Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
14 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
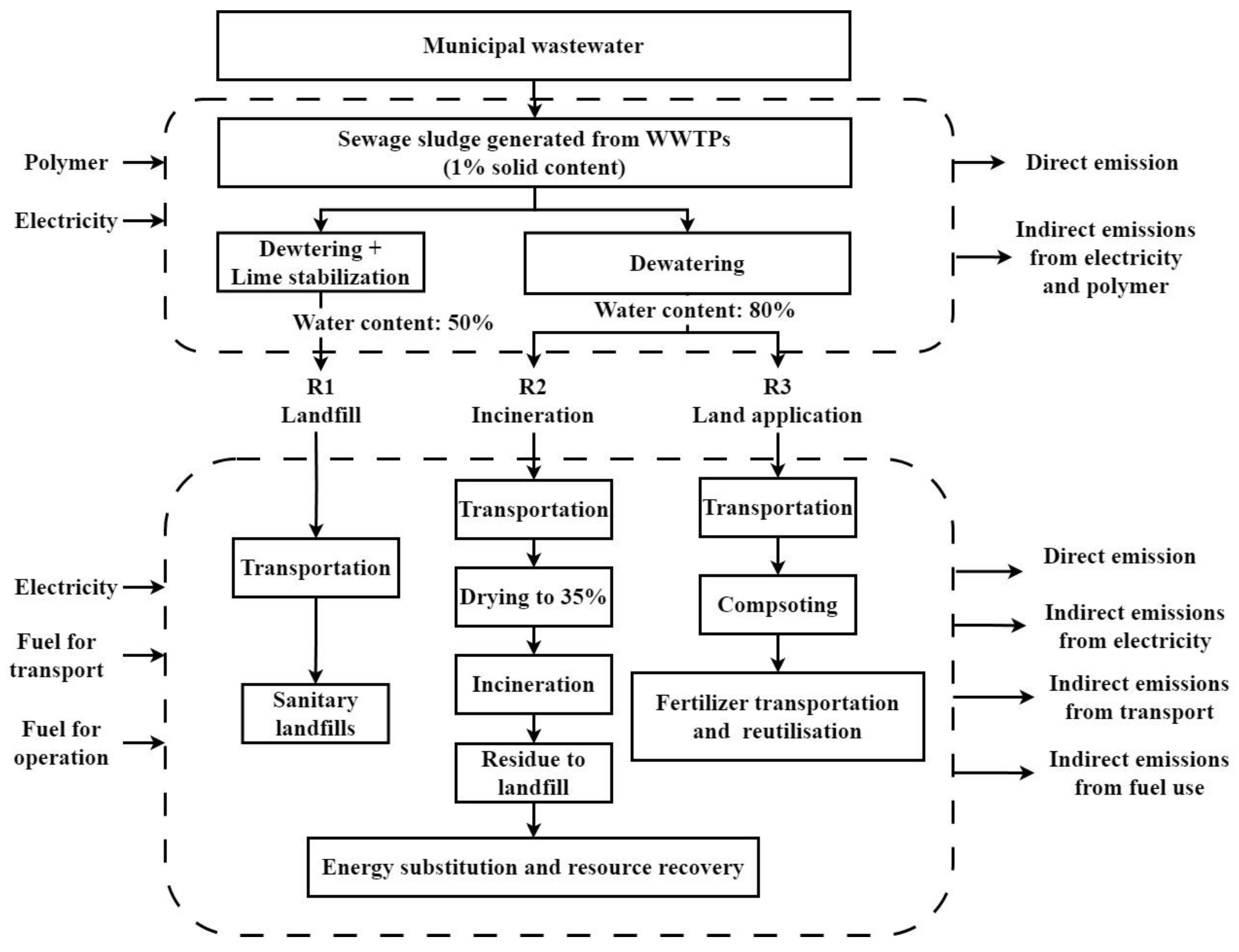
2.1. System Boundary and Data Sources
2.2. GHG Emission Calculation
2.3. Principal Component Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
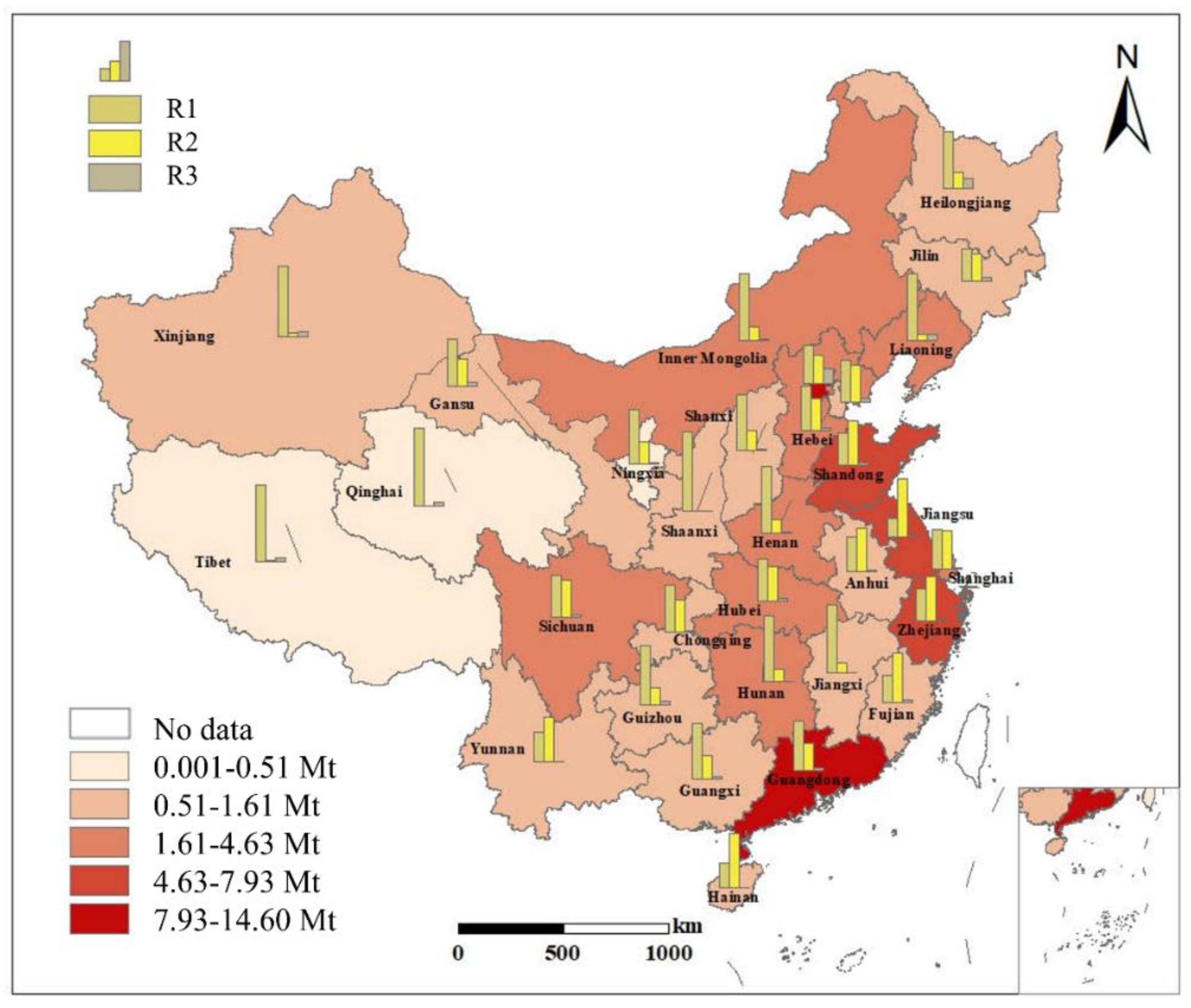
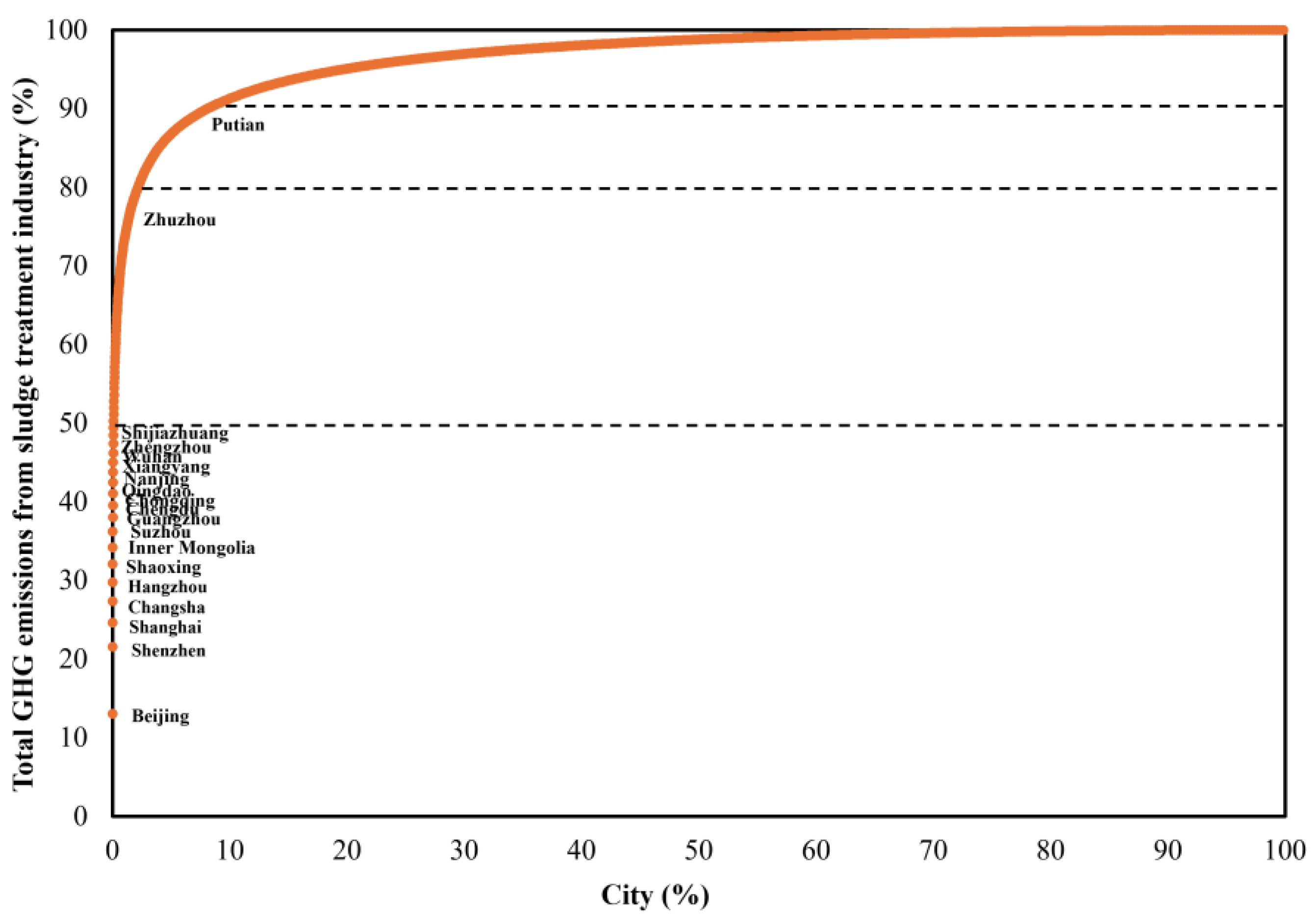
3.1. Statement of Sludge Treatment Industry in China
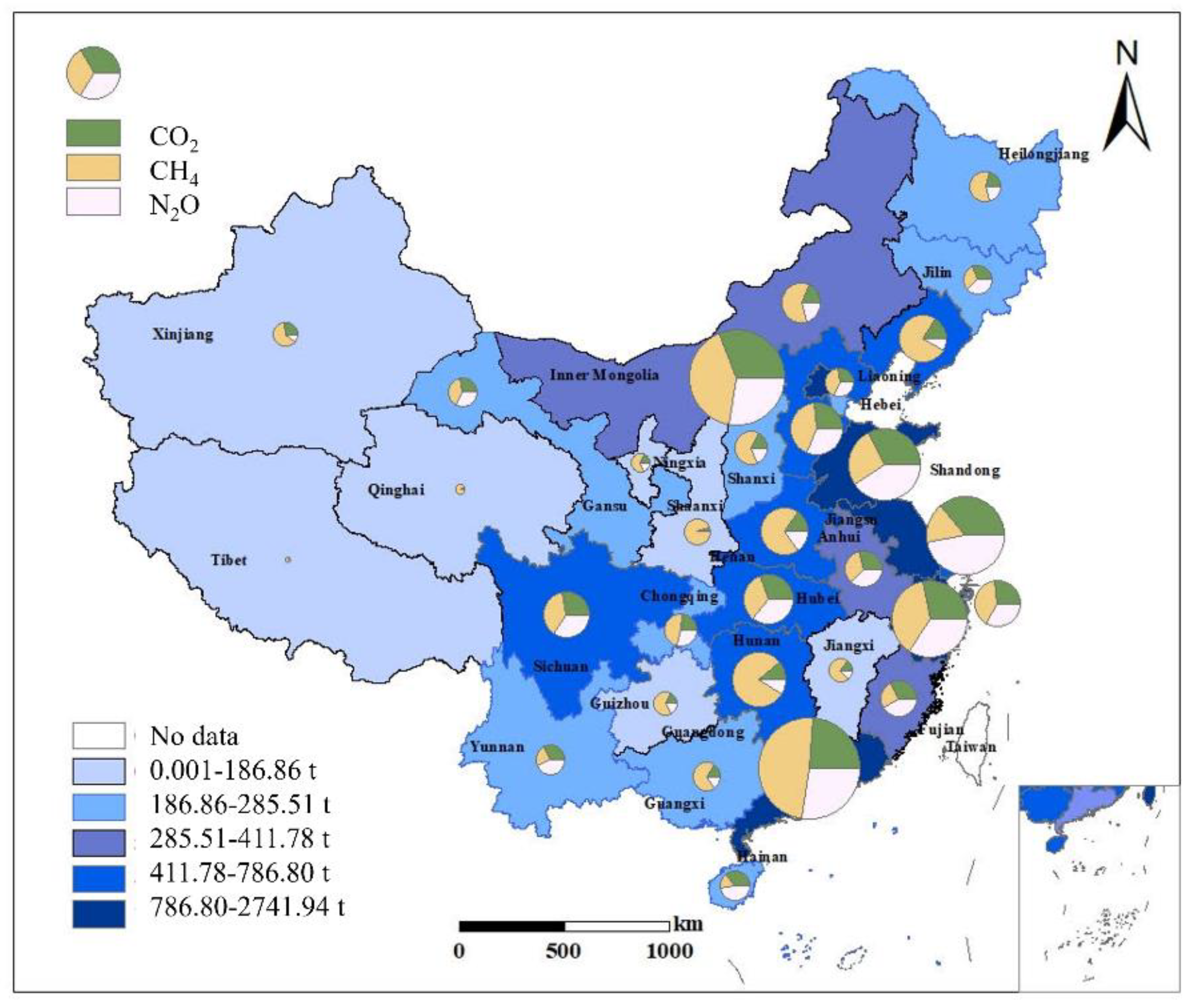
3.2. Quantification of GHG Emission
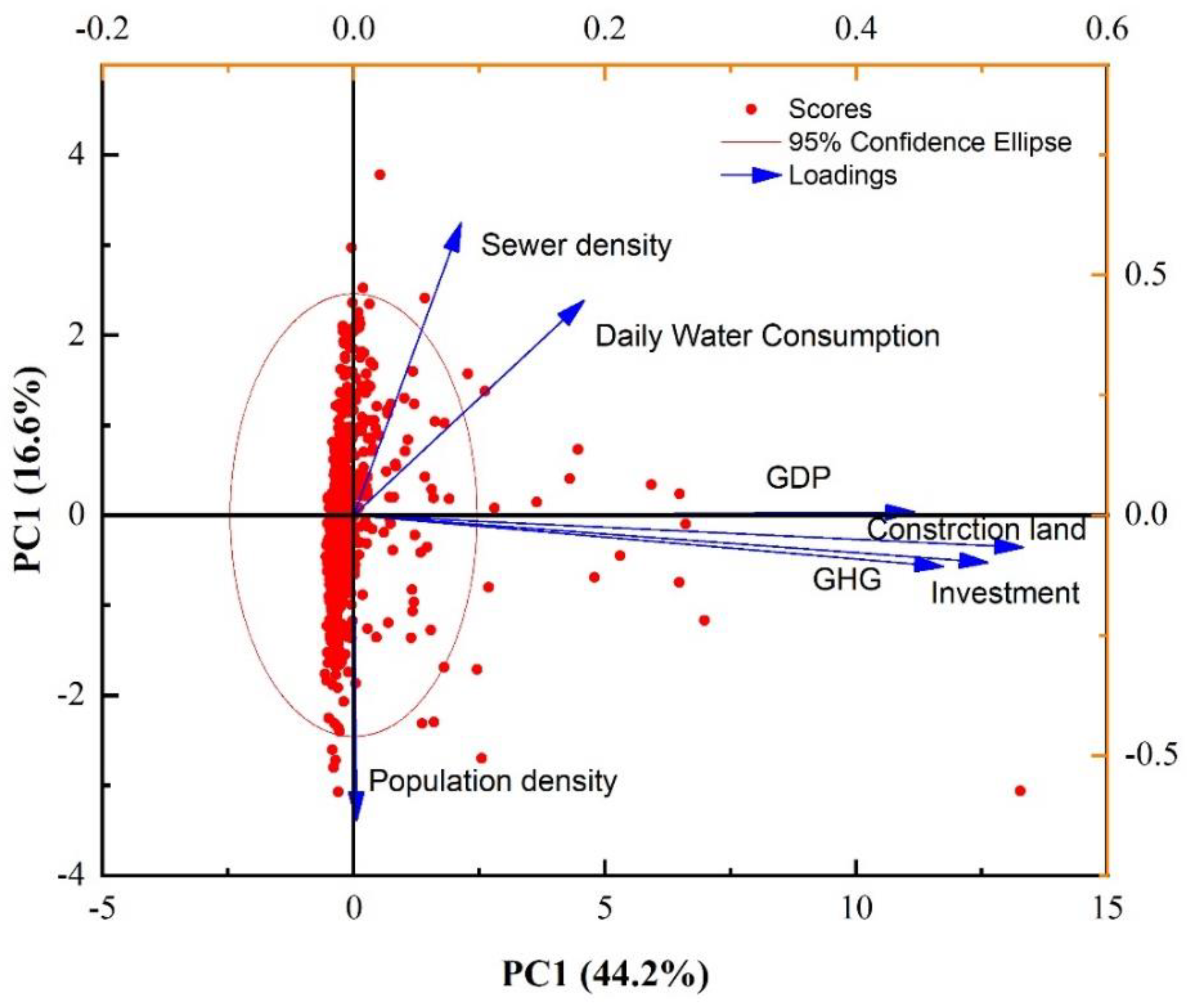
