Submitted:
18 June 2024
Posted:
19 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs
2.2. Preparation of Drugs (Bromelain, AC and BromAc®)
2.3. Preparation of Mucus Simulant
2.4. Ventilator Settings and Measurements
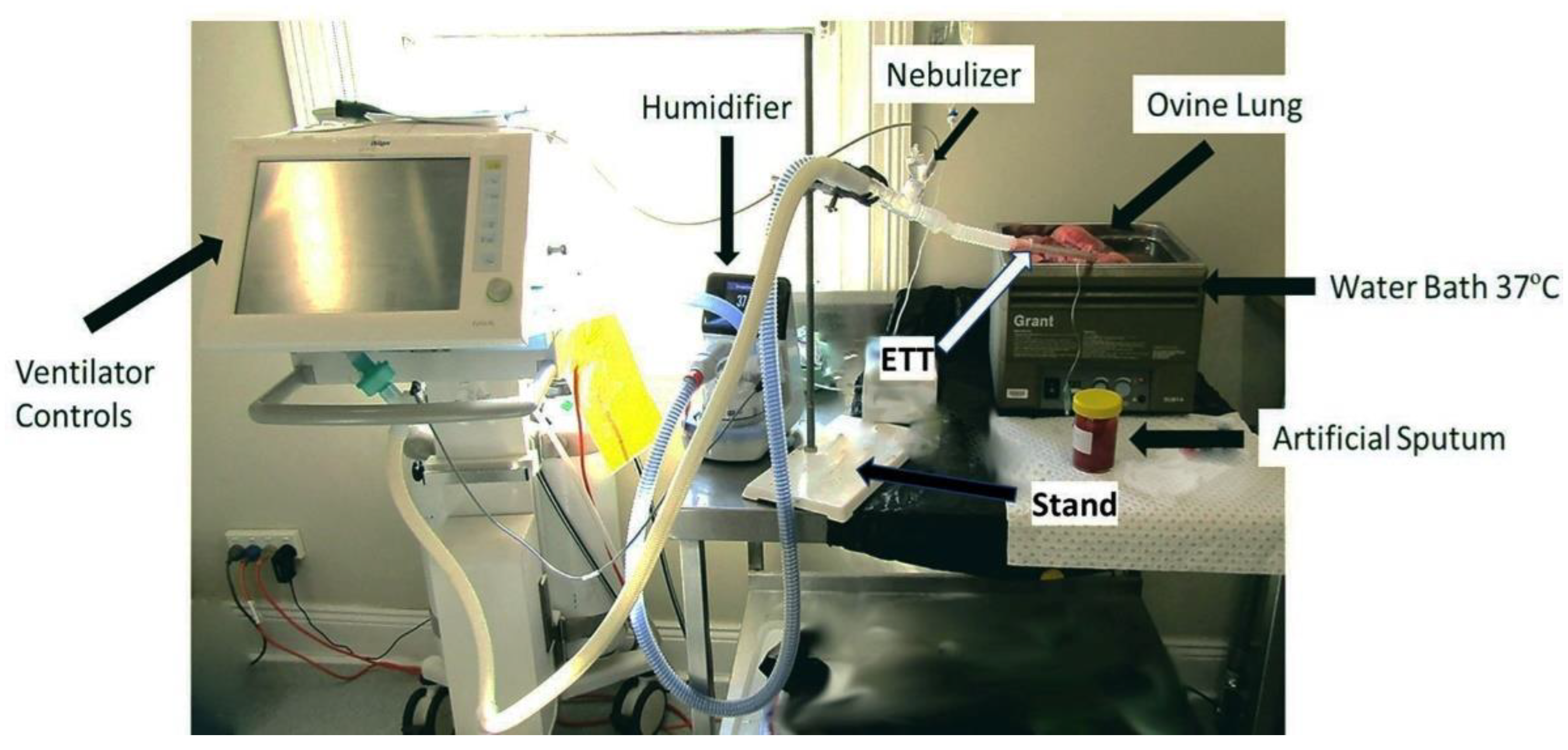
2.5. Mucus Simulant Administration and Nebulisation of Drugs in Ovine Lung
2.6. Rheology Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
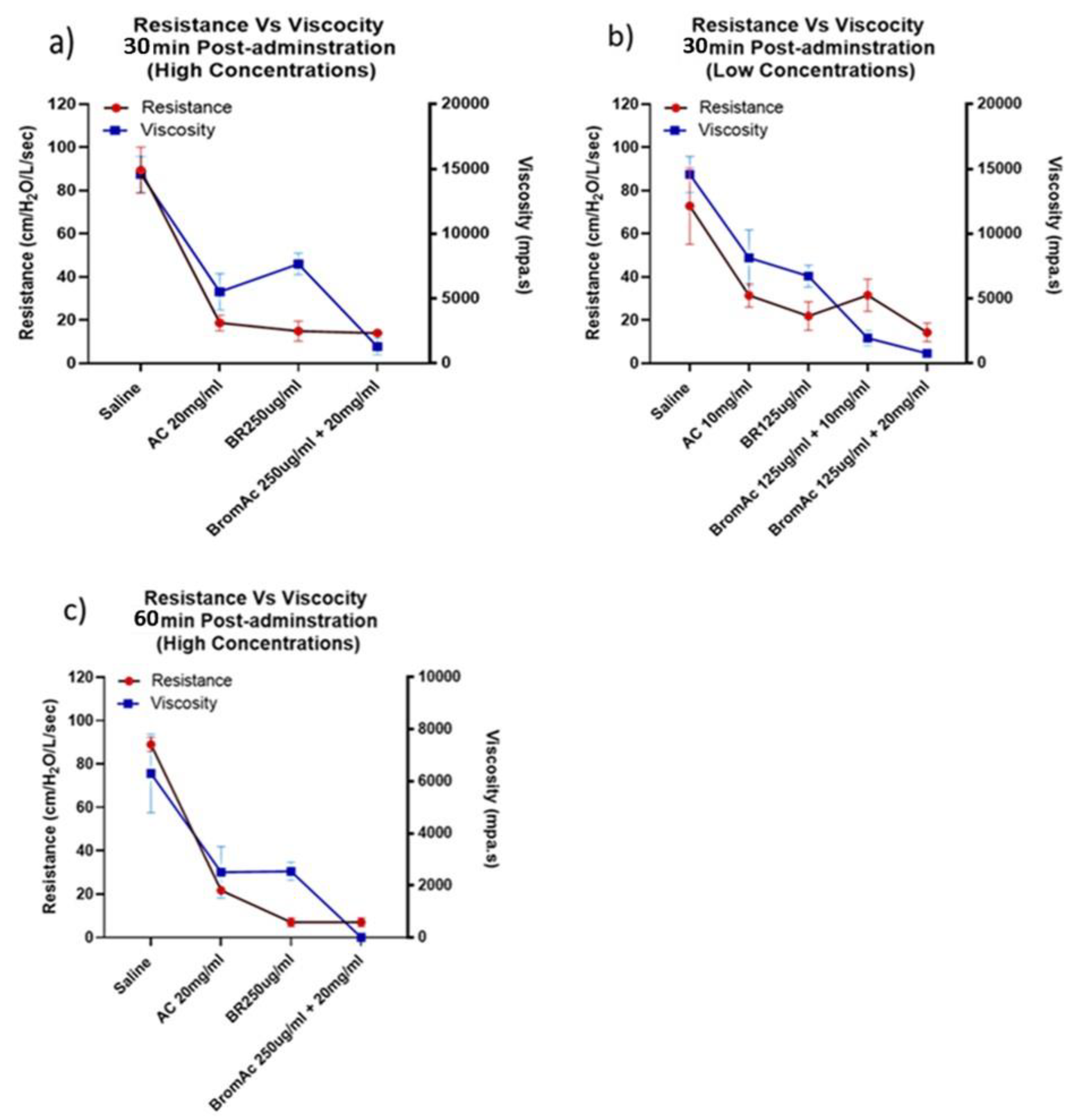
3. Results
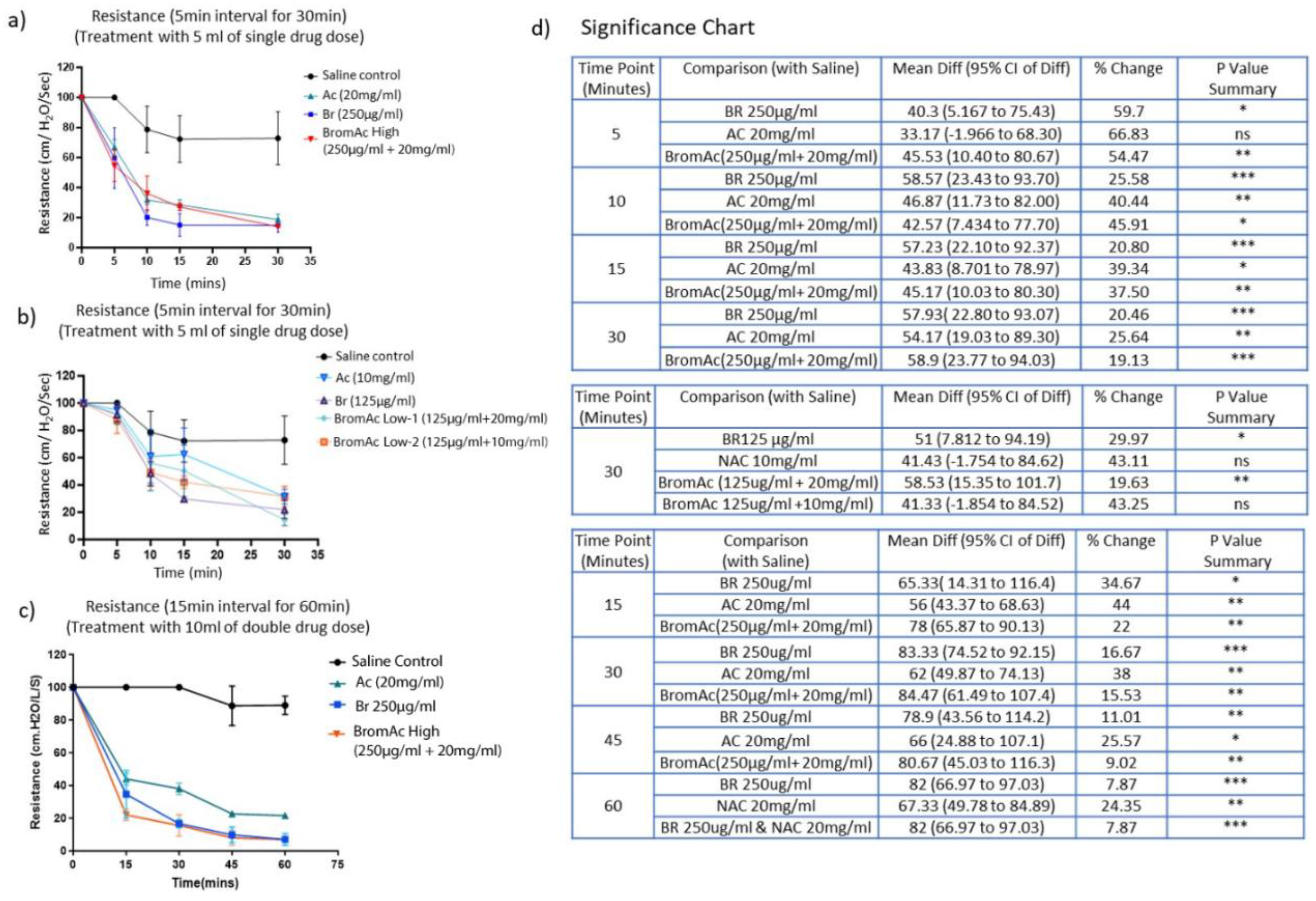
3.1. Effect of Bromelain, Ac and BromAc on Ventilatory Resistance
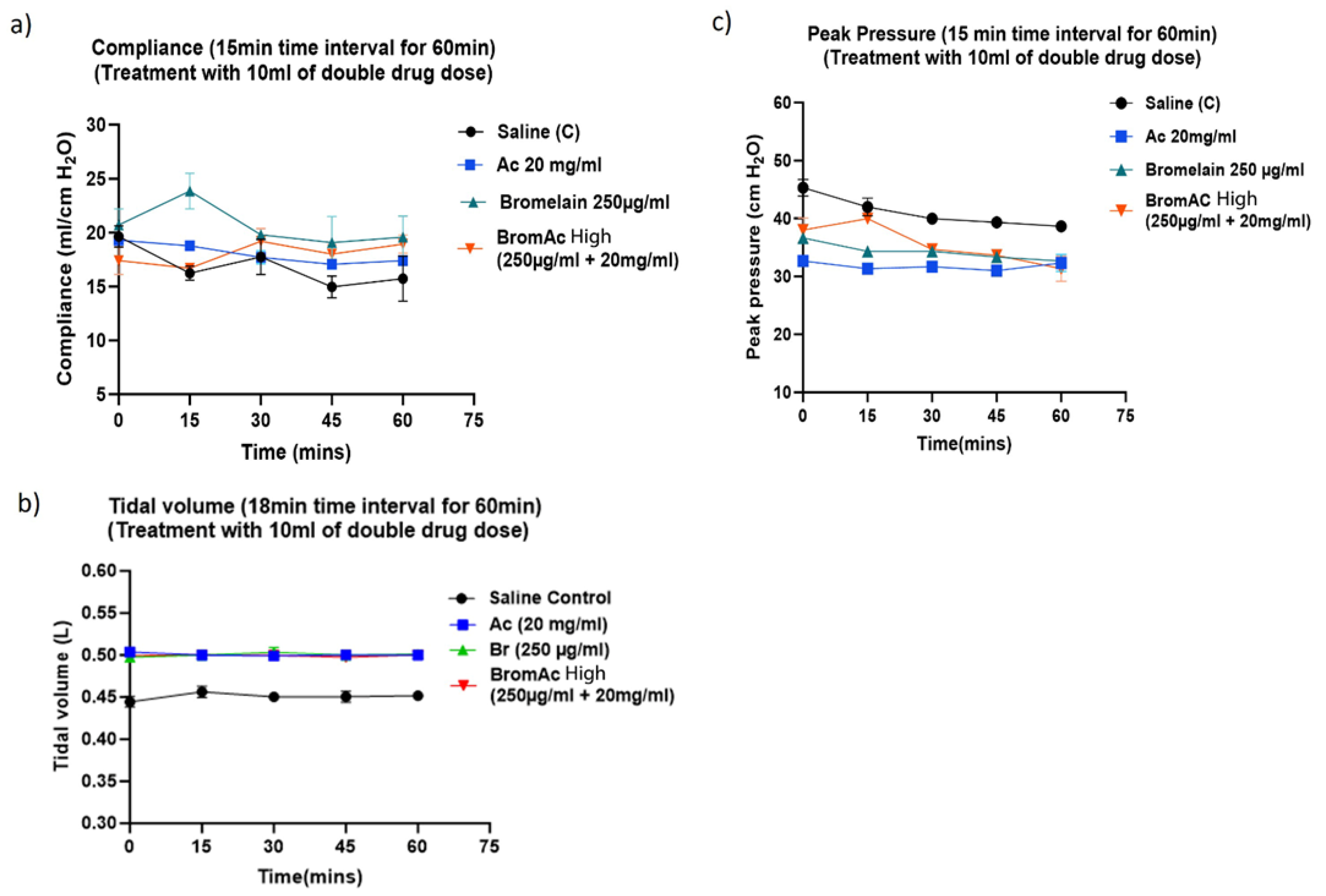
3.2. Effect of Bromelain, Ac and BromAc on Ventilatory Compliance, Tidal Volume and Peak Pressure
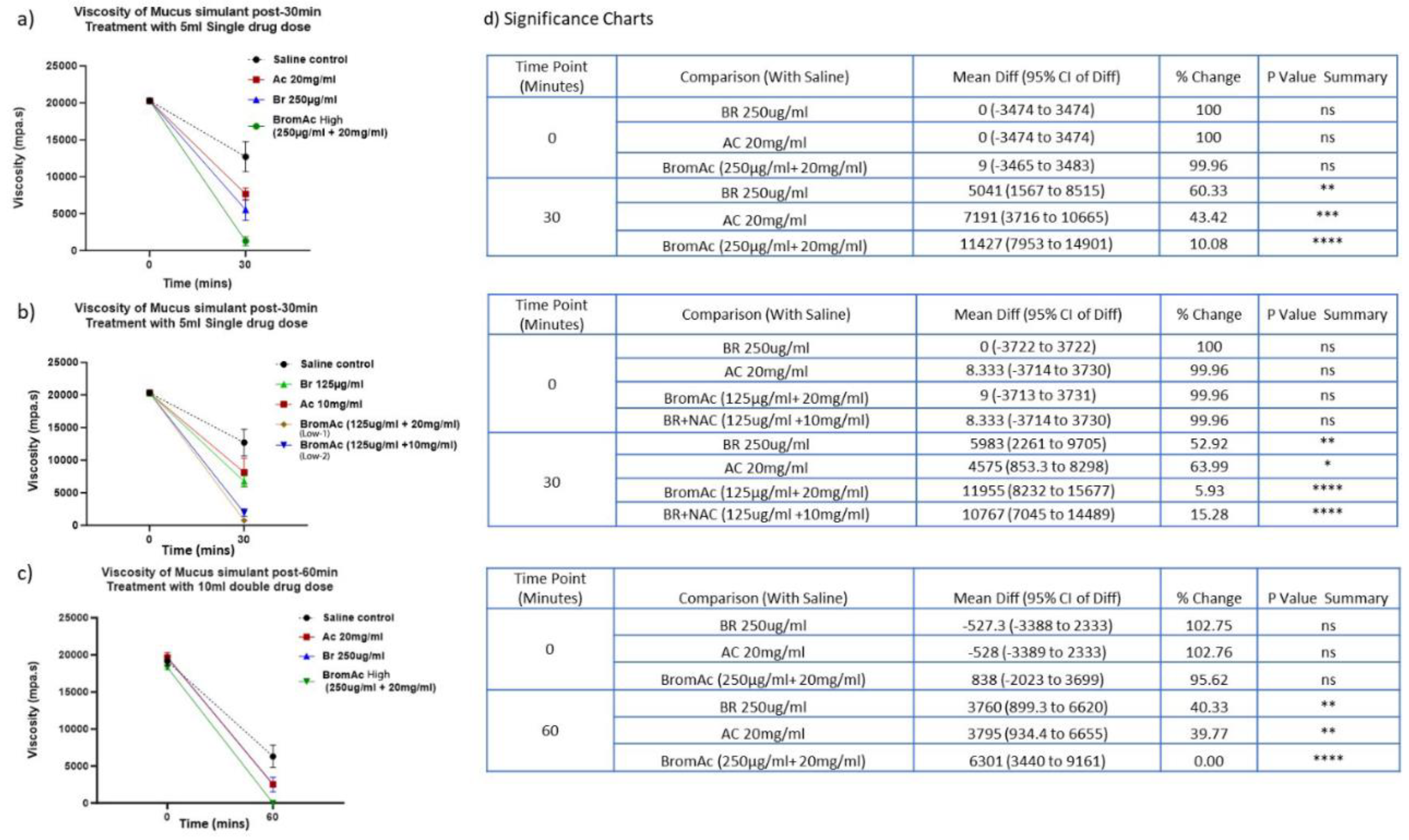
