Submitted:
24 May 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
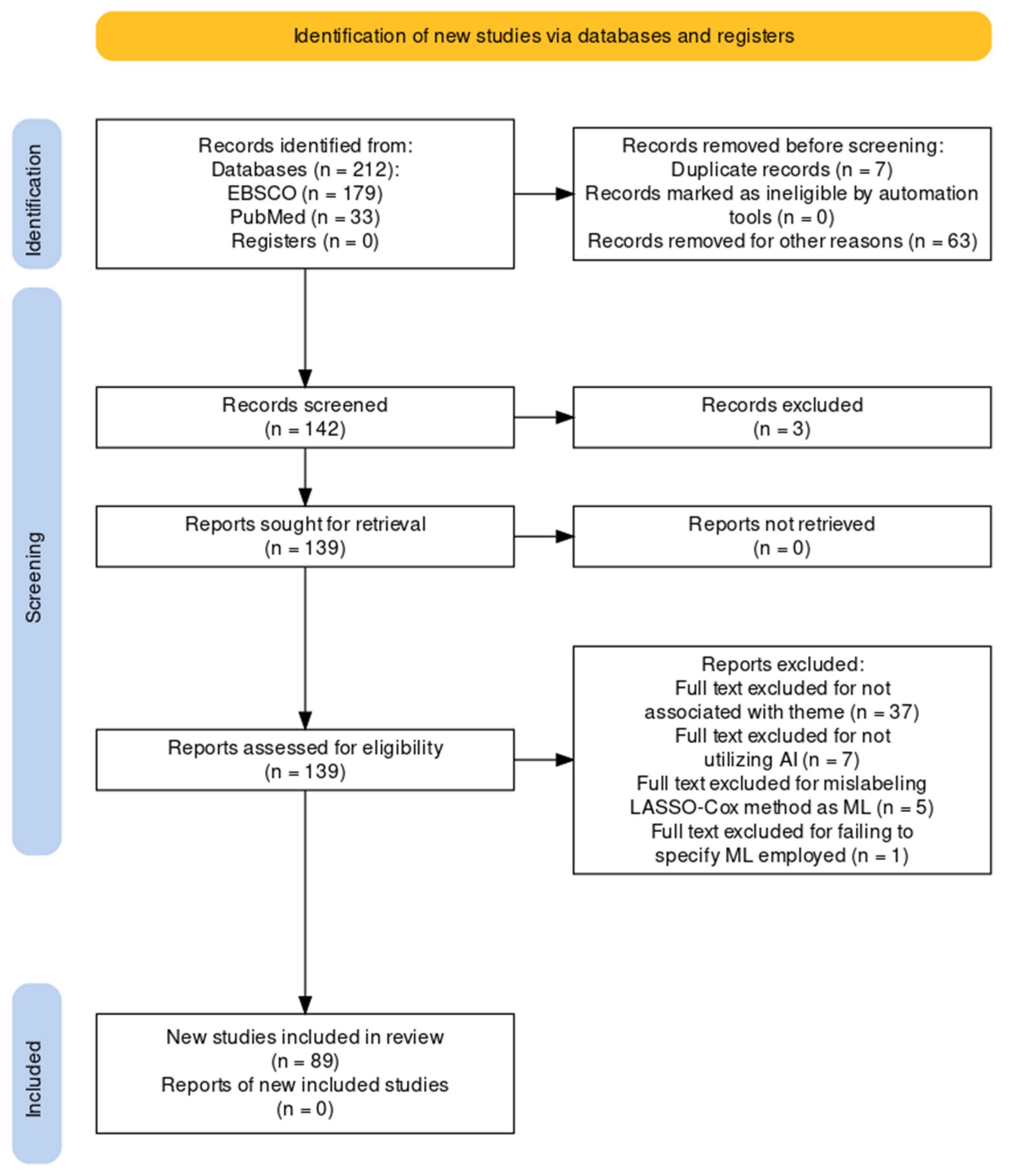
2. Materials and Methods
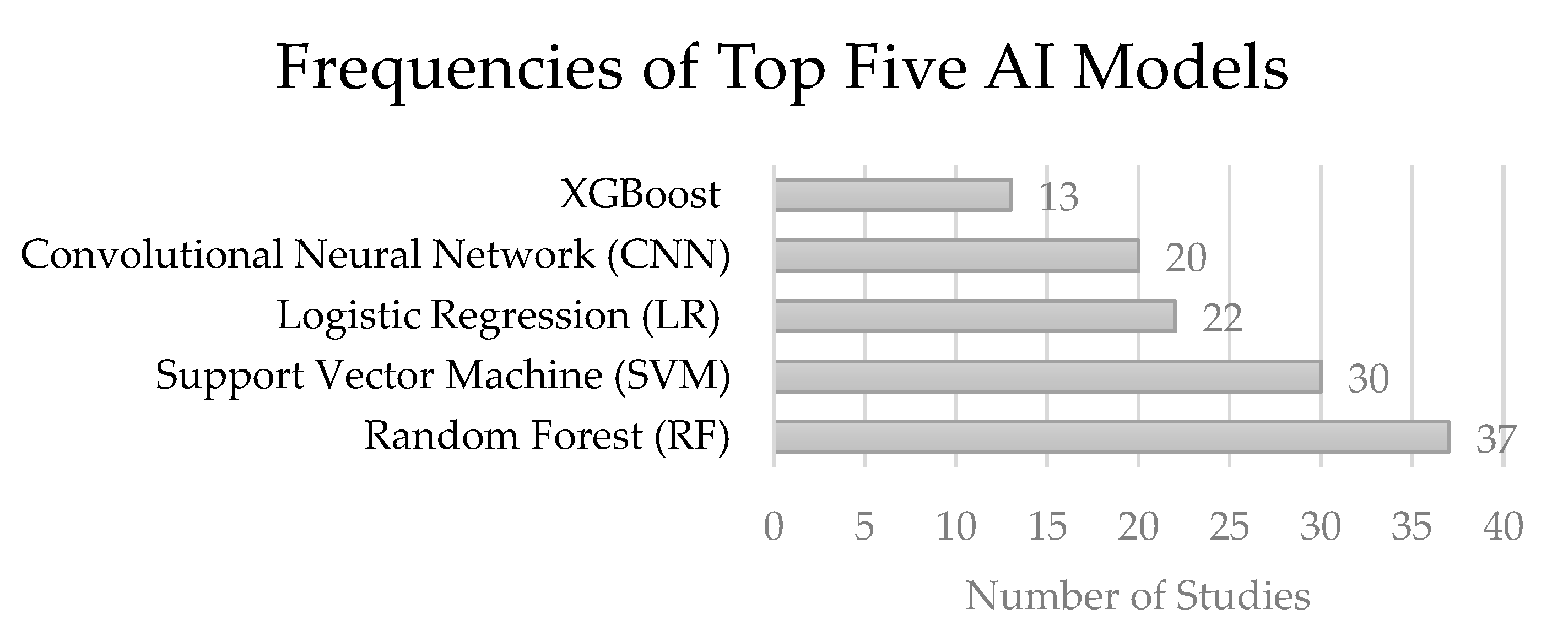
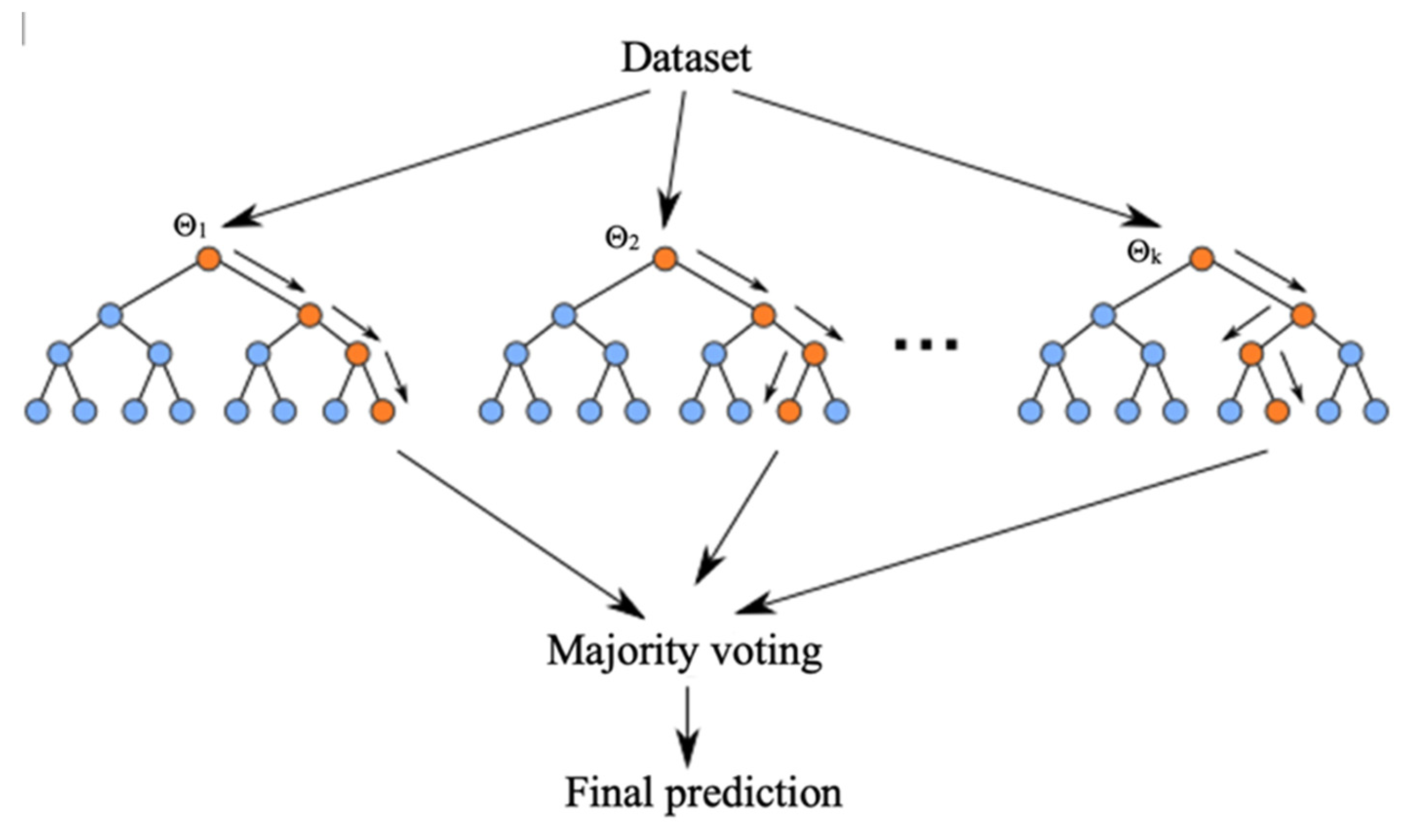
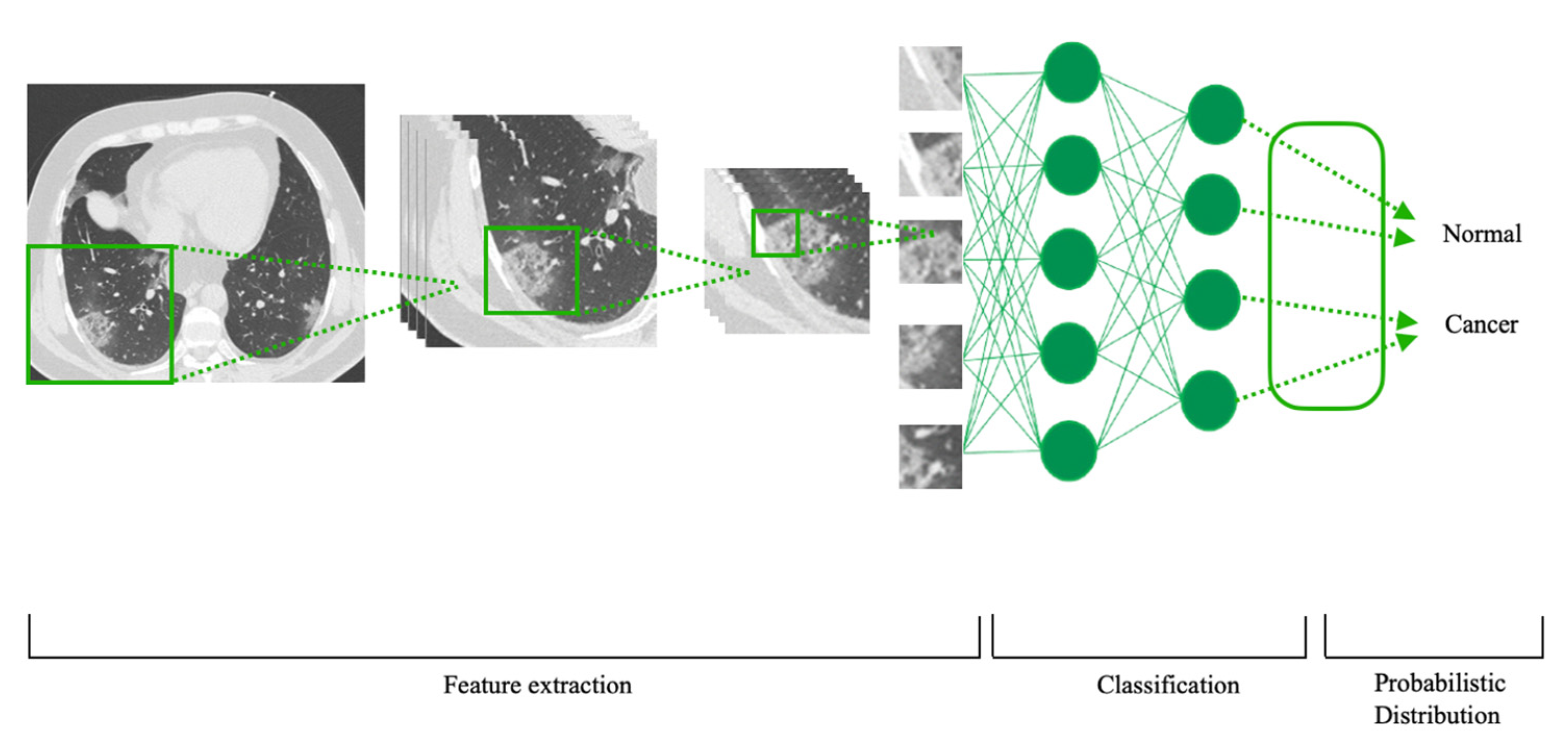
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Applications Based on Genomics
3.1.1. Genomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Prognosis
3.2. Clinical Applications Based on Transcriptomics
3.2.1. Transcriptomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
3.3. Clinical Applications Based on Epigenomics
3.3.1. Epigenomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
3.4. Clinical Applications Based on Proteomics and Metabolomics
3.4.1. Proteomics and Metabolomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Diagnosis
3.5. Clinical Applications Based on Multiomics Data
3.5.1. Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis Based on Multiomics Data
3.6. Clinical Applications Based on Radiomics
3.6.1. Radiomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
3.7. Clinical Applications Based on Pathomics
3.7.1. Pathomics-Based Prediction of Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
3.8. Clinical Applications Based on Clinical and Laboratory Data
3.8.1. Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis Based on Clinical and Laboratory Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Copeland, B. “Alan Turing and the beginning of AI,” Encyclopedia Britannica. 2024. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/Alan-Turing-and-the-beginning-of-AI (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Göndöcs, D.; Dörfler, V. AI in medical diagnosis: AI prediction & human judgment. Artif. Intell. Med. 2024, 149, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep Learning for Medical Image-Based Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaras, A.; Bekiaridou, A.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Moysidis, D.V.; Tsoumakas, G.; Bamidis, P.; Tsigkas, G.; Lazaros, G.; Kassimis, G.; Fragakis, N.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based mining of electronic health record data to accelerate the digital transformation of the national cardiovascular ecosystem: design protocol of the CardioMining study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e068698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, R.; Irfan, M.; Gondal, T.M.; Khan, S.; Wu, J.; Hadi, M.U.; Heymach, J.; Le, X.; Yan, H.; Alam, T. AI in drug discovery and its clinical relevance. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17575–e17575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- F. M. Shiri, T. Perumal, N. Mustapha, and R. Mohamed, “A Comprehensive Overview and Comparative Analysis on Deep Learning Models: CNN, RNN, LSTM, GRU.” arXiv, Jun. 01, 2023. Accessed: Feb. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.17473.
