1. Introduction
The main objective of this study can be considered for the decision making of actions associated with Energy Efficiency. This article introduces a novel approach to studying a total of 180 desalination plants at the territorial level in the Canary Islands. The global scarcity of freshwater resources has greatly contributed to the development of desalination technologies, in which reverse osmosis is one of the most widely used and highly regarded methods.
This study focuses on seawater reverse osmosis desalination plants in the Canary Islands. This manuscript studies to optimize the operation of these plants with impact on energy consumption, water quality, costs, and emissions, to make this process more efficient and sustainable. It is necessary to analyze the energy efficiency of desalination plants, from the point of view of the emissions produced, the carbon and ecological footprint of the system, where a model for this is developed. The aim is to introduce energy improvements in RO processes for desalination plants that is valid for any seawater facility in the world [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
This study can be used for decision-making in processes related to improving energy efficiency in seawater reverse osmosis plants. Improvements in seawater desalination are studied, based on the reduction of energy consumption in the production of fresh water. As a result, the RO process is the most suitable because it has the lowest energy consumption per cubic meter of water produced, and therefore occupies a privileged position in the sector [
6,
7,
8,
9].
It is interesting to consider the design and implementation of pilots in desalination plants, in a systematic way, to evaluate energy improvements in water desalination processes. In this sense, it is proposed to carry out tailor-made pilots according to the situation to make the right decision and execute the investment with the minimum risk. Therefore, in these pilots, an assessment of boron, water quality, a diagnostic analysis of energy, carbon footprint, ecological footprint, environmental sustainability and operation and maintenance costs are carried out [
10,
11,
12].
Membrane ageing is a decisive factor regarding the energy consumed in the plant, the permeate flow rate and the emissions produced. Therefore, a study methodology is established to make decisions about it. The decision to change membranes is very important for the lifetime of the plant and many variables must be considered, such as working pressure, feed and permeate water quality of the reverse osmosis system, conversion, temperature, etc. With the introduction of state-of-the-art membranes with low energy consumption and high salt rejection, we can produce water of the required quality under more efficient and sustainable conditions than with standard membranes [
13,
14,
15].
The desalination of seawater in water treatment plants has evolved a lot in the last five decades, in which the desalination process and its technology has changed and has become more and more cost-effective and efficient. Initially, the desalination process was a thermal process that has been changing with scientific and technological advances towards a reverse osmosis process that dominates the market today. The primary objective of the improvements studied in seawater desalination is based on the reduction of energy consumption in the production of fresh water. Consequently, reverse osmosis is the most suitable process due to its lower energy consumption per cubic meter of product water, which is why it occupies a privileged position in the sector [16-19}.
So far in the 21st century, research efforts in water desalination have focused on advances in reverse osmosis membranes, which have a larger surface area and lower energy consumption, as well as on pressure exchangers to recover the energy pressure of the brine or reject from the water desalination process. Later, it is studied the operation, maintenance, and handling of membranes in detail, due to their importance in energy saving, showing how to optimize all the processes where they are involved with the aim of continuously improving their efficiency [20-25}.
Energy efficiency in desalination plants is directly linked to the required permeate water quality. In this case in Spain, according to Royal Decree 140/2003, for drinking water, Boron is the bottleneck for all ions, as it is required to be less than 1 ppm, which requires either a second step, i.e. practically doubling the number of membranes in the plant if the second step is total, by passing the permeate through a new reverse osmosis refining process, which is very expensive, or working with high rejection membranes in a single step but with pressures below 1 ppm, which is very costly, or working with high rejection membranes in a single step but with higher pressures, thus consuming more energy, the cost of which is also one of the most significant of the variable costs of the installation [
26,
27,
28,
29].
The WHO, however, is more flexible with Boron requirements for drinking water and allows a maximum of 2.4 ppm. This international regulation is followed in many countries in the world where water desalination is very important and among others we can mention Chile where the plant designs consume less energy because they work at lower pressures since the Boron does not have to be less than 1 ppm but less than 2.4 ppm; or in other areas of the planet such as North Africa, the Middle East, etc., where they are also adapting to this regulation [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35].
2. Materials and methods
The two most important parameters for describing the separation performance in reverse osmosis processes are the permeate flow rate and the salt rejection. Both quantities are mainly influenced by the following parameters: pressure, temperature, recovery and salt concentration in the feed [
36,
37,
38,
39].
Pressure
The permeate flow rate increases with increasing feed pressure. However, the concentration of salts in the permeate decreases with increasing feed pressure. This corresponds to an increase in the rejection coefficient [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44].
Temperature
Temperature is another very important factor because it directly affects the operation of the RO system. When the temperature drops there is a decrease in the permeate flow rate and conversely when the temperature rises there is an increase in permeate production. The rejection coefficient, R, however, decreases with increasing temperature. This means that more dissolved substances pass through the membrane [
45,
46,
47,
48,
49].
Pilots
Pilot tests with the latest generation of reverse osmosis membranes in large desalination plants are becoming increasingly common, as small-scale experiments are carried out on the operation of new generation membranes with better salt rejection and lower energy consumption, to achieve optimal water quality standard at the lowest possible cost.
In this way, pilot tests are being carried out before the decision is made whether or not to change the reverse osmosis membranes, as this represents a significant investment and minimizing the risk of errors in order to ensure the best results in terms of energy consumption, operating costs and reducing the environmental impact while complying with the required water quality [
50,
51,
52,
53,
54].