3.3. Effect of Bromelain, Acetylcysteine and BromAc®™ on Mucus Viscosity Using Rheology
3.4. Viscosity and Ventilatory Parameters and Relation in the Treatment Group and Control
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schluger, N.W.; Koppaka, R. Lung Disease in a Global Context. A Call for Public Health Action. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 2014, 11, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Puerta-Puerta, J.M.; Ruiz, C.; Melguizo-Rodriguez, L. SARS-CoV-2 infection: The role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, T.; Hassani, F.; Ghaffari, N.; Ebrahimi, B.; Yarahmadi, A.; Hassanzadeh, G. COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: A narrative review on potential mechanisms. J Mol Histol 2020, 51, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Han, T.; Zhou, J.; Bi, L. Sputum characteristics and airway clearance methods in patients with severe COVID-19. Medicine 2020, 99, e23257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.S.; Binu, A.; Devan, A.R.; Nath, L.R. Mucus targeting as a plausible approach to improve lung function in COVID-19 patients. Med Hypotheses. 2021, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.B.; Sandholdt, H.; Moller, M.E.E.; Perez-Alos, L.; Pedersen, L.; Israelsen, S.B.; et al. Prediction of Respiratory Failure and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients Using Long Pentraxin PTX3. J Innate Immun. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Charles, M.; Pratap, P.; Naeem, A.; Siddiqui, Z.; et al. Cytokine Storm and Mucus Hypersecretion in COVID-19: Review of Mechanisms. J Inflamm Res. 2021, 14, 175–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottestad, W.; Sovik, S. COVID-19 patients with respiratory failure: What can we learn from aviation medicine? Brit J Anaesth 2020, 125, E280–E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manckoundia, P.; Franon, E. Is Persistent Thick Copious Mucus a Long-Term Symptom of COVID-19? Eur J Case Rep Intern Med 2020, 7, 002145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N Engl J Med 2010, 363, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, H.R.; Chalmers, J.D. Pathophysiology of Bronchiectasis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2021, 42, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, G.; de Gracia, J.; Buxó, M.; Alvarez, A.; Vendrell, M. Long-term benefits of airway clearance in bronchiectasis: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. European Respiratory Journal 2018, 51, 1701926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegerter, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The Pathology of Asthma: What Is Obstructing Our View? Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 2023, 18, null. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trawoger, R.; Kolobow, T.; Cereda, M.; Giacomini, M.; Usuki, J.; Horiba, K.; et al. Clearance of Mucus from Endotracheal Tubes during Intratracheal Pulmonary Ventilation Anesthesiology 1997, 86, 1367–1374.