- Hasin, Y.; Seldin, M.; Lusis, A. Multi-omics approaches to disease. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCague, C.; Ramlee, S.; Reinius, M.; Selby, I.; Hulse, D.; Piyatissa, P.; Bura, V.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Sala, E.; Woitek, R. Introduction to radiomics for a clinical audience. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kurc, T.; Sharma, A.; Almeida, J.S.; Saltz, J. The Emergence of Pathomics. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2019, 7, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rguibi, Z.; Hajami, A.; Zitouni, D.; ElQaraoui, A.; Bedraoui, A. CXAI: Explaining Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Imaging Diagnostic. Electronics 2022, 11, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Guan, Y.Q.; Shen, K.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Cai, H.D.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Cao, Y.; et al. Novel bioinformatic classification system for genetic signatures identification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Luo, M.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y.; et al. Prediction of radiosensitivity and radiocurability using a novel supervised artificial neural network. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, C.; Chawla, S.; Thakral, D.; Pant, H.; Verma, P.; Malik, P.S.; Jayadeva; Gupta, R. ; Ahuja, G.; Sengupta, D. Molecular signature comprising 11 platelet-genes enables accurate blood-based diagnosis of NSCLC. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostavi, M.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y. CancerSiamese: one-shot learning for predicting primary and metastatic tumor types unseen during model training. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- F. Carrillo-Perez, F. M. Ortuno, A. Börjesson, I. Rojas, and L. J. Herrera, “Performance comparison between multi-center histopathology datasets of a weakly-supervised deep learning model for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma detection.,” Cancer Imaging Off. Publ. Int. Cancer Imaging Soc., vol. 23, no. 1, p. 66, 2023.
- Ding, D.; Lang, T.; Zou, D.; Tan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Machine learning-based prediction of survival prognosis in cervical cancer. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Lin, X.; Zheng, H.; Xie, B.; Fu, D. Characterization of stemness features and construction of a stemness subtype classifier to predict survival and treatment responses in lung squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgueira, A.M.; Arias, J. .D.; López, M.C.; Raíndo, A.P.; Rodríguez, B.A.; Santos, C.A.; Vence, N.A.; López,.B.; Blanco, A.A.; Pérez, L.B.; et al. Improved personalized survival prediction of patients with diffuse large B-cell Lymphoma using gene expression profiling. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Si, A.; Wei, X.; Lin, X.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, H.; Guo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; et al. Combining a machine-learning derived 4-lncRNA signature with AFP and TNM stages in predicting early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravkin, H.D.; Givton, O.; Geffen, D.B.; Rubin, E. Direct comparison shows that mRNA-based diagnostics incorporate information which cannot be learned directly from genomic mutations. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, E.Y.; Tsai, J.J.P.; Chang, J.-G.; Ng, K.-L. A novel miRNA-based classification model of risks and stages for clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemin, J.-P.; Lorenzi, C.; Cabrillac, M.-S.; Oldfield, A.; Ritchie, W.; Luco, R.F. A cell-to-patient machine learning transfer approach uncovers novel basal-like breast cancer prognostic markers amongst alternative splice variants. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, M.; Pu, X.; Li, C.; Wen, Z. Uncovering the prognostic gene signatures for the improvement of risk stratification in cancers by using deep learning algorithm coupled with wavelet transform. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kleinjans, J.; Caiment, F. Identifying novel transcript biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using RNA-Seq datasets and machine learning. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-X.; Sun, X.-M.; Cheng, W.-G.; Ruan, H.-J.; Liu, K.; Chen, P.; Xu, H.-J.; Gao, S.-G.; Feng, X.-S.; Qi, Y.-J. Using a machine learning approach to identify key prognostic molecules for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Lei, T. Systematical identifications of prognostic meaningful lung adenocarcinoma subtypes and the underlying mutational and expressional characters. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Allaire, A.; Diamandis, P.; Bisaillon, M.; Scott, M.S.; Richer, M. A machine learning analysis of a “normal-like” IDH-WT diffuse glioma transcriptomic subgroup associated with prolonged survival reveals novel immune and neurotransmitter-related actionable targets. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Fang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Fang, F. Comprehensive analysis of prognostic gene signatures based on immune infiltration of ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Chen, S.; Lin, H.; Luo, Y.; He, J. Selection of M7G-related lncRNAs in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and their putative diagnostic and prognostic role. BMC Urol. 2023, 23, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, O.; Alkhateeb, A.; Zheng, J.; Kandalam, S.; Rueda, L. Prediction of tumor location in prostate cancer tissue using a machine learning system on gene expression data. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, E.A.; Pujol, T.A.; McDonald, J.F.; Qiu, P. Leveraging TCGA gene expression data to build predictive models for cancer drug response. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Sato, S.; Shintani, D.; Hanaoka, M.; Ogasawara, A.; Miwa, M.; Yabuno, A.; Kurosaki, A.; Yoshida, H.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. Clinical significance of metabolism-related genes and FAK activity in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Uhl, B.; Gires, O.; Reichel, C.A. A transcriptomic pan-cancer signature for survival prognostication and prediction of immunotherapy response based on endothelial senescence. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.T.; Alom, Z.; Orr, B.A. Comprehensive study of semi-supervised learning for DNA methylation-based supervised classification of central nervous system tumors. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, R.P.; Ohira, M.; Mansai, S.P.; Kamijo, T. Comparative epigenomics by machine learning approach for neuroblastoma. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, H.; Barberis, A.; Chervova, O.; Nassiri, I.; Voloshin, V.; Sato, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Fairfax, B.; Buffa, F.; Humphrey, T.C. A role for SETD2 loss in tumorigenesis through DNA methylation dysregulation. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Lin, Y.; Yue, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Mi, N.; Bai, M.; Fu, W.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, N.; et al. Identification of a novel bile marker clusterin and a public online prediction platform based on deep learning for cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Du, Y.; Ma, R.; Teng, N.; Ou, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, X. Construction of the XGBoost model for early lung cancer prediction based on metabolic indices. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, T.; Shen, Z. A machine learning framework that integrates multi-omics data predicts cancer-related LncRNAs. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.M.; Chae, H. moBRCA-net: a breast cancer subtype classification framework based on multi-omics attention neural networks. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.; Kalakoti, Y.; Sundar, D. Deep learning assisted multi-omics integration for survival and drug-response prediction in breast cancer. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhu, M.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, P.; He, C.K.; Zhang, M.; Peng, X.; Wu, B.; Feng, R.; et al. Deep learning algorithm reveals two prognostic subtypes in patients with gliomas. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Mitchel, J.; Chatlin, K.; Wang, M.D. Deep learning based feature-level integration of multi-omics data for breast cancer patients survival analysis. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, A.R.; McInerney, C.E.; Prise, K.M.; McArt, D.G.; Jurek-Loughrey, A. Novel deep learning-based solution for identification of prognostic subgroups in liver cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma). BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, M.; Zhao, R. Discovering the molecular differences between right- and left-sided colon cancer using machine learning methods. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolisnik, T.; Sulit, A.K.; Schmeier, S.; Frizelle, F.; Purcell, R.; Smith, A.; Silander, O. Identifying important microbial and genomic biomarkers for differentiating right- versus left-sided colorectal cancer using random forest models. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Shi, F.; Tian, Y.; Gao, L.; Ying, Y.; Pan, Q.; et al. Deep learning approaches for differentiating thyroid nodules with calcification: a two-center study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Tian, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, S.; Shao, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, D.; et al. Classification prediction of pancreatic cystic neoplasms based on radiomics deep learning models. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Lu, F.; Pang, P.; Shao, G. Can computed tomography-based radiomics potentially discriminate between anterior mediastinal cysts and type B1 and B2 thymomas? Biomed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wan, C.; Hao, K.; Cai, A.; Liu, L. A novel fusion algorithm for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on CT images. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Gu, J.; Xu, D.; Song, L.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Tian, S.; Yang, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Deep learning radiomics based on contrast-enhanced ultrasound images for assisted diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wei, Y.; Shi, F.; Ren, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, B. The diagnostic and prognostic value of radiomics and deep learning technologies for patients with solid pulmonary nodules in chest CT images. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, L.; Qi, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Feng, H.; Shi, G. Radiomics nomogram for preoperative differentiation of pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma from tuberculoma in solitary pulmonary solid nodules. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, H.; Tian, Y.; Na, F.; Yan, J.; Wu, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M. PB-LNet: a model for predicting pathological subtypes of pulmonary nodules on CT images. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Meng, Z.; Fan, X.; Duan, Y.; Jia, Y.; Dong, T.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Deep learning radiomics of dual-modality ultrasound images for hierarchical diagnosis of unexplained cervical lymphadenopathy. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, H.; Mao, G.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, G.; Ao, W. Deep learning–based radiomic nomograms for predicting Ki67 expression in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H. Noninvasive KRAS mutation estimation in colorectal cancer using a deep learning method based on CT imaging. BMC Med Imaging 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, C.; Yu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, H. Prediction of lymphovascular space invasion using a combination of tenascin-C, cox-2, and PET/CT radiomics in patients with early-stage cervical squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, P. Automated breast volume scanner based Radiomics for non-invasively prediction of lymphovascular invasion status in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Arefan, D.; Tan, Y.; Dan, H.; Zhang, J. A CT-based radiomics model for predicting renal capsule invasion in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Med Imaging 2022, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Mao, N.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, G.; Han, X.; Dong, L.; Che, K.; Wang, Q.; et al. Extrathyroidal Extension Prediction of Papillary Thyroid Cancer With Computed Tomography Based Radiomics Nomogram: A Multicenter Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 874396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H. Computed tomography-based radiomics machine learning models for prediction of histological invasiveness with sub-centimeter subsolid pulmonary nodules: a retrospective study. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatz, S.; Böth, I.; Ackermann, J.; Burck, I.; Mahmoudi, S.; Lenga, L.; Martin, S.S.; Scholtz, J.-E.; Koch, V.; Grünewald, L.D.; et al. Radiomics for therapy-specific head and neck squamous cell carcinoma survival prognostication (part I). BMC Med Imaging 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.-B.; Xiong, M.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, B.; Luo, Y.-F.; Zhou, S.; Chu, C.; Li, Q.-W.; Wang, B.; et al. CT radiomics-based long-term survival prediction for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy using features from tumor and tumor organismal environment. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Xin, B.; Hao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Guo, X. Radiomic analysis for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer from preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kang, S.-R.; Oh, I.-J.; Kim, M.-S. Deep learning model integrating positron emission tomography and clinical data for prognosis prediction in non-small cell lung cancer patients. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eresen, A.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Shangguan, J.; Velichko, Y.; Yaghmai, V.; Benson, A.B.; Zhang, Z. Preoperative assessment of lymph node metastasis in Colon Cancer patients using machine learning: a pilot study. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Shen, J.; Zheng, Y. Prediction of lymph node status in patients with early-stage cervical cancer based on radiomic features of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. BMC Med Imaging 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, C.M.; Su, S.; Wang, W.J.; Fan, L.P.; Shu, J. Machine learning-based Radiomics analysis for differentiation degree and lymphatic node metastasis of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Mu, F.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Prediction of distant metastasis in esophageal cancer using a radiomics–clinical model. Eur. J. Med Res. 2022, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujima, N.; Andreu-Arasa, V.C.; Meibom, S.K.; Mercier, G.A.; Truong, M.T.; Hirata, K.; Yasuda, K.; Kano, S.; Homma, A.; Kudo, K.; et al. Prediction of the local treatment outcome in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using deep learning analysis of pretreatment FDG-PET images. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Sun, K.; Jin, S.; Wang, K.-Y.; Jiang, N.; Shan, S.-Q.; Lu, Q.; Lv, G.-Y.; Dong, J.-H. Predicting the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma downstaging with the use of clinical and radiomics features. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Yin, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Yao, X. Development and validation of a radiopathomic model for predicting pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, A.; Lin, Y.; Gu, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Shao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Xu, Z. Radiation pneumonitis prediction after stereotactic body radiation therapy based on 3D dose distribution: dosiomics and/or deep learning-based radiomics features. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Dong, D.; Zhao, X.; Ou, X.-M.; Yi, J.-L.; Guan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao-Fei, L.; Xie, C.-M.; Luo, D.-H.; et al. Radiomic signatures reveal multiscale intratumor heterogeneity associated with tissue tolerance and survival in re-irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a multicenter study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lian, Z.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Mo, X.; Huang, W.; Yang, W.; et al. Machine-learning based MRI radiomics models for early detection of radiation-induced brain injury in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.S.; Yu, G.; Xu, C.; Meng, X.H.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, C.; Deng, Z.; Shang, L.; Liu, R.; Su, S.; et al. Accurate diagnosis of colorectal cancer based on histopathology images using artificial intelligence. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, F.; Rao, X.; Lv, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Ren, F.; Zheng, C.; et al. Richer fusion network for breast cancer classification based on multimodal data. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.-H.; Hu, V.; Wang, F.; Matulonis, U.A.; Mutter, G.L.; Golden, J.A.; Kohane, I.S. Deciphering serous ovarian carcinoma histopathology and platinum response by convolutional neural networks. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux, M.E.; Reveles, X.T.; Rebeles, J.; Bederka, L.H.; Araujo, P.R.; Sanchez, J.R.; Grayson, M.; Lai, S.