Use of pilots
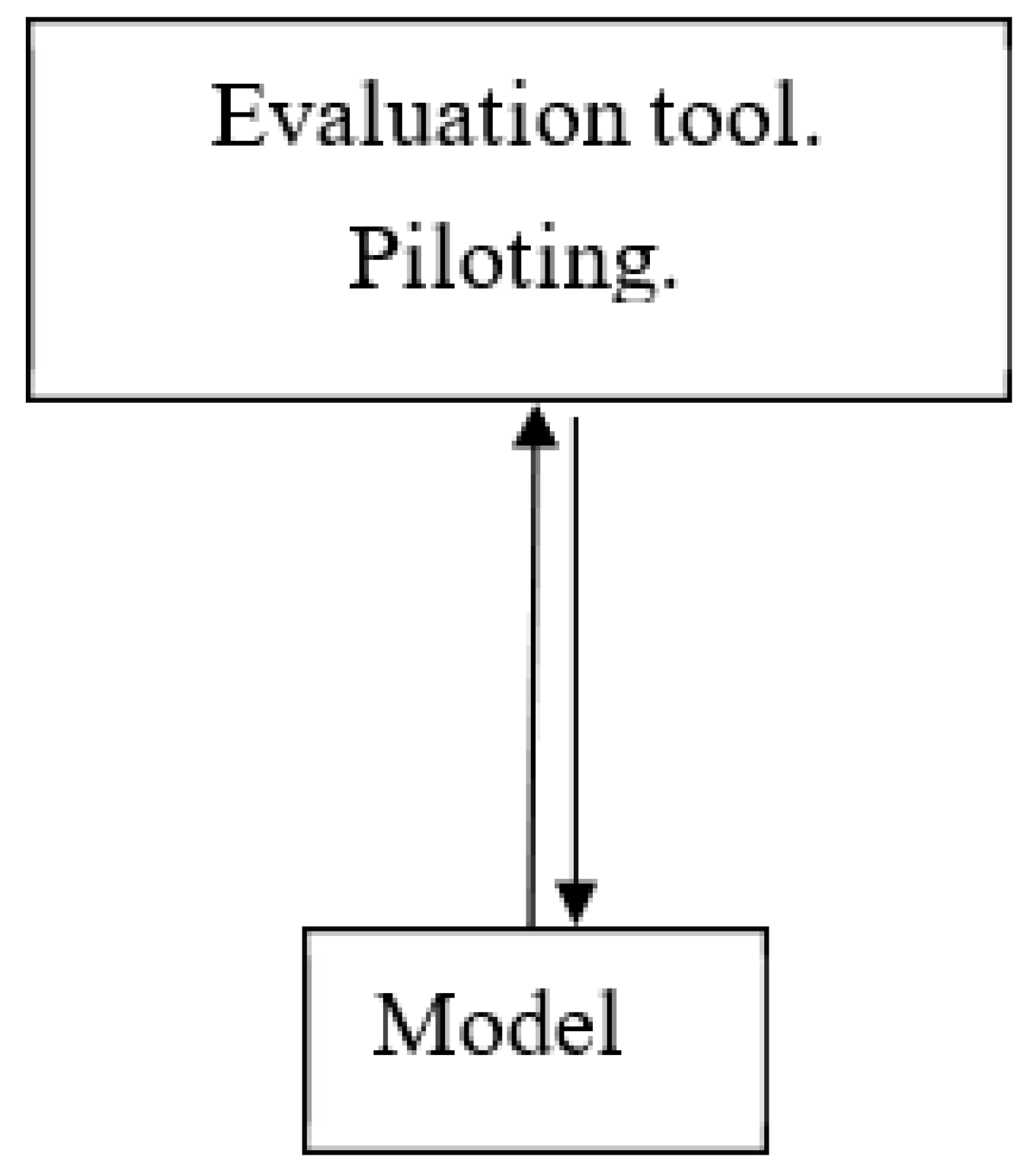
The introduction of RO piloting in a seawater desalination plant, whose energy consumption is very high and inlet salinity is higher than for the treatment of other types of water, is essential to optimize its resources. The following
Figure 1 shows this.
Pilot plant cold be equipped with a vessel and the following elements to a full monitoring and control of the operational conditions (pressure and flows of the seawater, brine and permeate flows).
Feed seawater flow: a control valve at the HPV inlet for the water flow and pressure control, a pressure transmitter, a drop pressure transmitter.
Permeate flow: a flow meter, a pressure transmitter (the one of the full scale rack).
Brine flow: three valves, in order to control the brine flow and appropriately make the brine discharge from 65 bars to atmospheric pressure, a flowmeter.
The introduction of RO piloting in a seawater desalination plant, whose energy consumption is very high, could be beneficial in optimizing its resources. Without a pilot plant, there is a risk of missing out on the opportunity to test a membrane that optimizes energy consumption and improves the quality of the water produced. Feed water collection is important due to an open intake could increase the dirty in the surface of the reverse osmosis membranes and the temperature range is also higher than a well intake. This includes directly in the energy consumption because the fouling and the low temperatures increase the operation pressure to maintain the permeate flow. Moreover, to use high rejection membranes increase the operation pressure and it influences directly in the energy consumption. Therefore, it is mandatory to use low energy consumption membranes if it is possible to get the quality requirements from the client.
Not having a pilot plant can have a very high opportunity cost, as it is not possible to test a membrane that optimises energy consumption and improves the quality of the water produced. This makes it possible to test its operation on a small scale and then take it to a large scale in the plant, minimising the risk of not meeting the planned objectives. If we do not have such a pilot plant, the cost of which for large seawater plants is not significant compared to the investment that would have to be made in membranes in the installation, we can make a mistake if we choose the wrong membrane for our type of water without first having tested it in situ and lose a large amount of money [
55,
56,
57,
58,
59].
Therefore, having the appropriate tests and the necessary instrumentation in a plant of this type to carry out pilot tests has a direct impact on the energy efficiency of the system. In this sense, different types of tests can be carried out: membrane ageing, piloting or collection depth, among others. In the first of these tests, the membranes are operated in a pressure pipe, in parallel to the rest of the train, and under the same operating conditions as the plant. In this way, the membranes age and we can pilot them a posteriori in more real working conditions, not only in start-up conditions where it is more difficult to find problems. The second test is the actual piloting, where we vary the working conditions of the membrane as we wish to obtain results in different scenarios. Finally, a test of the catchment depth helps to characterise the feed water to the installation in terms of temperature, water quality, etc [
60,
61].
