Submitted:
19 June 2024
Posted:
19 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Research
2.1. Research on Open Data Utilization
2.2. Research on Machine Learning Application
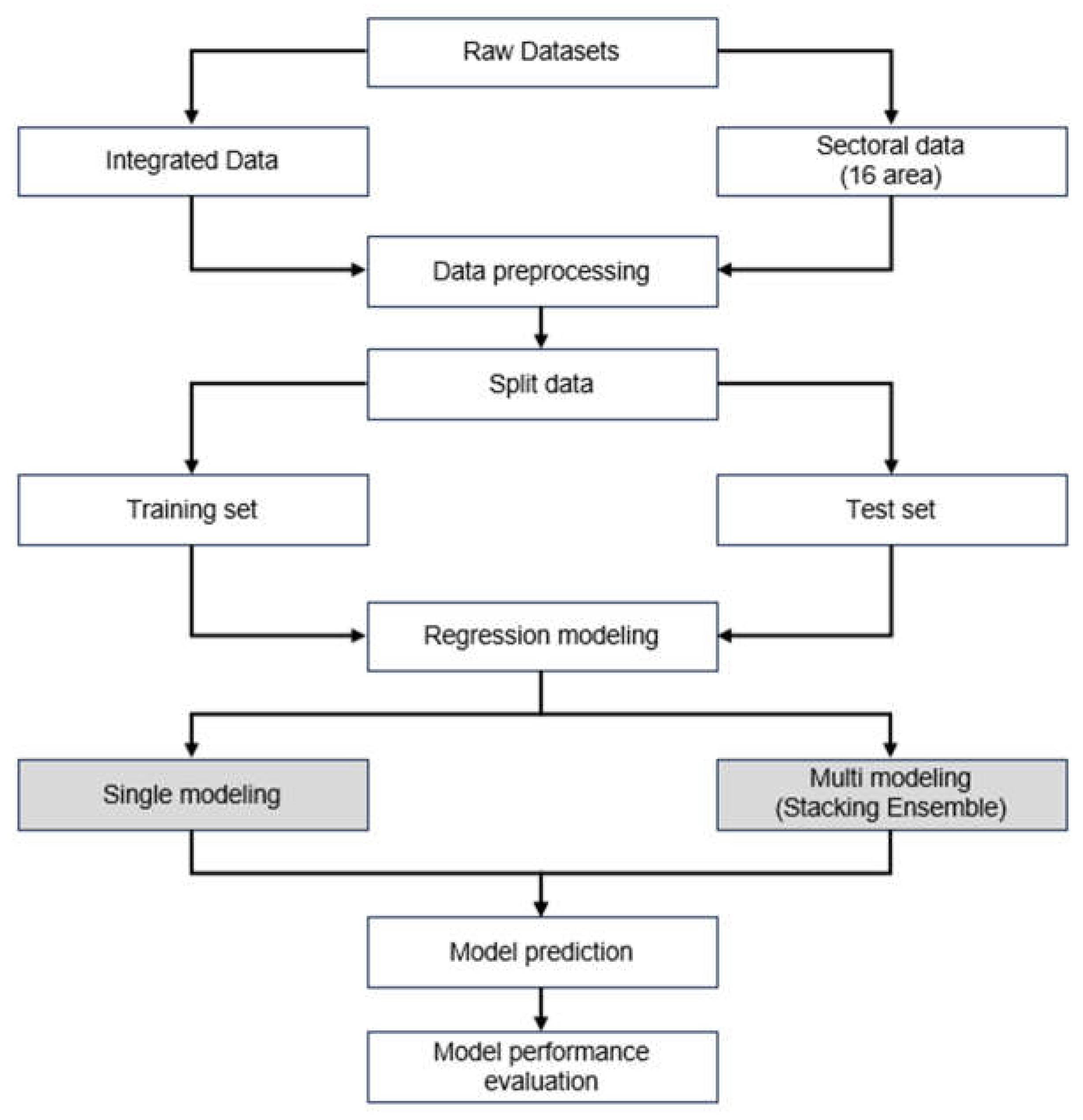
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Input Variables
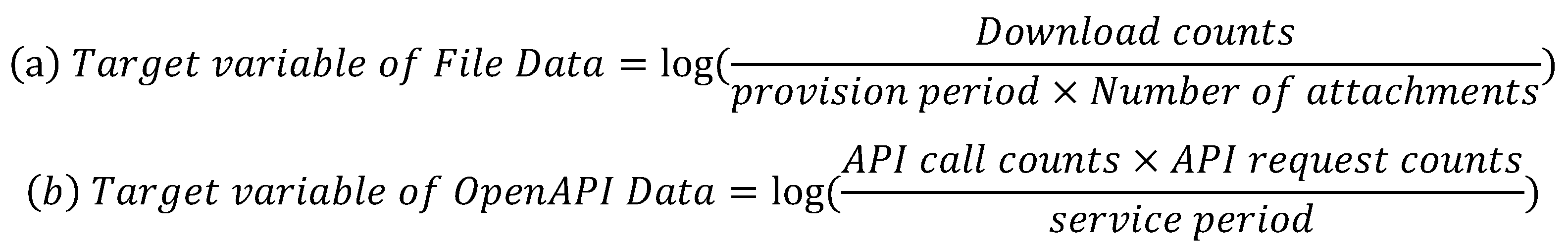
3.1.2. Target Variables
3.2. Proposed Methods
3.2.1. Single Model Methods
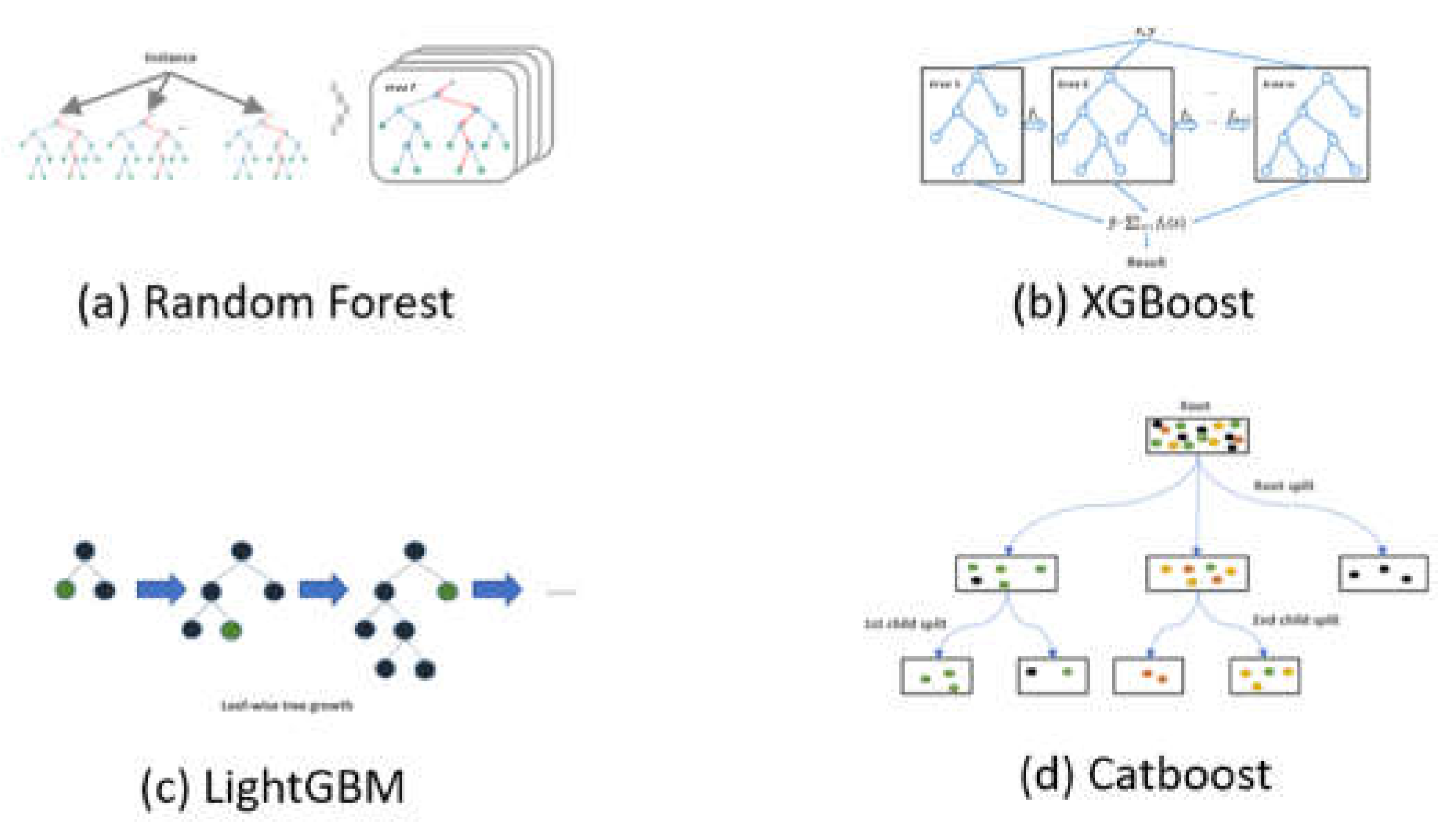
- Random Forest: Random forest algorithms are primarily composed of decision trees, and the results of these trees are summed to produce a final result that maximizes algorithm performance [71]. The advantage of decision tree analysis is the easy and intuitive understanding it provides as the results are presented in a single tree structure; the disadvantage is its lower predictiveness owing to the consideration of only one predictor when dividing the tree branches. Small data changes can also transform tree composition [71,72]. Therefore, while decision tree analysis has a relatively low bias, it has a high variance error, rendering model generalization more difficult. A machine learning algorithm used to overcome this weakness is random forest, which analyzes and aggregates multiple decision trees to form a forest of randomly sampled decision trees, which then is used to create a final prediction model. Random forest algorithms iteratively create independent decision trees to maximize sample and variable selection randomness, hence reducing prediction error by lowering variance and sustaining a low bias in the decision tree [71,72]. When using data with multiple explanatory variables, random forest algorithms also provide stability by considering interactions and nonlinearities between the explanatory variables. A visual representation of a random forest model is presented in Figure 2(a).
- eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost): XGBoost is an algorithm proposed by Chen et al. [73] for use with large-scale datasets, and is meant to compensate for overfitting issues while improving stability and training speed. XGBoost is known for its performance and effectiveness owing to the implementation of the gradient boost learning technique, which is a well-known technique