Submitted:
09 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Histological Findings of the Primary Tumor
3.3. Clinical Features of BM from TC
3.4. Treatment
3.5. Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pu W, Shi X, Yu P, Zhang M, Liu Z, Tan L, Han P, Wang Y, Ji D, Gan H, Wei W, Lu Z, Qu N, Hu J, Hu X, Luo Z, Li H, Ji Q, Wang J, Zhang X, Wang YL. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of the tumor ecosystems underlying initiation and progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 6058.
- Hong YW, Lin JD, Yu MC, Hsu CC, Lin YS. Outcomes and prognostic factors in thyroid cancer patients with cranial metastases: A retrospective cohort study of 4,683 patients. Int J Surg. 2018, 55, 182–187. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim SS, Kim SM, Park M, Suh SH, Ahn SJ. Clinico-radiological features of brain metastases from thyroid cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e28069. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih EA, Hussein MH, Zerfaoui M, Attia AS, Marzouk Ellythy A, Mostafa A, Ruiz EML, Shama MA, Russell JO, Randolph GW, Kandil E. Site-specific metastasis and survival in papillary thyroid cancer: the importance of brain and multi-organ disease. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1625. [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Gordoa, T. Multimodal approach to the treatment of patients with radioiodine refractory differentiated thyroid cancer and metastases to the central nervous system. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell AL, Gandhi A, Scott-Coombes D, Perros P. Management of thyroid cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines. J Laryngol Otol 2016, 130, S150–S160. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbiotti MA, Livolsi V. Brain metastases of papillary thyroid carcinoma origin are derived from aggressive histologic variants and demonstrate similar adverse morphology in the metastatic lesion. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2023, 227, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo J, Kim HJ, Kim SM, Park HH. Prognostic factors to predict the efficacy of surgical interventions against brain metastasis secondary to thyroid cancer. Eur Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e220087. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon JH, Jeon MJ, Kim M, Hong AR, Kim HK, Shin DY, Kim BH, Kim WB, Shong YK, Kang HC. Unusual metastases from differentiated thyroid cancers: A multicenter study in Korea. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0238207.
- Saito F, Uruno T, Shibuya H, Kitagawa W, Nagahama M, Sugino K, Ito K. Prognosis after brain metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg. 2016, 40, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques de Figueiredo B, Godbert Y, Soubeyran I, Carrat X, Lagarde P, Cazeau AL, Italiano A, Sargos P, Kantor G, Loiseau H, Bonichon F. Brain metastases from thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study of 21 patients. Thyroid. 2014, 24, 270–6.
- Wu SS, Lamarre ED, Scharpf J, Prendes B, Ku JA, Silver N, Burkey B, Woody N, Campbell SR, Yilmaz E, Koyfman SA, Geiger J. Survival Outcomes of Advanced Thyroid Cancer Enriched in Brain Metastases Following Treatment With Small Molecule Inhibitors. Endocr Pract. 2023, 29, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu T, Jiao Z, Li Y, Peng J, Yao F, Chen W, Yang A. Brain metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study of 22 patients. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021, 12, 730025.
- Alimonti P, Gonzalez Castro LN. The current landscape of immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy for primary and metastatic brain tumors. Antibodies (Basel). 2023, 12, 27.