3.3. Impacts of GHG Emissions
4. Potential of GHG Emission Mitigation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y., Liu, R., Yang, D. & Dai, X. Sludge treatment and resource recovery towards carbon neutrality in China: current status and future perspective. Blue-Green Systems 3, 119–127 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Statistical Yearbook of Urban Construction, 2021. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (2021).
- Yu, Y. & Zhang, W. Greenhouse gas emissions from solid waste in Beijing: The rising trend and the mitigation effects by management improvements. Waste Management and Research 34, 368–377 (2016).
- Guo, D. et al. Revisiting China’s domestic greenhouse gas emission from wastewater treatment: A quantitative process life-cycle assessment. Science of the Total Environment 876, (2023).
- Ding, A. et al. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Science of the Total Environment vol. 769 Preprint at (2021). [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. et al. Greenhouse gases emission control in WWTS via potential operational strategies: A critical review. Chemosphere vol. 273 Preprint at (2021). [CrossRef]
- Tarpani, R.R.Z. & Azapagic, A. Life cycle sustainability assessment of advanced treatment techniques for urban wastewater reuse and sewage sludge resource recovery. Science of the Total Environment 869, (2023). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H., Zhang, W., Li, L., Zhang, M. & Wang, D. Environmental impact and optimization of lake dredged-sludge treatment and disposal technologies based on life cycle assessment (LCA) analysis. Science of the Total Environment 787, (2021).
- SYUC. Statistical Yearbook of Urban Construction. (https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/file/old/2020/20200327/w02020032722244243052500000.xls, China, 2017).
- Guo, S.J., H.H.W. & D. X. Y. et al. Calculation of greenhouse gas emissions of municipal wastewater treatment and its temporal and spatial trend in China (in Chinese). Water & Wastewater Engineering 45, (2019).
- MEE. Ministry of Ecological Environment. Ministry of Ecological Environment (http://www.tanjiaoyi.com/article-25419-1.html, China, 2017).