in machine learning. Specifically, it uses a greedy algorithm to construct the most optimal model and improve weak classifiers, and this occurs while controlling complexity using distributed processing to compute optimal weights; this all serves to minimize learning loss and overfitting. This algorithm can be trained on categorical and continuous data, and each leaf contributes to the final score of the model; its analysis procedure is as follows: 1) measure the accuracy of the generated tree classifiers; 2) randomly generate strong-to-weak classifiers in each order; 3) sequentially improve the classifiers to generate a strong tree classifier. XGBoost proceeds to the max_depth parameterized during training, and then prunes in reverse if the improvement in the loss function does not reach a certain level [73]. During this process, the model can be pruned to remove unnecessary parts of the tree classifier and prevent overfitting. A visual representation of the XGBoost algorithm is presented in Figure 2(b).
- Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM): developed by Microsoft, this model uses the leaf-wise partitioning method to create highly-accurate models [74]. It is based on the gradient boosting decision tree ensemble learning technique, which has the advantage of dividing the branches at each node based on the best-fit nodes. It uses this learning technique with various algorithms to reduce the number of dimensions of individual data. This technique uses level wise for horizontal growth and the traverse of the nodes of the decision tree preferentially from the root node. For vertical growth, it splits at the node with the largest maximum delta loss, assuming that the loss can be further reduced by growing the same leaf. Furthermore, the two methods used in LightGBM to reduce the number of samples and features are gradient-based one-side sampling and exclusive feature bundling. Gradient-based one-side sampling is an under-sampling technique guided by the training set’s skewness, considering that samples with a larger skewness in absolute value contribute more to learning; accordingly, those with a smaller gradient are randomly removed. A visual representation of the LightGBM algorithm is shown in Figure 2(c).
