Submitted:
07 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Docking Analysis
2.2. The Virtual Screening Program.
- Linear Regression
- 2.
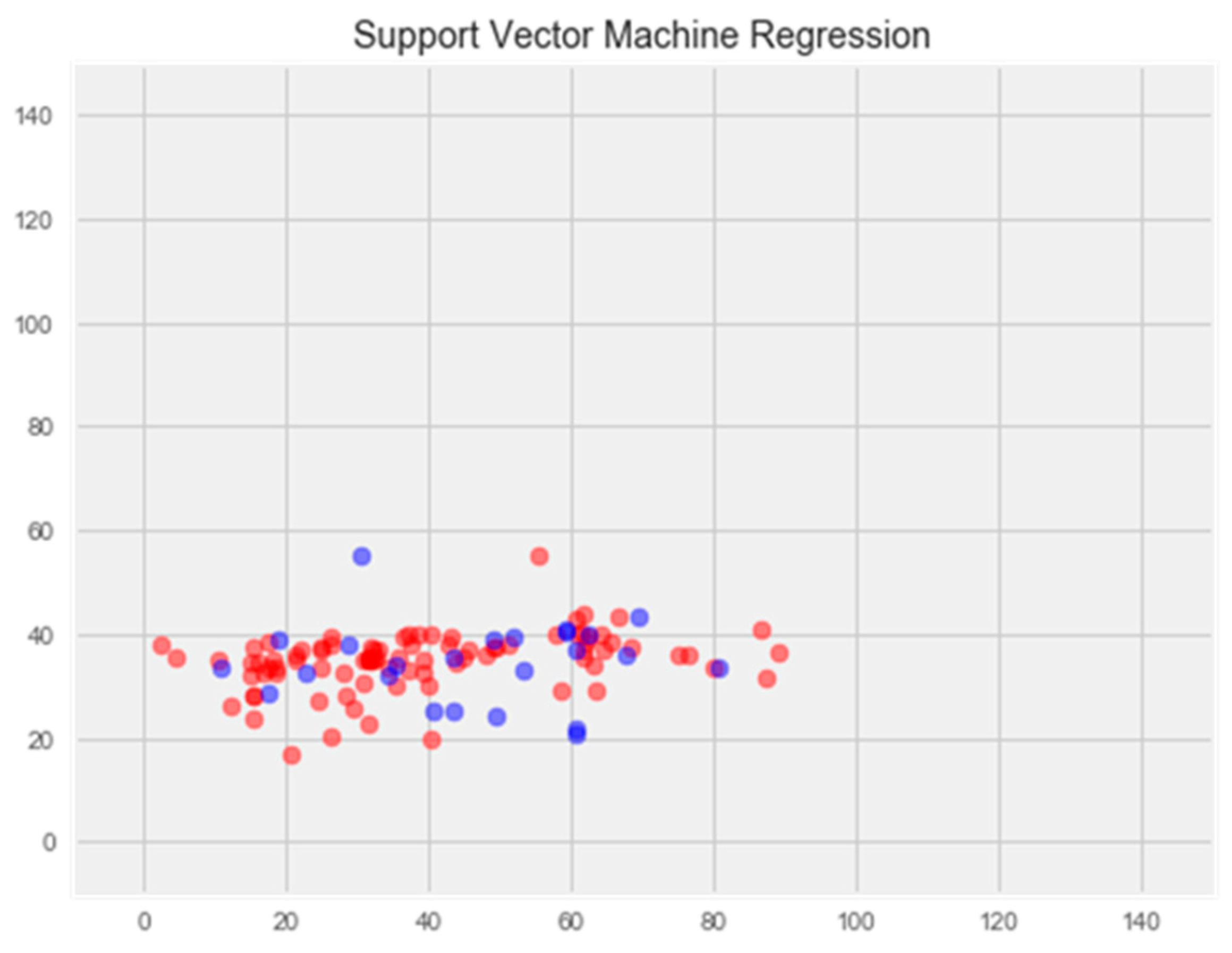
- Support Vector Machine Regression
- 3.
