Submitted:
10 June 2024
Posted:
12 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
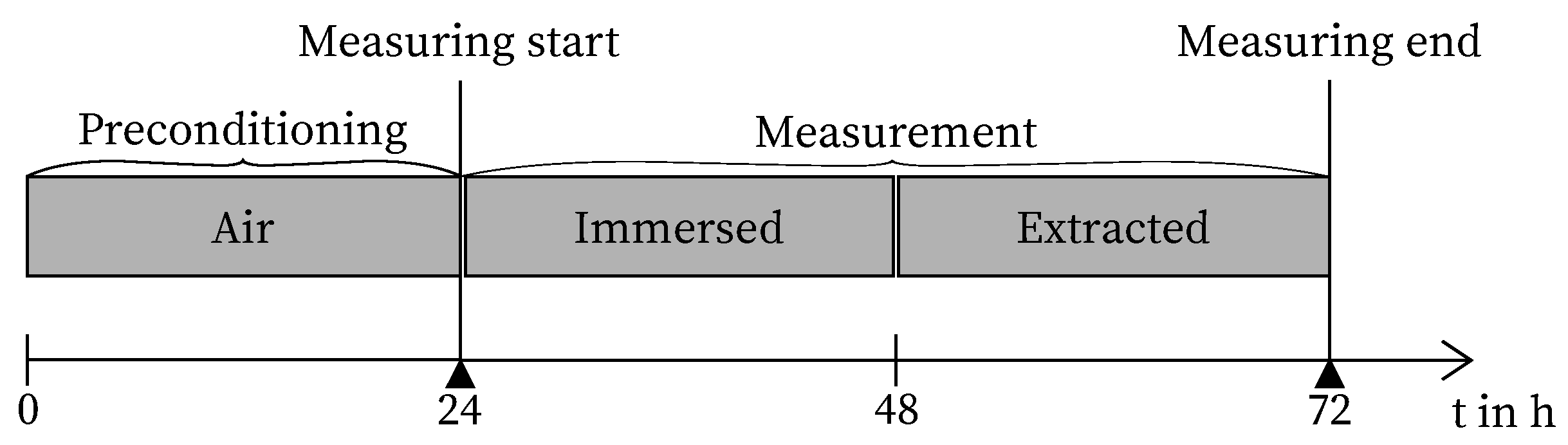
2.1. Experimental Design

2.2. Material
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
- The ambient humidity and the concentration of various salts exert a significant influence on the swelling and shrinkage of the polymer coating material of optical fibers.
- This results in a notable impact on the outcomes of a fiber optic strain or temperature measurement, which is conducted through the use of Brillouin or Rayleigh backscattering.
- In the case of the ORMOCER®- and polyimide-coated fibers, these effects were largely reversible. In the case of the acrylate-coated fiber, hysteresis was observed in deionized water, cement solution, and NaCl solution.
- The potential for hysteresis during long-term or repeated exposure remains uncertain with regard to the ORMOCER®- and polyimide-coated fiber.
- The preconditioning (humidity and temperature) appears to significantly influence the deformation effect of fiber coatings.
- Further research is required to investigate the effects of preconditioning, salt concentrations, and climatic conditions, as well as the variation of coating materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrias, A.; Rius, J.R.C.; Herrero, S.V. Fatigue testing of reinforced concrete beam instrumented with distributed optical fiber sensors (DOFS). Civil Engineering Research in Ireland (CERI 2018) 2018, 2018, 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Barrias, A.; Casas, J.; Villalba, S. A Review of Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors for Civil Engineering Applications. Sensors 2016, 16(5), 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanowicz, K.; Gebauer, D.; Koschemann, M.; Speck, K.; Steinbock, O.; Beckmann, B.; Marx, S. Distributed fiber optic sensors for measuring strains of concrete, steel, and textile reinforcement: Possible fields of application. Structural Concrete 2022, 23(6), 3367–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, I.; Mao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hveding, F.; Bukhamsin, A.Y.; Ng, T.K.; Ooi, B.S. A Review of Distributed Fiber–Optic Sensing in the Oil and Gas Industry. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2022, 40(5), 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanagiotis, C.; Krebber, K. Machine Learning Approaches in Brillouin Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23(13), 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.X. Recent progress of using Brillouin distributed fiber optic sensors for geotechnical health monitoring. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2017, 258, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrich, M.; Messerer, D.; Holschemacher, K. The Challenges and Advantages of Distributed Fiber Optic Strain Monitoring in and on the Cementitious Matrix of Concrete Beams. Sensors 2023, 23(23), 9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoult, R.D.; Bertholet, A.; de Almeida, J.P. Core versus Surface Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Comparison of Fiber-Optic Strain Sensing to Conventional Instrumentation. Sensors 2023, 23(3), 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisbrich, M.; Holschemacher, K. Comparison between different fiber coatings and adhesives on steel surfaces for distributed optical strain measurements based on Rayleigh backscattering. Journal of Sensors and Sensor Systems 2018, 7(2), 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, D.; Sugiyama, J.I.; Zushi, H.; Murayama, H. An optical fiber sensing technique for temperature distribution measurements in microwave heating. Measurement Science and Technology 2015, 26(8), 085105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrich, M.; Holschemacher, K.; Bier, T. Comparison of different fiber coatings for distributed strain measurement in cementitious matrices. Journal of Sensors and Sensor Systems 2020, 9(2), 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrich, M. 2020. Verbesserte Dehnungsmessung im Betonbau durch verteilte faseroptische Sensorik. PH.D. thesis, Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, December 16, https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:105-qucosa2-733605.
