Submitted:
10 June 2024
Posted:
12 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Their Tumor and Lung Tissue Samples
2.2. Ex Vivo Isolation of Cells and Production of Ex Vivo Cell Preparations
2.3. Cell Staining
2.4. Histology
2.5. Microscopy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics of NSCLC Patients
3.2. Experimental Design and Cell Composition after Ex Vivo Expansion from Tumor Samples
3.3. Tumor-Related Markers Expressed by the Cancer Cells That Were Studied in Ex Vivo and Histological Analyses at Once
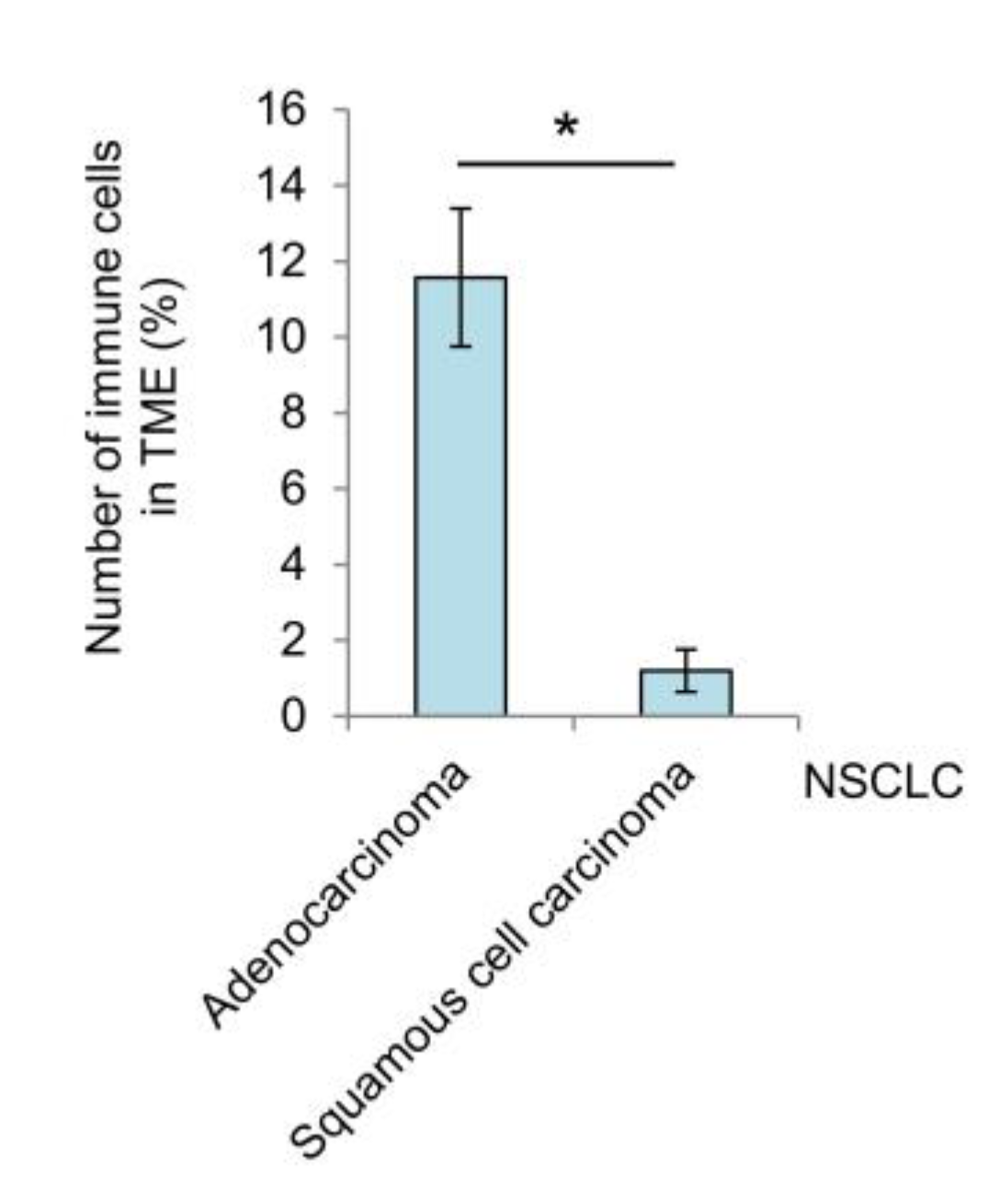
3.4. Immune Cell Landscape in the Tumor Microenvironment and Lung Tissue of NSCLC Patients
3.5. The Expression Pattern of Immune-Related Markers by Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Alveolar Macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer progress and priorities: lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Renteria, E.; Sharp, L.; Weiderpass, E.; Comber, H.; Baas, P.; Bray, F.; Coebergh, J.W.; Soerjomataram, I. Convergence of decreasing male and increasing female incidence rates in major tobacco-related cancers in Europe in 1988–2010. Eur. J. Cancer. 2015, 51, 1144–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharayil, H.; Varghese, J.; John, M.C.; Rajanikant, G.K.; Wilson, C.M.; Al-Yozbaki, M.; Renu, K.; Dewanjee, S.; Sanyal, R.; Dey, A.; et al. Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Implications on molecular pathology and advances in early diagnostics and therapeutics. Genes Diseases 2023, 10, 960–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-Y.; Huang, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, S.-H.; Hung, W.-H.; Cheng, Y.-F. The comparison between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, L.; Askin, F.; Gabrielson, E.; Li, Q.K. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Katzenstein, A.-L.A. Subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas lacking morphologic differentiation on biopsy specimens: utility of an immunohistochemical panel containing TTF-1, Napsin A, p63, and CK5/6. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, K.; Cremer, M.; Zgorzelski, C.; Harms, A.; Muley, T.; Winter, H.; Kazdal, D.; Warth, A.; Kriegsmann, M. Agreement of CK5/6, p40, and p63 immunoreactivity in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathology 2019, 51, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.A.; Morrison, L.E.; Behman, L.J.; Draganova-Tacheva, R.; O'Neill, R.; Solomides, C.C. Chromogenic immunohistochemical quadruplex provides accurate diagnostic differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer. Annals Diagnos. Pathol. 2020, 45, 151454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.M.; Candido, S.; Lavoro, A.; Vivarelli, S.; Gattuso, G.; Calina, D.; Libra, M.; Falzone, L. Clinical relevance of targeted therapy and immune-checkpoint inhibition in lung cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, A.; McCoach, C.E.; Rotow, J.K.; Harris, L.; Haderk, F.; Kerr, D.L.; Yu, E.A.; Schenk, E.L.; Tan, W.; Zee, A.; et al. Therapy-induced evolution of human lung cancer revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Cell 2020, 182, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Bauml, J.M.; Langer, C.J. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 13, 676–683. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-J.; Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. The immunotherapy for colorectal cancer, lung cancer and pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, M.A.; Aricak, O.; Kis, L.; Yoshikawa, A.; De Petris, L.; Grundberg, O.; Pham, H.H.N.; Roden, A.C.; Fukuoka, J.; Attanoos, R.; et al. Clinicopathological significance of the expression of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Diagnos. Pathol. 2021, 51, 151701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuya, T.; Carbone, D.P. Predictive markers for the efficacy of anti–PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.K.; Pan, A.; Davis, A.A.; Raparia, K.; Mohindra, N.A.; Matsangou, M.; Giles, F.J. Biomarkers for PD-1/PD-l1 blockade therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: is PD-L1 expression a good marker for patient selection? Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallqvist, A.; Rohlin, A.; Raghavan, S. Immune checkpoint blockade and biomarkers of clinical response in non–small cell lung cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, F.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X. Research progress of biomarkers in the prediction of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapeutic efficiency in lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1227797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, K.M.; Tsao, M.