Submitted:
15 June 2024
Posted:
19 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
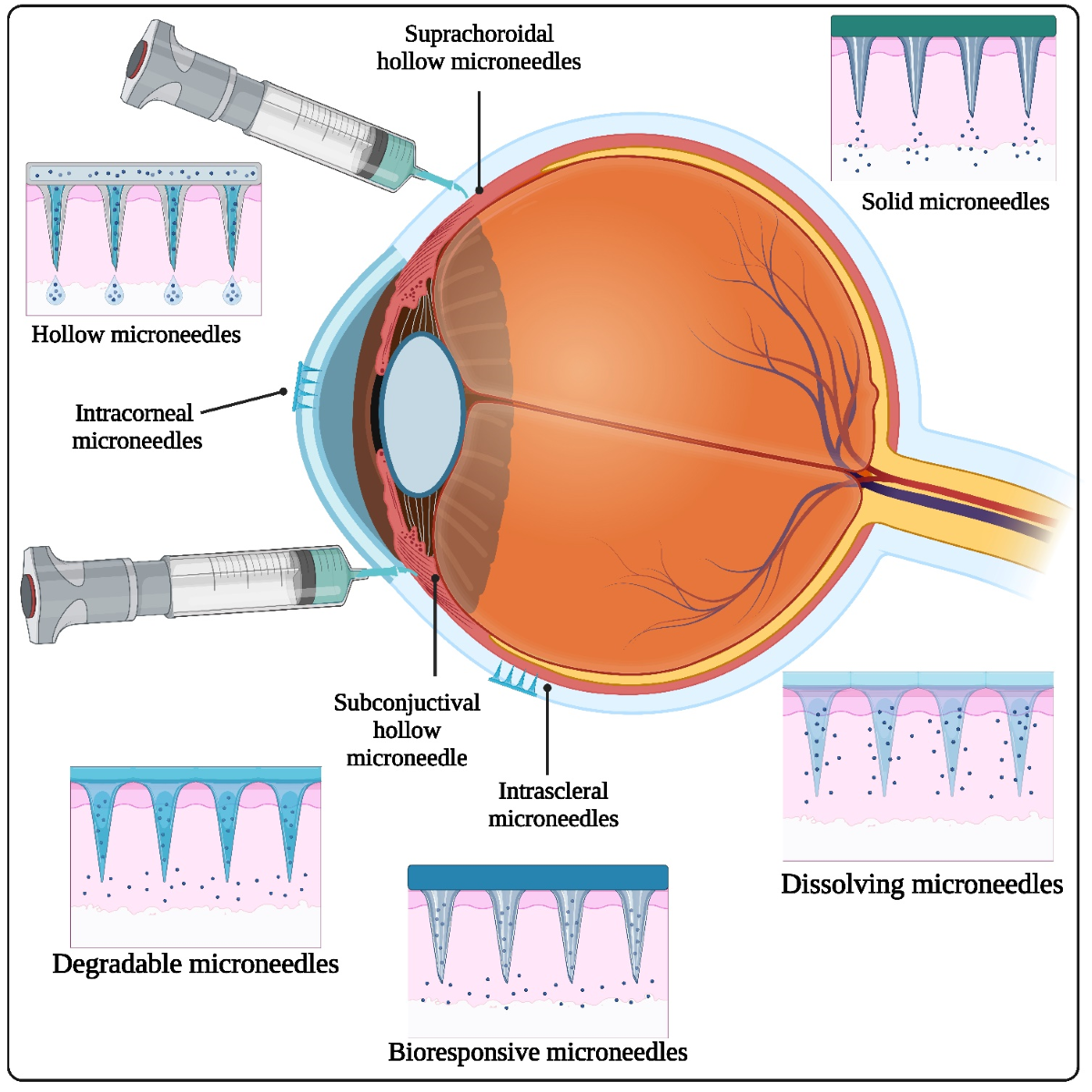
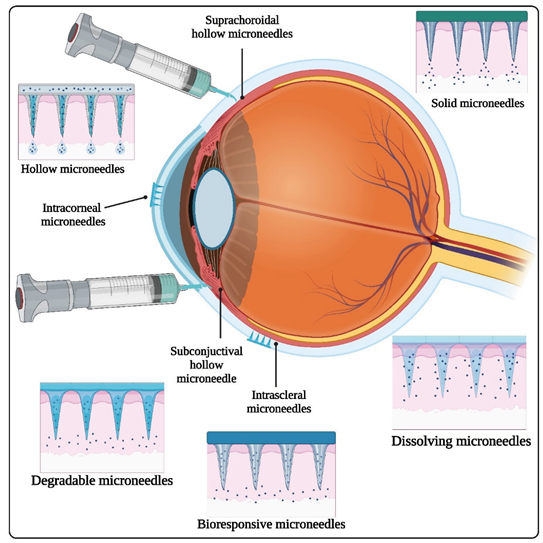
Keywords:
Graphical Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Microneedle Technology
1.3. Purpose of the Review
2. Microneedle Design and Fabrication
2.1. Types of Ophthalmic Microneedles
2.1.1. Solid Microneedles
2.1.2. Hollow Microneedles
2.1.3. Dissolving Microneedles
2.1.4. Coated Microneedles
2.1.5. Coating Single Microneedles
2.1.6. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles
2.1.7. Biodegradable Microneedles
| Sr. No. |
Type of microneedles | Material used | Fabrication method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solid microneedles | (i) Silicon microneedles (ii) Metal microneedles (iii) Polymer microneedles (iv) Ceramic microneedles |
Etching | [75] |
| 2 | Coated microneedles | (i) Stainless steel (ii) Glass (iii) Chitosan |
Spraying | [76] |
| 3 | Dissolving microneedles | (i) Polymers (ii) Sugars (iii) Proteins |
Encapsulation | [77] |
| 4 | Hollow microneedles | (i) Metals (ii) Silicon (iii) Glass (iv) Polymers (v) Nickel |
Centrifugation | [77] |
| 5 | Hydrogel forming microneedles | (i) PVP (ii) Hydrophilic polymers |
Dispersion of solution | [78] |
| 6 | Biodegradable microneedle | (i) PVP (ii) PLGA (iii) PGA |
Molding or casting | [74] |
| Material | Mechanical characteristics | Biocompatibility | Drug loading capacity | Transparency | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Excellent mechanical strength | Biocompatible | Moderate to high | Not transparent | Good mechanical properties | Brittle and easily broken | Transdermal sensing and drug delivery | [79] |
| Metal | High mechanical strength | Biocompatible | Moderate to high | Not transparent | High mechanical strength | Corrosion risk, potential allergic reactions | Diagnostics and drug delivery | [80] |
| Polymer | Flexible | Biocompatible | Low to moderate | Not transparent | Flexible and easily fabricated | Limited mechanical strength, potential degradation | Drug administration, biosensing | [81] |
| Glass | Brittle | Biocompatible | Low to moderate | Transparent | Excellent optical transparency | Fragile and can break easily | Transdermal sensing and drug delivery using microneedle arrays | [82] |
| Dissolving | Varies | Biocompatible | Low to moderate | Varies | Dissolves entirely in the body | Short needle length, limited drug loading capacity | Transdermal drug administration | [83] |
| Hydrogel | Soft and adaptable | Biocompatible | Low to moderate | Not transparent | Soft and biocompatible | Mechanical weakness, potential swelling | Transdermal drug delivery, wound healing, biosensing | [84] |
| Ceramic | High mechanical strength | Biocompatible | Moderate to high | Not transparent | High mechanical strength, good chemical stability | Difficulty in fabrication, brittleness | Drug administration, biosensing | [85] |
| Biodegradable | Varies | Biocompatible | Moderate to high | Varies | Dissolves completely in the body | Limited mechanical strength, potential degradation | Drug administration, biosensing | [86] |
2.2. Fabrication Techniques
2.2.1. Photolithography
2.2.2. Micro-Molding
2.2.3. 3D Printing
2.3. Advantages of Microneedle Drug Delivery
| Sr. No. | Advantages | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimally Invasive | (i) Microneedles are tiny, causing minimal trauma during drug delivery. (ii) Patients experience reduced pain and discomfort compared to traditional injections. |
[116] |
| 2. | Improved Patient Compliance | (i) Microneedles enhance patient acceptance due to their less invasive nature. (ii) Allows for convenient self-administration, improving patient compliance. |
[117] |
| 3. | Enhanced Bioavailability | (i) Microneedles enable targeted delivery, improving drug absorption. (ii) Particularly beneficial for drugs with poor oral bioavailability. |
[15] |
| 4. | Rapid Onset of Action | (i) Facilitates quick drug delivery into the bloodstream, leading to a rapid onset of therapeutic effects. | [118] |
| 5. | Preventing First-Pass Metabolism | (i) Bypass the digestive system, preventing first-pass metabolism in the liver. | [119] |
| 6. | Improved Stability of Biologics | (i) Enables the delivery of biologics (proteins, peptides) with enhanced stability, preventing degradation. | [120] |
| 7. | Tailored Release Profiles | (i) Microneedles can be designed for controlled and sustained drug release, ensuring predictable pharmacokinetics. |
[121] |
| 8. | Reduced Needlestick Injuries | (i) Smaller needles reduce the risk of needlestick injuries, improving safety. | [122] |
| 9. | Potential for Self-Administration | (i) Empower patients to self-administer treatments, reducing healthcare costs and improving convenience. | [123] |
| 10. | Versatility | (i) Applicable to various administration routes, including transdermal, intradermal, and mucosal surfaces. | [124] |
2.4. Case Studies of Drug-Loaded Microneedles
| Sr. No. | Drug | Potential Applications |
Loading per patch |
Formulation type |
Composition / Characteristics | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Paclitaxel | Treatment for a range of malignancies, including lung, ovarian, and breast cancer | 54.13 µg | Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) |
Cetyl Palmitate and tricaprin, 230 nm | [133] |
| 2. | Capsaicin | Topical analgesia for localized pain relief | EE- 99.9 % | Colloidal nanoparticles |
HA and PVP (ratio 1:1), 167 ± 4 nm | [134] |
| 3. | Vitamin D3 / Cholecalciferol | Vitamin D supplementation for individuals with deficiency | 265 ± 32 µg | Nano-microparticles | PLGA, 400 nm to 3.6 µm | [141] |
| 4. | IR-780 | Near-infrared fluorescence imaging for tumor detection | - | SLNs | Cetyl Palmitate and tricaprin, 230 nm |
[133] |
| 5. | Doxycycline | Management of rosacea symptoms | 0.84 ± 0.02 mg | SLNs | 100 nm | [142] |
| 6. | Albendazole | Control of other parasitic infections (e.g., trichinellosis) | 0.94 ± 0.03 mg | SLNs | 100 nm | [142] |
| 7. | Cisplatin | Management of bladder cancer | -- | Lipid NPs | DOTAP, cholesterol, and DSPE-PEG-AA | [143] |
| 8. | Itraconazole | Therapy for fungal nail infections (onychomycosis) | 3.3 mg | Nanosuspension | 300 nm | [144] |
| 9. | Rilpivirine | 4 mg | Nanosuspension | [145] | ||
| 10. | Methotrexate (free acid) | Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis | 2.48 mg | Nanosuspension | 680 nm | [135] |
| 11. | Dutasteride | - | 11/12 % (w/w) | Nanosuspension | - | [146] |
| 12. | Curcumin | Treatment of wounds and burns | 10.9 ± 1.1 µg | Nanosuspension | 520 ± 40 nm | [147] |
| 13. | Ivermectin | - | 0.86 ± 0.07 mg | Nanosuspension | 98.12 ± 7.76 nm | [148] |
| 14. | Levonorgestrel | Contraception (long-acting reversible contraception) | 66.94 µg | Inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins | Hydroxypropyl- β -cyclodextrin (HP-β - CD) |
[136] |
| 15. | TA | 80.28 to 92.52 µg | Inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins | (HP-β - CD) | [137] | |
| 16. | Etonogestrel | Contraception (long-acting reversible contraception) | 550 µg | Microcrystal particles/Powder |
10 – 30 µm | [149] |
| 17. | Lumefantrine | Treatment for simple malaria brought on by strains of Plasmodium vivax and falciparum | 8806 ± 461 µg | Nanosuspension | 321.00 ± 16.50 nm | [138] |
| 18. | Artemether | - | 30,027 ± 69.5 µg | Nanosuspension | 148.10 ± 4.27 nm | [138] |
| 19. | Atorvastatin calcium trihydrate | Management of hypercholesterolemia | 1.9 to 3.4 mg | Solid dispersion | - | [138] |
| 20. | TA | - | 117.06 ± 9.07 µg | Nanosuspension | 264 nm | [150] |
| 21. | Leuprolide acetate | Hormonal therapy for transgender individuals | 14.3 µg | Solid dispersion | - | [151] |