- Weisbrich, M.; Holschemacher, K.; Bier, T. Validierung verteilter faseroptischer Sensorik zur Dehnungsmessung im Betonbau. Beton- und Stahlbetonbau 2021, 116, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbers, M.; Richter, B.; Gebauer, D.; Classen, M.; Marx, S. Crack monitoring on concrete structures: Comparison of various distributed fiber optic sensors with digital image correlation method. Structural Concrete 2023, 24, 6123–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbers, M.; Richter, B.; Marx, S. Crack Monitoring on Concrete Structures using Robust Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. ce/papers 2023, 6, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, J.; Herbers, M.; Liebold, F.; Wagner, F.; Grzesiak, S.; de Sousa, C.; Pahn, M.; Maas, H.G.; Marx, S.; Curbach, M.; Beckmann, B. Investigation of the Crack Behavior of CRC Using 4D Computed Tomography, Photogrammetry, and Fiber Optic Sensing. Buildings 2023, 13(10), 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, C.G.; Fernandez, I.; Rempling, R. Crack monitoring in reinforced concrete beams by distributed optical fiber sensors. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering 2020, 17(1), 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, G. Effect of the plastic coating on strain measurement of concrete by fiber optic sensor. Measurement 2003, 34(3), 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J. Investigation of a coated optical fiber strain sensor embedded in a linear strain matrix material. Optics and Lasers in Engineering 2001, 35(4), 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhou, L. Sensitivity coefficient evaluation of an embedded fiber-optic strain sensor. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 1998, 69, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiang, P.; Jiang, L. Strain transfer theory of industrialized optical fiber-based sensors in civil engineering: A review on measurement accuracy, design and calibration. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2019, 285, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liehr, S.; Breithaupt, M.; Krebber, K. Distributed Humidity Sensing in PMMA Optical Fibers at 500 nm and 650 nm Wavelengths. Sensors 2017, 17(4), 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, T.; Magalhães, R.; Scherino, L.; Martin-Lopez, S.; Martins, H.F.; Petagna, P.; Thévenaz, L. Humidity Effect on Acrylate- and Polyimide-Coated Fibres for Distributed Sensing Applications. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Sensors Conference 2020 Special Edition. Washington, DC, United States, T3.73., 8–-12 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajanca, P.; Hicke, K.; Krebber, K. Distributed Fiberoptic Sensor for