Submitted:
08 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Context
1.2. Research Questions
- RQ1. Among surgeons performing surgery (P), does the incorporation of mixed reality tools (I), lead to increased precision, accuracy, and overall performance during surgery compared to conventional approaches (O)?
- RQ2. In patients undergoing surgery (P), does the use of mixed reality technology during the surgical procedure (I), result in improved surgical outcomes, such as reduced operation time, lower complication rates, or enhanced patient recovery compared to traditional surgical methods (O)?
- RQ3. In the context of surgery (P), how does the application of mixed reality technology (I), impact the learning curve and skill acquisition for surgical trainees compared to traditional training methods?
- RQ4. Among healthcare institutions implementing mixed reality in surgery (P), what are the cost implications and resource requirements (I), and how do these factors compare to traditional surgical approaches in terms of overall economic feasibility and sustainability (O)?
1.3. Document Structure
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
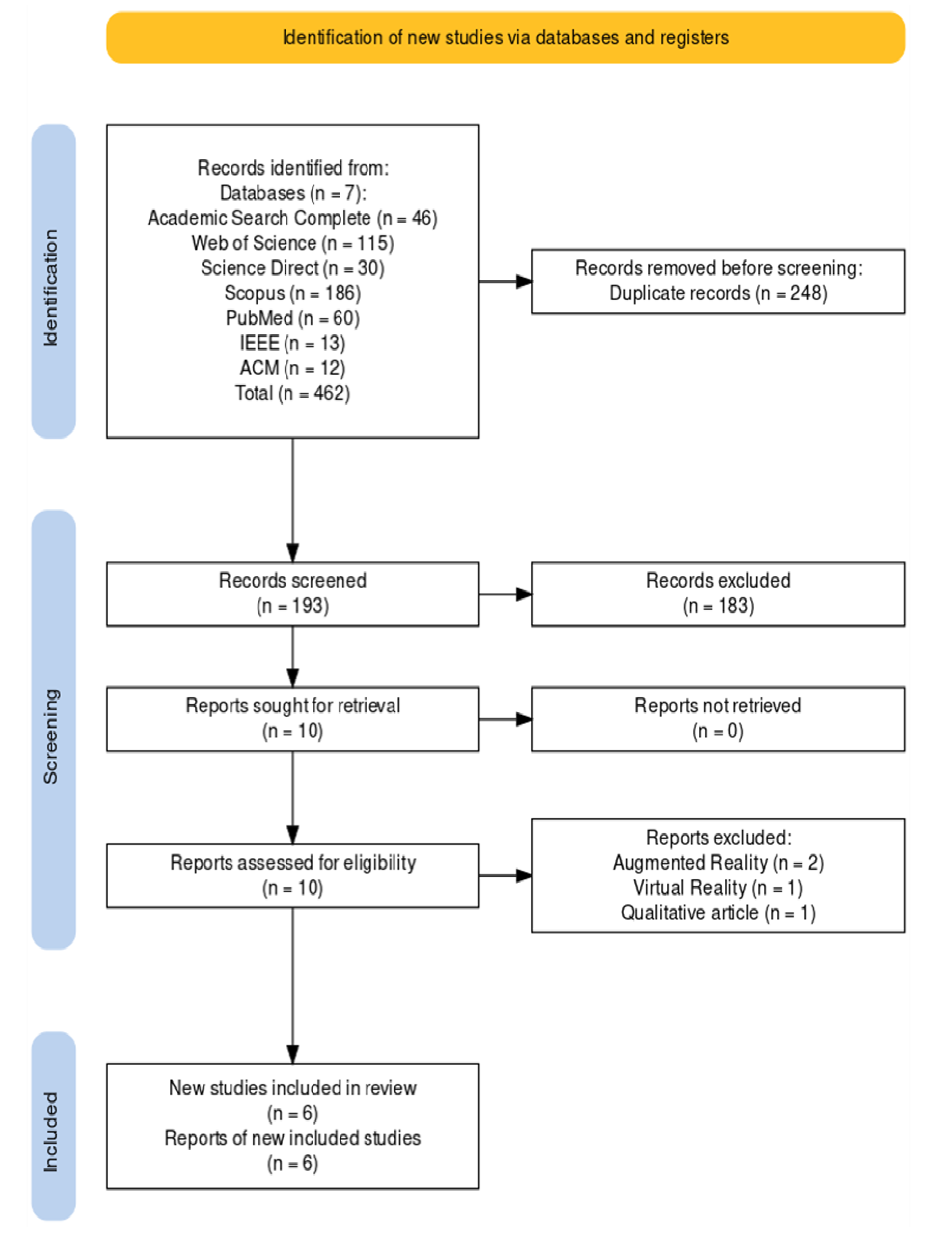
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Quality Assessment in Systematic Reviews
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