- Categorical Boosting (CatBoost): This is is a library based on gradient boosting [75]. CatBoost performs well with categorical data [76], and processes them using the statistics of the target values while converting each categorical variable to a number. Thus, it is a great performer for most machine learning tasks that require categorical data processing [77]. In a past study, CatBoost performed better than other gradient boosting libraries because of its ability to handle categorical variables and its optimized algorithm [76]. As aforementioned, it converts categorical variables into numbers using various methods, implying the non-need for the preprocessing of categorical data and the possibility of directly processing it using this algorithm [75]. CatBoost also uses multiple strategies to avoid overfitting, which is a common problem in gradient boosting [77]. This algorithm is hence primarily used as a tool for solving classification and regression problems, performing particularly well on categorical data-related problems [78]. A visual representation of the CatBoost algorithm is presented in Figure 2(d).
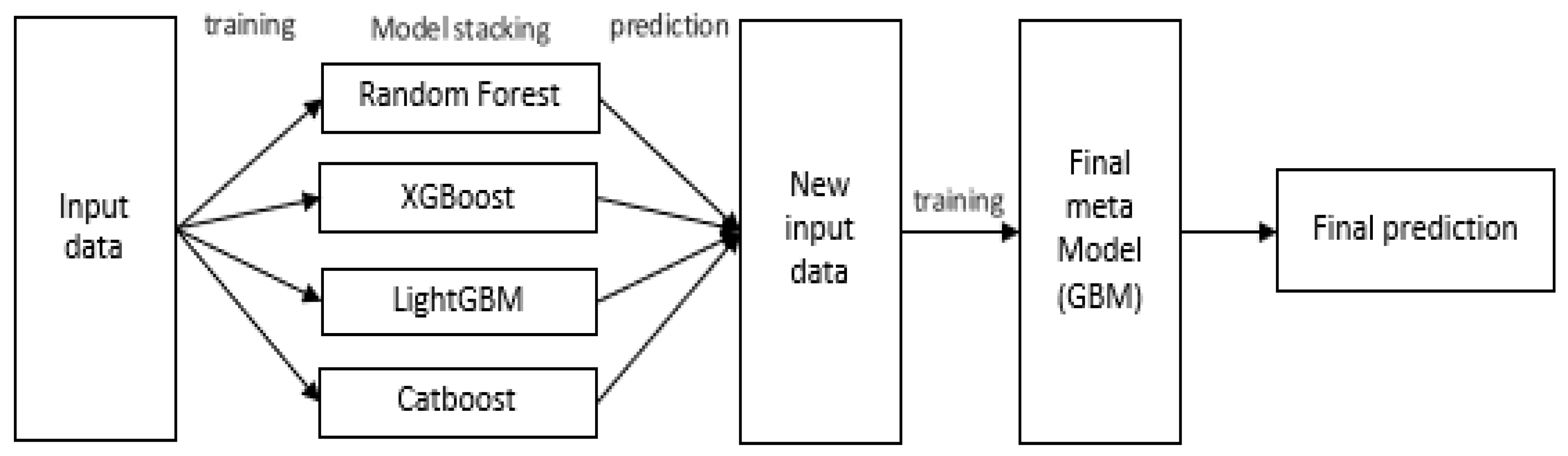
3.2.2. Multi-Model Method (Stacking Ensemble)
3.3. Model Performance Evaluation
4. Results
4.1. File Data
4.2. OpenAPI Data
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabryelczyk, R. Has COVID-19 accelerated digital transformation? Initial lessons learned for public administrations. Information Systems Management 2020, 37((4)), 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J.; Sjöklint, M.; Ukkonen, A. The sharing economy: Why people participate in collaborative consumption. Journal of the association for information science and technology 2016, 67((9)), 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niankara, I. In Sustainability through open data sharing and reuse in the digital economy, 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT), 2022; pp 1-11.
- Helbig, R.; von Höveling, S.; Solsbach, A.; Marx Gómez, J., Strategic analysis of providing corporate sustainability open data. Intelligent Systems in Accounting, Finance and Management 2021, 28, (3), 195-214.
- Peled, A. When transparency and collaboration collide: The USA open data program. Journal of the American society for information science and technology 2011, 62((11)), 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, K. In Transparency, open data and trust in government: shaping the infosphere, Proceedings of the 4th annual ACM web science conference, 2012; pp 223-232.
- Lnenicka, M.; Nikiforova, A. , Transparency-by-design: What is the role of open data portals? Telematics and Informatics 2021, 61, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y., A Study on Policies for Activating the Use of Public Data. Journal of the Korean Data & Information Science Society, 2014, 25, 4, 769-777.
- Janssen, M.; Charalabidis, Y.; Zuiderwijk, A., Benefits, adoption barriers and myths of open data and open government. Information systems management, 2012, 29, (4), 258-268.
- Weerakkody, V.; Irani, Z.; Kapoor, K.; Sivarajah, U.; Dwivedi, Y. K. Open data and its usability: an empirical view from the Citizen’s perspective. Information Systems Frontiers 2017, 19, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, K., Study on Value Creation Strategies of Public Data. Proceedings of the Korean Association of Public Administration 2018, 2018, 3473-3491.
- Yoon, S. O.; Hyun, J. W. A Study on the Current Status Analysis and Improvement Measures of Public Data Opening Policies: Focusing on the Case of National Priority Data Opening in the Public Data Portal. Korean Journal of Public Administration 2019, 33((1)), 219–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Eun-Seon, A Study on Legal System Improvement Measures for Promoting the Openness and Utilization of Public Data - Focusing on Cases of Refusal to Provide Public Data. Information Policy 2023, 30, (2), 46-67.