Simultaneous Humidity and Temperature Monitoring Based on Polyimide-Coated Optical Fibers. Sensors 2019, 19(23), 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totland, C.; Thomas, P.J.; Stordal, I.F.; Eek, E. A Fully Distributed Fibre Optic Sensor for the Detection of Liquid Hydrocarbons. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21(6), 7631–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.d.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2015–2019). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92(1), 397–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Shull, K.R.; Papatheodorou, T.; Styrkas, D.A.; Keddie, J.L. Equilibrium Swelling of Hydrophilic Polyacrylates in Humid Environments. Macromolecules 1999, 32(1), 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, H.; Fang, L.; Tan, T. Superabsorbent hydrogels from poly(aspartic acid) with salt-, temperature- and pH-responsiveness properties. Polymer 2005, 46(14), 5368–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, S.; Soto, M.A.; Jderu, A.; Dorobantu, D.; Enachescu, M.; Ziegler, D. Swelling-Based Distributed Chemical Sensing with Standard Acrylate Coated Optical Fibers. Sensors 2021, 21(3), 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, D.; Jderu, A.; Enachescu, M.; Ziegler, D. Fabrication of Optical Fibers with Multiple Coatings for Swelling-Based Chemical Sensing. Micromachines 2021, 12(8), 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna Inc. ODiSI-B Optical Distributed Sensor Interrogator. Available online: https://www.advancedphotonix.