-S.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Wistuba, I.I.; Hirsch, F.R. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 immunohistochemistry in lung cancer: In what state is this art? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Long-Mira, E.; Bence, C.; Butori, C.; Lassalle, S.; Bouhlel, L.; Fazzalari, L.; Zahaf, K.; Lalvée, S.; Washetine, K.; et al. Comparative study of the PD-L1 status between surgically resected specimens and matched biopsies of NSCLC patients reveal major discordances: a potential issue for anti-PD-L1 therapeutic strategies. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, C.; Mok, T.S.; Zhuang, W.; Xu, H.; Miao, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. Comparison of 22C3 PD-L1 expression between surgically resected specimens and paired tissue microarrays in non–small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gniadek1, T.J.; Li, Q.K.; Tully, E.; Chatterjee, S.; Nimmagadda, S.; Gabrielson, E. Heterogeneous expression of PD-L1 in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: implications for assessment by small biopsy. Modern Pathol. 2017, 30, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munari, E.; Zamboni, G.; Lunardi, G.; Marchionni, L.; Marconi, M.; Sommaggio, M.; Brunelli, M.; Martignoni, G.; Netto, G.J.; Hoque, M.O.; et al. PD-L1 expression heterogeneity in non–small cell lung cancer: defining criteria for harmonization between biopsy specimens and whole sections. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, T.; Udagawa, H.; Sato, J.; Horinouchi, H.; Murakami, S.; Goto, Y.; Kanda, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Zenke, Y.; et al. A minimum of 100 tumor cells in a single biopsy sample is required to assess programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in predicting patient response to nivolumab treatment in nonsquamous non–small cell lung carcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunnissen, E.; Kerr, K.M.; Dafni, U.; Bubendorf, L.; Finn, S.P.; Soltermann, A.; Biernat, W.; Cheney, R.; Verbeken, E.; Warth, A.; et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression influenced by tissue sample size. Scoring based on tissue microarrays’ and cross-validation with resections, in patients with, stage I–III, non-small cell lung carcinoma of the European Thoracic Oncology Platform Lungscape cohort. Modern Pathol. 