- Kim, Min-Ho; Lee, Bo-Oak, Trends and Implications of the Revision of the EU Directive on Public Open Data. Sungkyunkwan Law Review 2020, 32, (1), 1-30.
- Devins, C.; Felin, T.; Kauffman, S.; Koppl, R., The law and big data. Cornell JL & Public Policy 2017, 27, 357.
- Tan, E., Designing an AI compatible open government data ecosystem for public governance. 2022.
- Kim Geun-Hyun, Jung Seong-Hoon, Yang Jae-Dong, and Wi Joo-Yeon, A Policy Study on Public Data for the Past 10 Years Using Big Data Analysis Techniques: Focusing on Comparative Analysis by Administration. National Policy Research 2023, 37((4)), 45–67.
- Jetzek, T.; Avital, M.; Bjørn-Andersen, N. In Generating Value from Open Government Data, ICIS, 2013; 2013.
- Osagie, E.; Waqar, M.; Adebayo, S.; Stasiewicz, A.; Porwol, L.; Ojo, A. In Usability evaluation of an open data platform, Proceedings of the 18th annual international conference on digital government research, 2017; 2017; pp 495-504.
- Máchová, R.; Volejníková, J.; Lněnička, M. Impact of e-government development on the level of corruption: Measuring the effects of related indices in time and dimensions. Review of Economic Perspectives 2018, 18((2)), 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, M. M.; Zakaria, N. H.; Rashid, A.; Shafique, M. N. Examining the factors of open government data usability from academician’s perspective. International Journal of Information Technology Project Management (IJITPM) 2018, 9((3)), 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, L.; Keller, T. E.; Yerden, X.; Luna-Reyes, L. F. , Open data visualizations and analytics as tools for policy-making. Government Information Quarterly 2019, (4), 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A., Schumpeter, The theory of economic development: An inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. 1934.
- Bason, C., Leading public sector innovation. Bristol: Policy Press: 2010; Vol. 10.
- Zuiderwijk, A.; Janssen, M.; Davis, C., Innovation with open data: Essential elements of open data ecosystems. Information polity 2014, 19, (1-2), 17-33.
- Blakemore, M.; Craglia, M. Access to public-sector information in Europe: Policy, rights, and obligations. The Information Society 2006, 22((1)), 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalabidis, Y.; Zuiderwijk, A.; Alexopoulos, C.; Janssen, M.; Höchtl, J.; Ferro, E., The world of open data. Public Administration and Information Technology. Cham: Springer International Publishing. doi 2018, 978-3.
- European Commission, “Digital agenda: Turning government data into gold, European Commission, Brussels”, 2011.
- Zhang, J.; Dawes, S. S.; Sarkis, J. Exploring stakeholders’ expectations of the benefits and barriers of e-government knowledge sharing. Journal of Enterprise Information Management 2005, 18((5)), 548–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F.; Papachristos, N.; Kamariotou, M. In Business models for open data ecosystem: Challenges and motivations for entrepreneurship and innovation, 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI), 2017; IEEE: 2017; pp 398-407.
- European Commission, “Digital agenda: Commission’s open data strategy, questions & answers”, 2013.
- Ministry of the Interior and Safety, “2021 Administrative Safety White Paper”, 2022.
- Janssen, M.; Zuiderwijk, A. Infomediary business models for connecting open data providers and users. Social Science Computer Review 2014, 32((5)), 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgesius, F. Z.; Gray, J.; Van Eechoud, M. Open data, privacy, and fair information principles: Towards a balancing framework. Berkeley Technology Law Journal 2015, 30((3)), 2073–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, N.; Ravindran, R.; Nicosia, S. Government data does not mean data governance: Lessons learned from a public sector application audit. Government information quarterly 2015, 32((3)), 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderwijk, A.; Janssen, M. Open data policies, their implementation and impact: A framework for comparison. Government information quarterly 2014, 31((1)), 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertot, J. C.; Gorham, U.; Jaeger, P. T.; Sarin, L. C.; Choi, H., Big data, open government and e-government: Issues, policies and recommendations. Information polity 2014, 19, (1-2), 5-16.
- Máchová, R.; Lněnička, M. Evaluating the quality of open data portals on the national level. Journal of theoretical and applied electronic commerce research 2017, 12((1)), 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osagie, E.; Waqar, M.; Adebayo, S.; Stasiewicz, A.; Porwol, L.; Ojo, A. In Usability evaluation of an open data platform, Proceedings of the 18th annual international conference on digital government research, 2017; 2017; pp 495-504.
- Vetrò, A.; Canova, L.; Torchiano, M.; Minotas, C. O.; Iemma, R.; Morando, F. Open data quality measurement framework: Definition and application to Open Government Data. Government Information Quarterly 2016, 33((2)), 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourou, K.; Exarchos, T. P.; Exarchos, K. P.; Karamouzis, M. V.; Fotiadis, D. I. Machine learning applications in cancer prognosis and prediction. Computational and structural biotechnology journal 2015, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Yoo, B.; Chae, K. J.; Lee, C. H. Machine Learning-based Prediction of Relative Regional Air Volume Change from Healthy Human Lung CTs. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2023, 17((2)), 576–590. [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa, J.; Ziegler, A.; König, I. R. , Risk estimation and risk prediction using machine-learning methods. Human genetics 2012, 131, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xayasouk, T.; Lee, H.; Lee, G. , Air pollution prediction using long short-term memory (LSTM) and deep autoencoder (DAE) models. Sustainability 2020, 12((6)), 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.-w. Flood prediction using machine learning models: Literature review. Water 2018, 10((11)), 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. N.; Othman, F. B.; Afan, H. A.; Ibrahim, R. K.; Fai, C. M.; Hossain, M. S.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Machine learning methods for better water quality prediction. Journal of Hydrology 2019, 578, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Choi, W. I.; Nam, Y.; Park, Y.-S. Predicting potential occurrence of pine wilt disease based on environmental factors in South Korea using machine learning algorithms. Ecological informatics 2021, 64, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, Y.; Fu, Y.; Livingood, W. A review of machine learning in building load prediction. Applied Energy 2021, 285, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltrinieri, N.; Comfort, L.; Reniers, G. Learning about risk: Machine learning for risk assessment. Safety science 2019, 118, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, J.; Rokseth, B. Applications of machine learning methods for engineering risk assessment–A review. Safety science 2020, 122, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, G.; Morris Lampert, C., Entrepreneurship in the large corporation: A longitudinal study of how established firms create breakthrough inventions. Strategic management journal 2001, 22, (6-7), 521-543.