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/ODB5_DataSheet_Rev13_020217.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- FBGS International, N.V. DTG coating Ormocer®-T for Temperature Sensing Applications. Available online: https://fbgs.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Introducing_and_evaluating_Ormocer-T_for_temperature_sensing_applications.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Guangzhou Aosong Electronic Co., Ltd. AHT20 - Humidity and Temperature Sensor. Available online: http://http://www.aosong.com/userfiles/files/media/Data%20Sheet%20AHT20.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Sensirion, AG. Datasheet SHTC3 - Humidity and Temperature Sensor IC. Available online: https://sensirion.com/media/documents/643F9C8E/63A5A436/Datasheet_SHTC3.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Microchip Technology Inc. ±0.5 ∘C Maximum Accuracy Digital Temperature Sensor. Available online: https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/25095A.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- MACHEREY-NAGEL GmbH & Co. KG. Datasheet Filter paper MN 615. Available online: https://www.mn-net.com/media/pdf/26/7b/bd/Data-sheet-MN-615.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Leyva-Porras, C.; Estrada-Moreno, I.A.; Piñón-Balderrama, C.I.; Flores-Gallardo, S.G.; Márquez-Lucero, A. Thermodynamic Parameters of Crosslinked Elastomers (BR, SBR and NBR) and Their Blends. Polymers 2024, 16(3), 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejcus, K.; Spitalniak, M.; Dabrowska, J. Swelling Behaviour of Superabsorbent Polymers for Soil Amendment under Different Loads. Polymers 2018, 10(3), 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apelblat, A.; Korin, E. The vapour pressures of saturated aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sodium bromide, sodium nitrate, sodium nitrite, potassium iodate, and rubidium chloride at temperatures from 227 K to 323 K. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics 1998, 30(1), 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falbe, J.; Regitz, M. Römpp Chemie Lexikon, 9th ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 1992; ISBN 3-13-734609-6. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, L. Humidity Fixed Points of Binary Saturated Aqueous Solutions. Journal of research of the National Bureau of Standards - A: Physics and Chemistry 1977, 81, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, R.; Herring, G.; Madura, J.; Bissonnette, C. Petrucci’s General Chemistry: Modern Principles and Applications, 12th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, United Kingdom, 2023; ISBN 978-1-292-72613-7. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula ans James Keeler, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, 12th ed.; Oxford University Press: London, United Kingdom, 2022; ISBN 978-0-198-84781-6. [Google Scholar]
- Buchholz, F.L.; Graham, A.T. Modern Superabsorbent Polymer Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-471-19411-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttscheid, A. 2004. Synthesis and characterization of superabsorbent polymers with core/shell structure. PH.D. thesis, Universität Duisburg - Essen, Duisburg, Germany, January 14, https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:hbz:464-duett-03192004-1308391.
- Paulsen, H. 2018. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydrogels prepared by Free Radical Polymerization. PH.D. thesis, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, July 6, https://nbn-resolving.org/urn%3Anbn%3Ade%3Agbv%3A18-92819.
- Wack, H. 2006. Zum Quellendruck von polymeren Hydrogelen. PH.D. thesis, Universität Duisburg - Essen, Duisburg, Germany, December 21, https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:hbz:465-20070814-102048-6.
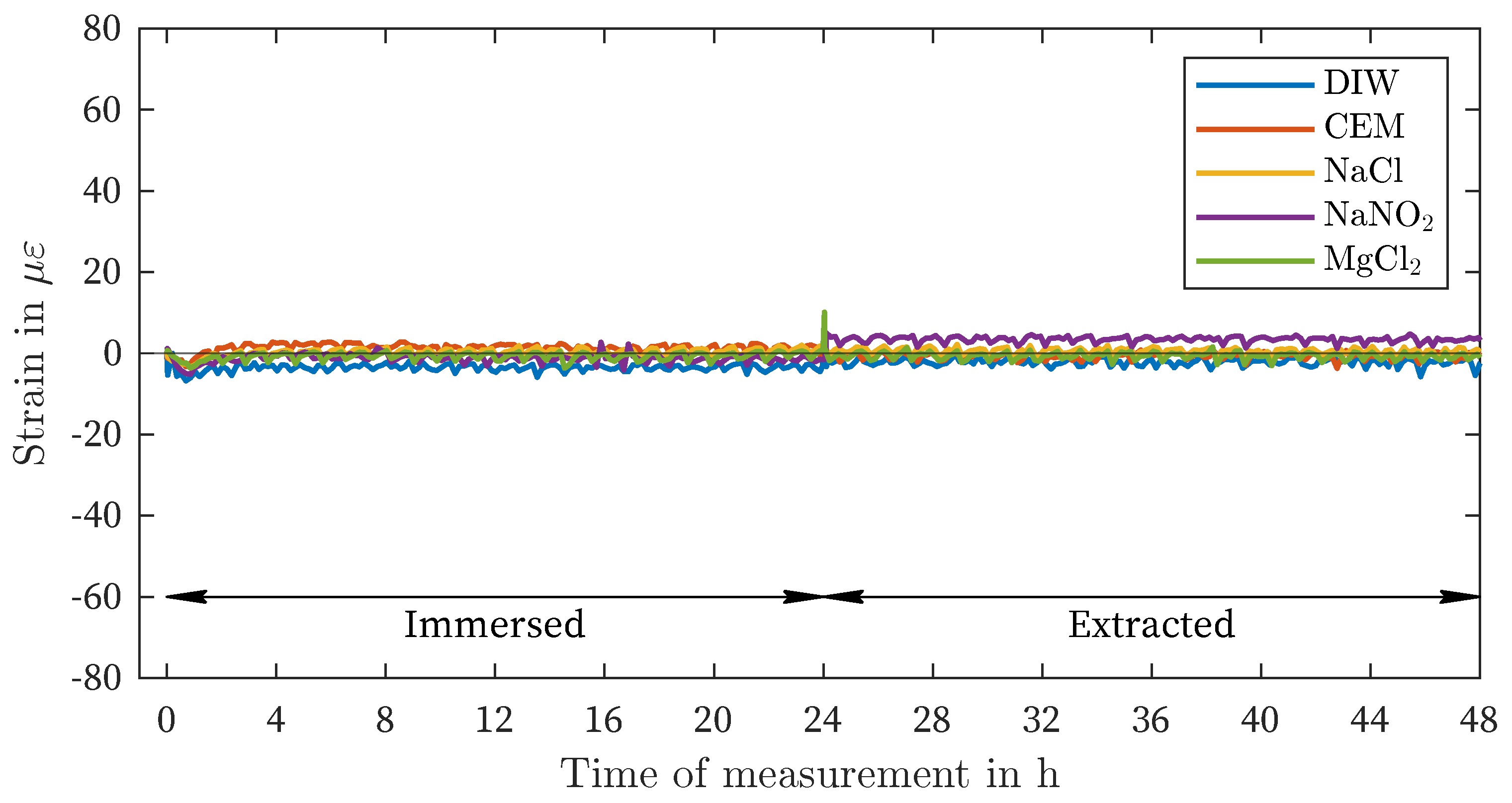
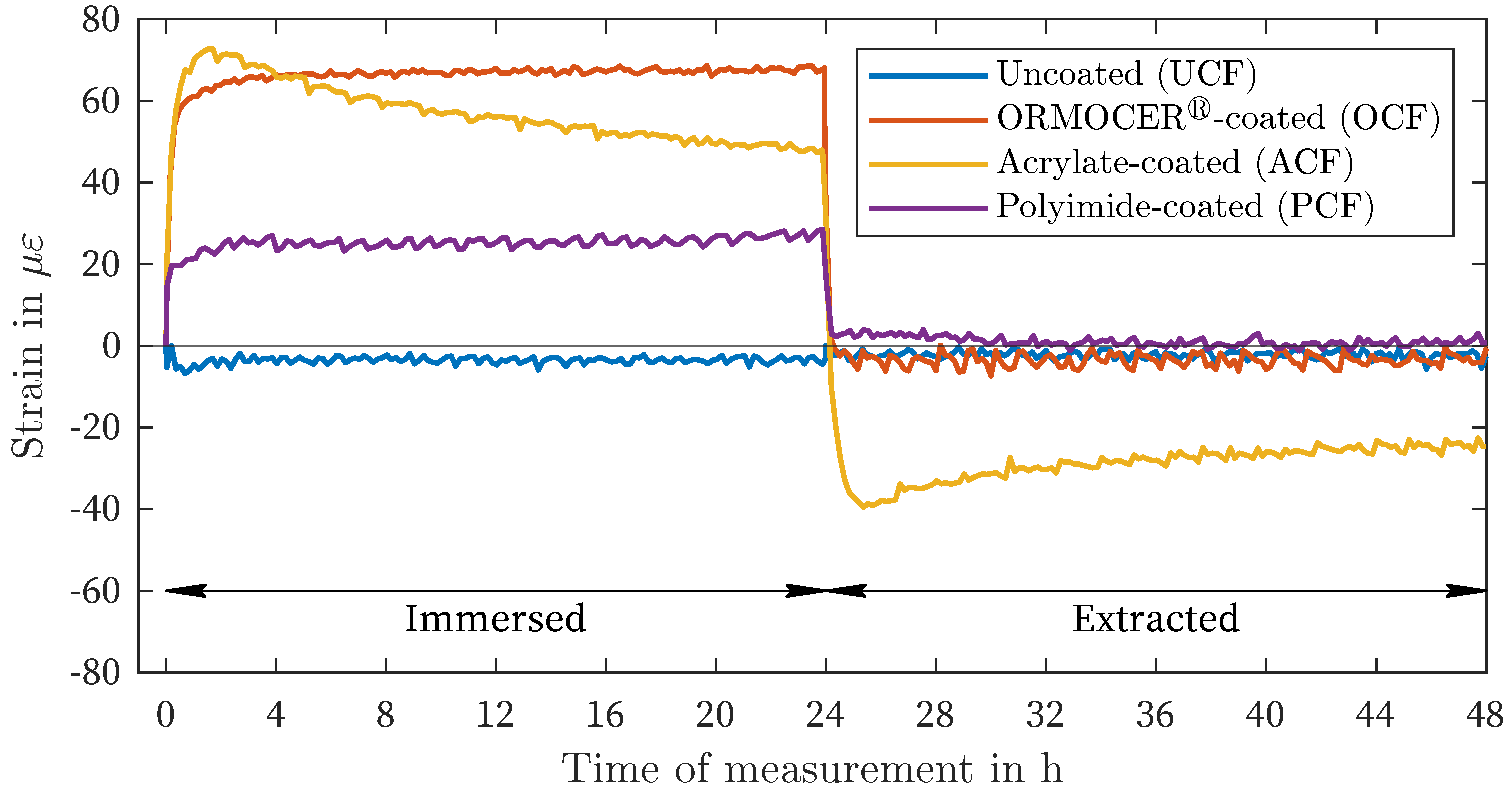