-C.; DePalo, L.R.; Habib, S.A.; et al. Detection of early-stage lung cancer in sputum using automated flow cytometry and machine learning. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Li, G.; Zeng, Z.; Zheng, B.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Yu, S. Establishment of early diagnosis models for cervical precancerous lesions using large-scale cervical cancer screening datasets. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Qian, C.; Wei, C.; Chen, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; et al. Artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer based on multimodal data: a multicenter study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Yue, M.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, A.; Xia, X.; Liu, W.; Yu, R.; Yang, S.; et al. Accurate prediction of HCC risk after SVR in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis based on longitudinal data. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Dai, X.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Z.; Jin, X.; Mei, K.; Huang, H.; Wu, Z. Machine learning-based prediction model and visual interpretation for prostate cancer. BMC Urol. 2023, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, J.-N.; Schmittmann, T.; Riechert, S.; Kramer, M.; Sulaiman, A.S.; Sockel, K.; Kroschinsky, F.; Schetelig, J.; Wagenführ, L.; Schuler, U.; et al. Deep learning identifies Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia in bone marrow smears. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, K.; Li, Y.; et al. The Classification of Six Common Skin Diseases Based on Xiangya-Derm: Development of a Chinese Database for Artificial Intelligence. J. Med Internet Res. 2021, 23, e26025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Tang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; et al. Development and validation of an artificial intelligence system for grading colposcopic impressions and guiding biopsies. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, J. Machine learning prediction models for different stages of non-small cell lung cancer based on tongue and tumor marker: a pilot study. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.B.; Grazal, C.; Wedin, R.; Kuo, C.; Chen, Y.; Christensen, B.R.; Cullen, J.; Forsberg, J.A. Machine learning algorithms to estimate 10-Year survival in patients with bone metastases due to prostate cancer: toward a disease-specific survival estimation tool. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Duan, H.; Wu, N.; Lu, X. An ensemble learning with active sampling to predict the prognosis of postoperative non-small cell lung cancer patients. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.-W.; Jiao, C.-Y.; Xu, Z.-G.; Li, X.-C.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.-H. Development and validation of a gradient boosting machine to predict prognosis after liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantidakis, G.; Putter, H.; Litière, S.; Fiocco, M. Statistical models versus machine learning for competing risks: development and validation of prognostic models. BMC Med Res. Methodol. 2023, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, P.; Lai, S.; Wang, J.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Y. Prognostic models for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma patients after radical nephroureterectomy based on a novel systemic immune-inflammation score with machine learning. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, M.; Che, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, Y.; et al. The potential of high-order features of routine blood test in predicting the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, B.; Park, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.; Choi, C.I.; Choi, B.K.; Seo, K.I.; Park, Y.-H.; Yang, K.; Lee, S.; Ha, T.; et al. Machine learning-based survival rate prediction of Korean hepatocellular carcinoma patients using multi-center data. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Huang, T.; Feng, B.; Lyu, J. Deep-learning model for predicting the survival of rectal adenocarcinoma patients based on a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lan, A.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. Development and testing of a random forest-based machine learning model for predicting events among breast cancer patients with a poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur. J. Med Res. 2023, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Byun, S.-S.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Hwang, E.C.; Kang, S.H.; Chung, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ha, Y.-S.; et al. Machine learning-based prediction model for late recurrence after surgery in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Med Informatics Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardini, E.; Zhang, X.; Canahuate, G.; Wentzel, A.; Mohamed, A.S.R.; Van Dijk, L.; Fuller, C.D.; Marai, G.E. Optimal Treatment Selection in Sequential Systemic and Locoregional Therapy of Oropharyngeal Squamous Carcinomas: Deep Q-Learning With a Patient-Physician Digital Twin Dyad. J. Med Internet Res. 2022, 24, e29455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldner-Busztin, D.; Nisantzis, P.F.; Edmunds, S.J.; Boza, G.; Racimo, F.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Limborg, M.T.; Lahti, L.; de Polavieja, G.G. Dealing with dimensionality: the application of machine learning to multi-omics data. Bioinformatics 2023, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics-based prediction of prognostic biomarker | |||
| To identify overlapping genetic patterns in DLBCL patients | Zhang et al., 2020 [13]. | ||
| 8 (14.8%), 10 (16.9%), 17 (18.7%), and 43 (59.7%) cases were predicted to exhibit the MYC-trans, BCL2-trans, BCL6-trans, and MC signatures. | Random forest (RF) | ||
| Genomics-based prediction of treatment responses | |||
| To predict treatment response to radiotherapy based on gene patterns | Zeng et al., 2022 [14]. | ||
| Mean root square error (0.1587) of ANN-SCGP was lowest among other traditional MLs, including RF, SVM, and ANN. Mean root square error assesses the average difference between the predicted values generated by a model and actual values. | ANN with Selective Connection based on Gene Patterns (ANN-SCGP) RF, support vector machine (SVM), ANN, DeepSurv |
||
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcriptomics-based cancer detection | |||
| To discriminate between non-metastatic NSCLC cases and healthy samples using 11 platelet-genes | Goswami et al., 2020 [15]. | ||
| 11-gene panel was validated with GB for accuracy in distinguishing NSCLC cases from healthy controls. Among the three classifiers, GBM offered the highest AUC = 0.97. | Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM), RF, and Linear | ||
| The model trained with 19 primary cancer types achieved the highest performance with 89.67%, 87.32%, and 84.59% accuracy for 6, 8, and 10-way predictions in test samples. | Siamese convolutional neural network (SCNN) | To predict cancer types for primary and metastatic tumors from gene expression data | Mostavi et al., 2021 [16]. |
| Transcriptomics-based classification of malignant vs benign tumors | |||
| To predict treatment response to radiotherapy based on gene patterns | Carrillo-Perez et al., 2021 [17]. | ||
| Mean root square error (0.1587) of ANN-SCGP was lowest among other traditional MLs, including RF, SVM, and ANN. Mean root square error assesses the average difference between the predicted values generated by a model and actual values. | ANN with Selective Connection based on Gene Patterns (ANN-SCGP)RF, support vector machine (SVM), ANN, DeepSurv | ||
| Transcriptomics-based survival prediction | |||
| AUC values of 4 survival groups were all above 90%. The patient groups predicted by the SVM model demonstrated comparable survival outcomes to those clustered by the K-means algorithm. | Combination of K-means clustering and SVM | To evaluate a microRNA-based machine learning survival prediction model | Ding et al., 2021 [18]. |
| The stemness subtype classifier by RF showed good performance in the classification with an AUC of 0.956, and the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 86.15%, 91.03% and 88.9%. | RF | To predict transcriptional stemness indices of lung cancer from RNA expression data | Lai et al., 2023 [19]. |
| RF-approach outperformed traditional prognostic variables like disease stage and cell of origin (COO) in predictive accuracy for DLBCL patients. | RF | To evaluate a new machine learning-based models of survival prediction using transcriptomic and clinical data | Mosquera Orgueira et al., 2020 [20]. |
| Transcriptomics-based recurrence prediction | |||