| 22. | Shikonin | Promotion of wound healing | 0.805 ± 0.017 µg / mg | Micelles | 130 ± 8 nm | [152] |
| 23. | Finasteride | Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) | 47.36 ± 0.92 µg | Lipid NPs | Glyceryl monostearate and squalene, 180 nm | [153] |
| 24. | Lidocaine hydrochloride | Pain management during medical or cosmetic procedures (e.g., injections, tattooing) | 3.43 ± 0.12 mg | Matrix interaction | - | [139] |
| 25. | Diethylcarbamazine | Treatment of lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis) | 0.55 ± 0.00 mg | SLNs | 100 nm | [142] |
| 26. | OVA | - | 10 µg | PLGA NPs | 358 nm | [154] |
| 27. | 5-aminolevulinic acid | Management of superficial basal cell carcinoma. Therapy for acne vulgaris | 69.38 ± 4.89 µg | Matrix interaction | - | [155] |
| 28. | Methotrexate | Management of psoriasis | Up to 65.3 ± 2.9 µg | Matrix interaction | - | [156] |
| 29. | OVA | Immunization and vaccination against specific antigens or pathogens | 4.15 ± 1.93 µg (delivered 24%) | PLGA NPs | 170 nm | [32] |
| 30. | Lidocaine hydrochloride | Local anesthesia for minor surgical procedures | 3.43 ± 0.12 mg | Matrix interaction | - | [139] |
2.5. Evaluation Parameters for Ocular Microneedles
2.5.1. Biocompatibility:
2.5.2. Mechanical strength
2.5.3. Insertion efficiency
2.5.4. Drug loading and release
2.5.5. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
2.5.6. Safety and tolerability
2.6. Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
2.6.1. Needle Length and Geometry
2.6.2. Material Biocompatibility
| Hypersensitivity-inducing element | Cr, Co, V |
|---|---|
| Poor cellular compatibility element | Cu, Co, V, Fe |
| Excellent cellular compatibility element | Mo, Ti, Sn, Zr |
| Enhanced mechanical strength | Zr, Sn |
| β-phase stabilizing element | Ta, Nb, V, Cr, Mo, Fe |
3. Route of Administration for Ocular Microneedles
3.1. Intrastromal Injection
3.2. Intravitreal Injection
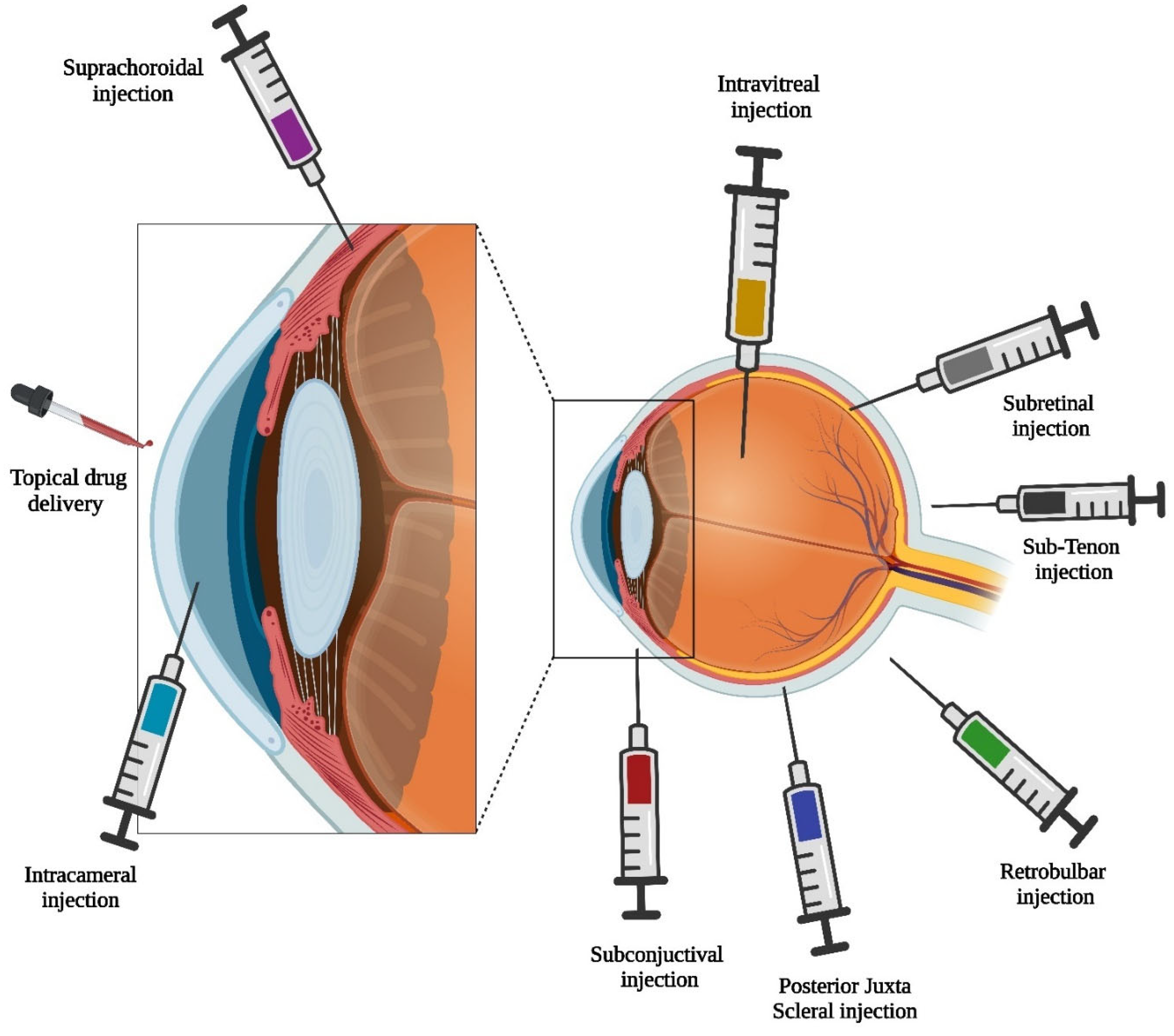
3.3. Subconjunctival Injection
3.4. Suprachoroidal Injection
3.5. Transscleral Delivery
4. Therapeutic Agents Delivered via Microneedles
4.1. Antibiotics
4.2. Steroids
4.3. Anti-VEGF Agents
4.4. Anti-Inflammatory Agents
5. Applications of Microneedles in Ocular Disease
5.1. Age-Related Macular Degeneration
5.1.1. Microneedle-Based Therapies for AMD
5.2. Diabetic Retinopathy
5.3. Glaucoma
5.3.1. Microneedle Therapy for Glaucoma Management
5.4. Other Ophthalmic Conditions
5.4.1. Retinal Vascular Occlusion
5.4.2. Uveitis
5.4.3. Retinitis pigmentosa
5.4.4. Conjunctivitis
5.4.5. Corneal Neovascularization
6. Clinical Trials and Regulatory Considerations
6.1. Overview of Ongoing Clinical Trials
| NCT number | Sponsor | Drug | Phase | Dose | Time | Status | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02747030 | Universitaire Ziekenhuizen Leuven | Ocriplasmin intravenously | Phase I | - | 12/2016–08/11/2017 | Completed | Central retinal vein occlusion |
| NCT03203447 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | Suprachoroidal CLS-TA | Phase III | 4 mg in 0.1 mL | 03/05/2018-12/18/2018 | Terminated | Macular edema |
| NCT03126786 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | IVT aflibercept | Phase II | 4 mg in 0.1 mL | 07/11/2017–04/17/2018 | Completed | Diabetic macular edema |
| NCT02949024 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | Suprachoroidal CLS-TA | Phase I/II |
4 mg in 0.1 mL | 11/10/2016–10/17/2017 | Completed | Diabetic macular edema |
| NCT03097315 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | Suprachoroidal CLS-TA | Phase III | 4 mg in 0.1 mL | 04/04/2017–01/24/2018 | Completed | Non-infectious Uveitis |
| NCT02595398 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | Suprachoroidal CLS-TA | Phase III | 4 mg in 0.1 mL | 11/17/2015–01/18/2018 | Completed | Macular edema with non-infectious uveitis |
| NCT02255032 | Clearside Biomedical, Inc. | CLS-TA | Phase II |
0.8 mg in 0.1 mL | 10/2014-01/ 2016 |
Completed | Macular edema with non-infectious uveitis |
| NCT02895815 | Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. | CNTO 2476 (6.0 × 104 cells) in 50 μL | Phase II |
- | 04/09/2018–08/19/2022 | Withdrawn | Visual acuity |
6.2. Regulatory Challenges
6.2.1. FDA and International Approvals
6.2.2. Safety and Efficacy Requirements
7. Challenges and Future Directions
7.1. Current Limitations of Microneedle-Based Ophthalmics
7.1.1. Pain Perception and Patient Compliance
7.1.2. Depth Control, Drug Loading and Release
7.1.3. Biodegradability
7.1.4. Patient Acceptance and Compliance
7.1.5. Sterility and Contamination
7.1.6. Scalability of Manufacturing
7.2. Future Innovations and Improvements
7.2.1. Potential for Personalized Medicine
7.2.2. Smart Microneedles and Real-Time Monitoring
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Urtti, A. Challenges and Obstacles of Ocular Pharmacokinetics and Drug Delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2006, 58, 1131–1135. [CrossRef]
- Ilochonwu, B.C.; van der Lugt, S.A.; Annala, A.; Di Marco, G.; Sampon, T.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. Thermo-Responsive Diels-Alder Stabilized Hydrogels for Ocular Drug Delivery of a Corticosteroid and an Anti-VEGF Fab Fragment. Journal of Controlled Release 2023, 361, 334–349. [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.C. Ocular Drug Delivery Conventional Ocular Formulations. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 1995, 16, 39–43. [CrossRef]
- Reardon, G.; Kotak; Schwartz, G. Objective Assessment of Compliance and Persistence among Patients Treated for Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Patient Preference and Adherence 2011, 441. [CrossRef]
- Scheive, M.; Yazdani, S.; Hajrasouliha, A.R. The Utility and Risks of Therapeutic Nanotechnology in the Retina. Therapeutic Advances in Ophthalmology 2021, 13, 251584142110033. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Sharma, R.; Singh, P.; Verma, V.; Karkhur, S.; Verma, S.; Soni, D.; Sharma, B. Age-Related Cataract - Prevalence, Epidemiological Pattern and Emerging Risk Factors in a Cross-Sectional Study from Central India. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology 2023, 71, 1905–1912. [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.; Patel, D.; Alabi, O. Epidemiology of Glaucoma: The Past, Present, and Predictions for the Future. Cureus 2020. [CrossRef]
- Vyawahare, H.; Shinde, P. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Cureus 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Epidemiology of Diabetic Retinopathy, Diabetic Macular Edema and Related Vision Loss. Eye and Vision 2015, 2, 17. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Chiang, B.; Wu, X.; Prausnitz, M.R. Ocular Delivery of Macromolecules. Journal of Controlled Release 2014, 190, 172–181. [CrossRef]
- Glover, K.; Mishra, D.; Gade, S.; Vora, L.K.; Wu, Y.; Paredes, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R. Microneedles for Advanced Ocular Drug Delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2023, 201, 115082. [CrossRef]
- Gadziński, P.; Froelich, A.; Wojtyłko, M.; Białek, A.; Krysztofiak, J.; Osmałek, T. Microneedle-Based Ocular Drug Delivery Systems – Recent Advances and Challenges. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2022, 13, 1167–1184. [CrossRef]
- Gaudana, R.; Ananthula, H.K.; Parenky, A.; Mitra, A.K. Ocular Drug Delivery. The AAPS Journal 2010, 12, 348–360. [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Marques, F.B.; Fernandes, R.; Alves, C.; Velpandian, T. Drug Transport Across Blood-Ocular Barriers and Pharmacokinetics. In Pharmacology of Ocular Therapeutics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 37–63.