- Osborne JR, Kondraciuk JD, Rice SL, Zhou X, Knezevic A, Spratt DE, Sabra M, Larson SM, Grewal RK. Thyroid Cancer Brain metastasis: survival and genomic characteristics of a large tertiary care cohort. Clin Nucl Med 2019, 44, 544–549. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Lima C., J. , Wu, D., Rao, S. N., Punukollu, S., Hritani, R., Zeymo, A., Burman, K. D. Brain metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma: prevalence, current therapies, and outcomes. Journal of the Endocrine Society 2019, 3, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatz T, Levy A, Merenzon M, Bystrom L, Berry K, Morell A, Bhatia S, Daggubati L, Higgins D, Schlumbrecht M, Komotar RJ, Shah AH, Ivan ME. Surgically treated brain metastases from uterine origin: a case series and systematic review. World Neurosurg 2023, 173, e91–e108. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos N, Lampros MG, Filis P, Voulgaris S, Alexiou GA. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiotherapy after resection of solitary brain metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg X. 2023, 18, 100170. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostampour N, Badrigilan S, Rezaeian S, Sarbakhsh P, Meola A, Choupani J, Doosti-Irani A, Nemati H, Almasi T, Chang SD. Efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery as single or combined therapy for brain metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2023, 186, 104015. [CrossRef]
- Blomain E, Berta S, Hug N, Giao D, Meola A, Binkley M, Hui C, Churilla T, Shahsavari N, Desai K, Chang S, Soltys S, Pollom E. Radiotherapy for brain metastases from thyroid cancer: an institutional and national retrospective cohort study. Thyroid. 2022, 32, 781–788. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo H, Liao X, Qin Y, Hou Q, Xue Z, Liu Y, Shen F, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Song L, Chen H, Zhang L, Wei T, Dai L, Yang L, Zhang W, Li Z, Xu H, Zhu J, Shu Y. Longitudinal genomic evolution of conventional papillary thyroid cancer with brain metastasis. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 620924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsabbagh R, Ahmed M, Alqudah MAY, Hamoudi R, Harati R. Insights into the molecular mechanisms mediating extravasation in brain metastasis of breast cancer, melanoma, and lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 2258. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann EJ, Petrakakis I, Polemikos M, Raab P, Cinibulak Z, Nakamura M, Krauss JK. Electromagnetic navigationguided surgery in the semi-sitting position for posterior fossa tumours: a safety and feasibility study. Acta Neurochir 2015, 157, 1229–1237. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong B, Wiese B, Bremer M, Heissler HE, Heidenreich F, Krauss JK, Nakamura M. Multiple microsurgical resections for repeated recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013, 36, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Bunevicius A, Fribance S, Pikis S, Lee JYK, Buch LY, Moran M, Yang AI, Bernstein K, Mathieu D, Perron R, Liscak R, Simonova G, Patel S, Trifiletti DM, Martínez Álvarez R, Martínez Moreno N, Lee CC, Yang HC, Strickland BA, Zada G, Chang EL, Kondziolka D, Sheehan J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for differentiated thyroid cancer brain metastases: an international, multicenter study. Thyroid. 2021, 31, 1244–1252.
- Colombo E, Ottini A, Licitra L. Oligometastatic disease from differentiated thyroid cancer: best treatment schemes. Curr Opin Oncol 2023, 35, 15–21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi J, Kim JW, Keum YS, Lee IJ. The Largest known survival analysis of patients with brain metastasis from thyroid cancer based on prognostic groups. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0154739. [Google Scholar]
- Park H, Park J, Park SY, Kim TH, Kim SW, Chung JH. Clinical course from diagnosis to death in patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 2323. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota N, Robinson B, Shah M, Hoff AO, Taylor MH, Li D, Dutcus CE, Lee EK, Kim SB, Tahara M. Defining radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: efficacy and safety of lenvatinib by radioiodine-refractory criteria in the SELECT Trial. Thyroid 2017, 27, 1135–1141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon H, Kim JW, Park M, Kim JW, Kim M, Suh SH, Chang YS, Ahn SJ, Lee JM. Brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma may preferentially involve the distal middle cerebral artery territory and cerebellum. Front Oncol. 2020, 10, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyeong S, Cha YJ, Ahn SG, Suh SH, Son EJ, Ahn SJ. Subtypes of breast cancer show different spatial distributions of brain metastases. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0188542. [Google Scholar]
- Lee JS, Lee JS, Yun HJ, Chang H, Kim SM, Lee YS, Chang HS, Park CS. Prognosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer with distant metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui JK, Perlow HK, Upadhyay R, McCalla A, Raval RR, Thomas EM, Blakaj DM, Beyer SJ, Palmer JD. Advances in radiotherapy for brain metastases. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2023, 32, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha LN, Khanh LQ, Hanh NTM, Seo HJ, Son MH. Screening and treatment of brain metastasis from papillary thyroid carcinoma: a case series. Thyroid Res. 2023, 16, 1. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng J, Yan Z, Cheng W, Wang Z, Chen Z, You W, Wang Z. Long-term survival of patients with intracranial metastases from thyroid cancer presenting with seizures: a case report and literature review. Transl Cancer Res 2023, 12, 439–446. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahed BV, Alvarez-Breckenridge C, Brastianos PK, Shih H, Sloan A, Ammirati M, Kuo JS, Ryken TC, Kalkanis SN, Olson JJ. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Role of Surgery in the Management of Adults With Metastatic Brain Tumors. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, E152–E155.
