Submitted:
12 June 2024
Posted:
13 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell and Viruses
2.3. Mouse Experiments
2.4. Generation of SMEN VLPs
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. SMEN VLPs Vaccination Regimen and SARS-CoV-2 Challenge
2.7. Passive Transfer of Sera
2.8. Immunodepletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
2.9. Bioluminescence Imaging (BLI) of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
2.10. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay and Calculation of Cross-Reactive Neutralization Index
2.11. Fc-Signaling Assay and Calculation of Cross-Reactive Fc-Signaling Index
2.12. Plaque Forming Assay
2.13. Measurement of Viral Burden
2.14. mRNA Expression Analyses of Signature Inflammatory Cytokines and Lung Injury/Repair Genes
2.15. Disease Burden and Bliss Index Scores
2.16. Cryo-Electron Tomography of SARS-CoV-2 VLPs
2.17. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
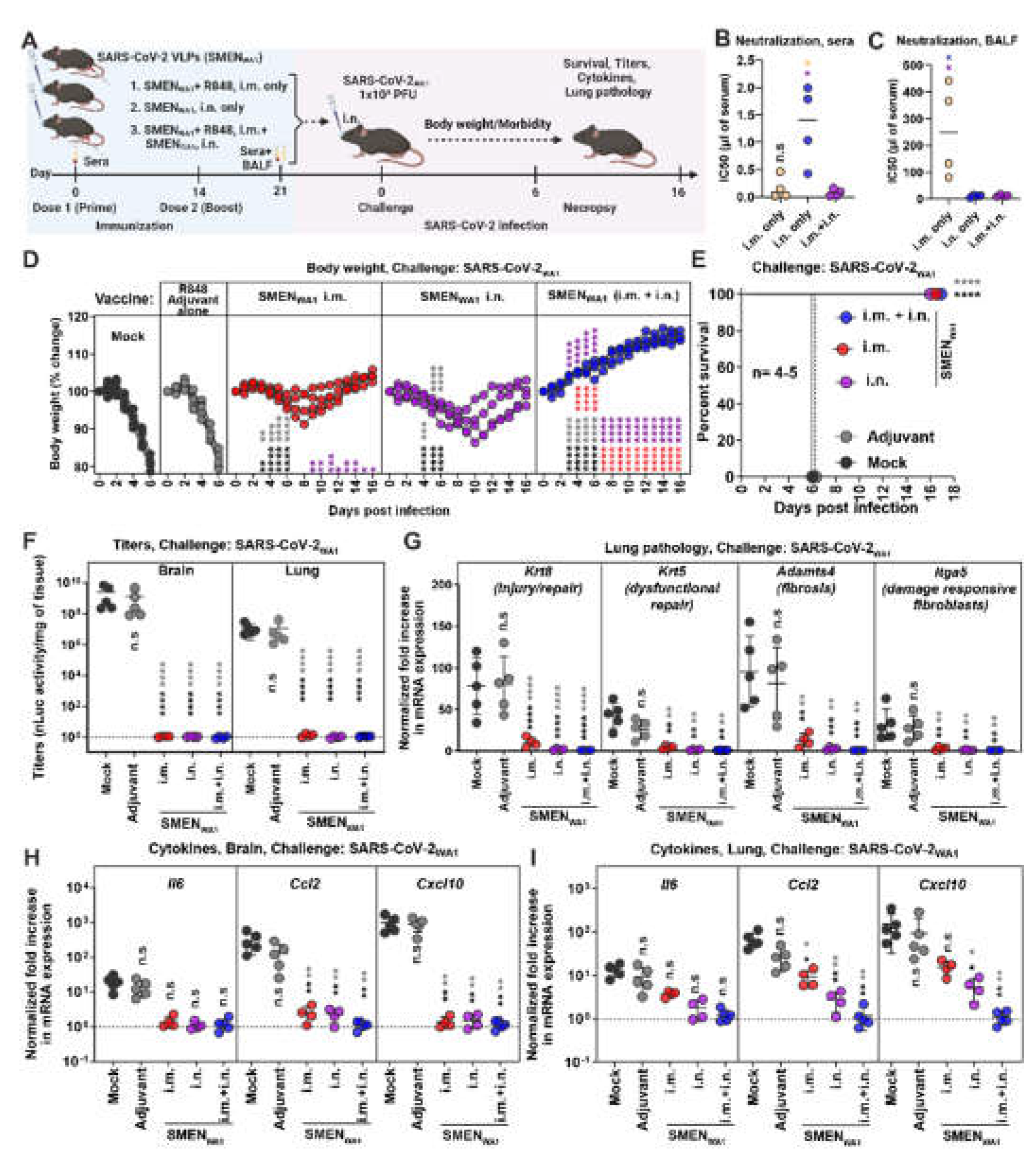