It is therefore proposed to carry out pilot tests to experiment on a small scale with the operation of new generation membranes with high rejection, but also with low energy consumption, looking for the one that considerably reduces, depending on the type of water in each plant, energy, economic and environmental consumption while complying with the required water quality. Once the best membrane has been chosen for each plant, through the introduction of these pilot tests, the energy, economic and environmental improvement that has been chosen will be carried out on an industrial scale of the entire plant, frame by frame. These economic, energy and environmental assessments are shown in the diagram and are also included earlier in this chapter [
62,
63,
64].
If these periodic pilot tests are not carried out with the membranes that are coming onto the market and partial replacements are not made of the membranes that are operating in the plant, over time, these will age and not only will water production decrease, but it will also be of poorer quality and the working pressure will increase, which means higher energy consumption and operating costs for the plant. Therefore, it will be more expensive not to carry out pilot tests than to carry them out with membranes that the manufacturers do not normally leave at zero cost for them to have real information on their operation. Continuing to work with membranes that consume more and more energy to produce the same amount of water or less with worse quality, will also have an environmental cost, represented in an increase in the carbon footprint and the planet's ecological footprint as will be calculated later in chapter 4 of the results [
65,
66,
67,
68].
Likewise, working with ERI, DWEER, OSMOREC, etc. energy recovery systems will reduce the energy consumption of the installation compared to working with Pelton or Francis turbines and therefore it is also advisable to rely on these systems that will reduce the environmental cost of the system, the ecological and carbon footprint of the plant.
This working model will help us to respond to the different dimensions that are required for the proper operation of a desalination plant and that can be extended to all of them. In this sense, the main factor to comply with, depending on the geographical and political location where we are, will be the drinking water regulations if it is a desalination plant for human consumption, which is the majority of cases throughout the world. If we are in Spain, it is the Royal Decree 140/2003 of 7 February that we must comply with, where the biggest bottleneck is to ensure that the boron rejection of RO elements is sufficiently loose so that the total permeate is below 1 ppm. This is the main factor to meet, water quality. For this we have developed the above model where we study how boron and hence water quality can vary depending on the use of different RO membranes. This will be carried out later with real data at the Alicante 1 desalination plant [
69,
70].
Therefore, the model for water quality requires us to work with membranes with high salt rejection and particularly boron to achieve this value, and when it is not possible to do a second osmosis step where we treat the permeate from the first step again with brackish water membranes partially or totally and often incurring the cost of chemical products to raise the pH. We do this so that the boron, which is mainly boric acid, becomes borate, which is a salt, so the membrane is more likely to reject it, as it is designed to reject salts.
Once we meet the water quality, if possible, in one step only, so as not to make the plant more expensive with a second osmosis step in terms of membranes, pressure pipes, pumps, piping, valves and energy consumption; secondly, we seek to keep the pressure required in our system as low as possible by using state-of-the-art membranes with low energy consumption and working at not too low temperatures.
Therefore, in our model, we relate water quality to a high salt rejection which means high energy consumption, so we introduce the latest generation membranes to reduce the energy required while maintaining the necessary quality. The pilot tests carried out at the Carboneras desalination plant are along these lines and, using different membranes from various manufacturers, we were able to choose the best one that firstly met the water quality requirements and secondly did so with reverse osmosis membranes at the lowest possible energy consumption [
71].
In this sense the water quality model is directly linked to the energy consumption of the plant which is also a function of the water temperature. In our model we introduce the necessary tools to identify what energy is needed in our process and calculate it.
Similarly, in our model we also relate water quality and the energy consumption of the desalination plant to the economic and environmental dimension of the system, since the lower our energy consumption, the lower the monetary and environmental costs of our installation. This methodology is applicable to all seawater desalination plants, which is why we are also going to extend the study to all these installations in the Canary Islands and to the studies carried out in Alicante 1 and Carboneras, as will be seen in later chapters.
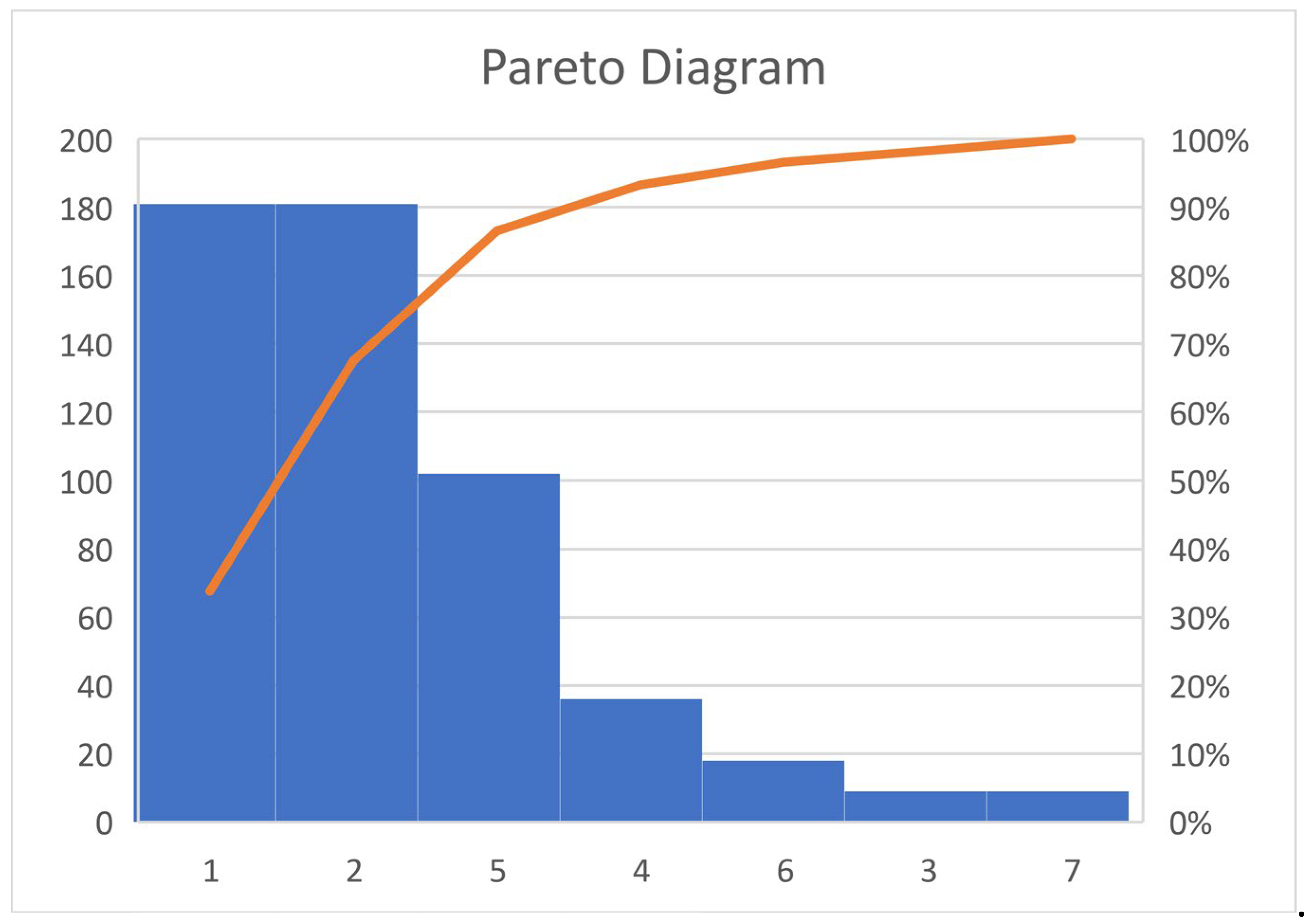
Similarly, the Pareto diagram tool is used to identify which aspects of the desalination plant are the most significant and have the greatest impact on its energy consumption.