- Wu, J.-L.; Chang, P.-C.; Tsao, C.-C.; Fan, C.-Y. A patent quality analysis and classification system using self-organizing maps with support vector machine. Applied soft computing 2016, 41, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho Hyunjin; Lee Hakyun, Patent Quality Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques. Proceedings of the Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers Spring Conference 2018, 1343-1350.
- Erdogan, Z.; Altuntas, S.; Dereli, T., Predicting patent quality based on machine learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management 2022.
- Kim, K.; Hong, J.-s., A hybrid decision tree algorithm for mixed numeric and categorical data in regression analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters 2017, 98, 39-45.
- Cha, G.-W.; Moon, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-C., Comparison of random forest and gradient boosting machine models for predicting demolition waste based on small datasets and categorical variables. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, (16), 8530.
- Foody, G. M.; Mathur, A.; Sanchez-Hernandez, C.; Boyd, D. S., Training set size requirements for the classification of a specific class. Remote Sensing of Environment 2006, 104, (1), 1-14.
- Ramezan, C. A.; Warner, T. A.; Maxwell, A. E.; Price, B. S., Effects of training set size on supervised machine-learning land-cover classification of large-area high-resolution remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, (3), 368.
- Ahmad, I.; Basheri, M.; Iqbal, M. J.; Rahim, A., Performance comparison of support vector machine, random forest, and extreme learning machine for intrusion detection. IEEE access 2018, 6, 33789-33795.
- Daghistani, T.; Alshammari, R. Comparison of statistical logistic regression and random forest machine learning techniques in predicting diabetes. Journal of Advances in Information Technology Vol 2020, 11((2)), 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, D.; Takase, Y.; Abe, T.; Orita, G.; Ando, S. In Prediction accuracy of Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM, and artificial neural network for shear resistance of post-installed anchors, Structures, 2023; Elsevier: 2023; pp 1252-1263.
- Shehadeh, A.; Alshboul, O.; Al Mamlook, R. E.; Hamedat, O. Machine learning models for predicting the residual value of heavy construction equipment: An evaluation of modified decision tree, LightGBM, and XGBoost regression. Automation in Construction 2021, 129, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, M. A.; Dasril, Y. Company bankruptcy prediction framework based on the most influential features using XGBoost and stacking ensemble learning. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) 2021, 11((6)), 5549–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebala, G.; Ravi, A.; Churiwala, S.; Rebala, G.; Ravi, A.; Churiwala, S. Machine learning definition and basics. An introduction to machine learning 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- West, S. G.; Finch, J. F.; Curran, P. J., Structural equation models with nonnormal variables: Problems and remedies. 1995.
- Hong, S.; Malik, M. L.; Lee, M.-K. Testing configural, metric, scalar, and latent mean invariance across genders in sociotropy and autonomy using a non-Western sample. Educational and psychological measurement 2003, 63((4)), 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Park, J.; Lee, Y. Stacking ensemble technique for classifying breast cancer. Healthcare informatics research 2019, 25((4)), 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painsky, A.; Rosset, S.; Feder, M. Large alphabet source coding using independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2017, 63((10)), 6514–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Hong, J.-s. A hybrid decision tree algorithm for mixed numeric and categorical data in regression analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters 2017, 98, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Han, J. Variable selection issues in tree-based regression models. Transportation Research Record 2008, 2061((1)), 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géron, A., Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow. “ O’Reilly Media, Inc.”: 2022.
- Dangeti, P., Statistics for machine learning. Packt Publishing Ltd.: 2017.
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. In Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system, Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 2016; 2016; pp 785-794.
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y., Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30.
- Hancock, J. T.; Khoshgoftaar, T. M. CatBoost for big data: an interdisciplinary review. Journal of big data 2020, 7((1)), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Rao, C.; Xiao, X.; Chen, L.; Goh, M. Risk assessment of cardiovascular disease based on SOLSSA-CatBoost model. Expert Systems with Applications 2023, 219, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeur, S. B.; Gharib, C.; Mefteh-Wali, S.; Arfi, W. B. CatBoost model and artificial intelligence techniques for corporate failure prediction. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2021, 166, 120658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qiao, J.; Qiu, S.; Sun, Y. Combination of feature selection and catboost for prediction: The first application to the estimation of aboveground biomass. Forests 2021, 12((2)), 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ye, X.; Ye, Q.; Wang, T.; Cheng, J.; Yan, X. , Demand forecasting of online car-hailing with stacking ensemble learning approach and large-scale datasets. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 199513–199522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, J.; Owusu, D. K.; Anafo, A. , Application of Stacked Ensemble Techniques for Classifying Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis. Asian Journal of Research in Computer Science 2024, 17((4)), 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E. K.; Demir, S. , Greedy-AutoML: A novel greedy-based stacking ensemble learning framework for assessing soil liquefaction potential. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 119, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswin, S.; Geetha, P.; Vinayakumar, R. In Deep learning models for the prediction of rainfall, 2018 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), 2018; IEEE: 2018; pp 0657-0661.
- Almalaq, A.; Edwards, G. In A review of deep learning methods applied on load forecasting, 2017 16th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA), 2017; IEEE: 2017; pp 511-516.