- McWilliams RR, Giannini C, Hay ID, Atkinson JL, Stafford SL, Buckner JC. Management of brain metastases from thyroid carcinoma: a study of 16 pathologically confirmed cases over 25 years. Cancer 2003, 98, 356–62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu NW, Jiang HJ, Wu CW, Chiang FY, Chiou HC, Hsiao PJ. Lenvatinib complementary with radioiodine therapy for patients with advanced differentiated thyroid carcinoma: case reports and literature review. World J Surg Oncol. 2019, 17, 84. [CrossRef]
- Slutzky-Shraga I, Gorshtein A, Popovitzer A, Robenshtok E, Tsvetov G, Akirov A, Hirsch D, Benbassat C. Clinical characteristics and disease outcome of patients with non-medullary thyroid cancer and brain metastases. Oncol Lett. 2018, 15, 672–676.
- Akiba T, Kunieda E, Kogawa A, Komatsu T, Tamai Y, Ohizumi Y. Re-irradiation for metastatic brain tumors with whole-brain radiotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012, 42, 264–269. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu AC, Delpassand ES, Sherman SI. Prognosis and treatment of brain metastases in thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997, 82, 3637.
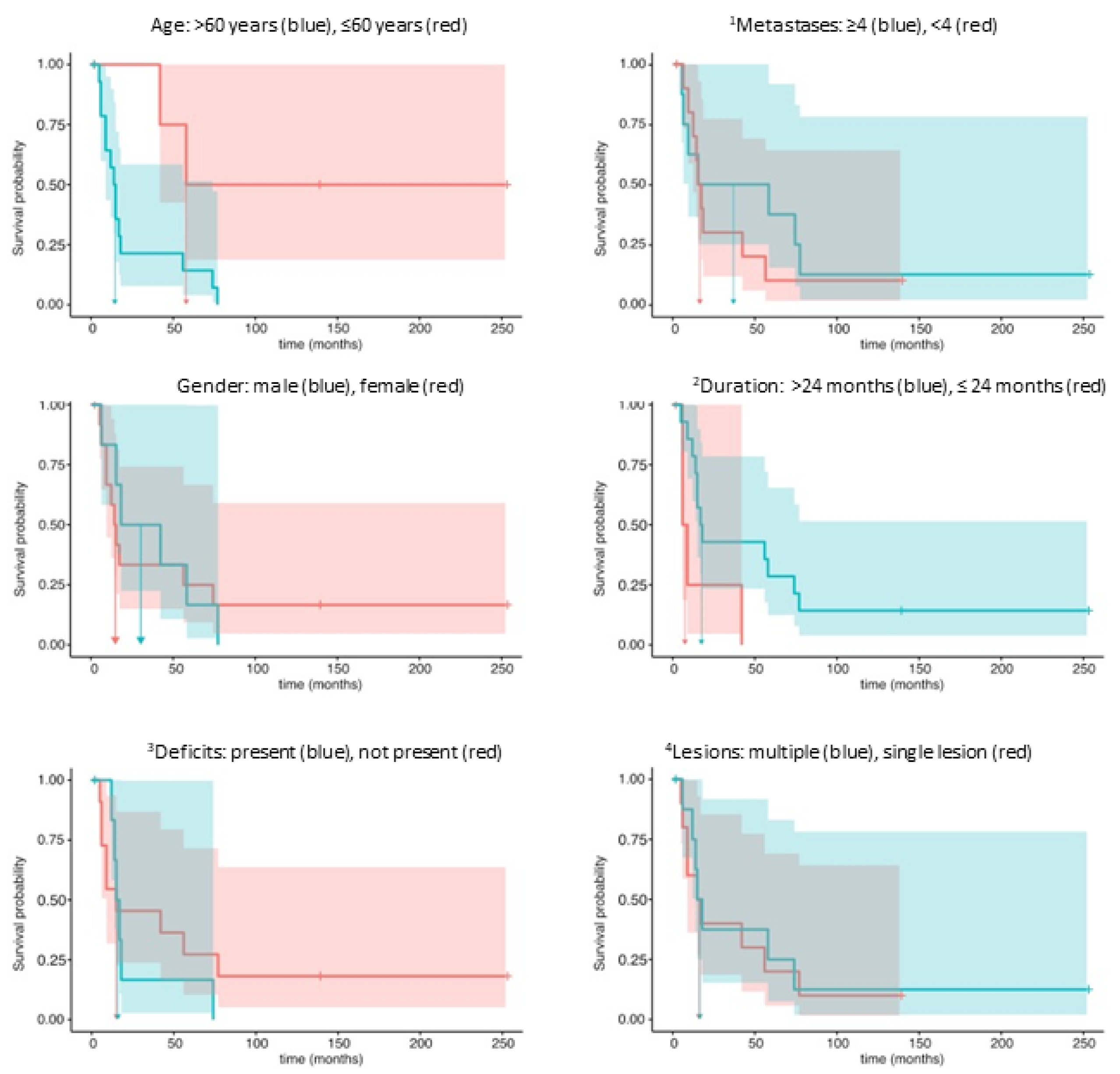
| Predictor | Meaning | Threshold | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | patients’ age | ≤60, >60 | years |
| Duration | time interval between the initial and brain metastasis diagnostics | ≤24, >24 | months |
| Metastases | number of metastases found | ≤4, >4 | |
| Neurological deficits | existence of neurological deficits | yes, no | |