Figure 2 shows the most important elements to be considered in the installation.
Pareto analysis.
Pareto analysis is used to identify the 2 or 3 most significant causes which affect to more than 80% of the costs. In this sense,
Figure 3 below shows the Pareto diagram for the energy improvement of N plants in a given territory. A series of factors that can affect this energy improvement have been numbered from 1 to 7, such as the seawater intake, the decision on the membranes, the energy recuperators, the high-pressure pump, the decisions on the pre-treatment, the feed pump or the post-treatment.
The aim is to determine which would be the most significant effects. In this example, it can be seen how the most important decisions are based on factors 1, 2 and 3, which influence 90% of the possible energy improvement of the system. In this sense, the first two elements will be mainly studied in terms of the decision making on factors 1 and 2 for the installation, which represents between 70% and 80% of the influence on the proposed energy improvement. The third factor is also considered, although to a lesser extent, to reach 90% of the effects on the energy improvement of the desalination plants in the territory to be considered.
Membrane decisions can be made on the basis of a pilot test in the plant, with the specific type of water to be treated, or directly based on the supplier's projections and guarantees. In this sense, the technical specifications of the manufacturer Toray show how, in the case of a desalination plant, an uncertainty of around 20% in water quality can be expected, due to the safety factors of the very conservative manufacturer's specifications and even more so the system guarantees that may be requested a posteriori depending on each particular project. This demonstrates the need for piloting in a desalination plant to eliminate this uncertainty at virtually no cost to the operator, as the membranes for these tests are normally supplied free of charge by the supplier avoiding the risk of making a mistake with the membrane model, with all the costs that this entails, and are tested in a prepared pipe that is released from the plant for this test. Depending on the size of the plant, we can make a colour coded classification according to the incidence of piloting as shown in table 3.9. For example, level 1, green, refers to desalination plants with a production of less than 100 tCO2/day, with a very slight impact, as the percentage of salt rejection and energy consumption is very similar per m3 of product water, as it is a small amount of permeated water, this value is low, but as the product flow of the installation increases, this product shoots up to multiply by a thousand in the case of level 5, red, with a very serious impact on the energy efficiency of the installation, economic and environmental cost (
Table 1).
3. Results
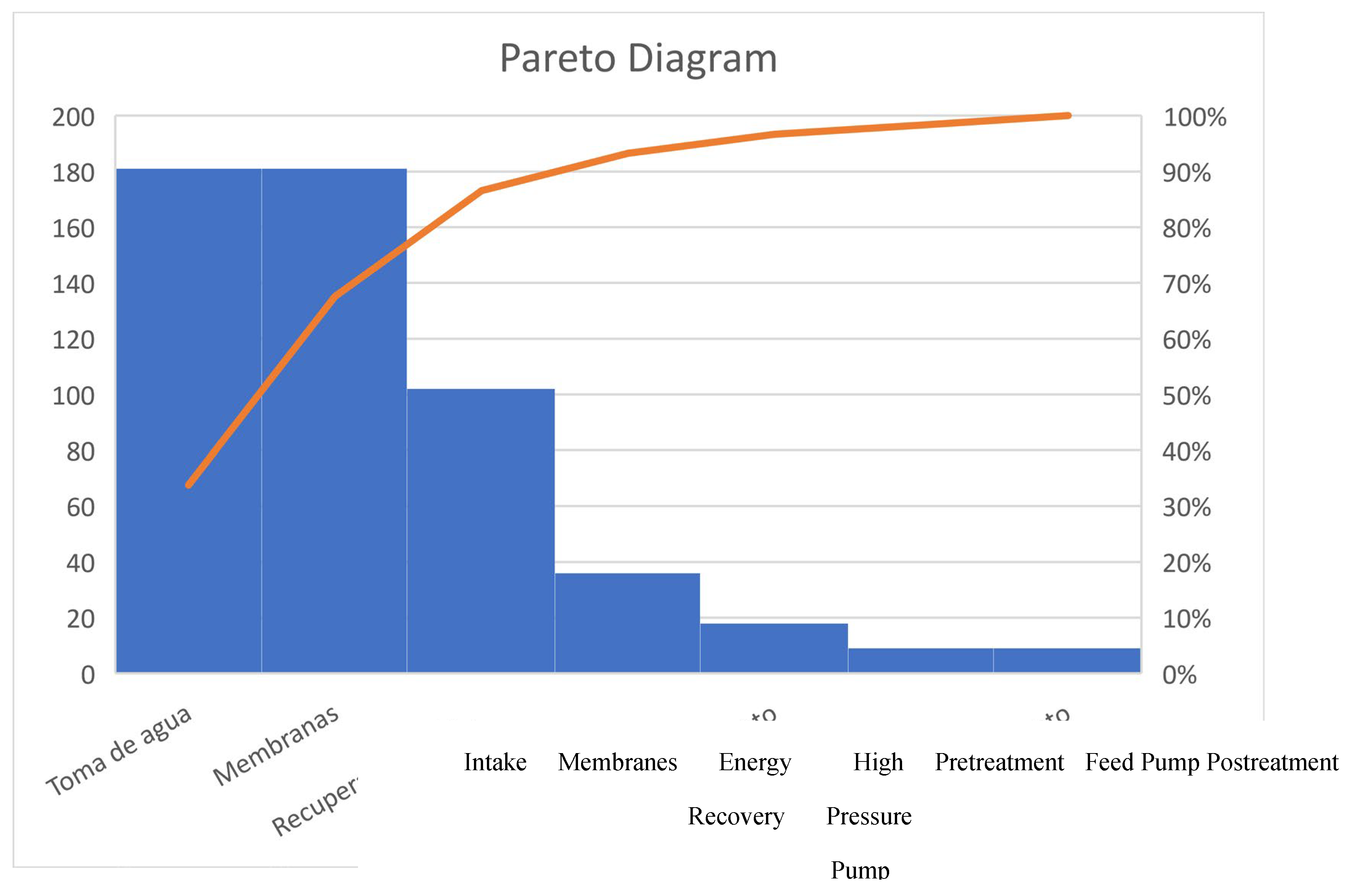
Territorial Pareto Diagram
The Pareto diagram, already discussed before, has been studied at territorial level for the Canary Islands, where a total of 180 seawater desalination plants have been included for this study.
Figure 4 shows the corresponding Pareto diagram.
The most important decision making is based on the decision on the collection of feed water, the membranes and the energy recovery units, which influence 90% of the possible energy improvement of the system. In this sense, the first two elements will be mainly studied in terms of decision-making on seawater collection and the type of membranes to be chosen for the installation, which represent between 70% and 80% of the influence on the proposed energy improvement. The third aspect, energy recovery, is not the subject of this study because it is not subject to possible pilots in the plant, but rather to the installation or not of these, whose operation has been demonstrated in seawater plants. In any case, it is advisable whenever possible to introduce energy recovery equipment of the Dweer or ERI type that makes maximum use of the pressure energy of the brine.