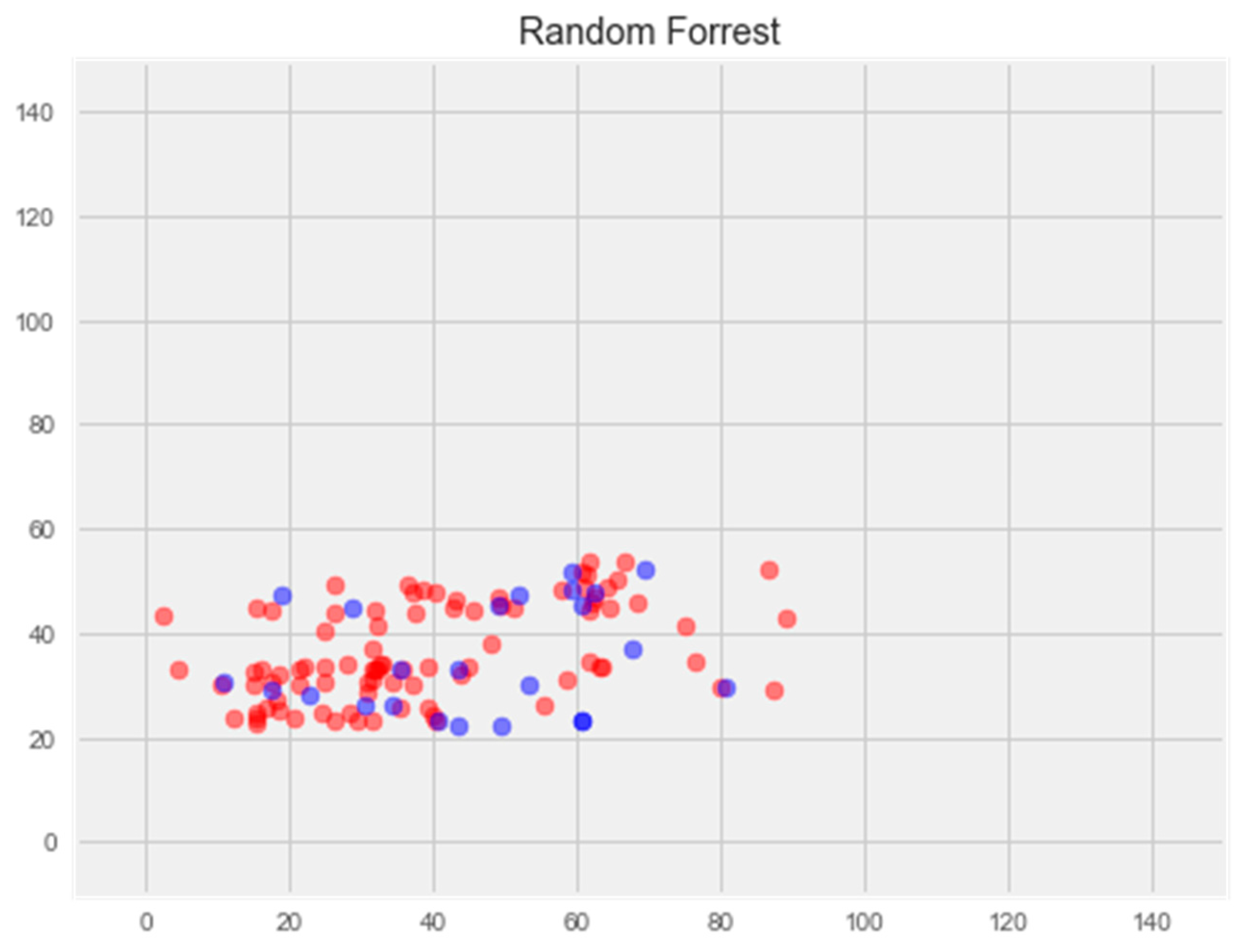
- Random Forest Regression
- 4.
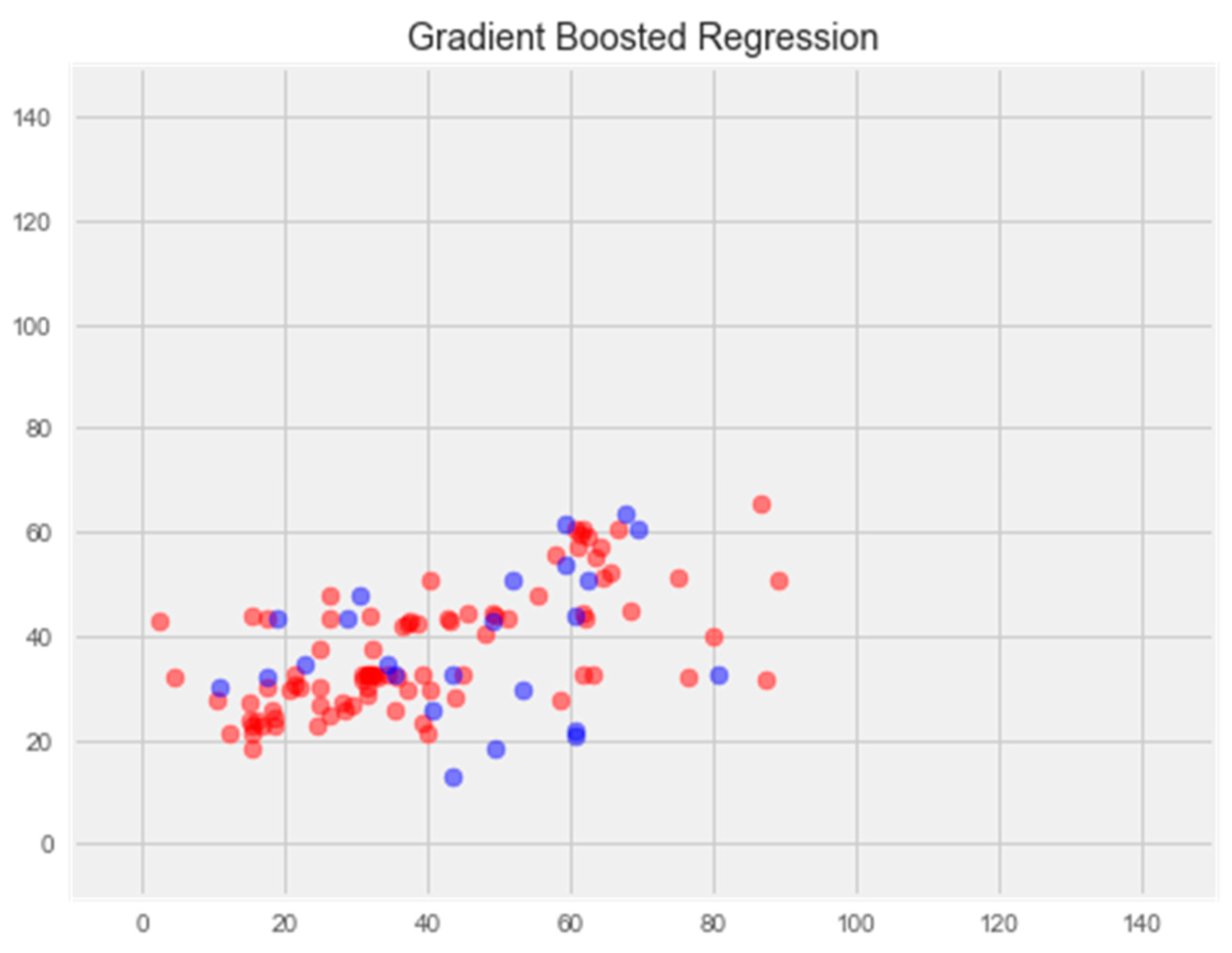
- Gradient Boosting Regression
- 5.