2020, 33, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naso, J.R.; Banyi, N.; Al-Hashami, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Ionescu, D.N.; Ho, C. Discordance in PD-L1 scores on repeat testing of non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cancer Treatm. Res. Communic. 2021, 27, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; McElhinny, A.; Stanforth, D.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Jansson, M.; Kulangara, K.; Richardson, W.; Towne, P.; Hanks, D.; Vennapusa, B.; et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for lung cancer: results from phase 1 of the Blueprint PD-L1 IHC assay comparison project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunnissen, E.; de Langen, A.J.; Smit, E.F. PD-L1 IHC in NSCLC with a global and methodological perspective. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, D.P.; Yang, Y.; Boisot, S.; Sudarsanam, S.; Wang, J.-F.; Chizhevsky, V.; Zhao, G.; Arain, S.; Weiss, L.M. Immunohistochemical detection of PD-L1 among diverse human neoplasms in a reference laboratory: observations based upon 62,896 cases. Modern Pathol. 2019, 32, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.A.; Han, G.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.E.; Wasserman, B.E.; Pelekanou, V.; Mani, N.L.; McLaughlin, J.; Schalper, K.A.; Rimm, D.L. Quantitative and pathologist-read comparison of the heterogeneity of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Modern Pathol. 2017, 30, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunnström, H.; Johansson, A.; Westbom-Fremer, S.; Backman, M.; Djureinovic, D.; Patthey, A.; Isaksson-Mettävainio, M.; Gulyas, M.; Micke, P. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry in clinical diagnostics of lung cancer: inter-pathologist variability is higher than assay variability. Modern Pathol. 2017, 30, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butter, R.; Halfwerk, H.; Radonic, T.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.; Thunnissen, E. The impact of impaired tissue fixation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer on protein deterioration and DNA degradation. Lung Cancer 2023, 178, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travert, C.; Barlesi, F.; Greillier, L.; Tomasini, P. Immune oncology biomarkers in lung cancer: an overview. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashireva, L.A.; Muravyova, D.T.; Popova, N.O.; Goldberg, V.E.; Vtorushin, S.V.; Perelmuter, V.M. Parameters of tumor microenvironment determine effectiveness of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2021, 86, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chau, Y.-F.; Bai, H.; Wu, X.; Duan, J. Biomarkers for immunotherapy in driver-gene-negative advanced NSCLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J. (Ed.) Tumor stroma. Biology and therapeutics, first ed.; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, M.; Li, A.; Zhou, L.; Chu, Q.; Luo, S.; Wu, K. Immune signature-based risk stratification and prediction of immune checkpoint inhibitor’s efficacy for lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rączkowska, A.; Paśnik, I.; Kukiełka, M.; Nicoś, M.; Budzinska, M.A.; Kucharczyk, T.; Szumiło, J.; Krawczyk, P.; Crosetto, N.; Szczurek, E. Deep learning-based tumor microenvironment segmentation is predictive of tumor mutations and patient survival in non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirlog, R.; Chiroi, P.; Rusu, I.; Jurj, A.M.; Budisan, L.; Pop-Bica, C.; Braicu, C.; Crisan, D.; Sabourin, J.-C. , Berindan-Neagoe, I. Cellular and molecular profiling of tumor microenvironment and early-stage lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahchan, N.S.; Mujal, A.M.; Pollack, J.L.; Binnewies, M.; Sriram, V.; Reyno, L.; Krummel, M.F. Tuning the tumor myeloid microenvironment to fight cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghy, K.; Ladanyi, A.; Reszegi, A.; Kovalszky, I. Insights into the tumor microenvironment—components, functions and therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, T.-D. Breakthroughs in cancer immunotherapy: an overview of T cell, NK cell, Mφ, and DC-based treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmetova, D.A.; Kozlov, V.V.; Gulyaeva, L.F. New insight into the role of AhR in lung carcinogenesis. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2022, 87, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.N.; Karim, K.; Sung, M.; Le, L.W.; Lau, S.C.M.; Sacher, A.; Leighl, N.B. Tobacco exposure and immunotherapy response in PD-L1 positive lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishanova, A.Y.; Perepechaeva, M.L. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in oxidative stress as a double agent and its biological and therapeutic significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, K.K.; Kobylecki, C.J.; Skov-Jeppesen, S.M.; Bojesen, S.E. Development and validation of a simple general population lung cancer risk model including AHRR-methylation. Lung Cancer 2023, 181, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ufimtseva, E.; Eremeeva, N.; Petrunina, E.; Umpeleva, T.; Karskanova, S.; Baiborodin, S.; Vakhrusheva, D.; Kravchenko, M.; Skornyakov, S. Ex vivo expansion of alveolar macrophages with Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the resected lungs of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Moriyama, T.; Onimaru, M.; Nakata, K.; Nabae, T.; Ueki, T.; Sato, N.; Tominaga, Y.; et al. Prospectively isolated cancer-associated CD10+ fibroblasts have stronger interactions with CD133+ colon cancer cells than with CD133- cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola, A.G.P.; Bashover, E.; Joseph, C.; Staerkel, G.; Wang, W.-L.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S. The usefulness of various cytologic specimen preparations for PD-L1 immunostaining in non-small cell lung carcinoma. J. Amer. Soc. Cytopathol. 2018, 7, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.M.; Rabindranath, M.; Weiss, J.; Li, J.J.N.; Fung, A.S.; Mullen, D.; Alshamlan, N.; Ruff, H.M.; Tong, L.C.B.; Pal, P.; et al. PD-L1 assessment in cytology samples predicts treatment response to checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2022, 171, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikou, K.; Rossi, T.; Verlicchi, A.; Priano, I.; Cravero, P.; Burgio, M.A.; Crinò, L.; Bandini, S.; Ulivi, P.; Delmonte, A. Circulating tumour cells: Detection and application in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, T.-F.; Chiu, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chou, T.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chiang, C.-L.; Huang, C.-S.; Tuang, I.-S.; Ho, Y.-H.; et al. Proliferative ability of circulating tumor cells is a prognostic factor in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2023, 178, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.M.; Freitag, H.; Hartmann, J.S.; Niehaus, K.; Galanis, M.; Griesshammer, M.; Kellner, U.; Bednarz, H. Subtyping non-small cell lung cancer by histology-guided spatial metabolomics. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Takanashi, Y.; Uebayashi, A.; Oka, M.; Mizuno, K.; Kawase, A.; Oyama, S.; Kitamoto, T.; Kondo, M.; Omori, S.; et al. Lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma difficult for immunohistochemical diagnosis can be distinguished by lipid profile. Scient. Rep. 2023, 13, 12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xing, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X. From targeted therapy to a novel way: Immunogenic cell death in lung cancer. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencz, B.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; Csende, K.; Fillinger, J.; Poór, V.; Lantos, A.; Pipek, O.; Sólyom-Tisza, A.; Rényi-Vámos, F.; Schelch, K.; et al. Comparative expression analysis of immune-related markers in surgically resected lung neuroendocrine neoplasms. Lung Cancer 2023, 181, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibille, A.; Corhay, J.-L.; Louis, R.; Ninane, V.; Jerusalem, G.; Duysinx, B. Eosinophils and lung cancer: From bench to bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
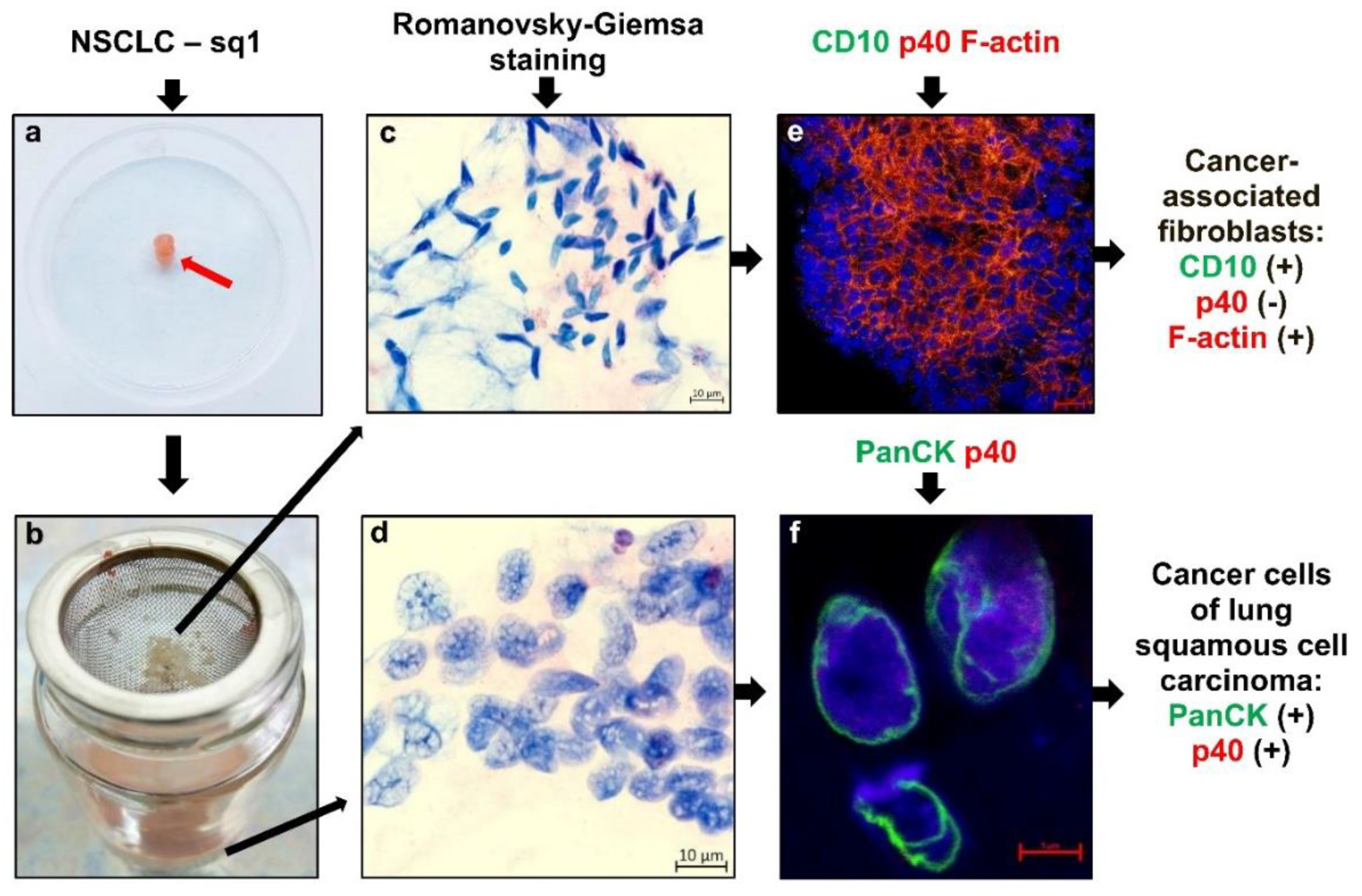
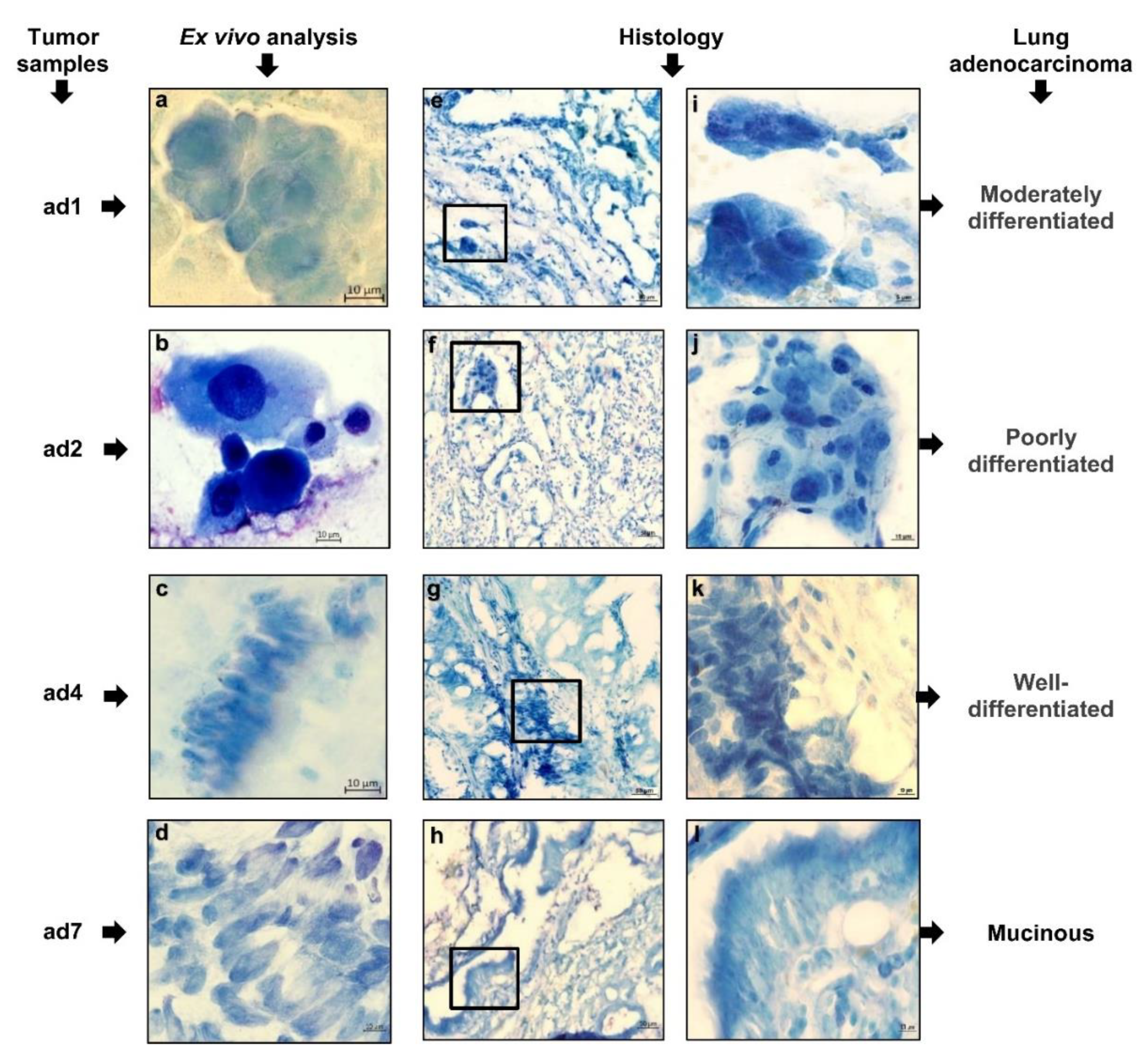
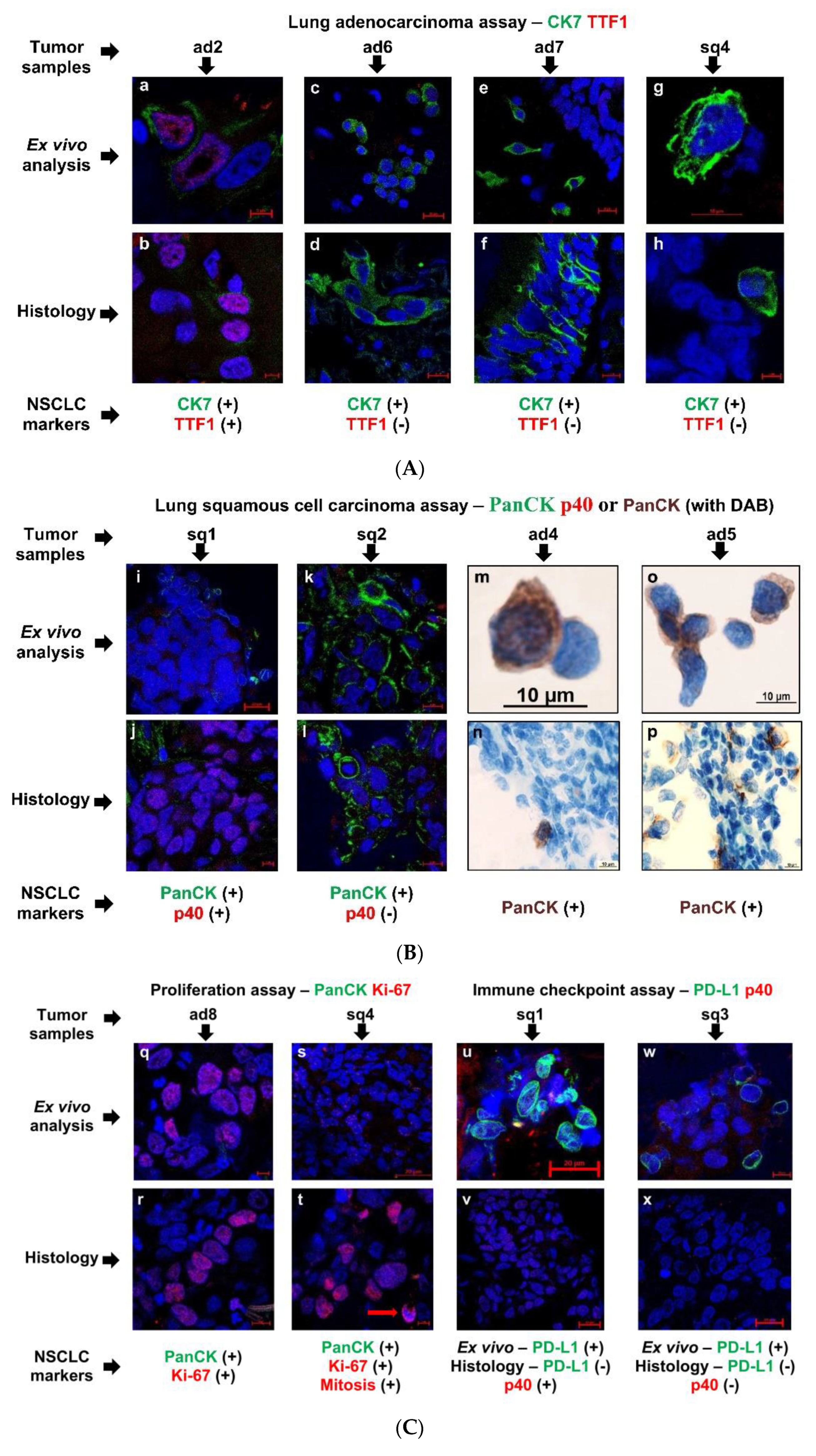
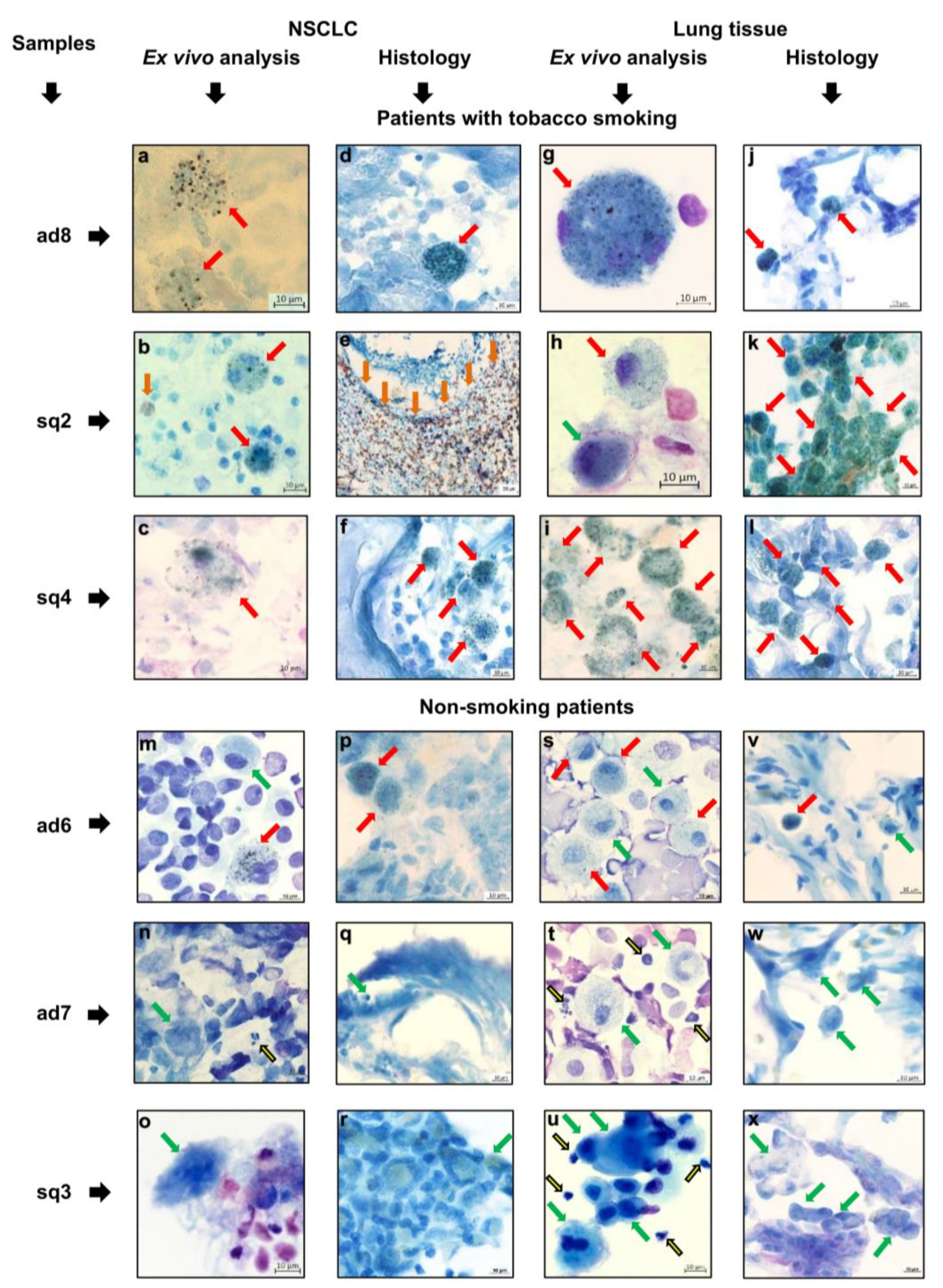
| NSCLC patients 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Tumor samples (g) 2 | TNM classification | Sex 3 | Age (years) |
Smoking status (years) 4 | Attendant pulmonology diseases | Surgery 5 |
| Adenocarcinoma | |||||||
| ad1 | 1.06 | Т1сN2А2М0(IIIА) | M | 72 | 45 | LLL | |
| ad2 | 0.12 | Т2аN0М0(IВ) | F | 68 | 50 | COPD | RLL |
| ad3 | 0.19 | Т1сN0М0(IА3) | M | 62 | 50 | Chronic bronchitis | LUL |
| ad4 | 0.20 | Т1сN1М0(IIВ) | M | 58 | 45 | RLL | |
| ad5 | 0.17 | Т2N0М0(IВ) | M | 63 | 40 | LUL | |
| ad6 | 0.04 | T2aN0M0(IВ) | F | 55 | - | RUL | |
| ad7 | 0.09 | T2bN0M0(IIA) | F | 64 | - | RLL | |
| ad8 | 0.12 | T1bN0M0(IА2) | M | 63 | 54 | RLL | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | |||||||
| sq1 | 0.07 | Т1сN0М0(IА3) | M | 63 | 45 | Chronic bronchitis | RL |
| sq2 | 0.13 | Т1сN0М0(IА3) | M | 66 | 50 | LUL | |
| sq3 | 0.12 | Т3NхМ0 | M | 67 | 40 (+), 10 (-) |
RLL | |
| sq4 | 0.12 | T1cN1M0(IIВ) | M | 72 | 51 | COPD, pneumosclerosis | RUL |