3.1. Systemic and Mucosal Vaccination of the SARS-CoV-2 VLPs (SMEN) Vaccine Provides Enhanced Protection in K18-hACE2 Mice against a Lethal Virus Challenge
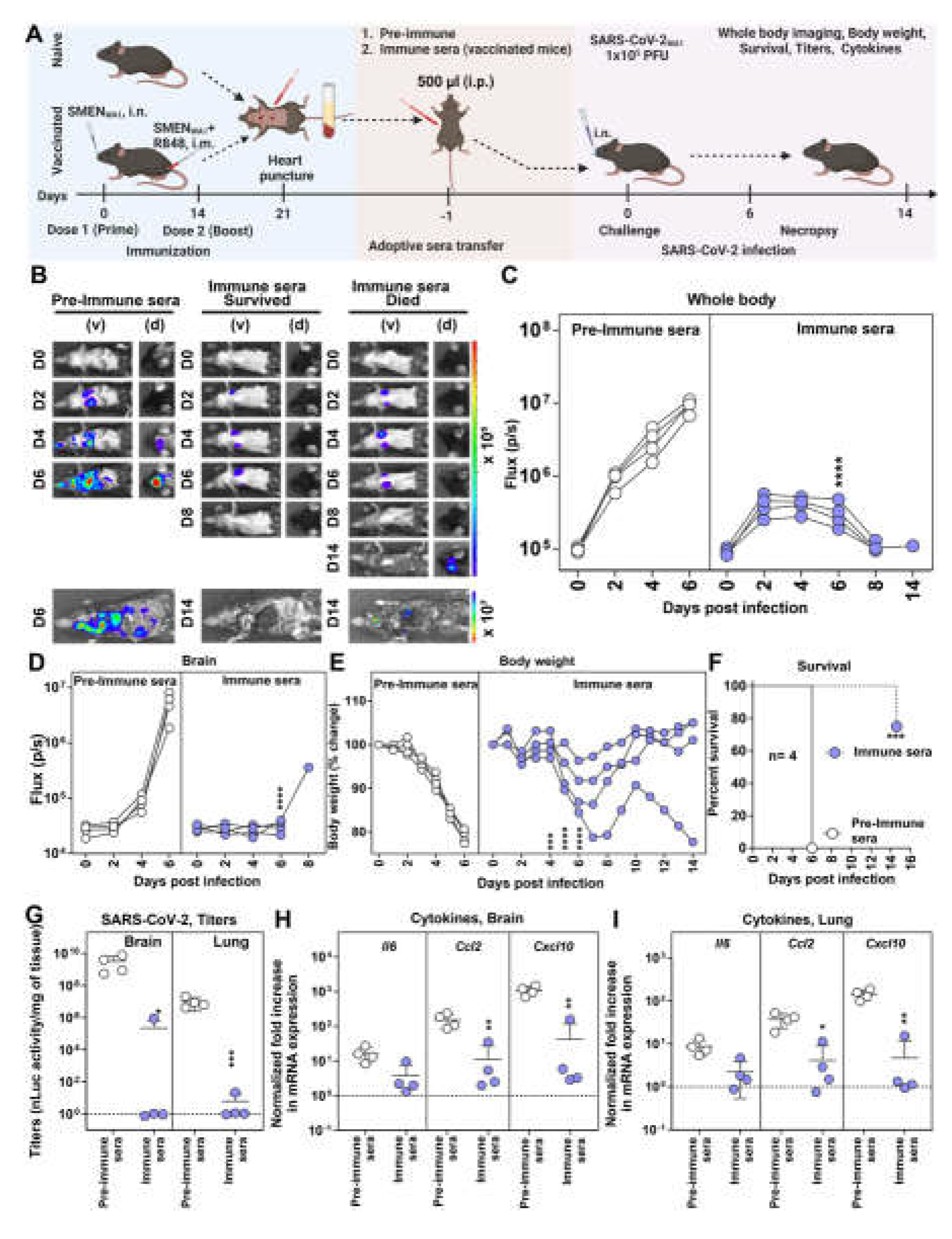
3.2. Antibodies Play a Major Role in SMEN Vaccine-Mediated Protection
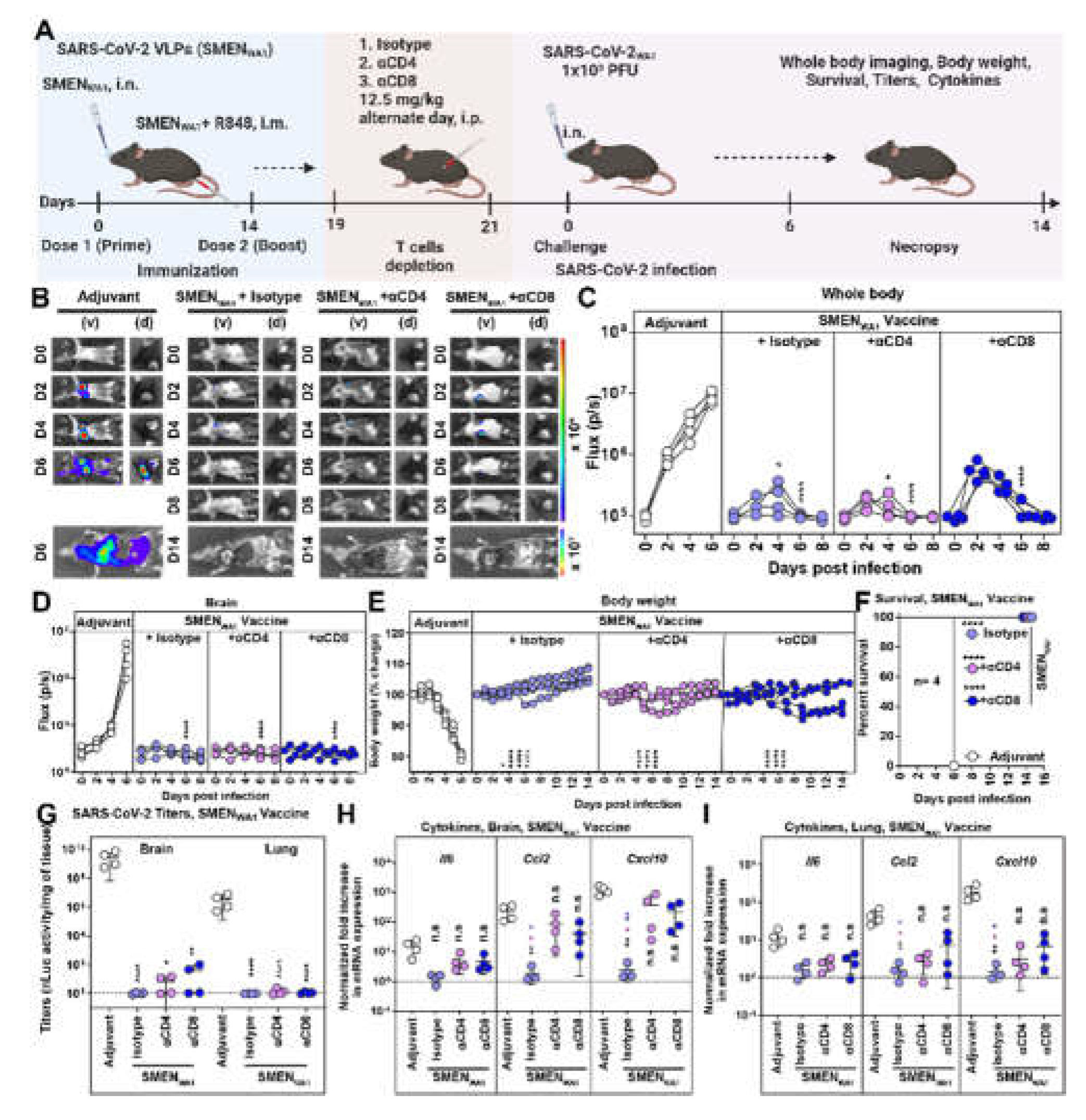
3.3. CD8+ and CD4+ T Cells Elicited by SMEN Vaccine Play a Minor but Distinct Role in Immunity by Contributing to Diminishing Virus Spread and Reducing Inflammation
