of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in Iranian Olive Industrial Cluster. Journal of Agricultural Science. 3(1): 228-232. /: https. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, J. and Yazdani, S. (2004). Determination of Comparative Advantage of the Main Horticultural Products in Iran. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Development 46(2): 41-72.
- Azizi, J. and Yazdani, S. (2007). Investigation stability income of export date of Iran. Iranian Journal of Agricultural Science. 13(2):2-19.
- Azizi, J. , and Yazdani, S. (2006). Investigating Export market of Iran apple emphasized on the principle of comparative advantage export. Journal of Construction and Research in Agriculture and Horticulture, Vol 73, pp.
- Azizi, J. , Zarei, N. & Ali, S. (2022). The short- and long-term impacts of climate change on the irrigated barley yield in Iran: an application of dynamic ordinary least squares approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 40169–40177. [CrossRef]
- Azzam, Z. A. & Ali, N. (2019). The Relationship between Product Mix Elements and Consumer Buying Behavior: A Case of Jordan. Global Journal of Economics and Business. 6(2), 375- 384.
- Bayat V, Paknejad F, Ardakani MR, Vazan S, Azizi J, Mafakheri S (2012). Effect of methanol spraying on physiological characteristics, oil and protein yields of soybean (CV. Williams) under deficit irrigation. Ann Biol Res 3:871-883.
- Chegini Asli, R. & Saleh Ardestani, A. (2016). Measuring the impact of Green Marketing Tools on Consumer Purchasing Behavior (Case study: West of Tehran). Quarterly Journal of Management and Accounting Studies, 2(2): 1-13.
- Chovanová, H. H. , Korshunov, A. I. & Babčanová, D. (2015). Impact of Brand on Consumer Behavior. Procedia Economics and Finance, 34, 615–621. /: http. [CrossRef]
- Davari Farid, R. , Azizi, J., Allahyari, M. S., Damalas, C. A., & Sadeghpour, H. (2019). Marketing mix for the promotion of biological control among small-scale paddy farmers. International Journal of Pest Management, 65(1), 59–65. [CrossRef]
- Delafrooz, N. & Moghaddam, S. S. (2017). Green Product Consumers Segmentation Using Self Organizing Maps in Iran, International Journal of Agricultural Management and Development (IJAMAD), 7(3): 347-356.
- Dodds, W. B. , Monroe, K. B. & Grewal, D. (1991). Effects of Price, Brand, and Store Information on Buyers’ Product Evaluations. Journal of Marketing Research, 28(3), 307–319. /: http. [CrossRef]
- Elvinda. L., Evanita, S. & Patrisia, D. (2018). The Effect of Marketing Mix Satisfaction on Purchase intentions of GM Brand Helm on Students of State University of Padang. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 64. Business and Management Research, 64.
- Eskandari, S. , ZeraatKish, Y., Moghaddasi, R. and Azizi, J. (2022). Determinant factors energy efficiency and emission of pollutants Co2 & So2 in Iran's agricultural sector. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1717–1728. [CrossRef]
- Food, Industry, and Health Association. (2020). The importance of paying attention to the factors threatening the food health of the community. Available on: https://fihs.mui.ac.
- Gholampour, A. , Naami, A. & Meshbaki Esfahani, A. (2019). Presenting a social media-based marketing model in the Iranian food and organic beverages industry using them analysis method, Journal of Agricultural Economics Research, 4(11): 31-58.
- Govender, R., Bisconti, M. & Chinsamy, A. (2016). A late Miocene–early Pliocene baleen whale assemblage from Langebaanweg, west coast of South Africa (Mammalia, Cetacea, Mysticeti), Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, 40(4): 542-555. [CrossRef]
- Han, M. , Lin, H., Wang, J., Wang, Y., & Jiang, W. (2019). Turning corporate environmental ethics into firm performance: The role of green marketing programs. Business Strategy and the Environment. /: http. [CrossRef]
- Hisolp. M. (2001). An Overview of Branding and Brand name Measurement of On-Line Marketers, Dynamic Logic Branding, 101, 1-22.
- Holt. D. B. (2015). Brands and Branding, Cultural Strategy Group.
- Indumathi, N. , & Dawood, D. (2016). Impact of Marketing mix on consumer buying behavior in Organic Product. International Journal of Research in Finance and Marketing, 6: 43-54.
- Kotler, P. & Keller, K. (2016). Marketing Management, Global Edition. 15th Edition. Jilan Wineyer Publication USA.
- Kotler, P. , & Armstrong, G. (2008). Principles of Marketing, Pearson Education Internationa; 12th edition.