| NSCLC markers 1 | NSCLC patients | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | Squamous cell carcinoma | |||||||||||
| ad1 | ad2 | ad3 | ad4 | ad5 | ad6 | ad7 | ad8 | sq1 | sq2 | sq3 | sq4 | |
| Lung adenocarcinoma-specific markers | ||||||||||||
| CK7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 5 | 2 | - | - | nd | nd | 0.5 |
| TTF1 | - | 30 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - |
| Lung squamous cell carcinoma-specific markers | ||||||||||||
| PanCK | 5 | - | - | 5 | 10 | nd | nd | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | - | - |
| p40 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | - | 30 | - | - | - |
| Proliferation marker | ||||||||||||
| Ki-67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | 50 | - | - | 20 |
| Immunotherapy marker | ||||||||||||
| PD-L1 | - | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | 10 | - | 2 | - |
| PD-L1 (histology) 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lung carcinogenesis markers | ||||||||||||
| AhR | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | nd |
| AhRR | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| CYP1A1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | - | 10 | - | - | - |
| Tobacco smoking 3 | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | + |
| Immune cells 4 in the TME | ||||||||||||
| Macrophages | 72.7 | 1.5 | 16.1 | 75 | 71.4 | 86.7 | 58.3 | 75 | 33.3 | 5.8 | 42.9 | 87.1 |
| Neutrophils | 22.7 | 95.5 | 28.6 | - | 14.3 | 3.3 | 16.7 | - | 66.7 | 2.5 | 42.9 | - |
| Lymphocytes | 4.6 | 3 | 1.2 | - | - | 10 | 25 | 25 | - | 0.8 | 14.3 | - |
| Eosinophils | - | - | 54.2 | 25 | 28.6 | - | - | - | - | 90.9 | - | 12.9 |
| Total number 5 | 7.4 | 41.2 | 18.4 | 11.8 | 13.8 | 14.2 | 12.4 | 3 | 0.9 | 28.6 | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| Immune cells 4 in the lung tissue | ||||||||||||
| Macrophages | 100 | 54 | 65.7 | 82.1 | 63.9 | 94 | 90.2 | 96.5 | 44.6 | 52.5 | 64.8 | 99 |
| Neutrophils | - | 39.1 | 16.2 | 4.1 | 22.2 | 1.2 | 7 | 3.5 | 14.3 | 29.5 | 31.5 | - |
| Lymphocytes | - | 6.9 | 18.2 | - | 12.5 | 4.8 | 2.8 | - | 41.1 | 11.5 | 3.7 | - |
| Eosinophils | - | - | - | 13.8 | 1.4 | - | - | - | - | 6.6 | - | 1 |
| Attendant immune diseases 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Asthma | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