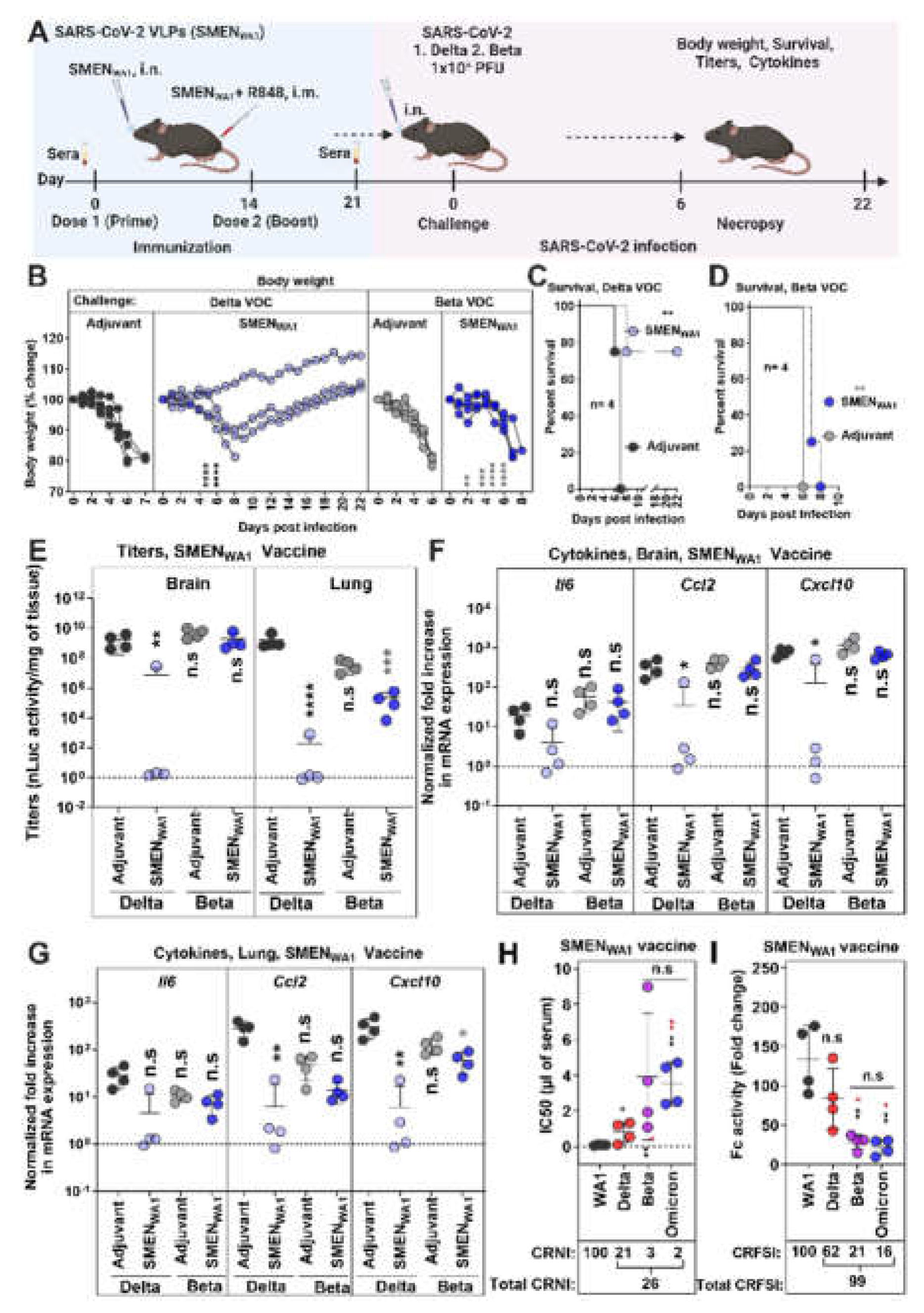
3.4. Cross-Protective Efficacy of SMENWA1 Vaccine is reduced Against Delta and ineffective against Beta VOC
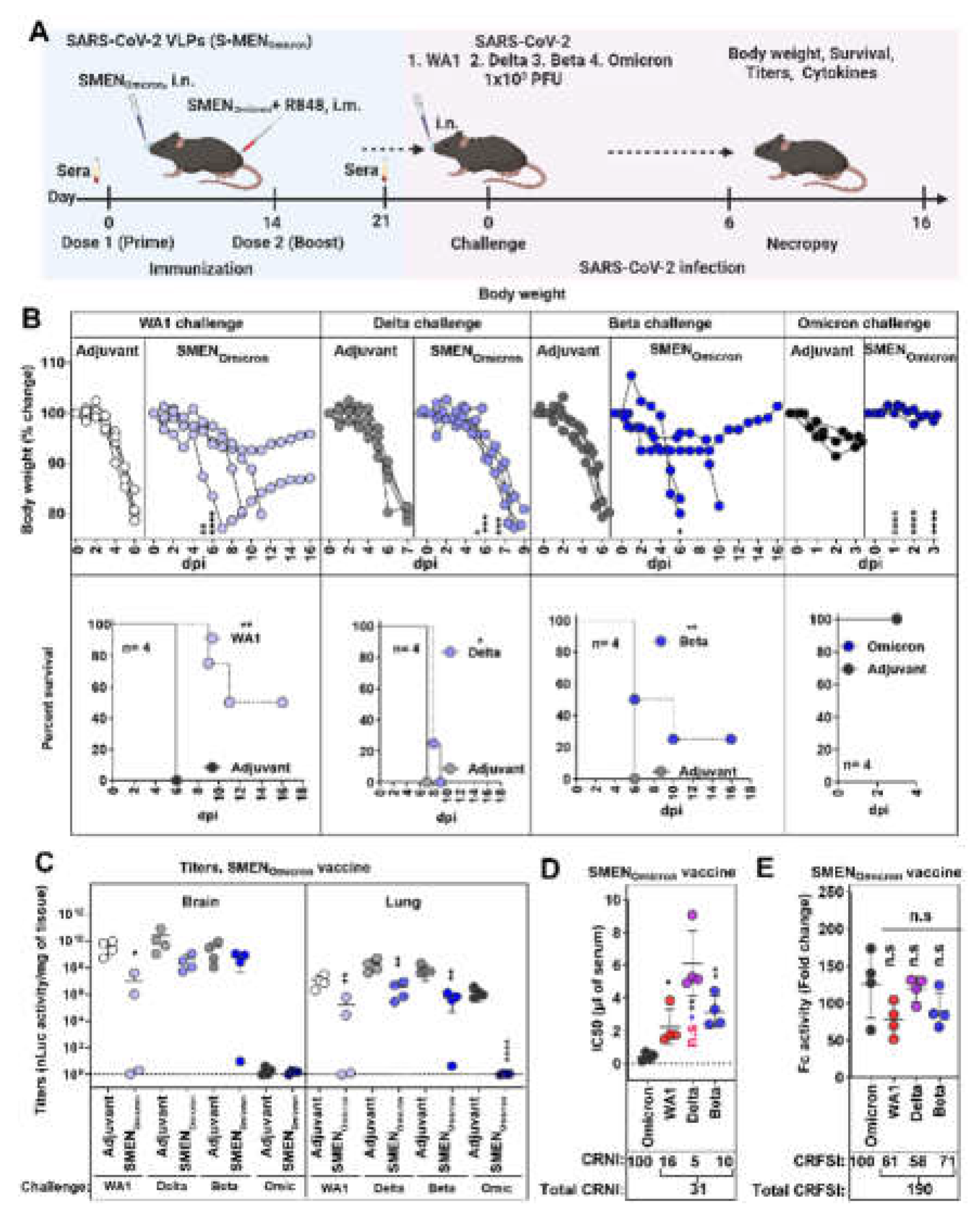
3.5. SMENOmicron Vaccine Provides Diminished Cross-Protection against Previous Variants of SARS-CoV-2.
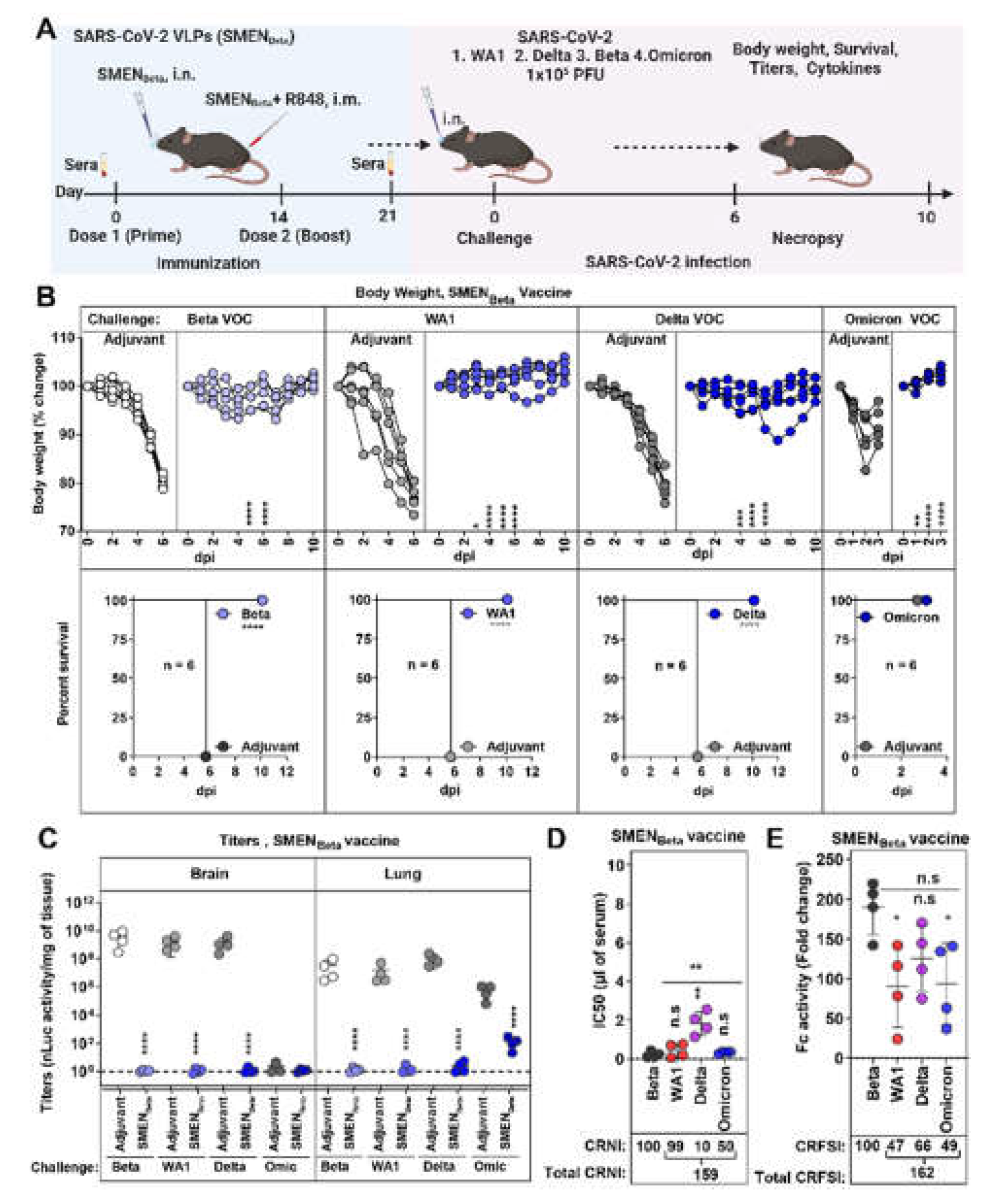
3.6. SMENBeta Vaccine Provides Broad Cross-Protection against Heterlogous Variants of SARS-CoV-2.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Shan, C.; Duan, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, P.; Song, J.; Song, T.; Bi, X.; Han, C.; Wu, L.; et al. A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 584, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomerie, I.; Bird, T.W.; Palmer, O.R.; Mason, N.C.; Pankhurst, T.E.; Lawley, B.; Hernández, L.C.; Harfoot, R.; Authier-Hall, A.; Anderson, D.E.; et al. Incorporation of SARS-CoV-2 spike NTD to RBD protein vaccine improves immunity against viral variants. iScience 2023, 26, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Su, S.-C.; Liang, K.-H.; Lin, H.-T.; Lu, Y.-F.; Chen, K.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Wu, H.-C. Bivalent mRNA vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Journal of Biomedical Science 2023, 30, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer Zu Natrup, C.; Tscherne, A.; Dahlke, C.; Ciurkiewicz, M.; Shin, D.L.; Fathi, A.; Rohde, C.; Kalodimou, G.; Halwe, S.; Limpinsel, L.; et al. Stabilized recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen enhances vaccine immunogenicity and protective capacity. J Clin Invest 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Lan, T.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Baptista-Hon, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Wei, X. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Immune escape and vaccine development. MedComm (2020) 2022, 3, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.J.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Leung, K.; Lee, C.K.; Hachim, A.; Tsang, L.C.H.; Yam, K.W.H.; Chaothai, S.; Kwan, K.K.H.; Chai, Z.Y.H.; et al. Real-world COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron BA.2 variant in a SARS-CoV-2 infection-naive population. Nature Medicine 2023, 29, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Mahmud, S.; Uddin Mian, A.; Hasan, P.; Muyeed, A.; Taif Ali, M.; Faysal Ahmed, F.; Islam, A.; Maliha Rahman, M.; Islam, M.; et al. Side effects of COVID-19 vaccines and perceptions about COVID-19 and its vaccines in Bangladesh: A Cross-sectional study. Vaccine X 2022, 12, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, I.; Oltrogge, J.H.; Nestoriuc, Y.; Warren, C.V.; Brassen, S.; Blattner, M.; Lühmann, D.; Tinnermann, A.; Scherer, M.; Büchel, C. Expectations and Prior Experiences Associated With Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccination. JAMA Network Open 2023, 6, e234732–e234732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís Arce, J.S.; Warren, S.S.; Meriggi, N.F.; Scacco, A.; McMurry, N.; Voors, M.; Syunyaev, G.; Malik, A.A.; Aboutajdine, S.; Adeojo, O.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and hesitancy in low- and middle-income countries. Nature Medicine 2021, 27, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Kamat, I.; Hotez, P.J. Myocarditis With COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines. Circulation 2021, 144, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekal, S.; Husari, G.; Okura, M.; Huang, C.A.; Bukari, M.S. Thrombosis Development After mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Administration: A Case Series. Cureus 2023, 15, e41371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SeyedAlinaghi, S.; Karimi, A.; Pashaei, Z.; Afzalian, A.; Mirzapour, P.; Ghorbanzadeh, K.