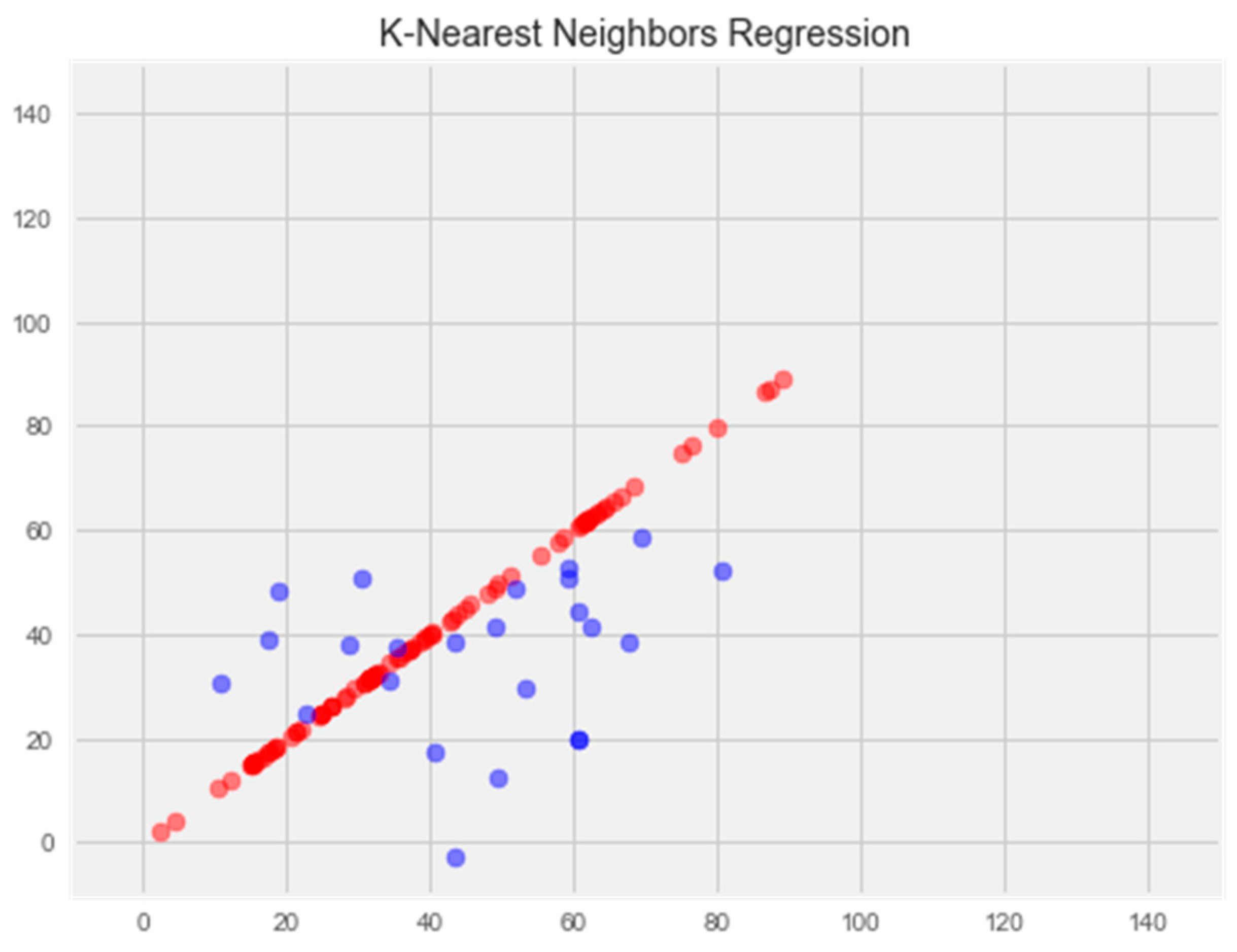
- K-Nearest Neighbors Regression
2.2.1. Linear Regression Model
2.2.2. Regression Model Using the Support Vector Method
2.2.3. Random Forest Model
2.2.4. Graded Boosting Model
2.2.5. K-Nearest Neighbors Model
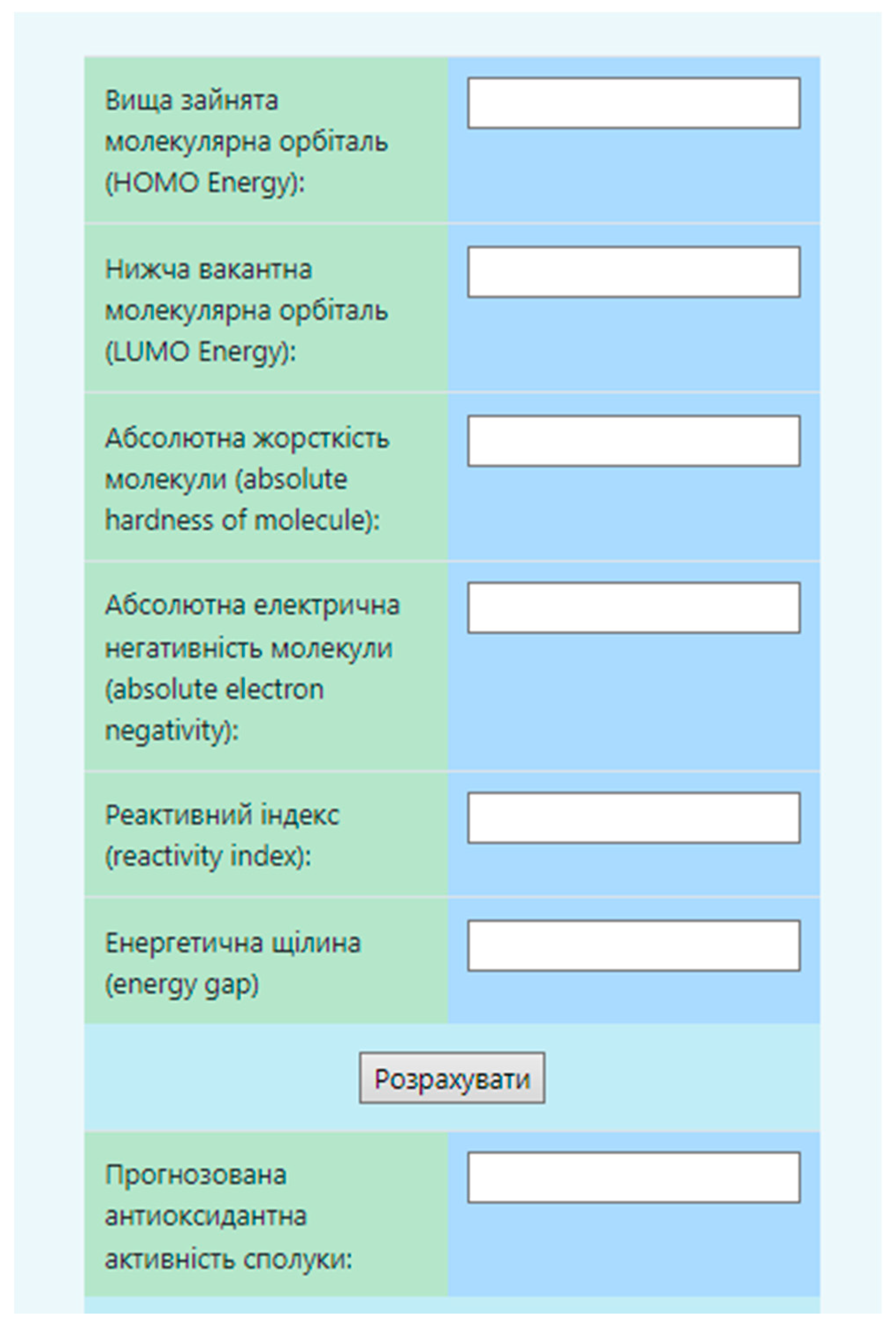
2.3. In Vitro Studies.
2.4. Experimental Model of Multiple Sclerosis
2.5. Drugs and Doses.
2.6. Preparation of Biological Material
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
2.8. Statistical Methods of the Study
3. Results and Discussion
| Experimental groups | 280 nm (protein binding) |
225 nm (level of displaced thyroxine) |
|---|---|---|
| indicators | ∆ | ∆ |
| control | 0±0 | 0±0 |
| catechin | 0,063±0,0001 | 0,082±0,0002 |
| Compound | Affinity (kcal/mol) to human transthyretin |
Docking 2D visualization |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroxin | -6.4 | 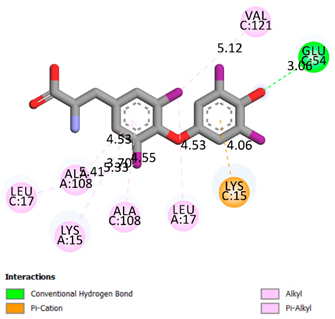 |
| Quercetin | -6.7 | 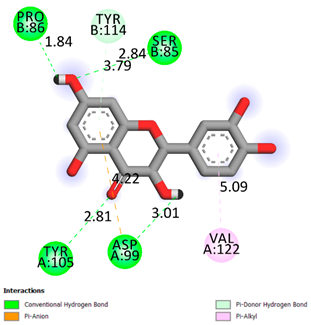 |
| Catechin | -6.2 |
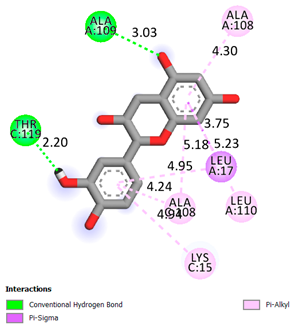 |
| Compound | Affinity (kcal/mol) to human transthyretin |
Docking 2D visualization |
|---|---|---|
| Epicatechin | -7.2 | 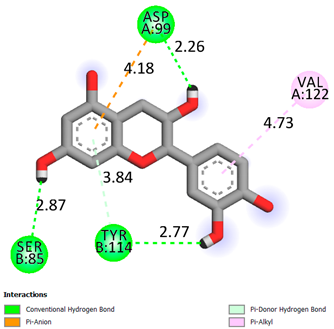 |
| Catechin-3-gallate | -7.6 | 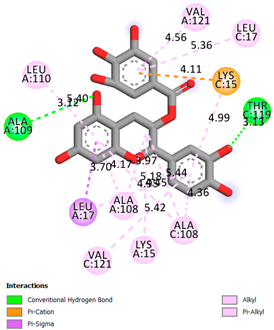 |
| Epicatechin-3-gallate | -7.3 | 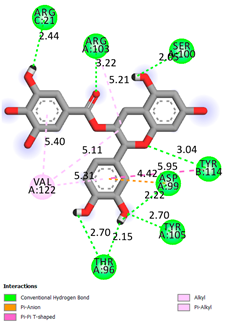 |
| Compound |
Affinity (kcal/mol) to human transthyretin |
Docking 2D visualization |
| Epigallocatechin 3-O-Gallate | -7.7 | 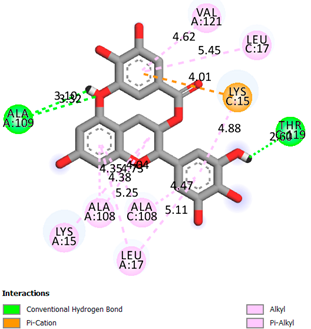 |
| Gallocatechin-3-gallate | -7.5 | 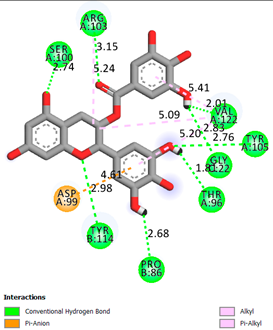 |
| Kaempferol | -7.2 | 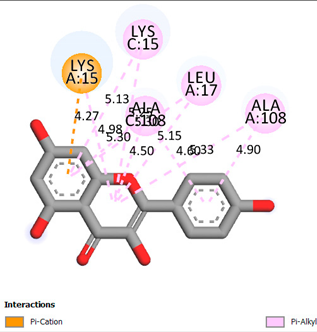 |
| Compound |
Affinity (kcal/mol) to human transthyretin |
Docking 2D visualization |
| Luteolin | -8.0 | 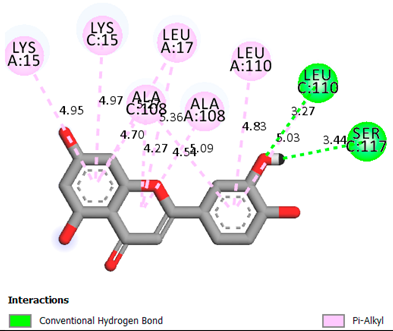 |
| Procyanidin B1 | -7.4 | 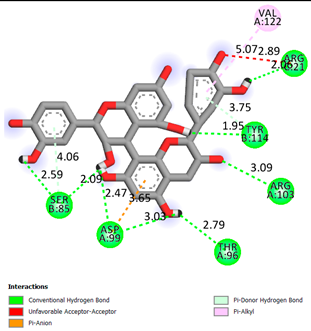 |
| Procyanidin B2 | -8.6 | 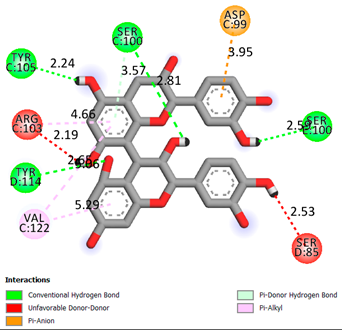 |