Decisions on membranes can be made based on a pilot test in the plant, with the specific type of water to be treated, or based directly on the projections and guarantees of the supplier. It is demonstrated the need to carry out a pilot test in a desalination plant to eliminate this uncertainty at practically no cost to the operator, as the membranes for these tests are normally supplied free of charge by the supplier, avoiding the risk of making a mistake with the membrane model, with the costs of all kinds that this entails, and are tested in a prepared pipe that is released from the plant for this test.
Regarding the decision to take decisions on the collection of feed water, if possible, we recommend taking the water from a beach well or borehole to take advantage of the filtration of the ground and improve the quality of the feed water, which is cleaner and less polluted. If this is not possible due to the size of the plant, we would opt for an open intake and in both cases at the appropriate depth to stabilize the working temperature as much as possible. Similarly, the greater the depth, the lower the salinity of the seawater, which reduces the osmotic pressure and consequently the energy consumption of the installation.
In this sense, a deeper intake stabilizes the temperature and reduces its value in the summer- autumn periods when it is higher in the water, improving boron rejection in the most critical months. This helps us, by confirming pilots, to opt for membranes with low energy consumption as opposed to those with high rejection which consume much more. Increasing the depth of the intake also means an economic cost based on the cost of the GRP pipe of around 35 EUR/m and, if necessary, a higher-pressure pump, which in the case of Grundfos means 5.5% more cost, although normally the same pump is enough. Even so, these costs are quickly amortized against the large energy and economic savings that can be obtained per cubic meter of water produced. This also justifies the importance of the feed water intake.
Energy consumption is calculated multiplying the desalination capacity of each island times the consumption per kWh/m3 of permeate water. This consumption (kWh/m3) is obtained studying the characteristics and different energy recovery systems installed in the desalination plants of each island (
http://www.fcca.es).
In this sense, it can be confirmed that for an annual production of desalinated water in the Canary Islands of approximately 660000 m3/day and considering an average energy consumption of 3.04 kWh/m3, introducing equipment to recover energy from brine, we have a carbon footprint of 1203.84 tCO2/day, which means that there are 439402 tCO2 per year, as commented on in
Section 3. On the other hand, following this same criterion and using a global coefficient of the ecological footprint to calculate it [
22,
23,
24,
25], a value of 219701 ha/year of surface area is obtained to compensate for the ecological footprint that we have due to the production of desalinated water in the Canary Islands. This ecological footprint per person divided by the population of Canary Islands (2207225 habitants), supposes a value of 0.1 ha/person/year and consequently the emissions per inhabitant and year are 0.2 tCO2/person/year.
The carbon and ecological footprints calculated before are only for the desalination in Canary Islands. If we extend this calculation to the total annual consumption in all the sectors of the archipelago in 2019 of 8878271 MWh and considering an average value of 0.6 tCO2/MWh obtained [
25], it is estimated that 5326963 tCO2/year can be emitted. It represents 2.4 tCO2/person/year.