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Dashti, M.; Nazarian, N.; Vahedi, F.; et al. Safety and Adverse Events Related to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines; a Systematic Review. Arch Acad Emerg Med 2022, 10, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, R.; Askari, N. A review of neurological side effects of COVID-19 vaccination. Eur J Med Res 2023, 28, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Schonborn, L.; Warkentin, T.E.; Chataway, T.; Grosse, L.; Simioni, P.; Moll, S.; Greinacher, A.; Gordon, T.P. Antibody Fingerprints Linking Adenoviral Anti-PF4 Disorders. N Engl J Med 2024, 390, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.B.; Quan, F.S. Respiratory Viruses and Virus-like Particle Vaccine Development: How Far Have We Advanced? Viruses 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, G. A perspective on SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles vaccines. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 115, 109650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, I.C.; Ipekoglu, E.M.; Bulbul, A.; Turay, N.; Yildirim, M.; Evcili, I.; Yilmaz, N.S.; Guvencli, N.; Aydin, Y.; Gungor, B.; et al. Development and preclinical evaluation of virus-like particle vaccine against COVID-19 infection. Allergy 2022, 77, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskalska, A.; Dabrowska, A.; Szczepanski, A.; Jasik, K.P.; Gromadzka, B.; Pyrc, K. Functional Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Virus-Like Particles From Insect Cells. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 732998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.; Batool, S.; Asif, S.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Virus-Like Particles: Revolutionary Platforms for Developing Vaccines Against Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 790121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Hoseini, Z.S.; Katalani, C.; Hajizade, A.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers. J Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Garcia, M.; Colunga-Saucedo, M.; Rosales-Mendoza, S. The Role of Virus-Like Particles in Medical Biotechnology. Mol Pharm 2020, 17, 4407–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.M.; Taha, T.Y.; Tabata, T.; Chen, I.P.; Ciling, A.; Khalid, M.M.; Sreekumar, B.; Chen, P.Y.; Hayashi, J.M.; Soczek, K.M.; et al. Rapid assessment of SARS-CoV-2-evolved variants using virus-like particles. Science 2021, 374, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Valkenburg, S.A.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, L.F. Broad-spectrum pan-genus and pan-family virus vaccines. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 902–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Single-Molecule FRET Imaging of Virus Spike-Host Interactions. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, P.V.; Ghafari, M.; Beer, M.; Lythgoe, K.; Simmonds, P.; Stilianakis, N.I.; Katzourakis, A. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2023, 21, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, H.; Lan, K. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants: Why, how, and what’s next? Cell Insight 2022, 1, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, D.; Alter, G.; Crotty, S.; Plotkin, S.A. Correlates of protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease. Immunol Rev 2022, 310, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Escudie, F.; Scandale, I.; Gilani, Z.