| Compound |
Affinity (kcal/mol) to human transthyretin |
Docking 2D visualization |
| Procyanidin B3 | -8.7 | 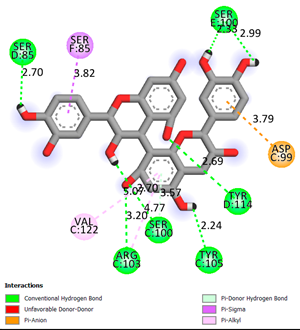 |
| Code | AOA results at 10-6 M | AOA prediction, %. | |
| E, M±m | % | 55.15 | |
| Catechin | 1.625±0.001 | 43.67 | |
| Control | 1.131±0.002 | - | |
| Indicators | Groups of animals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control, EAE (n=10) |
MP (n=10) |
Catechin + MP (n=10) | Mexidol + MP (n=10) |
|
| % of sick animals (total/severe) | 100/70 | 80/30 | 80/10*1 | 80/20* |
| Average clinic index at the peak of EAE, points | 2.6+0.5 | 1.80+0.5 | 0.9+0.5*1 | 1.65+0.152 |
| Average cumulative index, points | 27.2+ 1.5 | 9.4+0.4* | 6.2+0.4*1 | 7.5+0.6* |
| Duration of EAE, days (Student's test) | 16.0 + 1.2 | 8.4 + 0.7* | 6.4 + 0.2*1 | 7.2 + 0.8* |
| Experimental groups | NSE, ng/ml | S-100, ng/ml |
|---|---|---|
| Intact (n=10) | 0.223±0.015 | 0.088±0.002 |
| EAE (control) (n=10) | 9.11±0.151 | 0.97±0.0151 |
| MP (n=10) | 9.15±0.141 | 0.92±0.0331 |
| MP+ Mexidol (n=10) | 7.11±0.21*1,2 | 0.65±0.042*1,2 |
| MP+ catechin (n=10) | 5.74±0.11*1,2,3 | 0.438±0.014*1,2,3 |
| Experimental groups | Nitrotyrosine, ng/ml | IL-1b, ng/ml |
|---|---|---|
| Intact (n=10) | 0.88±0.042 | 0.31±0.018 |
| EAE (control) (n=10) | 9.89±0.331* | 3.88±0.0551 |
| MP (n=10) | 8.11±0.401 | 1.44±0.022*1 |
| MP+ Mexidol (n=10) | 5.32±0.32*1,2, | 1.39±0.033*1, |
| MP+ catechin (n=10) | 4.11±0.07*1,2,3 | 1.00±0.02*2,3 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papiri, G.; D'Andreamatteo, G.; Cacchiò, G. , Alia, S.; Silvestrini, M.; Paci, C.; Luzzi, S.; Vignini, A. Multiple Sclerosis: Inflammatory and Neuroglial Aspects. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023, 45, 1443–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasa, R.; Barcutean, L.; Mosora, O.; Manu, D. Reviewing the Significance of Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Multiple Sclerosis Pathology and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierhansl, L.; Hartung, H.P.; Aktas, O.; Ruck, T.; Roden, M.; Meuth, S.G. Thinking outside the box: non- canonical targets in multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 578–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kölliker-Frers, R.; Udovin, L.; Otero-Losada, M.; Kobiec, T.; Herrera, M.I.; Palacios, J.; Razzitte, G.; Capani, F. Neuroinflammation: An Integrating Overview of Reactive-Neuroimmune Cell Interactions in Health and Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9999146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isik, S.; Kiyak, B.Y.; Akbayir, R.; Seyhali, R.; Arpaci, T. Microglia Mediated Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells. 2023, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alraawi, Z.; Banerjee, N.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, T.K.S. Amyloidogenesis: What Do We Know So Far? Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 13970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagla, B.M.; Buhimschi, I.A. Protein Misfolding in Pregnancy: Current Insights, Potential Mechanisms, and Implications for the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia. Molecules. 2024, 29, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjiagapiou, M.S.; Krashias, G.; Deeba, E.; Christodoulou, C.; Pantzaris, M.; Lambrianides, A. A Preclinical Investigation on the Role of IgG Antibodies against Coagulant Components in Multiple Sclerosis. Biomedicines. 2023, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Shin, Y.; Ju, S.; Han, S.; Choe, W.; Yoon, K.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, I. Heat Shock Response and Heat Shock Proteins: Current Understanding and Future Opportunities in Human Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.; Popazova, O.; Bukhtiyarova, N.; Savchenko, D.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Modulating Nitric Oxide: Implications for Cytotoxicity and Cytoprotection. Antioxidants. 