- Lu, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Zhu, A.; Lin, Y.; et al. Elevated MUC1 and MUC5AC mucin protein levels in airway mucus of critical ill COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol 2021, 93, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra Mitjà, P.; Centeno, C.; Garcia-Olivé, I.; Antuori, A.; Casadellà, M.; Tazi, R.; et al. Bronchoscopy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Findings, Microbiological Profile, and Coinfection. Journal of Bronchology & Interventional Pulmonology. 2022, 29.
- Valle, S.J.; Akhter, J.; Mekkawy, A.H.; Lodh, S.; Pillai, K.; Badar, S.; et al. A novel treatment of bromelain and Acetylcysteine (BromAc®) in patients with peritoneal mucinous tumours: A phase I first in man study. Eur J Surg Oncol 2021, 47, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, K.; Akhter, J.; Chua, T.C.; Morris, D.L. A formulation for in situ lysis of mucin secreted in pseudomyxoma peritonei. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho dos Reis, J.G.A.; Ferreira, G.M.; Lourenço, A.A.; Ribeiro, Á.L.; da Mata, C.P.d.S.M.; de Melo Oliveira, P.; et al. Ex-vivo mucolytic and anti-inflammatory activity of BromAc® in tracheal aspirates from COVID-19. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2022, 148, 112753. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, K.; Mekkawy, A.H.; Akhter, J.; Valle, S.J.; Morris, D.L. Effect of nebulised BromAc®®on rheology of artificial sputum: Relevance to muco-obstructive respiratory diseases including COVID-19. bioRxiv, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Serisier, D.J.; Carroll, M.P.; Shute, J.K.; Young, S.A. Macrorheology of cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease & normal sputum. Respiratory Research 2009, 10, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcellos, C.A.; Allen, P.G.; Wohl, M.E.; Drazen, J.M.; Janmey, P.A.; Stossel, T.P. Reduction in Viscosity of Cystic Fibrosis Sputum in Vitro by Gelsolin. Science 1994, 263, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussig, S.J.; Batkin, S. Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. J Ethnopharmacol 1988, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001, 58, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, K.; Akhter, J.; Morris, D.L. Assessment of a novel mucolytic solution for dissolving mucus in pseudomyxoma peritonei: An ex vivo and in vitro study. Pleura Peritoneum 2017, 2, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.; Pillai, K.; Chua, T.C.; Alzarin, N.; Morris, D.L. Efficacy of a novel mucolytic agent on pseudomyxoma peritonei mucin, with potential for treatment through peritoneal catheters. Am J Cancer Res 2014, 4, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guerini, M.; Condrò, G.; Friuli, V.; Maggi, L.; Perugini, P. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and Its Role in Clinical Practice Management of Cystic Fibrosis (CF): A Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.K.; Richardson, P.S.; Fung, D.C.; Howard, M.; Thornton, D.J. Analysis of respiratory mucus glycoproteins in asthma: A detailed study from a patient who died in status asthmaticus. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 1995, 13, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georas, S.N. All plugged up — noninvasive mucus score to assess airway dysfunction in asthma. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2018, 128, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Flower, O.; Soni, N. Deadspace ventilation: A waste of breath! Intensive Care Med 2011, 37, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Carlesso, E.; Brioni, M.; Cressoni, M. Airway driving pressure and lung stress in ARDS patients. Critical Care. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitler, J.R.; Malhotra, A.; Thompson, B.T. Ventilator-induced Lung Injury. Clin Chest Med 2016, 37, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L. SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation. Physiological Reports 2021, 9, e14726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