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Gaudette, F.; Mowbray, C.; Fraisse, L.; Bazin, R.; Finzi, A.; et al. Bioluminescence imaging reveals enhanced SARS-CoV-2 clearance in mice with combinatorial regimens. iScience 2024, 27, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Ono, C.; Suzuki, R.; Morioka, Y.; Anzai, I.; Fauzyah, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Kamitani, W.; Fukuhara, T.; Matsuura, Y. Establishment of a reverse genetics system for SARS-CoV-2 using circular polymerase extension reaction. Cell Rep 2021, 35, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarilla, A.A.; Sng, J.D.J.; Parry, R.; Deerain, J.M.; Potter, J.R.; Setoh, Y.X.; Rawle, D.J.; Le, T.T.; Modhiran, N.; Wang, X.; et al. A versatile reverse genetics platform for SARS-CoV-2 and other positive-strand RNA viruses. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Prevost, J.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Stone, H.; Lu, M.; Anand, S.P.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Symmes, K.; Benlarbi, M.; Ding, S.; et al. Live imaging of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice reveals that neutralizing antibodies require Fc function for optimal efficacy. Immunity 2021, 54, 2143–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Symmes, K.; Cloutier, M.; Ducas, E.; Tauzin, A.; Laumaea, A.; Grunst, M.W.; Dionne, K.; Richard, J.; et al. The Fc-effector function of COVID-19 convalescent plasma contributes to SARS-CoV-2 treatment efficacy in mice. Cell Rep Med 2023, 4, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, C.; Ullah, I.; Ranjan, A.P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Spasov, K.A.; Zhang, C.; Mothes, W.; Crawford, J.M.; Lindenbach, B.D.; et al. Proof-of-concept studies with a computationally designed M(pro) inhibitor as a synergistic combination regimen alternative to Paxlovid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2024, 121, e2320713121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, A.; Tomasi, M.; Ullah, I.; Bertelli, C.; Vanzo, T.; Accordini, S.; Gagliardi, A.; Zanella, I.; Benedet, M.; Corbellari, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and Pre-Clinical Efficacy of an OMV-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J Struct Biol 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, W.J.H.; Wan, W.; Briggs, J.A.G. Implementation of a cryo-electron tomography tilt-scheme optimized for high resolution subtomogram averaging. J Struct Biol 2017, 197, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Palovcak, E.; Armache, J.P.; Verba, K.A.; Cheng, Y.; Agard, D.A. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronarde, D.N.; Held, S.R. Automated tilt series alignment and tomographic reconstruction in IMOD. J Struct Biol 2017, 197, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, E.R.; Burelbach, K.R.; McBride, M.A.; Stothers, C.L.; Owen, A.M.; Hernandez, A.; Patil, N.K.; Williams, D.L.; Bohannon, J.K. Innate Immune Memory and the Host Response to Infection. J Immunol 2022, 208, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Netea, M.G.; Chavakis, T. Innate immune memory, trained immunity and nomenclature clarification. Nat Immunol 2023, 24, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, A.E.; Brumwell, A.N.; Xi, Y.; Gotts, J.E.; Brownfield, D.G.; Treutlein, B.; Tan, K.; Tan, V.; Liu, F.C.; Looney, M.R.; et al. Lineage-negative progenitors mobilize to regenerate lung epithelium after major injury. Nature 2015, 517, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunz, M.; Simon, L.M.; Ansari, M.; Kathiriya, J.J.; Angelidis, I.; Mayr, C.H.; Tsidiridis, G.; Lange, M.; Mattner, L.F.; Yee, M.; et al. Alveolar regeneration through a Krt8+ transitional stem cell state that persists in human lung fibrosis. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Chiba, N.; Yao, C.; Guan, X.; McConnell, A.M.; Brockway, B.; Que, L.; McQualter, J.L.; Stripp, B.R. Rare SOX2(+) Airway Progenitor Cells Generate KRT5(+) Cells that Repopulate Damaged Alveolar Parenchyma following Influenza Virus Infection. Stem Cell Reports 2016, 7, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Hu, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hoe, N.B.; Wei, T.S.; Mu, D.; Sun, Y.; Joo, L.S.; Dagher, R.; Zielonka, E.M.; et al. Distal airway stem cells yield alveoli in vitro and during lung regeneration following H1N1 influenza infection. Cell 2011, 147, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.E.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Yanagita, M.; Koo, B.K.; Han, N.; Lee, J.H. Inflammatory Signals Induce AT2 Cell-Derived Damage-Associated Transient Progenitors that Mediate Alveolar Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.F.; Allen, E.K.; Randolph, A.G.; Guo, X.J.; Weng, Y.; Sanders, C.J.; Bajracharya, R.; Lee, N.K.; Guy, C.S.; Vogel, P.; et al. Exuberant fibroblast activity compromises lung function via ADAMTS4. Nature 2020, 587, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.K.; Tsung-Ning Huang, D.; Huang, L.M. SARS-CoV-2 variants—Evolution, spike protein, and vaccines. Biomed J 2022, 45, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannar, D.; Saville, J.W.; Zhu, X.; Srivastava, S.S.; Berezuk, A.M.; Tuttle, K.S.; Marquez, A.C.; Sekirov, I.; Subramaniam, S. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein-ACE2 complex. Science 2022, 375, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; He, F.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; et al. An intranasal combination vaccine induces systemic and mucosal immunity against COVID-19 and influenza. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Song, E.; Moriyama, M.; Wong, P.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, R.; Strohmeier, S.; Kleinstein, S.H.; Krammer, F.; Iwasaki, A. Intranasal priming induces local lung-resident B cell populations that secrete protective mucosal antiviral IgA. Sci Immunol 2021, 6, eabj5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Israelow, B.; Pena-Hernandez, M.A.; Suberi, A.; Zhou, L.; Luyten, S.; Reschke, M.; Dong, H.; Homer, R.J.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses. Science 2022, 378, eabo2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A. Exploiting Mucosal Immunity for Antiviral Vaccines. Annu Rev Immunol 2016, 34, 575–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.B.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science 2022, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; Astudillo, M.G.; Yang, D.; Miller, T.E.; Feldman, J.; Hauser, B.M.; Caradonna, T.M.; Clayton, K.L.; Nitido, A.D.; et al. COVID-19-neutralizing antibodies predict disease severity and survival. Cell 2021, 184, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Munoz, A.D.; Kosik, I.; Holly, J.; Yewdell, J.W. Cell surface SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein modulates innate and adaptive immunity. Sci Adv 2022, 8, eabp9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Munoz, A.D.; Santos, J.J.S.; Yewdell, J.W. Cell surface nucleocapsid protein expression: A betacoronavirus immunomodulatory strategy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2304087120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Karki, R.; Williams, E.P.; Yang, D.