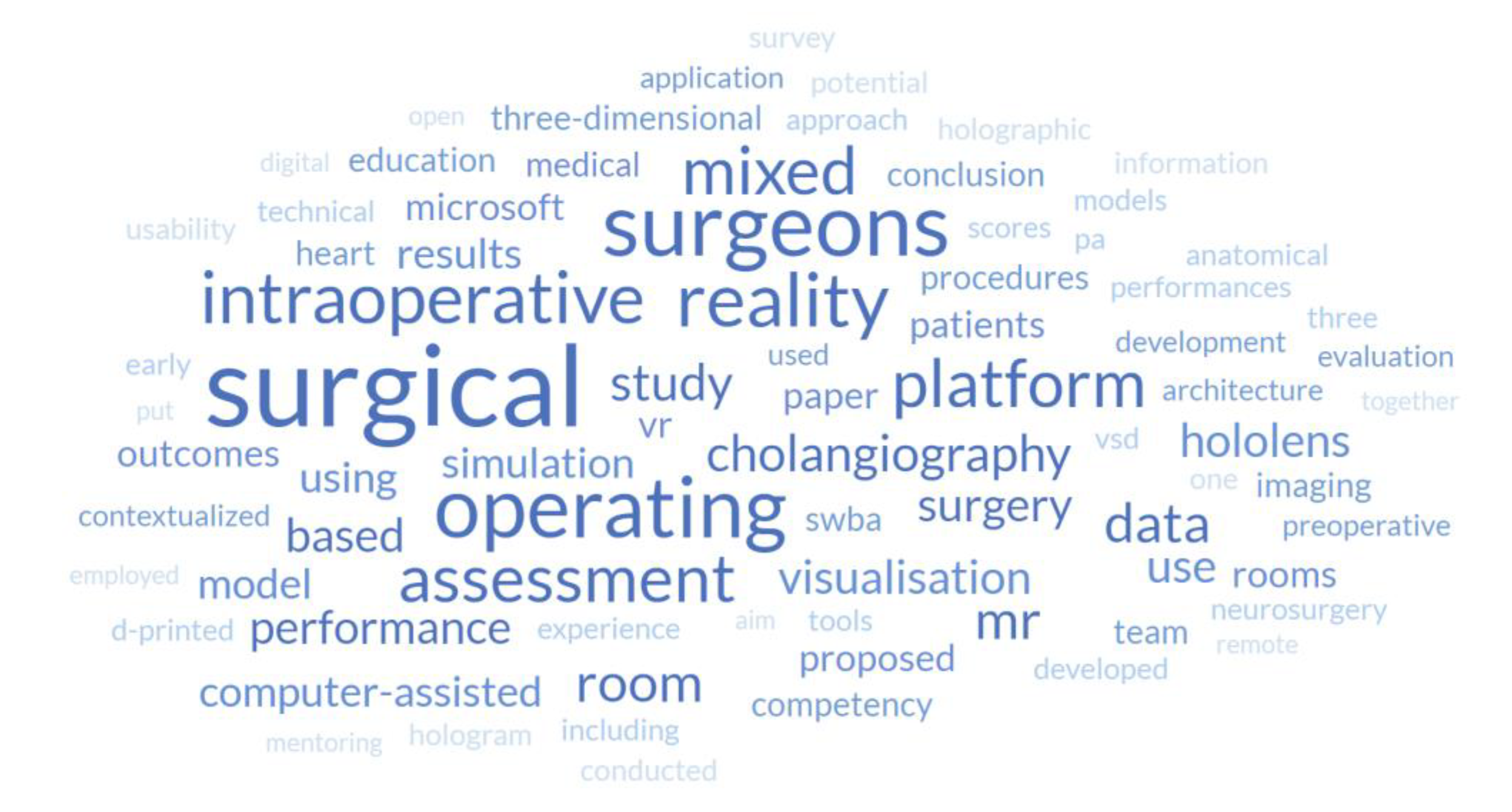
3.2. Keyword Identification and Frequency
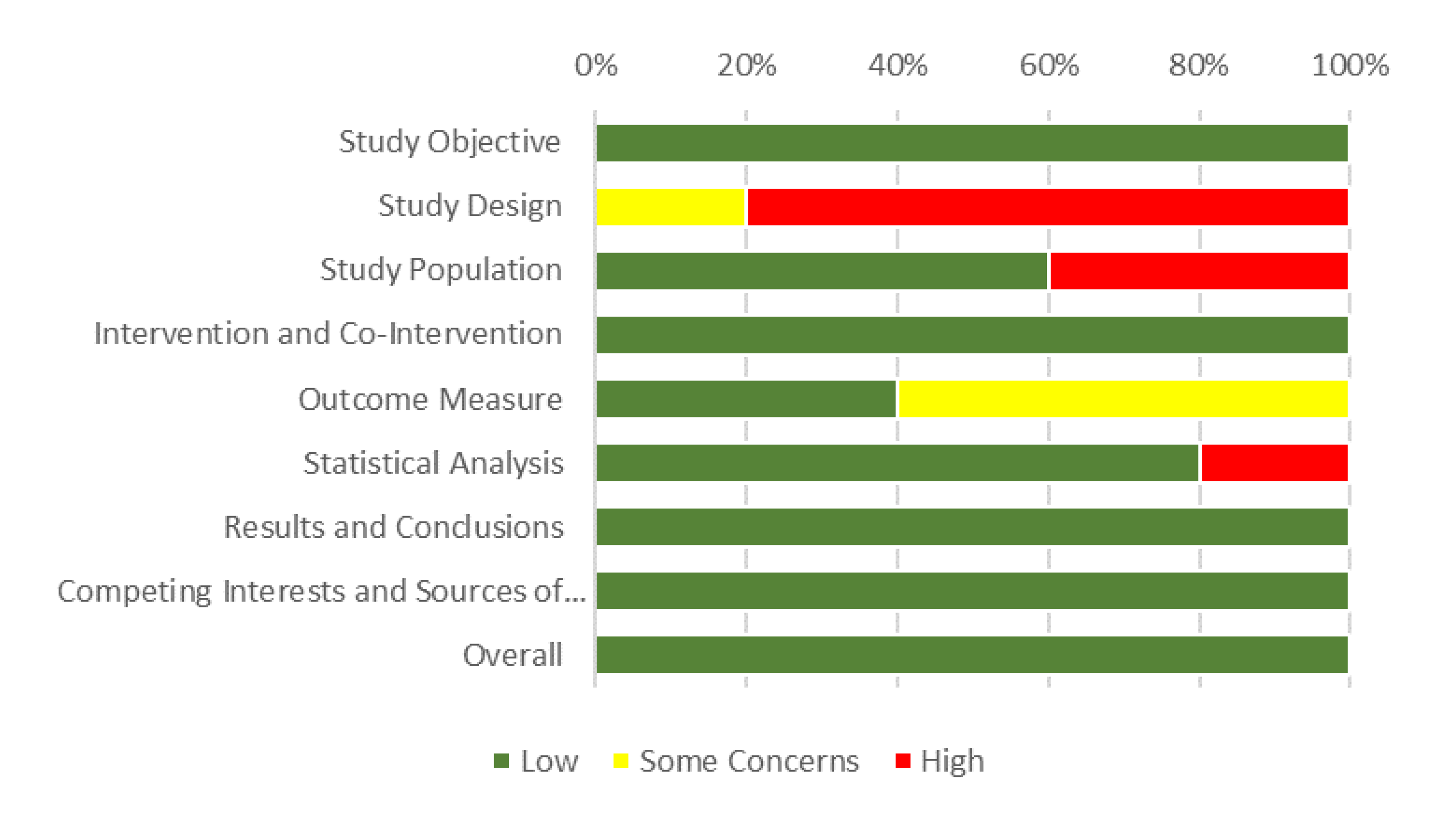
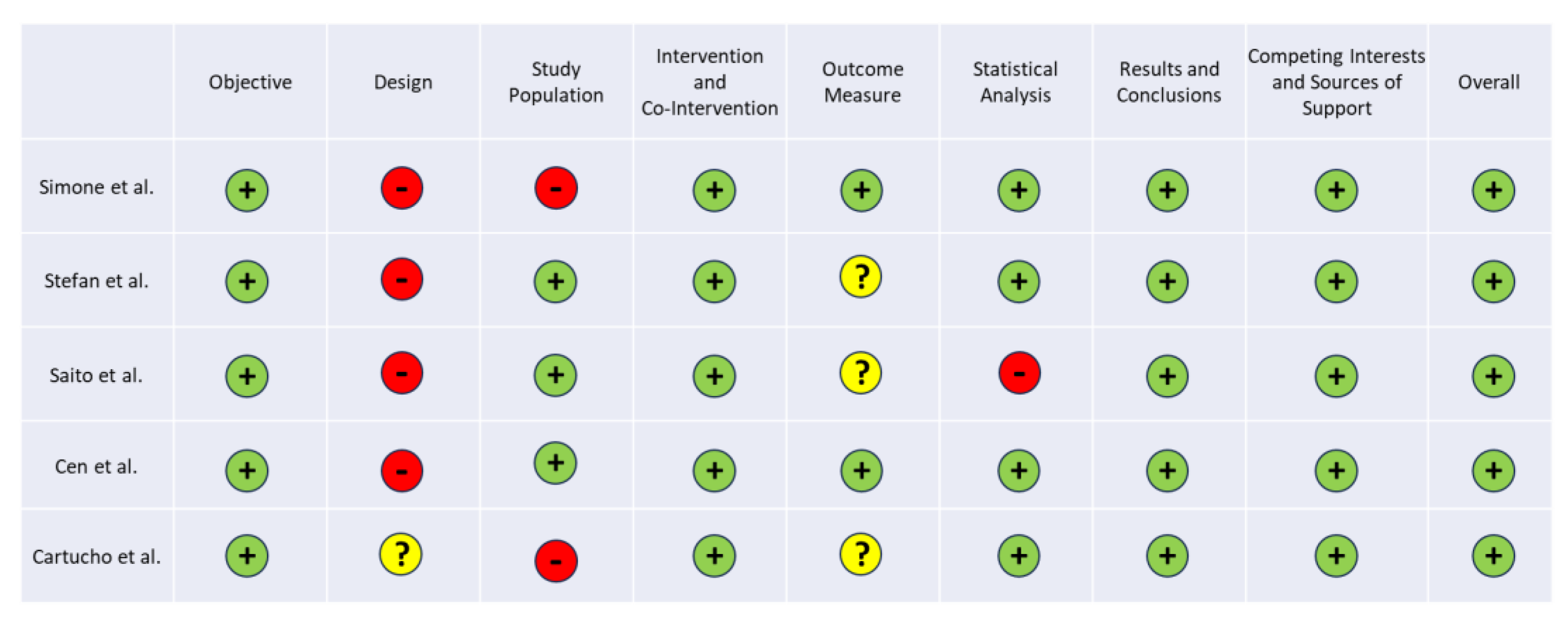
3.3. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Highlights
4.2. Answers to Research Questions
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
5.1. Mixed Reality in the Operating Room
5.2. Open Challenges and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- J. R. Kirkup, “The history and evolution of surgical instruments,” Ann R Coll Surg Engl, vol. 63, no. 4, 1981, Accessed: Nov. 03, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2493802/.
- K. E. Roberts, R. L. Bell, and A. J. Duffy, “Evolution of surgical skills training,” World Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 12, no. 20, pp. 3219–3224, May 2006. [CrossRef]
- L. Coelho, Q. Ricardo, and S. Reis, Emerging Advancements for Virtual and Augmented Reality in Healthcare. IGI Global, 2021.
- D. Kamińska, G. Zwolińsksi, A. Laska-Leśniewicz, and L. P. Coelho, “Virtual Reality in Healthcare: A Survey,” in Emerging Advancements for Virtual and Augmented Reality in Healthcare, IGI Global, 2022, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- B. L. Wong and S. A. Clark, “Assessing the effectiveness of animation and virtual reality in teaching operative dentistry,” Journal of Dentistry, vol. 1, no. 1, 2000.