- Rzhevskiy, A.S.; Singh, T.R.R.; Donnelly, R.F.; Anissimov, Y.G. Microneedles as the Technique of Drug Delivery Enhancement in Diverse Organs and Tissues. Journal of Controlled Release 2018, 270, 184–202. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Chiang, B.; Wu, X.; Prausnitz, M.R. Ocular Delivery of Macromolecules. Journal of Controlled Release 2014, 190, 172–181. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Li, J.; Ruan, H.; Xia, Q.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, T.; Zhu, C.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y. Microneedle-Mediated Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery for Improved Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Journal of Controlled Release 2024, 366, 712–731. [CrossRef]
- Glover, K.; Mishra, D.; Gade, S.; Vora, L.K.; Wu, Y.; Paredes, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R. Microneedles for Advanced Ocular Drug Delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2023, 201, 115082. [CrossRef]
- Zheng Chao, Chen Dong, H.F. Current Perspective on Microneedles for Ocular Drug Delivery. Saudi J. Med. Pharm. Sci 2017, 4929, 772–776. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, D.; Lei, L.; Vakal, S.; Wang, J.; Li, X. A Rapid Corneal Healing Microneedle for Efficient Ocular Drug Delivery. Small 2022, 18. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.; Damiri, F.; Rojekar, S.; Zehravi, M.; Ramproshad, S.; Dhoke, D.; Musale, S.; Mulani, A.A.; Modak, P.; Paradhi, R.; et al. Recent Advancements in Microneedle Technology for Multifaceted Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, Vol. 14, Page 1097 2022, 14, 1097. [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Gu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Huo, T.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wen, Y. Novel Microneedle Platforms for the Treatment of Wounds by Drug Delivery: A Review. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2024, 233, 113636. [CrossRef]
- Rojekar, S.; Vora, L.K.; Tekko, I.A.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; McCarthy, H.O.; Vavia, P.R.; .Donnelly, R.F. Etravirine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Arrays for Long-Acting Delivery. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2021, 165, 41–51. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Yadav, K.S. Applications of Microneedles in Delivering Drugs for Various Ocular Diseases. Life Sciences 2019, 237, 116907. [CrossRef]
- Mdanda, S.; Ubanako, P.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E. Recent Advances in Microneedle Platforms for Transdermal Drug Delivery Technologies. Polymers 2021, 13, 2405. [CrossRef]
- Vitore, J.G.; Pagar, S.; Singh, N.; Karunakaran, B.; Salve, S.; Hatvate, N.; Rojekar, S.; Benival, D. A Comprehensive Review of Nanosuspension Loaded Microneedles: Fabrication Methods, Applications, and Recent Developments. J Pharm Investig 2023, 53, 475–504. [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, K.; Wang, Y.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal and Intraocular Drug Delivery. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2017, 36, 14–21. [CrossRef]
- Faraji Rad, Z.; Prewett, P.D.; Davies, G.J. An Overview of Microneedle Applications, Materials, and Fabrication Methods. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2021, 12, 1034–1046. [CrossRef]
- Song, H.B.; Lee, K.J.; Seo, I.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, W. Impact Insertion of Transfer-Molded Microneedle for Localized and Minimally Invasive Ocular Drug Delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2015, 209, 272–279. [CrossRef]
- Thakur Singh, R.R.; Tekko, I.; McAvoy, K.; McMillan, H.; Jones, D.; Donnelly, R.F. Minimally Invasive Microneedles for Ocular Drug Delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2017, 14, 525–537. [CrossRef]
- Chopra, H.; Priyanka; Choudhary, O.P.; Emran, T.B. Microneedles for Ophthalmic Drug Delivery: Recent Developments. International journal of surgery (London, England) 2023, 109, 551–552. [CrossRef]
- Mönkäre, J.; Pontier, M.; van Kampen, E.E.M.; Du, G.; Leone, M.; Romeijn, S.; Nejadnik, M.R.; O’Mahony, C.; Slütter, B.; Jiskoot, W.; et al. Development of PLGA Nanoparticle Loaded Dissolving Microneedles and Comparison with Hollow Microneedles in Intradermal Vaccine Delivery. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2018, 129, 111–121. [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and Fabrication of Customizable Microneedles Enabled by 3D Printing for Biomedical Applications. Bioactive Materials 2024, 32, 222–241. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Vora, L.K.; Wang, Y.; Adrianto, M.F.; Tekko, I.A.; Waite, D.; Donnelly, R.F.; Thakur, R.R.S. Long-Acting Nanoparticle-Loaded Bilayer Microneedles for Protein Delivery to the Posterior Segment of the Eye. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2021, 165, 306–318. [CrossRef]
- Migalska, K.; Morrow, D.I.J.; Garland, M.J.; Thakur, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Laser-Engineered Dissolving Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Macromolecular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutical Research 2011, 28, 1919–1930. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.R.S.; Tekko, I.A.; Al-Shammari, F.; Ali, A.A.; McCarthy, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Rapidly Dissolving Polymeric Microneedles for Minimally Invasive Intraocular Drug Delivery. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2016, 6, 800–815. [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.; Chen, R.K. Self-Adhesive Microneedles with Interlocking Features for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery. Macromolecular Bioscience 2020, 20. [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D. V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated Needles for Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules and Nanoparticles: Fabrication Methods and Transport Studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [CrossRef]
- Makhijani, S.; Elossaily, G.M.; Rojekar, S.; Ingle, R.G. MRNA-Based Vaccines – Global Approach, Challenges, and Could Be a Promising Wayout for Future Pandemics. Pharm Dev Technol 2024, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Ashraf, M.W.; Tayyaba, S. A Review on Solid Microneedles for Biomedical Applications. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation 2022, 17, 1464–1483. [CrossRef]
- Wei-ze, L.; Mei-rong, H.; Jian-ping, Z.; Yong-qiang, Z.; Bao-hua, H. Super-Short Solid Silicon Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2010, 389, 122–129. [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Kumar, S.; Monohar, M. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy Microneedles : A Smart Approach and Increasing Potential for Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.T.; Zhou, W.; Dou, M.; Tavakoli, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Recent Advances of Controlled Drug Delivery Using Microfluidic Platforms. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2018, 128, 3–28. [CrossRef]
- Ita, K. Ceramic Microneedles and Hollow Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Two Decades of Research. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2018, 44, 314–322. [CrossRef]
- Aich, K.; Singh, T.; Dang, S. Advances in Microneedle-Based Transdermal Delivery for Drugs and Peptides. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2022, 12, 1556–1568. [CrossRef]
- Bal, S.M.; Ding, Z.; van Riet, E.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J.A. Advances in Transcutaneous Vaccine Delivery: Do All Ways Lead to Rome? Journal of Controlled Release 2010, 148, 266–282. [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.J.; Gupta, J.; Patel, S.R.; Park, S.; Jarrahian, C.; Zehrung, D.; Prausnitz, M.R. Reliability and Accuracy of Intradermal Injection by Mantoux Technique, Hypodermic Needle Adapter, and Hollow Microneedle in Pigs. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2014, 4, 126–130. [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.T.; Zhou, W.; Dou, M.; Tavakoli, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Recent Advances of Controlled Drug Delivery Using Microfluidic Platforms. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2018, 128, 3–28. [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.J.; Gupta, J.; Patel, S.R.; Park, S.; Jarrahian, C.; Zehrung, D.; Prausnitz, M.R. Reliability and Accuracy of Intradermal Injection by Mantoux Technique, Hypodermic Needle Adapter, and Hollow Microneedle in Pigs. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2014, 4, 126–130. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Kim, M.; Yang, H.; Lee, K.; Jung, H. Droplet-Born Air Blowing: Novel Dissolving Microneedle Fabrication. Journal of Controlled Release 2013, 170, 430–436. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Jung, H. Dissolving Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Administration Prepared by Stepwise Controlled Drawing of Maltose. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3134–3140. [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; Mönkäre, J.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Kersten, G. Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Dermal Vaccination. Pharmaceutical Research 2017, 34, 2223–2240. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R. Rapidly Dissolving Bilayer Microneedles Enabling Minimally Invasive and Efficient Protein Delivery to the Posterior Segment of the Eye. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2023, 13, 2142–2158. [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Vavia, P.R.; Larrañeta, E.; Bell, S.E.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Novel Nanosuspension-based Dissolving Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Delivery of a Hydrophobic Drug. Journal of Interdisciplinary Nanomedicine 2018, 3, 89–101. [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2007, 117, 227–237. [CrossRef]
- Tarbox, T.N.; Watts, A.B.; Cui, Z.; Williams, R.O. An Update on Coating/Manufacturing Techniques of Microneedles. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2018, 8, 1828–1843. [CrossRef]
- Ingrole, R.S.J.; Gill, H.S. Microneedle Coating Methods: A Review with a Perspective. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2019, 370, 555–569. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, Y.; Milewski, M.; Dick, L.; Zhang, J.; Bothe, J.R.; Gehrt, M.; Manser, K.; Nissley, B.; Petrescu, I.; Johnson, P.; et al. Coated Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of a Potent Pharmaceutical Peptide. Biomedical Microdevices 2020, 22, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ingrole, R.S.J.; Gill, H.S. Microneedle Coating Methods: A Review with a Perspective. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2019, 370, 555–569. [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Microneedles: Materials, Fabrication, and Biomedical Applications. Biomedical Microdevices 2023, 25, 20. [CrossRef]
- Khandan, O.; Famili, A.; Kahook, M.Y.; Rao, M.P. Titanium-Based, Fenestrated, in-Plane Microneedles for Passive Ocular Drug Delivery. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; IEEE, August 2012; pp. 6572–6575.
- Mamun, A. Al; Zhao, F. In-Plane Si Microneedles: Fabrication, Characterization, Modeling and Applications. Micromachines 2022, 13, 657. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Saeed AL-Japairai, K.; Mahmood, S.; Hamed Almurisi, S.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Rebhi Hilles, A.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current Trends in Polymer Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2020, 587, 119673. [CrossRef]
- Jakka, D.; Matadh, A. V.; Shankar, V.K.; Shivakumar, H.N.; Narasimha Murthy, S. Polymer Coated Polymeric (PCP) Microneedles for Controlled Delivery of Drugs (Dermal and Intravitreal). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2022, 111, 2867–2878. [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; White, L.R.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles: Current Advancements and Future Trends. Macromolecular Bioscience 2021, 21, 2000307. [CrossRef]
- Migdadi, E.M.; Courtenay, A.J.; Tekko, I.A.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Kearney, M.C.; McAlister, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles Enhance Transdermal Delivery of Metformin Hydrochloride. Journal of Controlled Release 2018, 285, 142–151. [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Rojekar, S.; Bachra, Y.; Varma, R.S.; Andra, S.; Balu, S.; Pardeshi, C.V.; Patel, P.J.; Patel, H.M.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; et al. Polysaccharide-Based Nanogels for Biomedical Applications: A Comprehensive Review. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2023, 84, 104447. [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Larrañeta, E.; McAlister, E.; Courtenay, A.J.; Kearney, M.C.; Raj Singh, T.R.; McCarthy, H.O.; Kett, V.L.; et al. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles Prepared from “Super Swelling” Polymers Combined with Lyophilised Wafers for Transdermal Drug Delivery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kasasbeh, R.; Brady, A.J.; Courtenay, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; O’Kane, D.; Liggett, S.; Donnelly, R.F. Evaluation of the Clinical Impact of Repeat Application of Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Array Patches. Drug delivery and translational research 2020, 10, 690–705. [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Garland, M.J.; Migalska, K.; Majithiya, R.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kole, P.L.; Mahmood, T.M.T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Advanced Functional Materials 2012, 22, 4879–4890. [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Casadiego, D.A.; Miranda-Muñoz, K.A.; Roberts, J.L.; Crowell, A.D.; Gonzalez-Nino, D.; Choudhury, D.; Aparicio-Solis, F.O.; Servoss, S.L.; Rosales, A.M.; Prinz, G.; et al. Biodegradable Microneedle Patch for Delivery of Meloxicam for Managing Pain in Cattle. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272169. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Xiaoyun Hong; Zaozhan Wu; Lizhu Chen; Liu, Z.; Fei Wu; Liangming Wei, L. Dissolving and Biodegradable Microneedle Technologies for Transdermal Sustained Delivery of Drug and Vaccine. Drug Design, Development and Therapy 2013, 945. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Chen, B.Z.; Wang, Q.L.; Guo, X.D. A Solid Polymer Microneedle Patch Pretreatment Enhances the Permeation of Drug Molecules into the Skin. RSC Advances 2017, 7, 15408–15415. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, M.; Baek, S.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, S.-O. Spray-Formed Layered Polymer Microneedles for Controlled Biphasic Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 369. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sun, J.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. Microneedle System for Transdermal Drug and Vaccine Delivery: Devices, Safety, and Prospects. Dose-Response 2019, 17, 155932581987858. [CrossRef]
- Haj-Ahmad, R.; Khan, H.; Arshad, M.; Rasekh, M.; Hussain, A.; Walsh, S.; Li, X.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z. Microneedle Coating Techniques for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 486–502. [CrossRef]
- Tucak, A.; Sirbubalo, M.; Hindija, L.; Rahić, O.; Hadžiabdić, J.; Muhamedagić, K.; Čekić, A.; Vranić, E. Microneedles: Characteristics, Materials, Production Methods and Commercial Development. Micromachines 2020, 11, 961. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, D.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leung, W.K. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles with Applications in Oral Diseases Management. Materials 2023, 16, 4805. [CrossRef]
- Howells, O.; Blayney, G.J.; Gualeni, B.; Birchall, J.C.; Eng, P.F.; Ashraf, H.; Sharma, S.; Guy, O.J. Design, Fabrication, and Characterisation of a Silicon Microneedle Array for Transdermal Therapeutic Delivery Using a Single Step Wet Etch Process. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2022, 171, 19–28. [CrossRef]
- Sargioti, N.; Levingstone, T.J.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D.; McCarthy, H.O.; Dunne, N.J. Metallic Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Applications, Fabrication Techniques and the Effect of Geometrical Characteristics. Bioengineering 2022, 10, 24. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Saeed AL-Japairai, K.; Mahmood, S.; Hamed Almurisi, S.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Rebhi Hilles, A.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current Trends in Polymer Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2020, 587, 119673. [CrossRef]
- Sartawi, Z.; Blackshields, C.; Ariamanesh, A.; Farag, F.F.; Griffin, B.; Crean, A.; Devine, K.; Elkhashab, M.; Aldejohann, A.M.; Kurzai, O.; et al. Glass Microneedles: A Case Study for Regulatory Approval Using a Quality by Design Approach. Advanced Materials 2023, 35. [CrossRef]
- Sartawi, Z.; Blackshields, C.; Faisal, W. Dissolving Microneedles: Applications and Growing Therapeutic Potential. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 348, 186–205. [CrossRef]
- Filho, D.; Guerrero, M.; Pariguana, M.; Marican, A.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Hydrogel-Based Microneedle as a Drug Delivery System. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2444. [CrossRef]
- Ita, K. Ceramic Microneedles and Hollow Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Two Decades of Research. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2018, 44, 314–322. [CrossRef]
- Dabholkar, N.; Gorantla, S.; Waghule, T.; Rapalli, V.K.; Kothuru, A.; Goel, S.; Singhvi, G. Biodegradable Microneedles Fabricated with Carbohydrates and Proteins: Revolutionary Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 170, 602–621. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Thiele, J.; Abdelmohsen, L.; Xu, J.; Huck, W.T.S. Biocompatible Macro-Initiators Controlling Radical Retention in Microfluidic on-Chip Photo-Polymerization of Water-in-Oil Emulsions. Chemical Communications 2014, 50, 112–114. [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.T.M.; Nguyen, T.D. Lithography-Based Methods to Manufacture Biomaterials at Small Scales. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 2017, 2, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Rassaei, L.; Singh, P.S.; Lemay, S.G. Lithography-Based Nanoelectrochemistry. Analytical Chemistry 2011, 83, 3974–3980. [CrossRef]
- del Campo, A.; Arzt, E. Fabrication Approaches for Generating Complex Micro- and Nanopatterns on Polymeric Surfaces. Chemical Reviews 2008, 108, 911–945. [CrossRef]
- Po-Chun Wang; Wester, B.A.; Rajaraman, S.; Seung-Joon Paik; Seong-Hyok Kim; Allen, M.G. Hollow Polymer Microneedle Array Fabricated by Photolithography Process Combined with Micromolding Technique. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; IEEE, September 2009; pp. 7026–7029.
- Zhao, J.; Mayes, R.H.; Chen, G.; Xie, H.; Chan, P.S. Effects of Process Parameters on the Micro Molding Process. Polymer Engineering & Science 2003, 43, 1542–1554. [CrossRef]
- DEVELOPMENT OF BIOFABRICATION TECHNIQUES TO ENGINEER 3D IN VITRO AVATARS DEVELOPMENT OF BIOFABRICATION TECHNIQUES TO ENGINEER 3D IN VITRO AVATARS.