- Si, B.; Ni, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, F. Interactive effects of hyperparameter optimization techniques and data characteristics on the performance of machine learning algorithms for building energy metamodeling. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering 2024, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoła, A.; Satoła, K. Performance comparison of machine learning models used for predicting subclinical mastitis in dairy cows: bagging, boosting, stacking and super-learner ensembles versus single machine learning models. Journal of Dairy Science 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, T. Stacking Model for Photovoltaic-Power-Generation Prediction. Sustainability 2022, 14((9)), 5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, U.; Kang, Y.; Lee, H.; Yun, S. A stacking heterogeneous ensemble learning method for the prediction of building construction project costs. Applied sciences 2022, 12((19)), 9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um Hanuel; Kim Jaesung; Choi Sangok, Verification of Machine Learning-Based Corporate Bankruptcy Risk Prediction Model and Policy Suggestions: Focused on Improvement through Stacking Ensemble Model. Journal of Intelligence and Information Systems Research 2020, 26, 105–129.
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A. V.; Gulin, A., CatBoost: unbiased boosting with categorical features. Advances in neural information processing systems 2018, 31.
- Sugiyama, M., Introduction to statistical machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann: 2015.
- Grimes, D. A., Epidemiologic research using administrative databases: garbage in, garbage out. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2010, 116, (5), 1018-1019.
- Kilkenny, M. F.; Robinson, K. M., Data quality:“Garbage in–garbage out”. In SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, England: 2018; Vol. 47, pp 103-105.
- Hartung, F.; Ramme, F. Digital rights management and watermarking of multimedia content for m-commerce applications. IEEE communications magazine 2000, 38((11)), 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
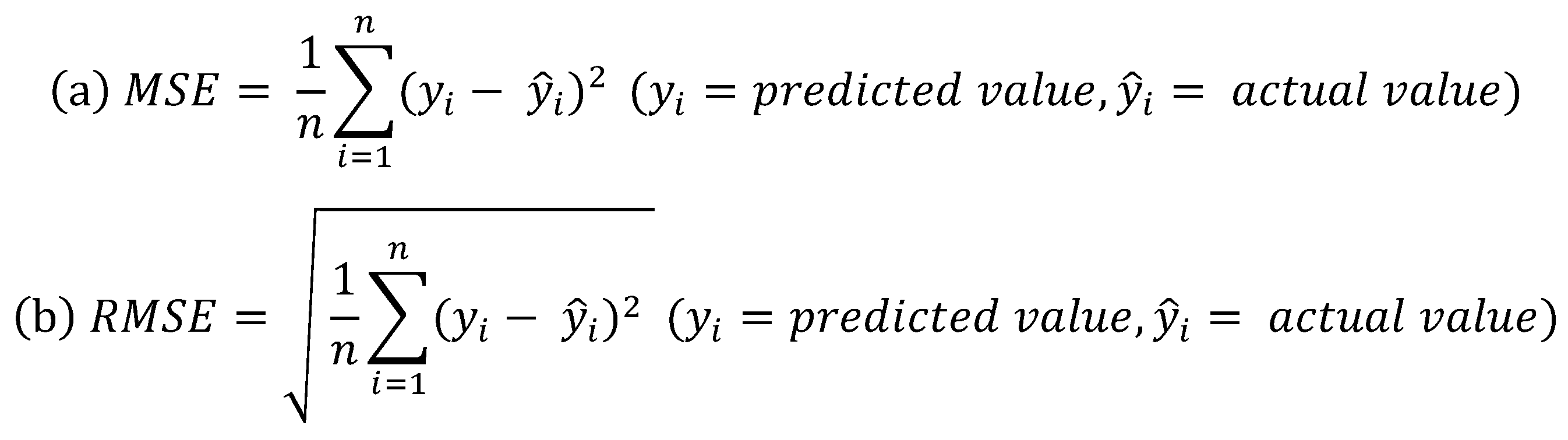
| Item | Model | Training Data | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Administration | Catboost | Integrated | 0.665 | 0.443 |
| Science & Technology | Catboost | Field | 0.718 | 0.516 |
| Education | Catboost | Integrated | 0.625 | 0.390 |
| Transportation & Logistics | Catboost | Integrated | 0.643 | 0.414 |
| Land Management | Catboost | Integrated | 0.598 | 0.358 |
| Agriculture & Fisheries | Catboost | Integrated | 0.652 | 0.425 |
| Culture & Tourism | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 0.701 | 0.491 |
| Law | Catboost | Integrated | 0.506 | 0.256 |
| Healthcare | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 0.627 | 0.393 |
| Social Welfare | Catboost | Integrated | 0.638 | 0.407 |
| Industry & Employment | Catboost | Integrated | 0.637 | 0.405 |
| Food & Health | Catboost | Integrated | 0.584 | 0.341 |
| Disaster Safety | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 0.622 | 0.387 |
| Finance | Catboost | Field | 0.557 | 0.311 |
| Unification & Diplomacy | Catboost | Integrated | 0.623 | 0.388 |
| Environment & Meteorology | Catboost | Integrated | 0.671 | 0.450 |
| Item | Method | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Model | Multi-Model (Stacking Ensemble) |
||||||||||||
| Algorithm | Random Forest | XGBoost | LightGBM | CatBoost | |||||||||
| Training Data | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | |||
| Field | Public Administration | 0.556 | 0.541 | 0.533 | 0.527 | 0.534 | 0.504 | 0.443 | 0.501 | 0.505 | 0.494 | ||
| Science & Technology | 0.793 | 0.592 | 0.754 | 0.555 | 0.736 | 0.616 | 0.678 | 0.516 | 0.763 | 0.607 | |||
| Education | 0.478 | 0.528 | 0.472 | 0.559 | 0.470 | 0.503 | 0.390 | 0.484 | 0.450 | 0.509 | |||
| Transportation & Logistics | 0.538 | 0.631 | 0.552 | 0.621 | 0.553 | 0.657 | 0.414 | 0.593 | 0.511 | 0.618 | |||
| Land Management | 0.534 | 0.501 | 0.557 | 0.495 | 0.549 | 0.490 | 0.358 | 0.488 | 0.516 | 0.523 | |||