2024, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho Costa, V.G.; Araújo, S.E.-S.; Alves-Leon, S.V.; Gomes, F.C.A. Central nervous system demyelinating diseases: glial cells at the hub of pathology. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1135540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullsiek, R.; Li, Y.; Snyder, K.M.; Wang, S.; Di, D.; Borgatti, A.; Lee, C.; Moore, P.F.; Zhu, C.; Fattori, C.; Modiano, J.F.; Wu,J. and Walcheck, B. Examination of IgG Fc Receptor CD16A and CD64 Expression by Canine Leukocytes and Their ADCC Activity in Engineered NK Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 841859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.A.; Mendoza-Magaña, M.L.; Ramírez-Herrera, M.A.; Hernández-Nazara, Z.H.; Domínguez-Rosales, J.A. Nitrooxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Caused by Air Pollutants Are Associated with the Biological Markers of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants. 2024, 13, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.Y.; Jamerlan, A.; Shim, K.H.; An, S.S.A. Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches Involving Transthyretin in Amyloidogenic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguinetti, C.; Minniti, M.; Susini, V.; Caponi, L.; Panichella, G.; Castiglione, V.; Aimo, A.; Emdin, M.; Vergaro, G.; Franzini, M. The Journey of Human Transthyretin: Synthesis, Structure Stability, and Catabolism. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, E.; Ożyhar, A. Transthyretin: From Structural Stability to Osteoarticular and Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells. 2021, 10, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.A.; Alanazi, F.K.; Raish, M. (2023) Design and synthesis of multi-functional small-molecule based inhibitors of amyloid-β aggregation: Molecular modeling and in vitro evaluation. PLoS ONE. 2023, 18, e0286195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinauro, D.J.; Chiti, F.; Vendruscolo, M. Misfolded protein oligomers: mechanisms of formation, cytotoxic effects, and pharmacological approaches against protein misfolding diseases. Mol Neurodegeneration. 