- Katoh, T.; Tokuno, R.; Zhang, Y.; Abe, M.; Akita, K.; Akamatsu, M. Micro Injection Molding for Mass Production Using LIGA Mold Inserts. Microsystem Technologies 2008, 14, 1507–1514. [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Lee, N.; Kang, S. Fabrication of a Microlens Array Using Micro-Compression Molding with an Electroformed Mold Insert. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 2003, 13, 98–103. [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H. Experimental Investigation into Effects of Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes in Micro-Extrusion Process. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2021, 67, 427–437. [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.S.; Goswami, A. Recent Developments in Hot Embossing – a Review. Materials and Manufacturing Processes 2021, 36, 501–543. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Yang, S.-Y.; Huang, L.-S.; Jeng, T.-M. A Novel Method for Rapid Fabrication of Microlens Arrays Using Micro-Transfer Molding with Soft Mold. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 2006, 16, 999–1005. [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. SOFT LITHOGRAPHY. Annual Review of Materials Science 1998, 28, 153–184. [CrossRef]
- Gentili, E.; Tabaglio, L.; Aggogeri, F. Review on Micromachining Techniques. CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, Courses and Lectures 2005, 486, 387–396. [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J. Nanoimprint Lithography: Methods and Material Requirements. Advanced Materials 2007, 19, 495–513. [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and Fabrication of Customizable Microneedles Enabled by 3D Printing for Biomedical Applications. Bioactive Materials 2024, 32, 222–241. [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, S.R.; Sarabi, M.R.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Sokullu, E.; Yetisen, A.K.; Tasoglu, S. 3D-Printed Microneedles in Biomedical Applications. iScience 2021, 24, 102012. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Rastogi, C.K.; Rani, S.; Singh, G.P.; Saxena, S.; Shukla, S. Two Decades of Two-Photon Lithography: Materials Science Perspective for Additive Manufacturing of 2D/3D Nano-Microstructures. iScience 2023, 26, 106374. [CrossRef]
- Lupone, F.; Padovano, E.; Casamento, F.; Badini, C. Process Phenomena and Material Properties in Selective Laser Sintering of Polymers: A Review. Materials 2021, 15, 183. [CrossRef]
- Faraji Rad, Z.; Prewett, P.D.; Davies, G.J. An Overview of Microneedle Applications, Materials, and Fabrication Methods. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2021, 12, 1034–1046. [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The Role of 3D Printing Technology in Microengineering of Microneedles. Small 2022, 18. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Gou, M. Fast Customization of Hollow Microneedle Patches for Insulin Delivery. International Journal of Bioprinting 2022, 8, 553. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Park, J.; Lee, S. 3D Printing Fabrication Process for Fine Control of Microneedle Shape. Micro and Nano Systems Letters 2023, 11, 1. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Bei, H.-P.; Yuen, H.-Y.; James Cheung, C.-W.; Wong, M.-S.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Going below and beyond the Surface: Microneedle Structure, Materials, Drugs, Fabrication, and Applications for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Bioactive Materials 2023, 27, 303–326. [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The Role of 3D Printing Technology in Microengineering of Microneedles. Small 2022, 18. [CrossRef]
- Gittard, S.D.; Ovsianikov, A.; Chichkov, B.N.; Doraiswamy, A.; Narayan, R.J. Two-Photon Polymerization of Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2010, 7, 513–533. [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and Fabrication of Customizable Microneedles Enabled by 3D Printing for Biomedical Applications. Bioactive Materials 2024, 32, 222–241. [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.; Jin, S.; Jung, J. Fabricating High-Resolution and High-Dimensional Microneedle Mold through the Resolution Improvement of Stereolithography 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 766. [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and Fabrication of Customizable Microneedles Enabled by 3D Printing for Biomedical Applications. Bioactive Materials 2024, 32, 222–241. [CrossRef]
- Thakur Singh, R.R.; Tekko, I.; McAvoy, K.; McMillan, H.; Jones, D.; Donnelly, R.F. Minimally Invasive Microneedles for Ocular Drug Delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2017, 14, 525–537. [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mehmood, S.; Raza, A.; Hayat, U.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Microneedles in Smart Drug Delivery. Advances in Wound Care 2021, 10, 204–219. [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Yang, C.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, S.; Cai, R.; Li, H.; et al. Ultrarapid-Acting Microneedles for Immediate Delivery of Biotherapeutics. Advanced Materials 2023, 35. [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.-C.; McKenna, P.E.; Quinn, H.L.; Courtenay, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Development of Liquid Drug Reservoirs for Microneedle Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drug Molecules. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 605. [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, P.S.; Jadhav, T.P.; Chopade, S.S.; Gavade, T.T.; Sorate, R.C.; Shinde, T.U.; Maske, P.P.; Disouza, J.I.; Manjappa, A.S. Microneedles: An Advanced Approach for Transdermal Delivery of Biologics. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2021, 11, 46–54. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; He, Y.T.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Feng, Y.H.; Liang, L.; Peng, J.; Yang, C.Y.; Uyama, H.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Guo, X.D. Strategies to Develop Polymeric Microneedles for Controlled Drug Release. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2023, 203, 115109. [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; Yu, J.; Quek, Y.J.; Bai, B.; Li, X.; Shou, Y.; Myint, B.; Xu, C.; Tay, A. Design Principles of Microneedles for Drug Delivery and Sampling Applications. Materials Today 2023, 63, 137–169. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.B.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X.D. Self-Implanted Tiny Needles as Alternative to Traditional Parenteral Administrations for Controlled Transdermal Drug Delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2019, 556, 338–348. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, Y. Recent Advances of Microneedles for Biomedical Applications: Drug Delivery and Beyond. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2019, 9, 469–483. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Carrier, A.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X. Polymeric Microneedles for Controlled Transdermal Drug Delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2019, 315, 97–113. [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled Drug Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Treatment and Their Performance. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2018, 3, 7. [CrossRef]
- Park, K. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Past Forward and Future Back. Journal of Controlled Release 2014, 190, 3–8. [CrossRef]
- Petlin, D.G.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Anissimov, Y.G. Plasma Treatment as an Efficient Tool for Controlled Drug Release from Polymeric Materials: A Review. Journal of Controlled Release 2017, 266, 57–74. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Xia, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Guo, X.D. A Basal-Bolus Insulin Regimen Integrated Microneedle Patch for Intraday Postprandial Glucose Control. Science Advances 2020, 6. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, M.; Fu, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, C.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Recent Advances in Microneedles-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Protein and Peptide Drugs. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2021, 11, 2326–2343. [CrossRef]
- Ganeson, K.; Alias, A.H.; Murugaiyah, V.; Amirul, A.-A.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Vigneswari, S. Microneedles for Efficient and Precise Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 744. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Quan, G.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, P.; Feng, D.; Wen, T.; Hu, X.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Dissolving Microneedles with Spatiotemporally Controlled Pulsatile Release Nanosystem for Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Melanoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8179–8196. [CrossRef]
- Dangol, M.; Yang, H.; Li, C.G.; Lahiji, S.F.; Kim, S.; Ma, Y.; Jung, H. Innovative Polymeric System (IPS) for Solvent-Free Lipophilic Drug Transdermal Delivery via Dissolving Microneedles. Journal of Controlled Release 2016, 223, 118–125. [CrossRef]
- Tekko, I.A.; Permana, A.D.; Vora, L.; Hatahet, T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Localised and Sustained Intradermal Delivery of Methotrexate Using Nanocrystal-Loaded Microneedle Arrays: Potential for Enhanced Treatment of Psoriasis. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 152, 105469. [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Quan, G.; Lin, S.; Peng, T.; Wang, Q.; Ran, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Pan, X.; et al. Novel Dissolving Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Levonorgestrel: In Vitro and in Vivo Characterization. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2017, 534, 378–386. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Quan, G.; Hou, A.; Yang, P.; Peng, T.; Gu, Y.; Qin, W.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Pan, X.; et al. Strategy for Hypertrophic Scar Therapy: Improved Delivery of Triamcinolone Acetonide Using Mechanically Robust Tip-Concentrated Dissolving Microneedle Array. Journal of Controlled Release 2019, 306, 69–82. [CrossRef]
- Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Ferreira, L.T.; Permana, A.D.; Kirkby, M.; Paredes, A.J.; Vora, L.K.; P. Bonfanti, A.; Charlie-Silva, I.; Raposo, C.; Figueiredo, M.C.; et al. Artemether and Lumefantrine Dissolving Microneedle Patches with Improved Pharmacokinetic Performance and Antimalarial Efficacy in Mice Infected with Plasmodium Yoelii. Journal of Controlled Release 2021, 333, 298–315. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Ma, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Qian, Y. Application of Composite Dissolving Microneedles with High Drug Loading Ratio for Rapid Local Anesthesia. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2018, 121, 330–337. [CrossRef]
- Zaric, M.; Lyubomska, O.; Touzelet, O.; Poux, C.; Al-Zahrani, S.; Fay, F.; Wallace, L.; Terhorst, D.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S.; et al. Skin Dendritic Cell Targeting via Microneedle Arrays Laden with Antigen-Encapsulated Poly- d , l -Lactide- Co -Glycolide Nanoparticles Induces Efficient Antitumor and Antiviral Immune Responses. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2042–2055. [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E.; González-Vázquez, P.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Vavia, P.R. Novel Bilayer Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Concentrated PLGA Nano-Microparticles for Targeted Intradermal Delivery: Proof of Concept. Journal of Controlled Release 2017, 265, 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.D.; Tekko, I.A.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Anjani, Q.K.; Ramadon, D.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Solid Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Dissolving Microneedles: A Promising Intradermal Lymph Targeting Drug Delivery System with Potential for Enhanced Treatment of Lymphatic Filariasis. Journal of Controlled Release 2019, 316, 34–52. [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; She, J.; Lin, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Jin, L.; Xie, X.; Su, Y. Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Lipid-Coated Cisplatin Nanoparticles for Efficient and Safe Cancer Therapy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2018, 10, 33060–33069. [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.D.; Paredes, A.J.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Anjani, Q.K.; Utomo, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Dissolving Microneedle-Mediated Dermal Delivery of Itraconazole Nanocrystals for Improved Treatment of Cutaneous Candidiasis. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2020, 154, 50–61. [CrossRef]
- Mc Crudden, M.T.C.; Larrañeta, E.; Clark, A.; Jarrahian, C.; Rein-Weston, A.; Creelman, B.; Moyo, Y.; Lachau-Durand, S.; Niemeijer, N.; Williams, P.; et al. Design, Formulation, and Evaluation of Novel Dissolving Microarray Patches Containing Rilpivirine for Intravaginal Delivery. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Giffen, P.S.; Bhuiya, R.; Brackenborough, K.; Hobbs, M.J.; Qian, L.; Burke, M.D. Controlled Delivery of Dutasteride Using Dissolvable Microarrays: Initial Formulation and In Vivo Evaluation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 109, 1303–1311. [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, S.; Tekko, I.A.; Vora, L.; Larrañeta, E.; Permana, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Nanosuspension-Based Dissolving Microneedle Arrays for Intradermal Delivery of Curcumin. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 308. [CrossRef]
- Permana; McCrudden; Donnelly Enhanced Intradermal Delivery of Nanosuspensions of Antifilariasis Drugs Using Dissolving Microneedles: A Proof of Concept Study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 346. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-N.; Park, J.-H. Local Dermal Delivery of Cyclosporin A, a Hydrophobic and High Molecular Weight Drug, Using Dissolving Microneedles. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2018, 127, 237–243. [CrossRef]
- Quinn, H.L.; Bonham, L.; Hughes, C.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Design of a Dissolving Microneedle Platform for Transdermal Delivery of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Cardiovascular Drugs. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 104, 3490–3500. [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Murano, H.; Hamasaki, N.; Fukushima, K.; Takada, K. Incidence of Low Bioavailability of Leuprolide Acetate after Percutaneous Administration to Rats by Dissolving Microneedles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2011, 407, 126–131. [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Ruan, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Pei, L.; Hu, H.; He, Z.; Wu, T.; Ruan, S.; Guo, T.; et al. Keratinocyte Membrane-Mediated Nanodelivery System with Dissolving Microneedles for Targeted Therapy of Skin Diseases. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121142. [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Pang, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Microneedles Mediated Bioinspired Lipid Nanocarriers for Targeted Treatment of Alopecia. Journal of Controlled Release 2021, 329, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Zaric, M.; Lyubomska, O.; Touzelet, O.; Poux, C.; Al-Zahrani, S.; Fay, F.; Wallace, L.; Terhorst, D.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S.; et al. Skin Dendritic Cell Targeting via Microneedle Arrays Laden with Antigen-Encapsulated Poly- d , l -Lactide- Co -Glycolide Nanoparticles Induces Efficient Antitumor and Antiviral Immune Responses. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2042–2055. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Peng, T.; Hu, W.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Pan, X. Fully Armed Photodynamic Therapy with Spear and Shear for Topical Deep Hypertrophic Scar Treatment. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 343, 408–419. [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loaded with Methotrexate for Improved Treatment of Psoriasis. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [CrossRef]
- Glover, K.; Mishra, D.; Gade, S.; Vora, L.K.; Wu, Y.; Paredes, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R. Microneedles for Advanced Ocular Drug Delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2023, 201, 115082. [CrossRef]
- Dugam, S.; Tade, R.; Dhole, R.; Nangare, S. Emerging Era of Microneedle Array for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Toxicological Perspectives. Futur J Pharm Sci 2021, 7, 19. [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, S.; Damiri, F.; Zehravi, M.; Joshi, R.; Kapare, H.; Prajapati, M.K.; Munot, N.; Berrada, M.; Giram, P.S.; Rojekar, S.; et al. Functional Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Molecule to Material Design for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2022, Vol. 14, Page 3126 2022, 14, 3126. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.R.S.; Tekko, I.A.; Al-Shammari, F.; Ali, A.A.; McCarthy, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Rapidly Dissolving Polymeric Microneedles for Minimally Invasive Intraocular Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2016, 6, 800–815. [CrossRef]
- Damiri, F.; Rahman, M.H.; Zehravi, M.; Awaji, A.A.; Nasrullah, M.Z.; Gad, H.A.; Bani-Fwaz, M.Z.; Varma, R.S.; Germoush, M.O.; Al-Malky, H.S.; et al. MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-Embedded Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Materials 2022, Vol. 15, Page 1666 2022, 15, 1666. [CrossRef]
- PODOLEANU, A.Gh. Optical Coherence Tomography. Journal of Microscopy 2012, 247, 209–219. [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.; Mamalis, A.; Lev-Tov, H.; Jagdeo, J. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) of Collagen in Normal Skin and Skin Fibrosis. Archives of Dermatological Research 2014, 306, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Current Trends and Fabrication. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 2021, 51, 503–517. [CrossRef]
- Gadziński, P.; Froelich, A.; Wojtyłko, M.; Białek, A.; Krysztofiak, J.; Osmałek, T. Microneedle-Based Ocular Drug Delivery Systems – Recent Advances and Challenges. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2022, 13, 1167–1184. [CrossRef]
- Dul, M.; Alali, M.; Ameri, M.; Burke, M.D.; Craig, C.M.; Creelman, B.P.; Dick, L.; Donnelly, R.F.; Eakins, M.N.; Frivold, C.; et al. Assessing the Risk of a Clinically Significant Infection from a Microneedle Array Patch (MAP) Product. Journal of Controlled Release 2023, 361, 236–245. [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A Smart Approach and Increasing Potential for Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [CrossRef]
- McCrudden, M.T.C.; Alkilani, A.Z.; Courtenay, A.J.; McCrudden, C.M.; McCloskey, B.; Walker, C.; Alshraiedeh, N.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Gilmore, B.F.; Woolfson, A.D.; et al. Considerations in the Sterile Manufacture of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2015, 5, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y. The Current Status of Clinical Research Involving Microneedles: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1113. [CrossRef]
- Li, A.D.R.; Plott, J.; Chen, L.; Montgomery, J.S.; Shih, A. Needle Deflection and Tissue Sampling Length in Needle Biopsy. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2020, 104, 103632. [CrossRef]
- Sellin, A. Estimating the Needle Area from Geometric Measurements: Application of Different Calculation Methods to Norway Spruce. Trees - Structure and Function 2000, 14, 215–222. [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, K.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Technology. Drug Delivery Devices and Therapeutic Systems 2020, 345–366. [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.Z.; McLaughlin, P.W.; Shih, A.J. Novel Needle Cutting Edge Geometry for End-Cut Biopsy. Medical Physics 2012, 39, 99–108. [CrossRef]
- Rassaei, L.; Singh, P.S.; Lemay, S.G. Lithography-Based Nanoelectrochemistry. Analytical Chemistry 2011, 83, 3974–3980. [CrossRef]
- Po-Chun Wang; Wester, B.A.; Rajaraman, S.; Seung-Joon Paik; Seong-Hyok Kim; Allen, M.G. Hollow Polymer Microneedle Array Fabricated by Photolithography Process Combined with Micromolding Technique. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; IEEE, September 2009; pp. 7026–7029.