| Agriculture & Fisheries | 0.482 | 0.491 | 0.478 | 0.468 | 0.478 | 0.445 | 0.425 | 0.443 | 0.435 | 0.470 | |||
| Culture & Tourism | 0.535 | 0.581 | 0.519 | 0.539 | 0.546 | 0.552 | 0.501 | 0.557 | 0.491 | 0.544 | |||
| Law | 0.385 | 0.374 | 0.335 | 0.344 | 0.313 | 0.408 | 0.256 | 0.326 | 0.347 | 0.373 | |||
| Healthcare | 0.435 | 0.523 | 0.429 | 0.496 | 0.416 | 0.508 | 0.466 | 0.504 | 0.393 | 0.509 | |||
| Social Welfare | 0.486 | 0.483 | 0.433 | 0.487 | 0.450 | 0.479 | 0.407 | 0.480 | 0.433 | 0.461 | |||
| Industry & Employment | 0.497 | 0.515 | 0.476 | 0.519 | 0.463 | 0.471 | 0.405 | 0.478 | 0.453 | 0.476 | |||
| Food & Health | 0.544 | 0.518 | 0.515 | 0.429 | 0.518 | 0.450 | 0.341 | 0.435 | 0.500 | 0.475 | |||
| Disaster Safety | 0.451 | 0.663 | 0.416 | 0.698 | 0.424 | 0.678 | 0.525 | 0.631 | 0.387 | 0.635 | |||
| Finance | 0.360 | 0.350 | 0.348 | 0.313 | 0.356 | 0.329 | 0.396 | 0.311 | 0.330 | 0.314 | |||
| Unification & Diplomacy | 0.475 | 0.465 | 0.513 | 0.528 | 0.525 | 0.556 | 0.388 | 0.498 | 0.475 | 0.532 | |||
| Environment & Meteorology | 0.528 | 0.601 | 0.519 | 0.622 | 0.517 | 0.591 | 0.450 | 0.575 | 0.482 | 0.577 | |||
| Item | Method | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Model | Multi-Model (Stacking Ensemble) |
||||||||||
| Algorithm | Random Forest | XGBoost | LightGBM | CatBoost | |||||||
| Training Data | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | |
| Field | Public Administration | 0.745 | 0.735 | 0.730 | 0.726 | 0.731 | 0.710 | 0.665 | 0.708 | 0.710 | 0.703 |
| Science & Technology | 0.891 | 0.769 | 0.868 | 0.745 | 0.858 | 0.785 | 0.824 | 0.718 | 0.873 | 0.779 | |
| Education | 0.692 | 0.727 | 0.687 | 0.748 | 0.686 | 0.710 | 0.625 | 0.696 | 0.671 | 0.714 | |
| Transportation & Logistics | 0.733 | 0.794 | 0.743 | 0.788 | 0.743 | 0.811 | 0.643 | 0.770 | 0.715 | 0.786 | |
| Land Management | 0.731 | 0.708 | 0.746 | 0.704 | 0.741 | 0.700 | 0.598 | 0.698 | 0.718 | 0.723 | |
| Agriculture & Fisheries | 0.694 | 0.700 | 0.691 | 0.684 | 0.691 | 0.667 | 0.652 | 0.666 | 0.660 | 0.686 | |
| Culture & Tourism | 0.732 | 0.762 | 0.721 | 0.734 | 0.739 | 0.743 | 0.708 | 0.746 | 0.701 | 0.738 | |
| Law | 0.620 | 0.611 | 0.579 | 0.587 | 0.559 | 0.639 | 0.506 | 0.571 | 0.589 | 0.611 | |
| Healthcare | 0.660 | 0.723 | 0.655 | 0.705 | 0.645 | 0.713 | 0.683 | 0.710 | 0.627 | 0.713 | |
| Social Welfare | 0.697 | 0.695 | 0.658 | 0.698 | 0.671 | 0.692 | 0.638 | 0.693 | 0.658 | 0.679 | |
| Industry & Employment | 0.705 | 0.717 | 0.690 | 0.720 | 0.680 | 0.686 | 0.637 | 0.692 | 0.673 | 0.690 | |
| Food & Health | 0.738 | 0.720 | 0.718 | 0.655 | 0.720 | 0.671 | 0.584 | 0.660 | 0.707 | 0.689 | |
| Disaster Safety | 0.672 | 0.814 | 0.645 | 0.835 | 0.651 | 0.823 | 0.725 | 0.794 | 0.622 | 0.797 | |
| Finance | 0.600 | 0.592 | 0.590 | 0.560 | 0.597 | 0.573 | 0.629 | 0.557 | 0.575 | 0.560 | |
| Unification & Diplomacy | 0.689 | 0.682 | 0.717 | 0.727 | 0.724 | 0.746 | 0.623 | 0.705 | 0.689 | 0.730 | |
| Environment & Meteorology | 0.727 | 0.776 | 0.721 | 0.788 | 0.719 | 0.769 | 0.671 | 0.758 | 0.694 | 0.760 | |
| Item | Model | Training Data | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Administration | Random Forest | Field | 3.130 | 9.797 |
| Science & Technology | Random Forest | Field | 3.082 | 9.499 |
| Education | XGBoost | Integrated | 2.206 | 4.867 |
| Transportation & Logistics | LightGBM | Integrated | 3.769 | 14.204 |
| Land Management | LightGBM | Field | 2.986 | 8.915 |
| Agriculture & Fisheries | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 2.645 | 6.995 |
| Culture & Tourism | Random Forest | Integrated | 2.326 | 5.412 |
| Law | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 1.592 | 2.533 |
| Healthcare | Stacking Ensemble | Integrated | 2.048 | 4.193 |
| Social Welfare | Catboost | Field | 2.290 | 5.244 |
| Industry & Employment | XGBoost | Integrated | 2.725 | 7.427 |
| Food & Health | LightGBM | Field | 2.622 | 6.875 |
| Disaster Safety | Random Forest | Field | 2.140 | 4.580 |
| Finance | Random Forest | Field | 3.453 | 11.921 |