- Saylany, M. Spadola, R. Blue, N. Sharma, A. K. Ozturk, and J. W. Yoon, “The Use of a Novel Heads-Up Display (HUD) to View Intra-Operative X-Rays During a One-Level Cervical Arthroplasty,” World Neurosurgery, vol. 138, pp. 369–373, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Milgram and F. Kishino, “A Taxonomy of Mixed Reality Visual Displays,” IEICE Trans. Information Systems, vol. E77-D, no. 12, pp. 1321–1329, Dec. 1994.
- W. Qian, “What is mixed reality? - Mixed Reality.” Accessed: Oct. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/mixed-reality/discover/mixed-reality.
- P. Milgram, H. P. Milgram, H. Takemura, A. Utsumi, and F. Kishino, “Augmented reality: a class of displays on the reality-virtuality continuum,” in Telemanipulator and Telepresence Technologies, SPIE, Dec. 1995, pp. 282–292. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Vervoorn, M. M. T. Vervoorn, M. Wulfse, T. P. C. Van Doormaal, J. P. Ruurda, N. P. Van der Kaaij, and L. M. De Heer, “Mixed Reality in Modern Surgical and Interventional Practice: Narrative Review of the Literature,” JMIR Serious Games, vol. 11, p. e41297, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Sánchez-Margallo, C. Plaza de Miguel, R. A. Fernández Anzules, and F. M. Sánchez-Margallo, “Application of Mixed Reality in Medical Training and Surgical Planning Focused on Minimally Invasive Surgery,” Frontiers in Virtual Reality, vol. 2, 2021, Accessed: Dec. 03, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frvir.2021.692641.
- P. Guha, J. Lawson, I. Minty, J. Kinross, and G. Martin, “Can mixed reality technologies teach surgical skills better than traditional methods? A prospective randomised feasibility study,” BMC Medical Education, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 144, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Bollen, L. Awad, B. Langridge, and P. E. M. Butler, “The intraoperative use of augmented and mixed reality technology to improve surgical outcomes: A systematic review,” Int J Med Robot, vol. 18, no. 6, p. e2450, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Page et al., “The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews,” BMJ, vol. 372, p. n71, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Moher, A. Liberati, J. Tetzlaff, D. G. Altman, and T. P. Group, “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement,” PLOS Medicine, vol. 6, no. 7, p. e1000097, Jul. 2009. [CrossRef]
- “IHE Quality Appraisal Checklist for Case Series Studies.” Accessed: Nov. 02, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ihe.ca/publications/ihe-quality-appraisal-checklist-for-case-series-studies.
- G. A. Wells et al., “The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses.” Accessed: Nov. 02, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.
- M. Simone et al., “Remote mentoring in laparotomic and laparoscopic cancer surgery during Covid-19 pandemic: an experimental setup based on mixed reality,” Medical Education Online, vol. 26, no. 1, p. 1996923, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Stefan et al., “Computer-assisted simulated workplace-based assessment in surgery: application of the universal framework of intraoperative performance within a mixed-reality simulation,” BMJ Surgery, Interventions, & Health Technologies, vol. 5, no. 1, p. e000135, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Cen et al., “Three-Dimensional Printing, Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality for Pulmonary Atresia: Early Surgical Outcomes Evaluation,” Heart, Lung and Circulation, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 296–302, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Saito et al., “Intraoperative support with three-dimensional holographic cholangiography in hepatobiliary surgery,” Langenbecks Arch Surg, vol. 407, no. 3, pp. 1285–1289, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Cartucho and D. Shapira, “Multimodal mixed reality visualisation for intraoperative surgical guidance | International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery,” International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, vol. 15, pp. 819--826, 2020.