- Shrestha, A. et al. Estimation of greenhouse gases emission from domestic wastewater in Nepal: A scenario-based analysis applicable for developing countries. Chemosphere 300, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z., Y.C.Z., H.J., et al. Predictive method research of sludge landfill gas production (in Chinese). China Environ. Sci. 30, (2010).
- Hong, J., Hong, J., Otaki, M. & Jolliet, O. Environmental and economic life cycle assessment for sewage sludge treatment processes in Japan. Waste Management 29, 696–703 (2009).
- IPCC. 2007 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. (2007).
- Wei, L. et al. Development, current state and future trends of sludge management in China: Based on exploratory data and CO2-equivaient emissions analysis. Environ Int 144, (2020).
- Liu, H.T., Zheng, H.X., Chen, T.B., Zheng, G.D. & Gao, D. Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from sewage sludge aerobic compost in China. Water Science and Technology 69, 1129–1135 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Liu, B., Wei, Q., Zhang, B. & Bi, J. Life cycle GHG emissions of sewage sludge treatment and disposal options in Tai Lake Watershed, China. Science of the Total Environment 447, 361–369 (2013).
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Japan. (Japan, 2006).
- Li, Y., Chen, Y. & Wu, J. Enhancement of methane production in anaerobic digestion process: A review. Applied Energy vol. 240 120–137 Preprint at (2019). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H. et al. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environment International vols 92–93 11–22 Preprint at (2016). [CrossRef]
- Twagirayezu, E. et al. Comparative life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment in Wuhan, China: Sustainability evaluation and potential implications. Science of the Total Environment 913, (2024). [CrossRef]
- Lishan, X., Tao, L., Yin, W., Zhilong, Y. & Jiangfu, L. Comparative life cycle assessment of sludge management: A case study of Xiamen, China. J Clean Prod 192, 354–363 (2018).
- Zhang, H. et al. Environmental and economic assessment of electro-dewatering application to sewage sludge: A case study of an Italian wastewater treatment plant. J Clean Prod 210, 1180–1192 (2019).
- Pradel, M. & Reverdy, A.L. Assessing GHG Emissions from Sludge Treatment and Disposal Routes: The Method behind GESTABoues Tool. https://hal.science/hal-00781673 (2020).
- Nakakubo, T., Yoshida, N. & Hattori, Y. Analysis of greenhouse gas emission reductions by collaboratively updating equipment in sewage treatment and municipal solid waste incineration plants. J Clean Prod 168, 803–813 (2017).
- Liu, Y. et al. Feasibility of using different hydrothermal processes for sewage sludge management in China. Science of the Total Environment vol. 838 Preprint at (2022). [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. et al. The GHG mitigation opportunity of sludge management in China. Environ Res 212, (2022).
- Yuan, H. et al. Environmental and economic life cycle assessment of emerging sludge treatment routes. J Clean Prod 449, (2024).
- Guo, D., Li, B., Yu, W., Baroutian, S. & Young, B.R. A system engineering perspective for net zero carbon emission in wastewater and sludge treatment industry: A review. Sustainable Production and Consumption vol. 46 369–381 Preprint at (2024). [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. et al. Comprehensive competitiveness assessment of four typical municipal sludge treatment routes in China based on environmental and techno-economic analysis. Science of the Total Environment 895, (2023).
- Hao, X., Chen, Q., van Loosdrecht, M.C.M., Li, J. & Jiang, H. Sustainable disposal of excess sludge: Incineration without anaerobic digestion. Water Research vol. 170 Preprint at (2020). [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, P. et al. Principles and potential of thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge to enhance anaerobic digestion. Environ Res 214, (2022).
- Yin, Z. et al. Application and improvement methods of sludge alkaline fermentation liquid as a carbon source for biological nutrient removal: A review. Science of the Total Environment vol. 873 Preprint at (2023). [CrossRef]

| Methods | Reduction potential (t CO2-eq/t DS) | Cost (USD/t DS) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasification | 0.33-0.46 | 200-400 | [22] |
| AD | 0.09-0.30 | 100-200 | [27,28] |
| HTP | 0.20-0.40 | 300-500 | [23,27] |
| WO | 0.10-0.30 | 150-300 | [29,30] |
| Pyrolysis | 0.15-0.30* | 250-450 | [27,31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