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Current Trends and Fabrication. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 2021, 51, 503–517.
- Alimardani, V.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Yousefi, G.; Rahiminezhad, Z.; Abedi, M.; Tamaddon, A.; Ahadian, S. Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2021, 10, 181. [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Current Trends and Fabrication. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 2021, 51, 503–517. [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Tang, J.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Effect of Surface Interactions on Microsphere Loading in Dissolving Microneedle Patches. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces 2022, 14, 29577–29587. [CrossRef]
- Fakhraei Lahiji, S.; Jang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dangol, M.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.; Jung, H. Effects of Dissolving Microneedle Fabrication Parameters on the Activity of Encapsulated Lysozyme. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2018, 117, 290–296. [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Tang, J.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Effect of Surface Interactions on Microsphere Loading in Dissolving Microneedle Patches. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces 2022, 14, 29577–29587. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. A Porous Reservoir-Backed Boronate Gel Microneedle for Efficient Skin Penetration and Sustained Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Gels 2022, 8, 74. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Yu, H.L.; Liu, R.X.; Shen, C.B.; Zhang, W.F.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. Kinetic Stability Studies of HBV Vaccine in a Microneedle Patch. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2019, 567, 118489. [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2815. [CrossRef]
- Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Bei, H.-P.; Yuen, H.-Y.; James Cheung, C.-W.; Wong, M.-S.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Going below and beyond the Surface: Microneedle Structure, Materials, Drugs, Fabrication, and Applications for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Bioactive Materials 2023, 27, 303–326. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Gao, M.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X. Dissolvable Microneedles Based on Panax Notoginseng Polysaccharide for Transdermal Drug Delivery and Skin Dendritic Cell Activation. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 268, 118211. [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Jinnin, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Uetsuji, Y.; Nakamachi, E. Design and Development of a Biocompatible Painless Microneedle by the Ion Sputtering Deposition Method. Precision Engineering 2010, 34, 461–466. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Intrastromal Delivery of Bevacizumab Using Microneedles to Treat Corneal Neovascularization. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2014, 55, 7376. [CrossRef]
- Varela-Fernández, R.; Díaz-Tomé, V.; Luaces-Rodríguez, A.; Conde-Penedo, A.; García-Otero, X.; Luzardo-Álvarez, A.; Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Otero-Espinar, F. Drug Delivery to the Posterior Segment of the Eye: Biopharmaceutic and Pharmacokinetic Considerations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 269. [CrossRef]
- Peyman, G.A.; Hosseini, K.; Cormier, M. A Minimally Invasive Jet Injector for Intravitreal and Subconjunctival Injection. Ophthalmic Surgery, Lasers and Imaging Retina 2012, 43, 57–62. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Fujioka, J.K.; Gholamian, T.; Zaharia, M.; Tran, S.D. Suprachoroidal Injection: A Novel Approach for Targeted Drug Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1241. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Targeted Delivery of Antiglaucoma Drugs to the Supraciliary Space Using Microneedles. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2014, 55, 7387. [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Raghu, T.; Singh, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F.; Raghu, T.; Singh, R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-Based Drug Delivery Systems : Microfabrication , Drug Delivery , and Safety Microneedle-Based Drug Delivery Systems : Microfabrication , Drug Delivery , and Safety. informahealthcare 2010, 7544. [CrossRef]
- Tun, K.; Shurko, J.F.; Ryan, L.; Lee, G.C. Age-Based Health and Economic Burden of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in the United States, 2000 and 2012. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206893. [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.-H.; Harkins, C.P.; Schwardt, N.H.; Portillo, J.A.; Zimmerman, M.D.; Carter, C.L.; Hossen, M.A.; Peer, C.J.; Polley, E.C.; Dartois, V.; et al. Alterations of Human Skin Microbiome and Expansion of Antimicrobial Resistance after Systemic Antibiotics. Science Translational Medicine 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Tuan-Mahmood, T.-M.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Torrisi, B.M.; McAlister, E.; Garland, M.J.; Singh, T.R.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for Intradermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013, 50, 623–637. [CrossRef]
- González-Vázquez, P.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Jarrahian, C.; Rein-Weston, A.; Quintanar-Solares, M.; Zehrung, D.; McCarthy, H.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Delivery of Gentamicin Using Dissolving Microneedle Arrays for Potential Treatment of Neonatal Sepsis. Journal of Controlled Release 2017, 265, 30–40. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Danehy, R.; Cai, H.; Ao, Z.; Pu, M.; Nusawardhana, A.; Rowe-Magnus, D.; Guo, F. Microneedle Patch-Mediated Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2019, 11, 14640–14646. [CrossRef]
- Tsioris, K.; Raja, W.K.; Pritchard, E.M.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery. Advanced Functional Materials 2012, 22, 330–335. [CrossRef]
- Gaware, S.A.; Rokade, K.A.; Bala, P.; Kale, S.N. Microneedles of Chitosan-porous Carbon Nanocomposites: Stimuli (PH and Electric Field)-initiated Drug Delivery and Toxicological Studies. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2019, 107, 1582–1596. [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.D.; Mir, M.; Utomo, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Bacterially Sensitive Nanoparticle-Based Dissolving Microneedles of Doxycycline for Enhanced Treatment of Bacterial Biofilm Skin Infection: A Proof of Concept Study. International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X 2020, 2, 100047. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y. Bioinspired Adhesive and Antibacterial Microneedles for Versatile Transdermal Drug Delivery. Research 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ziesmer, J.; Tajpara, P.; Hempel, N.; Ehrström, M.; Melican, K.; Eidsmo, L.; Sotiriou, G.A. Vancomycin-Loaded Microneedle Arrays against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections. Advanced Materials Technologies 2021, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, P.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Gu, Z. ROS-Responsive Microneedle Patch for Acne Vulgaris Treatment. Advanced Therapeutics 2018, 1. [CrossRef]
- Ziesmer, J.; Venckute Larsson, J.; Sotiriou, G.A. Hybrid Microneedle Arrays for Antibiotic and Near-IR Photothermal Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 462, 142127. [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; Laabei, M.; Li, S.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. Antimicrobial Releasing Hydrogel Forming Microneedles. Biomaterials Advances 2023, 151, 213467. [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Saju, A.; Cheerla, K.D.; Gade, S.K.; Garg, P.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Corneal Delivery of Besifloxacin Using Rapidly Dissolving Polymeric Microneedles. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2018, 8, 473–483. [CrossRef]
- Albadr, A.A.; Tekko, I.A.; Vora, L.K.; Ali, A.A.; Laverty, G.; Donnelly, R.F.; Thakur, R.R.S. Rapidly Dissolving Microneedle Patch of Amphotericin B for Intracorneal Fungal Infections. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2022, 12, 931–943. [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.; Sherje, A.P. Nano Intervention in Topical Delivery of Corticosteroid for Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis—A Systematic Review. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 2021, 32, 88. [CrossRef]
- Dey, V. Misuse of Topical Corticosteroids: A Clinical Study of Adverse Effects. Indian Dermatology Online Journal 2014, 5, 436. [CrossRef]
- Dawud, H.; Abu Ammar, A.A. Rapidly Dissolving Microneedles for the Delivery of Steroid-Loaded Nanoparticles Intended for the Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 526. [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Kang, B.M.; Yang, H.; Ohn, J.; Kwon, O.; Jung, H. High-Dose Steroid Dissolving Microneedle for Relieving Atopic Dermatitis. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.U.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, H.K.; Joo, C.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Song, S.; Chu, H.; Lee, J.S.; et al. The Use of Biodegradable Microneedle Patches to Increase Penetration of Topical Steroid for Prurigo Nodularis. European Journal of Dermatology 2018, 28, 71–77. [CrossRef]
- Penn, J.S.; Madan, A.; Caldwell, R.B.; Bartoli, M.; Caldwell, R.W.; Hartnett, M.E. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Eye Disease. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2008, 27, 331–371. [CrossRef]
- Rieke, E.R.; Amaral, J.; Becerra, S.P.; Lutz, R.J. Sustained Subconjunctival Protein Delivery Using a Thermosetting Gel Delivery System. Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2010, 26, 55–64. [CrossRef]
- Coyne, J.; Davis, B.; Kauffman, D.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y. Polymer Microneedle Mediated Local Aptamer Delivery for Blocking the Function of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2017, 3, 3395–3403. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Flach, A.J.; Jampol, L.M. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Ophthalmology. Survey of Ophthalmology 2010, 55, 108–133. [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.; Huitema, D.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Prescriptions for Adaptive Comanagement: The Case of Flood Management in the German Rhine Basin. Ecology and Society 2015, 20. [CrossRef]
- Garhofer, G.; Datlinger, P.; Tittl, M.; Geyer, W.; Maar, N.; Schmetterer, L. Qualitative Assessment of Visual Impairment in Patients with Age-Related Macular Degeneration Using Standardized, Image-Based Questionnaires. British Journal of Visual Impairment 2019, 37, 174–182. [CrossRef]
- Gholap, A.D.; Kapare, H.S.; Pagar, S.; Kamandar, P.; Bhowmik, D.; Vishwakarma, N.; Raikwar, S.; Garkal, A.; Mehta, T.A.; Rojekar, S.; et al. Exploring Modified Chitosan-Based Gene Delivery Technologies for Therapeutic Advancements. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 260, 129581. [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, A.; Kocak, N.; Akan, P.; Calan, O.; Ozturk, T.; Kaya, M.; Karahan, E.; Kaynak, S. Comparison of Macular Pigment Optical Density in Patients with Dry and Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology 2017, 65, 477. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice 2015, 42, 377–391. [CrossRef]
- Serener, A.; Serte, S. Dry and Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration Classification Using OCT Images and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 Scientific Meeting on Electrical-Electronics & Biomedical Engineering and Computer Science (EBBT); IEEE, April 2019; pp. 1–4.
- Apte, R.S. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. New England Journal of Medicine 2021, 385, 539–547. [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Lawrenson, J.G. Antioxidant Vitamin and Mineral Supplements for Slowing the Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ramin, S.; Soheilian, M.; Habibi, G.; Ghazavi, R.; Gharebaghi, R.; Heidary, F. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Scientometric Analysis. Medical hypothesis, discovery & innovation ophthalmology journal 2015, 4, 39–49.