| Unification & Diplomacy | Random Forest | Field | 2.463 | 6.069 |
| Environment & Meteorology | Catboost | Integrated | 2.093 | 4.380 |
| Item | Method | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Model | Multi-Model (Stacking Ensemble) |
|||||||||||
| Algorithm | Random Forest | XGBoost | LightGBM | CatBoost | ||||||||
| Training Data | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | ||
| Field | Public Administration | 11.357 | 9.797 | 10.784 | 11.223 | 11.103 | 11.608 | 11.385 | 10.832 | 10.204 | 10.869 | |
| Science & Technology | 25.342 | 9.499 | 30.019 | 15.414 | 26.606 | 22.801 | 27.600 | 11.134 | 27.830 | 22.103 | ||
| Education | 6.712 | 5.316 | 4.867 | 7.509 | 4.930 | 8.096 | 5.530 | 6.386 | 5.002 | 7.271 | ||
| Transportation & Logistics | 17.987 | 18.608 | 16.565 | 18.705 | 14.204 | 22.423 | 17.206 | 16.982 | 15.825 | 19.322 | ||
| Land Management | 11.695 | 10.516 | 13.604 | 10.062 | 11.494 | 8.915 | 11.877 | 10.045 | 13.185 | 10.850 | ||
| Agriculture & Fisheries | 7.624 | 9.431 | 7.856 | 8.825 | 7.232 | 10.403 | 8.266 | 9.274 | 6.995 | 9.945 | ||
| Culture & Tourism | 5.412 | 7.830 | 5.713 | 6.900 | 5.760 | 8.535 | 5.859 | 7.249 | 5.470 | 8.095 | ||
| Law | 2.906 | 29.163 | 9.217 | 48.547 | 9.736 | 14.011 | 4.332 | 28.268 | 2.533 | 35.837 | ||
| Healthcare | 5.347 | 6.348 | 4.239 | 7.688 | 4.259 | 6.668 | 4.972 | 6.672 | 4.193 | 4.843 | ||
| Social Welfare | 6.825 | 5.335 | 6.534 | 6.437 | 7.095 | 7.565 | 6.845 | 5.244 | 6.295 | 6.590 | ||
| Industry & Employment | 8.810 | 11.382 | 7.427 | 14.137 | 8.058 | 12.263 | 8.677 | 10.555 | 8.037 | 11.853 | ||
| Food & Health | 8.227 | 7.005 | 7.594 | 7.805 | 8.309 | 6.875 | 9.990 | 7.347 | 7.677 | 12.030 | ||
| Disaster Safety | 7.477 | 4.580 | 9.845 | 6.434 | 8.911 | 6.150 | 9.368 | 5.572 | 8.386 | 5.418 | ||
| Finance | 18.654 | 11.921 | 20.085 | 16.463 | 17.981 | 14.147 | 17.611 | 14.247 | 19.444 | 14.862 | ||
| Unification & Diplomacy | 12.790 | 6.069 | 8.613 | 9.562 | 8.792 | 7.075 | 7.125 | 7.535 | 6.480 | 7.565 | ||
| Environment & Meteorology | 6.628 | 11.139 | 5.459 | 11.387 | 4.447 | 10.458 | 4.380 | 9.506 | 5.252 | 10.120 | ||
| Item | Method | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Model | Multi-Model (Stacking Ensemble) |
||||||||||
| Algorithm | Random Forest | XGBoost | LightGBM | CatBoost | |||||||
| Training Data | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | Integrated | Field | |
| Field | Public Administration | 3.370 | 3.130 | 3.284 | 3.350 | 3.332 | 3.407 | 3.374 | 3.291 | 3.194 | 3.297 |
| Science & Technology | 5.034 | 3.082 | 5.479 | 3.926 | 5.158 | 4.775 | 5.254 | 3.337 | 5.275 | 4.701 | |
| Education | 2.591 | 2.306 | 2.206 | 2.740 | 2.220 | 2.845 | 2.352 | 2.527 | 2.237 | 2.697 | |
| Transportation & Logistics | 4.241 | 4.314 | 4.070 | 4.325 | 3.769 | 4.735 | 4.148 | 4.121 | 3.978 | 4.396 | |
| Land Management | 3.420 | 3.243 | 3.688 | 3.172 | 3.390 | 2.986 | 3.446 | 3.169 | 3.631 | 3.294 | |
| Agriculture & Fisheries | 2.761 | 3.071 | 2.803 | 2.971 | 2.689 | 3.225 | 2.875 | 3.045 | 2.645 | 3.154 | |
| Culture & Tourism | 2.326 | 2.798 | 2.390 | 2.627 | 2.400 | 2.922 | 2.421 | 2.692 | 2.339 | 2.845 | |
| Law | 1.705 | 5.400 | 3.036 | 6.968 | 3.120 | 3.743 | 2.081 | 5.317 | 1.592 | 5.986 | |
| Healthcare | 2.312 | 2.519 | 2.059 | 2.773 | 2.064 | 2.582 | 2.230 | 2.583 | 2.048 | 2.201 | |
| Social Welfare | 2.613 | 2.310 | 2.556 | 2.537 | 2.664 | 2.750 | 2.616 | 2.290 | 2.509 | 2.567 | |
| Industry & Employment | 2.968 | 3.374 | 2.725 | 3.760 | 2.839 | 3.502 | 2.946 | 3.249 | 2.835 | 3.443 | |
| Food & Health | 2.868 | 2.647 | 2.756 | 2.794 | 2.882 | 2.622 | 3.161 | 2.711 | 2.771 | 3.468 | |
| Disaster Safety | 2.734 | 2.140 | 3.138 | 2.537 | 2.985 | 2.480 | 3.061 | 2.361 | 2.896 | 2.328 | |
| Finance | 4.319 | 3.453 | 4.482 | 4.057 | 4.240 | 3.761 | 4.197 | 3.774 | 4.410 | 3.855 | |
| Unification & Diplomacy | 3.576 | 2.463 | 2.935 | 3.092 | 2.965 | 2.660 | 2.669 | 2.745 | 2.546 | 2.751 | |
| Environment & Meteorology | 2.574 | 3.337 | 2.337 | 3.374 | 2.109 | 3.234 | 2.093 | 3.083 | 2.292 | 3.181 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