- R. Galati, M. Simone, G. Barile, R. De Luca, C. Cartanese, and G. Grassi, “Experimental Setup Employed in the Operating Room Based on Virtual and Mixed Reality: Analysis of Pros and Cons in Open Abdomen Surgery,” Journal of Healthcare Engineering, vol. 2020, p. e8851964, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Veloso, R. Magalhães, A. Marques, P. V. Gomes, and J. Pereira, “Mixed Reality in an Operating Room Using Hololens 2—The Use of the Remote Assistance from Manufacturers Technicians during the Surgeries,” Engineering Proceedings, vol. 7, no. 1, Art. no. 1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Zhu, A. Hadadgar, I. Masiello, and N. Zary, “Augmented reality in healthcare education: an integrative review,” PeerJ, vol. 2, p. e469, Jul. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Reis, P. Guimarães, F. Coelho, E. Nogueira, and L. Coelho, “A framework for simulation systems and technologies for medical training,” in 2018 Global Medical Engineering Physics Exchanges/Pan American Health Care Exchanges (GMEPE/PAHCE), Mar. 2018, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
| Study | Country | Technology | Areas of Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simone et al. [18] | Italy | HMD | Remote mentoring |
| Stefan et al. [19] | Germany and Austria | HMD | Competency assessment of professionals |
| Cen et al. [20] | China | HoloLens | Assisting tool to cardiac surgery |
| Saito et al. [21] | Japan | HoloLens, HoloeyesXR and Magic Leap 1 | Intraoperative support system: 3D holographic cholangiography in hepatobiliary surgery |
| Cartucho et al. [22] | UK/Switzerland | HoloLens | Image-guided surgery |
| Galati et al. [23] | Italy | HoloLens | Open abdomen surgery |
| Study | Metrics | Results | Implemented Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simone et al. [18] | Likert-type scale questioning the students about the experience | Well accepted by the trainees | Mentoring students remotely using Mixed Reality |
| Stefan et al. [19] | OSATS and OTAS assessment scores | Established method to evaluate the intraoperative performance | Use of a mixed-reality environment to simulate the surgical procedure |
| Cen et al. [20] | Surgery duration, patient’s stay duration and recovery, RV to aortic peak systolic pressure ratio and change in baseline oxygen saturation | Easier to understand the surgical procedure and more interactive and simpler for trainees | Perioperative assistive tool during surgery, for visualization |
| Saito et al. [21] | Qualitative analysis | Operators can move the hologram from the respective operators’ angles by means of easy gesture-handling without any monitors, and several surgeons wearing HMDs can share the same hologram. A more accurate reappearance of the bile duct can decrease the surgeon’s stress level and facilitate the performance of a safer and more precise operation; | 3D holographic cholangiography; remote medical education sessions |
| Cartucho et al. [22] | Usability questionnaire filled out by surgeons and subsequently analyzed | Improve surgical outcomes by providing real-time guidance and enhancing the surgeon's understanding of the patient's anatomy | MR visualization platform which projects multiple imaging modalities to assist intraoperative surgical guidance |
| Galati et al. [23] | Table with user feedback on the procedure with and without HoloLens | It can increase the execution speed by allowing multitasking procedures, by checking medical images at high resolution without leaving the operating table and the patient | Visualize information about the results of medical screenings, such as radiography, blood tests, and magnetic resonance imaging; visual information on the patient’s body by using mixed reality tools; sharing information with other professionals, this being useful for training, remote tutoring, and for receiving external advice from other physicians |
| Study | Effects and Costs | Challenges and Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Simone et al. [18] | Low-cost implementation that allows remote teaching | Complex technical tuning |
| Stefan et al. [19] | Possibility to evaluate intraoperative competences, in an immersive simulation | Lack of confidence with the technology, hesitation while during observation |
| Cen et al. [20] | Facilitates the surgical planning and more dynamic than 3D printed models | Harder to learn for older professors and dizziness. Imaging techniques require contrast |
| Saito et al. [21] | Better accuracy, the operator could perform the dissection more safely with better imaging; improved observation of the 3D biliary anatomy from various angles and sharing of the same hologram from the respective operators' angles; it revealed several new intraoperative findings regarding the biliary anatomy. | 3D holographic cholangiography; remote medical education sessions |
| Cartucho et al. [22] | Scrolling through volumetric data and adjusting the virtual objects transparency to avoid obstructing the surgeons view of the operating site | MR visualization platform which projects multiple imaging modalities to assist intraoperative surgical guidance |
| Galati et al. [23] | It can increase the execution speed of surgical procedures by allowing multitasking procedures, such as checking medical images at high resolution without leaving the operating table and the patient | Visualize information about the results of medical screenings, sharing information with other professionals, this being useful for training, remote tutoring, and for receiving external advice from other physicians |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