- Bradley, J.; Ju, M.; Robinson, G.S. Combination Therapy for the Treatment of Ocular Neovascularization. Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 141–148. [CrossRef]
- Cougnard-Grégoire, A.; Delyfer, M.-N.; Korobelnik, J.-F.; Rougier, M.-B.; Malet, F.; Le Goff, M.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Colin, J.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Delcourt, C. Long-Term Blood Pressure and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The ALIENOR Study. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2013, 54, 1905. [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 301 Acute and Chronic Diseases and Injuries in 188 Countries, 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [CrossRef]
- Maller, J.; George, S.; Purcell, S.; Fagerness, J.; Altshuler, D.; Daly, M.J.; Seddon, J.M. Common Variation in Three Genes, Including a Noncoding Variant in CFH, Strongly Influences Risk of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nature Genetics 2006, 38, 1055–1059. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J. Recognizing Age-Related Macular Degeneration in Primary Care. JAAPA 2017, 30, 18–22. [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.; Edwards, R.; Mitchell, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Buchan, I.; Kelly, S.P. Smoking and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Review of Association. Eye 2005, 19, 935–944. [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Clearfield, E.; Soliman, M.K.; Sadiq, M.A.; Baldwin, A.J.; Hanout, M.; Agarwal, A.; Sepah, Y.J.; Do, D. V; Nguyen, Q.D. Aflibercept for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, 2016. [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.K.; Geerlings, M.J.; den Hollander, A.I. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. In Genetics and Genomics of Eye Disease; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 155–180.
- Ghasemi Falavarjani, K.; Nguyen, Q.D. Adverse Events and Complications Associated with Intravitreal Injection of Anti-VEGF Agents: A Review of Literature. Eye 2013, 27, 787–794. [CrossRef]
- Ratnapriya, R.; Chew, E.Y. Age-related Macular Degeneration—Clinical Review and Genetics Update. Clinical Genetics 2013, 84, 160–166. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Patel, M.; Chan, C.-C. Molecular Pathology of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2009, 28, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, S.; Peynshaert, K.; Lajunen, T.; Devoldere, J.; del Amo, E.M.; Ruponen, M.; De Smedt, S.C.; Remaut, K.; Urtti, A. Ocular Barriers to Retinal Delivery of Intravitreal Liposomes: Impact of Vitreoretinal Interface. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 328, 952–961. [CrossRef]
- van Lookeren Campagne, M.; LeCouter, J.; Yaspan, B.L.; Ye, W. Mechanisms of Age-related Macular Degeneration and Therapeutic Opportunities. The Journal of Pathology 2014, 232, 151–164. [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.; Chen, R.K. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Sustained and Controlled Ocular Drug Delivery. Journal of Engineering and Science in Medical Diagnostics and Therapy 2020, 3. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Canton, V.; Fromow-Guerra, J.; Salinas Longoria, S.; Romero Vera, R.; Widmann, M.; Patel, S.; Yerxa, B. Suprachoroidal Microinjection of Bevacizumab Is Well Tolerated in Human Patients. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2013, 54, 3299.
- Klein, R. Prevalence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the US Population. Archives of Ophthalmology 2011, 129, 75. [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, T.; Patel, N. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 2009, 102, 56–61. [CrossRef]
- García-Quintanilla, L.; Luaces-Rodríguez, A.; Gil-Martínez, M.; Mondelo-García, C.; Maroñas, O.; Mangas-Sanjuan, V.; González-Barcia, M.; Zarra-Ferro, I.; Aguiar, P.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Drugs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 365. [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, U.; Wong, T.Y.; Fletcher, A.; Piault, E.; Evans, C.; Zlateva, G.; Buggage, R.; Pleil, A.; Mitchell, P. Clinical Risk Factors for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Ophthalmology 2010, 10, 31. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Zaveri, J.; Becker, N. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR). Disease-a-Month 2021, 67, 101140. [CrossRef]
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.; Gardner, T.W.; King, G.L.; Blankenship, G.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Ferris, F.L.; Klein, R. Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 226–229. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L. How Effective Are Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy? JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association 1993, 269, 1290. [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M.; Chen, M.; Medina, R.J.; McKay, G.J.; Jenkins, A.; Gardiner, T.A.; Lyons, T.J.; Hammes, H.-P.; Simó, R.; et al. The Progress in Understanding and Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2016, 51, 156–186. [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.M. Perspectives on Diabetic Retinopathy. American Journal of Ophthalmology 2003, 136, 122–135. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L. How Effective Are Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy? JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association 1993, 269, 1290. [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, S.; Peynshaert, K.; Lajunen, T.; Devoldere, J.; del Amo, E.M.; Ruponen, M.; De Smedt, S.C.; Remaut, K.; Urtti, A. Ocular Barriers to Retinal Delivery of Intravitreal Liposomes: Impact of Vitreoretinal Interface. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 328, 952–961. [CrossRef]
- van Lookeren Campagne, M.; LeCouter, J.; Yaspan, B.L.; Ye, W. Mechanisms of Age-related Macular Degeneration and Therapeutic Opportunities. The Journal of Pathology 2014, 232, 151–164. [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Sundstrom, J.M.; Antonetti, D.A. Ocular Anti-VEGF Therapy for Diabetic Retinopathy: The Role of VEGF in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 893–899. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L.; Davis, M.D.; Aiello, L.M. Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. New England Journal of Medicine 1999, 341, 667–678. [CrossRef]
- Osaadon, P.; Fagan, X.J.; Lifshitz, T.; Levy, J. A Review of Anti-VEGF Agents for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Eye 2014, 28, 510–520. [CrossRef]
- Duh, E.J.; Sun, J.K.; Stitt, A.W. Diabetic Retinopathy: Current Understanding, Mechanisms, and Treatment Strategies. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [CrossRef]
- Pieramici, D.J.; Rabena, M.D. Anti-VEGF Therapy: Comparison of Current and Future Agents. Eye 2008, 22, 1330–1336. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.; Khurana, R.N.; Shah, M.; Henry, C.R.; Wang, R.C.; Kissner, J.M.; Ciulla, T.A.; Noronha, G. Efficacy and Safety of Suprachoroidal CLS-TA for Macular Edema Secondary to Noninfectious Uveitis. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 948–955. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Yadav, K.S. Applications of Microneedles in Delivering Drugs for Various Ocular Diseases. Life Sciences 2019, 237, 116907. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gill, H.S.; Ghate, D.; McCarey, B.E.; Patel, S.R.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated Microneedles for Drug Delivery to the Eye. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2007, 48, 4038. [CrossRef]
- Song, H.B.; Lee, K.J.; Seo, I.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, W. Impact Insertion of Transfer-Molded Microneedle for Localized and Minimally Invasive Ocular Drug Delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2015, 209, 272–279. [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, K.; Wang, Y.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal and Intraocular Drug Delivery. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2017, 36, 14–21. [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Lin, A.S.P.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Suprachoroidal Drug Delivery to the Back of the Eye Using Hollow Microneedles. Pharmaceutical Research 2011, 28, 166–176. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Targeted Delivery of Antiglaucoma Drugs to the Supraciliary Space Using Microneedles. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2014, 55, 7387. [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.; Galigama, R.D.; Thorat, V.S.; Garg, P.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedle Ocular Patch: Fabrication, Characterization, and Ex-Vivo Evaluation Using Pilocarpine as Model Drug. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 2020, 46, 1114–1122. [CrossRef]
- Khandan, O.; Kahook, M.Y.; Rao, M.P. Fenestrated Microneedles for Ocular Drug Delivery. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2016, 223, 15–23. [CrossRef]
- Kadonosono, K.; Yamane, S.; Arakawa, A.; Inoue, M.; Yamakawa, T.; Uchio, E.; Yanagi, Y.; Amano, S. Endovascular Cannulation With a Microneedle for Central Retinal Vein Occlusion. JAMA Ophthalmology 2013, 131, 783. [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Lawrenson, J.G. Antioxidant Vitamin and Mineral Supplements for Slowing the Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ramin, S.; Soheilian, M.; Habibi, G.; Ghazavi, R.; Gharebaghi, R.; Heidary, F. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Scientometric Analysis. Medical hypothesis, discovery & innovation ophthalmology journal 2015, 4, 39–49.
- Ronday, M.J.H.; Stilma, J.S.; Barbe, R.F.; McElroy, W.J.; Luyendijk, L.; Kolk, A.H.J.; Bakker, M.; Kijlstra, A.; Rothova, A. Aetiology of Uveitis in Sierra Leone, West Africa. British Journal of Ophthalmology 1996, 80, 956–961. [CrossRef]
- de Smet, M.D.; Taylor, S.R.J.; Bodaghi, B.; Miserocchi, E.; Murray, P.I.; Pleyer, U.; Zierhut, M.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; LeHoang, P.; Lightman, S. Understanding Uveitis: The Impact of Research on Visual Outcomes. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2011, 30, 452–470. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Retinitis Pigmentosa. Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology 2016, 5, 265–271. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J. Recognizing Age-Related Macular Degeneration in Primary Care. JAAPA 2017, 30, 18–22. [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.; Edwards, R.; Mitchell, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Buchan, I.; Kelly, S.P. Smoking and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Review of Association. Eye 2005, 19, 935–944. [CrossRef]
- Dalkara, D.; Goureau, O.; Marazova, K.; Sahel, J.-A. Let There Be Light: Gene and Cell Therapy for Blindness. Human Gene Therapy 2016, 27, 134–147. [CrossRef]
- Buch, P.; MacLaren, R.; Ali, R. Neuroprotective Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Current Gene Therapy 2007, 7, 434–445. [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Arabi, A. Conjunctivitis: A Systematic Review. Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research 2020. [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. Ocular Drug Delivery Systems: An Overview. World Journal of Pharmacology 2013, 2, 47. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Bei, H.-P.; Yuen, H.-Y.; James Cheung, C.-W.; Wong, M.-S.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Going below and beyond the Surface: Microneedle Structure, Materials, Drugs, Fabrication, and Applications for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Bioactive Materials 2023, 27, 303–326. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, Z.; Sharif, W. Corneal Neovascularization: Updates on Pathophysiology, Investigations & Management. romanian journal of ophthalmology 2019, 63, 15–22. [CrossRef]
- Irimia, T.; Ghica, M.; Popa, L.; Anuţa, V.; Arsene, A.-L.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E. Strategies for Improving Ocular Drug Bioavailability and Corneal Wound Healing with Chitosan-Based Delivery Systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 1221. [CrossRef]
- Clearside Biomedical, Inc. Suprachoroidal Injection of CLS-TA in Subjects With Macular Edema Associated With Non-Infectious Uveitis (PEACHTREE).
- Yeh, S.; Khurana, R.N.; Shah, M.; Henry, C.R.; Wang, R.C.; Kissner, J.M.; Ciulla, T.A.; Noronha, G. Efficacy and Safety of Suprachoroidal CLS-TA for Macular Edema Secondary to Noninfectious Uveitis. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 948–955. [CrossRef]
- Shaun Ian Retief Lampen, Rahul N. Khurana, David M Brown, C.C.W. Suprachoroidal Space Alterations after Delivery of Triamcinolone Acetonide: Post-Hoc Analysis of the Phase 1/2 HULK Study of Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1096.
- Zakaria, Y.G.; Salman, A.G.; Said, A.; Abdelatif, M.K. Suprachoroidal versus Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema. Clinical Ophthalmology 2022, Volume 16, 733–746. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.A.; Do, D.; Noronha, G.; Kissner, J.M.; Srivastava, S.K.; Nguyen, Q.D. Suprachoroidal Corticosteroid Administration: A Novel Route for Local Treatment of Noninfectious Uveitis. Translational Vision Science & Technology 2016, 5, 14. [CrossRef]
- Willekens, K.; Gijbels, A.; Smits, J.; Schoevaerdts, L.; Blanckaert, J.; Feyen, J.H.M.; Reynaerts, D.; Stalmans, P. Phase I Trial on Robot Assisted Retinal Vein Cannulation with Ocriplasmin Infusion for Central Retinal Vein Occlusion. Acta Ophthalmologica 2021, 99, 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Kim, L.; Albini, T.; Yeh, S. Triamcinolone Acetonide Injectable Suspension for Suprachoroidal Use in the Treatment of Macular Edema Associated with Uveitis. Expert Review of Ophthalmology 2022, 17, 165–173. [CrossRef]
- Boote, C.; Sigal, I.A.; Grytz, R.; Hua, Y.; Nguyen, T.D.; Girard, M.J.A. Scleral Structure and Biomechanics. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2020, 74, 100773. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Moore, J.S.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Intrascleral Drug Delivery to the Eye Using Hollow Microneedles. Pharmaceutical Research 2009, 26, 395–403. [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Encapsulation, Protection, and Delivery of Bioactive Proteins and Peptides Using Nanoparticle and Microparticle Systems: A Review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2018, 253, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Dugam, S.; Tade, R.; Dhole, R.; Nangare, S. Emerging Era of Microneedle Array for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Toxicological Perspectives. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021, 7, 19. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gill, H.S.; Ghate, D.; McCarey, B.E.; Patel, S.R.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated Microneedles for Drug Delivery to the Eye. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2007, 48, 4038. [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, U.; Wong, T.Y.; Fletcher, A.; Piault, E.; Evans, C.; Zlateva, G.; Buggage, R.; Pleil, A.; Mitchell, P. Clinical Risk Factors for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Ophthalmology 2010, 10, 31. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Zaveri, J.; Becker, N. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR). Disease-a-Month 2021, 67, 101140. [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Lam, H. Microneedle Delivery of Ophthalmic Macromolecules. 2014, 1–19.