2024, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroo, E.; Koopman, M.; Nollen, E.A.; Mata-Cabana, A. Cellular Regulation of Amyloid Formation in Aging and Disease. Front Neurosci. 2017, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chenet, Y. p53 amyloid aggregation in cancer: function, mechanism, and therapy. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakterzada, F.; Jové, M.; Cantero, J.L.; Pamplona, R.; Piñoll-Ripoll, G. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid nonenzymatic protein damage is sustained in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutha, R.E.; Tatiya, A.U.; Surana, S.J. Flavonoids as natural phenolic compounds and their role in therapeutics: an overview. Futur J Pharm Sci. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, K.; Mendonca, P.; Soliman, K.F.A. The Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of the Chalcone Cardamonin for Alzheimer's Disease. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccone, L.; Tonali, N.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Barlettani, L.; Rossello, A.; Braca, A.; Orlandini, E.; Nencetti, S. Antioxidant Quercetin 3-O-Glycosylated Plant Flavonols Contribute to Transthyretin Stabilization. Crystals. 2022, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokra, D.; Adamcakova, J.; Mokry, J. Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG): A Time for a New Player in the Treatment of Respiratory Diseases? Antioxidants (Basel). 2022, 11, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules. 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoc, T.D.; Le, T.N.; Nguyen, T.V.A.; Mechler. A.; Hoa, N.T.; Nam, N.L.; Vo, Q.V. Mechanistic and Kinetic Studies of the Radical Scavenging Activity of 5-O-Methylnorbergenin: Theoretical and Experimental Insights. The J Phys Chem B. 2022, 126, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florio, P.; Folli, C.; Cianci, M.; Del Rio, D.; Zanotti, G.; Berni, R. Transthyretin Binding Heterogeneity and Anti-amyloidogenic Activity of Natural Polyphenols and Their Metabolites. J Biol Chem. 2015, 290, 29769–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nefodov, O.O.; Belenichev, I.F.; Fedchenko, M.P.; Popazova, O.O.; Ryzhenko, V.P.; Morozova, O.V. Evaluation of methods of modeling and formation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Research Results in Pharmacology. 2022, 8, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaño, T.E.; Zanotti, G.; Parisi, G.; Fernandez-Alberti, S. Evaluating the effect of mutations and ligand binding on transthyretin homotetramer dynamics. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0181019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, V.; Truong, J.Q.; Holdsworth, B.A.; Holien, J.K.; Richardson, S.J.; Chalmers, D.K.; Craik, D.J. Structural Analysis of the Complex of Human Transthyretin with 3',5'-Dichlorophenylanthranilic Acid at 1.5 Å Resolution. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forloni, G. Alpha Synuclein: Neurodegeneration and Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Q. Insights Into the Mechanism of Tyrosine Nitration in Preventing β-Amyloid Aggregation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 619836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Wu, D.; Tan, X.; Zhong, M.; Xing, J.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Cao, F. The Role of Catechins in Regulating Diabetes: An Update Review. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
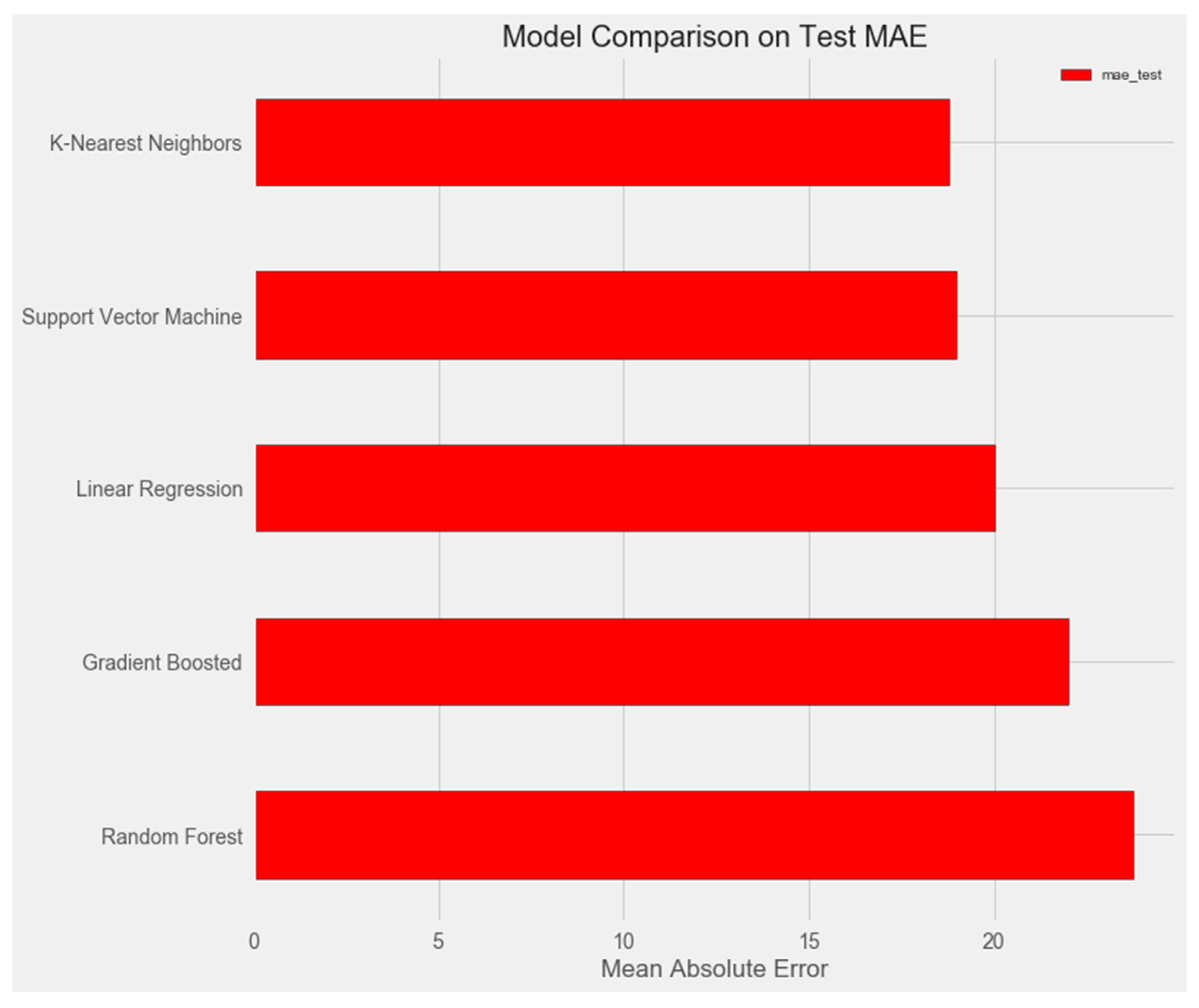
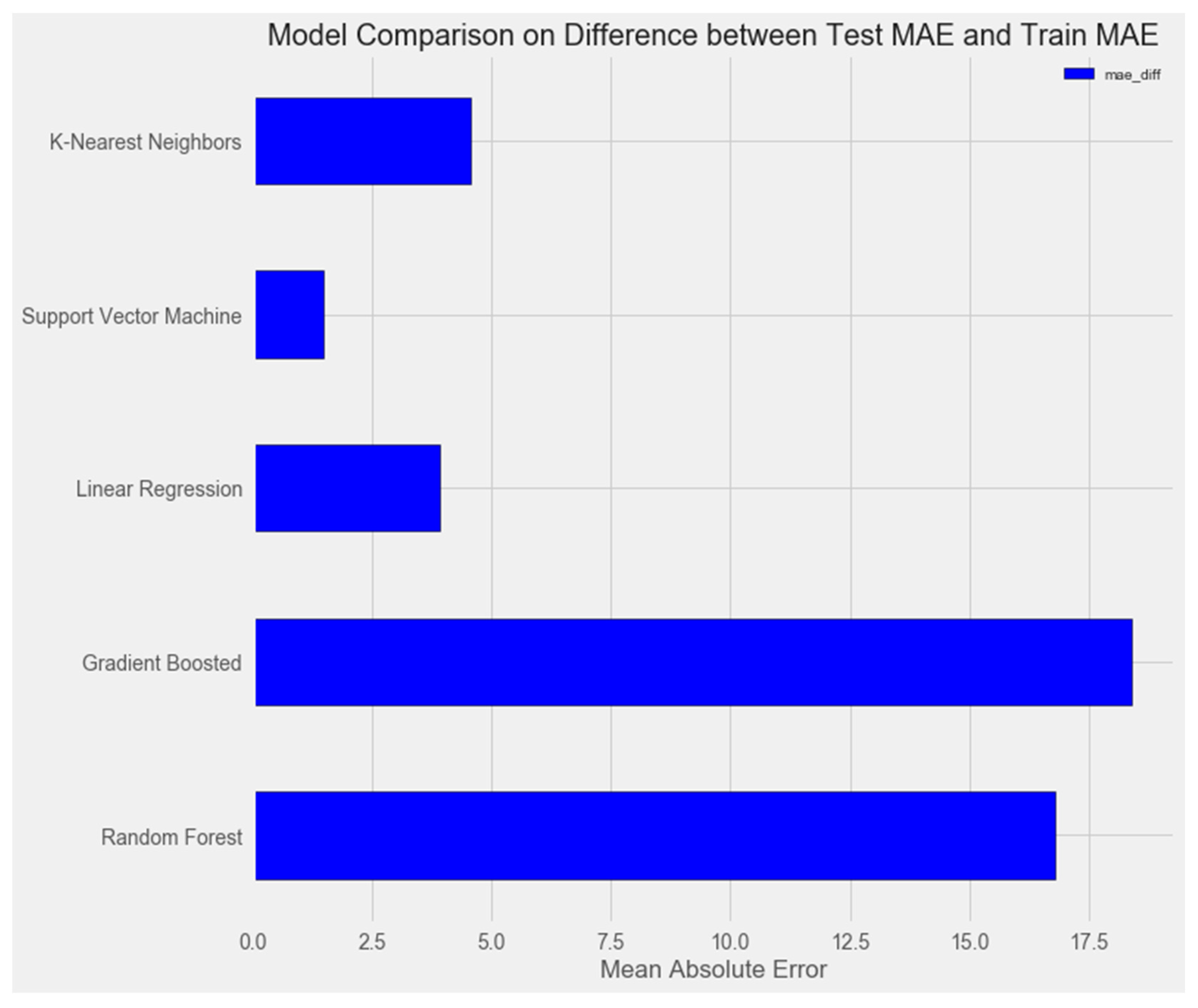
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