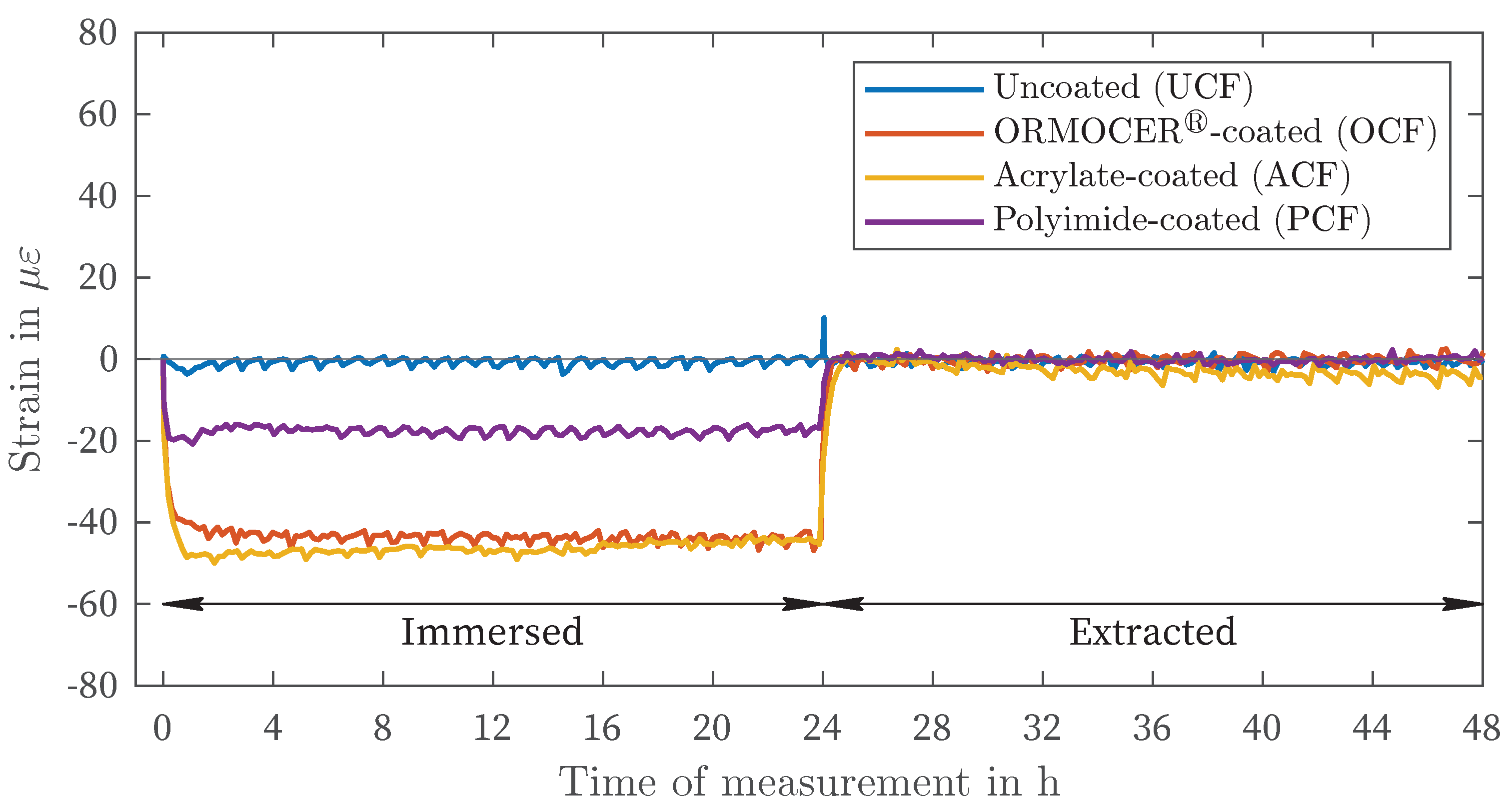
| Liquid / Solution | Nomenclature | Concentration in g/L |
Solubility1 in g/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deionized water | DIW | - | - |
| Cement solution (CEM I 42,5 R) | CEM | - | - |
| Sodium cloride | NaCl | 640 | 358 |
| Sodium nitrite | NaNO2 | 1640 | 820 |
| Magnesium chloride (MgCl26H2O) | MgCl2 | 3400 | 2350 |
| 1 at 20°C. |
| Nomenclature | OCF | PCF | ACF | UCF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | ORMOCER® | Polyimid | Acrylate | Uncoated |
| Fibertype | LAL-1550-125 | SM1550P | SMF-28e+ | SMF-28e+ |
| Core in | }9 | 9(0.5) | 8.2 | 8.2 |
| Cladding in | } | 125(1:3) | 125(0.7) | 125(0.7) |
| Coating in | }195 | 145(5) | 242(5) | - |
| Attenuation in | } | 0.7 | 0.02 | - |
| Strain coefficients in | } | -6.67 | -6.67 | -6.67 |
| UCF | OCF | PCF | ACF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | |
| Liquid | in | in | in | in | ||||
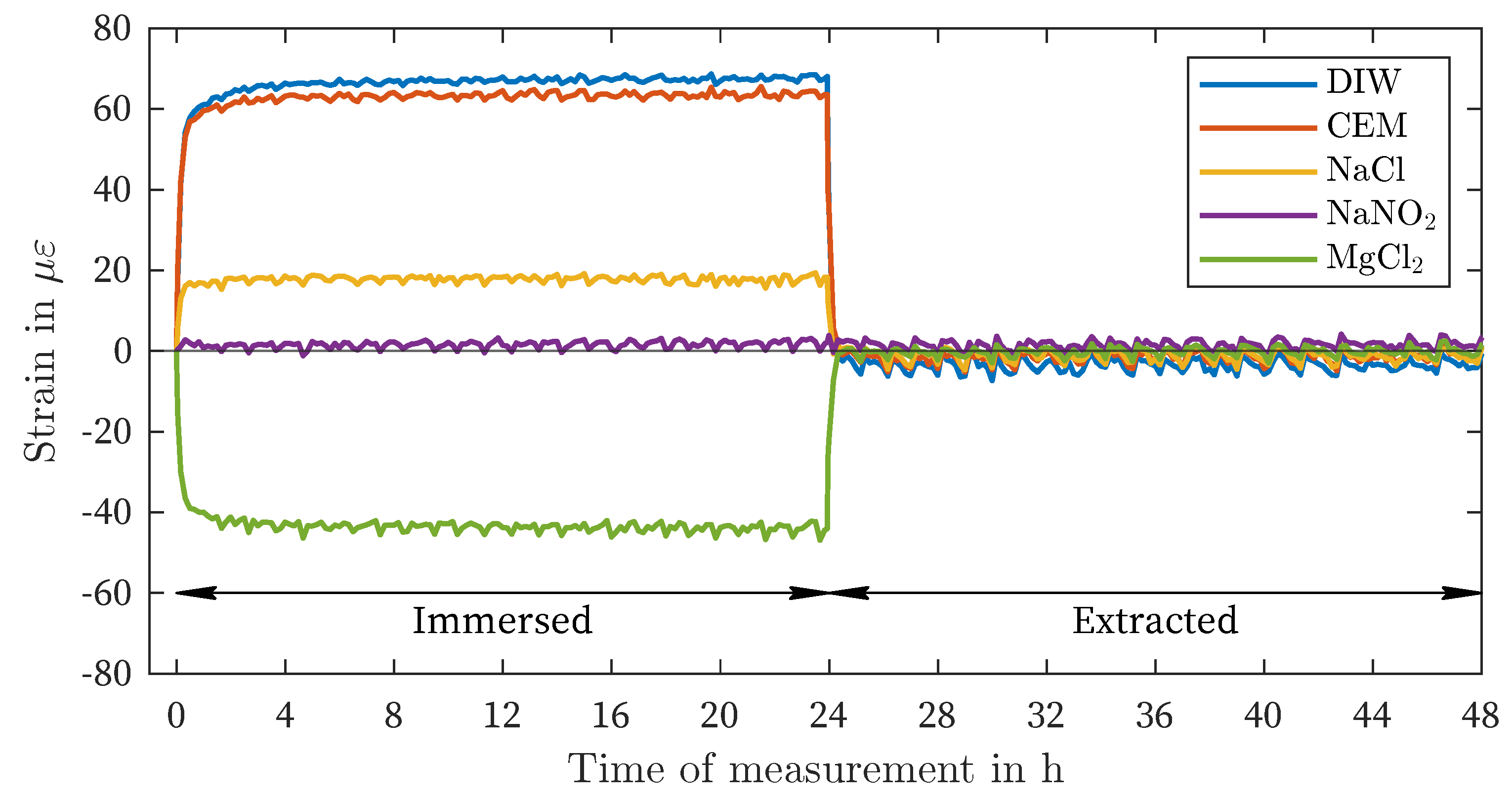
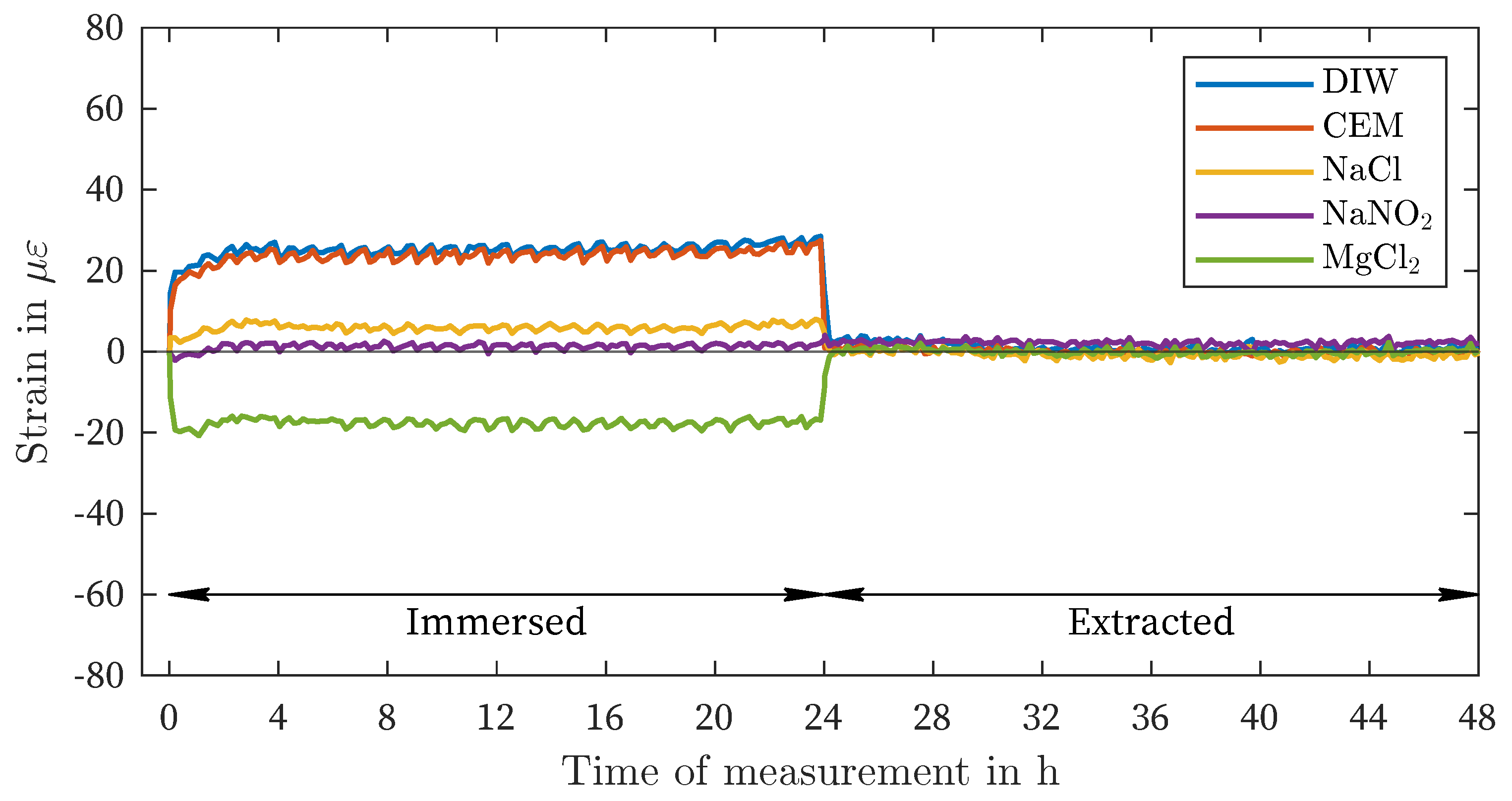
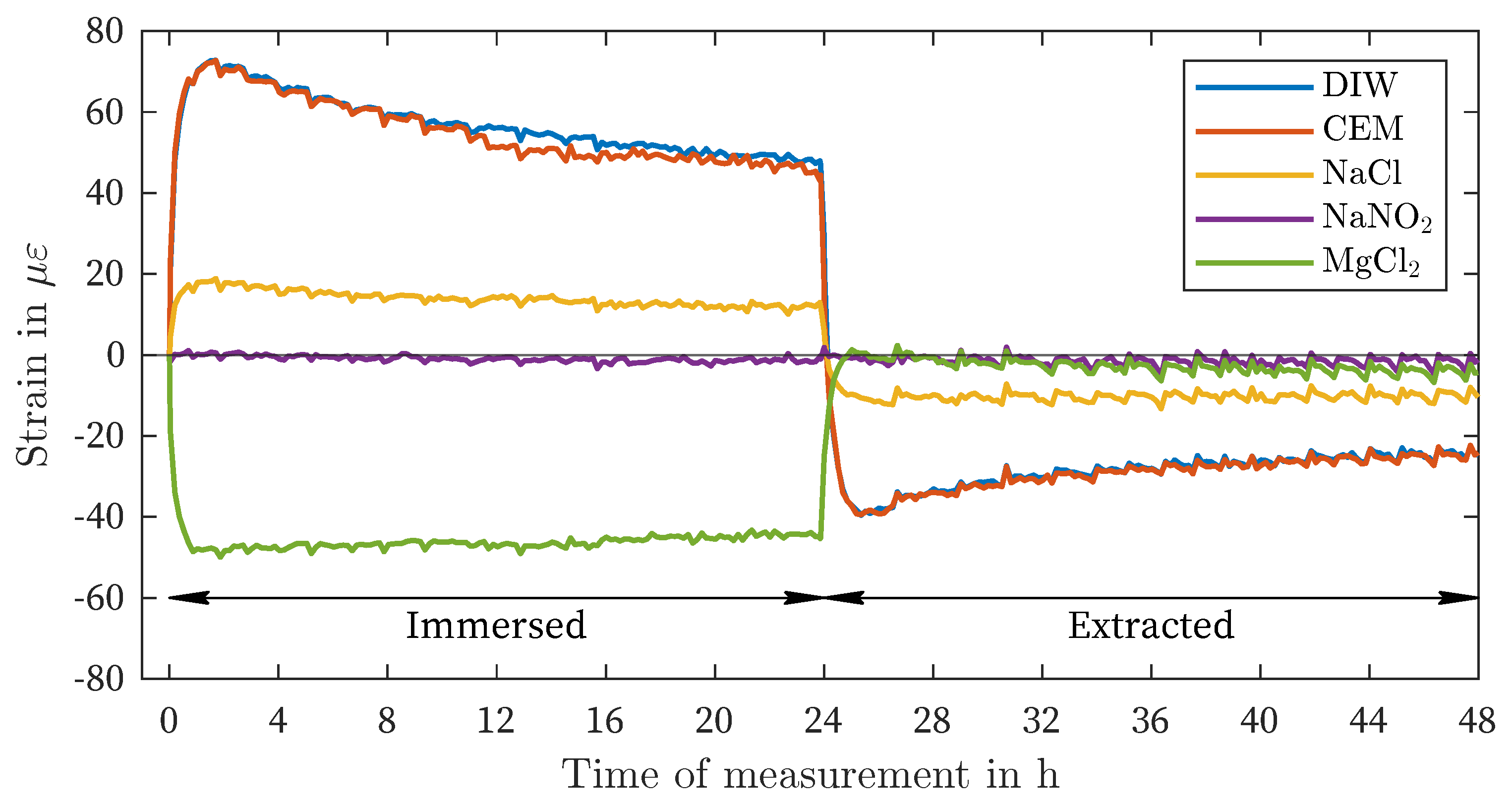
| DIW | -4 | -3 | 67 | 69 | 25 | 28 | 51 | 73 |
| CEM | 1 | 5 | 64 | 66 | 23 | 27 | 49 | 73 |
| NaCl | 1 | 10 | 18 | 19 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 19 |
| NaNO2 | -1 | -7 | 2 | 4 | -1 | 4 | -1 | -5 |
| MgCl2 | -1 | -4 | -44 | -47 | -17 | -21 | -46 | -50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