- Lee, M. (2014). The Effect of Product Information On Consumer Attitudes and Purchasing Intentions of Fashio Product Made of Fu, Leather, and Wool. Graduate Thesis and Dissertation. Lowa State University.Available online at: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/cgi/viewcontent. 4847. [Google Scholar]
- Maftoon, F. Farzadi, F. Aeenparast, A. Azin, A. Omidvari, S. Jahangiri, K. Sadighi, J. Ebadi, M. Montazeri, A. Vahdaninia, M. (2011). Who is responsible for health: Iranian health perception survey (IHPS). Payesh (health Monitor) Journal. 10 (3): 347-353.
- Maheshwari, S. (2014). Awareness of Green Marketing and its Influence on Buying Behavior of Consumers: Special Reference to Madhya Pradesh, India. Journal of Management & Research (AIMA), 8(4).
- Majerova, J. (2015). Analysis of Slovak Consumer's Perception of the Green Marketing Activities. Procedia Economics and Finance, 26: 553-560.
- Manafzadeh, Z. , Ghafarloo, A., Cheshm Sayadan, M., Sharifi Sendi, J., Elahi,S., Hosseinzadeh, S. & Janati, N. (2012). Does Marketing Mix Have Effect on Consumers Behavior of Dairy Products?, Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 2(6): 5823-5827.
- Masoumi, H. , Azizi, J., Masoumi, M., Rahimi MK. (2014). Effects of different levels of water deficit stress on the morphologic properties of root, antioxidants activity and the seed yield in five cultivars of soybean (Glycine max L.). Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 3: 2319–1473.
- Nakhaei, A. & Kheiry, B. (2012). Investigating the Impact of Selected Factors on Consumer Green Purchase Intention. Marketing Management Quarterly. 7(15): 105-130.
- Nasirun, N. , Noor S. M., Sultan A. A, Haniffza W. M. H. W. M. (2019). Role of Marketing Mix and Halal Certificate towards Purchase Intention of Agro Based Products. International Journal of Modern Trends in Business Research (IJMTBR), 2(7): 37-46.
- Nikzadi Panah, M. , Azizi, J. ( 12(48), 1–22.
- Nugroho, A. R. & Irena, A. (2017). "The Impact of Marketing Mix, Consumer's Characteristics, and Psychological Factors to Consumer's Purchase Intention on Brand “W” in Surabaya." iBuss Management, 5(1): 55-69.
- Onigbinde I., O. & Odunlami S. A. (2015). The influence of brand image and promotional mix on consumer buying decision-a study of beverage consumers in Lagos State, Nigeria. British Journal of Marketing Studies, 3(4): 97-109.
- Rahmati Ghofrani, Y. , Taleghani, M, & Chirani, E. (2017). Organic agriculture: food for future green consumers in Iran, International Journal of agriculture management and development, 7(2): 179-189.
- Ranaei Kordshooli, H. & Allahyari Bouzanjani, A. (2012). Investigating the Effect of Green Marketing Mix on Green Purchasing Decision of Consumers with a Case Study on Consumers of Shiraz Pegah Dairy Company. New Marketing Research Journal, 2(5): 165-180.
- Rostamzadeh, R. & Alimohammadi Siyaban, A. (2016). The Effects of Environmental Factors on Green Marketing Performance (Case Study: Shirin Asal Company). Journal of Value Chain Management, 1(1): 47-72. Sabouri, Sh. (2011). Green Marketing in Iran: Potentials and challenges, The First Green Marketing Conference in Iran, 14-23.
- Saleki, Z. S. , Seyedsaleki, S. M., & Rahimi, M. R. (2012). Organic Food Purchasing Behaviour in Iran. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(13): 278-285.
- Shirai, M. (2015). Impact of “High Quality, Low Price” Appeal on Consumer Evaluations. Journal of Promotion Management, 21(6), 776–797. /: http. [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A. & Santhosh, J. (2015). A study on consumers’ perception on eco-friendly product with reference to Kollam district in Kerala. EPRA International Journal of economic and business review. 3(7): 146-148. Available on: http://epratrust.com/articles/upload/25.Anu%20Varghese%20&%20Santhosh%20J.
- Winkielman, P. , Shwarz, N. & Fazenderio, A. T. (2000). Affective and Cognitive Consequences of Visual Fluency: When Seeing is Easy on the Mind in, Visual Pre. Ed. Ann-Arobor. Michigan, USA.
- Zarei, Nasibeh and Azizi, Jafar, Correlation Between Food Security, Climate Change, and Women Role (, 2024). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn. 24 February 4737. [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