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Vogel, P.; Jonsson, C.B.; Kanneganti, T.D. TLR2 senses the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein to produce inflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol 2021, 22, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozek-Latecka, M.; Kozlowski, P.; Hoser, G.; Bandyszewska, M.; Hanusek, K.; Nowis, D.; Golab, J.; Grzanka, M.; Piekielko-Witkowska, A.; Schulz, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and its ORF3a, E and M viroporins activate inflammasome in human macrophages and induce of IL-1alpha in pulmonary epithelial and endothelial cells. Cell Death Discov 2024, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helft, J.; Manicassamy, B.; Guermonprez, P.; Hashimoto, D.; Silvin, A.; Agudo, J.; Brown, B.D.; Schmolke, M.; Miller, J.C.; Leboeuf, M.; et al. Cross-presenting CD103+ dendritic cells are protected from influenza virus infection. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, R.M. On cross-priming of MHC class I-specific CTL: rule or exception? Eur J Immunol 2002, 32, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.R.; Ramelli, S.C.; Grazioli, A.; Chung, J.Y.; Singh, M.; Yinda, C.K.; Winkler, C.W.; Sun, J.; Dickey, J.M.; Ylaya, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy. Nature 2022, 612, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, S.; Jagannathan, P.; Henrich, T.J.; Sherif, Z.A.; Bime, C.; Quinlan, E.; Portman, M.A.; Gennaro, M.; Rehman, J.; Force, R.M.P.T. Immune mechanisms underlying COVID-19 pathology and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC). Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.; Thibault, D.; Holland, T.L.; Yang, S.; Young, A.R.; Arnold Egloff, S.A.; Thomas, L.E. Dexamethasone for Inpatients With COVID-19 in a National Cohort. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e238516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat Med 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.I.; Manamela, N.P.; Motsoeneng, B.M.; Kaldine, H.; Ayres, F.; Makhado, Z.; Mennen, M.; Skelem, S.; Williams, N.; Sullivan, N.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Beta and Delta variants trigger Fc effector function with increased cross-reactivity. Cell Rep Med 2022, 3, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S.; Gilman, M.S.A.; McLellan, J.S. Structure-Based Vaccine Antigen Design. Annu Rev Med 2019, 70, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P. Virus vaccines: proteins prefer prolines. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.O.; McLellan, J.S. Principles and practical applications of structure-based vaccine design. Curr Opin Immunol 2022, 77, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Schaub, J.M.; DiVenere, A.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Science 2020, 369, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ma, X.; Castillo-Menendez, L.R.; Gorman, J.; Alsahafi, N.; Ermel, U.; Terry, D.S.; Chambers, M.; Peng, D.; Zhang, B.; et al. Associating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structures with states on the virus observed by smFRET. Nature 2019, 568, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponholtz, M.R.; Byrne, P.O.; Lee, A.G.; Ramamohan, A.R.; Goldsmith, J.A.; McCool, R.S.; Zhou, L.; Johnson, N.V.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Connors, M.; et al. Structure-based design of a soluble human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B antigen stabilized in a prefusion-like conformation. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