| SVM-REF and Random Forest analyses selected 66 and 30 lncRNA prognostic signatures, respectively. | RF and Support Vector Machine Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) | To evaluate a lncRNA-based signature for predicting HCC early recurrence | Fu et al., 2023 [21]. |
| Prediction of breast cancer recurrence with XGBoost performed better with mRNA data (AUC=0.74) alone compared to mutation alone (AUC=0.62). | XGBoost | To evaluate prognostic utility of genomic mutations to that of gene expression using breast cancer data | Ravkin et al., 2020 [22]. |
| Transcriptomics-based prediction of risk stratification | |||
| SVMR achieved the best classification performance (accuracy = 0.923, sensitivity = 0.927, specificity = 0.919) compared to other classifiers. | Support vector machine with radial kernel (SVMR) | To identify a novel miRNA signature related to tumor stage and prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients | Dessie et al., 2021 [23]. |
| Combining differentially spliced and expression levels of RNA yielded the most performant RF-classifier compared to splicing signature only or expression levels only. | RF | To subclassify highly aggressive breast cancers with transcriptomics analysis of alternative splicing events | Villemin et al., 2021 [24]. |
| SWT-CNN outperformed other machine learning algorithms including support vector machine (SVM) and logistic regression (LR). SWT-CNN performed comparably with RF in predicting tumor stages. | Combination of a convolutional neural network with stationary wavelet transform (SWT-CNN) | To stratify the prognostic risk for cancer patients by using SWT-CNN | Zhao et al., 2020 [25]. |
| Transcriptomics-based prediction of prognostic biomarker | |||
| RF exhibited the highest Area Under the Curve (AUC) across all datasets, while SVM demonstrated the highest sensitivity and specificity. | RF, KNN, SVM, naïve bayes (NB), and neural networks (NNET) for feature extraction | To identify transcript biomarkers that could help in early prognosis for HCC | Gupta et al., 2021 [26]. |
| The top 5 significant molecules pinpointed by each machine learning algorithm revealed a single intersecting molecule which is SFN. | Logical regression (LR), SVM, artificial neural network (ANN), RF, and XGBoost | To identify key prognostic molecule with multiple MLs | Li et al., 2021 [27]. |
| RF ranked top 10 important master genes for two prognostic groups including CCNA2, CBX7, TMEM48, SPC25, GAPDH, WDHD1, PSMD2, ERO1L, DDX52, ARNTL2. | RF | To identify the key prognosis impacting genes and relevant subtypes for lung adenocarcinoma | Lv and Lei., 2020 [28]. |
| A machine learning-based approach identified C5AR1/SYT5 and MSR1/SLC32A1 signatures which were able to discriminate NL IDH-WT gliomas with high sensitivity and specificity in various glioma expression datasets. | K-nearest neighbor (KNN) | To characterize novel biomarker in glioma | Nguyen et al., 2020 [29]. |
| SVM-RFE yielded 72 prognostic features with classification accuracy of 0.934. | SVM-RFE | To evaluate the association between immune infiltration and the prognosis in ovarian cancer | Yan et al., 2020 [30]. |
| The intersection of the top 10 feature lncRNAs obtained from both the XGBoost and Boruta algorithms resulted in eight intersecting lncRNAs. | XGBoost and Boruta algorithm | To identify and explore prognostic biomarkers associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Zhong et al., 2023 [31]. |
| Transcriptomics-based prediction of laterality of cancer | |||
| SVM-RBF classified the different locations by the highest accuracy of 99%. RF classified with high accuracy. NB was not satisfactory. | NB, SVM-RBF, and RF | To identify biomarkers which are associated with specific tumor locations | Hamzeh et al., 2020 [32]. |
| Transcriptomics-based prediction of treatment responses | |||
| RF yielded best results with mean accuracy of 84.1% for 5-FU and 82.3% for GCB. | RF, SVM, LR | To predict treatment response of multiple cancer types to 5-Fluorouracil and Gemcitabine | Clayton et al., 2020 [33]. |
| Cluster 2 exhibited a notably poorer prognosis compared to Cluster 1. | K means clustering | To examine relationships between the effects of platinum-containing drugs with of metabolic genes and FAK activity in advanced ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma | Sato et al. 2022 [34]. |
| KNN derived AUC of 0.72. This model performed better than previously published pan-cancer predictive models for immunotherapy efficacy. | KNN | To predict survival and immunotherapy response with transcriptomic marker from tumor endothelial cells | Wu et al., 2023 [35]. |
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epigenomics-based classification of malignant vs benign tumors | |||
| SETRED with SVM base learner performed the best with mean accuracy above 0.95 and AUC for methylation class and family prediction (AUC = 0.73 and 0.94, respectively).The NN model exhibited notably higher balanced accuracy (92.9% and 97.5%) compared to the RF classifier (70.9% and 72.3%). | 11 semi-supervised learning models based on SVM, decision tree, and one nearest neighbor2 supervised classification models: RF and NN | To explore utility of semi-supervised in methylation data | Tran et al., 2022 [36]. |
| Epigenomics-based classification of tumor staging | |||
| To classify neuroblastoma staging with epigenomic data | Sugino et al., 2022 [37]. | ||
| Precisions for groups A-D were 0.931, 0.833, 0.577, and 0.414. | RF | ||
| Epigenomics-based prediction of biomarker for cancer prognosis | |||
| The model yielded a sensitivity of 0.94, specificity of 0.82, and a false negative rate of 0.06. | Binomial logistic regression | To develop and validate a 3-CpG methylation signature to predict SETD2 mutation status | Javaid et al., 2023 [38]. |
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteomics-based prediction of diagnostic biomarker | |||
| A diagnostic model (RF) incorporating seven factors (CLU, CA19-9, IBIL, GGT, LDL-C, TG, and TBA), showed a high diagnostic utility with AUC: 0.947, sensitivity: 90.3%, specificity: 84.9%. | RF | To evaluate diagnostic performance of proteomic biomarker for cholangiocarcinoma | Gao et al., 2023 [39]. |
| Metabolimics-based cancer prediction | |||
| To predict lung cancer with metabolic data | Guan et al., 2023 [40]. | ||
| The XGBoost model showed best predictive power (AUC = 0.81, accuracy = 75.29%, sensitivity = 74%). | XGBoost, SVM, KNN, RF | ||
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer prediction based on multiomics data | |||
| To identify cancer-related lncRNAs | Yuan et al., 2021 [41]. | ||
| The AUC of LGDLDA was 0.880, which was 0.034, 0.088, 0.053 and 0.208 higher than that of IDHI-MIRW, NCPLDA, LncDisAP and NCPHLDA, respectively. | LncRNA-Gene-Disease association networks based LncRNA-Disease Association prediction (LGDLDA): base model is a neural network | ||
| Subclassification of malignant tumors based on multiomics data | |||
| To evaluate moBRCA-net | Choi and Chae, 2023 [42]. | ||
| Mean root square error (0.1587) of ANN-SCGP was lowest among other traditional MLs, including RF, SVM, and ANN. Mean root square error assesses the average difference between the predicted values generated by a model and actual values. | moBRCA-net: base model is a neural network | ||
| Survival prediction based on multiomics data | |||
| Survival prediction: accuracy of 94% and AUC of 0.98Drug response prediction: AUC of 0.83 and 0.78 for Docitaxel and Gemcitabine | Neural network-based classifier | To predict survival and drug response for breast cancer patients | Malik et al., 2021 [43]. |
| Autoencoder outperformed 2 statistical methods with C-index 0.92 (PCA and iCluster). | Combination of Autoencoder and SVM | To identify survival subtype of glioma with RNA expression and DNA methylation data | Tian et al., 2022 [44]. |
| DNA methylation and miRNA expression resulted in best performance with C-index of 0.641 | Concatenation autoencoder (ConcatAE) and CrossAE | To predict breast cancer survival by integrating multi-omics data | Tong et al., 2020 [45]. |
| Multiomics-based prediction of prognostic biomarker | |||
| 75 mRNAs identified as prognostic in TCGA cohort. 29 mRNAs identified as prognostic in LIRI-JP dataset. | Autoencoder | To identify biomarkers that distinguish prognostic subgroups in liver cancer | Owens et al., 2021 [46]. |
| Multiomics-based prediction of laterality of cancer | |||
| The classification model derived from the 17 gene expressions resulted in an AUC of 0.96. | XGBoost | To identify gene mutation and expression patterns between left-sided and right-sided colon cancer | Jiang et al., 2020 [47]. |
| The accuracies of the RF models were 90%, 70%, and 87% with corresponding area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.9, 0.76, and 0.89 for the human genomic, microbial, and combined feature sets, respectively. | RF | To predict sidedness of colon cancer | Kolisnik et al., 2023 [48]. |