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A Smart Approach and Increasing Potential for Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Voyer, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, X.; Chen, X. Laser Microporation Facilitates Topical Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review about Preclinical Development and Clinical Application. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2023, 20, 31–54. [CrossRef]
- Salahshoori, I.; Golriz, M.; Nobre, M.A.L.; Mahdavi, S.; Eshaghi Malekshah, R.; Javdani-Mallak, A.; Namayandeh Jorabchi, M.; Ali Khonakdar, H.; Wang, Q.; Mohammadi, A.H.; et al. Simulation-Based Approaches for Drug Delivery Systems: Navigating Advancements, Opportunities, and Challenges. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2024, 395, 123888. [CrossRef]
- Truckenmüller, R.; Giselbrecht, S.; Rivron, N.; Gottwald, E.; Saile, V.; van den Berg, A.; Wessling, M.; van Blitterswijk, C. Thermoforming of Film-Based Biomedical Microdevices. Advanced Materials 2011, 23, 1311–1329. [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Woolfson, A.D. Patient Safety and beyond: What Should We Expect from Microneedle Arrays in the Transdermal Delivery Arena? Therapeutic Delivery 2014, 5, 653–662. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C. Factors Affecting Therapeutic Compliance: A Review from the Patient’s Perspective. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management 2008, Volume 4, 269–286. [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.; Chen, R.K. Self-Adhesive Microneedles with Interlocking Features for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery. Macromolecular Bioscience 2020, 20. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, Y. Recent Advances of Microneedles for Biomedical Applications: Drug Delivery and Beyond. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2019, 9, 469–483. [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, S.R.; Sarabi, M.R.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Sokullu, E.; Yetisen, A.K. IScience in Biomedical Applications. iScience 2021, 24, 102012. [CrossRef]
- Gholap, A.D.; Rojekar, S.; Kapare, H.S.; Vishwakarma, N.; Raikwar, S.; Garkal, A.; Mehta, T.A.; Jadhav, H.; Prajapati, M.K.; Annapure, U. Chitosan Scaffolds: Expanding Horizons in Biomedical Applications. Carbohydr Polym 2024, 323, 121394. [CrossRef]
- Bohr, A.; Memarzadeh, K. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Applications. In Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 25–60.
- Shajari, S.; Kuruvinashetti, K.; Komeili, A.; Sundararaj, U. The Emergence of AI-Based Wearable Sensors for Digital Health Technology: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 9498. [CrossRef]
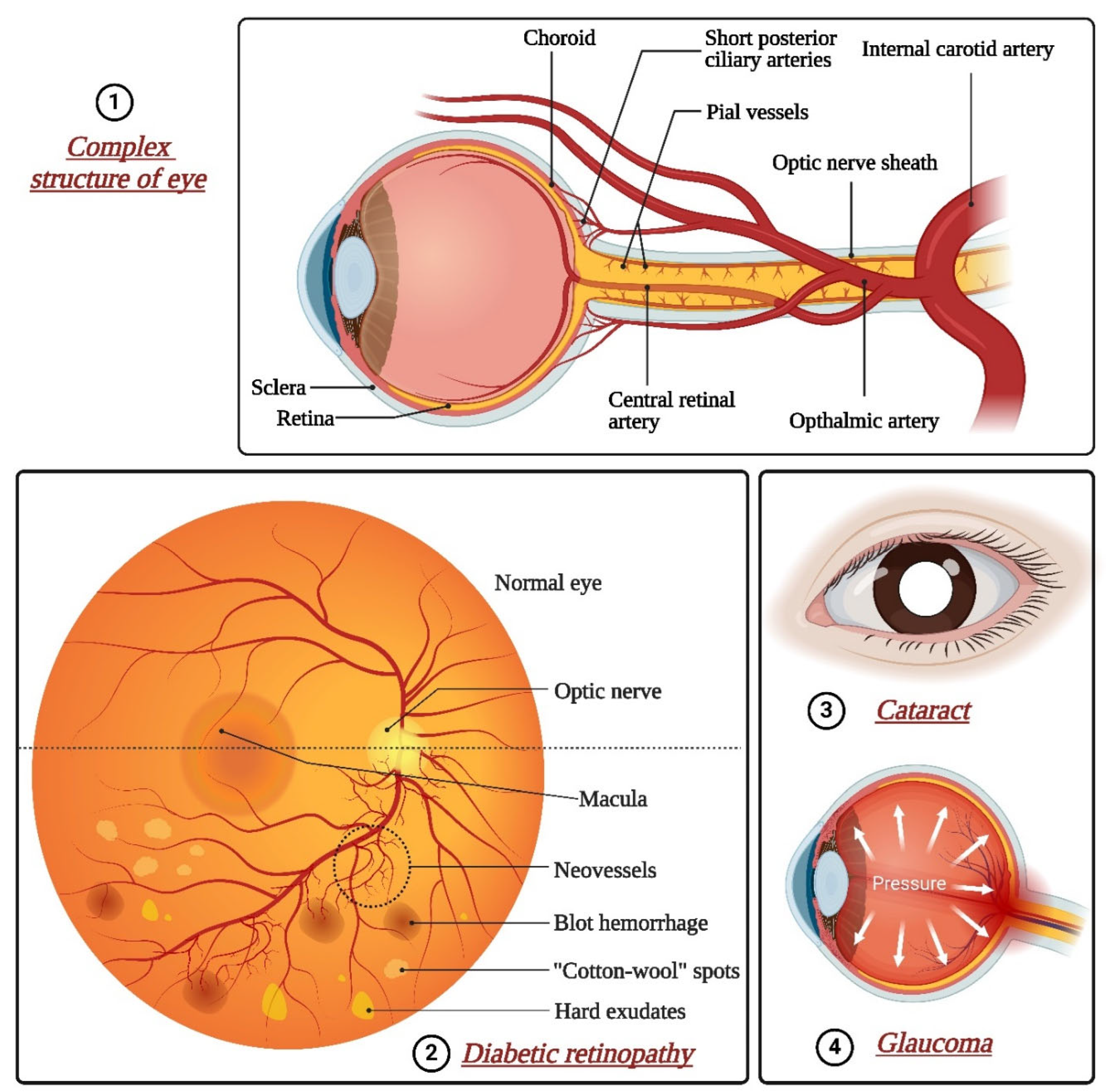
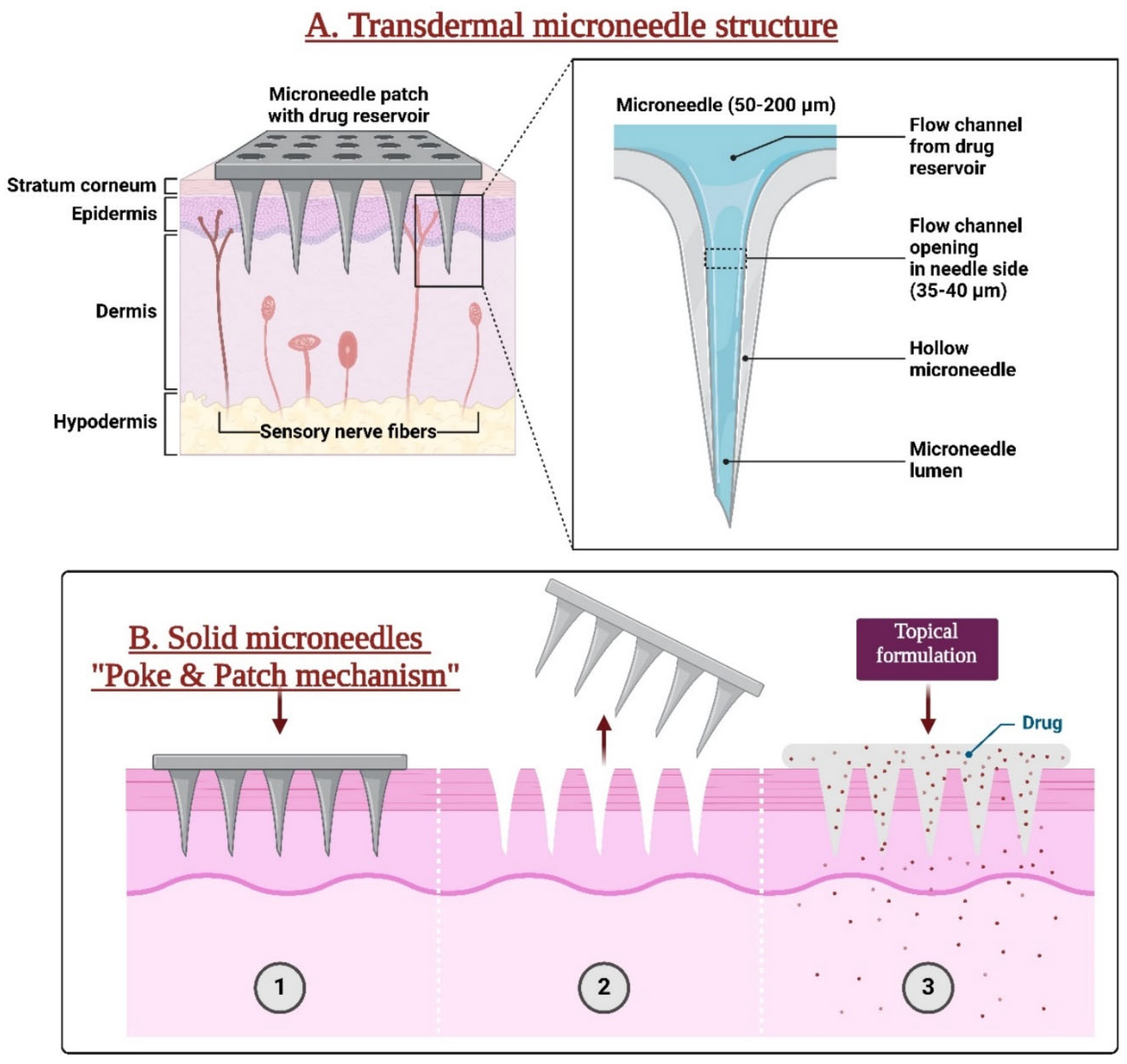
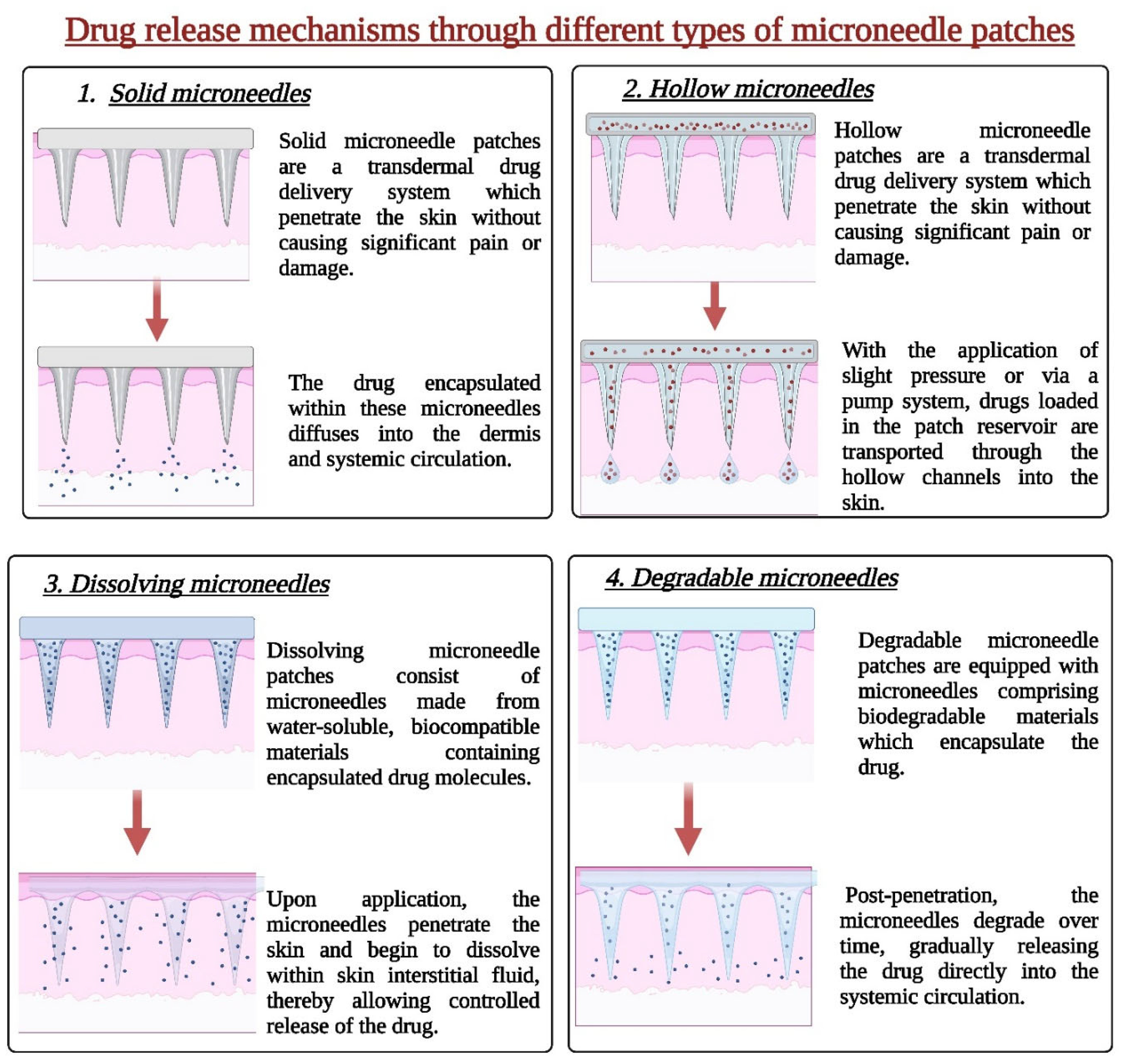
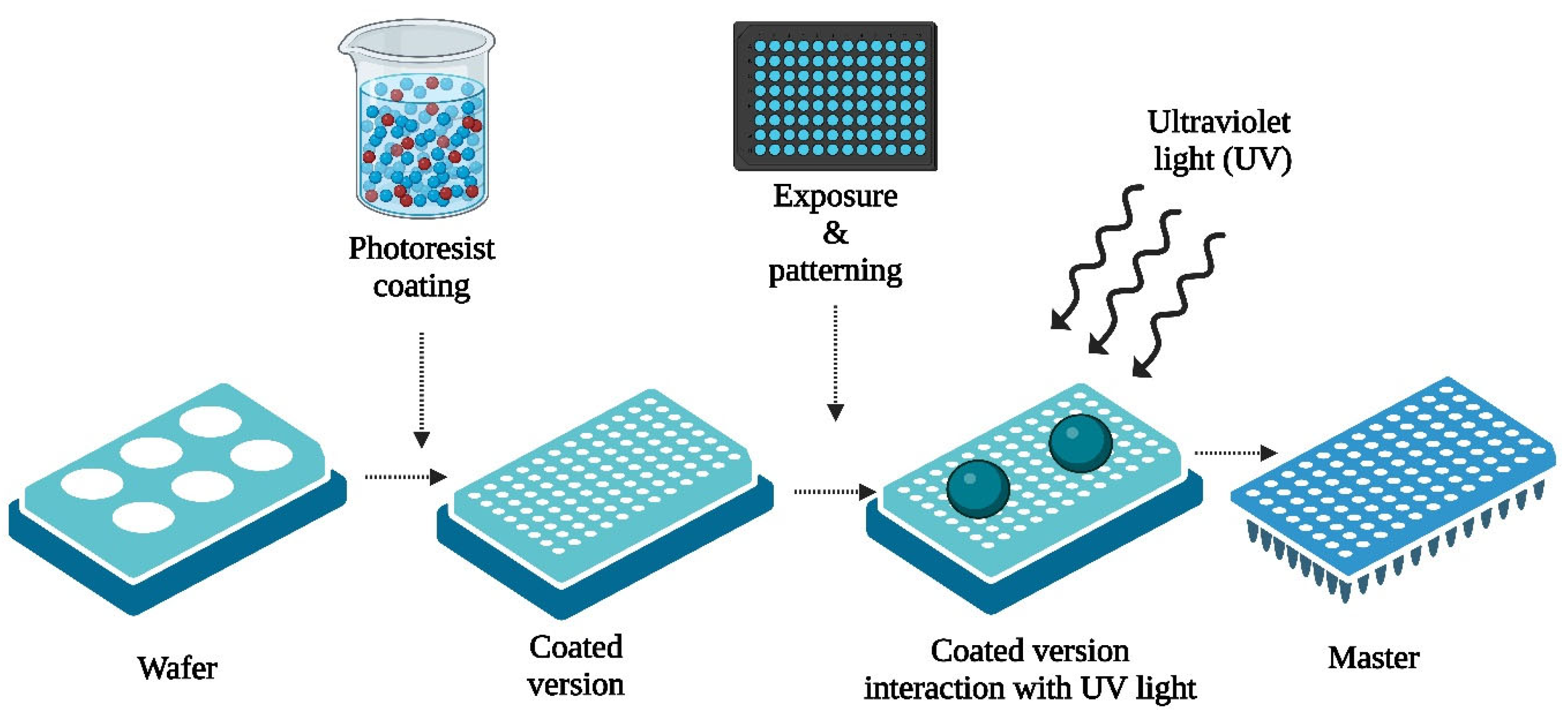
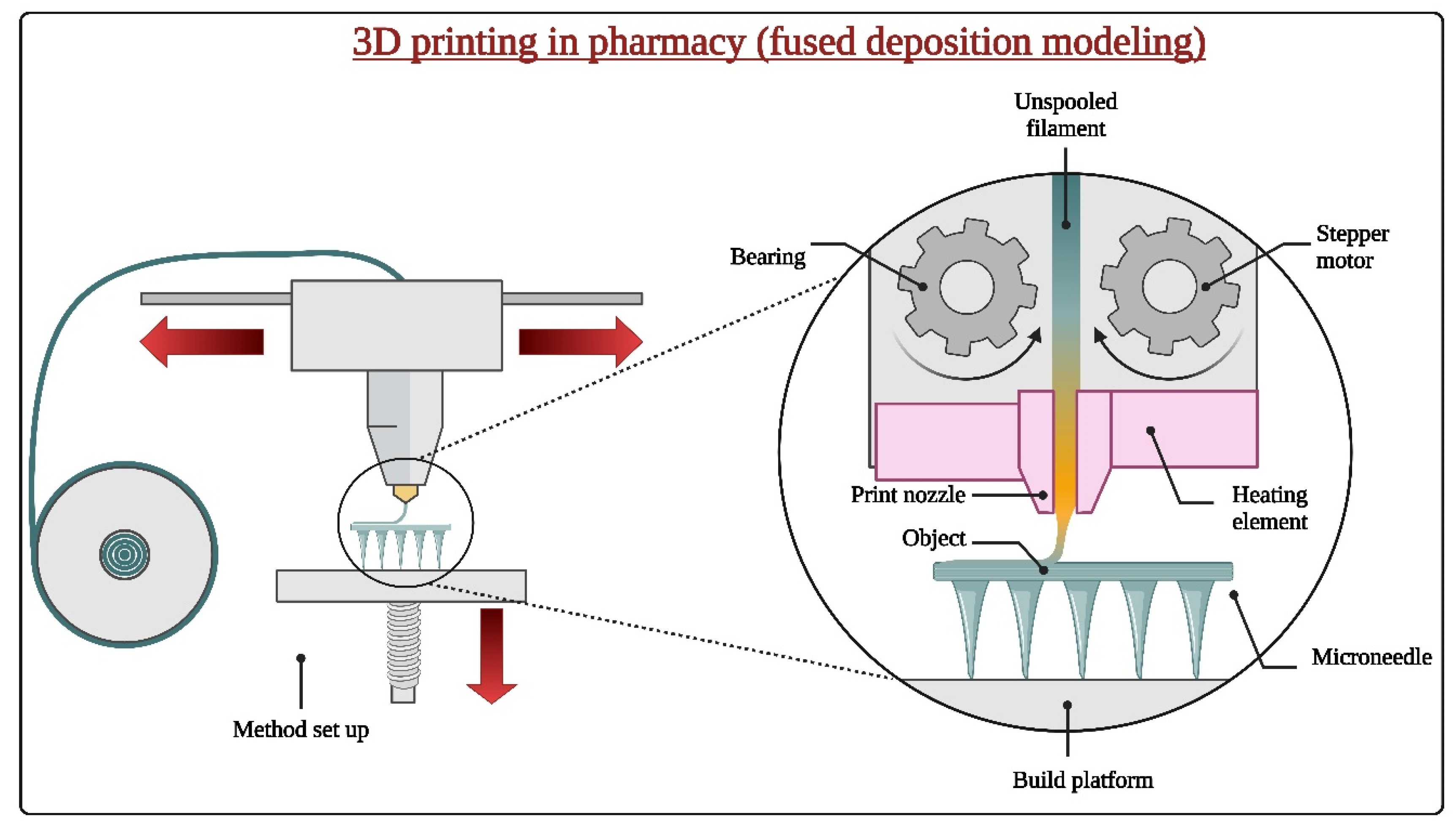

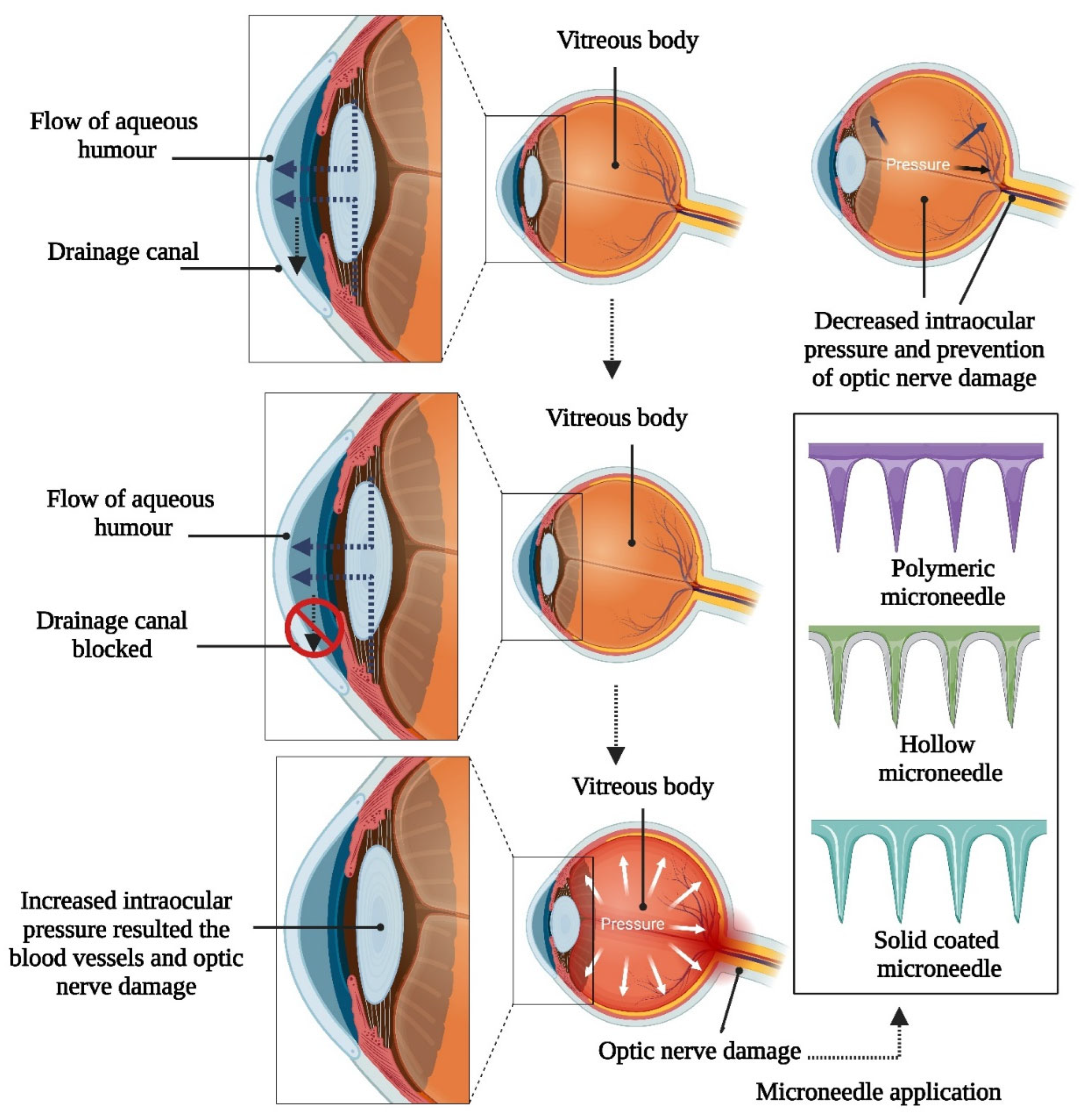
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Indications | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-Injection Molding | High precision and repeatability | High initial tooling costs | Mass production of small, intricate parts | Electronics, medical devices, automotive components | [94] |
| Micro-Compression Molding | Suitable for thermosetting polymers | Limited to certain types of materials | Molding small components with precise dimensions | Packaging, aerospace components, microfluidic devices | [95] |