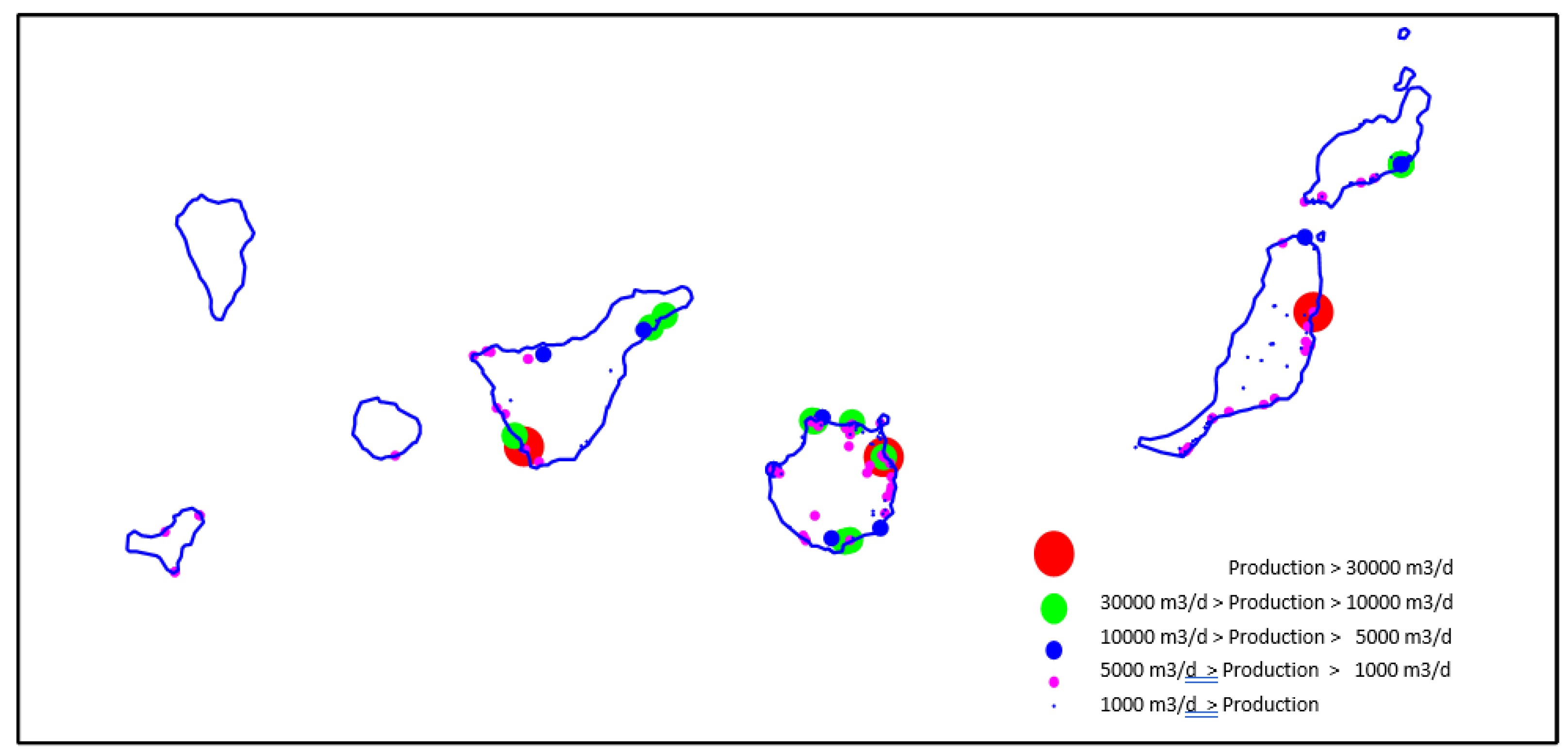
Figure 5 shows the most significant plants in the Canary Islands in terms of size that produce most of the ecological footprint mentioned.
4. Conclusions
The novelty of this article is to apply Pareto diagram to a study of a total of 180 seawater desalination plants at territorial level in Canary Islands. The introduction of RO piloting in a seawater desalination plant, whose energy consumption is very high, could be beneficial in optimizing its resources. Without a pilot plant, there is a risk of missing out on the opportunity to test a membrane that optimizes energy consumption and improves the quality of the water produced.
The Pareto analysis is used to highlight the 2 or 3 most significant causes whose treatment affects more than 80% of the possible energy improvement to be implemented.
In this example, it can be seen how the most important decisions are based on factors 1, 2 and 3, which influence 90% of the possible energy improvement of the system. In this sense, the first two elements will be mainly studied in terms of the decision making on factors 1 and 2 for the installation, which represents between 70% and 80% of the influence on the proposed energy improvement. The third factor is also considered, although to a lesser extent, to reach 90% of the effects on the energy improvement of the desalination plants in the territory to be considered.
The cost and energy required in the process depend on the quality of water required and the type of membrane used. It is confirmed the importance of operational efficiency and cost reduction, due to the highest cost of the installation is the electrical consume of the high-pressure pump. To reduce the feed pressure influences directly in the highest economical cost of the sea water reverse osmosis desalination plant. Feed water collection is important due to an open intake could increase the dirty on the surface of the reverse osmosis membranes and it increases the energy consumption. Moreover, to use high rejection membranes increase the operation pressure and it influences directly in the energy consumption and in the economic cost of the installation. Therefore, it is mandatory to use low energy consumption membranes to get a cost reduction in the operation of the plant.
The study of standard RO elements for a seawater desalination plant helps to choose a reverse osmosis element that lowers the energy consumption, and therefore the operating costs of the plant as energy is the most expensive part of the plant.