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiomics-based classification of malignant vs benign tumors | |||
| Xception: AUC 0.970 DenseNet169: AUC 0.959 Both DLs outperformed radiologists (P < 0.05). |
Xception DenseNet169 DenseNet121 NASNetLarge ResNet101v2 |
To evaluate diagnostic performance of DLs in distinguishing benign vs malignant thyroid calcified nodules | Chen et al., 2023 [49]. |
| Fusion model achieved AUC 0.916 for SCA diagnosis and AUC 0.973 for MCA and IPMN diagnosis. | Fused model: Based on logistic regression (LR) and SVM | To evaluate diagnostic models based on radiomics and deep learning algorithms to differentiate three types of pancreatic cystic neoplasms | Liang et al., 2022 [50]. |
| A total of 180 tumor texture features were extracted from enhanced CT and unenhanced CT. | AK software (Artificial Intelligence Kit V3.0.0.R) by GE Healthcare | To diagnose anterior mediastinal cysts vs thymomas with radiomic features | Liu et al., 2020 [51]. |
| Mean accuracy of 93.25%, a sensitivity of 89.22%, a specificity of 95.82%, and AUC of 0.9629. | RGB: combination of 5 CNNs and 1 GCN | To evaluate RGB model classify benign vs malignant lung nodules | Ma et al., 2023 [52]. |
| The DLR model achieved an AUC of 0.986, 0.978, 0.967, and 0.953 in the training, internal validation, and external validation. | DLR model: based on ResNet50 | To evaluate role of deep learning radiomics on contrast-enhanced US in distinguishing pancreatic adenocarcinoma vs chronic pancreatitis | Tong et al., 2022 [53]. |
| CNN model with clinical features achieved the highest AUC 0.819. | CNN and RF | To distinguish benign vs malignant lung nodules in chest CT | Zhang et al., 2022 [54]. |
| The model established by the LR method had the best performance, and the AUC values in the training group and test group were 0.840 and 0.960. AUC of the combined model was 0.940, 0.990 and 0.960 in the training group, test group and external validation group. |
Radiomics model: RF, SVM, and LR Combined model: LR |
To differentiate pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma from tuberculoma based on features from CT images and clinical features | Zhang et al., 2023 [55]. |
| The accuracy of the test set was 0.84. 96 images from the test set without data augmentation were analyzed and the accuracy was 0.89. |
PB-LNet: Based on ResNext50 and Bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM) | To classify CT images of lung nodules into six categories based on pathological subtypes | Zhang et al., 2023 [56]. |
| AUCs for lymphoma ranged 0.670 to 0.936 in three testing sets. AUCs for metastatic carcinoma ranged 0.804 to 0.855 in three testing sets. |
ResNet50 | To accurately diagnose unexplained cervical lymphadenopathy with ultrasound | Zhu et al., 2022 [57]. |
| Radiomics-based prediction of gene expression in malignant tumors | |||
| AUCs of the clinical model (LR) in the testing, internal validation, and external validation sets were 0.794, 0.711, and 0.75. AUCs of the deep models and joint models ranged from 0.939 to 0.993. The predictive performance of the DLRS-Resnet model was inferior to that of the Nomogram-Resnet model (p < 0.01). |
1 ML model: LR 3 DL models: DLRS-Resnet, DLRS-Inception, and DLRS-Densenet 3 joint models: Nomogram-Resnet, Nomogram-Inception, and Nomogram-Densenet |
To predict Ki67 expression in prostate cancer with MRI radiomics | Deng et al., 2023 [58]. |
| ResNet model in the axial direction achieved the higher AUC 0.90 in the testing cohort than coronal or sagittal directions. AUC of radiomics model (RF) in testing cohorts was 0.818. |
ResNet and RF | To predict KRAS mutation in colorectal cancer with CT radiomics | He et al., 2020 [59]. |
| Radiomics-based prediction of cancer invasion | |||
| Radiomics model (LR) performed best in training and external data set. Combined model (LR) performed best in testing set. |
LR | To predict lymphovascular invasion status in cervical cancer | Li et al., 2021 [60]. |
| Three SVM-based prediction models demonstrated relatively high efficacy in identifying LVI of breast cancer, with AUCs of 79.00%, 80.00% and 79.40% and an accuracy of 71.00%, 80.00% and 75.00% in the validation cohort for AP, SP and CP plane image. Fusion model achieved the highest AUC of 87.90% and an accuracy of 85.00% in the validation cohort. |
SVM | To predict the lymphovascular invasion status in breast cancer | Li et al., 2023 [61]. |
| FNN performed the best with CMP demonstrating the highest AUC 0.81. | SVM-RBF, KNN, LR, Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), Forward neural network (FNN) | To predict capsule invasion in renal cell carcinoma | Yang et al., 2022 [62]. |
| The six models showed the certain value of radiomics, with AUCs from 0.642 to 0.701. LR demonstrated best performance. | KNN, LR, Decision tree, Linear-SVM, Gaussian-SVM, Polynomial-SVM | To predict extrathyroidal extension (ETE) in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) patients | Yu et al., 2022 [63]. |
| XGBoost model demonstrated best performance in both training and testing set with AUC 0.917 and 0.874. | LR, SVM, XGBoost | To predict histological invasiveness of sub-centimeter subsolid pulmonary nodules | Zhang et al., 2023 [64]. |
| Radiomics-based survival prediction | |||
| EN and RF achieved top prognostication performances of AUC = 0.795 and AUC = 0.811. RF prognostication slightly outperformed the EN for the complete and radiochemotherapy cohort. |
Elastic Net (EN) RF |
To predict survival of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck with CT radiomics | Bernatz et al., 2023 [65]. |
| The overall prediction accuracy for 3-year survival status in training and validation cohort was 92.50% and 85.71%, and the AUC was 0.965 and 0.869. | SVM | To predict survival of unresectable lung cancer patients with CT radiomics | Chen et al., 2022 [66]. |
| RF models built with clinical, CT and PET features outperformed other models with solely clinical, PET or CT features with C-index 0.780 and 0.820 in training and testing set. | RF | To predict survival of colorectal cancer patients with 8F- FDG PET/CT radiomic features | Lv et al., 2022 [67]. |
| For 2- and 5-year survival predictions, ResNet 50 achieved best performance for 2D PET images, while ResNet 34 achieved best performance for 3D PET images. ResNet 34 demonstrated best performance with C-index 0.749. | ResNet50 for 2D PET images ResNet3D34 for 3D PET images |
To predict survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients with PET radiomics | Oh et al., 2023 [68]. |
| Radiomics-based metastasis prediction | |||
| The patient-demographic model resulted in an accuracy of 67.31% and 73.08% and AUC of 0.706 and 0.773 for training and testing cohorts. The radiomic-derived model resulted in an accuracy of 81.09% and 79.49% and AUC of 0.882 and 0.825 for training and testing cohorts. |
SVM | To predict lymph node metastasis with pre-op CT | Eresen et al., 2020 [69]. |
| MNB outperformed other MLs with AUC, specificity, and accuracy on the testing set of 0.745, 0.900, and 0.778. | XGBoost, LR, Multinomial Naive Bayes (MNB), SVM, Decision Tree, RF, Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) | To predict lymph node metastasis in cervical cancer with MRI radiomics | Liu et al., 2023 [70]. |
| XGBoost outperformed other MLs with AUC 0.98, sensitivity 0.75, and specificity 0.94. | Ada Boosting (ADA), Bagging Classifier (BAGC), Bernoulli Naïve Bayes (BNB), Decision Tree, Gaussian Naïve Bayes (GNB), KNN, RF, Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), SVM, and XGBoost | To predict lymph node metastasis in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Tang et al., 2021 [71]. |
| LR demonstrated best performance, achieving an AUC of 0.754. | SVM, KNN, RF, and LR | To predict distant metastasis in esophageal cancer | Zhu et al., 2022 [72]. |
| Radiomics-based prediction of treatment responses | |||
| The axial and coronal combination model in ResNet (AUC = 0.85) demonstrated best performance. | AlexNet, GoogLeNet Inception v3, and ResNet-101 | To predict treatment outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma by DLs | Fujima et al., 2021 [73]. |
| The average accuracy of C-SVM, R-SVM, and C-R SVM were 0.712, 0.792, and 0.844, respectively, while the average AUC values were 0.775, 0.804, and 0.877. | SVM | To predict prognosis of downstaging treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma | Wang et al., 2023 [74]. |
| DLRPM exhibited superior prediction performance compared to single-scale prediction models, achieving an AUC of 0.927 in the validation set. | DLRPM: based on SVM | To predict response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients | Zhang et al., 2023 [75]. |
| Radiomics-based prediction of treatment complications | |||