| Micro-Extrusion Molding | Continuous production of micro-sized profiles | Limited to materials with good melt flow properties | Production of microtubing, microfilaments | Medical tubing, microcables, microfluidic channels | [96] |
| Hot Embossing | High replication fidelity and resolution | Requires high-precision molds and equipment | Fabrication of microstructures on polymer substrates | Microfluidic devices, optical components, biosensors | [97] |
| Micro-transfer molding | Allows for assembly of pre-formed micro-components | Complex assembly process | Integrating micro-scale components onto substrates | MEMS fabrication, microelectronics assembly | [98] |
| Soft lithography | Versatile for patterning soft materials | Limited to certain types of soft materials | Patterning of elastomers and hydrogels at the microscale | Bioengineering, microfluidics, flexible electronics | [99] |
| Laser micromachining | High precision and flexibility in feature creation | Limited to certain materials and geometries | Prototyping, microfabrication of complex structures | Micro-optics, MEMS devices, microfluidics | [100] |
| Nanoimprint lithography | High-resolution patterning at nanoscale | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Nanotechnology, semiconductor manufacturing | Nanophotonics, nanoelectronics, optical devices | [101] |
| Fabrication method | Conjunct technology | Material(s) | Design | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application(s) | Reference. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP | - | IP-S photoresist | Hollow microneedles | Minimal Post-Processing | Material Limitations | Drug delivery | [108] |
| FDM | Chemical etching | PLA | Cylindrical microneedles | Support Material Dissolvability, Low Cost |
Warping and Shrinkage, Anisotropic Mechanical Properties |
Drug delivery | [109] |
| TPP | Iron sputtering deposition | Photoresist | Magnetic microneedles in cylindrical, pyramidal, and conical shapes | Material Versatility | Equipment Complexity and Cost | Drug delivery, tissue engineering, and single-cell analysis | [110] |
| SLA | Micromolding | Resin for master microneedles; carboxymethyl cellulose for microneedles | Conical microneedles | High Resolution | Material Limitations | Drug delivery | [111] |
| TPP | Micromolding | Polyethylene glycol600 diacrylate | Cylindrical microneedles with conical tips | High Resolution | Slow Fabrication Speed | Drug delivery for antibacterial agent | [112] |
| SLA | Isotropic shrinkage technique | RGD 720 resin for master microneedles; PVP for microneedles | Slanted-needle arrays | Smooth Surface Finish |
Post-Curing Required | Drug delivery | [109] |
| TPP | Micromolding and pulsed laser deposition | SR 259 polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate and Irgacure® 369 for master microneedles; Ormocer for microneedles | Cylindrical microneedles with conical tips | 3D Microfabrication | Limited Build Volume | Drug delivery for antibacterial agent | [113] |
| TPP | Micromolding | Polyethylene glycol (200) and Irgacure® 369 for master microneedles; eShell 200 for microneedles | Conical microneedles | Non-contact Process, | Process Sensitivity | Insulin delivery | [28] |
| SLA | Inkjet printing | Class I biocompatible resin | Conical and pyramidal microneedles | Wide Range of Materials | Limited Build Volume | Insulin delivery | [114] |
| SLA | Inkjet printing | Class I biocompatible resin | Pyramidal and flat spear-shaped microneedles | Complex Geometries Possible | Support Removal Can Be Difficult | Insulin delivery | [115] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