Within the total cost of water production, the most important influences are the energy consumed and the type of RO element chosen.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C., P.M., C.A.M.-P. and F.L.-Z.; Data curation, N.C., P.M., C.A.M.-P., and F.L.-Z.; Formal analysis, C.A.M.-P., and F.L.-Z.; Funding acquisition, F.L.-Z and C.A.M.-P.; Investigation, N.C., P.M., F.L.Z. and C.A.M.-P..; Methodology, .C.L.M., P.M., F.L.Z. and C.A.M.-P; Project administration, C.A.M.-P., and F.L.-Z; Resources, N.C., P.M., F.L.Z. and C.A.M.-P; Software, N.C. and C.A.M.-P.; Supervision, C.A.M.-P. and, F.L.-Z.; Validation, C.A.M.-P. and, F.L.-Z.; Visualization, N.C., C.A.M.-P. and, F.L.-Z; Writing—original draft, N.C.; Writing—review and editing, N.C., C.A.M.-P. and, F.L.-Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was co-funded by the INTERREG V-A Cooperation, Spain–Portugal MAC (Madeira-Azores-Canaries) 2014–2020 programme, MITIMAC project (MAC2/1.1a/263)
References
- Liao, J.; Li, S.; et al. Multi-Objective Optimization Based on Simulation Integrated Pareto Analysis to Achieve Low-Carbon and Economical Operation of a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water 2024, 16, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, C.G.; Ilinca, C. Evaluation of Various Generalized Pareto Probability Distributions for Flood Frequency Analysis. Water 2023, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; et al. Optimization of the Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic Process by Integrating ASM2d with Pareto Analysis of Variance and Response Surface Methodology. Water 2022, 14, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariane, A.B.; Sabokdast, M.M.; Karami, F.; Asadi, R.; Ponnambalam, K.; Mousavi, S.J. Integrated Operation of Multi-Reservoir and Many-Objective System Using Fuzzified Hedging Rule and Strength Pareto Evolutionary Optimization Algorithm (SPEA2). Water 2021, 13, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; et al. Multi-Objective Optimization Based on Simulation Integrated Pareto Analysis to Achieve Low-Carbon and Economical Operation of a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water 2021, 13, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; et al. Study of the Seawater Desalination Performance by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Melián-Martel, N.; Nuez, I. Short Review on Predicting Fouling in RO Desalination. Membranes 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, F.; Ramos, A.; Vaswani, J.; Mendieta, C.; Brito, S. . Climate Change Mitigation Strategy through Membranes Replacement and Determination Methodology of Carbon Footprint in Reverse Osmosis RO Desalination Plants for Islands and Isolated Territories. Water 2021, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, M. Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination. Membranes 2021, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudle, D.D.; Tucker, J.H.; Cooper, J.L.; Arnold, B.B.; Papastamataki, A. Electrochemical demineralization of water with carbon electrodes; U.S. Dept. of the Interior: Washington, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Almadani, H.M.N., «Renewable Energy,» pp. 1915–1924., 2003.
- López, M.D.P.M.; Mendizábal, R.I.; Uribe, I.O.; Martínez, M.J.R. Electrodiálisis con membranas bipolares: fundamentos y aplicaciones. Ingeniería química 2004, 418, 166–182. [Google Scholar]
- Porada, S.; Zhao, R.; van del Wal, A.; Presser, V.; Biesheuvel, P.M. Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Progress in Materials Science 2013, 58, 1388–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-B.; Park, K.-K.; Eum, H.-M.; Lee, C.-W. Desalination of a thermal power plant wastewater by membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 2006, 195, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z. Electrosorptive desalination by carbon nanotubes and nanofibres electrodes and ion-exchange membranes. Water Res 2008, 42, 4923–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; van der Wal, A. Membrane capacitive deionization. J Membrane Sci 2009, 346, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, J.-H. Improvement of desalination efficiency in capacitive deionization using a carbon electrode coated with an ion-exchange polymer. Water Res 2010, 44, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; Zhao, R.; Porada, S.; van der Wal, A. Theory of membrane capacitive deionization including the effect of the electrode pore space. J Colloid Interface Sci 2011, 360, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhadana, Y.; Ben-Tzion, M.; Soffer, A.; Aurbach, D. A control system for operating and investigating reactors: the demonstration of parasitic reactions in the water desalination by capacitive de-ionization. Desalination 2011, 268, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, O.N.; Naylor, R.M.; Rios Perez, C.A.; Wilkes, E.; Hidrovo, C. Energetic performance optimization of a capacitive deionization system operating with transient cycles and brackish water. Desalination 2013, 314, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugolecki, P.; van der Wal, A. Energy recovery in membrane capacitive deionization. Environ Sci Technol 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Suss, M.E.; Baumann, T.F.; Bourcier, W.L.; Spadaccini, C.M.; Rose, K.A.; Santiago, J.G.; et al; et al. , Capacitive desalination with flow-through electrodes. Energy Environ Sci 2012, 5, 9511–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadana, Y.; Avraham, E.; Noked, M.; Ben-Tzion, M.; Soffer, A.; Aurbach, D. Capacitive deionization of NaCl solutions at non-steady-state conditions: inversion functionality of the carbon electrodes. J Phys Chem C 2011, 115, 16567–16573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.-I.; Park, H.-R.; Yeo, J.-G.; Yang, S.; Cho, C.H.; Han, M.H.; et al. Desalination via a new membrane capacitive deionization process utilizing flow electrodes. Energy Environ Sci 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.W.; Murphy, G.W. Electrochemical demineralization of water with porous electrodes of large surface area. Saline watter conversion. American Chemical Society 1960, 206–223. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, B.B.; Murphy, G.W. Studies on electrochemistry of carbon and chemically modified carbon surfaces. J Phys Chem 1961, 65, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.W.; Cooper, J.L.; Hunter, J.A. Activated carbon used as electrodes in electrochemical demineralization of saline water; U.S. Dept. of the Interior: Washington, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, G.W.; Caudle, D.D. Mathematical theory of electrochemical demineralization in flowing systems. Electrochim Acta 1967, 12, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Hamilton, W.S. The mechanism of demineralization at carbon electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 1966, 113, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Accomazzo, M.A.; Accomazzo, J.E. Electrochemically controlled ion exchange. J Electrochem Soc 1969, 116, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.W.; Townsend, F.M.; Stevens, A.M. Filed operation of a 20 gallons per day pilot plant unit for electrochemical desalination of brackish water.
- Washington: U.S. Dept. of the Interio, 1968. C. B.E. y i. S. W. N. M. W.G. Pell, «7th International Seminar on Double Layer,» de Florida Educational Seminars: Boca, 1997.