| Gender | patient gender | male, female | |
| Lesions | number of intracranial lesions | single, multiple |
| N | |
|
Mean age at BM diagnosis (yr) |
64.8 (26-89) |
|
Mean interval between initial diagnosis to BM diagnosis (months) |
63.4 ± 58.4 |
|
Mean interval between BM diagnosis to death (months) |
41.2 ± 60.7 |
|
Symptoms associated with BM |
|
| Yes | 11 |
| No | 9 |
|
Modalitiy of diagnosis |
|
| MRI | 8 |
| CT | 6 |
| FDG-PET-CT | 3 |
| 131J-Scinti | 3 |
|
KPSS |
|
| > 70% | 17 |
| ≤ 70% | 3 |
|
Number of intracranial lesions |
|
| Single | 10 |
| Multiple | 10 |
|
Number of distant metastases |
|
| ≤ 3 | 11 |
| > 3 | 8 |
| Unknown | 1 |
|
Treatment |
|
| Surgery | 15 |
| Radiosurgery | 1 |
| WBRT | 3 |
| Isotretinoin | 1 |
|
Postoperative adjuvant therapy |
|
| WBRT | 10 |
| RCT | 1 |
| Radioactive iodine | 1 |
| WBRT + TKI | 1 |
| WBRT + Isotretinoin | 1 |
| None | 6 |
| Covariate | Coef | HR | 95% - CIcoef | LR Test | p | unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (>60) | 1,8228 | 6.1892 | 0,6865, 3,5655 | chi2(1) = 12,0981 | 0.0005 | years |
| Duration (>24) | -1,5682 | 0.2084 | -2,8077, -0,5466 | chi2(1) = 9,2470 | 0.0024 | months |
| Metastases (<4) | 0,4846 | 1.6235 | -0,1578, 1,2459 | chi2(1) = 2,1383 | 0.1437 | |
| Neurological deficits (no) | -0,2417 | 0.7853 | -1,1459, 0,7033 | chi2(1) = 0,2721 | 0.6020 | |
| Gender (female) | 0,0712 | 1.0738 | -0,5441, 0,7342 | chi2(1) = 0,0501 | 0.8229 | |
| Lesions (multiple) | -0,0267 | 0.9737 | -0,7675, 0,7816 | chi2(1) =0,0048 | 0.9450 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