| Combined model (RF) of radiation dose and radiomics resulted in best performance with AUC 0.9993 and 0.9000 in training and testing set. | ResNet50 for feature extraction RF for classification |
To predict radiation pneumonitis after radiotherapy | Huang et al., 2022 [76]. |
| RF achieved AUC range of 0.713 to 0.756. | Linear SVM for feature extraction RF for classification |
To predict post-radiation nasopharyngeal necrosis after radiotherapy | Liu et al., 2023 [77]. |
| The radiomic models (N1, N2, N3) with longitudinal MRI yielded AUCs of 0.872, 0.836, and 0.780 for RTLI prediction. | RF | To predict radiation-induced brain injury after radiotherapy | Zhang et al., 2020 [78]. |
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathomics-based prediction of cancer diagnosis | |||
| Google Inception V3 yielded average AUC of 98.06%. | Google Inception V3 | To diagnose colorectal cancer with DL on weakly-labeled WSIs | Wang et al., 2021 [79]. |
| Pathomics-based classification of malignant vs benign tumors | |||
| Richer fusion network outperformed other models in the literature with average accuracy of 92.9%. | Richer fusion network: based on Sparse denoising autoencoder and VGG16 | To classify benign vs malignant breast lesions with WSIs and EMR | Yan et al., 2021 [80]. |
| Pathomics-based prediction of treatment responses | |||
| VGGNet had best predictive ability and was utilized as a backbone model to identify transcriptomic subtypes and predict therapy response. | AlexNet, GoogLeNet, and VGGNet | To evaluate a CNN model that diagnose ovarian cancer and predict treatment response | Yu et al., 2020 [81]. |
| Outcome/Performance | Modality of AI | Study aim | Author, year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer prediction based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| CyPath resulted in AUC 0.89, sensitivity of 82.1%, and sensitivity of 87.7% for test set and AUC 0.94 for test set. | CyPath Lung: based on LR | To detect lung cancer in sputum with ML | Lemieux et al., 2023 [82]. |
| XGboost generated the highest AUC value of models, which were 0.915, 0.9529, 0.9557, 0.9614 for diagnosing ASCUS higher, ASC-H higher, LSIL higher, and HSIL higher staged cervical lesions, indicating the acceptable accuracy of the selected diagnostic model. | LR for feature selection Six MLs for classification: Decision Tree, XGBoost, RF, SVM, LR, and Neural net |
To predict cervical cancer with HPV screening dataset | Meng et al., 2022 [83]. |
|
AutoML had the highest AUC 0.807 of 4 MLs. AutoML had encouraging discriminative power with AUCs of 0.820 in the validation cohort and 0.807 and 0.850 in the two prospective test cohorts. |
RF for feature selection AutoML, LR, RF, XGBoost for model establishment |
To diagnose prostate cancer with clinical data | Zhang et al., 2023 [84]. |
| RF model incorporating selected features, exhibited excellent performance in predicting HCC events occurring within 1 year, achieving an AUC of 0.9507. Predictions for the 2-year and 3-year time frames also yielded favorable results, with AUCs of 0.8767 and 0.8307, respectively. |
RF | To predict risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis | Zou et al., 2023 [85]. |
| Classification of malignant vs benign tumors based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| The XGBoost model provided better performance (AUC 0.82) compared with free-to-total PSA ratio (AUC 0.75), total PSA (AUC 0.68) and free PSA (AUC 0.61). | XGBoost | To distinguish benign prostate hyperplasia from prostate cancer using ML | Chen et al., 2023 [86]. |
| Xception CNN showed an AUROC of 0.8741, 0.9199, and 0.8363 for the detection of myeloblasts, promyelocytes, and Auer rods. ENNs resulted in AUCs of 0.8575 and 0.9585 in distinguishing between APL and non-APL AML as well as APL and healthy donors. |
XceptionCNN to label cell border Binary ensemble neural nets (ENNs) for classification |
To predict acute promyelocytic leukemia from bone marrow smear images | Eckardt et al., 2022 [87]. |
| Xy-SkinNet achieved a 64.75% accuracy rate for its top-ranked diagnosis, surpassing the average performance of dermatologists, which stood at 62.13%. | Xy-SkinNet: based on ResNet and Fast R-CNN | To classify six common skin disease with AI | Huang et al., 2021 [88]. |
| Tumor grading based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| Incorporating additional non-image information such as cytology and HPV status improved CAIADS’ diagnostic performance, with an AUC of 0.712 for LSIL and 0.829 for HSIL and cancer. CAIADS surpassed the diagnostic performance of colposcopists, achieving an AUC of 0.678 for LSIL and 0.777 for HSIL. |
Colposcopic Artificial Intelligence Auxiliary Diagnostic System (CAIADS): | To evaluate AI system that diagnose colposcopy images | Xue et al., 2020 [89]. |
| Tumor staging based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| Neural Network, RF, and NB demonstrated superior classification ability with combined input. Accuracies of Neural network, RF, and NB were 0.767, 0.718, and 0.688, respectively, and the AUCs were 0.793, 0.779, and 0.771. |
Decision tree, LR, SVM, RF, Naive bayes (NB), and Neural network | To diagnose lung cancer staging based on tongue images and tumor markers | Shi et al., 2023 [90]. |
| Survival prediction based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| All six models demonstrated satisfactory predictive performance, with AUC ranging from 0.73 to 0.86. The 3-year model exhibited the highest performance, achieving an AUC of 0.86. |
Gradient boosting machine (GBM) | To estimate survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer | Anderson et al., 2022 [91]. |
| SVM-ELAS performed better than LR-ELAS and CART-ELAS. SVM-ELAS exhibited superior performance with an average AUC of 0.736, demonstrating significant enhancements over SVM-AdaBoost, SVM-Bagging, SVM-SMOTE, and SVM-TomekLinks. |
SVM-ELAS, LR-ELAS, CART-ELAS | To predict survival and recurrence in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Hu et al., 2022 [92]. |
| The GBM model demonstrated a predictive accuracy for survival with a C-index of 0.751. | GBM | To predict survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after liver resection | Ji et al., 2022 [93]. |
| The cause-specific Cox model and PLANN demonstrated the highest performance, closely followed by the Fine-Gray model, RF, and PLANN original. | RF, Partial logistic artificial neural network (PLANN) | To predict survival with data on competing risk | Kantidakis et al., 2023 [94]. |
| The 1-, 3-, and 5-year AUCs were 0.794, 0.849, and 0.872. |
RF | To predict survival of patients with urothelial carcinoma | Liu et al., 2023 [95]. |
| A nomogram predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival was created using selected LOFs and HOFs by DeepSurv, demonstrating favorable predictive efficacy for lung cancer patients at 1 and 3 years, with a C-index of 0.744. | DeepSurv: based on a neural network | To predict survival with different features from routine blood test | Luo et al., 2023 [96]. |
| XGBoost yielded the best outcome with highest AUCs. XGBoost achieved an accuracy of 83% in predicting the mortality rate for Group 1 post-surgical resection and 69% accuracy for Group 2 post-trans arterial chemoembolization (TACE). |
Voting ensembles, LR, KNN, Decision Tree, SVM, RF, XG Boost, Light GBM, and Natural Gradient Boosting (NG Boost) | To predict mortality rate with clinical features | Noh et al., 2022 [97]. |
| DeepSurv yielded a C-index of 0.824 using the training cohort, while validation using the test cohort yielded a C-index of 0.821. | DeepSurv | To predict survival with SEER database | Yu et al., 2022 [98]. |
| Recurrence prediction based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| For 1-year post-NAC, RF outperformed LR with AUC 0.810. For 5-year post-NAC, RF again outperformed LR with AUC 0.829. And for external validation set with SEER database, RF outperformed LR with AUC 0.779. | RF and LR | To predict breast cancer relapse or metastasis with clinical data | Jin et al., 2023 [99]. |
| AdaBoost showed a prediction performance of a sensitivity of 0.673, specificity of 0.807, accuracy of 0.799, AUC of 0.740. | SVM, LR, KNN, NB, RF, gradient boost, AdaBoost, and XGBoost | To predict recurrence in renal cell carcinoma with clinical data | Kim et al., 2022 [100]. |
| Cancer treatment response prediction based on clinical and laboratory data | |||
| The average accuracy from D1 to D3 in predicting outcomes on the test set was 83.21%, with specific accuracies of 83.96% for survival. The optimal DQL model (survival + dysphagia, 2 neural network layers, without radiomics input) demonstrated a 70.4% similarity to physician decisions on the training set and 69.65% on the test set. |
Deep Q Learning (DQL): based on neural network | To select treatment and its outcome with clinical data using DQL | Tardini et al., 2022 [101]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