- Zubieta, L.; Bonert, R. Characterization of Double-Layer Capacitors for Power Electronics Applications. IEEE, 2000.
- B. E. C. A. Lasia, J. Bockris y R. White, «Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications, Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry,» New.
- York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 1999. E. Karde, S. Buller y R. D. Doncker, «Electrochim,» 2002.
- C. Schiller, «Main error sources at AC measurements,» 1997.
- EN 62391-1:2006, «Condensadores eléctricos fijos de doble capa para su uso en equipos electrónicos. Parte 1: Especificación genérica (IEC 62391-1:2006) (Ratificada por AENOR en septiembre de 2006),» 2006.
- EN 62391-2-1:2006, «Condensadores eléctricos fijos de doble capa para su uso en equipos electrónicos. Parte 2-1: Especificación marco particular: Condensadores eléctricos de doble capa para aplicación de potencia. Nivel de evaluación EZ (IEC 62391-2-1:2006),» 2006.
- EN 62391-2:2006, «Condensadores eléctricos fijos de doble capa para su uso en equipos electrónicos. Parte 2: Especificación intermedia: Condensadores eléctricos de doble capa para aplicación de potencia (IEC 62391-2:2006) (Ratificada por AENOR en septiembre de 2006),» 2006.
- EN 62576:2010, «Condensadores eléctricos fijos de doble capa para vehículos eléctricos híbridos. Métodos de ensayo de las características eléctricas. (Ratificada por AENOR en febrero de 2011),» 2010.
- Gualous, H.; Bouquain, D.; Berthon, A.; Kauffmann, J.M. Experimental study of supercapacitor serial resistance and capacitance variations with temperature. J. Power Sources 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Brouji, H.; Vinassa, J.M.; Briat, O.; Bertrand, N.; Woirgard, E. Ultracapacitors self discharge modelling using a physical description of porous electrode impedance. IEEE, 2008.
- B. Conway y W. Pell, «Analysis of power limitations at porous,» 2001.
- Fabregat, F.; Mora, G.G.I.; Bisquert, J. Cyclic Voltammetry Studies. J. Phys. Chem 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, A.; Miller, J. testing of Electrochemical Capacitors: Capacitance. Nantes 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R. R. Martín, Hernández, «Análisis, modelado e identificación de los Condensadores Electroquímicos de Doble Capa,» 2014.
- Texas Instruments, «OPA548 High-Voltage, High-Current Operational Amplifier,» [On Line]. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/opa548.pdf (accessed on May 2018).
- Arduino, «Arduino Nano,» [On Line]. Available online: https://store.arduino.cc/usa/arduino-nano (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- BQ, «Arduino Nano pinout,» [On Line]. Available online: https://www.bq.com/es/ (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Spark Fun Electronics, «MCP4725,» [On Line]. Available online: https://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/BreakoutBoards/MCP4725.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Adafruit, «MCP4725 Breakout Board - 12-Bit DAC w/I2C Interface,» [On Line]. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/product/935 (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Texas Instruments, «ADS111x Ultra-Small, Low-Power, I2C -Compatible, 860-SPS, 16-Bit ADCs With Internal Reference, Oscillator, and Programmable Comparator,» [On Line]. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ads1115.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Adafruit, «ADS1115 16-Bit ADC - 4 Channel with Programmable Gain Amplifier,» [On Line]. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/product/1085 (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Texas Instruments, «High Accuracy INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER,» [On Line]. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/sbos133/sbos133.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Analog Devices, «ADM3260,» [On Line]. Available online: http://www.analog.com/en/products/interface- isolation/isolation/isopower/adm3260.html#product-overview (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Texas Instruments, «OPA549 High-Voltage, High-Current Operational Amplifier,» [On Lie]. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/opa548.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Zhao, R.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Van der Wal, A. Energy consumption and constant current operation in membrane capacitive deionization. Energy Environ Sci 2012, 5, 9520–9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas instruments, «LMx58-N Low-Power, Dual-Operational Amplifiers,» [On Line]. Available online: LMx58-N Low-Power, Dual-Operational Amplifiers. [February 2018].
- Song, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Gao, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, S. Analysis, experiment and application of a power-saving actuator applied in the piston type energy recovery device. Desalination 2015, 361, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Mohamed, E.; Karavas, C.; Papadakis, G. Experimental comparison of the performance of two reverse osmosis desalination units equipped with different energy recovery devices. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 3019–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Mohamed, E.S.; Kyriakarakos, G.; Papadakis, G. Experimental investigation of the performance of a reverse osmosis desalination unit under full-and part-load operation. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3170–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, F.J.; Báez, S.O.; Gotor, A.G. Energy performance of a reverse osmosis desalination plant operating with variable pressure and flow. Desalination 2015, 366, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherjl, J.; Mnif, A.; Bejaoui, I.; Humrouni, B. Study of the influence of operating parameters on boron removal by a reverse osmosis membrane. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar]
- Schallenberg-Rodriguez, J.; Veza, J.M.; Blanco-Marigorta, A. Energy efficiency and desalination in the Canary Islands. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, N.; Gray, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Ostarcevic, E.; Liubinas, A.; Atherton, P.; Roeszler, G.; Gibbs, A.; Duke, M. Pilot trial of membrane distillation driven by low grade waste heat: Membrane fouling and energy assessment. Desalination 2016, 391, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.M.; Peshev, D.; Livingston, A.G. Energy consumption for desalination – A comparison of forward osmosis with reverse osmosis, and the potential for perfect membranes. Desalination 2016, 377, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, N.R.G. Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids – what is their precise relationship? Desalination 1989, 72, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerlage, S.; Nada, N. Algal toxin removal in seawater desalination processes. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 2575–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilstad, T.; Protasova, E.; Simonova, A.; Stornes, S.; Yuneizi, I. Wind-powered RO desalination. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 3106–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, V.G. Desalination and sustainability – An appraisal and current perspective. Water Res. 2016, 89, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, F.A.; Ramos, A. Analysis of high efficiency membrane pilot testing for membrane design optimization. Desalination and Water Treatment 2017, 73, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).